OFLOXACIN solution/ drops
Ofloxacin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Ofloxacin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Somerset Therapeutics, LLC, Somerset Therapeutics Private Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Ofloxacin otic solution 0.3% is a sterile aqueous anti-infective (anti-bacterial) solution for otic use. Chemically, ofloxacin has three condensed 6-membered rings made up of a fluorinated carboxyquinolone with a benzoxazine ring. The chemical name of ofloxacin is: (±)-9- fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid. The empirical formula of ofloxacin is C18H20FN3O4 and its molecular weight is 361.38. The structural formula is:
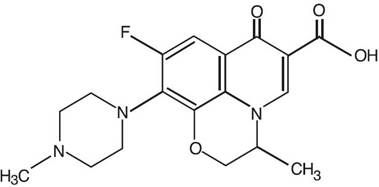
Ofloxacin otic contains 0.3% (3mg/mL) ofloxacin with benzalkonium chloride (0.0025%), sodium chloride (0.9%), and water for injection. Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are added to adjust the pH between 6.0 and 6.6.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacokinetics: Drug concentrations in serum (in subjects with tympanostomy tubes and perforated tympanic membranes), in otorrhea, and in mucosa of the middle ear (in subjects with perforated tympanic membranes) were determined following otic administration of ofloxacin solution. In two single-dose studies, mean ofloxacin serum concentrations were low in adult patients with tympanostomy tubes, with and without otorrhea, after otic administration of a 0.3% solution (4.1 ng/mL (n=3) and 5.4 ng/mL (n=5), respectively). In adults with perforated tympanic membranes, the maximum serum drug level of ofloxacin detected was 10 ng/mL after administration of a 0.3% solution. Ofloxacin was detectable in the middle ear mucosa of some adult subjects with perforated tympanic membranes (11 of 16 subjects). The variability of ofloxacin concentration in middle ear mucosa was high. The concentrations ranged from 1.2 to 602 μg/g after otic administration of a 0.3% solution. Ofloxacin was present in high concentrations in otorrhea (389 - 2850 μg/g, n=13) 30 minutes after otic administration of a 0.3% solution in subjects with chronic suppurative otitis media and perforated tympanic membranes. However, the measurement of ofloxacin in the otorrhea does not necessarily reflect the exposure of the middle ear to ofloxacin.
Microbiology: Ofloxacin has in vitro activity against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. Ofloxacin exerts its antibacterial activity by inhibiting DNA gyrase, a bacterial topoisomerase. DNA gyrase is an essential enzyme which controls DNA topology and assists in DNA replication, repair, deactivation, and transcription. Cross-resistance has been observed between ofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones. There is generally no cross-resistance between ofloxacin and other classes of antibacterial agents such as beta-lactams or aminoglycosides.
Ofloxacin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and clinically in otic infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section.
AEROBES, GRAM-POSITIVE:
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus pneumoniae
AEROBES, GRAM-NEGATIVE:
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Moraxella catarrhalis
Proteus mirabilis
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ofloxacin otic solution 0.3% is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible isolates of the designated microorganisms in the specific conditions listed below:
Otitis Externa in adults and pediatric patients, 6 months and older, due to Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus
Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media in patients 12 years and older with perforated tympanic membranes due to, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus.
Acute Otitis Media in pediatric patients one year and older with tympanostomy tubes due to Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
NOT FOR INJECTION.
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions, some following the first dose, have been reported in patients receiving systemic quinolones, including ofloxacin. Some reactions were accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, angioedema (including laryngeal, pharyngeal or facial edema), airway obstruction, dyspnea, urticaria, and itching. If an allergic reaction to ofloxacin is suspected, stop the drug. Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions may require immediate emergency treatment. Oxygen and airway management, including intubation, should be administered as clinically indicated.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General: As with other anti-infective preparations, prolonged use may result in over-growth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi. If the infection is not improved after one week, cultures should be obtained to guide further treatment. If otorrhea persists after a full course of therapy, or if two or more episodes of otorrhea occur within six months, further evaluation is recommended to exclude an underlying condition such as cholesteatoma, foreign body, or a tumor.
The systemic administration of quinolones, including ofloxacin at doses much higher than given or absorbed by the otic route, has led to lesions or erosions of the cartilage in weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature animals of various species.
Young growing guinea pigs dosed in the middle ear with 0.3% ofloxacin otic solution showed no systemic effects, lesions or erosions of the cartilage in weight-bearing joints, or other signs of arthropathy. No drug-related structural or functional changes of the cochlea and no lesions in the ossicles were noted in the guinea pig following otic administration of 0.3% ofloxacin for one month.
No signs of local irritation were found when 0.3% ofloxacin was applied topically in the rabbit eye. Ofloxacin was also shown to lack dermal sensitizing potential in the guinea pig maximization study.
Information for Patients: Avoid contaminating the applicator tip with material from the fingers or other sources. This precaution is necessary if the sterility of the drops is to be preserved. Systemic quinolones, including ofloxacin, have been associated with hypersensitivity reactions, even following a single dose. Discontinue use immediately and contact your physician at the first sign of a rash or allergic reaction.
Otitis Externa
Prior to administration of ofloxacin otic solution, the solution should be warmed by holding the bottle in the hand for one or two minutes to avoid dizziness which may result from the instillation of a cold solution. The patient should lie with the affected ear upward, and then the drops should be instilled. This position should be maintained for five minutes to facilitate penetration of the drops into the ear canal. Repeat, if necessary, for the opposite ear (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Acute Otitis Media and Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media
Prior to administration of ofloxacin otic solution, the solution should be warmed by holding the bottle in the hand for one or two minutes to avoid dizziness which may result from the instillation of a cold solution. The patient should lie with the affected ear upward, and then the drops should be instilled. The tragus should then be pumped 4 times by pushing inward to facilitate penetration of the drops into the middle ear. This position should be maintained for five minutes. Repeat, if necessary, for the opposite ear (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Drug Interactions: Specific drug interaction studies have not been conducted with ofloxacin otic solution.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies to determine the carcinogenic potential of ofloxacin have not been conducted. Ofloxacin was not mutagenic in the Ames test, the sister chromatid exchange assay (Chinese hamster and human cell lines), the unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) assay using human fibroblasts, the dominant lethal assay, or the mouse micronucleus assay. Ofloxacin was positive in the rat hepatocyte UDS assay, and in the mouse lymphoma assay. In rats, ofloxacin did not affect male or female reproductive performance at oral doses up to 360 mg/kg/day. This would be over 1000 times the maximum recommended clinical dose, based upon body surface area, assuming total absorption of ofloxacin from the ear of a patient treated with ofloxacin otic solution. twice per day.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects: Pregnancy Category C. Ofloxacin has been shown to have an embryocidal effect in rats at a dose of 810 mg/kg/day and in rabbits at 160 mg/kg/day.
These dosages resulted in decreased fetal body weights and increased fetal mortality in rats and rabbits, respectively. Minor fetal skeletal variations were reported in rats receiving doses of 810 mg/kg/day. Ofloxacin has not been shown to be teratogenic at doses as high as 810 mg/kg/day and 160 mg/kg/day when administered to pregnant rats and rabbits, respectively.
Ofloxacin has not been shown to have any adverse effects on the developing embryo or fetus at doses relevant to the amount of ofloxacin that will be delivered ototopically at the recommended clinical doses.
Nonteratogenic Effects: Additional studies in the rat demonstrated that doses up to 360 mg/kg/day during late gestation had no adverse effects on late fetal development, labor, delivery, lactation, neonatal viability, or growth of the newborn. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Ofloxacin otic solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers: In nursing women, a single 200 mg oral dose resulted in concentrations of ofloxacin in milk which were similar to those found in plasma. It is not known whether ofloxacin is excreted in human milk following topical otic administration. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from ofloxacin in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use: Safety and efficacy have been demonstrated in pediatric patients of the following ages for the listed indications:
- six months and older; otitis externa with intact tympanic membranes
- one year and older: acute otitis media with tympanostomy tubes.
- Twelve years and older: chronic suppurative otitis media with perforated tympanic membranes
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients below these ages have not been established.
Although no data are available on patients less than age 6 months, there are no known safety concerns or differences in the disease process in this population that will preclude use of this product.
No changes in hearing function occurred in 30 pediatric subjects treated with ofloxacin otic and tested for audiometric parameters. Although quinolones, including ofloxacin, have been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals after systemic administration, young growing guinea pigs dosed in the middle ear with 0.3% ofloxacin otic solution for one month showed no systemic effects, quinolone-induced lesions, erosions of the cartilage in weight-bearing joints, or other signs of arthropathy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In the Phase III clinical trials performed in support of once-daily dosing, 799 subjects with otitis externa and intact tympanic membranes were treated with ofloxacin otic solution. The studies, which served as the basis for approval, were 020 (pediatric, adolescents and adults), 016 (adolescents and adults) and 017 (pediatric). The following treatment-related adverse events occurred in 2 or more of the subjects:
†Studies 002/003 (BID) and 016/017 (QD) were active-controlled and comparative.
Adverse Event
Incidence Rate
Studies 002/003† BID
(N=229)
Studies 016/017† QD
(N=310)
Studies 020† QD
(N=489)
Application Site
3%
16.8%
0.6%
Reaction
Pruritus
4%
1.2%
1.0%
Earache
1%
0.6%
0.8%
Dizziness
1%
0.0%
0.6%
Headache
0%
0.3%
0.2%
Vertigo
1%
0.0%
0.0%
Study 020 (QD) was open and non-comparative.
An unexpected increased incidence of application site reaction was seen in studies 016/017 and was similar for both ofloxacin and the active control drug (neomycin-polymyxin B sulfate- hydrocortisone). This finding is believed to be the result of specific questioning of the subjects regarding the incidence of application site reactions.
In once daily dosing studies, there were also single reports of nausea, seborrhea, transient loss of hearing, tinnitus, otitis externa, otitis media, tremor, hypertension and fungal infection.
In twice daily dosing studies, the following treatment-related adverse events were each reported in a single subject: dermatitis, eczema, erythematous rash, follicular rash, hypoaesthesia, tinnitus, dyspepsia, hot flushes, flushing and otorrhagia.
Subjects with Acute Otitis Media with Tympanostomy Tubes (AOM TT) and Subjects with Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) with Perforated Tympanic Membranes
In Phase III clinical trials which formed the basis for approval, the following treatment-related adverse events occurred in 1% or more of the 656 subjects with non-intact tympanic membranes in AOM TT or CSOM treated twice-daily with ofloxacin otic solution:
Adverse Event
Incidence (N=656)
Taste Perversion
7%
Earache
1%
Pruritus
1%
Paraesthesia
1%
Rash
1%
Dizziness
1%
Other treatment-related adverse reactions reported in subjects with non-intact tympanic membranes included: diarrhea (0.6%), nausea (0.3%), vomiting (0.3%), dry mouth (0.5%), headache (0.3%), vertigo (0.5%), otorrhagia (0.6%), tinnitus (0.3%), fever (0.3%). The following treatment-related adverse events were each reported in a single subject: application site reaction, otitis externa, urticaria, abdominal pain, dysaesthesia, hyperkinesia, halitosis, inflammation, pain, insomnia, coughing, pharyngitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, and tachycardia.
Post-Marketing Adverse Events
Cases of uncommon transient neuropsychiatric disturbances have been included in spontaneous post- marketing reports. A causal relationship with ofloxacin otic solution 0.3% is unknown.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Otitis Externa: The recommended dosage regimen for the treatment of otitis externa is:
- For pediatric patients (from 6 months to 13 years old): Five drops (0.25 mL, 0.75 mg ofloxacin) instilled into the affected ear once daily for seven days.
- For patients 13 years and older: Ten drops (0.5 mL, 1.5 mg ofloxacin) instilled into the affected ear once daily for seven days.
- The solution should be warmed by holding the bottle in the hand for one or two minutes to avoid dizziness which may result from the instillation of a cold solution. The patient should lie with the affected ear upward, and then the drops should be instilled. This position should be maintained for five minutes to facilitate penetration of the drops into the ear canal. Repeat, if necessary, for the opposite ear.
Acute Otitis Media in pediatric patients with tympanostomy tubes: The recommended dosage regimen for the treatment of acute otitis media in pediatric patients (from 1 to 12 years old) with tympanostomy tubes is:
Five drops (0.25 mL, 0.75 mg ofloxacin) instilled into the affected ear twice daily for ten days. The solution should be warmed by holding the bottle in the hand for one or two minutes to avoid dizziness that may result from the instillation of a cold solution. The patient should lie with the affected ear upward, and then the drops should be instilled. The tragus should then be pumped 4 times by pushing inward to facilitate penetration of the drops into the middle ear. This position should be maintained for five minutes. Repeat, if necessary, for the opposite ear.
Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media with perforated tympanic membranes: The recommended dosage regimen for the treatment of chronic suppurative otitis media with perforated tympanic membranes in patients 12 years and older is:
Ten drops (0.5 mL, 1.5 mg ofloxacin) instilled into the affected ear twice daily for fourteen days. The solution should be warmed by holding the bottle in the hand for one or two minutes to avoid dizziness that may result from the instillation of a cold solution. The patient should lie with the affected ear upward, before instilling the drops. The tragus should then be pumped 4 times by pushing inward to facilitate penetration into the middle ear. This position should be maintained for five minutes. Repeat, if necessary, for the opposite ear.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Ofloxacin otic solution 0.3% is supplied in plastic dropper bottles containing 5 mL and 10 mL.
NDC 70069-686-01 Ofloxacin Otic solution (5mL)
NDC 70069-687-01 Ofloxacin Otic solution (10 mL)
Store at 25 °C (77 °F), excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59-86 °F). Protect from light.
Rx Only
Manufactured for:
Somerset Therapeutics, LLC
Somerset, NJ 08873
Made in India
Code No.: KR/DRUGS/KTK/28/289/97
1201075
ST-OFO/P/00
Revised: October, 2024
-
PATIENT INFORMATION
IMPORTANT PATIENT INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS.
READ BEFORE USE.
What is ofloxacin otic solution?
Ofloxacin otic solution is an antibiotic in a sterile solution used to treat ear infections caused by certain bacteria found in:
- patients (12 years and older) who have a middle ear infection and have a hole in the eardrum
- pediatric patients (between 1 and 12 years of age) who have a middle ear infection and have a tube in the eardrum
- patients (6 months and older) who have an infection in the ear canal.
Middle Ear Infection: A middle ear infection is a bacterial infection behind the eardrum. People with a hole or a tube in the eardrum may notice a discharge (fluid draining) from the ear canal.
Ear Canal Infection: An ear canal infection (also known as "Swimmer's Ear") is a bacterial infection of the ear canal. The ear canal and the outer part of the ear may swell, turn red, and be painful. Also, a fluid discharge may appear in the ear canal.
Who should NOT use ofloxacin otic solution?
- Do not use this product if you are allergic to ofloxacin or to other quinolone antibiotics.
- Do not give this product to pediatric patients who:
- have an ear canal infection and are less than 6 months of age because no data were collected from this population
- have a middle ear infection and have a tube in the eardrum and are less than one year of age because no data were collected from this population
- have a middle ear infection and have a hole in the eardrum and are less than 12 years of age because no data were collected from this population.
How should ofloxacin otic solution be given?
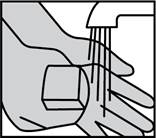
1. Wash hands
The person giving ofloxacin otic solution should wash his/her hands with soap and water.
Gently clean any discharge that can be removed easily from the outer ear.
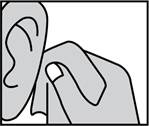
DO NOT INSERT ANY OBJECT OR SWAB INTO THE EAR CANAL.
Hold the bottle of ofloxacin otic solution in the hand for one or two minutes to warm the solution.
3. Add drops
For a Middle Ear Infection:
The person receiving ofloxacin otic solution should lie on his/her side with the infected ear up. Patients (12 and older) should have 10 drops of ofloxacin otic solution put into the infected ear. Pediatric patients under 12 should have 5 drops put into the infected ear. The tip of the bottle should not touch the fingers or the ear or any other surfaces.
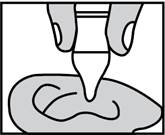
For an Ear Canal Infection ("Swimmer's Ear"):
The person receiving ofloxacin otic solution should lie on his/her side with the infected ear up. Patients (13 and older) should have 10 drops of ofloxacin otic solution put into the infected ear. Pediatric patients under 13 should have 5 drops put into the infected ear. The tip of the bottle should not touch the fingers or the ear or any other surfaces.
BE SURE TO FOLLOW THE INSTRUCTIONS BELOW FOR THE PATIENT'S SPECIFIC EAR INFECTION.
4. Press ear or pull ear
For a Middle Ear Infection:
While the person receiving ofloxacin otic solution lies on his/her side, the person giving the drops should gently press the TRAGUS (see diagram) 4 times in a pumping motion. This will allow the drops to pass through the hole or tube in the eardrum and into the middle ear.
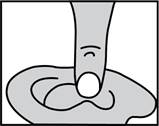
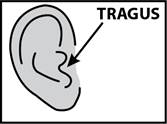
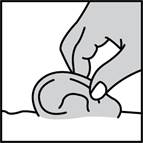
For an Ear Canal Infection ("Swimmer's Ear"):
While the person receiving the drops lies on his/her side, the person giving the drops should gently pull the outer ear upward and backward. This will allow the ear drops to flow down into the ear canal.
The person who received the ear drops should remain on his/her side for at least 5 minutes.
Repeat Steps 2-5 for the other ear if both ears are infected.
How often should ofloxacin otic solution be given?
In patients with an Ear Canal Infection ("Swimmer's Ear"), ofloxacin otic solution ear drops should be given once daily at about the same time each day (for example, 8 AM or 8 PM) in each infected ear unless the doctor has instructed otherwise.
In patients with a Middle Ear Infection, ofloxacin otic solution ear drops should be given 2 times each day (about 12 hours apart, for example 8 AM and 8 PM) in each infected ear unless the doctor has instructed otherwise. The best times to use the ear drops are in the morning and at night.
It is very important to use the ear drops for as long as the doctor has instructed, even if the symptoms improve. If ofloxacin otic solution ear drops are not used for as long as the doctor has instructed, the infection may be more likely to return.
What if a dose is missed?
In patients with an Ear Canal Infection ("Swimmer's Ear"), it is important that you take the drops every day. If you miss a dose which may have been scheduled for earlier in the day, (for example, 8:00 AM), you should take that day's dose as soon as possible and then go back to your regular daily dosing schedule.
In patients with a Middle Ear Infection, if a dose of ofloxacin otic solution is missed, it should be given as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to the regular dosing schedule.
Do not use a double dose unless the doctor has instructed you to do so. If the infection is not improved after one week, you should consult your doctor. If you have two or more episodes of drainage within six months, it is recommended that you see your doctor for further evaluation.
What activities should be avoided while using ofloxacin otic solution?
It is important that the infected ear(s) remain clean and dry. When bathing, avoid getting the infected ear(s) wet. Avoid swimming unless the doctor has instructed otherwise.
What are some of the possible side effects of ofloxacin otic solution?
During the testing of ofloxacin otic solution in external ear infections, the most common side effect was discomfort upon application which happened in 7% of patients. If the pain is severe, the medication should be stopped and you should contact your doctor. Other side effects were: itching (1%), earache (0.8%), and dizziness (0.4%).
During the testing of ofloxacin otic solution in middle ear infections, the most common side effect was a bitter taste which happened in 7% of patients with a middle ear infection. This may occur when some of the medication passes from the middle ear to the back of the mouth. This side effect is not serious and there is no need to stop the medicine if this should happen. Other side effects which were found in 1% of the patients were: earache, itching, abnormal sensation, rash, and dizziness.
Call your doctor about these or other side effects if they occur.
If a rash or an allergic reaction to ofloxacin otic solution occurs, stop using the product and contact your doctor.
DO NOT TAKE OFLOXACIN OTIC SOLUTION BY MOUTH.
If ofloxacin otic solution is accidentally swallowed or an overdose occurs, call the doctor immediately. This medicine is available only with a doctor's prescription. Use only as directed. Do not use this medicine if outdated.
If you wish to learn more about ofloxacin otic solution, ask the doctor or pharmacist. Complete prescribing information is printed on the reverse side.
HOW SUPPLIED.
Plastic dropper bottles containing 5 mL and 10 mL
Storage Conditions: Store at 25°C (77°F), excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F). Protect from light.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
Somerset Therapeutics, LLC
Somerset, NJ 08873
Revised: October, 2024
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
OFLOXACIN
ofloxacin solution/ dropsProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70069-686 Route of Administration AURICULAR (OTIC) Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength OFLOXACIN (UNII: A4P49JAZ9H) (OFLOXACIN - UNII:A4P49JAZ9H) OFLOXACIN 3 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70069-686-01 1 in 1 CARTON 10/31/2024 1 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA216328 10/31/2024 OFLOXACIN
ofloxacin solution/ dropsProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70069-687 Route of Administration AURICULAR (OTIC) Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength OFLOXACIN (UNII: A4P49JAZ9H) (OFLOXACIN - UNII:A4P49JAZ9H) OFLOXACIN 3 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70069-687-01 1 in 1 CARTON 10/31/2024 1 10 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA216328 10/31/2024 Labeler - Somerset Therapeutics, LLC (079947873) Registrant - Somerset Therapeutics, LLC (079947873) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Somerset Therapeutics Private Limited 677236695 ANALYSIS(70069-686, 70069-687) , LABEL(70069-686, 70069-687) , PACK(70069-686, 70069-687) , MANUFACTURE(70069-686, 70069-687)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.



