DIOVAN- valsartan tablet
Diovan by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Diovan by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DIOVAN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DIOVAN.
DIOVAN ® (valsartan) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1996INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Diovan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) indicated for:
-
Treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions (
1.1)
-
Treatment of heart failure (NYHA class II-IV); Diovan significantly reduced hospitalization for heart failure (
1.2)
- Post-myocardial infarction; for the reduction of cardiovascular mortality in clinically stable patients with left ventricular failure or left ventricular dysfunction following myocardial infarction ( 1.3)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
* As tolerated by patient Indication Starting Dose Dose Range Target Maintenance Dose* Adult Hypertension ( 2.1) 80 or 160 mg once daily 80-320 mg once daily --- Pediatric Hypertension (6-16 years) ( 2.2) 1.3 mg/kg once daily (up to 40 mg total) 1.3-2.7 mg/kg once daily (up to 40-160 mg total) --- Heart Failure ( 2.3) 40 mg twice daily 40-160 mg twice daily 160 mg twice daily Post-Myocardial Infarction ( 2.4) 20 mg twice daily 20-160 mg twice daily 160 mg twice daily DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets (mg): 40 (scored), 80, 160, 320 (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known hypersensitivity to any component.
Do not coadminister aliskiren with Diovan in patients with diabetes ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Hypertension: Most common adverse reactions are headache, dizziness, viral infection, fatigue and abdominal pain ( 6.1)
Heart Failure: Most common adverse reactions are dizziness, hypotension, diarrhea, arthralgia, back pain, fatigue and hyperkalemia ( 6.1)
Post-Myocardial Infarction: Most common adverse reactions which caused patients to discontinue therapy are hypotension, cough and increased blood creatinine ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements or salt substitutes may lead to increases in serum potassium, and in heart failure patients, increases in serum creatinine (
7.1)
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID) use may lead to increased risk of renal impairment and loss of antihypertensive effect ( 7.2)
- Dual inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system: Increased risk of renal impairment, hypotension, and hyperkalemia ( 7.3)
- Lithium: Increases in serum lithium level and lithium toxicity ( 7.4)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2019
-
Treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions (
1.1)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: FETAL TOXICITY
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Hypertension
1.2 Heart Failure
1.3 Post-Myocardial Infarction
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adult Hypertension
2.2 Pediatric Hypertension 6 to 16 Years of Age
2.3 Heart Failure
2.4 Post-Myocardial Infarction
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fetal Toxicity
5.2 Hypotension
5.3 Impaired Renal Function
5.4 Hyperkalemia
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Agents Increasing Serum Potassium
7.2 Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents Including Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors (COX-2 Inhibitors)
7.3 Dual Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS)
7.4 Lithium
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Hypertension
14.2 Heart Failure
14.3 Post-Myocardial Infarction
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- BOXED WARNING (What is this?)
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Hypertension
Diovan ® (valsartan) is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure in adults and pediatric patients six years of age and older. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including the class to which valsartan principally belongs. There are no controlled trials in hypertensive patients demonstrating risk reduction with Diovan.
Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC).
Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly.
Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (e.g., patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal.
Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy.
Diovan may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adult Hypertension
The recommended starting dose of Diovan (valsartan) is 80 mg or 160 mg once daily when used as monotherapy in patients who are not volume-depleted. Patients requiring greater reductions may be started at the higher dose. Diovan may be used over a dose range of 80 mg to 320 mg daily, administered once a day.
The antihypertensive effect is substantially present within 2 weeks and maximal reduction is generally attained after 4 weeks. If additional antihypertensive effect is required over the starting dose range, the dose may be increased to a maximum of 320 mg or a diuretic may be added. Addition of a diuretic has a greater effect than dose increases beyond 80 mg.
Diovan may be administered with other antihypertensive agents.
2.2 Pediatric Hypertension 6 to 16 Years of Age
For pediatric patients who can swallow tablets, the usual recommended starting dose is 1.3 mg/kg once daily (up to 40 mg total). The dosage should be adjusted according to blood pressure response. Doses higher than 2.7 mg/kg (up to 160 mg) once daily have not been studied in pediatric patients 6 to 16 years old.
For pediatric patients who cannot swallow tablets, or children for whom the calculated dosage (mg/kg) does not correspond to the available tablet strengths of Diovan, the use of a suspension is recommended. Follow the suspension preparation instructions below to administer valsartan as a suspension. When the suspension is replaced by a tablet, the dose of valsartan may have to be increased. The exposure to valsartan with the suspension is 1.6 times greater than with the tablet.
No data are available in pediatric patients either undergoing dialysis or with a glomerular filtration rate < 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Diovan is not recommended for patients < 6 years old [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Preparation of Suspension (for 160 mL of a 4 mg/mL suspension)
Add 80 mL of Ora-Plus ®* oral suspending vehicle to an amber glass bottle containing 8 Diovan 80 mg tablets, and shake for a minimum of 2 minutes. Allow the suspension to stand for a minimum of 1 hour. After the standing time, shake the suspension for a minimum of 1 additional minute. Add 80 mL of Ora-Sweet SF ®* oral sweetening vehicle to the bottle and shake the suspension for at least 10 seconds to disperse the ingredients. The suspension is homogenous and can be stored for either up to 30 days at room temperature (below 30ºC/86ºF) or up to 75 days at refrigerated conditions (2ºC-8ºC/35ºF-46ºF) in the glass bottle with a child-resistant screw-cap closure. Shake the bottle well (at least 10 seconds) prior to dispensing the suspension.
*Ora-Sweet SF ® and Ora-Plus ® are registered trademarks of Paddock Laboratories, Inc.
2.3 Heart Failure
The recommended starting dose of Diovan is 40 mg twice daily. Uptitrate to 80 mg and 160 mg twice daily or to the highest dose tolerated by the patient. Consider reducing the dose of concomitant diuretics. The maximum daily dose administered in clinical trials is 320 mg in divided doses.
2.4 Post-Myocardial Infarction
Diovan may be initiated as early as 12 hours after a myocardial infarction. The recommended starting dose of Diovan is 20 mg twice daily. Patients may be uptitrated within 7 days to 40 mg twice daily, with subsequent titrations to a target maintenance dose of 160 mg twice daily, as tolerated by the patient. If symptomatic hypotension or renal dysfunction occurs, consider dosage reduction. Diovan may be given with other standard post-myocardial infarction treatment, including thrombolytics, aspirin, beta-blockers, and statins.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
40 mg are scored yellow ovaloid tablets with beveled edges, imprinted NVR/DO (Side 1/Side 2)
80 mg are pale red almond-shaped tablets with beveled edges, imprinted NVR/DV
160 mg are grey-orange almond-shaped tablets with beveled edges, imprinted NVR/DX
320 mg are dark grey-violet almond-shaped tablets with beveled edges, imprinted NVR/DXL
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fetal Toxicity
Diovan can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Use of drugs that act on the renin-angiotensin system during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces fetal renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. Resulting oligohydramnios can be associated with fetal lung hypoplasia and skeletal deformations. Potential neonatal adverse effects include skull hypoplasia, anuria, hypotension, renal failure, and death. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue Diovan as soon as possible [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.2 Hypotension
Excessive hypotension was rarely seen (0.1%) in patients with uncomplicated hypertension treated with Diovan alone. In patients with an activated renin-angiotensin system, such as volume- and/or salt-depleted patients receiving high doses of diuretics, symptomatic hypotension may occur. This condition should be corrected prior to administration of Diovan, or the treatment should start under close medical supervision.
Patients with heart failure or post-myocardial infarction patients given Diovan commonly have some reduction in blood pressure, but discontinuation of therapy because of continuing symptomatic hypotension usually is not necessary when dosing instructions are followed. In controlled trials in heart failure patients, the incidence of hypotension in valsartan-treated patients was 5.5% compared to 1.8% in placebo-treated patients. In the VALsartan In Acute myocardial iNfarcTion trial (VALIANT), hypotension in post-myocardial infarction patients led to permanent discontinuation of therapy in 1.4% of valsartan-treated patients and 0.8% of captopril-treated patients.
If excessive hypotension occurs, place the patient in the supine position and, if necessary, give intravenous normal saline. A transient hypotensive response is not a contraindication to further treatment, which usually can be continued without difficulty once the blood pressure has stabilized.
5.3 Impaired Renal Function
Changes in renal function including acute renal failure can be caused by drugs that inhibit the renin-angiotensin system and by diuretics. Patients whose renal function may depend in part on the activity of the renin-angiotensin system (e.g., patients with renal artery stenosis, chronic kidney disease, severe congestive heart failure, or volume depletion) may be at particular risk of developing acute renal failure on Diovan. Monitor renal function periodically in these patients. Consider withholding or discontinuing therapy in patients who develop a clinically significant decrease in renal function on Diovan [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.4 Hyperkalemia
Some patients with heart failure have developed increases in potassium. These effects are usually minor and transient, and they are more likely to occur in patients with pre-existing renal impairment. Dosage reduction and/or discontinuation of Diovan may be required [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adult Hypertension
Diovan (valsartan) has been evaluated for safety in more than 4,000 patients, including over 400 treated for over 6 months, and more than 160 for over 1 year. Adverse reactions have generally been mild and transient in nature and have only infrequently required discontinuation of therapy. The overall incidence of adverse reactions with Diovan was similar to placebo.
The overall frequency of adverse reactions was neither dose-related nor related to gender, age, race, or regimen. Discontinuation of therapy due to side effects was required in 2.3% of valsartan patients and 2.0% of placebo patients. The most common reasons for discontinuation of therapy with Diovan were headache and dizziness.
The adverse reactions that occurred in placebo-controlled clinical trials in at least 1% of patients treated with Diovan and at a higher incidence in valsartan (n=2,316) than placebo (n=888) patients included viral infection (3% vs. 2%), fatigue (2% vs. 1%), and abdominal pain (2% vs. 1%).
In trials in which valsartan was compared to an ACE inhibitor with or without placebo, the incidence of dry cough was significantly greater in the ACE-inhibitor group (7.9%) than in the groups who received valsartan (2.6%) or placebo (1.5%). In a 129-patient trial limited to patients who had had dry cough when they had previously received ACE inhibitors, the incidences of cough in patients who received valsartan, HCTZ, or lisinopril were 20%, 19%, and 69% respectively (p < 0.001).
Dose-related orthostatic effects were seen in less than 1% of patients. An increase in the incidence of dizziness was observed in patients treated with Diovan 320 mg (8%) compared to 10 to 160 mg (2% to 4%).
Pediatric Hypertension
Diovan has been evaluated for safety in over 400 pediatric patients aged 6 to 17 years and more than 160 pediatric patients aged 6 months to 5 years. No relevant differences were identified between the adverse experience profile for pediatric patients aged 6 to 16 years and that previously reported for adult patients. Headache and hyperkalemia were the most common adverse events suspected to be study drug-related in older children (6 to 17 years old) and younger children (6 months to 5 years old), respectively. Hyperkalemia was mainly observed in children with underlying renal disease. Neurocognitive and developmental assessment of pediatric patients aged 6 to 16 years revealed no overall clinically relevant adverse impact after treatment with Diovan for up to 1 year.
Diovan is not recommended for pediatric patients under 6 years of age. In a study (n=90) of pediatric patients (1 to 5 years), two deaths and three cases of on-treatment transaminase elevations were seen in the one-year open-label extension phase. These 5 events occurred in a study population in which patients frequently had significant co-morbidities. A causal relationship to Diovan has not been established. In a second study of 6-months duration in 75 children aged 1 to 5 years, there were no deaths; one case of marked liver transaminase elevations occurred following 6 months of treatment. The most common adverse reaction in children less than 6 years old was hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia was mainly observed in children with underlying renal disease.
Heart Failure
In the Valsartan Heart Failure Trial, comparing valsartan in total daily doses up to 320 mg (n=2,506) to placebo (n=2,494), 10% of valsartan patients discontinued for adverse reactions vs. 7% of placebo patients.
The table shows adverse reactions in double-blind short-term heart failure trials, including the first 4 months of the Valsartan Heart Failure Trial, with an incidence of at least 2% that were more frequent in valsartan-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients. All patients received standard drug therapy for heart failure, frequently as multiple medications, which could include diuretics, digitalis, beta-blockers. About 93% of patients received concomitant ACE inhibitors.
Valsartan (n=3,282) Placebo (n=2,740) Dizziness 17% 9% Hypotension 7% 2% Diarrhea 5% 4% Arthralgia 3% 2% Fatigue 3% 2% Back Pain 3% 2% Dizziness, postural 2% 1% Hyperkalemia 2% 1% Hypotension, postural 2% 1% Discontinuations occurred in 0.5% of valsartan-treated patients and 0.1% of placebo patients for each of the following: elevations in creatinine and elevations in potassium.
Other adverse reactions with an incidence greater than 1% and greater than placebo included headache, nausea, renal impairment, syncope, blurred vision, upper abdominal pain and vertigo.
From the long-term data in the Valsartan Heart Failure Trial, there did not appear to be any significant adverse reactions not previously identified.
Post-Myocardial Infarction
The table shows the percentage of patients discontinued in the valsartan and captopril-treated groups in the VALsartan In Acute myocardial iNfarcTion trial (VALIANT) with a rate of at least 0.5% in either of the treatment groups.
Discontinuations due to renal dysfunction occurred in 1.1% of valsartan-treated patients and 0.8% of captopril-treated patients.
Valsartan (n=4,885) Captopril (n=4,879) Discontinuation for adverse reaction 5.8% 7.7% Adverse reactions Hypotension NOS 1.4% 0.8% Cough 0.6% 2.5% Blood creatinine increased 0.6% 0.4% Rash NOS 0.2% 0.6% Clinical Laboratory Test Findings
Creatinine: In heart failure trials, greater than 50% increases in creatinine were observed in 3.9% of Diovan-treated patients compared to 0.9% of placebo-treated patients. In post-myocardial infarction patients, doubling of serum creatinine was observed in 4.2% of valsartan-treated patients and 3.4% of captopril-treated patients.
Neutropenia: Neutropenia was observed in 1.9% of patients treated with Diovan and 0.8% of patients treated with placebo.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN): In heart failure trials, greater than 50% increases in BUN were observed in 16.6% of Diovan-treated patients compared to 6.3% of placebo-treated patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported in postmarketing use of Diovan. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity: Angioedema has been reported. Some of these patients previously experienced angioedema with other drugs including ACE inhibitors. Diovan should not be re-administered to patients who have had angioedema.
Digestive: Elevated liver enzymes and very rare reports of hepatitis
Musculoskeletal: Rhabdomyolysis
Renal: Impaired renal function, renal failure
Dermatologic: Alopecia, bullous dermatitis
Blood and Lymphatic: Thrombocytopenia
Vascular: Vasculitis
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Agents Increasing Serum Potassium
Concomitant use of valsartan with other agents that block the renin-angiotensin system, potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride), potassium supplements, salt substitutes containing potassium or other drugs that may increase potassium levels (e.g., heparin) may lead to increases in serum potassium and in heart failure patients to increases in serum creatinine. If co-medication is considered necessary, monitoring of serum potassium is advisable.
7.2 Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents Including Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors (COX-2 Inhibitors)
In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or with compromised renal function, coadministration of NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors, with angiotensin II receptor antagonists, including valsartan, may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. These effects are usually reversible. Monitor renal function periodically in patients receiving valsartan and NSAID therapy.
The antihypertensive effect of angiotensin II receptor antagonists, including valsartan, may be attenuated by NSAIDs including selective COX-2 inhibitors.
7.3 Dual Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS)
Dual blockade of the RAS with angiotensin receptor blockers, ACE inhibitors, or aliskiren is associated with increased risks of hypotension, hyperkalemia, and changes in renal function (including acute renal failure) compared to monotherapy. Most patients receiving the combination of two RAS inhibitors do not obtain any additional benefit compared to monotherapy [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. In general, avoid combined use of RAS inhibitors. Closely monitor blood pressure, renal function and electrolytes in patients on Diovan and other agents that affect the RAS.
Do not coadminister aliskiren with Diovan in patients with diabetes. Avoid use of aliskiren with Diovan in patients with renal impairment (GFR < 60 mL/min).
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Diovan can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Use of drugs that act on the renin-angiotensin system during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces fetal renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. Most epidemiologic studies examining fetal abnormalities after exposure to antihypertensive use in the first trimester have not distinguished drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system from other antihypertensive agents. Published reports include cases of anhydramnios and oligohydramnios in pregnant women treated with valsartan (see Clinical Considerations).
When pregnancy is detected, consider alternative drug treatment and discontinue Diovan as soon as possible.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Hypertension in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes, premature delivery, and delivery complications (e.g., need for cesarean section, and post-partum hemorrhage). Hypertension increases the fetal risk for intrauterine growth restriction and intrauterine death. Pregnant women with hypertension should be carefully monitored and managed accordingly.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Oligohydramnios in pregnant women who use drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy can result in the following: reduced fetal renal function leading to anuria and renal failure, fetal lung hypoplasia, skeletal deformations, including skull hypoplasia, hypotension and death. In the unusual case that there is no appropriate alternative to therapy with drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system for a particular patient, apprise the mother of the potential risk to the fetus.
In patients taking Diovan during pregnancy, perform serial ultrasound examinations to assess the intra-amniotic environment. Fetal testing may be appropriate, based on the week of gestation. Patients and physicians should be aware, however, that oligohydramnios may not appear until after the fetus has sustained irreversible injury. If oligohydramnios is observed, consider alternative drug treatment. Closely observe neonates with histories of in utero exposure to Diovan for hypotension, oliguria, and hyperkalemia. In neonates with a history of in utero exposure to Diovan, if oliguria or hypotension occurs, support blood pressure and renal perfusion. Exchange transfusions or dialysis may be required as a means of reversing hypotension and replacing renal function.
Data
Animal Data
No teratogenic effects were observed when valsartan was administered to pregnant mice and rats at oral doses of up to 600 mg/kg/day (9 and 18 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m 2 basis) and to pregnant rabbits at oral doses of up to 10 mg/kg/day.
In rats, oral valsartan administered at maternally toxic doses (600 mg/kg/day) during organogenesis or late gestation and lactation, resulted in decreased fetal and pup weight, pup survival and delayed developmental milestones. In rabbits administered maternally toxic doses of 5 and 10 mg/kg/day, fetotoxicity was observed.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of Diovan in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Diovan is present in rat milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from exposure to valsartan, advise a nursing woman that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with Diovan.
Data
Valsartan was detected in the milk of lactating rats 15 minutes after oral administration of a 3 mg/kg dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The antihypertensive effects of Diovan have been evaluated in two randomized, double-blind clinical studies in pediatric patients from 1-5 and 6-16 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The pharmacokinetics of Diovan have been evaluated in pediatric patients 1 to 16 years of age [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Diovan was generally well tolerated in children 6 to 16 years and the adverse experience profile was similar to that described for adults.
In children and adolescents with hypertension where underlying renal abnormalities may be more common, renal function and serum potassium should be closely monitored as clinically indicated.
Diovan is not recommended for pediatric patients under 6 years of age due to safety findings for which a relationship to treatment could not be excluded [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
No data are available in pediatric patients either undergoing dialysis or with a glomerular filtration rate < 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2.
There is limited clinical experience with Diovan in pediatric patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the controlled clinical trials of valsartan, 1,214 (36.2%) hypertensive patients treated with valsartan were ≥ 65 years and 265 (7.9%) were ≥ 75 years. No overall difference in the efficacy or safety of valsartan was observed in this patient population, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. Exposure [measured by area under the curve (AUC)] to valsartan is higher by 70% in the elderly than in the young, however no dosage adjustment is necessary [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Of the 2,511 patients with heart failure randomized to valsartan in the Valsartan Heart Failure Trial, 45% (1,141) were 65 years of age or older. In the VALsartan In Acute myocardial iNfarcTion trial (VALIANT), 53% (2,596) of the 4,909 patients treated with valsartan and 51% (2,515) of the 4,885 patients treated with valsartan + captopril were 65 years of age or older. There were no notable differences in efficacy or safety between older and younger patients in either trial.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Limited data are available related to overdosage in humans. The most likely manifestations of overdosage would be hypotension and tachycardia; bradycardia could occur from parasympathetic (vagal) stimulation. Depressed level of consciousness, circulatory collapse and shock have been reported. If symptomatic hypotension should occur, institute supportive treatment.
Diovan (valsartan) is not removed from the plasma by hemodialysis.
Valsartan was without grossly observable adverse effects at single oral doses up to 2000 mg/kg in rats and up to 1000 mg/kg in marmosets, except for salivation and diarrhea in the rat and vomiting in the marmoset at the highest dose (60 and 31 times, respectively, the MRHD dose on a mg/m 2 basis) (Calculations assume an oral dose of 320 mg/day and a 60-kg patient).
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Diovan (valsartan) is a nonpeptide, orally active, and specific angiotensin II receptor blocker acting on the AT 1 receptor subtype.
Valsartan is chemically described as N-(1-oxopentyl)- N-[[2′-(1 H-tetrazol-5-yl) [1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-L-valine. Its empirical formula is C 24H 29N 5O 3, its molecular weight is 435.5, and its structural formula is:
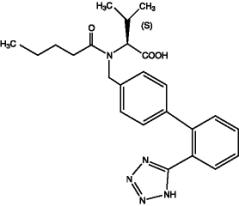
Valsartan is a white to practically white fine powder. It is soluble in ethanol and methanol and slightly soluble in water.
Diovan is available as tablets for oral administration, containing 40 mg, 80 mg, 160 mg or 320 mg of valsartan. The inactive ingredients of the tablets are colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, iron oxides (yellow, black and/or red), magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol 8000, and titanium dioxide.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Angiotensin II is formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE, kininase II). Angiotensin II is the principal pressor agent of the renin-angiotensin system, with effects that include vasoconstriction, stimulation of synthesis and release of aldosterone, cardiac stimulation, and renal reabsorption of sodium. Diovan (valsartan) blocks the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT 1 receptor in many tissues, such as vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland. Its action is therefore independent of the pathways for angiotensin II synthesis.
There is also an AT 2 receptor found in many tissues, but AT 2 is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Valsartan has much greater affinity (about 20,000-fold) for the AT 1 receptor than for the AT 2 receptor. The increased plasma levels of angiotensin II following AT 1 receptor blockade with valsartan may stimulate the unblocked AT 2 receptor. The primary metabolite of valsartan is essentially inactive with an affinity for the AT 1 receptor about one-200th that of valsartan itself.
Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system with ACE inhibitors, which inhibit the biosynthesis of angiotensin II from angiotensin I, is widely used in the treatment of hypertension. ACE inhibitors also inhibit the degradation of bradykinin, a reaction also catalyzed by ACE. Because valsartan does not inhibit ACE (kininase II), it does not affect the response to bradykinin. Whether this difference has clinical relevance is not yet known. Valsartan does not bind to or block other hormone receptors or ion channels known to be important in cardiovascular regulation.
Blockade of the angiotensin II receptor inhibits the negative regulatory feedback of angiotensin II on renin secretion, but the resulting increased plasma renin activity and angiotensin II circulating levels do not overcome the effect of valsartan on blood pressure.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Valsartan inhibits the pressor effect of angiotensin II infusions. An oral dose of 80 mg inhibits the pressor effect by about 80% at peak with approximately 30% inhibition persisting for 24 hours. No information on the effect of larger doses is available.
Removal of the negative feedback of angiotensin II causes a 2- to 3-fold rise in plasma renin and consequent rise in angiotensin II plasma concentration in hypertensive patients. Minimal decreases in plasma aldosterone were observed after administration of valsartan; very little effect on serum potassium was observed.
In multiple-dose studies in hypertensive patients with stable renal insufficiency and patients with renovascular hypertension, valsartan had no clinically significant effects on glomerular filtration rate, filtration fraction, creatinine clearance, or renal plasma flow.
In multiple-dose studies in hypertensive patients, valsartan had no notable effects on total cholesterol, fasting triglycerides, fasting serum glucose, or uric acid.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
In healthy volunteers, valsartan peak plasma concentration is reached 2 to 4 hours after dosing. Valsartan shows bi-exponential decay kinetics following intravenous administration, with an average elimination half-life of about 6 hours. Absolute bioavailability for Diovan is about 25% (range 10% to 35%). The bioavailability of the suspension [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] is 1.6 times as great as with the tablet. AUC and C max values of valsartan increase approximately linearly with increasing dose over the clinical dosing range (80-320 mg). Valsartan does not accumulate appreciably in plasma following repeated administration of 200 mg once daily.
In heart failure patients, the average time to peak plasma concentration and elimination half-life of valsartan are similar to those observed in healthy volunteers. The average accumulation factor is about 1.7 in heart failure patients following repeated administration of 160 mg twice daily. AUC and C max values of valsartan increase linearly and are almost proportional with increasing dose from 40 to 160 mg twice a day.
Effect of Food
With the tablet, food decreases the exposure (as measured by AUC) to valsartan by about 40% and peak plasma concentration (C max) by about 50%. Diovan can be administered with or without food.
Distribution:
The steady state volume of distribution of valsartan after intravenous administration is small (17 L), indicating that valsartan does not distribute into tissues extensively. Valsartan is highly bound to serum proteins (95%), mainly serum albumin.
Metabolism:
The primary metabolite, accounting for about 9% of dose, is valeryl 4-hydroxy valsartan. In vitro metabolism studies involving recombinant CYP 450 enzymes indicated that the CYP 2C9 isoenzyme is responsible for the formation of valeryl-4-hydroxy valsartan. Valsartan does not inhibit CYP 450 isozymes at clinically relevant concentrations. CYP 450 mediated drug interaction between valsartan and coadministered drugs are unlikely because of the low extent of metabolism.
Excretion
Valsartan, when administered as an oral solution, is primarily recovered in feces (about 83% of dose) and urine (about 13% of dose). The recovery is mainly as unchanged drug, with only about 20% of dose recovered as metabolites.
Following intravenous administration, plasma clearance of valsartan is about 2 L/h and its renal clearance is 0.62 L/h (about 30% of total clearance).
The apparent clearance of valsartan following oral administration is approximately 4.5 L/h in heart failure patients. Age does not affect the apparent clearance in heart failure patients.
Specific Populations:
Geriatric: Exposure (measured by AUC) to valsartan is higher by 70% and the half-life is longer by 35% in the elderly than in the young [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Pediatric: In a study of pediatric hypertensive patients (n=26, 1 to 16 years of age) given single doses of a suspension of Diovan (mean: 0.9 to 2 mg/kg), the clearance (L/h/kg) of valsartan for children was similar to that of adults receiving the same formulation.
Gender: Pharmacokinetics of valsartan does not differ significantly between males and females.
Renal Insufficiency: There is no apparent correlation between renal function (measured by creatinine clearance) and exposure (measured by AUC) to valsartan in patients with different degrees of renal impairment (down to creatinine clearance of 10 mL/min). Valsartan is not removed from the plasma by hemodialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Hepatic Insufficiency: On average, patients with mild-to-moderate chronic liver disease have twice the exposure (measured by AUC values) to valsartan of healthy volunteers (matched by age, sex, and weight) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Drug Interaction Studies
No clinically significant pharmacokinetic interactions were observed when Diovan (valsartan) was coadministered with amlodipine, atenolol, cimetidine, digoxin, furosemide, glyburide, hydrochlorothiazide, or indomethacin. The valsartan-atenolol combination was more antihypertensive than either component, but it did not lower the heart rate more than atenolol alone.
Coadministration of valsartan and warfarin did not change the pharmacokinetics of valsartan or the time-course of the anticoagulant properties of warfarin.
Transporters: The results from an in vitro study with human liver tissue indicate that valsartan is a substrate of the hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1 and the hepatic efflux transporter MRP2. Coadministration of inhibitors of the uptake transporter (rifampin, cyclosporine) or efflux transporter (ritonavir) may increase the systemic exposure to valsartan.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
There was no evidence of carcinogenicity when valsartan was administered in the diet to mice and rats for up to 2 years at doses up to 160 and 200 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses in mice and rats are about 2.6 and 6 times, respectively, the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis (Calculations assume an oral dose of 320 mg/day and a 60-kg patient).
Mutagenicity assays did not reveal any valsartan-related effects at either the gene or chromosome level. These assays included bacterial mutagenicity tests with Salmonella (Ames) and E coli; a gene mutation test with Chinese hamster V79 cells; a cytogenetic test with Chinese hamster ovary cells; and a rat micronucleus test.
Valsartan had no adverse effects on the reproductive performance of male or female rats at oral doses up to 200 mg/kg/day. This dose is 6 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis (Calculations assume an oral dose of 320 mg/day and a 60-kg patient).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Daily oral dosing of neonatal/juvenile rats with valsartan at doses as low as 1 mg/kg/day (about 10% of the maximum recommended pediatric dose on a mg/m2 basis) from postnatal day 7 to postnatal day 70 produced persistent, irreversible kidney damage. These kidney effects in neonatal rats represent expected exaggerated pharmacological effects that are observed if rats are treated during the first 13 days of life.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Hypertension
Adult Hypertension
The antihypertensive effects of Diovan (valsartan) were demonstrated principally in 7 placebo-controlled, 4- to 12-week trials (1 in patients over 65 years) of dosages from 10 to 320 mg/day in patients with baseline diastolic blood pressures of 95-115 mmHg. The studies allowed comparison of once-daily and twice-daily regimens of 160 mg/day; comparison of peak and trough effects; comparison (in pooled data) of response by gender, age, and race; and evaluation of incremental effects of hydrochlorothiazide.
Administration of valsartan to patients with essential hypertension results in a significant reduction of sitting, supine, and standing systolic and diastolic blood pressure, usually with little or no orthostatic change.
In most patients, after administration of a single oral dose, onset of antihypertensive activity occurs at approximately 2 hours, and maximum reduction of blood pressure is achieved within 6 hours. The antihypertensive effect persists for 24 hours after dosing, but there is a decrease from peak effect at lower doses (40 mg) presumably reflecting loss of inhibition of angiotensin II. At higher doses, however (160 mg), there is little difference in peak and trough effect. During repeated dosing, the reduction in blood pressure with any dose is substantially present within 2 weeks, and maximal reduction is generally attained after 4 weeks. In long-term follow-up studies (without placebo control), the effect of valsartan appeared to be maintained for up to 2 years. The antihypertensive effect is independent of age, gender or race. The latter finding regarding race is based on pooled data and should be viewed with caution, because antihypertensive drugs that affect the renin-angiotensin system (that is, ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II blockers) have generally been found to be less effective in low-renin hypertensives (frequently blacks) than in high-renin hypertensives (frequently whites). In pooled, randomized, controlled trials of Diovan that included a total of 140 blacks and 830 whites, valsartan and an ACE-inhibitor control were generally at least as effective in blacks as whites. The explanation for this difference from previous findings is unclear.
Abrupt withdrawal of valsartan has not been associated with a rapid increase in blood pressure.
The blood pressure-lowering effect of valsartan and thiazide-type diuretics are approximately additive.
The 7 studies of valsartan monotherapy included over 2,000 patients randomized to various doses of valsartan and about 800 patients randomized to placebo. Doses below 80 mg were not consistently distinguished from those of placebo at trough, but doses of 80, 160 and 320 mg produced dose-related decreases in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, with the difference from placebo of approximately 6-9/3-5 mmHg at 80 to 160 mg and 9/6 mmHg at 320 mg. In a controlled trial the addition of HCTZ to valsartan 80 mg resulted in additional lowering of systolic and diastolic blood pressure by approximately 6/3 and 12/5 mmHg for 12.5 and 25 mg of HCTZ, respectively, compared to valsartan 80 mg alone.
Patients with an inadequate response to 80 mg once daily were titrated to either 160 mg once daily or 80 mg twice daily, which resulted in a similar response in both groups.
In controlled trials, the antihypertensive effect of once-daily valsartan 80 mg was similar to that of once-daily enalapril 20 mg or once-daily lisinopril 10 mg.
There are no trials of Diovan demonstrating reductions in cardiovascular risk in patients with hypertension, but at least one pharmacologically similar drug has demonstrated such benefits.
There was essentially no change in heart rate in valsartan-treated patients in controlled trials.
Pediatric Hypertension
The antihypertensive effects of Diovan were evaluated in two randomized, double-blind clinical studies.
In a clinical study involving 261 hypertensive pediatric patients 6 to 16 years of age, patients who weighed < 35 kg received 10, 40 or 80 mg of valsartan daily (low, medium and high doses), and patients who weighed ≥ 35 kg received 20, 80, and 160 mg of valsartan daily (low, medium and high doses). Renal and urinary disorders, and essential hypertension with or without obesity were the most common underlying causes of hypertension in children enrolled in this study. At the end of 2 weeks, valsartan reduced both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a dose-dependent manner. Overall, the three dose levels of valsartan (low, medium and high) significantly reduced systolic blood pressure by -8, -10, -12 mm Hg from the baseline, respectively. Patients were re-randomized to either continue receiving the same dose of valsartan or were switched to placebo. In patients who continued to receive the medium and high doses of valsartan, systolic blood pressure at trough was -4 and -7 mm Hg lower than patients who received the placebo treatment. In patients receiving the low dose of valsartan, systolic blood pressure at trough was similar to that of patients who received the placebo treatment. Overall, the dose-dependent antihypertensive effect of valsartan was consistent across all the demographic subgroups.
In a clinical study involving 90 hypertensive pediatric patients 1 to 5 years of age with a similar study design, there was some evidence of effectiveness, but safety findings for which a relationship to treatment could not be excluded mitigate against recommending use in this age group [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
14.2 Heart Failure
The Valsartan Heart Failure Trial (Val-HeFT) was a multinational, double-blind study in which 5,010 patients with NYHA class II (62%) to IV (2%) heart failure and LVEF < 40%, on baseline therapy chosen by their physicians, were randomized to placebo or valsartan (titrated from 40 mg twice daily to the highest tolerated dose or 160 mg twice daily) and followed for a mean of about 2 years. Although Val-HeFT’s primary goal was to examine the effect of valsartan when added to an ACE inhibitor, about 7% were not receiving an ACE inhibitor. Other background therapy included diuretics (86%), digoxin (67%), and beta-blockers (36%). The population studied was 80% male, 46% 65 years or older and 89% Caucasian. At the end of the trial, patients in the valsartan group had a blood pressure that was 4 mmHg systolic and 2 mmHg diastolic lower than the placebo group. There were two primary end points, both assessed as time to first event: all-cause mortality and heart failure morbidity, the latter defined as all-cause mortality, sudden death with resuscitation, hospitalization for heart failure, and the need for intravenous inotropic or vasodilatory drugs for at least 4 hours. These results are summarized in the following table.
Placebo Valsartan Hazard Ratio Nominal (N=2,499) (N=2,511) (95% CI*) p-value All-cause mortality 484 495 1.02 0.8 (19.4%) (19.7%) (0.90-1.15) HF morbidity 801 723 0.87 0.009 (32.1%) (28.8%) (0.79-0.97) * CI = Confidence Interval Although the overall morbidity result favored valsartan, this result was largely driven by the 7% of patients not receiving an ACE inhibitor, as shown in the following table.
Without ACE Inhibitor With ACE Inhibitor Placebo Valsartan Placebo Valsartan (N=181) (N=185) (N=2,318) (N=2,326) Events (%) 77 (42.5%) 46 (24.9%) 724 (31.2%) 677 (29.1%) Hazard ratio (95% CI) 0.51 (0.35, 0.73) 0.92 (0.82, 1.02) p-value 0.0002 0.0965 The modest favorable trend in the group receiving an ACE inhibitor was largely driven by the patients receiving less than the recommended dose of ACE inhibitor. Thus, there is little evidence of further clinical benefit when valsartan is added to an adequate dose of ACE inhibitor.
Secondary end points in the subgroup not receiving ACE inhibitors were as follows.
Placebo Valsartan Hazard Ratio (N=181) (N=185) (95% CI) Components of HF morbidity All-cause mortality 49 (27.1%) 32 (17.3%) 0.59 (0.37, 0.91) Sudden death with resuscitation 2 (1.1%) 1 (0.5%) 0.47 (0.04, 5.20) CHF therapy 1 (0.6%) 0 (0.0%) – CHF hospitalization 48 (26.5%) 24 (13.0%) 0.43 (0.27, 0.71) Cardiovascular mortality 40 (22.1%) 29 (15.7%) 0.65 (0.40, 1.05) Non-fatal morbidity 49 (27.1%) 24 (13.0%) 0.42 (0.26, 0.69) In patients not receiving an ACE inhibitor, valsartan-treated patients had an increase in ejection fraction and reduction in left ventricular internal diastolic diameter (LVIDD).
Effects were generally consistent across subgroups defined by age and gender for the population of patients not receiving an ACE inhibitor. The number of black patients was small and does not permit a meaningful assessment in this subset of patients.
14.3 Post-Myocardial Infarction
The VALsartan In Acute myocardial iNfarcTion trial (VALIANT) was a randomized, controlled, multinational, double-blind study in 14,703 patients with acute myocardial infarction and either heart failure (signs, symptoms or radiological evidence) or left ventricular systolic dysfunction (ejection fraction ≤ 40% by radionuclide ventriculography or ≤ 35% by echocardiography or ventricular contrast angiography). Patients were randomized within 12 hours to 10 days after the onset of myocardial infarction symptoms to one of three treatment groups: valsartan (titrated from 20 or 40 mg twice daily to the highest tolerated dose up to a maximum of 160 mg twice daily), the ACE inhibitor, captopril (titrated from 6.25 mg three times daily to the highest tolerated dose up to a maximum of 50 mg three times daily), or the combination of valsartan plus captopril. In the combination group, the dose of valsartan was titrated from 20 mg twice daily to the highest tolerated dose up to a maximum of 80 mg twice daily; the dose of captopril was the same as for monotherapy. The population studied was 69% male, 94% Caucasian, and 53% were 65 years of age or older. Baseline therapy included aspirin (91%), beta-blockers (70%), ACE inhibitors (40%), thrombolytics (35%) and statins (34%). The mean treatment duration was 2 years. The mean daily dose of Diovan in the monotherapy group was 217 mg.
The primary endpoint was time to all-cause mortality. Secondary endpoints included (1) time to cardiovascular (CV) mortality, and (2) time to the first event of cardiovascular mortality, reinfarction, or hospitalization for heart failure. The results are summarized in the following table.
Valsartan vs. Captopril
(N=4,909) (N=4,909)Valsartan + Captopril vs. Captopril
(N=4,885) (N=4,909)No. of Deaths
Valsartan/CaptoprilHazard Ratio
CIp-value No. of Deaths
Comb/CaptoprilHazard Ratio
CIp-value All-cause mortality
979 (19.9%)
/958 (19.5%)1.001
(0.902, 1.111)
0.98 941 (19.3%)
/958 (19.5%)0.984
(0.886, 1.093)
0.73 CV mortality 827 (16.8%)
/830 (16.9%)0.976
(0.875, 1.090)CV mortality, hospitalization for HF, and recurrent non-fatal MI
1,529 (31.1%)
/1,567 (31.9%)
0.955
(0.881, 1.035)
There was no difference in overall mortality among the three treatment groups. There was thus no evidence that combining the ACE inhibitor captopril and the angiotensin II blocker valsartan was of value.
The data were assessed to see whether the effectiveness of valsartan could be demonstrated by showing in a non-inferiority analysis that it preserved a fraction of the effect of captopril, a drug with a demonstrated survival effect in this setting. A conservative estimate of the effect of captopril (based on a pooled analysis of 3 post-infarction studies of captopril and 2 other ACE inhibitors) was a 14% to 16% reduction in mortality compared to placebo. Valsartan would be considered effective if it preserved a meaningful fraction of that effect and unequivocally preserved some of that effect. As shown in the table, the upper bound of the CI for the hazard ratio (valsartan/captopril) for overall or CV mortality is 1.09 to 1.11, a difference of about 9% to 11%, thus making it unlikely that valsartan has less than about half of the estimated effect of captopril and clearly demonstrating an effect of valsartan. The other secondary endpoints were consistent with this conclusion.
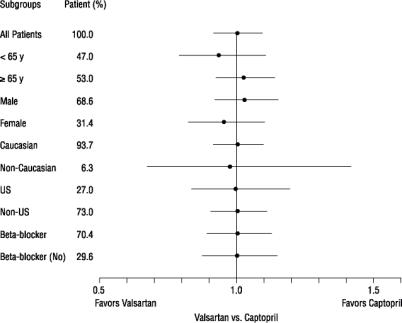
There were no clear differences in all-cause mortality based on age, gender, race, or baseline therapies, as shown in the figure above.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Diovan (valsartan) is available as tablets containing valsartan 80 mg.
The 80 mg pale red tablets are unscored and almond-shaped with bevelled-edges.
The tablets have NVR on one side and DV on the other side.
Supplied in bottles of:
20 tablets NDC: 55289-825-20
30 tablets NDC: 55289-825-30
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C-30°C (59°F-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from moisture.
Dispense in tight container (USP).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Pregnancy: Advise female patients of childbearing age about the consequences of exposure to Diovan during pregnancy. Discuss treatment options with women planning to become pregnant. Ask patients to report pregnancies to their healthcare provider as soon as possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with Diovan [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Symptomatic Hypotension: Advise patients that lightheadedness can occur, especially during the first days of therapy, and that it should be reported to their healthcare provider. Tell patients that if syncope occurs to discontinue Diovan until the physician has been consulted. Caution all patients that inadequate fluid intake, excessive perspiration, diarrhea, or vomiting can lead to an excessive fall in blood pressure, with the same consequences of lightheadedness and possible syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hyperkalemia: Advise patients not to use salt substitutes without consulting their healthcare provider [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
T2019-66
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
DIOVAN ® (DYE’-o-van)
(valsartan) Tablets
Read the Patient Information that comes with DIOVAN before you take it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or treatment. If you have any questions about DIOVAN, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
What is the most important information I should know about DIOVAN?
DIOVAN can cause harm or death to an unborn baby. Talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your blood pressure if you plan to become pregnant. If you get pregnant while taking DIOVAN, tell your doctor right away.
What is DIOVAN?
DIOVAN is a prescription medicine called an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB). It is used in adults to:
- lower high blood pressure (hypertension) in adults and children, 6 to 16 years of age.
- treat heart failure in adults. In these patients, DIOVAN may lower the need for hospitalization that happens from heart failure.
- improve the chance of living longer after a heart attack (myocardial infarction) in adults.
DIOVAN is not for children under 6 years of age or children with certain kidney problems.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension). Blood pressure is the force in your blood vessels when your heart beats and when your heart rests. You have high blood pressure when the force is too much. DIOVAN can help your blood vessels relax so your blood pressure is lower. Medicines that lower your blood pressure lower your chance of having a stroke or heart attack.
High blood pressure makes the heart work harder to pump blood throughout the body and causes damage to the blood vessels. If high blood pressure is not treated, it can lead to stroke, heart attack, heart failure, kidney failure and vision problems.
Heart Failure occurs when the heart is weak and cannot pump enough blood to your lungs and the rest of your body. Just walking or moving can make you short of breath, so you may have to rest a lot.
Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): A heart attack is caused by a blocked artery that results in damage to the heart muscle.
What should I tell my doctor before taking DIOVAN?
Tell your doctor about all your medical conditions including whether you:
- have any allergies. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in DIOVAN.
- have a heart condition
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. See “What is the most important information I should know about DIOVAN?”
- are breastfeeding. It is not known if DIOVAN passes into your breast milk, or effects your breastfed baby or milk production. Do not breastfeed while you are taking DIOVAN. Talk with your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take DIOVAN.
- have ever had a reaction called angioedema, to another blood pressure medicine. Angioedema causes swelling of the face, lips, tongue and/or throat, and may cause difficulty breathing.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- other medicines for high blood pressure or a heart problem
- water pills (also called “diuretics”)
- potassium supplements. Your doctor may check the amount of potassium in your blood periodically
- a salt substitute. Your doctor may check the amount of potassium in your blood periodically
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (like ibuprofen or naproxen)
- certain antibiotics (rifamycin group), a drug used to protect against transplant rejection (cyclosporine) or an antiretroviral drug used to treat HIV/AIDS infection (ritonavir). These drugs may increase the effect of valsartan.
- Lithium, a medicine used in some types of depression
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show to your doctor and pharmacist when a new medicine is prescribed. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before you start taking any new medicine. Your doctor or pharmacist will know what medicines are safe to take together.
How should I take DIOVAN?
- Take DIOVAN exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- For treatment of high blood pressure, take DIOVAN one time each day, at the same time each day.
- If your child cannot swallow tablets, or if tablets are not available in the prescribed strength, your pharmacist will mix DIOVAN as a liquid suspension for your child. If your child switches between taking the tablet and the suspension, your doctor will adjust the dose as needed. Shake the bottle of suspension well for at least 10 seconds before pouring the dose of medicine to give to your child.
- For adult patients with heart failure or who have had a heart attack, take DIOVAN two times each day, at the same time each day. Your doctor may start you on a low dose of DIOVAN and may increase the dose during your treatment.
- DIOVAN can be taken with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is close to your next dose, do not take the missed dose. Take the next dose at your regular time.
- If you take too much DIOVAN, call your doctor or Poison Control Center, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
What are the possible side effects of DIOVAN?
DIOVAN may cause the following serious side effects:
Injury or death to an unborn baby. See “What is the most important information I should know about DIOVAN?”
Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension). Low blood pressure is most likely to happen if you also take water pills, are on a low-salt diet, get dialysis treatments, have heart problems, or get sick with vomiting or diarrhea. Lie down, if you feel faint or dizzy. Call your doctor right away.
Kidney problems. Kidney problems may get worse if you already have kidney disease. Some patients will have changes on blood tests for kidney function and may need a lower dose of DIOVAN. Call your doctor if you get swelling in your feet, ankles, or hands, or unexplained weight gain. If you have heart failure, your doctor should check your kidney function before prescribing DIOVAN.
The most common side effects of DIOVAN used to treat people with high blood pressure include:
- headache
- dizziness
- flu symptoms
- tiredness
- stomach (abdominal) pain
Side effects were generally mild and brief. They generally have not caused patients to stop taking DIOVAN.
The most common side effects of DIOVAN used to treat people with heart failure include:
- dizziness
- low blood pressure
- diarrhea
- joint and back pain
- tiredness
- high blood potassium
Common side effects of DIOVAN used to treat people after a heart attack which caused them to stop taking the drug include:
- low blood pressure
- cough
- high blood creatinine (decreased kidney function)
- rash
Tell your doctor if you get any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of DIOVAN. For a complete list, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How do I store DIOVAN?
- Store DIOVAN tablets at room temperature between 59ºF - 86ºF (15ºC - 30ºC).
- Keep DIOVAN tablets in a closed container in a dry place.
- Store bottles of DIOVAN suspension at room temperature less than 86ºF (30ºC) for up to 30 days, or refrigerate between 35ºF - 46ºF (2ºC - 8ºC) for up to 75 days.
- Keep DIOVAN and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about DIOVAN
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use DIOVAN for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give DIOVAN to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about DIOVAN. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about DIOVAN that is written for health professionals.
For more information about DIOVAN, ask your pharmacist or doctor, visit www.DIOVAN.com on the Internet, or call 1-866-404-6361.
What are the ingredients in DIOVAN?
Active ingredient: valsartan
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, iron oxides (yellow, black and/or red), magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol 8000, and titanium dioxide
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, NJ 07936
© Novartis
T2019-67
Revised: 06/2019 - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DIOVAN
valsartan tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 55289-825(NDC:0078-0358) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VALSARTAN (UNII: 80M03YXJ7I) (VALSARTAN - UNII:80M03YXJ7I) VALSARTAN 80 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CROSPOVIDONE (UNII: 68401960MK) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Product Characteristics Color red (pale red) Score no score Shape OVAL (almond-shaped with bevelled edges) Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code NVR;DV Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 55289-825-20 20 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/20/2011 2 NDC: 55289-825-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/20/2011 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021283 07/01/2001 Labeler - PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (156893695) Registrant - PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (156893695) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 156893695 repack(55289-825)
Trademark Results [Diovan]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 DIOVAN 77527298 3819018 Live/Registered |
Novartis Corporation 2008-07-21 |
 DIOVAN 75000813 2177116 Live/Registered |
NOVARTIS CORPORATION 1995-10-02 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
