LOFEXIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE tablet, film coated
Lofexidine hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Lofexidine hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Prasco Laboratories, A+ Secure Packaging, LLC, Acceleration Laboratory Services Inc., Catalent Pharma Solutions, LLC, UFAG Laboratorien AG. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LOFEXIDINE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Lofexidine tablets.
Lofexidine tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Lofexidine tablets are a central alpha-2 adrenergic agonist indicated for mitigation of opioid withdrawal symptoms to facilitate abrupt opioid discontinuation in adults. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The usual Lofexidine tablet dosage is three 0.18 mg tablets taken orally 4 times daily at 5- to 6-hour intervals. Lofexidine tablet treatment may be continued for up to 14 days with dosing guided by symptoms. (2.1)
- Discontinue Lofexidine tablets with a gradual dose reduction over 2 to 4 days. (2.1)
- Hepatic or Renal Impairment: Dosage adjustments are recommended based on degree of impairment. (2.2, 2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 0.18 mg. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk of Hypotension, Bradycardia, and Syncope: May cause a decrease in blood pressure, a decrease in pulse, and syncope. Monitor vital signs before dosing and advise patients on how to minimize the risk of these cardiovascular effects and manage symptoms, should they occur. Monitor symptoms related to bradycardia and orthostasis. When using in outpatients, ensure that patients are capable of self-monitoring for signs and symptoms. Avoid use in patients with severe coronary insufficiency, recent myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disease, or chronic renal failure, as well as in patients with marked bradycardia. (5.1)
- Risk of QT Prolongation: Lofexidine tablets prolong the QT interval. Avoid use in patients with congenital long QT syndrome. Monitor ECG in patients with electrolyte abnormalities, congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, hepatic or renal impairment, or in patients taking other medicinal products that lead to QT prolongation. (5.2)
- Increased Risk of CNS Depression with Concomitant use of CNS Depressant Drugs: Lofexidine tablets potentiate the CNS depressant effects of benzodiazepines and may potentiate the CNS depressant effects of alcohol, barbiturates, and other sedating drugs. (5.3)
- Increased Risk of Opioid Overdose after Opioid Discontinuation: Patients who complete opioid discontinuation are at an increased risk of fatal overdose should they resume opioid use. Use in conjunction with a comprehensive management program for treatment of opioid use disorder and inform patients and caregivers of increased risk of overdose. (5.4)
- Risk of Discontinuation Symptoms: Instruct patients not to discontinue therapy without consulting their healthcare provider. When discontinuing therapy, reduce dose gradually. (5.5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 10% and notably more frequent than placebo) are orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, hypotension, dizziness, somnolence, sedation, and dry mouth. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact US WorldMeds at 1-888-900-8796 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Methadone: Methadone and Lofexidine tablets both prolong the QT interval. ECG monitoring is recommended when used concomitantly. (7.1)
- Oral Naltrexone: Concomitant use may reduce efficacy of oral naltrexone. (7.2)
- CYP2D6 Inhibitors: Concomitant use of paroxetine resulted in increased plasma levels of Lofexidine. Monitor for symptoms of orthostasis and bradycardia with concomitant use of a CYP2D6 inhibitor. (7.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 8/2023
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Information
2.2 Dosage Recommendations for Patients with Hepatic Impairment
2.3 Dosage Recommendations for Patients with Renal Impairment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Hypotension, Bradycardia, and Syncope
5.2 Risk of QT Prolongation
5.3 Increased Risk of Central Nervous System Depression with Concomitant use of CNS Depressant Drugs
5.4 Increased Risk of Opioid Overdose after Opioid Discontinuation
5.5 Risk of Discontinuation Symptoms
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Methadone
7.2 Oral Naltrexone
7.3 CNS Depressant Drugs
7.4 CYP2D6 Inhibitor - Paroxetine
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
8.8 CYP2D6 Poor Metabolizers
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Information
The usual Lofexidine tablet starting dosage is three 0.18 mg tablets taken orally 4 times daily during the period of peak withdrawal symptoms (generally the first 5 to 7 days following last use of opioid) with dosing guided by symptoms and side effects. There should be 5 to 6 hours between each dose. The total daily dosage of Lofexidine tablets should not exceed 2.88 mg (16 tablets) and no single dose should exceed 0.72 mg (4 tablets).
Lofexidine tablet treatment may be continued for up to 14 days with dosing guided by symptoms.
Discontinue Lofexidine tablets with a gradual dose reduction over a 2- to 4-day period to mitigate Lofexidine tablet withdrawal symptoms (e.g., reducing by 1 tablet per dose every 1 to 2 days) [see Warnings & Precautions (5.5)]. The Lofexidine tablet dose should be reduced, held, or discontinued for individuals who demonstrate a greater sensitivity to Lofexidine tablets side effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Lower doses may be appropriate as opioid withdrawal symptoms wane.
Lofexidine tablets can be administered in the presence or absence of food.
2.2 Dosage Recommendations for Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Recommended dosage adjustments based on the degree of hepatic impairment are shown in Table 1. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 1: Dosage Recommendations in Patients with Hepatic Impairment Mild Impairment Moderate Impairment Severe Impairment Child-Pugh score 5-6 7-9 > 9 Recommended dose 3 tablets
4 times daily
(2.16 mg per day)2 tablets
4 times daily
(1.44 mg per day)1 tablet
4 times daily
(0.72 mg per day)2.3 Dosage Recommendations for Patients with Renal Impairment
Recommended dosage adjustments based on the degree of renal impairment are shown in Table 2. Lofexidine tablets may be administered without regard to the timing of dialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 2: Dosage Recommendations in Patients with Renal Impairment Moderate Impairment Severe Impairment, End-Stage Renal Disease, or on Dialysis Estimated GFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 30-89.9 < 30 Recommended dose 2 tablets
4 times daily
(1.44 mg per day)1 tablet
4 times daily
(0.72 mg per day) - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Hypotension, Bradycardia, and Syncope
Lofexidine tablets can cause a decrease in blood pressure, a decrease in pulse, and syncope [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Monitor vital signs before dosing. Monitor symptoms related to bradycardia and orthostasis.
Patients being given Lofexidine tablets in an outpatient setting should be capable of and instructed on self-monitoring for hypotension, orthostasis, bradycardia, and associated symptoms. If clinically significant or symptomatic hypotension and/or bradycardia occur, the next dose of Lofexidine tablets should be reduced in amount, delayed, or skipped.
Inform patients that Lofexidine tablets may cause hypotension and that patients moving from a supine to an upright position may be at increased risk for hypotension and orthostatic effects. Instruct patients to stay hydrated, on how to recognize symptoms of low blood pressure, and on how to reduce the risk of serious consequences should hypotension occur (e.g., sit or lie down, carefully rise from a sitting or lying position). Instruct outpatients to withhold Lofexidine tablets doses when experiencing symptoms of hypotension or bradycardia and to contact their healthcare provider for guidance on how to adjust dosing.
Avoid using Lofexidine tablets in patients with severe coronary insufficiency, recent myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disease, chronic renal failure, and in patients with marked bradycardia.
Avoid using Lofexidine tablets in combination with medications that decrease pulse or blood pressure to avoid the risk of excessive bradycardia and hypotension.
5.2 Risk of QT Prolongation
Lofexidine tablets prolong the QT interval.
Avoid using Lofexidine tablets in patients with congenital long QT syndrome.
Monitor ECG in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, hepatic impairment, renal impairment, or patients taking other medicinal products that lead to QT prolongation (e.g., methadone). In patients with electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia), correct these abnormalities first, and monitor ECG upon initiation of Lofexidine tablets [see Dosing and Administration (2.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Special Populations (8.6, 8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
5.3 Increased Risk of Central Nervous System Depression with Concomitant use of CNS Depressant Drugs
Lofexidine tablets potentiate the CNS depressive effects of benzodiazepines and can also be expected to potentiate the CNS depressive effects of alcohol, barbiturates, and other sedating drugs. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of other medications they are taking, including alcohol.
Advise patients using Lofexidine tablets in an outpatient setting that, until they learn how they respond to Lofexidine tablets, they should be careful or avoid doing activities such as driving or operating heavy machinery.
5.4 Increased Risk of Opioid Overdose after Opioid Discontinuation
Lofexidine tablets are not a treatment for opioid use disorder. Patients who complete opioid discontinuation are likely to have a reduced tolerance to opioids and are at increased risk of fatal overdose should they resume opioid use. Use Lofexidine tablets in patients with opioid use disorder only in conjunction with a comprehensive management program for the treatment of opioid use disorder and inform patients and caregivers of this increased risk of overdose.
5.5 Risk of Discontinuation Symptoms
Stopping Lofexidine tablets abruptly can cause a marked rise in blood pressure. Symptoms including diarrhea, insomnia, anxiety, chills, hyperhidrosis, and extremity pain have also been observed with Lofexidine tablets discontinuation. Instruct patients not to discontinue therapy without consulting their healthcare provider. When discontinuing therapy with Lofexidine tablets, gradually reduce the dose [see Dosing and Administration (2.1)].
Symptoms related to discontinuation can be managed by administration of the previous Lofexidine tablet dose and subsequent taper.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
- Hypotension, Bradycardia, and Syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- QT Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Central Nervous System Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Opioid Overdose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Discontinuation Symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to adverse reaction rates observed for another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of Lofexidine tablets was supported by three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials, an open-label study, and clinical pharmacology studies with concomitant administration of either methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone.
The three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials enrolled 935 subjects dependent on short-acting opioids undergoing abrupt opioid withdrawal. Patients were monitored before each dose in an inpatient setting.
Table 3 presents the incidence, rounded to the nearest percent, of adverse events that occurred in at least 10% of subjects treated with Lofexidine tablets and for which the incidence in patients treated with Lofexidine tablets were greater than the incidence in subjects treated with placebo in a study that tested two doses of Lofexidine tablets, 2.16 mg per day and 2.88 mg per day, and placebo. The overall safety profile in the combined dataset was similar.
Orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, hypotension, dizziness, somnolence, sedation, and dry mouth were notably more common in subjects treated with Lofexidine tablets than subjects treated with placebo.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions Reported by ≥10% of Lofexidine Tablet-Treated Patients and More Frequently than Placebo Adverse Reaction Lofexidine Tablets
2.16 mg* (%)
N=229Lofexidine Tablets
2.88 mg* (%)
N=222Placebo (%)
N=151- * Assigned dose; mean average daily dose received was 79% of assigned dose due to dose-holds for out-of-range vital signs.
Insomnia 51 55 48 Orthostatic Hypotension 29 42 5 Bradycardia 24 32 5 Hypotension 30 30 1 Dizziness 19 23 3 Somnolence 11 13 5 Sedation 13 12 5 Dry Mouth 10 11 0 Other notable adverse reactions associated with the use of Lofexidine tablets but reported in <10% of patients in the Lofexidine tablets group included:
- Syncope: 0.9%, 1.4% and 0% for Lofexidine tablets 2.16 mg/day and 2.88 mg/day and placebo, respectively
- Tinnitus: 0.9%, 3.2% and 0% for Lofexidine tablets 2.16 mg/day and 2.88 mg/day and placebo, respectively
Blood pressure changes and adverse reactions after Lofexidine tablets cessation
Elevations in blood pressure above normal values (≥140 mmHg systolic) and above a subject's pre-treatment baseline are associated with discontinuing Lofexidine tablets, and peaked on the second day after discontinuation, as shown in Table 4. Blood pressure values were evaluated for 3 days following the last dose of a 5-day course of Lofexidine tablets 2.88 mg/day.
Table 4: Blood Pressure Elevations after Stopping Treatment Abrupt Lofexidine Tablet Discontinuation
2.88 mg
(N = 134)Placebo
(N = 129)N at risk n (%) N at risk n (%) Systolic Blood Pressure on Day 2 after Discontinuation ≥ 140 mmHg and ≥ 20 mmHg increase from baseline 58 23 (39.7) 37 6 (16.2) ≥ 170 mmHg and ≥ 20 mmHg increase from baseline 58 5 (8.6) 37 0 Blood pressure elevations of a similar magnitude and incidence were observed in a small number of patients (N=10) that had a one-day, 50% dose reduction prior to discontinuation.
After stopping treatment, subjects who were taking Lofexidine tablets also had a higher incidence of diarrhea, insomnia, anxiety, chills, hyperhidrosis, and extremity pain compared to subjects who were taking placebo.
Sex-specific adverse event findings
Four out of 101 females (4%) had serious cardiovascular adverse events compared to 3 out of 289 (1%) males assigned to receive Lofexidine tablets 2.88 mg/day.
Discontinuations and dose-holds due to bradycardia and orthostatic hypotension, which are the most common adverse reactions associated with Lofexidine tablets, occurred with a greater incidence in females assigned to receive the highest studied dose of Lofexidine tablets, 2.88 mg/day as shown in Table 5.
Table 5: Discontinuations and Dose-Holds for Bradycardia and Orthostatic Hypotension by Lofexidine Tablets Dose and Sex Lofexidine Tablets 2.16 mg Lofexidine Tablets 2.88 mg Male 22/162 (14%) 29/158 (18%) Female 9/67 (13%) 20/64 (31%) 6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Lofexidine is marketed in other countries for relief of opioid withdrawal symptoms. The following events have been identified during postmarketing use of lofexidine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Since lofexidine's initial market introduction in 1992, the most frequently reported postmarketing adverse event with lofexidine has been hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. There has been one report of QT prolongation, bradycardia, torsades de pointes, and cardiac arrest with successful resuscitation in a patient who received lofexidine, and three reports of clinically significant QT prolongation in subjects concurrently receiving methadone with lofexidine.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Methadone
Lofexidine tablets and methadone both prolong the QT interval. ECG monitoring is recommended in patients receiving methadone and Lofexidine tablets concomitantly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Oral Naltrexone
Coadministration of Lofexidine tablets and oral naltrexone resulted in statistically significant differences in the steady-state pharmacokinetics of naltrexone. It is possible that oral naltrexone efficacy may be reduced if used concomitantly within 2 hours of Lofexidine tablets. This interaction is not expected if naltrexone is administered by non-oral routes [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 CNS Depressant Drugs
Lofexidine tablets potentiate the CNS depressant effects of benzodiazepines and may potentiate the CNS depressant effects of alcohol, barbiturates, and other sedating drugs. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of other medications they are taking, including alcohol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
7.4 CYP2D6 Inhibitor - Paroxetine
Coadministration of Lofexidine tablets and paroxetine resulted in a 28% increase in the extent of absorption of Lofexidine. Monitor for orthostatic hypotension and bradycardia when an inhibitor of CYP2D6 is used concomitantly with Lofexidine tablets [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The safety of Lofexidine tablets in pregnant women has not been established. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of lofexidine during organogenesis to pregnant rats and rabbits caused a reduction in fetal weights, increases in fetal resorptions, and litter loss at exposures below that in humans. When oral lofexidine was administered from the beginning of organogenesis through lactation, increased stillbirths and litter loss were noted along with decreased viability and lactation indices. The offspring exhibited delays in sexual maturation, auditory startle, and surface righting. These effects occurred at exposures below that in humans [see Animal Data].
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies carry some risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The background risk of major birth defects in the U.S. general population is 2% to 4% and of miscarriage is 15% to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal Data
Increased incidence of resorptions, decreased number of implantations, and a concomitant reduction in the number of fetuses were observed when pregnant rabbits were orally administered lofexidine hydrochloride during organogenesis (from gestation day [GD] 7 to 19) at a daily dose of 5.0 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.08 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of 2.88 mg lofexidine base on an AUC basis). Maternal toxicity evidenced by increased mortality was noted at the highest tested dose of 15 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.4 times the MRHD on an AUC basis).
Decreased implantations per dam and decreased mean fetal weights were noted in a study in which pregnant rats were treated with oral lofexidine hydrochloride during organogenesis (from GD 7 to 16) at a daily dose of 3.0 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.9 times the MRHD on an AUC basis). This dose was associated with maternal toxicity (decreased body weight gain and mortality). No malformations or evidence of developmental toxicity were evident at 1.0 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.2 times the MRHD on an AUC basis).
A dose-dependent increase in pup mortality was noted in all doses of lofexidine hydrochloride administered orally to pregnant rats from GD 6 through lactation at an exposure less than the human exposure based on AUC comparisons. Doses higher than 1.0 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.2 times the MRHD on an AUC basis) resulted in incidences of total litter loss and maternal toxicity (piloerection and decreased body weight gain). At the highest dose tested of 2.0 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.6 times the MRHD on an AUC basis), increased stillbirths as well as decreased viability and lactation indices were reported. Surviving offspring exhibited lower body weights, developmental delays, and increased delays in auditory startle at doses of 1.0 mg/kg/ day or higher. Sexual maturation was delayed in male offspring (preputial separation) at 2.0 mg/kg/day and in female offspring (vaginal opening) at 1.0 mg/kg/day or higher.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of lofexidine or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Caution should be exercised when Lofexidine tablets are administered to a nursing woman.
The developmental and health benefits should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Lofexidine tablets and any other potential adverse effects on breastfed children from Lofexidine tablets or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
In animal studies that included some fertility endpoints, lofexidine decreased breeding rate and increased resorptions at exposures below human exposures. The impact of lofexidine on male fertility has not been adequately characterized in animal studies [see Impairment of Fertility (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Lofexidine tablets have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
No studies have been performed to characterize the pharmacokinetics of Lofexidine tablets or to establish its safety and effectiveness in geriatric patients. Caution should be exercised when Lofexidine tablets are administered to patients over 65 years of age. Dosing adjustments similar to those recommended in patients with renal impairment should be considered [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Hepatic impairment slows the elimination of lofexidine but exhibits less effect on the peak plasma concentration than on AUC values following a single dose. Dosage adjustments are recommended based on the degree of hepatic impairment. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Clinically relevant QT prolongation may occur in subjects with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
Renal impairment slows the elimination of lofexidine but exhibits less effect on the peak plasma concentration than on AUC values following a single dose. Dosage adjustments are recommended based on the degree of renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Only a negligible fraction of the Lofexidine tablet dose is removed during a typical dialysis session, so no additional dose needs to be administered after a dialysis session; Lofexidine tablets may be administered without regard to the timing of dialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Clinically relevant QT prolongation may occur in subjects with renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
8.8 CYP2D6 Poor Metabolizers
Although the pharmacokinetics of Lofexidine tablets have not been systematically evaluated in patients who do not express the drug metabolizing enzyme CYP2D6, it is likely that the exposure to Lofexidine tablets would be increased similarly to taking strong CYP2D6 inhibitors (approximately 28%). Monitor adverse events such as orthostatic hypotension and bradycardia in known CYP2D6 poor metabolizers. Approximately 8% of Caucasians and 3 to 8% of Black/African Americans cannot metabolize CYP2D6 substrates and are classified as poor metabolizers (PM) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Lofexidine tablets contain lofexidine, a central alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, as the hydrochloride salt. Lofexidine hydrochloride is chemically designated as 2-[1-(2,6-dichlorophenoxy)ethyl]-4,5 dihydro-1H- imidazole monohydrochloride with a molecular formula of C11H12Cl2N2O∙HCl. Its molecular weight is 295.6 g/mole and its structural formula is:
Lofexidine hydrochloride is a white to off-white crystalline powder freely soluble in water, methanol, and ethanol. It is slightly soluble in chloroform and practically insoluble in n-hexane and benzene.
Lofexidine tablets are available as round, convex-shaped, peach-colored, film-coated tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 0.18 lofexidine, equivalent to 0.2 mg of lofexidine hydrochloride, and the following inactive ingredients: 92.6 mg lactose, 12.3 mg citric acid, 1.1 mg povidone, 5.7 mg microcrystalline cellulose, 1.4 mg calcium stearate, 0.7 mg sodium lauryl sulphate, and Opadry OY S 9480 (contains indigo carmine and sunset yellow).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Lofexidine is a central alpha-2 adrenergic agonist that binds to receptors on adrenergic neurons. This reduces the release of norepinephrine and decreases sympathetic tone.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Single lofexidine doses of 1.44 mg to 1.8 mg produced maximum mean change from baseline in QTcF (ΔQTcF) of 14.4 msec (upper two-sided 90% CI: 22.3 msec) and 13.6 msec (17.4 msec) for 1.44 mg and 1.8 mg respectively in healthy normal volunteers.
In a Phase 3 placebo-controlled, dose response study in opioid dependent subjects, lofexidine was associated with a maximum mean prolongation of the QTcF interval 7.3 (8.8) msec and 9.3 (10.9) msec at doses of 2.16 mg/day and 2.88 mg/day, respectively.
Patients with hepatic impairment
Administration of lofexidine to subjects with hepatic impairment was associated with prolongation of the QTc interval, which was more pronounced in subjects with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with renal impairment
Administration of lofexidine to subjects with renal impairment was associated with prolongation of the QTc interval, which was more pronounced in subjects with severe renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Lofexidine is well absorbed and achieves peak plasma concentration 3 to 5 hours after administration of a single dose.
Lofexidine shows approximately dose-proportional pharmacokinetics. Administration of lofexidine with food does not alter its pharmacokinetics.
The absolute bioavailability of a single oral lofexidine dose (0.36 mg in solution) compared with an intravenous infusion (0.2 mg infused for 200 minutes) was 72%. Mean lofexidine Cmax after the oral dose and intravenous infusion was 0.82 ng/mL (at median Tmax of 3 hours) and 0.64 ng/mL (at median Tmax of 4 hours), respectively. Mean estimates of overall systemic exposure (AUCinf) were 14.9 ng∙h/mL and 12.0 ng∙h/mL, respectively.
Distribution
Mean lofexidine apparent volume of distribution and volume of distribution values following the administration of an oral dose and an intravenous dose were 480.0 L and 297.9 L, respectively, which are appreciably greater than total body volume, suggesting extensive lofexidine distribution into body tissue.
Lofexidine protein binding is approximately 55%.
Lofexidine is not preferentially taken up by blood cells. In a study comparing lofexidine concentrations in plasma and whole blood at the time of peak lofexidine concentrations in human volunteers, it was determined that red blood cells contain approximately 27% the lofexidine concentration of the plasma.
Elimination
Metabolism
From absolute bioavailability results, approximately 30% of the administered lofexidine dose is converted to inactive metabolites during the first pass effect associated with drug absorption from the gut.
Lofexidine and its major metabolites did not induce or inhibit any CYP450 isoforms, with the exception of a slight inhibition of CYP2D6 by lofexidine, with an IC50 of 4551 nM (approximately 225 times the steady-state Cmax for lofexidine with 0.72 mg 4 times daily dosing). Any lofexidine interaction with CYP2D6 substrates is not expected to be clinically significant.
Lofexidine is metabolized when incubated in vitro with human liver microsomes, the major contributor to the hepatic metabolism of lofexidine is CYP2D6, with CYP1A2 and CYP2C19 also capable of metabolizing lofexidine.
Excretion
The elimination half-life is approximately 12 hours and mean clearance is 17.6 L/h following an IV infusion.
Lofexidine has a terminal half-life of approximately 11 to 13 hours following the first dose. At steady-state, the terminal half- life is approximately 17 to 22 hours. Accumulation occurs up to 4 days with repeat dosing, following the recommended dosing regimen.
A mass balance study of lofexidine showed nearly complete recovery of radiolabel in urine (93.5%) over 144 hours postdose, with an additional 0.92% recovered in the feces over 216 hours postdose. Thus, it appears that all, or nearly all, of the dose was absorbed, and that the primary route of elimination of the parent drug and its metabolites is via the kidney. Renal elimination of unchanged drug accounts for approximately 15% to 20% of the administered dose.
Specific Populations
Hepatic Impairment
Hepatic impairment slows the elimination of lofexidine but exhibits less effect on the peak plasma concentration following a single dose. In a study comparing the pharmacokinetics of lofexidine (0.36 mg) in mild, moderate, and severe hepatically impaired subjects to subjects with normal hepatic function (6 subjects in each hepatic function group), mean Cmax values were similar for subjects with normal, mild, and moderate hepatic impairment as shown in Table 6.
Table 6: Lofexidine Tablets Pharmacokinetics in Subjects with Hepatic Impairment Normal Mild Impairment Moderate Impairment Severe Impairment Child-Pugh Class & Score Normal Function Class A
5-6Class B
7-9Class C
10-15Cmax % of normal 100 114 117 166 AUClast % of normal 100 127 190 304 AUC∞ % of normal 100 117 185 260 t1/2 % of normal 100 139 281 401 Renal Impairment
Renal impairment slows the elimination of lofexidine but exhibits less effect on the peak plasma concentration following a single dose. In a study comparing the pharmacokinetics of lofexidine (0.36 mg) in 8 end-stage renal disease subjects on 3 times weekly hemodialysis to 8 subjects with normal renal function matched for sex, age, and body mass index, mean Cmax values were similar for end-stage renal disease and normal renal function subjects, indicating no change in maximum lofexidine exposure with renal impairment as shown in Table 7.
The impact of dialysis on the overall pharmacokinetics of lofexidine during a typical 4-hour dialysis was minimal; the drop in lofexidine plasma concentrations produced during the dialysis session was transient, with a rebound to nearly predialysis concentrations after re-equilibration within a few hours following completion of the dialysis cycle [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
In a study comparing the pharmacokinetics of lofexidine (0.36 mg) in 6 subjects each with normal renal function, mild renal impairment, and moderate renal impairment as well as 5 subjects with severe renal impairment but not requiring dialysis, there were similar increases in mean Cmax values in subjects with mild and moderate renal impairment in comparison to subjects with normal renal function, with additional increases in mean Cmax values in subjects with severe renal impairment. Mean AUClast, AUC∞, and t1/2 increased with severity of renal impairment as shown in Table 7.
Table 7: Lofexidine Tablets Pharmacokinetics in Subjects with Renal Impairment Normal Mild Impairment Moderate Impairment Severe Impairment ESRD or on dialysis eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) ≥ 90 60-89 30-59 15-29 < 15 Cmax % of normal 100 124 117 154 104 AUClast % of normal 100 157 187 272 181 AUC∞ % of normal 100 144 173 243 171 t1/2 % of normal 100 111 145 157 137 Drug Interaction Studies
Lofexidine coadministered with methadone
In a double-blind placebo-controlled study of 23 patients maintained on methadone (80 to 120 mg/day) concomitantly administered lofexidine up to 2.88 mg/day, lofexidine did not alter the pharmacokinetics of methadone. Lofexidine concentrations may be slightly increased when coadministered with methadone; however, the increase at concentrations expected with recommended dosing is not clinically meaningful [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Lofexidine coadministered with buprenorphine
In a double-blind placebo-controlled study of 30 subjects maintained on buprenorphine (16 to 24 mg/day) concomitantly administered lofexidine up to 2.88 mg/day, no pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic interactions between lofexidine and buprenorphine were seen.
Lofexidine coadministered with oral naltrexone
In an open-label, single-arm study of 24 healthy subjects, oral naltrexone (50 mg/day) did not significantly alter the single- dose pharmacokinetics of lofexidine (0.36 mg). The alteration in steady-state pharmacokinetics of oral naltrexone was statistically significant in the presence of lofexidine. The Tmax was delayed for both naltrexone and 6ß-naltrexol (2 to 3 hours), and overall exposure was slightly reduced when naltrexone was administered with lofexidine [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Lofexidine coadministered with paroxetine
In an open-label, single-sequence study of 24 healthy subjects, the strong CYP2D6 inhibitor paroxetine (40 mg/day) increased lofexidine (0.36 mg) Cmax and AUC∞ by approximately 11% and 28%, respectively [see Drug Interactions (7.4)].
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No adequate long-term animal studies have been completed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of lofexidine.
Mutagenesis
Lofexidine tested positive in the in vitro mouse lymphoma assay. Lofexidine tested negative in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames assay) and in the in vivo rat micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
In a female fertility study in rabbits, fertility was not adversely impacted by administration of lofexidine hydrochloride up to 6.4 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.1 times the MRHD of 2.88 mg on an AUC basis) when administered orally starting 2 weeks prior to mating and through gestation and lactation. However, decreased breeding rate and higher post- implantation loss was observed at this dose, which correlated with higher resorptions and reduced litter size. Maternal toxicity, which included increased mortality rate, reduced body weight gain, and moderate sedation was observed at 6.4 mg/kg/day. The NOAEL for female fertility was 6.4 mg/kg/day and the NOAEL for female-mediated developmental parameters was 0.4 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.005 times the MRHD on an AUC basis).
In a fertility study in rats, fertility was unaffected by administration of lofexidine up to 0.88 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.2 times the MRHD on an AUC basis) via diet to male and female rats prior to mating and to the dams through gestation and lactation. No evidence of maternal toxicity was observed. However, no assessment of sperm or reproductive organs were performed in this study.
Reduced testes, epididymis, and seminiferous tubule weights, as well as delayed sexual maturation of males and females and decreases in the number of corpora lutea and implantations after mating, were noted in offspring of pregnant rats administered lofexidine hydrochloride orally from GD 6 through lactation at exposures less than the human exposure based on AUC comparisons.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials supported the efficacy of lofexidine.
Study 1, NCT01863186
Study 1 was a 2-part efficacy, safety, and dose-response study conducted in the United States in patients meeting DSM-IV criteria for opioid dependence who were physically dependent on short-acting opioids (e.g., heroin, hydrocodone, oxycodone). The first part of the study was an inpatient, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled design consisting of 7 days of inpatient treatment (Days 1 – 7) with lofexidine 2.16 mg total daily dose (0.54 mg 4 times daily) (n=229), lofexidine 2.88 mg total daily dose (0.72 mg 4 times daily) (n=222), or matching placebo (n=151). Patients also had access to a variety of support medications for withdrawal symptoms (guaifenesin, antacids, dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, psyllium hydrocolloid suspension, bismuth sulfate, acetaminophen, and zolpidem). The second part of the study (Days 8 – 14) was an open-label design where all patients who successfully completed Days 1 – 7 were eligible to receive open-label treatment with variable dose lofexidine treatment (as determined by the investigator, but not to exceed 2.88 mg total daily dose) for up to an additional 7 days (Days 8 – 14) in either an inpatient or outpatient setting as determined by the investigator and the patient. No patient received lofexidine for more than 14 days.
The two endpoints to support efficacy were the mean Short Opiate Withdrawal Scale of Gossop (SOWS-Gossop) total score on Days 1 – 7 of treatment and the proportion of patients who completed 7 days of treatment. The SOWS-Gossop, a patient-reported outcome (PRO) instrument, evaluates the following opioid withdrawal symptoms: feeling sick, stomach cramps, muscle spasms/twitching, feeling of coldness, heart pounding, muscular tension, aches and pains, yawning, runny eyes and insomnia/problems sleeping. For each opioid withdrawal symptom, patients are asked to rate their symptom severity using four response options (none, mild, moderate, and severe). The SOWS-Gossop total score ranges from 0 to 30, where a higher score indicates greater withdrawal symptom severity. The SOWS-Gossop was administered at baseline and once daily 3.5 hours after the first morning dose on Days 1 – 7.
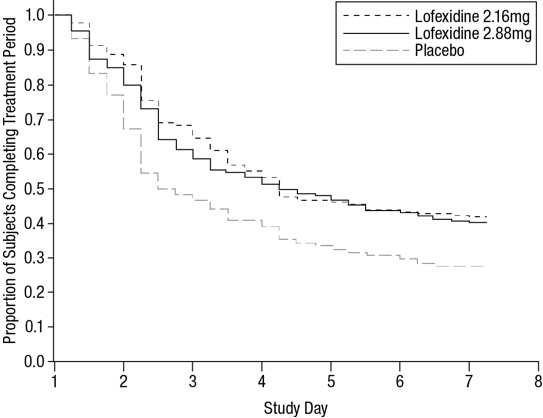
Of the randomized and treated patients, 28% of placebo patients, 41% of lofexidine 2.16 mg and 40% of lofexidine 2.88 mg patients completed 7 days of treatment. The difference in proportion in both lofexidine groups was significant compared to placebo. See Figure 1. Patients in the placebo group were more likely to drop out of the study prematurely due to lack of efficacy than patients treated with lofexidine.
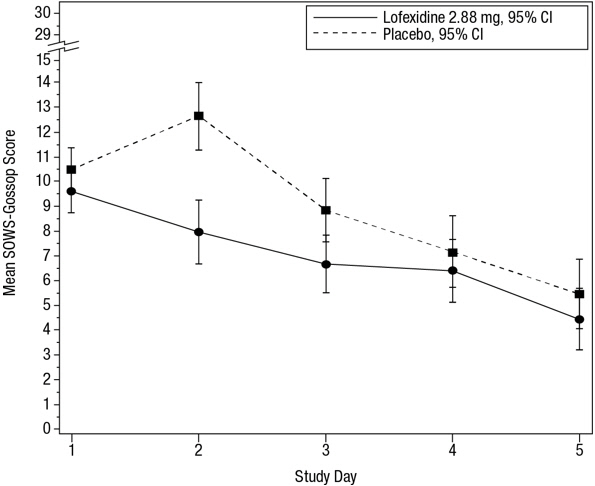
Figure 1: Completion of Treatment Period for Study 1
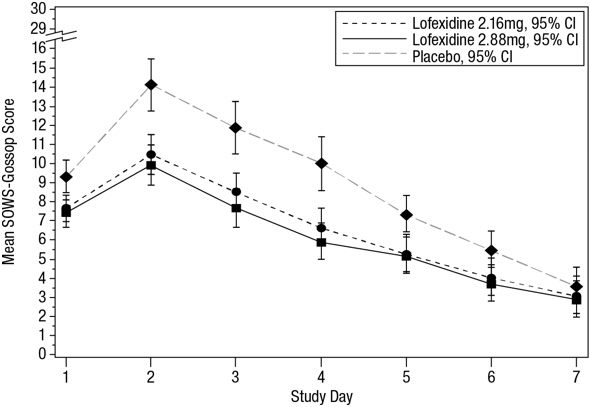
The mean SOWS-Gossop scores for Days 1 – 7 were 8.8, 6.5, and 6.1 for placebo, lofexidine 2.16 mg and lofexidine 2.88 mg, respectively. Results are shown in Figure 2. The mean difference between lofexidine 2.16 mg and placebo was -2.3 with a 95% CI of (-3.4, -1.2). The mean difference between lofexidine 2.88 mg and placebo was -2.7 with a 95% CI of (-3.9, -1.6). They were both significant. Symptoms assessed on the SOWS-Gossop were recorded as absent or mild for almost all patients remaining to the end of the assessment period.
Figure 2: Mean SOWS-Gossop Scores for Days 1 – 7 in Study 1
Study 2, NCT00235729
Study 2 was an inpatient, randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study carried out in the United States in patients meeting DSM-IV criteria for opioid dependence who were physically dependent on short-acting opioids (e.g., heroin, hydrocodone, oxycodone). Patients were treated with lofexidine tablets (2.88 mg/day [0.72 mg 4 times daily]) or matching placebo for 5 days (Days 1 – 5). Patients also had access to a variety of support medications for withdrawal symptoms (guaifenesin, antacids, dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, psyllium hydrocolloid suspension, bismuth sulfate, acetaminophen, and zolpidem). All patients then received placebo on Days 6 and 7 and were discharged on Day 8.
The two endpoints to support efficacy were the mean SOWS-Gossop total score on Days 1 – 5 of treatment and the proportion of patients who completed 5 days of treatment. The SOWS-Gossop was administered at baseline and once daily 3.5 hours after the first morning dose on Days 1 – 5.
A total of 264 patients were randomized into the study. Of these, 134 patients were randomized to lofexidine 2.88 mg/day and 130 patients to placebo.
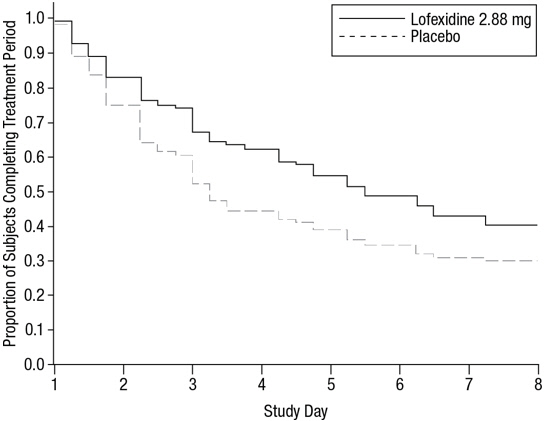
Of the randomized and treated patients, 33% of placebo patients and 49% of lofexidine patients completed 5 days of treatment. The difference in proportion between the two groups was significant. See Figure 3. Patients in the placebo group were more likely to drop out of the study prematurely due to lack of efficacy than patients treated with lofexidine.
Figure 3: Completion of Treatment Period in Study 2
The mean SOWS-Gossop scores for Days 1 – 5 were 8.9 and 7.0 for placebo and lofexidine 2.88 mg, respectively. Results are shown in Figure 4. The mean difference was -1.9 with a 95% CI of (-3.2, -0.6) and was statistically significant.
Figure 4: Mean SOWS-Gossop Scores for Days 1 – 5 in Study 2
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Available as 0.18 mg round, convex-shaped, peach colored, film-coated tablets, imprinted with "LFX" on one side and "18" on the other side; approximately 7 mm in diameter.
Bottles of 36 Tablets.............NDC: 66993-345-37
Bottles of 96 Tablets.............NDC: 66993-345-76Storage
Store in original container at controlled room temperature, 25°C (77°F); with excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep Lofexidine tablets away from excess heat and moisture both in the pharmacy and after dispensing. Do not remove desiccant packs from bottles until all tablets are used. Keep Lofexidine tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Lofexidine tablets may mitigate, but not completely prevent, the symptoms associated with opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may include feeling sick, stomach cramps, muscle spasms or twitching, feeling of cold, heart pounding, muscular tension, aches and pains, yawning, runny eyes and sleep problems (insomnia). Patients should be advised that withdrawal will not be easy. Additional supportive measures should be clearly advised, as needed.
Hypotension and Bradycardia
Inform patients to be alert for any symptoms of low blood pressure or pulse (e.g., dizziness, lightheadedness, or feelings of faintness at rest or upon abruptly standing). Advise patients on how to reduce the risk of serious consequences should hypotension occur (sit or lie down, carefully rise from a sitting or lying position).
Patients being given Lofexidine tablets in an outpatient setting should be capable of and instructed on self-monitoring for hypotension, orthostasis, and bradycardia and advised to withhold Lofexidine tablet doses and contact their healthcare provider for instructions if they experience these signs or related symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Advise patients to avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated, which may potentially increase the risks of hypotension and syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Concomitant Medications
Review with patients all concomitant medications being taken and request that they immediately inform their healthcare provider of any changes in concomitant medications, including any other medications that may be used to treat individual symptoms of withdrawal.
Increased Risk of CNS Depression with Concomitant use of CNS Depressant Drugs
Inform patients of the increased risk of CNS depression with concomitant use of benzodiazepines, alcohol, barbiturates, or other sedating drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Advise patients using Lofexidine tablets in an outpatient setting that, until they learn how they respond to Lofexidine tablets, they should be careful or avoid doing activities such as driving or operating heavy machinery.
Sudden Discontinuation of Lofexidine Tablets
Inform patients not to discontinue Lofexidine tablets without consulting their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Risk of Opioid Overdose After Discontinuation of Opioids
Advise patients that after a period of not using opioid drugs, they may be more sensitive to the effects of opioids and at greater risk of overdosing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Issued: 08/2023 PATIENT INFORMATION
LOFEXIDINE TABLETS
(loe fex' I deen)What is the most important information I should know about Lofexidine Tablets and discontinuing opioid drugs? Lofexidine Tablets can cause serious side effects, including low blood pressure (hypotension), slow heart rate (bradycardia), and fainting. If you have any of the following signs or symptoms, tell your healthcare provider right away: - low blood pressure
- slow heartbeat
- dizziness
- lightheadedness
- feeling faint at rest or when standing up
If you take Lofexidine tablets at home and have any of these signs and symptoms, do not take your next dose of Lofexidine tablets until you have talked to your healthcare provider. You should avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated during treatment with Lofexidine tablets, which may increase your risk of low blood pressure and fainting. You should also be careful not to stand up too suddenly from lying down or sitting. When your treatment is complete you will need to stop taking Lofexidine tablets gradually or your blood pressure could increase. For more information about side effects, see "What are the possible side effects of Lofexidine Tablets?" Increased risk of opioid overdose. After a period of time of not using opioid drugs, you can become more sensitive to the effects of opioids if you start using opioids again. This may increase your risk of overdose and death. What are Lofexidine Tablets? Lofexidine tablets are a non-opioid prescription medicine used in adults to help with the symptoms of opioid withdrawal that may happen when you stop taking an opioid suddenly. Lofexidine tablets will not completely prevent the symptoms of opioid withdrawal, which may include feeling sick, stomach cramps, muscle spasms or twitching, feeling of cold, heart pounding, muscular tension, aches and pains, yawning, runny eyes and sleep problems (insomnia). Lofexidine tablets are not a treatment for opioid use disorder. If you have been diagnosed with opioid use disorder (opioid addiction), your healthcare provider may prescribe Lofexidine tablets as part of a complete treatment program for your opioid use disorder (opioid addiction). It is not known if Lofexidine tablets are safe and effective in children. Before taking Lofexidine Tablets, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have low blood pressure
- have a slow heart rate
- have any heart problems, including history of heart attack or a condition called long QT syndrome
- have liver or kidney problems
- drink alcohol
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Lofexidine tablets can harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Lofexidine tablets pass into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with Lofexidine tablets.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, herbal supplements, and any medications you may take for the individual symptoms of opioid withdrawal (such as pain relievers or medications for upset stomach). Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take benzodiazepines, barbiturates, tranquilizers, or sleeping pills. Taking Lofexidine tablets with these medicines can cause serious side effects. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you are taking any of these medicines. How should I take Lofexidine Tablets? - Take Lofexidine tablets exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose if needed.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking Lofexidine tablets without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Take Lofexidine tablets with or without food.
- If you take too much Lofexidine tablets, go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking Lofexidine Tablets? Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or perform any other dangerous activities until you know how Lofexidine tablets affect you. What are the possible side effects of Lofexidine Tablets? The most common side effects of Lofexidine tablets include: - low blood pressure or symptoms of low blood pressure such as lightheadedness
- slow heart rate
- dizziness
- sleepiness
- dry mouth
These are not all the possible side effects of Lofexidine tablets. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to US WorldMeds at 1-888-900-8796. How should I store Lofexidine Tablets? - Store Lofexidine tablets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep Lofexidine tablets in its original container.
- Keep Lofexidine tablets away from heat and moisture.
- Lofexidine tablets bottles contain desiccant packs to help keep the tablets dry. Do not remove the desiccant packs until all the tablets are used.
Keep Lofexidine tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children. General information about the safe and effective use of Lofexidine Tablets. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Lofexidine tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Lofexidine tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Lofexidine tablets that is written for health professionals. What are the ingredients of Lofexidine Tablets? Active ingredient: lofexidine. Inactive ingredients: lactose, citric acid, povidone, microcrystalline cellulose, calcium stearate, sodium lauryl sulphate, and Opadry OY S 9480 (contains indigo carmine and sunset yellow). Manufactured for:
Prasco Laboratories
Mason, OH 45040 USA
For more information, call 1-888-900-8796
Under Sublicense from USWM, LLC.
640113 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.18 mg Tablet Carton 36 count
NDC: 66993-345-37
36 TabletsLofexidine Tablets
0.18 mgStore and dispense
in original container.
Protect from heat and moisture.
Do not remove desiccants.
Keep the bottle tightly closed.
Rx OnlyKeep out of reach of children.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.18 mg Tablet Carton 96 count
NDC: 66993-345-76
96 TabletsLofexidine Tablets
0.18 mgStore and dispense
in original container.
Protect from heat and moisture.
Do not remove desiccants.
Keep the bottle tightly closed.
Rx OnlyKeep out of reach of children.
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LOFEXIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
lofexidine hydrochloride tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 66993-345 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LOFEXIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: V47G1SDI1B) (LOFEXIDINE - UNII:UI82K0T627) LOFEXIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE 0.2 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: J2B2A4N98G) CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) microcrystalline cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) calcium stearate (UNII: 776XM7047L) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color orange (peach) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code LFX;18 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 66993-345-76 1 in 1 CARTON 08/29/2024 1 96 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 66993-345-37 1 in 1 CARTON 08/29/2024 2 36 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA authorized generic NDA209229 08/29/2024 Labeler - Prasco Laboratories (065969375) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations A+ Secure Packaging, LLC 963589036 label(66993-345) , pack(66993-345) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Acceleration Laboratory Services Inc. 187562629 analysis(66993-345) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Catalent Pharma Solutions, LLC 829672745 analysis(66993-345) , manufacture(66993-345) , pack(66993-345) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations UFAG Laboratorien AG 486383151 analysis(66993-345)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.