HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CLONIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CLONIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS. CLONIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE EXTENDED-RELEASE tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1974
Clonidine Hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Clonidine Hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Bluepharma - Industria Farmaceutica, S.A.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
CLONIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE- clonidine hydrochloride tablet, extended release
Bluepharma - Industria Farmaceutica, S.A.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CLONIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CLONIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS. CLONIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE EXTENDED-RELEASE tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1974 INDICATIONS AND USAGEDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSExtended-release tablets: 0.1 mg not scored. (3) (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSHistory of a hypersensitivity reaction to clonidine. Reactions have included generalized rash, urticaria, angioedema. (4) (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions (incidence at least 5% and twice the rate of placebo) as monotherapy in ADHD: somnolence, fatigue, irritability, nightmare, insomnia, constipation, dry mouth. (6.1) (6) Most common adverse reactions (incidence at least 5% and twice the rate of placebo) as adjunct therapy to psychostimulant in ADHD: somnolence, fatigue, decreased appetite, dizziness. (6.1) (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS , contact Upsher-Smith Laboratories, LLC at 1-855-899-9180 or FDA at 1-800-332-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6) DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
(8) See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. (8) (8) (8) Revised: 9/2017 (8) (8) Revised: 3/2019 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*2. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS4 CONTRAINDICATIONS5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS6 ADVERSE REACTIONS7 DRUG INTERACTIONS8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE10 OVERDOSAGE11 DESCRIPTION12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY14 CLINICAL STUDIES16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets are indicated for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) as monotherapy and as adjunctive therapy to stimulant medications [seeClinical Studies (14)].
2. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
Clonidine hydrochloride is an extended-release tablet to be taken orally with or without food. Swallow tablets whole. Do not crush, chew, or break tablets because this will increase the rate of clonidine release.
Due to the lack of controlled clinical trial data and differing pharmacokinetic profiles, substitution of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets for other clonidine products on a mg-per-mg basis is not recommended [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Dose Selection
The dose of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets, administered either as monotherapy or as adjunctive therapy to a psychostimulant, should be individualized according to the therapeutic needs and response of the patient. Dosing should be initiated with one 0.1 mg tablet at bedtime, and the daily dosage should be adjusted in increments of 0.1 mg/day at weekly intervals until the desired response is achieved. Doses should be taken twice a day, with either an equal or higher split dosage being given at bedtime (see Table 1).
Table 1 Clonidine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Dosing Guidance
|
Total Daily Dose |
Morning Dose |
Bedtime Dose |
|
0.1 mg/day |
0.1 mg |
|
|
0.2 mg/day |
0.1 mg |
0.1 mg |
|
0.3 mg/day |
0.1 mg |
0.2 mg |
|
0.4 mg/day |
0.2 mg |
0.2 mg |
Doses of clonidine hydrochloride higher than 0.4 mg/day (0.2 mg twice daily) were not evaluated in clinical trials for ADHD and are not recommended.
When clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets are being added‑on to a psychostimulant, the dose of the psychostimulant can be adjusted depending on the patient’s response to clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
2.3 Discontinuation
When discontinuing clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets, the total daily dose should be tapered in decrements of no more than 0.1 mg every 3 to 7 days to avoid rebound hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.4 Missed Doses
If patients miss a dose of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets, they should skip that dose and take the next dose as scheduled. Do not take more than the prescribed total daily amount of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets in any 24‑hour period.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets are available in a 0.1 mg strength formulation. The 0.1 mg tablets are white to off-white round, biconvex tablets with debossing: “U” on one side and “77” on the other side. Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets must be swallowed whole and never crushed, cut or chewed.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with a history of a hypersensitivity reaction to clonidine. Reactions have included generalized rash, urticaria, and angioedema [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypotension/Bradycardia
Treatment with clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets can cause dose-related decreases in blood pressure and heart rate [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Measure heart rate and blood pressure prior to initiation of therapy, following dose increases, and periodically while on therapy. Titrate clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets slowly in patients with a history of hypotension, and those with underlying conditions that may be worsened by hypotension and bradycardia; e.g., heart block, bradycardia, cardiovascular disease, vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, or chronic renal failure. In patients who have a history of syncope or may have a condition that predisposes them to syncope, such as hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, or dehydration, advise patients to avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated. Monitor blood pressure and heart rate, and adjust dosages accordingly in patients treated concomitantly with antihypertensives or other drugs that can reduce blood pressure or heart rate or increase the risk of syncope.
5.2 Sedation and Somnolence
Somnolence and sedation were commonly reported adverse reactions in clinical studies. In patients that completed 5 weeks of therapy in a controlled, fixed dose pediatric monotherapy study, 31% of patients treated with 0.4 mg/day and 38% treated with 0.2 mg/day versus 4% of placebo treated patients reported somnolence as an adverse event. In patients that completed 5 weeks of therapy in a controlled flexible dose pediatric adjunctive to stimulants study, 19% of patients treated with clonidine hydrochloride+stimulant versus 7% treated with placebo+stimulant reported somnolence. Before using clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets with other centrally active depressants (such as phenothiazines, barbiturates, or benzodiazepines), consider the potential for additive sedative effects. Caution patients against operating heavy equipment or driving until they know how they respond to treatment with clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets. Advise patients to avoid use with alcohol.
5.3 Rebound Hypertension
Abrupt discontinuation of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets can cause rebound hypertension. In adults with hypertension, sudden cessation of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release formulation treatment in the 0.2 to 0.6 mg/day range resulted in reports of headache, tachycardia, nausea, flushing, warm feeling, brief lightheadedness, tightness in chest, and anxiety. In adults with hypertension, sudden cessation of treatment with immediate-release clonidine has, in some cases, resulted in symptoms such as nervousness, agitation, headache, and tremor accompanied or followed by a rapid rise in blood pressure and elevated catecholamine concentrations in the plasma.
No studies evaluating abrupt discontinuation of clonidine hydrochloride in children with ADHD have been conducted; however, to minimize the risk of rebound hypertension, gradually reduce the dose of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets in decrements of no more than 0.1 mg every 3 to 7 days. Patients should be instructed not to discontinue clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets therapy without consulting their physician due to the potential risk of withdrawal effects.
5.4 Allergic Reactions
In patients who have developed localized contact sensitization to clonidine transdermal system, continuation of clonidine transdermal system or substitution of oral clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets therapy may be associated with the development of a generalized skin rash.
In patients who develop an allergic reaction from clonidine transdermal system, substitution of oral clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets may also elicit an allergic reaction (including generalized rash, urticaria, or angioedema).
5.5 Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities
The sympatholytic action of clonidine may worsen sinus node dysfunction and atrioventricular (AV) block, especially in patients taking other sympatholytic drugs. There have been post‑marketing reports of patients with conduction abnormalities and/or taking other sympatholytic drugs who developed severe bradycardia requiring IV atropine, IV isoproterenol, and temporary cardiac pacing while taking clonidine. Titrate clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets slowly and monitor vital signs frequently in patients with cardiac conduction abnormalities or patients concomitantly treated with other sympatholytic drugs.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described in greater detail elsewhere in labeling:
- Hypotension/bradycardia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Sedation and somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Rebound hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Allergic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Two clonidine hydrochloride ADHD clinical studies (Study 1, CLON‑301 and Study 2, CLON‑302) evaluated 256 patients in two 8‑week placebo-controlled studies.
A third clonidine hydrochloride ADHD clinical study (Study 3, SHN‑KAP‑401) evaluated 135 children and adolescents in a 40‑week placebo-controlled randomized-withdrawal study.
Study 1: Fixed-dose Clonidine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Monotherapy
Study 1 (CLON‑301) was a short-term, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of two fixed doses (0.2 mg/day or 0.4 mg/day) of clonidine hydrochloride in children and adolescents (6 to 17 years of age) who met DSM‑IV criteria for ADHD hyperactive or combined inattentive/hyperactive subtypes.
Most Common Adverse Reactions (incidence of ≥5% and at least twice the rate of placebo): somnolence, fatigue, irritability, insomnia, nightmare, constipation, dry mouth.
Adverse Events Leading to Discontinuation of Clonidine Hydrochloride – Five patients (7%) in the low dose group (0.2 mg), 15 patients (20%) in the high dose group (0.4 mg), and 1 patient in the placebo group (1%) reported adverse reactions that led to discontinuation. The most common adverse reactions that led to discontinuation were somnolence and fatigue.
Commonly observed adverse reactions (incidence of ≥2% in either active treatment group and greater than the rate on placebo) during the treatment period are listed in Table 2.
Table 2 Common Adverse Reactions in the Fixed-Dose Monotherapy Trial – Treatment Period (Study 1)
|
Percentage of Patients Reporting Event |
|||
|
|
Clonidine Hydrochloride
|
Clonidine Hydrochloride
|
|
|
PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
|
NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
|
GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
|
GENERAL DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
|
CARDIAC DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
|
INVESTIGATIONS
|
|
|
|
|
METABOLISM AND NUTRITION DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
* Somnolence includes the terms “somnolence” and “sedation”.
† Fatigue includes the terms “fatigue” and “lethargy”.
Commonly observed adverse reactions (incidence of >2% in either active treatment group and greater than the rate on placebo) during the taper period are listed in Table 3.
Table 3 Common Adverse Reactions in the Fixed-Dose Monotherapy Trial – Taper Period* (Study 1)
|
Percentage of Patients Reporting Event |
|||
|
|
Clonidine Hydrochloride
|
Clonidine Hydrochloride
|
|
|
Abdominal Pain Upper |
0% |
6% |
3% |
|
Headache |
5% |
2% |
3% |
|
Gastrointestinal Viral |
0% |
5% |
0% |
|
Somnolence |
2% |
3% |
0% |
|
Heart Rate Increased |
0% |
3% |
0% |
|
Otitis Media Acute |
3% |
0% |
0% |
* Taper Period: 0.2 mg dose, week 8; 0.4 mg dose, weeks 6 to 8; Placebo dose, weeks 6 to 8
Study 2: Flexible-dose Clonidine Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets as Adjunctive Therapy to Psychostimulants
Study 2 (CLON‑302) was a short-term, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of a flexible dose of clonidine hydrochloride as adjunctive therapy to a psychostimulant in children and adolescents (6 to 17 years) who met DSM‑IV criteria for ADHD hyperactive or combined inattentive/hyperactive subtypes during which clonidine hydrochloride was initiated at 0.1 mg/day and titrated up to 0.4 mg/day over a 3‑week period. Most clonidine hydrochloride treated patients (75.5%) were escalated to the maximum dose of 0.4 mg/day.
Most Common Adverse Reactions (incidence of ≥5% and at least twice the rate of placebo): somnolence, fatigue, decreased appetite, dizziness.
Adverse Events Leading to Discontinuation – There was one patient in the CLON+STM group (1%) who discontinued because of an adverse event (severe bradyphrenia, with severe fatigue).
Commonly observed adverse reactions (incidence of ≥2% in the treatment group and greater than the rate on placebo) during the treatment period are listed in Table 4.
Table 4 Common Adverse Reactions in the Flexible-Dose Adjunctive to Stimulant Therapy Trial – Treatment Period (Study 2)
|
|
Percentage of Patients Reporting Event |
|
|
Clonidine Hydrochloride+STM
|
PBO+STM
|
|
|
PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
GENERAL DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
METABOLISM AND NUTRITION DISORDERS
|
|
|
|
CARDIAC DISORDERS
|
|
|
* Somnolence includes the terms: “somnolence” and “sedation”.
† Fatigue includes the terms “fatigue” and “lethargy”.
Commonly observed adverse reactions (incidence of ≥2% in the treatment group and greater than the rate on placebo) during the taper period are listed in Table 5.
Table 5 Common Adverse Reactions in the Flexible-Dose Adjunctive to Stimulant Therapy Trial – Taper Period* (Study 2)
|
|
Percentage of Patients Reporting Event |
|
|
Clonidine
|
PBO+STM
|
|
|
Nasal Congestion |
4% |
2% |
|
Headache |
3% |
1% |
|
Irritability |
3% |
2% |
|
Throat Pain |
3% |
1% |
|
Gastroenteritis Viral |
2% |
0% |
|
Rash |
2% |
0% |
* Taper Period: weeks 6 to 8
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
Thirteen percent (13%) of patients receiving clonidine hydrochloride discontinued from the pediatric monotherapy study due to adverse events, compared to 1% in the placebo group. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of clonidine hydrochloride monotherapy treated patients were from somnolence/sedation (5%) and fatigue (4%).
Effect on Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
In patients that completed 5 weeks of treatment in a controlled, fixed-dose monotherapy study in pediatric patients, during the treatment period the maximum placebo-subtracted mean change in systolic blood pressure was -4.0 mmHg on clonidine hydrochloride 0.2 mg/day and -8.8 mmHg on clonidine hydrochloride 0.4 mg/day. The maximum placebo-subtracted mean change in diastolic blood pressure was ‑4.0 mmHg on clonidine hydrochloride 0.2 mg/day and ‑7.3 mmHg on clonidine hydrochloride 0.4 mg/day. The maximum placebo-subtracted mean change in heart rate was ‑4.0 beats per minute on clonidine hydrochloride 0.2 mg/day and ‑7.7 beats per minute on clonidine hydrochloride 0.4 mg/day.
During the taper period of the fixed-dose monotherapy study the maximum placebo-subtracted mean change in systolic blood pressure was +3.4 mmHg on clonidine hydrochloride 0.2 mg/day and ‑5.6 mmHg on clonidine hydrochloride 0.4 mg/day. The maximum placebo-subtracted mean change in diastolic blood pressure was +3.3 mmHg on clonidine hydrochloride 0.2 mg/day and ‑5.4 mmHg on clonidine hydrochloride 0.4 mg/day. The maximum placebo-subtracted mean change in heart rate was ‑0.6 beats per minute on clonidine hydrochloride 0.2 mg/day and ‑3.0 beats per minute on clonidine hydrochloride 0.4 mg/day.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of clonidine hydrochloride. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These events exclude those already mentioned in 6.1:
Psychiatric: hallucinations
Cardiovascular: Q‑T prolongation
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
The following have been reported with other oral immediate release formulations of clonidine:
Table 6 Clinically Important Drug Interactions
|
Concomitant Drug Name or Drug Class |
Clinical Rationale |
Clinical Recommendation |
|
Tricyclic antidepressants |
Increase blood pressure and may counteract clonidine’s hypotensive effects |
Monitor blood pressure and adjust as needed |
|
Antihypertensive drugs |
Potentiate clonidine’s hypotensive effects |
Monitor blood pressure and adjust as needed |
|
CNS depressants |
Potentiate sedating effects |
Avoid use |
|
Drugs that affect sinus node function or AV node conduction (e.g., digitalis, calcium channel blockers, beta blockers) |
Potentiate bradycardia and risk of AV block |
Avoid use |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C:
Risk Summary
There are no adequate or well-controlled studies with clonidine hydrochloride in pregnant women. In animal embryofetal studies, increased resorptions were seen in rats and mice administered oral clonidine hydrochloride from implantation through organogenesis at 10 and 5 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD). No embryotoxic or teratogenic effects were seen in rabbits administered oral clonidine hydrochloride during organogenesis at doses up to 3 times the MRHD. Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Animal Data
Oral administration of clonidine hydrochloride to pregnant rabbits during the period of embryo/fetal organogenesis at doses of up to 80 mcg/kg/day (approximately 3 times the oral maximum recommended daily dose [MRHD] of 0.4 mg/day on a mg/m 2 basis) produced no evidence of teratogenic or embryotoxic potential. In pregnant rats, however, doses as low as 15 mcg/kg/day ( 1/ 3 the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis) were associated with increased resorptions in a study in which dams were treated continuously from 2 months prior to mating and throughout gestation. Increased resorptions were not associated with treatment at the same or at higher dose levels (up to 3 times the MRHD) when treatment of the dams was restricted to gestation days 6 to 15. Increases in resorptions were observed in both rats and mice at 500 mcg/kg/day (10 and 5 times the MRHD in rats and mice, respectively) or higher when the animals were treated on gestation days 1 to 14; 500 mcg/kg/day was the lowest dose employed in this study.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Clonidine hydrochloride is present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets or from the underlying maternal condition. Exercise caution when clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets are administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of clonidine hydrochloride in the treatment of ADHD have been established in pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age. Use of clonidine hydrochloride in pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age is supported by three adequate and well-controlled studies; a short-term, placebo-controlled monotherapy trial, a short-term adjunctive therapy trial and a longer-term randomized monotherapy trial [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients below the age of 6 years has not been established.
Juvenile Animal Data
In studies in juvenile rats, clonidine hydrochloride alone or in combination with methylphenidate had an effect on bone growth at clinically relevant doses and produced a slight delay in sexual maturation in males at 3 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) for clonidine and methylphenidate.
In a study where juvenile rats were treated orally with clonidine hydrochloride from day 21 of age to adulthood, a slight delay in onset of preputial separation (delayed sexual maturation) was seen in males treated with 300 mcg/kg/day, which is approximately 3 times the MRHD of 0.4 mg/day on a mg/m 2 basis. The no‑effect dose was 100 mcg/kg/day, which is approximately equal to the MRHD. There was no drug effects on fertility or on other measures of sexual or neurobehavioral development.
In a study where juvenile rats were treated with clonidine alone (300 mcg/kg/day) or in combination with methylphenidate (10 mg/kg/day in females and 50/30 mg/kg/day in males; the dose was lowered from 50 to 30 mg/kg/day in males due to self-injurious behavior during the first week of treatment) from day 21 of age to adulthood, decreases in bone mineral density and mineral content were observed in males treated with 300 mcg/kg/day clonidine alone and in combination with 50/30 mg/kg/day methylphenidate and a decrease in femur length was observed in males treated with the combination at the end of the treatment period. These doses are approximately 3 times the MRHD of 0.4 mg/day clonidine and 54 mg/day methylphenidate on a mg/m 2 basis. All these effects in males were not reversed at the end of a 4‑week recovery period. In addition, similar findings were seen in males treated with a lower dose of clonidine (30 mcg/kg/day) in combination with 50 mg/kg/day of methylphenidate and a decrease in femur length was observed in females treated with clonidine alone at the end of the recovery period. These effects were accompanied by a decrease in body weight gain in treated animals during the treatment period but the effect was reversed at the end of the recovery period. A delay in preputial separation (sexual maturation) was observed in males treated with the combination treatment of 300 mcg/kg/day clonidine and 50/30 mg/kg/day methylphenidate. There was no effect on reproduction or sperm analysis in these males.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The impact of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of clonidine in children has not been assessed. The initial dosage of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be based on degree of impairment. Monitor patients carefully for hypotension and bradycardia, and titrate to higher doses cautiously. Since only a minimal amount of clonidine is removed during routine hemodialysis, there is no need to give supplemental clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets following dialysis.
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
Clonidine hydrochloride is not a controlled substance and has no known potential for abuse or dependence.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms
Clonidine overdose: hypertension may develop early and may be followed by hypotension, bradycardia, respiratory depression, hypothermia, drowsiness, decreased or absent reflexes, weakness, irritability and miosis. The frequency of CNS depression may be higher in children than adults. Large overdoses may result in reversible cardiac conduction defects or dysrhythmias, apnea, coma and seizures. Signs and symptoms of overdose generally occur within 30 minutes to two hours after exposure.
Treatment
Consult with a Certified Poison Control Center (1‑800‑222‑1222) for up‑to‑date guidance and advice.
11 DESCRIPTION
Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets are a centrally acting alpha 2-adrenergic agonist available as 0.1 mg extended-release tablet for oral administration. Each 0.1 mg tablet is equivalent to 0.087 mg of the free base.
The inactive ingredients are sodium lauryl sulfate, lactose monohydrate, hypromellose, pregelatinized starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, and magnesium stearate. The formulation is designed to delay the absorption of active drug in order to decrease peak to trough plasma concentration differences. Clonidine hydrochloride is an imidazoline derivative and exists as a mesomeric compound. The chemical name is 2‑(2,6‑dichlorophenylamino)-2-imidazoline hydrochloride. The following is the structural formula:
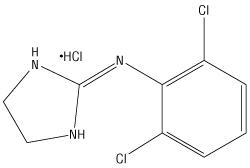
C 9H 9Cl 2N 3HCl Mol. Wt. 266.56
Clonidine hydrochloride, USP is an odorless, bitter, white, crystalline substance soluble in water and alcohol.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Clonidine stimulates alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in the brain. Clonidine is not a central nervous system stimulant. The mechanism of action of clonidine in ADHD is not known.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Clonidine is a known antihypertensive agent. By stimulating alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in the brain stem, clonidine reduces sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system and decreases peripheral resistance, renal vascular resistance, heart rate, and blood pressure.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Single-dose Pharmacokinetics in Adults
Immediate-release clonidine hydrochloride and clonidine hydrochloride extended-release have different pharmacokinetic characteristics; dose substitution on a milligram for milligram basis will result in differences in exposure. A comparison across studies suggests that the C max is 50% lower for clonidine hydrochloride extended-release compared to immediate-release clonidine hydrochloride.
Following oral administration of an immediate release formulation, plasma clonidine concentration peaks in approximately 3 to 5 hours and the plasma half-life ranges from 12 to 16 hours. The half-life increases up to 41 hours in patients with severe impairment of renal function. Following oral administration about 40% to 60% of the absorbed dose is recovered in the urine as unchanged drug in 24 hours.
About 50% of the absorbed dose is metabolized in the liver. Although studies of the effect of renal impairment and studies of clonidine excretion have not been performed with clonidine hydrochloride extended-release, results are likely to be similar to those of the immediate release formulation.
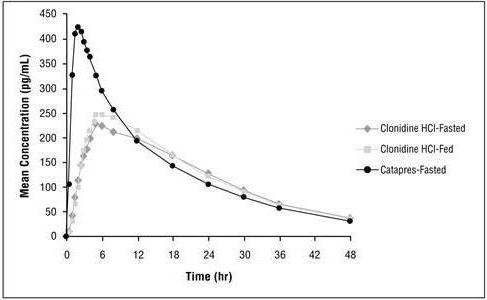
The pharmacokinetic profile of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release administration was evaluated in an open-label, three-period, randomized, crossover study of 15 healthy adult subjects who received three single-dose regimens of clonidine: 0.1 mg of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release under fasted conditions, 0.1 mg of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release following a high fat meal, and 0.1 mg of clonidine immediate-release (Catapres ®) under fasted conditions. Treatments were separated by one‑week washout periods.
Mean concentration-time data from the 3 treatments are shown in Table 7 and Figure 1. After administration of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release, maximum clonidine concentrations were approximately 50% of the Catapres maximum concentrations and occurred approximately 5 hours later relative to Catapres. Similar elimination half-lives were observed and total systemic bioavailability following clonidine hydrochloride extended-release was approximately 89% of that following Catapres.
Food had no effect on plasma concentrations, bioavailability, or elimination half-life.
Table 7 Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Clonidine in Healthy Adult Volunteers
|
CATAPRES-Fasted
|
Clonidine HydrochlorideExtended-Release-
|
Clonidine Hydrochloride Extended-Release-Fasted
|
||||
|
Parameter |
Mean |
SD |
Mean |
SD |
Mean |
SD |
|
C max (pg/mL) |
443 |
59.6 |
235 |
34.7 |
258 |
33.3 |
|
AUC inf (hr*pg/mL) |
7313 |
1812 |
6505 |
1728 |
6729 |
1650 |
|
hT max (hr) |
2.07 |
0.5 |
6.80 |
3.61 |
6.50 |
1.23 |
|
T 1/2 (hr) |
12.57 |
3.11 |
12.67 |
3.76 |
12.65 |
3.56 |
Figure 1 Mean Clonidine Concentration-Time Profiles after Single Dose Administration
Multiple-dose Pharmacokinetics in Children and Adolescents
Plasma clonidine concentrations in children and adolescents (0.1 mg bid and 0.2 mg bid) with ADHD are greater than those of adults with hypertension with children and adolescents receiving higher doses on a mg/kg basis. Body weight normalized clearance (CL/F) in children and adolescents was higher than CL/F observed in adults with hypertension. Clonidine concentrations in plasma increased with increases in dose over the dose range of 0.2 to 0.4 mg/day. Clonidine CL/F was independent of dose administered over the 0.2 to 0.4 mg/day dose range. Clonidine CL/F appeared to decrease slightly with increases in age over the range of 6 to 17 years, and females had a 23% lower CL/F than males. The incidence of “sedation-like” AEs (somnolence and fatigue) appeared to be independent of clonidine dose or concentration within the studied dose range in the titration study. Results from the add‑on study showed that clonidine CL/F was 11% higher in patients who were receiving methylphenidate and 44% lower in those receiving amphetamine compared to subjects not on adjunctive therapy.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
Clonidine hydrochloride was not carcinogenic when administered in the diet of rats (for up to 132 weeks) or mice (for up to 78 weeks) at doses of up to 1620 (male rats), 2040 (female rats), or 2500 (mice) mcg/kg/day. These doses are approximately 20, 25, and 15 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 0.4 mg/day on a mg/m 2 basis.
There was no evidence of genotoxicity in the Ames test for mutagenicity or mouse micronucleus test for clastogenicity.
Fertility of male or female rats was unaffected by clonidine hydrochloride doses as high as 150 mcg/kg/day (approximately 3 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis). In a separate experiment, fertility of female rats appeared to be adversely affected at dose levels of 500 and 2000 mcg/kg/day (10 and 40 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Efficacy of clonidine hydrochloride in the treatment of ADHD was established in children and adolescents (6 to 17 years) in:
One short-term, placebo-controlled monotherapy trial (Study 1)
One short-term adjunctive therapy to psychostimulants trial (Study 2)
One randomized withdrawal trial as monotherapy (Study 3)
Short-term Monotherapy and Adjunctive Therapy to Psychostimulant Studies for ADHD
The efficacy of clonidine hydrochloride in the treatment of ADHD was established in 2 (one monotherapy and one adjunctive therapy) placebo-controlled trials in pediatric patients aged 6 to 17, who met DSM IV criteria of ADHD hyperactive or combined hyperactive/inattentive subtypes. Signs and symptoms of ADHD were evaluated using the investigator administered and scored ADHD Rating Scale-IV-Parent Version (ADHDRS-IV) total score including hyperactive/impulsivity and inattentive subscales.
Study 1 (CLON 301), was an 8 week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed dose study of children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 (N=236) with a 5 week primary efficacy endpoint. Patients were randomly assigned to one of the following three treatment groups: clonidine hydrochloride (CLON) 0.2 mg/day (N=78), clonidine hydrochloride 0.4 mg/day (N=80), or placebo (N=78). Dosing for the clonidine hydrochloride groups started at 0.1 mg/day and was titrated in increments of 0.1 mg/week to their respective dose (as divided doses). Patients were maintained at their dose for a minimum of 2 weeks before being gradually tapered down to 0.1 mg/day at the last week of treatment. At both doses, improvements in ADHD symptoms were statistically significantly superior in clonidine hydrochloride-treated patients compared with placebo-treated patients at the end of 5 weeks as measured by the ADHDRS-IV total score (Table 8).
Study 2 (CLON 302) was an 8 week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, flexible dose study in children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 (N=198) with a 5 week primary efficacy end point. Patients had been treated with a psychostimulant (methylphenidate or amphetamine) for four weeks with inadequate response. Patients were randomly assigned to one of two treatment groups: clonidine hydrochloride adjunct to a psychostimulant (N=102) or psychostimulant alone (N=96). The clonidine hydrochloride dose was initiated at 0.1 mg/day and doses were titrated in increments of 0.1 mg/week up to 0.4 mg/day, as divided doses, over a 3 week period based on tolerability and clinical response. The dose was maintained for a minimum of 2 weeks before being gradually tapered to 0.1 mg/day at the last week of treatment. ADHD symptoms were statistically significantly improved in clonidine hydrochloride plus stimulant group compared with the stimulant alone group at the end of 5 weeks as measured by the ADHDRS-IV total score (Table 8).
Table 8 Short-Term Trials
|
Study Number |
Treatment Group |
Primary Efficacy Measure: ADHDRS‑IV Total Score |
||
|
Study 1 |
Clonidine HCl (0.2 mg/day) |
43.8 (7.47) |
-15.0 (1.38) |
-8.5 (-12.2, -4.8) |
|
Clonidine HCl (0.4 mg/day) |
44.6 (7.73) |
-15.6 (1.33) |
-9.1 (-12.8, -5.5) |
|
|
Placebo |
45.0 (8.53) |
-6.5 (1.35) |
-- |
|
|
Study 2 |
Clonidine HCl (0.4 mg/day) + Psychostimulant |
38.9 (6.95) |
-15.8 (1.18) |
-4.5 (-7.8, -1.1) |
|
Psychostimulant alone |
39.0 (7.68) |
-11.3 (1.24) |
-- |
|
SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error; LS Mean: least-squares mean; CI: unadjusted confidence interval.
a Difference (drug minus placebo) in least-squares mean change from baseline.
Maintenance Monotherapy for ADHD
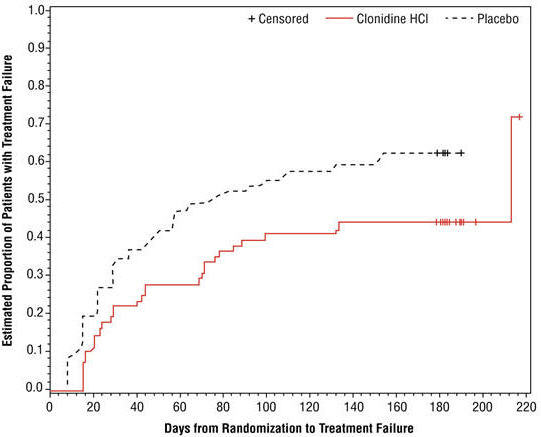
Study 3 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized-withdrawal study in children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 years (n=253) with DSM IV TR diagnosis of ADHD. The study consisted of a 10 week, open-label phase (4 weeks of dose optimization and 6 weeks of dose maintenance), a 26 week double-blind phase, and a 4 week taper down and follow up phase. All patients were initiated at 0.1 mg/day and increased at weekly intervals in increments of 0.1 mg/day until reaching personalized optimal dose (0.1, 0.2, 0.3 or 0.4 mg/day, as divided doses). Eligible patients had to demonstrate treatment response as defined by ≥30% reduction in ADHD RS IV total score and a Clinical Global Impression-Improvement score of 1 or 2 during the open label phase. Patients who sustained treatment response (n=135) until the end of the open label phase were randomly assigned to one of the two treatment groups, clonidine hydrochloride (N=68) and Placebo (N=67), to evaluate the long-term efficacy of maintenance dose of clonidine hydrochloride in the double-blind phase. The primary efficacy endpoint was the percentage of patients with treatment failure defined as a ≥30% increase (worsening) in ADHD RS IV total score and ≥2 points increase (worsening) in Clinical Global Impression – Severity Scale in 2 consecutive visits or early termination for any reason. A total of 73 patients experienced treatment failure in the double-blind phase: 31 patients (45.6%) in the clonidine hydrochloride group and 42 patients (62.7%) in the placebo group, with a statistically significant difference in the primary endpoint favoring clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets (Table 9). The cumulative proportion of patients with treatment failure over time during the double-blind phase is displayed in Figure 2.
Table 9 Treatment Failure: Double-Blind Full Analysis Set (Study 3)
|
Study 3 |
Double-Blind Full Analysis Set |
|
|
Clonidine Hydrochloride |
Placebo |
|
|
Number of subjects |
68 |
67 |
|
Number of treatment failures |
31 (45.6%) |
42 (62.7%) |
|
Basis of Treatment Failure | ||
|
Clinical criteria a,b |
11 (16.2%) |
9 (13.4%) |
|
Lack of efficacy c |
1 (1.5%) |
3 (4.5%) |
|
Withdrawal of informed assent/consent |
4 (5.9%) |
20 (29.9%) |
|
Other early terminations |
15 (22.1%) |
10 (14.9%) |
ADHD RS IV = Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder-Rating Scale-4th edition; CGI S = Clinical Global Impression-Severity
a At the same 2 consecutive visits a (1) 30% or greater reduction in ADHD RS IV, and (2) 2 point or more increase in CGI S.
b Two subjects (1 placebo and 1 Clonidine Hydrochloride) withdrew consent, but met the clinical criteria for treatment failure.
c Three subjects (all placebo) discontinued the study due to treatment failure, but met only the criterion for ADHD RS IV.
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Estimation of Cumulative Proportion of Patients with Treatment Failure (Study 3)
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablet 0.1 mg is a white to off-white round, biconvex tablets with debossing: “U” on one side and “77” on the other side and supplied as follows.
Bottles of 60 tablets with child-resistant closure, NDC: 0832-0777-60
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight container as defined in the USP.
Keep clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information)
Dosage and Administration
Advise patients that clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets must be swallowed whole, never crushed, cut, or chewed, and may be taken with or without food. When initiating treatment, provide dosage escalation instructions [seeDosage and Administration (2.1)].
Missed Dose
If patients miss a dose of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets, advise them to skip the dose and take the next dose as scheduled and not to take more than the prescribed total daily amount of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets in any 24‑hour period [seeDosage and Administration (2.4)].
Hypotension/Bradycardia
Advise patients who have a history of syncope or may have a condition that predisposes them to syncope, such as hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, or dehydration, to avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Sedation and Somnolence
Instruct patients to use caution when driving a car or operating hazardous machinery until they know how they will respond to treatment with clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets. Also advise patients to avoid the use of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets with other centrally active depressants and with alcohol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Rebound Hypertension
Advise patients not to discontinue clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets abruptly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Allergic Reactions
Advise patients to discontinue clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets and seek immediate medical attention if any signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction occur, such as generalized rash, urticaria, or angioedema [see Warningsand Precautions (5.4)].
Manufactured for
UPSHER-SMITH LABORATORIES, LLC
Maple Grove, MN 55369
Made in Portugal
The brand listed Catapres ® is a registered trademark of its respective owner.
Revised 0917
Patient Information
Clonidine Hydrochloride (kloe' ni deen hye'' droe klor' ide)
Extended-Release Tablets
Read the Patient Information that comes with clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Patient Information leaflet does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or treatment.
What are clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets?
Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets are a prescription medicine used for the treatment of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Your doctor may prescribe clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets alone or together with certain other ADHD medicines.
- Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets are not a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant.
- Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be used as part of a total treatment program for ADHD that may include counseling or other therapies.
Who should not take clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets?
- Do not take clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets if you are allergic to clonidine in clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
What should I tell my doctor before taking clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets?
Before you take clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets, tell your doctor if you:
- have kidney problems
- have low or high blood pressure
- have a history of passing out (syncope)
- have heart problems, including history of heart attack
- have had a stroke or have stroke symptoms
- had a skin reaction (such as a rash) after taking clonidine in a transdermal form (skin patch)
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets can pass into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines that you take, including prescription and non‑prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets and certain other medicines may affect each other causing serious side effects. Sometimes the doses of other medicines may need to be changed while taking clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- anti-depression medicines
- heart or blood pressure medicine
- other medicines that contain clonidine
- a medicine that makes you sleepy (sedation)
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure if your medicine is listed above.
Know the medicines that you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets?
- Take clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Your doctor will tell you how many clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets to take and when to take them. Your doctor may change your dose of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets. Do not change your dose of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets without talking to your doctor.
- Do not stop taking clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets without talking to your doctor.
- Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets can be taken with or without food.
- Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be taken 2 times a day (in the morning and at bedtime).
- If you miss a dose of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets, skip the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take two doses at the same time.
- Take clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets whole. Do not chew, crush or break clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets. Tell your doctor if you cannot swallow clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets whole. You may need a different medicine.
- If you take too much clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets, call your Poison Control Center or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets?
- Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets until you talk with your doctor. Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets taken with alcohol or medicines that cause sleepiness or dizziness may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse.
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery or do other dangerous activities until you know how clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets will affect you.
- Avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated.
What are possible side effects of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets?
Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets may cause serious side effects, including:
- Low blood pressure and low heart rate. Your doctor should check your heart rate and blood pressure before starting treatment and regularly during treatment with clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
- Sleepiness.
- Withdrawal symptoms. Suddenly stopping clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets may cause withdrawal symptoms including: increased blood pressure, headache, increased heart rate, lightheadedness, tightness in your chest and nervousness.
The most common side effects of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets include:
- sleepiness
- tiredness
- irritability
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- nightmare
- constipation
- dry mouth
- decreased appetite
- dizziness
Tell your doctor if you have any side effects that bother you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1‑800‑FDA‑1088.
How should I store clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets?
- Store clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets between 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Keep clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets in a tightly closed container.
- Clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets come in a child-resistant package.
Keep clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed.
Do not give clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can also ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information about clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets visit www.upsher-smith.com or call 1-888-650-3789.
What are the ingredients in clonidine hydrochloride extended-release tablets?
Active Ingredient: clonidine hydrochloride
Inactive Ingredients: sodium lauryl sulfate, lactose monohydrate, hypromellose, pregelatinized starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, and magnesium stearate
Manufactured for
UPSHER-SMITH LABORATORIES, LLC
Maple Grove, MN 55369
Made in Portugal
Revised 0917
| CLONIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
clonidine hydrochloride tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Bluepharma - Industria Farmaceutica, S.A. (449909329) |
| Registrant - Bluepharma - Industria Farmaceutica, S.A. (449909329) |
