CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE AND TRETINOIN gel
Clindamycin Phosphate and Tretinoin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Clindamycin Phosphate and Tretinoin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Actavis Pharma, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel 1.2% / 0.025%safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel 1.2% / 0.025%.
CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE and TRETINOIN Gel 1.2% / 0.025%, for topical use only
Initial U.S. Approval: 2006INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel 1.2% / 0.025% is a lincosamide antibiotic and retinoid combination product indicated for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris in patients 12 years or older. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Topical gel: Clindamycin phosphate, USP 1.2% and tretinoin, USP 0.025% gel in 30 and 60 gram tubes. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel is contraindicated in patients with regional enteritis, ulcerative colitis, or history of antibiotic–associated colitis. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Colitis: Clindamycin can cause severe colitis, which may result in death. Diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported with the use of clindamycin. Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel should be discontinued if significant diarrhea occurs. (5.1)
- Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposures: Avoid exposure to sunlight and sunlamps. Wear sunscreen daily. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Observed local adverse reactions in patients treated with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel were skin erythema, scaling, itching, burning, and stinging. Other most commonly reported adverse events (≥ 1% in patients treated with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel) were nasopharyngitis, pharyngolaryngeal pain, dry skin, cough, and sinusitis. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Actavis at 1-800-432-8534 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 1/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS & USAGE
2 DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Colitis
5.2 Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposure
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Concomitant Topical Medication
7.2 Erythromycin
7.3 Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 PREGNANCY
8.3 NURSING MOTHERS
8.4 PEDIATRIC USE
8.5 GERIATRIC USE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 MECHANISMS OF ACTION
12.3 PHARMACOKINETICS
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Instructions for Use
17.2 Skin Irritation
17.3 Colitis
17.4 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS & USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
At bedtime, squeeze a pea-sized amount of medication onto one fingertip, dot onto the chin, cheeks, nose, and forehead, then gently rub over the entire face. Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel should be kept away from the eyes, the mouth, angles of the nose, and mucous membranes.
Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel, a combination of a lincosamide antibiotic and a retinoid, contains clindamycin phosphate, USP 1.2% and tretinoin, USP 0.025%, formulated as a topical gel. Each gram of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel contains, as dispensed, 10 mg (1%) clindamycin as phosphate, USP, and 0.25 mg (0.025%) tretinoin, USP in an aqueous based gel. Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel is available in 30 gram and 60 gram tubes.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Colitis
Systemic absorption of clindamycin has been demonstrated following topical use of this product. Diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported with the use of topical clindamycin. When significant diarrhea occurs, clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel should be discontinued.
Severe colitis has occurred following oral or parenteral administration of clindamycin with an onset of up to several weeks following cessation of therapy. Antiperistaltic agents such as opiates and diphenoxylate with atropine may prolong and/or worsen severe colitis. Severe colitis may result in death.
Studies indicate a toxin(s) produced by clostridia is one primary cause of antibiotic-associated colitis. The colitis is usually characterized by severe persistent diarrhea and severe abdominal cramps and may be associated with the passage of blood and mucus. Stool cultures for Clostridium difficile and stool assay for C. difficile toxin may be helpful diagnostically.
5.2 Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposure
Exposure to sunlight, including sunlamps, should be avoided during the use of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel, and patients with sunburn should be advised not to use the product until fully recovered because of heightened susceptibility to sunlight as a result of the use of tretinoin. Patients who may be required to have considerable sun exposure due to occupation and those with inherent sensitivity to the sun should exercise particular caution. Daily use of sunscreen products and protective apparel (e.g., a hat) are recommended. Weather extremes, such as wind or cold, also may be irritating to patients under treatment with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under prescribed conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trial may not reflect the rates observed in practice. The adverse reaction information from clinical trials does, however, provide a basis for identifying the adverse reactions that appear to be related to drug use for approximating rates.
The safety data presented in Table 1 (below) reflects exposure to clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel in 1,853 patients with acne vulgaris. Patients were 12 years and older and were treated once daily for 12 weeks. Adverse reactions that were reported in ≥ 1% of patients treated with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel were compared to adverse reactions in patients treated with clindamycin phosphate 1.2% in vehicle gel, tretinoin 0.025% in vehicle gel, and the vehicle gel alone:
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Reported in at Least 1% of Patients Treated with Clindamycin Phosphate and Tretinoin Gel: 12-Week Studies Clindamycin Phosphate and Tretinoin Gel Clindamycin Tretinoin Vehicle N=1853 N=1428 N=846 N=423 N (%) N (%) N (%) N (%) Note: Formulations used in all treatment arms were in the clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin vehicle gel. PATIENTS WITH AT LEAST ONE AR 497 (27) 342 (24) 225 (27) 91 (22) Nasopharyngitis 65 (4) 64 (5) 16 (2) 5 (1) Pharyngolaryngeal pain 29 (2) 18 (1) 5 (1) 7 (2) Dry skin 23 (1) 7 (1) 3 (<1) 0 (0) Cough 19 (1) 21 (2) 9 (1) 2 (1) Sinusitis 19 (1) 19 (1) 15 (2) 4 (1) Cutaneous safety and tolerance evaluations were conducted at each study visit in all of the clinical trials by assessment of erythema, scaling, itching, burning, and stinging:
Table 2: Clindamycin Phosphate and Tretinoin Gel-Treated Patients with Local Skin Reactions Local Reaction Baseline End of Treatment N=1835 N=1614 N (%) N (%) Erythema 636 (35) 416 (26) Scaling 237 (13) 280 (17) Itching 189 (10) 70 (4) Burning 38 (2) 56 (4) Stinging 33 (2) 27 (2) At each study visit, application site reactions on a scale of 0 (none), 1 (mild), 2 (moderate), and 3 (severe), and the mean scores were calculated for each of the local skin reactions. In Studies 1 and 2, 1277 subjects enrolled with moderate to severe acne, 854 subjects treated with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel and 423 treated with vehicle. Analysis over the twelve week period demonstrated that cutaneous irritation scores for erythema, scaling, itching, burning, and stinging peaked at two weeks of therapy, and were slightly higher for the clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin-treated group, decreasing thereafter.
One open-label 12-month safety study for clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel showed a similar adverse reaction profile as seen in the 12-week studies. Eighteen out of 442 subjects (4%) reported gastrointestinal symptoms.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Concomitant Topical Medication
Concomitant topical medication, medicated or abrasive soaps and cleansers, soaps and cosmetics that have a strong drying effect, and products with high concentrations of alcohol, astringents, spices or lime should be used with caution. When used with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel, there may be increased skin irritation.
7.2 Erythromycin
Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel should not be used in combination with erythromycin-containing products due to its clindamycin component. In vitro studies have shown antagonism between these two antimicrobials. The clinical significance of this in vitro antagonism is not known.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 PREGNANCY
Pregnancy Category C. There are no well-controlled trials in pregnant women treated with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel. Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel was tested for maternal and developmental toxicity in New Zealand White Rabbits with topical doses of 60, 180 and 600 mg/kg/day. Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel at 600 mg/kg/day (approximately 12 times the recommended clinical dose assuming 100% absorption and based on body surface area comparison) was considered to be the no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) for maternal and developmental toxicity following dermal administration of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel for two weeks prior to artificial insemination and continuing until gestation day 18, inclusive. For purposes of comparisons of the animal exposure to human exposure, the recommended clinical dose is defined as 1 g of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel applied daily to a 60 kg person.
Clindamycin
Teratology (Segment II) studies using clindamycin were performed orally in rats (up to 600 mg/kg/day) and mice (up to 100 mg/kg/day) (583 and 49 times amount of clindamycin in the recommended clinical dose based on a body surface area comparison, respectively) or with subcutaneous doses of clindamycin up to 180 mg/kg/day (175 and 88 times the amount of clindamycin in the recommended clinical dose based on a body surface area comparison, respectively) revealed no evidence of teratogenicity.
Tretinoin
In oral Segment III studies in rats with tretinoin, decreased survival of neonates and growth retardation were observed at doses in excess of 2 mg/kg/day (~ 78 times the recommended clinical dose assuming 100% absorption and based on body surface area comparison).
With widespread use of any drug, a small number of birth defect reports associated temporally with the administration of the drug would be expected by chance alone. Thirty cases of temporally associated congenital malformations have been reported during two decades of clinical use of another formulation of topical tretinoin. Although no definite pattern of teratogenicity and no causal association have been established from these cases, 5 of the reports describe the rare birth defect category, holoprosencephaly (defects associated with incomplete midline development of the forebrain). The significance of these spontaneous reports in terms of risk to the fetus is not known.
Dermal tretinoin has been shown to be fetotoxic in rabbits when administered in doses 40 times the recommended human clinical dose based on a body surface area comparison. Oral tretinoin has been shown to be fetotoxic in rats when administered in doses 78 times the recommended clinical dose based on a body surface area comparison.
8.3 NURSING MOTHERS
It is not known whether clindamycin is excreted in human milk following use of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel. However, orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been reported to appear in breast milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. It is not known whether tretinoin is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 PEDIATRIC USE
Safety and effectiveness of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel in pediatric patients under the age of 12 have not been established.
Clinical trials of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel included patients 12 to 17 years of age. [See Clinical Studies (14)]
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel 1.2% / 0.025%, is an antibiotic and retinoid combination gel product with two active ingredients. Clindamycin phosphate, USP is a water-soluble ester of the semi-synthetic antibiotic produced by a 7(S)-chloro-substitution of the 7(R)-hydroxyl group of the parent antibiotic lincomycin.
The chemical name for clindamycin phosphate, USP is Methyl 7-chloro-6,7,8-trideoxy-6-(1-methyl-trans-4- propyl-L-2-pyrrolidinecarboxamido)-1-thio-L-threo-α-D-galacto-octopyranoside 2-(dihydrogen phosphate). The structural formula for clindamycin phosphate, USP is represented below:
Clindamycin phosphate, USP:
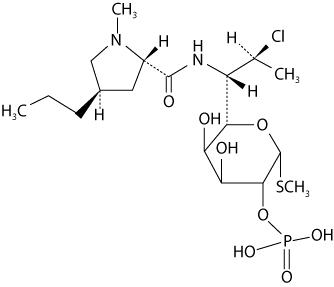
Molecular Formula: C18H34ClN2O8PS Molecular Weight: 504.97
The chemical name for tretinoin, USP is 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8- nonatetraenoic acid (all-trans form). The structural formula for tretinoin, USP is represented below:
Tretinoin, USP:
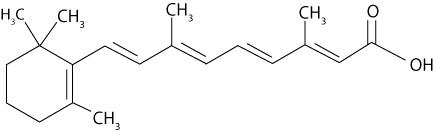
Molecular Formula: C20H28O2 Molecular Weight: 300.44
Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel 1.2% / 0.025% contains the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous citric acid, butylated hydroxytoluene, edetate disodium, hydroxyethyl cellulose, glycerin, methylparaben, polysorbate 80, propylparaben, purified water, tromethamine and xanthan gum.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 MECHANISMS OF ACTION
Clindamycin
[see Microbiology (12.4)].
Tretinoin
Although the exact mode of action of tretinoin is unknown, current evidence suggests that topical tretinoin decreases cohesiveness of follicular epithelial cells with decreased microcomedo formation. Additionally, tretinoin stimulates mitotic activity and increased turnover of follicular epithelial cells causing extrusion of the comedones.
12.3 PHARMACOKINETICS
In an open-label, multiple-dose study treating 12 subjects with moderate to severe acne, the percutaneous absorption of tretinoin following 14 consecutive daily applications of approximately 4 g of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel was minimal. Quantifiable tretinoin plasma concentrations ranged from 1.0 to 1.6 ng/mL, with unquantifiable plasma concentrations in 50% to 92% of subjects at any given timepoint following administration. The plasma concentrations of the key tretinoin metabolites, 13- cis -retinoic acid and 4-oxo-13-cis-retinoic acid, ranged from 1.0 to 1.4 ng/mL and from 1.6 to 6.5 ng/mL, respectively. Plasma concentrations for clindamycin generally did not exceed 3.5 ng/mL, with the exception of one subject whose plasma concentration reached 13.1 ng/mL.
12.4 Microbiology
Clindamycin binds to the 50S ribosomal subunits of susceptible bacteria and prevents elongation of peptide chains by interfering with peptidyl transfer, thereby suppressing bacterial protein synthesis. Clindamycin has been shown to have in vitro activity against Propionibacterium acnes, an organism which has been associated with acne vulgaris; however, the clinical significance of this activity against P. acnes was not examined in clinical trials with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel. P acnes resistance to clindamycin has been documented. Resistance to clindamycin is often associated with resistance to erythromycin.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity and impairment of fertility testing of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel have not been performed in any species.
Clindamycin
The carcinogenicity of a 1% clindamycin phosphate gel similar to clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel was evaluated by daily application to mice for two years. The daily doses used in this study were approximately 13 and 72 times higher than the human dose of clindamycin phosphate from clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel, assuming complete absorption and based on a body surface area comparison. No significant increase in tumors was noted in the treated animals. For purposes of comparisons of the animal exposure to human exposure, the recommended human topical clinical dose is defined as 1 g of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel applied daily to a 60 kg person.
Fertility (Segment 1) studies in rats treated orally with up to 300 mg/kg/day of clindamycin (approximately 290 times the amount of clindamycin delivered from the recommended clinical dose for clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel, based on a body surface area comparison) revealed no effects on fertility or mating ability.
Tretinoin
In two independent studies with long-term topical application of tretinoin in mice, carcinogenicity was not observed. In both studies, tretinoin was administered topically (0.025% or 0.1%) three times per week for up to two years. No carcinogenicity was observed with maximum effects of dermal amyloidosis in the basal layer of the skin.
Tretinoin has been shown to enhance photoco-carcinogenicity in properly performed specific studies, employing concurrent or intercurrent exposure to the drug and UV radiation. The contribution of clindamycin to that effect is unknown. Although the significance of these studies to humans is not clear, patients should minimize exposure to sun.
The genotoxic potential of tretinoin was evaluated in an in vitro Ames Salmonella reversion test and an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Both tests were negative.
In oral Segment 1 studies in rats treated with tretinoin, the no-observed-effect-level was 2 mg/kg/day (~78 times the recommended clinical dose assuming 100% absorption and based on body surface area comparison).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of once daily use of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel for treatment of acne vulgaris were assessed in three 12-week prospective, multi-center, randomized, blinded studies in patients 12 years and older. Studies 1 and 2 were of identical design, and compared clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel to clindamycin in the vehicle gel, tretinoin in the vehicle gel, and the vehicle gel alone. Patients with mild, moderate, or severe acne were enrolled in the studies. The co-primary efficacy variables were:
(1) Mean percent change from baseline at Week 12 in
- inflammatory lesion counts,
- non-inflammatory lesion counts, and
- total lesion counts
(2) Percent of subjects who cleared or almost cleared at Week 12 as judged by an Evaluator’s Global Severity (EGS) score.
The EGS scoring scale used in all of the clinical trials for clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel is as follows:
Grade Description Clear Normal, clear skin with no evidence of acne vulgaris Almost Clear Rare non-inflammatory lesions present, with rare non-inflamed papules (papules must be resolving and may be hyperpigmented, though not pink-red) Mild Some non-inflammatory lesions are present, with few inflammatory lesions (papules/pustules only; no nodulocystic lesions) Moderate Non-inflammatory lesions predominate, with multiple inflammatory lesions evident: several to many comedones and papules/pustules, and there may or may not be one small nodulo-cystic lesion Severe Inflammatory lesions are more apparent many comedones and papules/pustules, there may or may not be a few nodulocystic lesions Very Severe Highly inflammatory lesions predominate, variable number of comedones, many papules/pustules and many nodulocystic lesions In Study 1, a total of 1,252 patients were enrolled, and in Study 2, a total of 1,288 patients were enrolled. The combined results are presented in Table 3.
Table 3: Efficacy Results at Week 12 in Studies 1 and 2. Clindamycin Phosphate and Clindamycin Tretinoin Vehicle Tretinoin Gel N=845 N=426 N=846 N=423 * Success was defined as cleared or almost cleared at Week 12 Evaluator’s Global Severity: N (%) Patients achieving success* 180 (21%) 70 (16%) 122 (14%) 34 (8%) Inflammatory Lesion Count (% reduction from baseline) Mean 48% 42% 39% 26% Non-inflammatory Lesion Count (% reduction from baseline) Mean 36% 27% 31% 16% Total Lesion Count (% reduction from baseline) Mean 41% 34% 34% 20% In Study 3, clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel was compared to clindamycin gel in a total of 2,010 patients with moderate or severe acne vulgaris (see Table 3). As with Studies 1 and 2, the co-primary endpoints were mean percent reduction in lesion counts (inflammatory, non-inflammatory and total) and the Evaluator’s Global Severity score. In Study 3, success on the EGS score was assessed by the percentage of subjects who had at least 2 grades of improvement from Baseline to Week 12.
Table 4: Efficacy Results at Week 12 in Study 3 Clindamycin Phosphate and Tretinoin Gel Clindamycin N = 1008 N = 1002 * Success was defined as at least a 2-grade improvement at Week 12 from baseline. Evaluator’s Global Severity: N (%) Patients achieving success* 415 (41%) 345 (34%) Inflammatory Lesion Count (% reduction from baseline) Mean 61% 55% Non-inflammatory Lesion Count (% reduction from baseline) Mean 50% 41% Total Lesion Count (% reduction from baseline) Mean 54% 47%
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel 1.2% / 0.025% is supplied as follows:
30 gram tube NDC: 0472-1790-30
60 gram tube NDC: 0472-1790-60
Storage and Handling
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15 to 30°C (59 to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light. Protect from freezing. Keep away from heat.
Keep tube tightly closed.
Keep out of the reach of children.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (17.4).
17.1 Instructions for Use
- At bedtime, the face should be gently washed with a mild soap and warm water. After patting the skin dry, apply clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel as a thin layer over the entire face (excluding the eyes and lips).
- Patients should be advised not to use more than the recommended pea sized amount and not to apply more often than once daily (at bedtime) as this will not make for faster results and may increase irritation.
- A sunscreen should be applied every morning and reapplied over the course of the day as needed. Patients should be advised to avoid exposure to sunlight, sunlamp, ultraviolet light, and other medicines that may increase sensitivity to sunlight.
17.2 Skin Irritation
Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel may cause irritation such as erythema, scaling, itching, burning, or stinging.
17.3 Colitis
In the event a patient treated with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel experiences severe diarrhea or gastrointestinal discomfort, clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel should be discontinued and a physician should be contacted.
Distributed by: Actavis Pharma, Inc.
Parsippany, NJ 07054 USARev. A 1/2020
17.4 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
PATIENT INFORMATION
Clindamycin Phosphate and Tretinoin (klin-da-MYE-sin FOS-fate and TRET-i-noyn)
Gel 1.2% / 0.025%
IMPORTANT: Not for mouth, eye, or vaginal use.
Read the Patient Information that comes with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel before you start using it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your acne or treatment.
What is clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel?
Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel is an antibiotic and retinoid combination medicine used for the skin treatment of acne in patients 12 years and older.
Who should not use clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel?
Do not use clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel if you:
- have Crohn’s Disease
- have Ulcerative Colitis
- have developed colitis with past antibiotic use
Tell your doctor:
- if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel may harm your unborn baby.
- if you are breastfeeding. Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel may pass through your milk and may harm your baby.
-
about all the medicines and skin products you use:
- Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel should not be used with erythromycin-containing products.
- Avoid medicated or abrasive soaps and cleansers, soaps and cosmetics that have a strong drying effect, and skin products that contain alcohol, astringents, spices or lime. These products may cause increased skin irritation if used with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel.
How should I use clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel?
Use clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel exactly as prescribed. It may take some time for you to see improvement of your acne with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel. Your doctor will tell you how long to use clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel.
At bedtime:
- Wash your face gently with a mild soap and warm water.
- Pat the skin dry.
- Apply a pea-size amount of clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel to your fingertip and spread it over your face. Gently, smooth it into your skin. Do not get clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel in your eyes or mouth, on your lips, on the corners of your nose, or on open wounds.
In the morning:
- Apply a sunscreen and reapply during the day as needed.
- Do not apply clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel more than once a day
- Do not use too much clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel. Too much clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel may irritate your skin.
- Do not wash your face more than 2 to 3 times a day. Washing your face too often or scrubbing it may make your acne worse.
Avoid:
- excessive exposure to the sun, cold, and wind. Weather extremes can dry and burn the skin. Always use a sunscreen on clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel treated skin, even on cloudy days. Use other protective clothing such as a hat when you are in the sun.
- the use of sunlamps and tanning booths
If your face becomes sunburned, stop clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel until your skin has healed.
What are possible side effects with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel?
- Skin irritation. Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel may cause skin irritation such as dryness, redness, peeling, burning, or stinging. Stop clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel and call your doctor if your skin becomes very red, swollen, blistered, or crusted.
- Change in skin color. Clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel may cause a temporary skin color change (lighter or darker).
- Colitis. This occurs rarely. Stop clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel and call your doctor if you develop severe watery diarrhea, or bloody diarrhea.
Talk to your doctor about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the side effects with clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How should I store clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel?
- Store clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel at room temperature, 59 to 86°F (15 to 30°C). Do not freeze.
- Keep clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel away from heat and light.
- Keep the tube tightly closed.
- Keep clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in patient information leaflet. Do not use clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can also ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel that is written for healthcare professionals.
If you have questions about clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel you can also call Actavis at 1-800-432-8534.
What are the ingredients in clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gel?
Active Ingredients: clindamycin phosphate, USP 1.2% and tretinoin, USP 0.025%
Inactive Ingredients: anhydrous citric acid, butylated hydroxytoluene, edetate disodium, hydroxyethyl cellulose, glycerin, methylparaben, polysorbate 80, propylparaben, purified water, tromethamine and xanthan gum.
Distributed by:
Actavis Pharma, Inc.
Parsippany, NJ 07054 USARev. A 1/2020
-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Actavis
NDC: 0472-1790-30
Clindamycin Phosphate and Tretinoin Gel
1.2%/0.025%PHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying Patient Information Leaflet to each patient.
Rx Only
FOR TOPICAL USE ONLY.
NOT FOR OPTHALMIC, ORAL, OR INTRAVAGINAL USE.NET WT. 30 g
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE AND TRETINOIN
clindamycin phosphate and tretinoin gelProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0472-1790 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE (UNII: EH6D7113I8) (CLINDAMYCIN - UNII:3U02EL437C) CLINDAMYCIN 12 mg in 1 g TRETINOIN (UNII: 5688UTC01R) (TRETINOIN - UNII:5688UTC01R) TRETINOIN 0.25 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) BUTYLATED HYDROXYTOLUENE (UNII: 1P9D0Z171K) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) HYDROXYETHYL CELLULOSE (100 MPA.S AT 2%) (UNII: R33S7TK2EP) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) METHYLPARABEN (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) PROPYLPARABEN (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) TROMETHAMINE (UNII: 023C2WHX2V) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0472-1790-30 1 in 1 CARTON 07/05/2016 1 30 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 0472-1790-60 1 in 1 CARTON 07/05/2016 2 60 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA202564 07/05/2016 Labeler - Actavis Pharma, Inc. (119723554)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.