RETEVMO- selpercatinib capsule
RETEVMO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
RETEVMO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Eli Lilly and Company, Loxo Oncology, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RETEVMO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for RETEVMO.
RETEVMOTM (selpercatinib) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2020INDICATIONS AND USAGE
RETEVMO is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of:
- Adult patients with metastatic RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)1 (1.1)
- Adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) who require systemic therapy1 (1.2)
- Adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer who require systemic therapy and who are radioactive iodine-refractory (if radioactive iodine is appropriate)1 (1.3)
1 This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trial(s).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Select patients for treatment with RETEVMO based on the presence of a RET gene fusion (NSCLC or thyroid) or specific RET gene mutation (MTC). (2.1, 14)
- Recommended dosage in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age or older is based on weight (2.3):
- Less than 50 kg: 120 mg orally twice daily
- 50 kg or greater: 160 mg orally twice daily
- Reduce RETEVMO dose in patients with severe hepatic impairment. (2.7, 8.7)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Capsules: 40 mg, 80 mg. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor ALT and AST prior to initiating RETEVMO, every 2 weeks during the first 3 months, then monthly thereafter and as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue RETEVMO based on severity. (2.5, 5.1)
- Hypertension: Do not initiate RETEVMO in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Optimize blood pressure (BP) prior to initiating RETEVMO. Monitor BP after 1 week, at least monthly thereafter and as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue RETEVMO based on severity. (2.5, 5.2)
- QT Interval Prolongation: Monitor patients who are at significant risk of developing QTc prolongation. Assess QT interval, electrolytes and TSH at baseline and periodically during treatment. Monitor QT interval more frequently when RETEVMO is concomitantly administered with strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors or drugs known to prolong QTc interval. Withhold and dose reduce or permanently discontinue RETEVMO based on severity. (2.5, 5.3)
- Hemorrhagic Events: Permanently discontinue RETEVMO in patients with severe or life-threatening hemorrhage. (2.5, 5.4)
- Hypersensitivity: Withhold RETEVMO and initiate corticosteroids. Upon resolution, resume at a reduced dose and increase dose by 1 dose level each week until reaching the dose taken prior to onset of hypersensitivity. Continue steroids until patient reaches target dose and then taper. (2.5, 5.5)
- Risk of Impaired Wound Healing: Withhold RETEVMO for at least 7 days prior to elective surgery. Do not administer for at least 2 weeks following major surgery and until adequate wound healing. The safety of resumption of RETEVMO after resolution of wound healing complications has not been established. (5.6)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the possible risk to the fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.7, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, (≥ 25%) were increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST), increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), increased glucose, decreased leukocytes, decreased albumin, decreased calcium, dry mouth, diarrhea, increased creatinine, increased alkaline phosphatase, hypertension, fatigue, edema, decreased platelets, increased total cholesterol, rash, decreased sodium, and constipation. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Eli Lilly and Company at 1-800-LillyRx (1-800-545-5979) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Acid-Reducing Agents: Avoid coadministration. If coadministration cannot be avoided, take RETEVMO with food (with PPI) or modify its administration time (with H2 receptor antagonist or locally-acting antacid). (2.4, 7.1)
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Avoid coadministration. If coadministration cannot be avoided, reduce the RETEVMO dose. (2.6, 7.1)
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Avoid coadministration. (7.1)
- CYP2C8 and CYP3A Substrates: Avoid coadministration. If coadministration cannot be avoided, modify the substrate dosage as recommended in its product labeling. (7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 5/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
1.2 RET-Mutant Medullary Thyroid Cancer
1.3 RET Fusion-Positive Thyroid Cancer
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
2.2 Important Administration Instructions
2.3 Recommended Dosage
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use of Acid-Reducing Agents
2.5 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.6 Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use of Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
2.7 Dosage Modification for Severe Hepatic Impairment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hepatotoxicity
5.2 Hypertension
5.3 QT Interval Prolongation
5.4 Hemorrhagic Events
5.5 Hypersensitivity
5.6 Risk of Impaired Wound Healing
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on RETEVMO
7.2 Effects of RETEVMO on Other Drugs
7.3 Drugs that Prolong QT Interval
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
14.2 RET-Mutant Medullary Thyroid Cancer
14.3 RET Fusion-Positive Thyroid Cancer
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
RETEVMO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trial(s).
1.2 RET-Mutant Medullary Thyroid Cancer
RETEVMO is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) who require systemic therapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trial(s).
1.3 RET Fusion-Positive Thyroid Cancer
RETEVMO is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer who require systemic therapy and who are radioactive iodine-refractory (if radioactive iodine is appropriate).
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trial(s).
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment with RETEVMO based on the presence of a RET gene fusion (NSCLC or thyroid cancer) or specific RET gene mutation (MTC) in tumor specimens or plasma [see Clinical Studies (14)]. An FDA-approved test for the detection of RET gene fusions and RET gene mutations is not currently available.
2.2 Important Administration Instructions
RETEVMO may be taken with or without food unless coadministered with a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of RETEVMO based on body weight is:
- Less than 50 kg: 120 mg
- 50 kg or greater: 160 mg
Take RETEVMO orally twice daily (approximately every 12 hours) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Swallow the capsules whole. Do not crush or chew the capsules.
Do not take a missed dose unless it is more than 6 hours until next scheduled dose.
If vomiting occurs after RETEVMO administration, do not take an additional dose and continue to the next scheduled time for the next dose.
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use of Acid-Reducing Agents
Avoid concomitant use of a PPI, a histamine-2 (H2) receptor antagonist, or a locally-acting antacid with RETEVMO [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. If concomitant use cannot be avoided:
- Take RETEVMO with food when coadministered with a PPI.
- Take RETEVMO 2 hours before or 10 hours after administration of an H2 receptor antagonist.
- Take RETEVMO 2 hours before or 2 hours after administration of a locally-acting antacid.
2.5 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reductions for adverse reactions are provided in Table 1.
Table 1 Recommended RETEVMO Dose Reductions for Adverse Reactions Dose Reduction Patients Weighing
Less Than 50 kgPatients Weighing
50 kg or GreaterFirst 80 mg orally twice daily 120 mg orally twice daily Second 40 mg orally twice daily 80 mg orally twice daily Third 40 mg orally once daily 40 mg orally twice daily Permanently discontinue RETEVMO in patients unable to tolerate three dose reductions.
The recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
Table 2 Recommended RETEVMO Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions Adverse Reaction Severity Dosage Modification Hepatotoxicity
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]Grade 3
or
Grade 4- Withhold RETEVMO and monitor AST/ALT once weekly until resolution to Grade 1 or baseline.
- Resume at reduced dose by 2 dose levels and monitor AST and ALT once weekly until 4 weeks after reaching dose taken prior to the onset of Grade 3 or 4 increased AST or ALT.
- Increase dose by 1 dose level after a minimum of 2 weeks without recurrence and then increase to dose taken prior to the onset of Grade 3 or 4 increased AST or ALT after a minimum of 4 weeks without recurrence.
Hypertension
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]Grade 3
- Withhold RETEVMO for Grade 3 hypertension that persists despite optimal antihypertensive therapy. Resume at a reduced dose when hypertension is controlled.
Grade 4 - Discontinue RETEVMO.
QT Interval Prolongation
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]Grade 3 - Withhold RETEVMO until recovery to baseline or Grade 0 or 1.
- Resume at a reduced dose.
Grade 4 - Discontinue RETEVMO
Hemorrhagic Events
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]Grade 3
or
Grade 4- Withhold RETEVMO until recovery to baseline or Grade 0 or 1.
- Discontinue RETEVMO for severe or life-threatening hemorrhagic events.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]All Grades - Withhold RETEVMO until resolution of the event. Initiate corticosteroids.
- Resume at a reduced dose by 3 dose levels while continuing corticosteroids.
- Increase dose by 1 dose level each week until the dose taken prior to the onset of hypersensitivity is reached, then taper corticosteroids.
Other Adverse Reactions
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]Grade 3
or
Grade 4- Withhold RETEVMO until recovery to baseline or Grade 0 or 1.
- Resume at a reduced dose.
2.6 Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use of Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors with RETEVMO. If concomitant use of a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the RETEVMO dose as recommended in Table 3. After the inhibitor has been discontinued for 3 to 5 elimination half-lives, resume RETEVMO at the dose taken prior to initiating the CYP3A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Table 3 Recommended RETEVMO Dosage for Concomitant Use of Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors Current RETEVMO Dosage Recommended RETEVMO Dosage Moderate CYP3A Inhibitor Strong CYP3A Inhibitor 120 mg orally twice daily 80 mg orally twice daily 40 mg orally twice daily 160 mg orally twice daily 120 mg orally twice daily 80 mg orally twice daily 2.7 Dosage Modification for Severe Hepatic Impairment
Reduce the recommended dosage of RETEVMO for patients with severe hepatic impairment as recommended in Table 4 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Table 4 Recommended RETEVMO Dosage for Severe Hepatic Impairment Current RETEVMO Dosage Recommended RETEVMO Dosage 120 mg orally twice daily 80 mg orally twice daily 160 mg orally twice daily 80 mg orally twice daily - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hepatotoxicity
Serious hepatic adverse reactions occurred in 2.6% of patients treated with RETEVMO. Increased AST occurred in 51% of patients, including Grade 3 or 4 events in 8% and increased ALT occurred in 45% of patients, including Grade 3 or 4 events in 9% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The median time to first onset for increased AST was 4.1 weeks (range: 5 days to 2 years) and increased ALT was 4.1 weeks (range: 6 days to 1.5 years).
Monitor ALT and AST prior to initiating RETEVMO, every 2 weeks during the first 3 months, then monthly thereafter and as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce dose or permanently discontinue RETEVMO based on the severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.2 Hypertension
Hypertension occurred in 35% of patients, including Grade 3 hypertension in 17% and Grade 4 in one (0.1%) patient [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Overall, 4.6% had their dose interrupted and 1.3% had their dose reduced for hypertension. Treatment-emergent hypertension was most commonly managed with anti-hypertension medications.
Do not initiate RETEVMO in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Optimize blood pressure prior to initiating RETEVMO. Monitor blood pressure after 1 week, at least monthly thereafter and as clinically indicated. Initiate or adjust anti-hypertensive therapy as appropriate. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue RETEVMO based on the severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.3 QT Interval Prolongation
RETEVMO can cause concentration-dependent QT interval prolongation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. An increase in QTcF interval to >500 ms was measured in 6% of patients and an increase in the QTcF interval of at least 60 ms over baseline was measured in 15% of patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. RETEVMO has not been studied in patients with clinically significant active cardiovascular disease or recent myocardial infarction.
Monitor patients who are at significant risk of developing QTc prolongation, including patients with known long QT syndromes, clinically significant bradyarrhythmias, and severe or uncontrolled heart failure. Assess QT interval, electrolytes and TSH at baseline and periodically during treatment, adjusting frequency based upon risk factors including diarrhea. Correct hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia and hypocalcemia prior to initiating RETEVMO and during treatment.
Monitor the QT interval more frequently when RETEVMO is concomitantly administered with strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors or drugs known to prolong QTc interval. Withhold and dose reduce or permanently discontinue RETEVMO based on the severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.4 Hemorrhagic Events
Serious including fatal hemorrhagic events can occur with RETEVMO. Grade ≥ 3 hemorrhagic events occurred in 2.3% of patients treated with RETEVMO, including 3 (0.4%) patients with fatal hemorrhagic events, including one case each of cerebral hemorrhage, tracheostomy site hemorrhage, and hemoptysis.
Permanently discontinue RETEVMO in patients with severe or life-threatening hemorrhage [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.5 Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity occurred in 4.3% of patients receiving RETEVMO, including Grade 3 hypersensitivity in 1.6%. The median time to onset was 1.7 weeks (range: 6 days to 1.5 years). Signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity included fever, rash and arthralgias or myalgias with concurrent decreased platelets or transaminitis.
If hypersensitivity occurs, withhold RETEVMO and begin corticosteroids at a dose of 1 mg/kg. Upon resolution of the event, resume RETEVMO at a reduced dose and increase the dose of RETEVMO by 1 dose level each week as tolerated until reaching the dose taken prior to onset of hypersensitivity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Continue steroids until patient reaches target dose and then taper. Permanently discontinue RETEVMO for recurrent hypersensitivity.
5.6 Risk of Impaired Wound Healing
Impaired wound healing can occur in patients who receive drugs that inhibit the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway. Therefore, RETEVMO has the potential to adversely affect wound healing.
Withhold RETEVMO for at least 7 days prior to elective surgery. Do not administer for at least 2 weeks following major surgery and until adequate wound healing. The safety of resumption of RETEVMO after resolution of wound healing complications has not been established.
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on data from animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action, RETEVMO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Administration of selpercatinib to pregnant rats during organogenesis at maternal exposures that were approximately equal to those observed at the recommended human dose of 160 mg twice daily resulted in embryolethality and malformations.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with RETEVMO and for at least 1 week after the final dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with RETEVMO and for 1 week after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- QT Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hemorrhagic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Risk of Impaired Wound Healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
RET Gene Fusion or Gene Mutation Positive Solid Tumors
The pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS and below reflects exposure to RETEVMO as a single agent at 160 mg orally twice daily evaluated in 702 patients in LIBRETTO-001 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Among the 702 patients who received RETEVMO, 65% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 34% were exposed for greater than one year. Among these patients, 95% received at least one dose of RETEVMO at the recommended dosage of 160 mg orally twice daily.
The median age was 59 years (range: 15 to 92 years); 0.3% were pediatric patients 12 to 16 years of age; 52% were male; and 69% were White, 22% were Asian, 5% were Hispanic/Latino, and 3% were Black. The most common tumors were NSCLC (47%), MTC (44%), and non-medullary thyroid carcinoma (5%).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 33% of patients who received RETEVMO. The most frequent serious adverse reaction (in ≥ 2% of patients) was pneumonia. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3% of patients; fatal adverse reactions which occurred in > 1 patient included sepsis (n = 3), cardiac arrest (n = 3) and respiratory failure (n = 3).
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 5% of patients who received RETEVMO. Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation included increased ALT (0.4%), sepsis (0.4%), increased AST (0.3%), drug hypersensitivity (0.3%), fatigue (0.3%), and thrombocytopenia (0.3%).
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 42% of patients who received RETEVMO. Adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption in ≥ 2% of patients included ALT increased, AST increased, hypertension, diarrhea, pyrexia, and QT prolongation.
Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 31% of patients who received RETEVMO. Adverse reactions requiring dosage reductions in ≥ 2% of patients included ALT increased, AST increased, QT prolongation and fatigue.
The most common adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, (≥ 25%) were increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST), increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), increased glucose, decreased leukocytes, decreased albumin, decreased calcium, dry mouth, diarrhea, increased creatinine, increased alkaline phosphatase, hypertension, fatigue, edema, decreased platelets, increased total cholesterol, rash, decreased sodium, and constipation.
Table 5 summarizes the adverse reactions in LIBRETTO-001.
Table 5 Adverse Reactions (≥ 15%) in Patients Who Received RETEVMO in LIBRETTO-001 Adverse Reaction RETEVMO
(n = 702)Grades 1-4
(%)Grades 3-4
(%)1Diarrhea includes diarrhea, defecation urgency, frequent bowel movements, and anal incontinence
2Abdominal pain includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, abdominal discomfort, gastrointestinal pain
3Fatigue includes fatigue, asthenia, malaise.
4Edema includes edema, edema peripheral, face edema, eye edema, eyelid edema, generalized edema, localized edema, lymph edema, scrotal edema, peripheral swelling, scrotal swelling, swelling, swelling face, eye swelling, peripheral swelling
5Includes rash, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash maculopapular, rash morbilliform, rash pruritic
6Headache includes headache, sinus headache, tension headache
7Includes cough, productive cough
8Includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional, dyspnea at rest
9Hemorrhage includes epistaxis, hematuria, hemoptysis, contusion, rectal hemorrhage, vaginal hemorrhage, ecchymosis, hematochezia, petechiae, traumatic hematoma, anal hemorrhage, blood blister, blood urine present, cerebral hemorrhage, gastric hemorrhage, hemorrhage intracranial, spontaneous hematoma, abdominal wall hematoma, angina bullosa hemorrhagica, diverticulum intestinal hemorrhagic, eye hemorrhage, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gingival bleeding, hematemesis, hemorrhagic anemia, intraabdominal hemorrhage, lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, melena, mouth hemorrhage, occult blood positive, pelvic hematoma, periorbital hematoma, pharyngeal hemorrhage, pulmonary contusion, purpura, retroperitoneal hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, subdural hemorrhage, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, vessel puncture site hematoma*Only includes a grade 3 adverse reaction.
Gastrointestinal Dry Mouth 39 0 Diarrhea1 37 3.4* Constipation 25 0.6* Nausea 23 0.6* Abdominal pain2 23 1.9* Vomiting 15 0.3* Vascular Hypertension 35 18 General Fatigue3 35 2* Edema4 33 0.3* Skin Rash5 27 0.7* Nervous System Headache6 23 1.4* Respiratory Cough7 18 0 Dyspnea8 16 2.3 Investigations Prolonged QT interval 17 4* Blood and Lymphatic System Hemorrhage9 15 1.9 Clinically relevant adverse reactions in ≤ 15% of patients who received RETEVMO include hypothyroidism (9%).
Table 6 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in LIBRETTO-001.
Table 6 Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 20%) Worsening from Baseline in Patients Who Received RETEVMO in LIBRETTO-001 1 Denominator for each laboratory parameter is based on the number of patients with a baseline and post-treatment laboratory value available, which ranged from 675 to 692 patients.
Laboratory Abnormality RETEVMO1 Grades 1-4
(%)Grades 3-4
(%)Chemistry Increased AST 51 8 Increased ALT 45 9 Increased glucose 44 2.2 Decreased albumin 42 0.7 Decreased calcium 41 3.8 Increased creatinine 37 1.0 Increased alkaline phosphatase 36 2.3 Increased total cholesterol 31 0.1 Decreased sodium 27 7 Decreased magnesium 24 0.6 Increased potassium 24 1.2 Increased bilirubin 23 2.0 Decreased glucose 22 0.7 Hematology Decreased leukocytes 43 1.6 Decreased platelets 33 2.7 Increased Creatinine
In healthy subjects administered RETEVMO 160 mg orally twice daily, serum creatinine increased 18% after 10 days. Consider alternative markers of renal function if persistent elevations in serum creatinine are observed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on RETEVMO
Acid-Reducing Agents
Concomitant use of RETEVMO with acid-reducing agents decreases selpercatinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce RETEVMO anti-tumor activity.
Avoid concomitant use of PPIs, H2 receptor antagonists, and locally-acting antacids with RETEVMO. If coadministration cannot be avoided, take RETEVMO with food (with a PPI) or modify its administration time (with a H2 receptor antagonist or a locally-acting antacid) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Concomitant use of RETEVMO with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor increases selpercatinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of RETEVMO adverse reactions, including QTc interval prolongation.
Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors with RETEVMO. If concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce the RETEVMO dosage and monitor the QT interval with ECGs more frequently [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Warning and Precautions (5.3)].
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers
Concomitant use of RETEVMO with a strong or moderate CYP3A inducer decreases selpercatinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce RETEVMO anti-tumor activity.
Avoid coadministration of strong or moderate CYP3A inducers with RETEVMO.
7.2 Effects of RETEVMO on Other Drugs
CYP2C8 and CYP3A Substrates
RETEVMO is a moderate CYP2C8 inhibitor and a weak CYP3A inhibitor. Concomitant use of RETEVMO with CYP2C8 and CYP3A substrates increases their plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates. Avoid coadministration of RETEVMO with CYP2C8 and CYP3A substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to increased adverse reactions. If coadministration cannot be avoided, follow recommendations for CYP2C8 and CYP3A substrates provided in their approved product labeling.
7.3 Drugs that Prolong QT Interval
RETEVMO is associated with QTc interval prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Monitor the QT interval with ECGs more frequently in patients who require treatment with concomitant medications known to prolong the QT interval.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies, and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], RETEVMO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on RETEVMO use in pregnant women to inform drug-associated risk. Administration of selpercatinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryolethality and malformations at maternal exposures that were approximately equal to the human exposure at the clinical dose of 160 mg twice daily. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Selpercatinib administration to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at oral doses ≥ 100 mg/kg [approximately 3.6 times the human exposure based on the area under the curve (AUC) at the clinical dose of 160 mg twice daily] resulted in 100% post-implantation loss. At the dose of 50 mg/kg [approximately equal to the human exposure (AUC) at the clinical dose of 160 mg twice daily], 6 of 8 females had 100% early resorptions; the remaining 2 females had high levels of early resorptions with only 3 viable fetuses across the 2 litters. All viable fetuses had decreased fetal body weight and malformations (2 with short tail and one with small snout and localized edema of the neck and thorax).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of selpercatinib or its metabolites in human milk or on their effects on the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with RETEVMO and for 1 week after the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on animal data, RETEVMO can cause embryolethality and malformations at doses resulting in exposures less than or equal to the human exposure at the clinical dose of 160 mg twice daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating RETEVMO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Infertility
RETEVMO may impair fertility in females and males of reproductive potential [See Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of RETEVMO have been established in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older for medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) who require systemic therapy and for advanced RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer who require systemic therapy and are radioactive iodine-refractory (if radioactive iodine is appropriate). Use of RETEVMO for these indications is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with additional pharmacokinetic and safety data in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The safety and effectiveness of RETEVMO have not been established in these indications in patients less than 12 years of age.
The safety and effectiveness of RETEVMO have not been established in pediatric patients for other indications [see Indications and Usage (1)].
Animal Toxicity Data
In 4-week general toxicology studies in rats, animals showed signs of physeal hypertrophy and tooth dysplasia at doses resulting in exposures ≥ approximately 3 times the human exposure at the 160 mg twice daily clinical dose. Minipigs also showed signs of minimal to marked increases in physeal thickness at the 15 mg/kg high dose level (approximately 0.3 times the human exposure at the 160 mg twice daily clinical dose). Rats in both the 4- and 13-week toxicology studies had malocclusion and tooth discoloration at the high dose levels (≥ 1.5 times the human exposure at the 160 mg twice daily clinical dose) that persisted during the recovery period.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of 702 patients who received RETEVMO, 34% (239 patients) were ≥ 65 years of age and 10% (67 patients) were ≥ 75 years of age. No overall differences were observed in the safety or effectiveness of RETEVMO between patients who were ≥ 65 years of age and younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage modification is recommended for patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] ≥ 30 mL/min, estimated by Cockcroft-Gault). The recommended dosage has not been established for patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min) or end-stage renal disease [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Reduce the dose when administering RETEVMO to patients with severe [total bilirubin greater than 3 to 10 times upper limit of normal (ULN) and any AST] hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)]. No dosage modification is recommended for patients with mild (total bilirubin less than or equal to ULN with AST greater than ULN or total bilirubin greater than 1 to 1.5 times ULN with any AST) or moderate (total bilirubin greater than 1.5 to 3 times ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment. Monitor for RETEVMO-related adverse reactions in patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
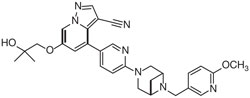
Selpercatinib is a kinase inhibitor. The molecular formula for selpercatinib is C29H31N7O3 and the molecular weight is 525.61 g/mol. The chemical name is 6-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy)-4-(6-(6-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methyl)-3,6-diazabicyclo[3.1.1]heptan-3-yl)pyridin-3-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-3-carbonitrile. Selpercatinib has the following chemical structure:
Selpercatinib is a white to light yellow powder that is slightly hygroscopic. The aqueous solubility of selpercatinib is pH dependent, from freely soluble at low pH to slightly soluble at neutral pH.
RETEVMO (selpercatinib) is supplied as 40 mg or 80 mg hard gelatin capsules for oral use. Each capsule contains inactive ingredients of microcrystalline cellulose and colloidal silicon dioxide. The 40 mg capsule shell is composed of gelatin, titanium dioxide, ferric oxide black and black ink. The 80 mg capsule shell is composed of gelatin, titanium dioxide, FD&C blue #1 and black ink. The black ink is composed of shellac, potassium hydroxide and ferric oxide black.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Selpercatinib is a kinase inhibitor. Selpercatinib inhibited wild-type RET and multiple mutated RET isoforms as well as VEGFR1 and VEGFR3 with IC50 values ranging from 0.92 nM to 67.8 nM. In other enzyme assays, selpercatinib also inhibited FGFR 1, 2, and 3 at higher concentrations that were still clinically achievable. In cellular assays, selpercatinib inhibited RET at approximately 60-fold lower concentrations than FGFR1 and 2 and approximately 8-fold lower concentration than VEGFR3.
Certain point mutations in RET or chromosomal rearrangements involving in-frame fusions of RET with various partners can result in constitutively activated chimeric RET fusion proteins that can act as oncogenic drivers by promoting cell proliferation of tumor cell lines. In in vitro and in vivo tumor models, selpercatinib demonstrated anti-tumor activity in cells harboring constitutive activation of RET protein resulting from gene fusions and mutations, including CCDC6-RET, KIF5B-RET, RET V804M, and RET M918T. In addition, selpercatinib showed anti-tumor activity in mice intracranially implanted with a patient-derived RET fusion positive tumor.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Exposure-Response Relationship
Selpercatinib exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response have not been fully characterized.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of RETEVMO on the QTc interval was evaluated in a thorough QT study in healthy subjects. The largest mean increase in QTc is predicted to be 10.6 msec (upper 90% confidence interval: 12.1 msec) at the mean steady-state maximum concentration (Cmax) observed in patients after administration of 160 mg twice daily. The increase in QTc was concentration-dependent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of selpercatinib were evaluated in patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors administered 160 mg twice daily unless otherwise specified. Steady-state selpercatinib AUC and Cmax increased in a slightly greater than dose proportional manner over the dose range of 20 mg once daily to 240 mg twice daily [0.06 to 1.5 times the maximum recommended total daily dosage].
Steady-state was reached by approximately 7 days and the median accumulation ratio after administration of 160 mg twice daily was 3.4-fold. Mean steady-state selpercatinib [coefficient of variation (CV%)] Cmax was 2,980 (53%) ng/mL and AUC0-24h was 51,600 (58%) ng*h/mL.
Absorption
The median tmax of selpercatinib is 2 hours. The mean absolute bioavailability of RETEVMO capsules is 73% (60% to 82%) in healthy subjects.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (Vss/F) of selpercatinib is 191 L.
Protein binding of selpercatinib is 97% in vitro and is independent of concentration. The blood-to-plasma concentration ratio is 0.7.
Elimination
The apparent clearance (CL/F) of selpercatinib is 6 L/h in patients and the half-life is 32 hours following oral administration of RETEVMO in healthy subjects.
Specific Populations
The apparent volume of distribution and clearance of selpercatinib increase with increasing body weight (27 kg to 177 kg).
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of selpercatinib were observed based on age (15 years to 90 years), sex, or mild or moderate renal impairment (CLcr ≥ 30 mL/min as estimated by Cockcroft-Gault). The effect of severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min) on selpercatinib pharmacokinetics has not been adequately studied.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The selpercatinib AUC0-INF increased by 7%, 32%, and 77% in subjects with mild (total bilirubin less than or equal to ULN with AST greater than ULN or total bilirubin greater than 1 to 1.5 times ULN with any AST ), moderate (total bilirubin greater than 1.5 to 3 times ULN and any AST), and severe (total bilirubin greater than 3 to 10 times ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment, respectively, compared to subjects with normal hepatic function.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Proton-Pump Inhibitors (PPI): Coadministration with multiple daily doses of omeprazole (PPI) decreased selpercatinib AUC0-INF and Cmax when RETEVMO was administered fasting. Coadministration with multiple daily doses of omeprazole did not significantly change the selpercatinib AUC0-INF and Cmax when RETEVMO was administered with food (Table 7).
Table 7 Change in Selpercatinib Exposure After Coadministration with PPI 1 High-fat meal: approximately 150, 250, and 500-600 calories from protein, carbohydrate, and fat, respectively; approximately 800 to 1000 calories total.
2 Low-fat meal: approximately 390 calories and 10 g of fat
Selpercatinib
AUC0-INFSelpercatinib
CmaxRETEVMO fasting Reference Reference RETEVMO fasting + PPI ↓ 69% ↓ 88% RETEVMO with a high-fat meal1 + PPI ↑ 2% ↓ 49% RETEVMO with a low-fat meal2 + PPI No change ↓ 22% H2 Receptor Antagonists: No clinically significant differences in selpercatinib pharmacokinetics were observed when coadministered with multiple daily doses of ranitidine (H2 receptor antagonist) given 10 hours prior to and 2 hours after the RETEVMO dose (administered fasting).
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Coadministration of multiple doses of itraconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitor) increased the selpercatinib AUC0-INF by 133% and Cmax by 30%.
Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Coadministration of multiple doses of diltiazem, fluconazole, or verapamil (moderate CYP3A inhibitors) is predicted to increase the selpercatinib AUC by 60-99% and Cmax by 46-76%.
Strong CYP3A Inducers: Coadministration of multiple doses of rifampin (strong CYP3A inducer) decreased the selpercatinib AUC0-INF by 87% and Cmax by 70%.
Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Coadministration of multiple doses of bosentan or efavirenz (moderate CYP3A inducers) is predicted to decrease the selpercatinib AUC by 40-70% and Cmax by 34-57%.
Weak CYP3A Inducers: Coadministration of multiple doses of modafinil (weak CYP3A inducer) is predicted to decrease the selpercatinib AUC by 33% and Cmax by 26%.
CYP2C8 Substrates: Coadministration of RETEVMO with repaglinide (sensitive CYP2C8 substrate) increased the repaglinide AUC0-INF by 188% and Cmax by 91%.
CYP3A Substrates: Coadministration of RETEVMO with midazolam (sensitive CYP3A) increased the midazolam AUC0-INF by 54% and Cmax by 39%.
In Vitro Studies
CYP Enzymes: Selpercatinib does not inhibit or induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP2D6 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Transporter Systems: Selpercatinib inhibits MATE1, P-gp, and BCRP, but does not inhibit OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, BSEP, and MATE2-K at clinically relevant concentrations. Selpercatinib may increase serum creatinine by decreasing renal tubular secretion of creatinine via inhibition of MATE1 [see Adverse Effects (6.1)]. Selpercatinib is a substrate for P-gp and BCRP, but not for OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, MATE1, or MATE2-K.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with selpercatinib. Selpercatinib was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assays, with or without metabolic activation, or clastogenic in the in vitro micronucleus assay in human peripheral lymphocytes, with or without metabolic activation. Selpercatinib was positive in the in vivo micronucleus assay in rats at concentrations > 7 times the Cmax at the human dose of 160 mg twice daily.
In general toxicology studies, male rats and minipigs exhibited testicular degeneration which was associated with luminal cell debris and/or reduced luminal sperm in the epididymis at selpercatinib exposures approximately 0.4 (rat) and 0.1 (minipig) times the clinical exposure by AUC at the recommended human dose. In a dedicated fertility study in male rats, administration of selpercatinib at doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately twice the clinical exposure by AUC at the 160 twice daily dose) for 28 days prior to cohabitation with untreated females did not affect mating or have clear effects on fertility. Males did, however, display a dose-dependent increase in testicular germ cell depletion and spermatid retention at doses ≥3 mg/kg (~0.2 times the clinical exposure by AUC at the 160 twice daily dose) accompanied by altered sperm morphology at 30 mg/kg.
In a dedicated fertility study in female rats treated with selpercatinib for 15 days before mating to Gestational Day 7, there were decreases in the number of estrous cycles at a dose of 75 mg/kg (approximately equal to the human exposure by AUC at the 160 mg twice daily clinical dose). While selpercatinib did not have clear effects on mating performance or ability to become pregnant at any dose level, half of females at the 75 mg/kg dose level had 100% nonviable embryos. At the same dose level in females with some viable embryos there were increases in post-implantation loss. In the general toxicology study in minipigs, there were findings of decreased or absent corpora lutea, decreased number and size of follicles and stromal proliferation at a selpercatinib dose of 15 mg/kg (approximately 0.3 times to the human exposure by AUC at the 160 mg twice daily clinical dose). Corpora luteal cysts were present in the minipig at selpercatinib doses ≥2 mg/kg (approximately 0.07 times the human exposure by AUC at the 160 mg twice daily clinical dose).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The efficacy of RETEVMO was evaluated in patients with advanced RET fusion-positive NSCLC enrolled in a multicenter, open-label, multi-cohort clinical trial (LIBRETTO-001, NCT03157128). The study enrolled patients with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC who had progressed on platinum-based chemotherapy and patients with advanced or metastatic NSCLC without prior systemic therapy in separate cohorts. Identification of a RET gene alteration was prospectively determined in local laboratories using next generation sequencing (NGS), polymerase chain reaction (PCR), or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Adult patients received RETEVMO 160 mg orally twice daily until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. The major efficacy outcome measures were confirmed overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR), as determined by a blinded independent review committee (BIRC) according to RECIST v1.1.
Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC Previously Treated with Platinum Chemotherapy
Efficacy was evaluated in 105 patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC previously treated with platinum chemotherapy enrolled into a cohort of LIBRETTO-001.
The median age was 61 years (range: 23 to 81); 59% were female; 52% were White, 38% were Asian, 4.8% were Black, and 3.8% were Hispanic/Latino. ECOG performance status was 0-1 (98%) or 2 (2%) and 98% of patients had metastatic disease. Patients received a median of 3 prior systemic therapies (range 1–15); 55% had prior anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. RET fusions were detected in 90% of patients using NGS (81.9% tumor samples; 7.6% blood or plasma samples), 8.6% using FISH, and 1.9% using PCR.
Efficacy results for RET fusion-positive NSCLC are summarized in Table 8.
Table 8 Efficacy Results in LIBRETTO-001 (Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC Previously Treated with Platinum Chemotherapy) 1 Confirmed overall response rate assessed by BICR.
2 Based on observed duration of response
NE = not estimable
RETEVMO
(n = 105)Overall Response Rate1 (95% CI) 64% (54%, 73%) Complete response 1.9% Partial response 62% Duration of Response Median in months (95% CI) 17.5 (12, NE) % with ≥ 6 months2 81 For the 58 patients who received an anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 therapy, either sequentially or concurrently with platinum-based chemotherapy, an exploratory subgroup analysis of ORR was 66% (95% CI: 52%, 78%) and the median DOR was 12.5 months (95% CI: 8.3, NE).
Among the 105 patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC, 11 had measurable CNS metastases at baseline as assessed by BIRC. No patients received radiation therapy (RT) to the brain within 2 months prior to study entry. Responses in intracranial lesions were observed in 10 of these 11 patients; all responders had a DOR of ≥ 6 months.
Treatment-naïve RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC
Efficacy was evaluated in 39 patients with treatment-naïve RET fusion-positive NSCLC enrolled into a cohort of LIBRETTO-001.
The median age was 61 years (range 23 to 86); 56% were female; 72% were White, 18% were Asian, and 8% were Black. ECOG performance status was 0-1 in all patients (100%) and all patients (100%) had metastatic disease. RET fusions were detected in 92% of patients using NGS (69% tumor samples; 23% in blood) and 8% using FISH.
Efficacy results for treatment naïve RET fusion-positive NSCLC are summarized in Table 9.
Table 9 Efficacy Results in LIBRETTO-001 (Treatment-Naïve Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC) 1 Confirmed overall response rate assessed by BICR.
2 Based on observed duration of response
NE = not estimable
RETEVMO
(n =39)Overall Response Rate1 (95% CI) 85% (70%, 94%) Complete response 0 Partial response 85% Duration of Response Median in months (95% CI) NE (12, NE) % with ≥ 6 months2 58 14.2 RET-Mutant Medullary Thyroid Cancer
The efficacy of RETEVMO was evaluated in patients with RET-mutant MTC enrolled in a multicenter, open-label, multi-cohort clinical trial (LIBRETTO-001, NCT03157128). The study enrolled patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had been previously treated with cabozantinib or vandetanib (or both) and patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who were naïve to cabozantinib and vandetanib in separate cohorts.
RET-Mutant MTC Previously Treated with Cabozantinib or Vandetanib
Efficacy was evaluated in 55 patients with RET-mutant advanced MTC who had previously treated with cabozantinib or vandetanib enrolled into a cohort of LIBRETTO-001.
The median age was 57 years (range: 17 to 84); 66% were male; 89% were White, 7% were Hispanic/Latino, and 1.8% were Black. ECOG performance status was 0-1 (95%) or 2 (5%) and 98% of patients had metastatic disease. Patients received a median of 2 prior systemic therapies (range 1 – 8). RET mutation status was detected in 82% of patients using NGS (78% tumor samples; 4% blood or plasma), 16% using PCR, and 2% using an unknown test. The protocol excluded patients with synonymous, frameshift or nonsense RET mutations; the specific mutations used to identify and enroll patients are described in Table 10.
Table 10 Mutations used to Identify and Enroll Patients with RET-Mutant MTC in LIBRETTO-001 1 Somatic or germline mutations; protein change.
2 Extracellular cysteine mutations involving cysteine residues 609, 611, 618, 620, 630, and 634
3 Other included: K666N (1), D631_L633delinsV (2), D631_L633delinsE (5), D378_G385delinsE (1), D898_E901del (2), A883F (4), E632_L633del (4), L790F (2), T636_V637insCRT(1), D898_E901del + D903_S904delinsEP (1)
4 One patient also had a M918T mutation
RET Mutation Type1 Previously Treated
(n = 55)Cabozantinib/ Vandetanib Naïve
(n = 88)Total
(n = 143)M918T 33 49 82 Extracellular cysteine mutation2 7 20 27 V804M or V804L 54 6 11 Other3 10 13 23 Efficacy results for RET-mutant MTC are summarized in Table 11.
Table 11 Efficacy Results in LIBRETTO-001 (RET-Mutant MTC Previously Treated with Cabozantinib or Vandetanib) 1 Confirmed overall response rate assessed by BICR.
2 Based on observed duration of response
NE = not estimableRETEVMO
(n = 55)Overall Response Rate1 (95% CI) 69% (55%, 81%) Complete response 9% Partial response 60% Duration of Response Median in months (95% CI) NE (19.1, NE) % with > 6 months2 76 Cabozantinib and Vandetanib-naïve RET-Mutant MTC
Efficacy was evaluated in 88 patients with RET-mutant MTC who were cabozantinib and vandetanib treatment-naïve enrolled into a cohort of LIBRETTO-001.
The median age was 58 years (range: 15 to 82) with two patients (2.3%) aged 12 to 16 years; 66% were male; and 86% were White, 4.5% were Asian, and 2.3% were Hispanic/Latino. ECOG performance status was 0-1 (97%) or 2 (3.4%). All patients (100%) had metastatic disease and 18% had received 1 or 2 prior systemic therapies (including 8% kinase inhibitors, 4.5% chemotherapy, 2.3% anti-PD1/PD-L1 therapy, and 1.1% radioactive iodine). RET mutation status was detected in 78.4% of patients using NGS (76.1 % tumor samples; 2.3% blood samples), 18.2% using PCR, and 3.4% using an unknown test. The mutations used to identify and enroll patients are described in Table 10.
Efficacy results for cabozantinib and vandetanib-naïve RET-mutant MTC are summarized in Table 12.
Table 12 Efficacy Results in LIBRETTO-001 (Cabozantinib and Vandetanib-naïve RET-Mutant MTC) 1 Confirmed overall response rate assessed by BICR.
2 Based on observed duration of response
NE = not estimable
RETEVMO
(n = 88)Overall Response Rate1 (95% CI) 73% (62%, 82%) Complete response 11% Partial response 61% Duration of Response Median in months (95% CI) 22.0 (NE, NE) % with > 6 months2 61 14.3 RET Fusion-Positive Thyroid Cancer
The efficacy of RETEVMO was evaluated in patients with advanced RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer enrolled in a multicenter, open-label, multi-cohort clinical trial (LIBRETTO-001, NCT03157128). Efficacy was evaluated in 27 patients with RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer who were radioactive iodine (RAI)-refractory (if RAI was an appropriate treatment option) and were systemic therapy naïve and patients with RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer who were RAI-refractory and had received sorafenib, lenvatinib, or both, in separate cohorts.
The median age was 54 years (range 20 to 88); 52% were male; 74% were White, 11% were Hispanic/Latino, 7.4% were Asian, and 3.7% were Black. ECOG performance status was 0-1 (89%) or 2 (11%). All (100%) patients had metastatic disease with primary tumor histologies including papillary thyroid cancer (78%), poorly differentiated thyroid cancer (11%), anaplastic thyroid cancer (7%) and Hurthle cell thyroid cancer (4%). Patients had received a median of 3 prior therapies (range 1–7). RET fusion-positive status was detected in 93% of patients using NGS tumor samples and in 7% using blood samples.
Efficacy results for RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer are summarized in Table 13.
Table 13 Efficacy Results in LIBRETTO-001 (RET Fusion-Positive Thyroid Cancer) 1Confirmed overall response rate assessed by BICR.
2 Based on observed duration of response
NE = not estimable
RETEVMO
Previously Treated
(n = 19)RETEVMO
Systemic Therapy Naïve
(n = 8)Overall Response Rate1 (95% CI) 79% (54%, 94%) 100% (63%, 100%) Complete response 5.3% 12.5% Partial response 74% 88% Duration of Response Median in months (95% CI) 18.4 (7.6, NE) NE (NE, NE) % with > 6 months2 87 75 -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
RETEVMO (selpercatinib) capsules are supplied as follows:
40 mg: Gray opaque, imprinted with “Lilly”, “3977” and “40 mg” in black ink - 60 count bottle
NDC# 0002-3977-60 80 mg: Blue opaque, imprinted with “Lilly”, “2980” and “80 mg” in black ink - 60 count bottle
NDC# 0002-2980-60 - 120 count bottle
NDC# 0002-2980-26 Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F) are permitted [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hepatotoxicity
Advise patients that hepatotoxicity can occur and to immediately contact their healthcare provider for signs or symptoms of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hypertension
Advise patients that they will require regular blood pressure monitoring and to contact their healthcare provider if they experience symptoms of increased blood pressure or elevated readings [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
QT Prolongation
Advise patients that RETEVMO can cause QTc interval prolongation and to inform their healthcare provider if they have any QTc interval prolongation symptoms, such as syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hemorrhagic Events
Advise patients that RETEVMO may increase the risk for bleeding and to contact their healthcare provider if they experience any signs or symptoms of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients to monitor for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions, particularly during the first month of treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Risk of Impaired Wound Healing
Advise patients that RETEVMO may impair wound healing. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of any planned surgical procedure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the possible risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during the treatment with RETEVMO and for at least 1 week after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with RETEVMO and for at least 1 week after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with RETEVMO and for 1 week following the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise males and females of reproductive potential that RETEVMO may impair fertility [See Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients and caregivers to inform their healthcare provider of all concomitant medications, including prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products. Inform patients to avoid St. John's wort, proton pump inhibitors, H2 receptor antagonists, and antacids while taking RETEVMO.
If PPIs are required, instruct patients to take RETEVMO with food. If H2 receptor antagonists are required, instruct patients to take RETEVMO 2 hours before or 10 hours after the H2 receptor antagonist. If locally-acting antacids are required, instruct patients to take RETEVMO 2 hours before or 2 hours after the locally-acting antacid [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
Marketed by: Lilly USA, LLC, Indianapolis, IN 46285, USA
Copyright © 2020, Eli Lilly and Company. All rights reserved.
RET-0001-USPI-202005 -
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 05/2020
PATIENT INFORMATION
RETEVMOTM (reh-TEHV-moh)
(selpercatinib)
capsules
What is RETEVMO?
RETEVMO is a prescription medicine that is used to treat certain cancers caused by abnormal RET genes in:
- adults with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has spread.
- adults and children 12 years of age and older with advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) or MTC that has spread who require a medicine by mouth or injection (systemic therapy).
- adults and children 12 years of age and older with advanced thyroid cancer or thyroid cancer that has spread who require a medicine by mouth or injection (systemic therapy) and who have received radioactive iodine and it did not work or is no longer working.
Your healthcare provider will perform a test to make sure that RETEVMO is right for you.
It is not known if RETEVMO is safe and effective in children younger than 12 years of age.Before taking RETEVMO, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver problems
- have high blood pressure
- have heart problems including a condition called QT prolongation
- have bleeding problems
- plan to have surgery. You should stop taking RETEVMO at least 7 days before your planned surgery. See “What are the possible side effects of RETEVMO?”.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. RETEVMO can harm your unborn baby. You should not become pregnant during treatment with RETEVMO.
- If you are able to become pregnant, your healthcare provider will do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with RETEVMO.
- Females who are able to become pregnant should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for at least 1 week after the final dose of RETEVMO. Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods that may be right for you.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you might be pregnant during treatment with RETEVMO.
- Males with female partners who are able to become pregnant should use effective birth control during treatment with RETEVMO and for at least 1 week after the final dose of RETEVMO.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if RETEVMO passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with RETEVMO and for 1 week after the last dose.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Certain other medicines may affect how RETEVMO works.
You should avoid taking St. John's wort, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs such as dexlansoprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole sodium, rabeprazole), H2 blockers (such as famotidine, nizatidine, and cimetidine), and antacids that contain aluminum, magnesium, calcium, simethicone, or buffered medicines during treatment with RETEVMO. If you cannot avoid taking PPIs, H2 blockers, or antacids, see “How should I take RETEVMO?” for more information on how to take RETEVMO with these medicines. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.- Take RETEVMO exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Your healthcare provider may stop treatment or change your dose of RETEVMO if you have side effects. Do not change your dose or stop taking RETEVMO unless your healthcare provider tells you.
- RETEVMO is taken by mouth, usually 2 times a day with or without food.
- If you take a proton-pump inhibitor (PPIs such as dexlansoprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole sodium, and rabeprazole), take RETEVMO with food.
- RETEVMO doses should be separated by 12 hours.
- If you take an antacid that contains aluminum, magnesium, calcium, simethicone, or buffered medicines, take RETEVMO 2 hours before or 2 hours after taking the antacid.
- If you take an H2 blocker (such as famotidine, nizatidine, and cimetidine), take RETEVMO 2 hours before or 10 hours after taking the H2 blocker.
- Swallow RETEVMO capsules whole. Do not chew or crush the capsules.
- If you vomit after taking a dose of RETEVMO, do not take an extra dose. Take the next dose of RETEVMO at your scheduled time.
- Do not take a missed dose of RETEVMO unless it is more than 6 hours until your next scheduled dose.
- If you take too much RETEVMO, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of RETEVMO?
RETEVMO may cause serious side effects, including:
-
Liver problems. Liver problems (increased liver enzymes) are common with RETEVMO and may sometimes be serious. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests before and during treatment with RETEVMO to check for liver problems. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms of liver problems during treatment:
- yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eyes (jaundice)
- dark “tea-colored” urine
- sleepiness
- bleeding or bruising
- loss of appetite
- nausea or vomiting
- pain on the upper right side of your stomach area
Your healthcare provider may temporarily stop treatment, lower your dose, or permanently stop RETEVMO if you develop liver problems with RETEVMO
-
High blood pressure (hypertension). High blood pressure is common with RETEVMO and may sometimes be serious. You should check your blood pressure regularly during treatment with RETEVMO. Tell your healthcare provider if you get any of the following symptoms:
- confusion
- headaches
- shortness of breath
- dizziness
- chest pain
- Heart rhythm changes (QT prolongation) can occur and may be serious. RETEVMO may cause very slow, very fast or irregular heartbeats. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
- loss of consciousness
- fainting
- dizziness
- a change in the way your heart beats (heart palpitations)
-
Bleeding problems. RETEVMO can cause bleeding which can be serious and may lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any signs of bleeding during treatment with RETEVMO, including:
- vomiting blood or if your vomit looks like coffee-grounds
- pink or brown urine
- red or black (looks like tar) stools
- coughing up blood or blood clots
- unusual bleeding or bruising of your skin
- menstrual bleeding that is heavier than normal
- unusual vaginal bleeding
- nose bleeds that happen often
- drowsiness or difficulty being awakened
- confusion
- headache
- change in speech
- Allergic reactions. RETEVMO can cause a fever, rash, muscle or joint pain, especially in the first month of treatment. Tell your healthcare provider if you get any of these symptoms. Your healthcare provider may temporarily stop treatment or lower your dose of RETEVMO.
-
Risk of wound healing problems. Wounds may not heal properly during treatment with RETEVMO. Tell your healthcare provider if you plan to have any surgery before or during treatment with RETEVMO.
- You should stop taking RETEVMO at least 7 days before planned surgery.
- Your healthcare provider should tell you when you may start taking RETEVMO again after surgery.
The most common side effects of RETEVMO include: - increased levels of liver enzymes
- increased blood sugar levels
- decrease in white blood cell count
- decreased protein levels (albumin) in the blood
- decreased levels of calcium in the blood
- dry mouth
- diarrhea
- increased creatinine (kidney function test)
- high blood pressure
- tiredness
- swelling of your arms, legs, hands, and feet (peripheral edema)
- decrease in platelet count
- increased cholesterol levels
- rash
- decreased levels of salt (sodium) in the blood
- constipation
RETEVMO may affect fertility in females and males, which may affect your ability to have children. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you.
These are not all the possible side effects with RETEVMO.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store RETEVMO?
- Store RETEVMO capsules at room temperature between 68˚F to 77˚F (20˚C to 25˚C).
Keep RETEVMO and all medicines out of the reach of children. General information about the safe and effective use of RETEVMO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use RETEVMO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give RETEVMO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for more information about RETEVMO that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in RETEVMO?
Active ingredient: selpercatinib
Inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide
Capsule: gelatin, titanium dioxide and edible ink
Marketed by: Lilly USA, LLC, Indianapolis, IN 46285, USA
RET-0001-PPI-202005
For more information, go to www.RETEVMO.com or call 1-800-545-5979 - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
RETEVMO
selpercatinib capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0002-3977 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength selpercatinib (UNII: CEGM9YBNGD) (selpercatinib - UNII:CEGM9YBNGD) selpercatinib 40 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength microcrystalline cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) silicon dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) gelatin, unspecified (UNII: 2G86QN327L) titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) ferrosoferric oxide (UNII: XM0M87F357) shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) alcohol (UNII: 3K9958V90M) isopropyl alcohol (UNII: ND2M416302) butyl alcohol (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) ammonia (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) potassium hydroxide (UNII: WZH3C48M4T) Product Characteristics Color GRAY (Gray Opaque) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code Lilly;3977;40mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0002-3977-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/08/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA213246 05/08/2020 RETEVMO
selpercatinib capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0002-2980 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength selpercatinib (UNII: CEGM9YBNGD) (selpercatinib - UNII:CEGM9YBNGD) selpercatinib 80 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength microcrystalline cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) silicon dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) gelatin, unspecified (UNII: 2G86QN327L) titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FD&C Blue No. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) alcohol (UNII: 3K9958V90M) isopropyl alcohol (UNII: ND2M416302) butyl alcohol (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) ammonia (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) potassium hydroxide (UNII: WZH3C48M4T) ferrosoferric oxide (UNII: XM0M87F357) Product Characteristics Color BLUE (Blue Opaque) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 22mm Flavor Imprint Code Lilly;2980;80mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0002-2980-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/08/2020 2 NDC: 0002-2980-26 120 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/08/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA213246 05/08/2020 Labeler - Eli Lilly and Company (006421325) Registrant - Loxo Oncology, Inc. (042572897)
Trademark Results [RETEVMO]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 RETEVMO 88332283 not registered Live/Pending |
Eli Lilly and Company 2019-03-08 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.