VILAMIT MB- methenamine, phenyl salicylate, sodium phosphate, monobasic, anhydrous, methylene blue anhydrous, and hyoscyamine sulfate capsule
Vilamit MB by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Vilamit MB by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Vilvet Pharmaceuticals Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Each Capsule Contains:
Methenamine 118 mg Sodium Phosphate Monobasic 40.8 mg Phenyl Salicylate 36 mg Methylene Blue 10 mg Hyoscyamine Sulfate 0.12 mg Inactive Ingredients: Dicalcium Phosphate, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Sodium Starch Gylcolate, Magnesium Stearate, Carbopol, FD&C Blue #1, Titanium Dioxide, FD&C Yellow 5. FD&C Red 3, Amaranth, and Purified Water.
METHENAMINE. [100-97-0] 1, 3, 5, 7 – Tetraazatricyclo [3.3.1.-13,7] decane; hexamethylenetetramine; HMT; HMTA; hexamine; 1, 3, 5, 7- tetraazaadamantane hexamethylenemine; Uritone; Urotropin. C6H12N4; mol wt 140.19; C 51.40%, H 8.63%, N 39.96%. Methenamine (hexamethylenetetramine) exists as colorless, lustrous crystals or white crystalline powder. Its solutions are alkaline to litmus. Freely soluble in water, soluble in alcohol and in chloroform.
SODIUM PHOSPHATE MONOBASIC. [7558-80-7] Phosphoric acid sodium salt (1:1); Sodium biphosphate; sodium dihydrogen phosphate; acid sodium phosphate; monosodium orthophosphate; primary sodium phosphate; H2NaO4P; mol wt 119.98, H 1.68%, Na 19.16%, O 53.34%, P 25.82 %. Monohydrate, white, odorless slightly deliquesce crystals or granules. At 100 °C loses all its water; when ignited it converts to metaphosphate. It is freely soluble in water and practically insoluble in alcohol. The aqueous solution is acid. pH of 0.1 molar aqueous solution at 25 °C: 4.5.
PHENYL SALICYLATE. [118-55-8] 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid phenyl ester; Salol. C13H10O3; mol wt 214.22, C 72.89%, H 4.71%, O 22.41%. Made by the action of phosphorous oxy-chloride on a mixture of phenol and salicylic acid. Phenyl Salicylate exists as white crystals with a melting point of 41° - 43°C. It is very slightly soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol.
METHYLENE BLUE. [61-73-4] 3,7-BIS(dimethylamino) phenothiazine-5-ium chloride; C.I. Basic Blue 9; methylthioninium chloride tetramethylthionine chloride; 3,7-bis(dimethylamino) phenazathionium chloride. C16H18ClN3S; mol wt 319.85, C 60.08%, H 5.67%, Cl 11.08%, N 13.14%, S 10.03%. Methylene Blue (Methylthionine chloride) exists as dark green crystals. It is soluble in water and in chloroform; sparingly soluble in alcohol.
HYOSCYAMINE SULFATE. [620-31-1] [3(S)-endo]-α-(Hydroxymethyl)-benzeneacetic acid 8-mehtyl-8-azabicyclo [3.2.1] oct-3-yl ester sulfate (2:1) (salt); 1αH, 5αH-tropan-3α-ol(-)-tropate (ester) sulfate (2:1) (salt); 3α-tropanyl S-(-)-tropate; I-tropic acid ester with tropine; I-tropine tropate. C34H48N2O10S. Hyoscyamine Sulfate is an alkaloid of belladonna. Exists as a white crystalline powder. Its solutions are alkaline to litmus. Affected by light, it is slightly soluble in water freely soluble in alcohol; sparingly soluble in ether.
-
VILAMIT MB - CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
METHENAMINE degrades in an acidic urine environment releasing formaldehyde which provide bactericidal or bacteriostatic action. It is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. 70% to 90% reaches the urine unchanged at which point it is hydrolyzed if the urine is acidic. Within 24 hours it is almost completely (90%) excreted; of this amount at pH 5, approximately 20% is formaldehyde. Protein binding – some formaldehyde is bound to substances in the urine and surrounding tissues. Methenamine is freely distributed to body tissue and fluids but is not clinically significant as it does not hydrolyze at pH greater than 6.8.
SODIUM PHOSPHATE MONOBASIC an acidifier, helps to maintain an acid pH in the urine necessary for the degradation of methenamine.
PHENYL SALICYLATE releases salicylate, a mild analgesic for pain.
METHYLENE BLUE possesses weak antiseptic properties. It is well absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract and is rapidly reduced to leukomethylene blue which is stabilized in some combination form in the urine. 75% is excreted unchanged.
HYOSCYAMINE SULFATE is a parasympatholytic drug which relaxes smooth muscles and this produces an antispasmodic effect. It is well absorbed form the gastrointestinal tract and is rapidly distributed throughout the body tissues. Most is excreted in the urine within 12 hours, 13% to 50% being unchanged. Protein binding for hyoscyamine sulfate is moderate and biotransformation is hepatic.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE FOR VILAMIT MB:
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
VILAMIT MB is contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients. Risk-benefit should be considered when the following medical problems exist: Cardiac disease (especially cardiac arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, coronary heart disease, and mitral stenosis); gastrointestinal tract obstructive disease; glaucoma; myasthenia gravis; acute urinary retention may be precipitated in obstructive uropathy (such as bladder neck obstruction due to prostatic hypertrophy).
- WARNINGS
-
PRECAUTIONS
Contains Methylene Blue and should NOT be taken with serotonergic psychiatric medications.
Cross sensitivity and/or related problems
Patients intolerant of other belladonna alkaloids may be intolerant of this medication also. Delay in gastric emptying could complicate the management of gastric ulcers.
Pregnancy/Reproduction (FDA Pregnancy Category C)
Hyoscyamine and methenamine cross the placenta. Studies have not been done in either animals or humans. It is not known whether VILAMIT MB can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. VILAMIT MB should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Methenamine and traces of Hyoscyamine are excreted in breast milk. Caution should be exercised when VILAMIT MB is administered to a nursing mother.
Prolonged Use
There have been no studies to establish the safety of prolonged use in humans. No known long-term animal studies have been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential.
Pediatric
Infants and young children are especially susceptible to the toxic effect of the belladonna alkaloids.
Geriatric
Use with caution in elderly patients as they may respond to the usual doses of the belladonna alkaloids with excitement, agitation, drowsiness, or confusion.
Drug Interactions
Although the exact mechanism of this drug interaction is unknown, methylene blue inhibits the action of monoamine oxidase A – an enzyme responsible for breaking down serotonin in the brain. It is believed that when methylene blue is given to patients taking serotonergic psychiatric medications, high levels of serotonin can build up in the brain, causing toxicity. This is referred to as Serotonin Syndrome. Signs and symptoms of Serotonin Syndrome include mental changes (confusion, hyperactivity, memory problems), muscle twitching, excessive sweating, shivering or shaking, diarrhea, and trouble with coordination and/or fever.
Additional Information for Healthcare Professionals
Methylene blue can interact with serotonergic psychiatric medications and cause serious CNS toxicity.
In emergency situations requiring life-threatening or urgent treatment with methylene blue (as described above), the availability of alternative interventions should be considered and the benefit of methylene blue treatment should be weighed against the risk of serotonin toxicity. If methylene blue must be administered to a patient receiving a serotonergic drug, the serotonergic drug must be immediately stopped, and the patient should be closely monitored for emergent symptoms of CNS toxicity for two weeks (five weeks if fluoxetine [Prozac] was taken), or until 24 hours after the last dose of methylene blue, whichever comes first.
In non-emergency situations when non-urgent treatment with methylene blue is contemplated and planned, the serotonergic psychiatric medication should be stopped to allow its activity in the brain to dissipate. Most serotonergic psychiatric drugs should be stopped at least 2 weeks in advance of methylene blue treatment. Fluoxetine (Prozac), which has a longer half-life compared to similar drugs, should be stopped at least 5 weeks in advance.
Treatment with the serotonergic psychiatric medication may be resumed 24 hours after the last dose of methylene blue.
Serotonergic psychiatric medications should not be started in a patient receiving methylene blue. Wait until 24 hours after the last dose of methylene blue before starting the antidepressant.
Educate your patients to recognize the symptoms of serotonin toxicity or CNS toxicity and advise them to contact a healthcare professional immediately if they experience any symptoms while taking serotonergic psychiatric medications or methylene blue.
As a result of hyoscyamine's effect on gastrointestinal motility and gastric emptying, absorption of other oral medications may be decreased during concurrent use with this combination medications.
Urinary alkalizers and thiazide diuretics
May cause the urine to become alkaline reducing the effectiveness of methenamine by inhibiting its conversion to formaldehyde.
Antimuscarinics
Concurrent use may intensify antimuscarinic effects of Hyoscyamine because of secondary antimuscarinic activities of these medications.
Antacids/antidiarrheals
Concurrent use may reduce absorption of Hyoscyamine resulting in decreased therapeutic effectiveness. Concurrent use with antacids may cause urine to become alkaline reducing the effectiveness of methenamine by inhibiting its conversion to formaldehyde. Doses of these medications should be spaced for 1 hour apart from doses of Hyoscyamine.
Antimyasthenics
Concurrent use with Hyoscyamine may further reduce intestinal motility, therefore, caution is recommended.
Ketoconazole and Hyoscyamine may cause increased gastrointestinal pH. Concurrent administration with Hyoscyamine may result in marked reduction in the absorption of ketoconazole. Patients should be advised to take this combination at least 2 hours after ketoconazole.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Cardiovascular – rapid pulse, flushing
Central Nervous System – blurred vision, dizziness, drowsiness
Respiratory – shortness of breath or troubled breathing
Genitourinary – difficult micturition, acute urinary retention
Gastrointestinal – dry mouth, nausea and vomiting
Serious allergic reactions to this drug are rare. Seek immediate medical attention if you notice symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including itching, rash, severe dizziness, swelling or trouble breathing.
This medication can cause urine and sometimes stools to turn blue to blue-green. This effect is harmless and will subside after medication is stopped.
Call your doctor or physician for medical advice about side effects. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Vilvet Pharmaceuticals Inc., at 1-888-705-4369 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088, www.fda.gov/medwatch.
- Drug Abuse and Dependence
-
OVERDOSAGE
Emesis or gastric lavage. Slow intravenous administration of physostigmine in doses of 1 to 4 mg (0.5 to 1 mg in children) repeated as needed in one to two hours to reverse severe antimuscarinic symptoms.
Administration of small doses of diazepam to control excitement and seizures. Artificial respiration with oxygen if needed for respiratory depression. Adequate hydration. Symptomatic treatment as necessary.
If overdose is suspected, contact the poison control center at 1-800-222-1222, or your local emergency room immediately.
- VILAMIT MB DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
-
STORAGE
Store in a cool, dry place at controlled room temperature 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). Keep container tightly closed. Protect from moisture and direct sunlight.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
IN CASE OF ACCIDENTAL OVERDOSE, SEEK PROFESSIONAL ASSISTANCE OR CONTACT A POISON CONTROL CENTER IMMEDIATELY.
Note: Patients should be advised that urine will be colored blue when taking this medication.
-
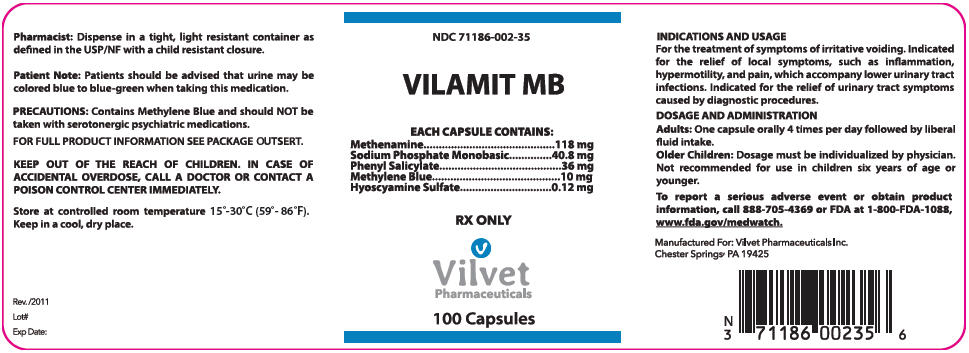
HOW IS VILAMIT MB SUPPLIED
VILAMIT MB capsules are purple opaque, oblong, imprinted with "VIP101" and plain on the other side, available in bottles of 100 capsules, NDC: 71186-002-35.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP/NF with a child resistant closure.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 Capsule Bottle Label
NDC: 71186-002-35
VILAMIT MB
EACH CAPSULE CONTAINS:
Methenamine
118 mg
Sodium Phosphate Monobasic
40.8 mg
Phenyl Salicylate
36 mg
Methylene Blue
10 mg
Hyoscyamine Sulfate
0.12 mgRX ONLY
Vilvet
Pharmaceuticals100 Capsules
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VILAMIT MB
methenamine, phenyl salicylate, sodium phosphate, monobasic, anhydrous, methylene blue anhydrous, and hyoscyamine sulfate capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 71186-002 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHENAMINE (UNII: J50OIX95QV) (METHENAMINE - UNII:J50OIX95QV) METHENAMINE 118 mg PHENYL SALICYLATE (UNII: 28A37T47QO) (PHENYL SALICYLATE - UNII:28A37T47QO) PHENYL SALICYLATE 36 mg SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC, ANHYDROUS (UNII: KH7I04HPUU) (PHOSPHATE ION - UNII:NK08V8K8HR) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC, ANHYDROUS 40.8 mg METHYLENE BLUE ANHYDROUS (UNII: 8NAP7826UB) (METHYLENE BLUE CATION - UNII:ZMZ79891ZH) METHYLENE BLUE 10 mg HYOSCYAMINE SULFATE (UNII: F2R8V82B84) (HYOSCYAMINE - UNII:PX44XO846X) HYOSCYAMINE SULFATE 0.12 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FD&C YELLOW NO. 5 (UNII: I753WB2F1M) FD&C RED NO. 3 (UNII: PN2ZH5LOQY) Amaranth (UNII: 37RBV3X49K) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color PURPLE Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code VIP101 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 71186-002-35 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/01/2011 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date UNAPPROVED DRUG OTHER 05/01/2011 Labeler - Vilvet Pharmaceuticals Inc (080444356)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.