ADHANSIA XR- methylphenidate hydrochloride capsule, extended release
ADHANSIA XR by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
ADHANSIA XR by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Adlon Therapeutics L.P., Glatt Air Techniques, Purdue Pharmaceuticals L.P., Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Noramco, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ADHANSIA XRTM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ADHANSIA XR.
ADHANSIA XR (methylphenidate hydrochloride) extended-release capsules, for oral use, CII
Initial U.S. Approval: 1955WARNING: ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ADHANSIA XR is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in patients 6 years and older. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended starting dose for patients 6 years and older: 25 mg once daily in the morning. (2.2)
- Dosage may be increased in increments of 10 to 15 mg at intervals of at least 5 days. (2.2)
- Dosages above 85 mg daily in adults and 70 mg and above daily in pediatric patients are associated with disproportionate increases in the incidence of certain adverse reactions. (2.2)
- Administer with or without food. (2.2)
- Capsules may be swallowed whole or opened and the entire contents sprinkled onto a tablespoon of applesauce or yogurt. If sprinkled, take the contents without crushing or chewing. (2.2)
- To avoid substitution errors and overdosage, do not substitute for other methylphenidate products on a milligram-per-milligram basis. (2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Extended-release Capsules: 25 mg, 35 mg, 45 mg, 55 mg, 70 mg and 85 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serious Cardiovascular Events: Sudden death has been reported in association with CNS stimulants at recommended doses in pediatric patients with structural cardiac abnormalities or other serious heart problems. In adults, sudden death, stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported. Avoid use in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart arrhythmias, or coronary artery disease. (5.2)
- Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases: Monitor blood pressure and pulse. Consider the benefits and risks in patients for whom an increase in blood pressure or heart rate would be problematic. (5.3)
- Psychiatric Adverse Reactions: Use of CNS stimulants may cause psychotic or manic symptoms in patients with no prior history, or exacerbation of symptoms in patients with pre-existing psychiatric illness. Evaluate for bipolar disorder prior to ADHANSIA XR use. (5.4)
- Priapism: Cases of painful and prolonged penile erections and priapism have been reported with methylphenidate products. Immediate medical attention should be sought if signs or symptoms of prolonged penile erections or priapism are observed. (5.5)
- Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Stimulants used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon. Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during treatment with ADHD stimulants. (5.6)
- Long-Term Suppression of Growth: Monitor height and weight at appropriate intervals in pediatric patients. (5.7)
- Allergic-Type Reactions: FD&C Yellow No. 5: ADHANSIA XR 45 mg capsules contain FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible persons. (5.8)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (≥5% and twice the rate of placebo) adverse reactions occurring with ADHANSIA XR in adults are insomnia, dry mouth, and decreased appetite.
The most common (≥5% and twice the rate of placebo) adverse reactions occurring with ADHANSIA XR in pediatric patients are decreased appetite, insomnia, and weight decreased. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Purdue Pharma L.P. at 1-888-726-7535 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Pretreatment Screening
2.2 General Dosing Information
2.3 Dose Reduction and Discontinuation
2.4 Switching from Other Methylphenidate Products
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potential for Abuse and Dependence
5.2 Serious Cardiovascular Events
5.3 Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases
5.4 Psychiatric Adverse Reactions
5.5 Priapism
5.6 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s Phenomenon
5.7 Long-Term Suppression of Growth
5.8 Allergic-Type Reactions: FD&C Yellow No. 5
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Clinically Important Drug Interactions
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
9.3 Dependence
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Signs and Symptoms
10.2 Management of Overdose
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
CNS stimulants, including ADHANSIA XR, other methylphenidate-containing products, and amphetamines, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing, and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
-
1 INDICATIONS
AND USAGE
ADHANSIA XRTM is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in patients 6 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Pretreatment Screening
Prior to initiating treatment with ADHANSIA XR, assess for the presence of cardiac disease (i.e., perform a careful history, family history of sudden death or ventricular arrhythmia, and physical exam) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy. Maintain careful prescription records, educate patients about abuse, and periodically re-evaluate the need for ADHANSIA XR use [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
2.2 General Dosing Information
Administer ADHANSIA XR orally once daily in the morning with or without food.
The recommended starting dose of ADHANSIA XR for patients 6 years or older is 25 mg once daily. Titrate the dose in increments of 10 to 15 mg at intervals of no less than 5 days. Dosages higher than 100 mg daily in adults and 85 mg daily in pediatric patients have not been evaluated in clinical trials and are not recommended. Although efficacy was demonstrated in short-term controlled trials in adults at dosages of 100 mg daily, dosages above 85 mg daily were associated with a disproportionate increase in the incidence of certain adverse reactions. In short-term controlled trials in pediatric patients, efficacy was demonstrated at dosages of 70 mg daily, but dosages 70 mg daily and higher were associated with a disproportionate increase in the incidence of certain adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14)]. Individualize dosage adjustments based upon assessment of clinical benefit and tolerability with careful consideration of the dose-related adverse reactions.
ADHANSIA XR may be taken whole or the capsule may be opened and the entire contents sprinkled onto a tablespoon of applesauce or yogurt. The entire mixture should be consumed immediately or within 10 minutes. If the mixture is not consumed within 10 minutes after mixing, it should be discarded and not stored. Patients should take the entire contents of the capsule sprinkled on the chosen food in its entirety, without chewing. The dose of a single capsule should not be divided. Patients should not take anything less than one capsule per day.
In the event of a missed dose, do not administer later in the day. Do not administer additional medication to make up for the missed dose [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14)].
Pharmacological treatment of ADHD may be needed for extended periods. Periodically re-evaluate the long-term use of ADHANSIA XR, and adjust dosage as needed.
2.3 Dose Reduction and Discontinuation
If paradoxical aggravation of symptoms or other adverse reactions occur, reduce the dosage, or, if necessary, discontinue the drug. ADHANSIA XR should be periodically discontinued to assess the patient's condition. If improvement is not observed after appropriate dosage adjustment over a one-month period, discontinue ADHANSIA XR.
2.4 Switching from Other Methylphenidate Products
If switching from other methylphenidate products, discontinue that treatment, and titrate with ADHANSIA XR using the titration schedule above.
Do not substitute ADHANSIA XR for other methylphenidate products on a milligram-per-milligram basis because of different methylphenidate base compositions and differing pharmacokinetic profiles [see Description (11) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
3 DOSAGE
FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
25 mg (methylphenidate hydrochloride) Extended-Release
Capsules – blue capsule
(imprinted with “MLR-02” on cap and “25 mg” on the body)
Contains 25 mg methylphenidate hydrochloride, equivalent to 21.6 mg of methylphenidate -
35 mg (methylphenidate hydrochloride) Extended-Release
Capsules – orange capsule
(imprinted with “MLR-02” on cap and “35 mg” on the body)
Contains 35 mg methylphenidate hydrochloride, equivalent to 30.3 mg of methylphenidate -
45 mg (methylphenidate hydrochloride) Extended-Release
Capsules – yellow capsule
(imprinted with “MLR-02” on cap and “45 mg” on the body)
Contains 45 mg methylphenidate hydrochloride, equivalent to 38.9 mg of methylphenidate -
55 mg (methylphenidate hydrochloride) Extended-Release
Capsules – light green capsule
(imprinted with “MLR-02” on cap and “55 mg” on the body)
Contains 55 mg methylphenidate hydrochloride, equivalent to 47.6 mg of methylphenidate -
70 mg (methylphenidate hydrochloride) Extended-Release
Capsules – iron gray capsule
(imprinted with “MLR-02” on cap and “70 mg” on the body)
Contains 70 mg methylphenidate hydrochloride, equivalent to 60.5 mg of methylphenidate -
85 mg (methylphenidate hydrochloride) Extended-Release
Capsules – white capsule
(imprinted with “MLR-02” on cap and “85 mg” on the body)
Contains 85 mg methylphenidate hydrochloride, equivalent to 73.5 mg of methylphenidate
-
25 mg (methylphenidate hydrochloride) Extended-Release
Capsules – blue capsule
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADHANSIA XR is contraindicated in patients:
- With a known hypersensitivity to methylphenidate or other components of ADHANSIA XR. Hypersensitivity reactions such as angioedema and anaphylactic reactions have been reported in patients treated with other methylphenidate products [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- Receiving concomitant treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), and also within 14 days following discontinuation of treatment with a MAOI, because of the risk of hypertensive crisis [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potential for Abuse and Dependence
CNS stimulants, including ADHANSIA XR, other methylphenidate-containing products, and amphetamines, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing, and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
5.2 Serious Cardiovascular Events
Sudden death, stroke and myocardial infarction have occurred in adults treated with CNS stimulant treatment at recommended doses. Sudden death has occurred in pediatric patients with structural cardiac abnormalities and other serious cardiac problems taking CNS stimulants at recommended doses for ADHD. Avoid use in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart arrhythmia, coronary artery disease, and other serious heart problems. Further evaluate patients who develop exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, or arrhythmias during ADHANSIA XR treatment.
5.3 Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases
CNS stimulants cause an increase in blood pressure (mean increase approximately 2 to 4 mmHg) and heart rate (mean increase approximately 3 to 6 bpm). Individuals may have larger increases. Monitor all patients for hypertension and tachycardia.
5.4 Psychiatric Adverse Reactions
Exacerbation of Pre-Existing Psychosis
CNS stimulants may exacerbate symptoms of behavior disturbance and thought disorder in patients with a pre-existing psychotic disorder.Induction of a Manic Episode in Patients with Bipolar Disorder
CNS stimulants may induce a manic or mixed episode in patients. Prior to initiating treatment, screen patients for risk factors for developing a manic episode (e.g., comorbid or history of depressive symptoms or a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, or depression).New Psychotic or Manic Symptoms
CNS stimulants, at recommended doses, may cause psychotic or manic symptoms (e.g., hallucinations, delusional thinking, or mania) in patients without a prior history of psychotic illness or mania. If such symptoms occur, consider discontinuing ADHANSIA XR. In a pooled analysis of multiple short-term, placebo-controlled studies of CNS stimulants, psychotic or manic symptoms occurred in approximately 0.1% of CNS stimulant-treated patients, compared to 0% in placebo-treated patients.5.5 Priapism
Prolonged and painful erections, sometimes requiring surgical intervention, have been reported with methylphenidate products, in both pediatric and adult patients. Priapism was not reported with drug initiation but developed after some time on the drug, often subsequent to an increase in dose. Priapism has also appeared during a period of drug withdrawal (drug holidays or during discontinuation). Patients who develop abnormally sustained or frequent and painful erections should seek immediate medical attention.
5.6 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s Phenomenon
CNS stimulants, including ADHANSIA XR, used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon. Signs and symptoms are usually intermittent and mild; however, very rare sequelae include digital ulceration and/or soft tissue breakdown. Effects of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon, were observed in post-marketing reports at different times and at therapeutic doses in all age groups throughout the course of treatment. Signs and symptoms generally improve after reduction in dose or discontinuation of drug. Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during treatment with ADHD stimulants. Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for certain patients.
5.7 Long-Term Suppression of Growth
CNS stimulants have been associated with weight loss and slowing of growth rate in pediatric patients.
Careful follow-up of weight and height in pediatric patients ages 7 to 10 years who were randomized to either methylphenidate or non-medication treatment groups over 14 months, as well as in naturalistic subgroups of newly methylphenidate-treated and non-medication treated pediatric patients over 36 months (to the ages of 10 to 13 years), suggests that consistently medicated pediatric patients (i.e., treatment for 7 days per week throughout the year) have a temporary slowing in growth rate (on average, a total of about 2 cm less growth in height and 2.7 kg less growth in weight over 3 years), without evidence of growth rebound during this period of development.
Closely monitor growth (weight and height) in pediatric patients treated with CNS stimulants, including ADHANSIA XR. Patients who are not growing or gaining height or weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted.
5.8 Allergic-Type Reactions: FD&C Yellow No. 5
ADHANSIA XR 45 mg capsules contain FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible persons. Although the overall incidence of FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) sensitivity in the general population is low, it is frequently seen in patients who also have aspirin hypersensitivity [see Contraindications (4)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Known hypersensitivity to methylphenidate or other ingredients of ADHANSIA XR [see Contraindications (4)]
- Hypertensive crisis when used concomitantly with monoamine oxidase inhibitors [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
- Drug dependence [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)]
- Serious cardiovascular reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Blood pressure and heart rate increases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Psychiatric adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Long-term suppression of growth [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Allergic Reactions FD&C Yellow No.5 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Clinical Trials Experience with Other Methylphenidate Products in Children, Adolescents, and Adults with ADHD
Commonly reported (≥2% of the methylphenidate group and twice the rate of the placebo group) adverse reactions from placebo-controlled trials of methylphenidate products include: appetite decreased, weight decreased, nausea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, dry mouth, vomiting, insomnia, anxiety, nervousness, restlessness, affect lability, agitation, irritability, dizziness, vertigo, tremor, blurred vision, blood pressure increased, heart rate increased, tachycardia, palpitations, hyperhidrosis, and pyrexia.Clinical Trials Experience with ADHANSIA XR
ADHANSIA XR was studied in adults (18 to 72 years) and pediatric patients (6 to 17 years) who met Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (DSM-5) criteria for ADHD.The safety data for adults is based on two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in doses of 25 mg to 100 mg per day. The safety data for pediatric patients (6 to 17 years) is based on randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in doses of 25 mg to 85 mg per day.
The total number of patients exposed to ADHANSIA XR during 1 to 4-week long, controlled treatment periods is 883; this included 434 adult patients and 449 pediatric patients [156 (6 to 12 years); 293 (12 to 17 years)], from two clinical trials in adults, one in pediatric patients ages 12 to 17 years, and one in pediatric patients ages 6 to 12 years [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation of Treatment
In controlled adult trials for Study 1, 3% of both of ADHANSIA XR-treated patients and placebo-treated patients discontinued due to adverse reactions. In an adult workplace environment study (Study 2), 10% of ADHANSIA XR-treated patients discontinued due to adverse reactions compared to 0% of placebo-treated patients. The following adverse reactions led to discontinuation at a frequency of 2% of ADHANSIA XR-treated patients: nausea, bronchitis, gastroenteritis viral, viral infection, blood pressure increased, and hypomania.In a controlled trial (Study 3) in pediatric patients (12 to 17 years), 3% of ADHANSIA XR-treated patients discontinued due to adverse reactions compared to 0% of placebo-treated patients. The most frequent adverse reactions leading to discontinuation in at least 1% of ADHANSIA XR-treated patients and at a rate greater that placebo was irritability (1%). Two patients taking ADHANSIA XR 70 or 85 mg had delirium leading to discontinuation.
In a controlled trial (Study 4) in pediatric patients (6 to 12 years), 1% of ADHANSIA XR-treated patients discontinued due to adverse reactions compared to 0% of placebo-treated patients.
Adult Patients with ADHD
The most common adverse reactions (incidence of ≥5% and at least twice placebo) of ADHANSIA XR occurring in controlled trials in adults were insomnia, dry mouth, and decreased appetite.Table 1 lists the adverse reactions that occurred ≥2% of adult patients and greater than placebo among ADHANSIA XR-treated adult patients.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 2% of Adult Patients with ADHD on ADHANSIA XR and Greater than Patients Taking Placebo in a 4-week Clinical Trial Adverse Reaction ADHANSIA XR All doses
ADHANSIA XRPlacebo 25 mg 45 mg 70 mg 100 mg N=375 (N=77) (N=73) (N=73) (N=74) (N=297) (N=78) Initial Insomnia 4% 8% 6% 7% 6% 1% Insomnia 17% 11% 16% 19% 16% 4% Dry mouth 8% 8% 7% 14% 9% 4% Nausea 4% 6% 4% 11% 6% 3% Diarrhea 1% 3% 7% 5% 4% 1% Decreased appetite 4% 7% 15% 19% 11% 3% Feeling jittery 1% 3% 8% 4% 4% 1% Weight decreased 3% 4% 3% 5% 4% 1% Upper respiratory tract infection 0% 4% 3% 3% 2% 1% Pediatric Patients (12 to 17 years) with ADHD
The most common (incidence ≥5% and at least twice placebo) adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients (12 to 17 years) were decreased appetite, insomnia, and weight decreased.Table 2 lists the adverse reactions that occurred ≥2% of pediatric patients (12 to 17 years) and greater than placebo among ADHANSIA XR-treated pediatric patients (12 to 17 years).
Table 2: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 2% of Pediatric Patients (12 to 17 years) with ADHD Taking ADHANSIA XR and Greater than Placebo in a 4-week Clinical Trial Adverse Reaction ADHANSIA XR All doses
ADHANSIA XRPlacebo 25 mg 45 mg 70 mg 85 mg (N=73) (N=72) (N=76) (N=72) (N=293) (N=74) Decreased appetite 7% 19% 28% 26% 20% 0% Insomnia 4% 0% 9% 13% 6% 1% Initial Insomnia 4% 7% 5% 4% 5% 1% Weight decreased 1% 3% 8% 13% 7% 0% Abdominal pain upper 5% 1% 5% 4% 4% 1% Nausea 3% 6% 7% 8% 6% 4% Dizziness 3% 0% 4% 4% 3% 0% Dry mouth 1% 0% 5% 4% 3% 1% Vomiting 1% 1% 3% 6% 3% 0% Pediatric Patients (6 to 12 years) with ADHD
Study 4, conducted in pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age, was comprised of a 6-week open-label dose-optimization phase in which all patients received ADHANSIA XR (n=156; mean dose 48 mg), followed by a 1-week, double-blind controlled phase in which patients were randomized to continue ADHANSIA XR (n=75) or switch to placebo (n=73). During the open-label ADHANSIA XR treatment phase, adverse reactions reported in > 5% of patients included: decreased appetite (35%), upper abdominal pain (15%), affect lability (13%), nausea or vomiting (13%), weight decreased (12%), insomnia (10%), irritability (10%), headache (10%), and heart rate increased (5%). Because of the trial design (6-week open-label active treatment phase followed by a 1-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled withdrawal), the adverse reaction rates described in the double-blind phase are lower than expected in clinical practice. No difference occurred in the incidence of adverse reactions between ADHANSIA XR and placebo during the 1-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment phase.6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of methylphenidate products. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These adverse reactions are as follows:
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura
Cardiac Disorders: angina pectoris, bradycardia, extrasystole, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular extrasystole
Eye Disorders: diplopia, mydriasis, visual impairment
General Disorders: chest pain, chest discomfort, hyperpyrexia
Hepatobiliary disorders: hepatocellular injury, acute hepatic failure
Immune System Disorders: hypersensitivity reactions such as angioedema, anaphylactic reactions, auricular swelling, bullous conditions, exfoliative conditions, urticarias, pruritus, rashes, eruptions, and exanthemas
Investigations: alkaline phosphatase increased, bilirubin increased, hepatic enzyme increased, platelet count decreased, white blood cell count abnormal
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue and Bone Disorders: arthralgia, myalgia, muscle twitching, rhabdomyolysis
Nervous System Disorders: convulsion, grand mal convulsion, dyskinesia, serotonin syndrome in combination with serotonergic drugs
Psychiatric Disorders: disorientation, hallucination, hallucination auditory, hallucination visual, libido changes, logorrhea, mania
-
7 DRUG
INTERACTIONS
7.1 Clinically Important Drug Interactions
Table 3 presents clinically important drug interactions with ADHANSIA XR.
Table 3: Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions with ADHANSIA XR Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI) Clinical Impact: Concomitant use of MAOIs and CNS stimulants can cause hypertensive crisis. Potential outcomes include death, stroke, myocardial infarction, aortic dissection, ophthalmological complications, eclampsia, pulmonary edema, and renal failure [see Contraindications (4)]. Intervention: Do not administer ADHANSIA XR concomitantly with MAOIs or within 14 days after discontinuing MAOI treatment. Examples: selegiline, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, phenelzine, linezolid, methylene blue Gastric pH Modulators Clinical Impact: May change the release, PK profiles and alter the pharmacodynamics of ADHANSIA XR. Intervention: Monitor patients for changes in clinical effect and use alternative therapy based on clinical response. Examples: Omeprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole, famotidine, sodium bicarbonate -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to ADHANSIA XR during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the National Pregnancy Registry for Psychostimulants at 1-866-961-2388.Risk Summary
Published studies and post-marketing reports on methylphenidate use during pregnancy are insufficient to identify a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are risks to the fetus associated with the use of central nervous system (CNS) stimulants during pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations). No effects on morphological development were observed in embryo-fetal studies with oral administration of methylphenidate to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses up to 7 and 11 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 85 mg/day given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis. However, fetal spina bifida was observed in rabbits at a dose 36 times the MRHD given to adolescents. A decrease in pup body weight was observed in a pre- and post-natal development study with oral administration of methylphenidate to rats throughout pregnancy and lactation at doses 4 times the MRHD given to adolescents [see Data].The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
CNS stimulants, such as ADHANSIA XR, can cause vasoconstriction and thereby decrease placental perfusion. No fetal and/or neonatal adverse reactions have been reported with the use of therapeutic doses of methylphenidate during pregnancy; however, premature delivery and low birth weight infants have been reported in amphetamine-dependent mothers.Data
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies conducted in rats and rabbits, methylphenidate was administered orally at doses of up to 75 and 200 mg/kg/day, respectively, during the period of organogenesis. Malformations (increased incidence of fetal spina bifida) were observed in rabbits at the highest dose. which is approximately 36 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 85 mg/day given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis. The no effect level for embryo-fetal development in rabbits was 60 mg/kg/day (11 times the MRHD given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis). There was no evidence of morphological development effects in rats, although increased incidences of fetal skeletal variations were seen at the highest dose level (7 times the MRHD given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis), which was also maternally toxic. The no effect level for embryo-fetal development in rats was 25 mg/kg/day. (2 times the MRHD given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis). When methylphenidate was administered to rats throughout pregnancy and lactation at doses of up to 45 mg/kg/day, offspring body weight gain was decreased at the highest dose (4 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis), but no other effects on postnatal development were observed. The no effect level for pre- and postnatal development in rats was 15 mg/kg/day (equivalent to the MRHD given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis).8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited published literature, based on breast milk sampling from five mothers, reports that methylphenidate is present in human milk, which resulted in infant doses of 0.16% to 0.7% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage and a milk/plasma ratio ranging between 1.1 and 2.7. There are no reports of adverse effects on the breastfed infant and no effects on milk production. Long-term neurodevelopmental effects on infants from stimulant exposure are unknown. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for ADHANSIA XR and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ADHANSIA XR or from the underlying maternal condition.Clinical Considerations
Monitor breastfeeding infants for adverse reactions, such as agitation, anorexia, and reduced weight gain.8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ADHANSIA XR in pediatric patients under the age of 6 years have not been established.
The safety and effectiveness of ADHANSIA XR have been established in one adequate and well-controlled 6-week study in pediatric patients ages 6 to 12 years, and in one adequate and well-controlled 4-week study in pediatric patients ages 12 to 17 years [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The long-term efficacy of methylphenidate in pediatric patients has not been established.
Long Term Suppression of Growth
Growth should be monitored during treatment with stimulants, including ADHANSIA XR. Pediatric patients who are not growing or gaining weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
Rats treated with methylphenidate early in the postnatal period through sexual maturation demonstrated a decrease in spontaneous locomotor activity in adulthood. A deficit in acquisition of a specific learning task was observed in females only. The doses at which these findings were observed are at least 3 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 85 mg/day given to children on a mg/m2 basis.In the study conducted in young rats, methylphenidate was administered orally at doses of up to 100 mg/kg/day for 9 weeks, starting early in the postnatal period (postnatal day 7) and continuing through sexual maturity (postnatal week 10). When these animals were tested as adults (postnatal weeks 13-14), decreased spontaneous locomotor activity was observed in males and females previously treated with 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 3 times the MRHD of 85 mg/day given to children on a mg/m2 basis) or greater, and a deficit in the acquisition of a specific learning task was observed in females exposed to the highest dose (6 times the MRHD given to children on a mg/m2 basis). The no effect level for juvenile neurobehavioral development in rats was 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.25 times the MRHD given to children on a mg/m2 basis). The clinical significance of the long-term behavioral effects observed in rats is unknown.
-
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.2 Abuse
CNS stimulants including ADHANSIA XR, other methylphenidate-containing products, and amphetamines have a high potential for abuse. Abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, to achieve a desired psychological or physiological effect. Abuse is characterized by impaired control over drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm, and craving.
Signs and symptoms of CNS stimulant abuse include increased heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and/or sweating, dilated pupils, hyperactivity, restlessness, insomnia, decreased appetite, loss of coordination, tremors, flushed skin, vomiting, and/or abdominal pain. Anxiety, psychosis, hostility, aggression, suicidal or homicidal ideation have also been observed. Abusers of CNS stimulants may chew, snort, inject, or use other unapproved routes of administration which can result in overdose and death [see Overdosage (10)].
To reduce the abuse of CNS stimulants including ADHANSIA XR, assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing. After prescribing, keep careful prescription records, educate patients and their families about abuse and on proper storage and disposal of CNS stimulants, monitor for signs of abuse while on therapy, and re-evaluate the need for ADHANSIA XR use.
9.3 Dependence
Tolerance
Tolerance (a state of adaptation in which exposure to a drug results in a reduction of the drug’s desired and/or undesired effects over time) may occur during chronic therapy with CNS stimulants including ADHANSIA XR.Dependence
Physical dependence (a state of adaptation manifested by a withdrawal syndrome produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, or administration of an antagonist) can occur in patients treated with CNS stimulants including ADHANSIA XR. Withdrawal symptoms after abrupt cessation following prolonged high-dosage administration of CNS stimulants include dysphoric mood; depression; fatigue; vivid, unpleasant dreams; insomnia or hypersomnia; increased appetite; and psychomotor retardation or agitation. -
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of acute methylphenidate overdosage, resulting principally from overstimulation of the CNS and from excessive sympathomimetic effects, may include the following: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, restlessness, anxiety, agitation, tremors, hyperflexia, muscle twitching, convulsion (may be followed by coma), euphoria, confusion, hallucinations, delirium, sweating, flushing, headache, hyperpyrexia, tachycardia, palpitations, cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension, hypotension, tachypnea, mydriasis, dryness of mucous membranes, and rhabdomyolysis.
10.2 Management of Overdose
Consult with a Certified Poison Control Center (1-800-222-1222) for up-to-date guidance and advice on the management of overdosage with methylphenidate. Provide supportive care, including close medical supervision and monitoring. Treatment should consist of general measures employed in the management of overdosage with any drug. Consider the possibility of multiple drug overdosage. Ensure an adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation. Monitor cardiac rhythm and vital signs. Use supportive and symptomatic measures.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ADHANSIA XR extended release capsules contains methylphenidate hydrochloride, a CNS stimulant. The capsules contain multilayered beads, composed of an immediate-release (IR) layer which contains approximately 20% of the methylphenidate dose, and a controlled release layer which contains approximately 80% of the methylphenidate dose, for oral administration. ADHANSIA XR is available in six capsule strengths. Each extended-release capsule contains 25 mg, 35 mg, 45 mg, 55 mg, 70 mg, or 85 mg of methylphenidate hydrochloride (HCl), which is equivalent to 21.6 mg, 30.3 mg, 38.9, mg, 47.6 mg, 60.5 mg, and 73.5 mg of methylphenidate free base, respectively. Chemically, methylphenidate HCl is d,l(racemic) methyl α-phenyl-2-piperidineacetate hydrochloride. Its molecular formula is C14H19NO2●HCl. Its structural formula is:
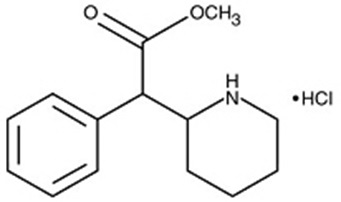
Methylphenidate HCl is a white to off-white, odorless, fine crystalline powder. Its solutions are acid to litmus. It is freely soluble in water and in methanol, soluble in alcohol, and slightly soluble in chloroform and in acetone. Its molecular weight is 269.8 g/mol.
Inactive Ingredients: ammonio methacrylate copolymer dispersion (type B), anionic copolymer (consisting of methyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate and methacrylic acid), glyceryl monostearate, hypromellose, poylethylene glycol, polysorbate, silicon dioxide, sodium hydroxide, sodium laurylsulfate, sorbic acid, sugar spheres, triethyl citrate.
Each strength capsule also contains colorant ingredients in the capsule shell as follows:
- 25 mg FD&C Blue No. 1
- 35 mg FD&C Yellow No. 6, Titanium Dioxide
- 45 mg FD&C Yellow No. 5, Titanium Dioxide
- 55 mg FD&C Blue No. 1, Yellow Iron Oxide, Titanium Dioxide
- 70 mg Black Iron Oxide, Titanium Dioxide
- 85 mg Titanium Dioxide
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Methylphenidate HCl is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. The mode of therapeutic action in ADHD is not known.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Methylphenidate is a racemic mixture comprised of the d- and l-isomers. The d-isomer is more pharmacologically active than the l-isomer. Methylphenidate blocks the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine into the presynaptic neuron and increase the release of these monoamines into the extraneuronal space.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
ADHANSIA XR contains a racemic mixture of d- and l-methylphenidate and produces two distinct peak concentrations (Cmax). The 1st median (range) time to Cmax occurred at about 1.5 (1- 2.5) hours and the 2nd about 12 (8.5- 16.0) hours after ADHANSIA XR administration. Following administration of ADHANSIA XR (100 mg once daily) and 60 mg of immediate-release (IR) methylphenidate (administered as 20 mg three times daily 4 hours apart) under fasted condition for 5 consecutive days to 21 healthy adult subjects, 1st d,l-methylphenidate mean Cmax was about 22% higher but the 2nd mean Cmax was similar for ADHANSIA XR compared to IR methylphenidate at steady state. The mean extent of exposure (AUC 0-24h) and minimum concentration (Cmin) of d,l-methylphenidate were about 50% and 288% higher, respectively for ADHANSIA XR compared to IR methylphenidate at steady state. (Figure 1). Following administration of ADHANSIA XR (100 mg once daily), the steady-state was reached from day 3.Figure 1: Mean Concentration-Time Profiles for d,l-Methylphenidate on Day 5 After Daily Dosing
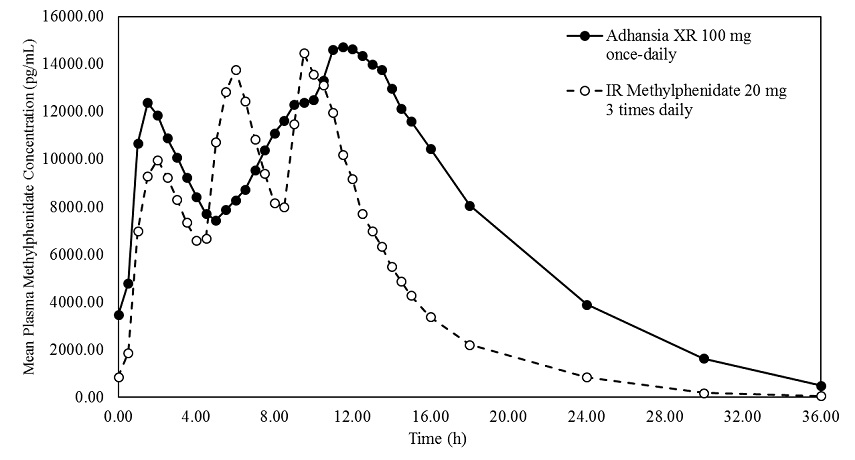
Effect of Food
High fat, high caloric meal (800 to 1000 calories) does not affect Cmax and extent of absorption (AUC) of d,l-methylphenidate when taken with ADHANSIA XR. The time to 1st and 2nd Cmax was increased by about 1 hour after administration with a high fat meal compared to under fasting condition. The absorption and exposure to d, l-methylphenidate were similar when ADHANSIA XR (100 mg) was administered following an overnight fast as an intact capsule or sprinkled on a tablespoonful of applesauce and yogurt in healthy adult subjects.Effect of Alcohol
In vitro studies were conducted to explore the effect of alcohol on the release characteristics of methylphenidate from ADHANSIA XR. No increase in the rate of release of methylphenidate from ADHANSIA XR was observed with the alcohol concentrations of 5%, 20%, and 40% at hour 1 and for 5% and 20% at hour 2. A faster release, 71% and 61% for 70 mg and 100 mg, respectively, was observed with the alcohol concentration of 40% at hour 2.In an in vivo alcohol interaction study, in fasted healthy adults, ADHANSIA XR 70 mg extended-release capsules with 40% alcohol concentration resulted in a 1.4-fold increase in the peak plasma methylphenidate concentration and a 1.3-fold increase in the extent of absorption.
Elimination
The mean plasma elimination half-life for d, l-methylphenidate was about 7 hours in healthy volunteers.Metabolism
In humans, methylphenidate is metabolized primarily via deesterification to alpha-phenyl-piperidine acetic acid (PPAA). The metabolite has little or no pharmacologic activity.Excretion
After oral dosing of radiolabeled methylphenidate in humans, about 90% of the radioactivity was recovered in urine. The main urinary metabolite was PPAA, accounting for approximately 80% of the dose.Specific Populations
Male and Female Patients
There is insufficient experience with the use of ADHANSIA XR to detect gender variations in pharmacokinetics.Racial or Ethnic Groups
There is insufficient experience with the use of ADHANSIA XR to detect ethnic variations in pharmacokinetics.Pediatric Patients
Results of the pharmacokinetic studies demonstrated that the pharmacokinetic profile in pediatric patients (6 to 12 years) is comparable to the pharmacokinetic profile in adults and pediatric patients (13 to 17 years) based on adjustment for body-weight.Pharmacokinetic studies of racemic methylphenidate after oral administration of ADHANSIA XR has been conducted in pediatric patients (6 to 17 years) with ADHD. Following administration of ADHANSIA XR, the median (range) 1st and 2nd peak plasma concentration for d, l-methylphenidate occurred in about 2 (1-4) and 10 (8-14) hours, respectively in pediatric patients (6 to 12 years) and 2 (1 – 4) and 11(8 – 14) hours, respectively in pediatric patients (13 to 17 years). The mean plasma elimination half-life for d, l-methylphenidate was about 4 to 7 hours in pediatric patients (6 to 12 years) and 5 hours in pediatric patients (13 to 17 years).
Patients with Renal Impairment
There is no experience with the use of ADHANSIA XR in patients with renal impairment. After oral administration of radiolabeled methylphenidate in humans, methylphenidate was extensively metabolized and approximately 80% of the radioactivity was excreted in the urine in the form of ritalinic acid metabolite. Since renal clearance is not an important route of methylphenidate clearance, renal insufficiency is expected to have little effect on the pharmacokinetics of ADHANSIA XR.Patients with Hepatic Impairment
There is no experience with the use of ADHANSIA XR in patients with hepatic impairment. -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a lifetime carcinogenicity study carried out in B6C3F1 mice, methylphenidate caused an increase in hepatocellular adenomas and, in males only, an increase in hepatoblastomas, at a daily dose of approximately 60 mg/kg/day. This dose is approximately 2 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 85 mg/day given to children on a mg/m2 basis. Hepatoblastoma is a relatively rare rodent malignant tumor type. There was no increase in total malignant hepatic tumors. The mouse strain used is sensitive to the development of hepatic tumors, and the significance of these results to humans is unknown.Methylphenidate did not cause any increase in tumors in a lifetime carcinogenicity study carried out in F344 rats; the highest dose used was approximately 45 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 3 times the MRHD given to children on a mg/m2 basis.
In a 24-week carcinogenicity study in the transgenic mouse strain p53+/-, which is sensitive to genotoxic carcinogens, there was no evidence of carcinogenicity. Male and female mice were fed diets containing the same concentration of methylphenidate as in the lifetime carcinogenicity study; the high-dose groups were exposed to 60 to 74 mg/kg/day of methylphenidate.
Mutagenesis
Methylphenidate was not mutagenic in the in vitro Ames reverse mutation assay or the in vitro mouse lymphoma cell forward mutation assay. Sister chromatid exchanges and chromosome aberrations were increased, indicative of a weak clastogenic response, in an in vitro assay in cultured Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells. Methylphenidate was negative in an in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.Impairment of Fertility
Methylphenidate did not impair fertility in male or female mice that were fed diets containing the drug in an 18-week Continuous Breeding study. The study was conducted at doses of up to 160 mg/kg/day, approximately 5 times the maximum recommended human dose of 85 mg/day given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis. -
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Adult Patients with ADHD
The efficacy of ADHANSIA XR for the treatment of ADHD in adults was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies. A 4-week, randomized, double-blind, multi-center, placebo-controlled, safety and efficacy study (Study 1 NCT02139124) involving adult patients aged 18 to 72 years (n=375) who met the DSM-5 criteria for ADHD was conducted. Patients were randomized to one of five treatment arms with ADHANSIA XR 25, 45, 70, 100 mg, or placebo. Doses were titrated to the randomized, fixed dose over a 2-week period and then maintained at the assigned dose for an additional 2 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint was defined as the change from baseline (Visit 2, Week 1) of the adult ADHD-Rating Scale (ADHD-5-RS) with prompts total score at Visit 6, Week 5. ADHANSIA XR demonstrated a statistically significant improvement for 45 mg and 100 mg compared to placebo on change of ADHD-RS total score from baseline (Visit 2, Week 1) to Visit 6, Week 5 (Study 1 in Table 4).A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover design, adult workplace environment (AWE) study (Study 2 NCT02225639) of ADHANSIA XR was conducted in adults (18 to 58 years) who met the DSM-5 criteria for ADHD. Subjects were titrated to an optimal dose (25 mg, 35 mg, 45 mg, 55 mg, 70 mg, 85 mg or 100 mg) of ADHANSIA XR in an open-label phase of between 2 and 7 weeks, familiarized with study procedures in a practice AWE session and then randomized to one of the two sequences: (i) ADHANSIA XR to PLACEBO or (ii) PLACEBO to ADHANSIA XR, and received one treatment for one week, followed by an AWE session, then crossed over to the other treatment for one week, followed by a second AWE session. Efficacy assessments were conducted at pre-dose and 1, 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, and 16 hours post-dose during the AWE sessions using the Permanent Product Measure of Performance Total (PERMP-T) score. PERMP-T is the combined score obtained by adding PERMP-A (number of math problems attempted) and PERMP-C (number of math problems answered correctly). The primary efficacy endpoint was the comparison of the ADHANSIA XR with placebo in mean PERMP-T scores, averaged across all timepoints on the AWE days. ADHANSIA XR demonstrated a statistically significant improvement over placebo based on the primary efficacy endpoint (Study 2 in Table 5). The secondary efficacy endpoints were onset and duration of clinical effect, as assessed by the treatment difference in PERMP-T scores at post-dose time points. ADHANSIA XR also demonstrated statistically significant improvement over placebo at 1, 2, 5, 8, 11 and 16 hours post-dose, but not at 14 hours post-dose.
Pediatric Patients (12 to 17 years) with ADHD
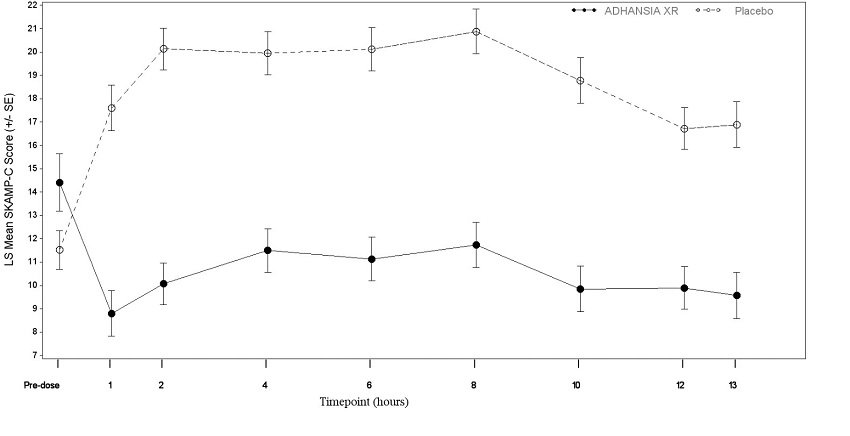
The efficacy of ADHANSIA XR for the treatment of ADHD was evaluated in a 4-week randomized, double-blind, multi-center, placebo-controlled, safety and efficacy study (Study 3 NCT0213911) involving pediatric patients (12 to 17 years) (n=354) who met the DSM-5 criteria for ADHD. Patients were randomized to one of five treatment arms with ADHANSIA XR 25, 45, 70, or 85 mg or placebo. Doses were titrated over a 2-week period and then maintained on the fixed dose for an additional 2-weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint was defined as the change from baseline of the pediatric ADHD-5-RS total score from baseline (Week 1) to Visit 6, Week 5 (Study 3 in Table 4). ADHANSIA XR demonstrated a statistically significant treatment effect compared with placebo at Visit 6, Week 5 for the 45 and 70 mg dose groups.Pediatric patients (6 to 12 years) with ADHD
The efficacy of ADHANSIA XR for the treatment of ADHD was evaluated in an analog classroom trial (Study 4 NCT03172481) conducted in pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age (n=147) who met the DSM-5 criteria for ADHD. Patients received ADHANSIA XR 25, 35, 45, 55, 70 or 85 mg (mean dose 48 mg) during a 6-week, open-label, dose-optimization period, followed by a 1-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind treatment phase. After 1 week of double-blind treatment, patients were evalu-ated at pre-dose and 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 13 hours post-dose on the analog classroom day using the Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham (SKAMP) rating scale, a 13-item teacher-rated scale that assesses manifestations of ADHD in a classroom setting. The primary efficacy endpoint was the comparison of the ADHANSIA XR with placebo in mean SKAMP-Combined scores, averaged across 8 timepoints on the analog classroom day. ADHANSIA XR demonstrated a statistically significant re-sponse over placebo (Study 4 in Table 5.). The secondary efficacy endpoints were onset and duration of clinical effect, as assessed by the treatment difference in SKAMP-Combined scores at post-dose time points. The SKAMP-Combined scores were also statistically significantly lower (improved) at all time points (1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 13 hours) post-dose with ADHANSIA XR compared to placebo (Figure 2).Table 4: Summary of Primary Efficacy Results from Studies in Adults (Study 1) and Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 years (Study 3) with ADHD n: number of subjects included in the primary efficacy analysis set; SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error; LS Mean: least-squares mean; CI: confidence interval, not adjusted for multiple comparisons.
a Difference (drug minus placebo) in least-squares mean change from baseline.
* Doses that are statistically significantly different from placebo after adjusting for multiplicity.Study Number Treatment Group (ADHANSIA XR dose level) Primary Efficacy Measure: Change from Baseline (Week 1, Visit 2) in ADHD-5-RS Total Score to Week 5 (Visit 6) n Mean Baseline Score (SD) LS Mean Change from Baseline (SE) Placebo-subtracted Differencea (95% CI) Study 1 25 mg 75 36.1 (8.1) -11.6 (1.31) -1.9 (-5.6, 1.7) 45 mg* 73 36.5 (7.2) -16.8 (1.34) -7.1 (-10.8, -3.4) 70 mg 71 35.4 (7.4) -12.0 (1.37) -2.3 (-6.0, 1.4) 100 mg* 72 37.0 (7.9) -17.6 (1.39) -7.9 (-11.6, -4.1) Placebo 77 35.7 (8.4) -9.7 (1.32) -- Study 3 25 mg 71 37.7 (8.7) -12.8 (1.35) -2.2 (-5.9, 1.6) 45 mg* 68 36.4 (8.5) -16.0 (1.39) -5.4 (-9.2, -1.6) 70 mg* 72 35.9 (8.4) -15.8 (1.35) -5.2 (-9.0, -1.4) 85 mg 70 37.8 (8.1) -15.0 (1.39) -4.4 (-8.2, -0.6) Placebo 71 37.3 (8.4) -10.6 (1.35) -- Table 5: Summary of Primary Efficacy Results from Laboratory Classroom Studies in Adults (Study 2) and Pediatric Patients 6 to 12 years (Study 4) with ADHD n: number of subjects in the primary efficacy analysis set; SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error; LS Mean: least-squares mean; CI: confidence interval, not adjusted for multiple comparisons.
a Difference (drug minus placebo) in least-squares mean of post-dose scores.Study Number Primary Efficacy Measure Treatment Group n Pre-dose Mean Score (SD) Post-Dose LS Mean Score (SE) Placebo-subtracted Differencea (95% CI) Study 2 Average PERMP ADHANSIA XR 45 225.1 (76.7) 281.3 (4.33) 26.80 (15.19, 38.41) Placebo 45 235.7 (65.4) 254.5 (4.63) -- Study 4 Average SKAMP ADHANSIA XR 74 14.4 (10.6) 10.3 (0.74) -8.6 (-10.6, -6.6) Placebo 73 11.5 (7.1) 18.9 (0.73) Figure 2: LS Mean SKAMP-Combined Score after Treatment with ADHANSIA XR or Placebo during Classroom Day in Pediatric Patients 6 to 12 years with ADHD (Study 4)
LS = Least squares.
SE = Standard Error.
The raw mean and SE bars are presented at the pre-dose timepoint, rather than the LS mean and SE bars. -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE
AND HANDLING
ADHANSIA XR (methylphenidate hydrochloride) extended-release capsules are available as follows:
-
25 mg Capsules – blue, (imprinted
with “MLR-02” and “25 mg”)
Bottles of 30 .........................................………………………………NDC 72912-525-30
-
35 mg Capsules – orange, (imprinted
with “MLR-02” and “35 mg”)
Bottles of 30 .........................................………………………………NDC 72912-535-30
-
45 mg Capsules – yellow, (imprinted
with “MLR-02” and “45 mg”)
Bottles of 30 .........................................………………………………NDC 72912-545-30
-
55 mg Capsules – light green,
(imprinted with “MLR-02” and “55 mg”)
Bottles of 30 .........................................………………………………NDC 72912-555-30
-
70 mg Capsules – iron gray,
(imprinted with “MLR-02” and “70 mg”)
Bottles of 30 .........................................………………………………NDC 72912-570-30
-
85 mg Capsules – white, (imprinted
with “MLR-02” and “85 mg”)
Bottles of 30 .........................................………………………………NDC 72912-585-30
Storage and Handling
Store between 20º C to 25º C (68º F to 77º F); excursions permitted from 15º C to 30º C (59º F to 86º F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light and moisture.Dispense in tight container (USP).
Disposal
Comply with local laws and regulations on drug disposal of CNS stimulants. Dispose of remaining, unused, or expired ADHANSIA XR by a medicine take-back program or by an authorized collector registered with the Drug Enforcement Administration. If no take-back program or authorized collector is available, mix ADHANSIA XR with an undesirable, nontoxic substance to make it less appealing to children and pets. Place the mixture in a container such as a sealed plastic bag and discard ADHANSIA XR in the household trash. -
25 mg Capsules – blue, (imprinted
with “MLR-02” and “25 mg”)
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Controlled Substance Status/High Potential for Abuse and Dependence
Advise patients and their caregivers that ADHANSIA XR is a federally controlled substance, and it can be abused and lead to dependence [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.1, 9.2, and 9.3)]. Instruct patients that they should not give ADHANSIA XR to anyone else. Advise patients to store ADHANSIA XR in a safe place, preferably locked, to prevent abuse. Advise patients and their caregivers to comply with laws and regulations on drug disposal. Advise patients and their caregivers to dispose of remaining, unused, or expired ADHANSIA XR by a medicine take-back program if available [Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3), How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].Instructions for Taking ADHANSIA XR
Advise patients and their caregivers that ADHANSIA XR can be taken with or without food. For patients who take ADHANSIA XR sprinkled over a tablespoon of applesauce or yogurt, the contents of the entire capsule should be consumed immediately or within 10 minutes of mixing; it should not be stored. Patients should take the applesauce or yogurt with sprinkled beads in its entirety without chewing. When initiating treatment with ADHANSIA XR, provide dosage escalation and administration instructions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].Serious Cardiovascular Risks
Advise patients, caregivers, and their family members that there is a potential serious cardiovascular risk including sudden death, myocardial infarction, and stroke with ADHANSIA XR use. Instruct patients to contact a healthcare provider immediately if they develop symptoms such as exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, or other symptoms suggestive of cardiac disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases
Advise patients and their caregivers that ADHANSIA XR can cause elevations of their blood pressure and pulse rate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].Psychiatric Risks
Advise patients and their caregivers that ADHANSIA XR, at recommended doses, can cause psychotic or manic symptoms, even in patients without prior history of psychotic symptoms or mania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].Priapism
Advise patients, caregivers, and family members of the possibility of painful or prolonged penile erections (priapism). Instruct them to seek immediate medical attention in the event of priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].Circulation Problems in Fingers and Toes [Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s Phenomenon]
- Instruct patients about the risk of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon, and associated signs and symptoms: fingers or toes may feel numb, cool, painful, and/or may change color from pale, to blue, to red.
- Instruct patients to report to their physician any new numbness, pain, skin color change, or sensitivity to temperature in fingers or toes.
- Instruct patients to call their physician immediately with any signs of unexplained wounds appearing on fingers or toes while taking ADHANSIA XR.
- Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for certain patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Suppression of Growth
Advise patients, families and caregivers that ADHANSIA XR may cause slowing of growth and weight loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].Alcohol Effect
Advise patients to avoid alcohol while taking ADHANSIA XR. Consumption of alcohol while taking ADHANSIA XR may result in a more rapid release of the dose of methylphenidate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Pregnancy Registry
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to ADHANSIA XR during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].Marketed by:
Adlon Therapeutics L.P.
Stamford, CT 06901-3431
A subsidiary of Purdue Pharma L.P.
Manufactured by:
Purdue Pharmaceuticals L.P.
Wilson, NC 27893ADHANSIA XR™ is a trademark of Purdue Pharma L.P.
U.S. Patent Numbers: 9,974,752, 10,111,839, 10,292,938 and 10,292,939 -
MEDICATION GUIDE
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: February 2019 MEDICATION GUIDE
ADHANSIA (ad han' see ah) XRTM
(methylphenidate hydrochloride)
extended-release capsules, CIIWhat is the most important information I should know about ADHANSIA XR?
ADHANSIA XR can cause serious side effects, including:-
Abuse and dependence. ADHANSIA XR, other methylphenidate
containing medicines, and amphetamines have a high chance for abuse
and can cause physical and psychological dependence. Your healthcare
provider should check you or your child for signs of abuse and dependence
before and during treatment with ADHANSIA XR.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you or your child have ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines, or street drugs.
- Your healthcare provider can tell you more about the differences between physical and psychological dependence and drug addiction.
-
Heart-related problems, including:
- sudden death, stroke, and heart attack in adults
- sudden death in children who have heart problems or heart defects
- increased blood pressure and heart rate
Your healthcare provider should check your or your child’s blood pressure and heart rate regularly during treatment with ADHANSIA XR.
Call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away if you or your child have any signs of heart problems such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting during treatment with ADHANSIA XR. -
Mental (psychiatric) problems, including:
- new or worse behavior and thought problems
- new or worse bipolar illness
- new psychotic symptoms (such as hearing voices, or seeing or believing things that are not real) or new manic symptoms
Call your healthcare provider right away if you or your child have any new or worsening mental symptoms or problems during treatment with ADHANSIA XR, especially hearing voices, seeing or believing things that are not real, or new manic symptoms.
What is ADHANSIA XR?
ADHANSIA XR is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant prescription medicine used for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in people 6 years of age and older. ADHANSIA XR may help increase attention and decrease impulsiveness and hyperactivity in people with ADHD.
It is not known if ADHANSIA XR is safe and effective in children under 6 years of age.
ADHANSIA XR is a federally controlled substance (CII) because it contains methylphenidate that can be a target for people who abuse prescription medicines or street drugs. Keep ADHANSIA XR in a safe place to protect it from theft. Never give your ADHANSIA XR to anyone else, because it may cause death or harm them. Selling or giving away ADHANSIA XR may harm others and is against the law.Do not take ADHANSIA XR if you or your child are:
- allergic to methylphenidate hydrochloride or any of the ingredients in ADHANSIA XR. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in ADHANSIA XR.
- taking, or have stopped taking within the past 14 days, a medicine used to treat depression called a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI).
Before taking ADHANSIA XR tell your healthcare provider about all medical conditions, including if you or your child: - have heart problems, heart defects, or high blood pressure
- have mental problems including psychosis, mania, bipolar illness, or depression, or have a family history of suicide, bipolar illness, or depression
- have circulation problems in fingers and toes
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known
if ADHANSIA XR will harm the unborn baby.
- There is a pregnancy registry for females who are exposed to ADHANSIA XR during pregnancy. The purpose of the registry is to collect information about the health of females exposed to ADHANSIA XR and their baby. If you or your child becomes pregnant during treatment with ADHANSIA XR, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the National Pregnancy Registry for Psychostimulants at 1-866-961-2388.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. ADHANSIA XR passes into breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed the baby during treatment with ADHANSIA XR.
ADHANSIA XR and some medicines may interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Sometimes the doses of other medicines will need to be changed during treatment with ADHANSIA XR. Your healthcare provider will decide whether ADHANSIA XR can be taken with other medicines.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you or your child take a medicine used to treat depression called a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI).
Know the medicines that you or your child take. Keep a list of the medicines with you to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist. Do not start any new medicine during treatment with ADHANSIA XR without talking to your healthcare provider first.How should ADHANSIA XR be taken? - Take ADHANSIA XR exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Your healthcare provider may change the dose if needed.
- Take ADHANSIA XR by mouth 1 time each day in the morning.
- ADHANSIA XR can be taken with or without food, but take
it the same way each time.
- Swallow ADHANSIA XR capsules whole. If ADHANSIA XR capsules
cannot be swallowed whole, the capsules may be opened and sprinkled
onto a tablespoonful of applesauce or yogurt. Make sure to sprinkle
all the medicine onto the applesauce or yogurt. The ADHANSIA XR dose
should not be divided.
- swallow all the applesauce or yogurt and medicine mixture without chewing right away or within 10 minutes
- do not chew the applesauce or yogurt
- do not store applesauce or yogurt and medicine mixture
- Swallow ADHANSIA XR capsules whole. If ADHANSIA XR capsules
cannot be swallowed whole, the capsules may be opened and sprinkled
onto a tablespoonful of applesauce or yogurt. Make sure to sprinkle
all the medicine onto the applesauce or yogurt. The ADHANSIA XR dose
should not be divided.
- Your healthcare provider may sometimes stop ADHANSIA XR treatment for a while to check ADHD symptoms.
- If a dose of ADHANSIA XR is missed do not take the dose later in the day or take an extra dose to make up for the missed dose, wait until the next morning to take the next scheduled dose.
What should be avoided during treatment with ADHANSIA XR?
Avoid drinking alcohol during treatment with ADHANSIA XR. This may cause a faster release of the ADHANSIA XR medicine.What are possible side effects of ADHANSIA XR?
ADHANSIA XR can cause serious side effects, including:- See “What is the most important information I should know about ADHANSIA XR?”
- Painful and prolonged erections (priapism). Priapism has happened in males who take products that contain methylphenidate. If you or your child develop priapism, get medical help right away.
-
Circulation problems in fingers and toes (peripheral
vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon). Signs and symptoms
may include:
- fingers or toes may feel numb, cool, painful
- fingers or toes may change color from pale, to blue, to red
Call your healthcare provider right away if your child have any signs of unexplained wounds appearing on fingers or toes during treatment with ADHANSIA XR. - Slowing of growth (height and weight) in children. Children should have their height and weight checked often while taking ADHANSIA XR. ADHANSIA XR treatment may be stopped if your child is not growing or gaining weight.
- FD&C Yellow No. 5. ADHANSIA XR 45 mg capsules contain FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain people, especially people who also have an allergy to aspirin.
The most common side effects of ADHANSIA XR in children include decreased appetite, trouble sleeping, and decreased weight.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store ADHANSIA XR? - Store ADHANSIA XR at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store ADHANSIA XR in a safe place, like a locked cabinet. Protect from light and moisture.
- Dispose of remaining, unused, or expired ADHANSIA XR by a medication take-back program at authorized collection sites such as retail pharmacies, hospital or clinic pharmacies, and law enforcement locations. If no take-back program or authorized collector is available, mix ADHANSIA XR with an undesirable, nontoxic substance such as dirt, cat litter, or used coffee grounds to make it less appealing to children and pets. Place the mixture in a container such as a sealed plastic bag and throw away ADHANSIA XR in the household trash.
General information about the safe and effective use of ADHANSIA XR.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use ADHANSIA XR for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ADHANSIA XR to other people, even if they have the same symptoms. It may harm them and it is against the law. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about ADHANSIA XR that was written for healthcare professionals.What are the ingredients in ADHANSIA XR?
Active Ingredient: methylphenidate hydrochloride
Inactive Ingredients: ammonio methacrylate copolymer dispersion (type B), anionic copolymer (consisting of methyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate and methacrylic acid), glyceryl monostearate, hypromellose, poylethylene glycol, polysorbate, silicon dioxide, sodium hydroxide, sodium laurylsulfate, sorbic acid, sugar spheres, triethyl citrate
Manufactured by: Purdue Pharmaceuticals L.P., Wilson, NC 27893
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Purdue Pharma L.P. at 1-888-726-7535 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. -
Abuse and dependence. ADHANSIA XR, other methylphenidate
containing medicines, and amphetamines have a high chance for abuse
and can cause physical and psychological dependence. Your healthcare
provider should check you or your child for signs of abuse and dependence
before and during treatment with ADHANSIA XR.
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ADHANSIA XR
methylphenidate hydrochloride capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72912-525 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 4B3SC438HI) (METHYLPHENIDATE - UNII:207ZZ9QZ49) METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE 25 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength AMMONIO METHACRYLATE COPOLYMER TYPE B (UNII: 161H3B14U2) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) SORBIC ACID (UNII: X045WJ989B) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) TRIETHYL CITRATE (UNII: 8Z96QXD6UM) Product Characteristics Color BLUE Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code MLR02;25mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72912-525-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/01/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212038 07/01/2019 ADHANSIA XR
methylphenidate hydrochloride capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72912-535 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 4B3SC438HI) (METHYLPHENIDATE - UNII:207ZZ9QZ49) METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE 35 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength AMMONIO METHACRYLATE COPOLYMER TYPE B (UNII: 161H3B14U2) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) SORBIC ACID (UNII: X045WJ989B) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) TRIETHYL CITRATE (UNII: 8Z96QXD6UM) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) Product Characteristics Color ORANGE Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code MLR02;35mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72912-535-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/01/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212038 07/01/2019 ADHANSIA XR
methylphenidate hydrochloride capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72912-545 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 4B3SC438HI) (METHYLPHENIDATE - UNII:207ZZ9QZ49) METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE 45 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength AMMONIO METHACRYLATE COPOLYMER TYPE B (UNII: 161H3B14U2) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) SORBIC ACID (UNII: X045WJ989B) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) TRIETHYL CITRATE (UNII: 8Z96QXD6UM) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FD&C YELLOW NO. 5 (UNII: I753WB2F1M) Product Characteristics Color YELLOW Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 22mm Flavor Imprint Code MLR02;45mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72912-545-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/01/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212038 07/01/2019 ADHANSIA XR
methylphenidate hydrochloride capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72912-555 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 4B3SC438HI) (METHYLPHENIDATE - UNII:207ZZ9QZ49) METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE 55 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength AMMONIO METHACRYLATE COPOLYMER TYPE B (UNII: 161H3B14U2) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) SORBIC ACID (UNII: X045WJ989B) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) TRIETHYL CITRATE (UNII: 8Z96QXD6UM) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) Product Characteristics Color GREEN Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 24mm Flavor Imprint Code MLR02;55mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72912-555-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/01/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212038 07/01/2019 ADHANSIA XR
methylphenidate hydrochloride capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72912-570 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 4B3SC438HI) (METHYLPHENIDATE - UNII:207ZZ9QZ49) METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE 70 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength AMMONIO METHACRYLATE COPOLYMER TYPE B (UNII: 161H3B14U2) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) SORBIC ACID (UNII: X045WJ989B) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) TRIETHYL CITRATE (UNII: 8Z96QXD6UM) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) Product Characteristics Color GRAY Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 24mm Flavor Imprint Code MLR02;70mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72912-570-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/01/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212038 07/01/2019 ADHANSIA XR
methylphenidate hydrochloride capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72912-585 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 4B3SC438HI) (METHYLPHENIDATE - UNII:207ZZ9QZ49) METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE 85 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength AMMONIO METHACRYLATE COPOLYMER TYPE B (UNII: 161H3B14U2) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) SORBIC ACID (UNII: X045WJ989B) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) TRIETHYL CITRATE (UNII: 8Z96QXD6UM) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 25mm Flavor Imprint Code MLR02;85mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72912-585-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/01/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212038 07/01/2019 Labeler - Adlon Therapeutics L.P. (116933715) Registrant - Adlon Therapeutics L.P. (116933715) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Glatt Air Techniques 790220628 MANUFACTURE(72912-535, 72912-585, 72912-525, 72912-545, 72912-570, 72912-555) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Purdue Pharmaceutical Products LP 132080875 MANUFACTURE(72912-535, 72912-585, 72912-525, 72912-545, 72912-570, 72912-555) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 080236951 API MANUFACTURE(72912-525, 72912-535, 72912-585, 72912-555, 72912-570, 72912-545) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Noramco, Inc. 166506142 API MANUFACTURE(72912-525, 72912-535, 72912-585, 72912-555, 72912-570, 72912-545) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Rhodes Technologies, Inc 157990263 API MANUFACTURE(72912-525, 72912-535, 72912-585, 72912-555, 72912-570, 72912-545)
Trademark Results [ADHANSIA XR]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ADHANSIA XR 87982478 not registered Live/Pending |
PURDUE PHARMA L.P. 2018-01-16 |
 ADHANSIA XR 87756623 not registered Live/Pending |
PURDUE PHARMA L.P. 2018-01-16 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.





