SILEO- dexmedetomidine gel
Sileo by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Sileo by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Zoetis Inc., Orion Corporation. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- CAUTION
-
DESCRIPTION
SILEO (dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel) is a synthetic alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist. Each ml of SILEO contains 0.09 mg dexmedetomidine (equivalent to 0.1 mg dexmedetomidine hydrochloride). The chemical name is (+)-4-[1-(2,3-dimethylphenyl) ethyl]-1H-imidazole monohydrochloride. It is a white, or almost white, crystalline, water soluble substance having a molecular weight of 236.7. The molecular formula is C13 H16 N2 HCl and the structural formula is:
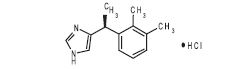
Structure
- INDICATIONS
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Always provide the Client Information Sheet with SILEO and instruct the client how to properly operate the SILEO dosing syringe (see Client Information Sheet for Owner/Handler Use and Safety).
To prevent accidental overdose, it is important to make sure that the ring-stop on the dosing syringe is in the locked position prior to administration.
SILEO is administered onto the oral mucosa between the dog’s cheek and gum at the dose of 125 mcg/m2. The gel is absorbed through the oral mucosa and therefore it should NOT be swallowed. If the gel is swallowed, the product may not be effective. If the gel is swallowed, do not repeat the dose for at least two hours.
The following table provides the acceptable dosage for each weight range. Each dot (●) represents 0.25 mL of SILEO.
Each ml contains the equivalent to 0.1mg dexmedetomidine hydrochloride.Table 1. Dosage by body weight
Bodyweight (lb)
Number of dots
4.4-12.1
1 ●
12.2-26.5
2 ●●
26.6-44.0
3 ●●●
44.1-63.9
4 ●●●●
64.0-86.0
5 ●●●●●
86.1-110.2
6 ●●●●●●
110.3-137.8
7 ●●●●●●●
137.9-166.4
8 ●●●●●●●●
166.5-196.2
9 ●●●●●●●●●
196.3-220.5
10 ●●●●●●●●●●
If the dose is more than 6 dots, divide the dose between both sides of the mouth.
The first dose of SILEO should be administered approximately
30-60 minutes before the fear and/or anxiety-eliciting noise stimulus, immediately after the dog shows first signs of anxiety or fear related to noise, or when the owner detects a typical noise stimulus (e.g. sound of fireworks) eliciting anxiety or fear in the dog. Typical signs of anxiety and fear associated with noise aversion are panting, trembling, pacing, seeking people, trying to hide, trying to escape, freezing behavior, refusing to eat food or treats, inappropriate urination or defecation, and salivation.
Administering SILEO without use of the SILEO syringe will result in incorrect dosing, which may result in lack of efficacy or overdose.
Dosing should be performed by an adult. Impermeable disposable gloves should be worn when administering SILEO and when handling the SILEO syringe.
If noise lasts longer than 2-3 hours and the dog’s signs of fear and/or anxiety reappear, another dose may need to be given. To avoid overdosing, there should always be at least two hours’ pause between dosages. No more than 5 doses can be given during one noise event.
A partially used syringe can be used again within 2 weeks after initial opening, if there is enough gel for a complete dose for the dog. To minimize the risk of incorrect dosing, a partially used syringe that does not have enough gel for a complete dose should not be used.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of according - CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Human Safety: Not for human use. Keep out of reach of children.
Avoid administering the product if pregnant, as exposure may induce uterine contractions and/or decrease fetal blood pressure.
Appropriate precautions should be taken while handling and using filled syringes. Impermeable disposable gloves should be worn when handling the syringe, administering SILEO, or when coming in contact with the dog’s mouth after application.
If skin is damaged, dexmedetomidine can be absorbed into the body. In case of skin contact, wash with soap and water. Remove contaminated clothing.
SILEO can be absorbed following direct exposure to skin, eyes, or mouth. In case of accidental eye exposure, flush with water for 15 minutes. If wearing contact lenses, eyes should be rinsed first, then remove contact lenses and continue rinsing, then seek medical advice immediately.
Accidental exposure may cause sedation and changes in blood pressure. In case of accidental exposure, seek medical attention immediately. Exposure to the product may induce a local or systemic allergic reaction in sensitized individuals.
Note to physician: This product contains an alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist.
The safety data sheet (SDS) contains more detailed occupational safety information. To report adverse reactions in users or to obtain a copy of the SDS for this product call 1-888-963-8471.
Animal Safety: SILEO should not be administered in the presence of pre-existing hypotension, hypoxia, or bradycardia. Sensitive dogs may experience a drop in body temperature and heart rate, and may appear sedated. These dogs should be kept warm and not offered food or water until SILEO’s effects have worn off (usually within a few hours). Do not use in dogs sedated from previous dosing.
-
PRECAUTIONS
SILEO is not meant to be swallowed. Instead, it must be placed onto the mucosa between the dog’s cheek and gum. If SILEO is swallowed, the product may not be effective. If SILEO is swallowed, do not repeat the dose for at least two hours. Feeding and giving treats within 15 minutes after administration should be avoided.
The use of other central nervous system depressants may potentiate the effects of SILEO.
As with all alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonists, the potential for isolated cases of hypersensitivity, including paradoxical response (excitation), exists.
SILEO has not been evaluated in dogs younger than 16 weeks of age or in dogs with dental or gingival diseases that could have an effect on SILEO’s absorption. SILEO has not been evaluated for aversion behaviors to thunderstorms.
The safety and effectiveness of SILEO in breeding, pregnant, and lactating dogs has not been evaluated. Administration to pregnant dogs may induce uterine contractions and/or decrease fetal blood pressure. -
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In a well-controlled European field study, which included a total of 182 dogs ranging from 2 to 17 years of age and representing both mixed and pure breed dogs (89 treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel and 93 treated with control), no serious adverse reactions were attributed to administration of dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel.
Table 2 shows the number of dogs displaying adverse reactions (some dogs experienced more than one adverse reaction).
Table 2. Adverse Reactions - Number (%) of dogs
Adverse Reaction
Control
N = 93
Dexmedetomidine 125 mcg/m2
N = 89
Emesis
1 ( 1.1)
4 ( 4.5)
Gastroenteritis
0
1 ( 1.1)
Periorbital edema
0
1 ( 1.1)
Drowsiness
0
1 ( 1.1)
Sedation
0
1 ( 1.1)
Pale mucous membranes were frequently seen in dogs treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel. In most cases, the effect was transient and no adverse reactions due to mucosal irritation were reported.
In a second well-controlled European field study which included a total of 36 dogs ranging from 2 to 17 years of age and representing both mixed and pure breed dogs (12 treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel at 125 mcg/m2, 12 treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel at 250 mcg/m2, and 12 treated with a vehicle control), no serious adverse reactions were attributed to administration of dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel.Table 3 shows the number of dogs displaying adverse reactions (some dogs experienced more than one adverse reaction).
Table 3. Adverse Reactions - Number (%) of dogs
Adverse
Reaction
Control
N = 12
Dexmedetomidine 125 mcg/m2
N = 12
Dexmedetomidine 250 mcg/m2
N = 12
Sedation
0
2 (16.7)
4 (33.3)
Lack of
effectiveness
4 (33.3)
0
1 (8.3)
Urinary
incontinence
0
1 (8.3)
1 (8.3)
Emesis
0
2 (16.7)
0
Head tremor
0
0
1 (8.3)
Inappropriate
urination
0
1 (8.3)
0
Ataxia
0
0
1 (8.3)
Mydriasis
0
0
1 (8.3)
Anxiety
disorder
0
0
1 (8.3)
Tachypnea
1 (8.3)
0
0
Lethargy
1 (8.3)
0
0
Tachycardia
1 (8.3)
0
0
To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the SDS call 1-888-963-8471.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Dexmedetomidine is a potent and selective alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist that inhibits the release of noradrenaline from noradrenergic neurons. A reduction of heart rate may occur. In a clinical safety study the mean heart rate dropped from 127 bpm to 98 bpm for dogs treated with the dexmedetomidine gel.
Oral bioavailability of dexmedetomidine is poor due to extensive first-pass metabolism. No measurable concentrations were found after gastro-intestinal tubing of dexmedetomidine to dogs. When administered via the oral mucosa, enhanced bioavailability is observed as a result of absorption in the oral cavity and the avoidance of first-pass metabolism in the liver.
The maximum concentration of dexmedetomidine occurs at about 0.6 hours after both IM and oromucosal administration in dogs. In a pharmacokinetic study in dogs, the oromucosal mean bioavailability of dexmedetomidine was 28%. The apparent volume of distribution of the drug is 0.9 L/kg. In the canine circulation, dexmedetomidine is largely bound to plasma proteins (93%).
Dexmedetomidine is eliminated by biotransformation mainly in the liver with a half-life ranging from 0.5 to 0.7 hours after intravenous (IV) administration and 0.5 to 3 hours after oromucosal administration in dogs. Metabolism accounts for more than 98% of the elimination. Known metabolites show no or negligible activity. Metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine with a minor fraction found in the feces. -
ANIMAL SAFETY
Canine safety study with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injectable
In a laboratory study of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection, doses of 375, 1125 and 1875 mcg/m2 were administered once daily IV or doses of 500, 1500 and 2500 mcg/m2 [low, mid, and high doses, respectively] were administered once daily IM on three consecutive days.
Dexmedetomidine-induced sedation occurred on each dosing day at all dose levels from 2 to 8 hours post-dosing. The duration of sedation increased with the dosage level. A decreased respiratory rate was observed in all groups on each day, but returned to normal within 4 hours in the low IV and IM groups and within
8 hours in the mid and high IV and IM groups. A decreased rectal temperature was observed in all groups on each day. In the low IV and IM groups, the rectal temperature returned to normal or near normal within
4 hours and in the mid and high IV and IM groups within 8 hours. A decreased heart rate was observed in all groups on each day, with greater decreases in the IV dosing groups. In the low groups, the duration of decrease was 2 hours with the values returning to normal 4 hours after dosing. In the mid groups, the duration of decrease was 4 hours with the values returning to normal 8 hours after dosing. In the high IV dose group, the values also returned to normal at 8 hours after dosing. However, in the high IM group, the values were still slightly depressed at 8 hours after dosing; the values returned to normal by 24 hours after dosing. On electrocardiography, QT time was prolonged in all groups due to decreased heart rate. In the low and mid IM groups, one case each of second degree A-V-block was observed. In the high IM group, one dog had first and second degree A-V block.
In the mid IV group, two dogs had second degree A-V block and one dog had first and second degree A-V block. In the mid and high IM groups, one dog each had elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) values. In the high IV group, two dogs had elevated ALT values.
Dexmedetomidine was well tolerated in the study even at the high doses, and adverse effects on physiology were related to the pharmacology of the drug. There were no toxicological effects on body weight, clinical variables, gross or microscopic pathology. -
EFFECTIVENESS
SILEO was evaluated in a European randomized multi-center, double-blind, vehicle-controlled field study. Effectiveness was evaluated in client-owned dogs, ranging in age between 2 and 17 years, and in body weight between 4 and 67 kg. A total of 187 dogs were randomized, 144 of which were evaluated for effectiveness: 71 dogs received 125 mcg/m2 of dexmedetomidine oromucosal and 73 dogs received the vehicle control gel up to 5 times as needed with a minimum interval of 2 hours between doses. All dogs had in previous years suffered from acute fear and/or anxiety due to fireworks.
The first dose was given on New Year’s Eve before or as soon as the dog showed the first signs of becoming anxious and/or fearful due to fireworks. Re-dosing could be performed as soon as the dog again demonstrated noise aversion behaviors, but at least 2 hours after the previous dose to allow time to assess observable effects of treatment and to avoid potential cumulative effects of dexmedetomidine.
For the first co-primary endpoint, the proportion of dogs with owner-assessed good or excellent treatment effect was higher in dogs treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel (53/71 dogs) than in those administered control (24/73 dogs). The proportion of dogs with some, no, or worse effect was higher in dogs administered control (49/73 dogs) than in those treated with dexmedetomidine (18/71 dogs). Refer to Table 4. below.Table 4. Owner assessment of treatment effect/score by treatment group
Treatment
Effect
Dexmedetomidine Control Total N=71 N=73 N=144
n(%) n(%) n(%) 1 Excellent effect
12 (16.9) 8 (11) 20 (13.9) 2 Good effect 41 (57.7) 16 (21.9) 57 (39.6) 3 Some effect 7 (9.9) 14 (19.1) 21 (14.6) 4 No effect 8 (11.2) 32 (43.8) 40 (27.7) 5 Worse 3 (4.2) 3 (4) 6 (4.2) There was a statistically significant difference (p<0.0001) between dexmedetomidine and control in favor of dexmedetomidine. The odds ratio was 5.5876, with 95% confidence interval (2.7635, 11.2976).
For the second co-primary variable, the mean sum of behavior scores over the treatment period was significantly different between dexmedetomidine and control (p=0.0069). Behavior scores consisted of a cumulative score using a number of outward signs of noise aversion in dogs such as panting, trembling, vocalizing, and seeking people. The mean score was lower (better) for the dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel treated group than for the control group (LSMeans: 4.9661, 7.2456 respectively). Refer to Table 5 below.Table 5. Mean behavioral sum scores by treatment and time point
Dosing Time Point
Dexmedetomidine
Control
Sum of Behavior Scores
(mean/number of animals)
Screening
18.75/71
19.01/73
Prior to dose 1
5.04/71
4.96/73
1 hour post-dose 1
3.75/68
4.72/71
Prior to dose 2
7.93/68
9.11/70
1 hour post-dose 2
4.21/52
9.1/60
Prior to dose 3
8.26/38
17.5/44
1 hour post-dose 3
6.35/34
11.0/39
Prior to dose 4
6.92/12
12.95/21
1 hour post-dose 4
5.42/12
12.7/21
Of the different types of behaviors, dogs treated with dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel displayed less panting, trembling and trying to hide than those treated with the control gel.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
SILEO is packaged in HDPE dosing syringe enabling doses from 0.25 to 3 ml. The syringe is fitted with plunger, dosing ring and end cap. Each syringe is further packed into a carton with a label and a leaflet.
Package sizes: (1 syringe per carton) 1 x 3 ml, 3 x 3 ml, 5 x 3 ml,
10 x 3 ml, 20 x 3 ml.
Not all package sizes may be marketed. -
STORAGE INFORMATION
SILEO is packaged in HDPE dosing syringe enabling doses from 0.25 to 3 ml. The syringe is fitted with plunger, dosing ring and end cap. Each syringe is further packed into a carton with a label and a leaflet.
Package sizes: (1 syringe per carton) 1 x 3 ml, 3 x 3 ml, 5 x 3 ml, 10 x 3 ml, 20 x 3 ml.
Not all package sizes may be marketed.
STORAGE INFORMATION:
Store unopened and opened syringes in the original package at controlled room temperature 20-25°C (68-77°F) with excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F). Use syringe contents within 2 weeks after opening the syringe.
SILEO® is a trademark of Orion Corporation.
Mfd by:
Orion Corporation
Turku, Finland
Dist by:
Zoetis Inc.
Kalamazoo, MI 49007
Made in Finland
Revised: July, 2017
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
KEEP THIS CLIENT INFORMATION SHEET IN THE CARTON WITH THE SILEO DOSING SYRINGE
REVIEW PRIOR TO GIVING EACH DOSE TO YOUR DOGSILEO (dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel)
CLIENT INFORMATION SHEET FOR OWNER/HANDLER USE AND SAFETY
This sheet summarizes the basic information about SILEO and does not replace the instructions from your veterinarian. Talk to your veterinarian if you have questions regarding any part of this information or if you want to know more about SILEO. The syringe must be used in order to correctly dose the drug to your dog. You may use either a full, unused syringe or a partially used syringe that contains enough gel for the desired dose.
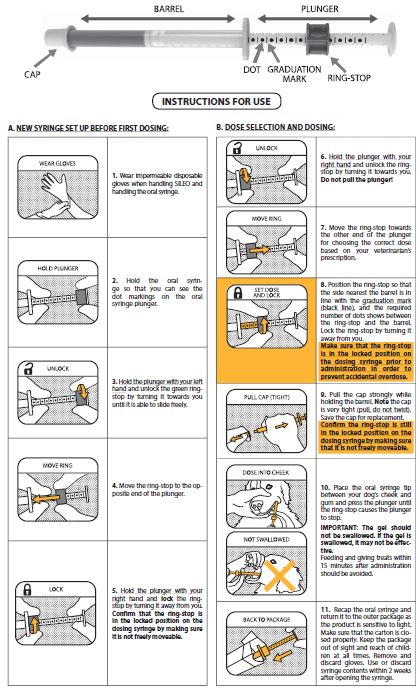
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
What is SILEO?
SILEO is a prescription product containing dexmedetomidine hydrochloride. It is used to treat noise aversion in dogs. Typical signs of anxiety and fear associated with noise aversion are panting, trembling , pacing, seeking people, trying to hide, trying to escape, freezing behavior, refusing to eat food or treats, inappropriate urination and/or defecation, and salivation. SILEO is packaged in a syringe that can be used to apply more than one dose. The medication should not be swallowed by your dog but should be placed in the dog’s mouth between the cheek and gum, so that it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. If SILEO is swallowed, it may not be effective. If you think this has happened, you should wait for two hours and if your dog is showing signs of fear and/or anxiety, then administer another dose.
How should the product be handled?
You should wear impermeable disposable gloves when administering the product and when handling the dosing syringe. Avoid administering the product if pregnant, as exposure may induce uterine contractions and/or decrease fetal blood pressure.
When to administer and what should I expect after administering SILEO?
The first dose of SILEO should be given immediately after your dog shows first signs of fear and/or anxiety associated with noise, or when the typical noise stimulus (e.g. sound of fireworks) inducing anxiety and/or fear in your dog is detected. If the dose for your dog is more than 6 dots, divide the dose between both sides of the mouth. The drug takes effect after approximately 30 minutes to one hour. Your dog should show less intense noise aversion behavior, despite the ongoing noise. Some dogs might be more sensitive to the drug; if your dog appears drowsy, keep it warm and do not offer food or water until the effect of the drug has worn off. This will normally happen within a few hours.
What should I do if SILEO does not work?
If you think that SILEO is not working, do not re-dose and contact your veterinarian to discuss further treatment options.
If needed, is it possible to give another dose of SILEO?
If noise lasts longer than 2-3 hours and your dog is still showing signs of fear and/or anxiety or the signs of fear and anxiety reappear, you may need to give your dog another dose. To avoid overdosing, there should always be at least two hours’ pause between dosages. Dogs sedated from previous dosing should not be given SILEO. No more than 5 doses can be given during one noise event. You can use a partially used syringe again within 48 hours after initial opening, if there is enough gel for a complete dose for your dog. To minimize the risk of incorrect dosing, do not use a partially used syringe that does not have enough gel for a complete dose. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of according to local law and Federal prescription drug disposal guidelines. Ask your veterinarian for this information.
What should I do if I have accidently given my dog too much SILEO?
Contact your veterinarian immediately.
What if I get the gel in my eyes, nose, or mouth?
The drug can be absorbed into your body through your eyes, nose, or mouth. If it comes in contact with your eyes, nose, or mouth, flush with water for 15 minutes. If wearing contact lenses, eyes should be rinsed first, then remove contact lenses and continue rinsing, then seek medical advice immediately. If the drug is absorbed into your body, it can cause symptoms such as lowered blood pressure (which may result in dizziness; fainting; lack of concentration; blurred vision; nausea; cold, clammy, or pale skin; rapid, shallow breathing), sleepiness, and slower heart rate. Share the package information with your physician and tell the physician that the product contains an alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist.
What if I get the gel on my skin?
You should wear impermeable disposable gloves when administering this product. If you have cuts or chapped skin, the drug can be absorbed into your body. In case of skin contact, wash immediately with large amounts of water. Remove contaminated clothing. Contact your physician if you have any questions or concerns. To report adverse reactions, call: 1-888-963-8471.
What else should I know about SILEO?
As with all prescription medicine, SILEO should only be given to the dog for which it was prescribed. This sheet provides a summary of information about SILEO. If you have any questions or concerns about SILEO or its effects on your dog, talk to your veterinarian or health care provider.
Which dogs should not take SILEO?
Dogs with severe cardiovascular, respiratory, liver or kidney disease or in dogs sedated from previous dosing should not be given SILEO.
What are the possible side effects that may occur in my dog after being given SILEO?
Possible side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, sedation, decreased heart rate, decreased respiratory rate and pale gums.
How do I store SILEO?
Store unopened and opened syringes at room temperature in the original package, as SILEO is sensitive to light. If syringe contents are not used within 48 hours after opening the syringe, the syringe should be discarded. Keep the package out of sight and reach of children at all times.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Carton
Sileo
(dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel)
0.09 mg/mL
For treatment of noise aversion in dogs.
Caution: Federal law restricts this
drug to use by or on the order of
a licensed veterinarian.Mfd by: Orion Corporation
Turku, Finland
Dist by: Zoetis Inc.
Kalamazoo, MI 49007
Made in Finland
NADA 141-456, Approved by FDA
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Carton
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SILEO
dexmedetomidine gelProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 54771-1050 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DEXMEDETOMIDINE (UNII: 67VB76HONO) (DEXMEDETOMIDINE - UNII:67VB76HONO) DEXMEDETOMIDINE 0.09 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 54771-1050-1 1 in 1 CARTON 1 3 mL in 1 SYRINGE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141456 12/18/2015 Labeler - Zoetis Inc. (828851555) Registrant - Orion Corporation (539763727)
Trademark Results [Sileo]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 SILEO 98241146 not registered Live/Pending |
SILEO HEALTH AND WELLNESS LLC 2023-10-26 |
 SILEO 88809022 not registered Live/Pending |
Sileo Capital, LLC 2020-02-25 |
 SILEO 88651389 not registered Live/Pending |
Know 2Solutions, LLC 2019-10-11 |
 SILEO 86170474 4666022 Live/Registered |
Orion Corporation 2014-01-21 |
 SILEO 79186775 5111742 Live/Registered |
Orion Corporation 2016-03-10 |
 SILEO 77355631 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Hunter Douglas Inc. 2007-12-19 |
 SILEO 76388988 2717248 Live/Registered |
Lombardini S.r.l. 2002-03-28 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.