Estrumate® (cloprostenol injection)
Estrumate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Estrumate by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., Vet Pharma Friesoythe GmbH, Piramal Healthcare UK Limited, Cayman Pharma s.r.o.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
ESTRUMATE- cloprostenol injection
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
----------
Estrumate®
(cloprostenol injection)
Estrumate® (cloprostenol sodium) is a synthetic prostaglandin analogue structurally related to prostaglandin F2 α (PGF2 α). Each mL of the colorless aqueous solution contains 263 mcg of cloprostenol sodium (equivalent to 250 mcg of cloprostenol) in a sodium citrate, anhydrous citric acid and sodium chloride buffer containing 0.1% w/v chlorocresol BP as a bactericide. pH is adjusted, as necessary, with sodium hydroxide or citric acid.
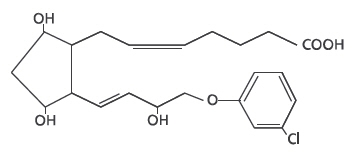
ACTION:
Estrumate causes functional and morphological regression of the corpus luteum (luteolysis) in cattle. In normal, nonpregnant cycling animals, this effect on the life span of the corpus luteum usually results in estrus 2 to 5 days after treatment. In animals with prolonged luteal function (pyometra, mummified fetus, and luteal cysts), the induced luteolysis usually results in resolution of the condition and return to cyclicity. Pregnant animals may abort depending on the stage of gestation.
INDICATIONS:
For intramuscular use to induce luteolysis in beef and dairy cattle. The luteolytic action of Estrumate can be utilized to manipulate the estrous cycle to better fit certain management practices, to terminate pregnancies resulting from mismatings, and to treat certain conditions associated with prolonged luteal function.
RECOMMENDED USES:
Unobserved or nondetected estrus
Cows which are not detected in estrus, although ovarian cyclicity continues, can be treated with Estrumate if a mature corpus luteum is present. Estrus is expected to occur 2 to 5 days following injection, at which time animals may be inseminated. Treated cattle should be inseminated at the usual time following detection of estrus. If estrous detection is not desirable or possible, treated animals may be inseminated twice at about 72 and 96 hours postinjection.
Pyometra or Chronic Endometritis
Damage to the reproductive tract at calving or postpartum retention of the placenta often leads to infection and inflammation of the uterus (endometritis). Under certain circumstances, this may progress into chronic endometritis with the uterus becoming distended with purulent matter. This condition, commonly referred to as pyometra, is characterized by a lack of cyclical estrous behavior and the presence of a persistent corpus luteum. Induction of luteolysis with Estrumate usually results in evacuation of the uterus and a return to normal cyclical activity within 14 days after treatment. After 14 days posttreatment, recovery rate of treated animals will not be different than that of untreated cattle.
Mummified Fetus
Death of the conceptus during gestation may be followed by its degeneration and dehydration. Induction of luteolysis with Estrumate usually results in expulsion of the mummified fetus from the uterus. (Manual assistance may be necessary to remove the fetus from the vagina). Normal cyclical activity usually follows.
Luteal Cysts
A cow may be noncyclic due to the presence of a luteal cyst (a single, anovulatory follicle with a thickened wall which is accompanied by no external signs and by no changes in palpable consistency of the uterus). Treatment with Estrumate can restore normal ovarian activity by causing regression of the luteal cyst.
Pregnancies from Mismating
Unwanted pregnancies can be safely and efficiently terminated from 1 week after mating until about 5 months of gestation. The induced abortion is normally uncomplicated and the fetus and placenta are usually expelled about 4 to 5 days after the injection with the reproductive tract returning to normal soon after the abortion. The ability of Estrumate to induce abortion decreases beyond the fifth month of gestation while the risk of dystocia and its consequences increases. Estrumate has not been sufficiently tested under feedlot conditions; therefore, recommendations cannot be made for its use in heifers placed in feedlots.
Controlled Breeding
The luteolytic action of Estrumate can be utilized to schedule estrus and ovulation for an individual cycling animal or a group of animals. This allows control of the time at which cycling cows or heifers can be bred. Estrumate can be incorporated into a controlled breeding program by the following methods:
- Single Estrumate injection: Only animals with a mature corpus luteum should be treated to obtain maximum response to the single injection. However, not all cycling cattle should be treated since a mature corpus luteum is present for only 11 to 12 days of the 21-day cycle.
Prior to treatment, cattle should be examined rectally and found to be anatomically normal, be nonpregnant, and have a mature corpus luteum. If these criteria are met, estrus is expected to occur 2 to 5 days following injection, at which time animals may be inseminated. Treated cattle should be inseminated at the usual time following detection of estrus. If estrous detection is not desirable or possible, treated animals may be inseminated either once at about 72 hours or twice at about 72 and 96 hours post injection.
With a single injection program, it may be desirable to assess the cyclicity status of the herd before Estrumate treatment. This can be accomplished by heat detecting and breeding at the usual time following detection of estrus for a 6-day period, all prior to injection. If by the sixth day the cyclicity status appears normal (approximately 25%-30% detected in estrus), all cattle not already inseminated should be palpated for normality, nonpregnancy, and cyclicity, then injected with Estrumate. Breeding should then be continued at the usual time following signs of estrus on the seventh and eighth days. On the ninth and tenth days, breeding may continue at the usual time following detection of estrus, or all cattle not already inseminated may be bred either once on the ninth day (at about 72 hours post injection) or on both the ninth and tenth days (at about 72 and 96 hours post injection). - Double Estrumate injections: prior to treatment, cattle should be examined rectally and found to be anatomically normal, nonpregnant, and cycling (the presence of a mature corpus luteum is not necessary when the first injection of a double injection regimen is given). A second injection should be given 11 days after the first injection. In normal, cycling cattle, estrus is expected 2 to 5 days following the second injection. Treated cattle should be inseminated at the usual time following detection of estrus. If estrous detection is not desirable or possible, treated animals may be inseminated either once at about 72 hours or twice at about 72 and 96 hours following the second Estrumate injection.
Many animals will come into estrus following the first injection; these animals can be inseminated at the usual time following detected estrus. Animals not inseminated should receive a second injection 11 days after the first injection. Animals receiving both injections may be inseminated at the usual time following detection of estrus or may be inseminated either once at about 72 hours or twice at about 72 and 96 hours post second injection.
Any controlled breeding program recommended should be completed by either:- observing animals (especially during the third week after injection) and inseminating or hand mating any animals returning to estrus, or
- turning in clean-up bull(s) 5 to 7 days after the last injection of Estrumate to cover any animals returning to estrus.
REQUIREMENTS FOR CONTROLLED BREEDING PROGRAMS:
A variety of programs can be designed to best meet the needs of individual management systems. A controlled breeding program should be selected which is appropriate for the existing circumstances and management practices.
Before a controlled breeding program is planned, the producer's objectives must be examined and he must be made aware of the projected results and limitations. The producer and his consulting veterinarian should review the operation's breeding history, herd health, and nutritional status and agree that a controlled breeding program is practical in the producer's specific situation. For any successful controlled breeding program:
- cows and heifers must be normal, nonpregnant, and cycling (rectal palpation should be performed);
- cattle must be in a fit and thrifty breeding condition and on an adequate or increasing plane of nutrition;
- proper program planning and record keeping are essential;
- if artificial insemination is used, it must be performed by competent inseminators using high-quality semen.
It is important to understand that Estrumate is effective only in animals with a mature corpus luteum (ovulation must have occurred at least 5 days prior to treatment). This must be considered when breeding is intended following a single Estrumate injection.
SAFETY AND TOXICITY:
At 50 and 100 times the recommended dose, mild side effects may be detected in some cattle. These include increased uneasiness, slight frothing, and milk let-down.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Estrumate should not be administered to a pregnant animal whose calf is not to be aborted.
PRECAUTIONS:
There is no effect on fertility following the single or double dosage regimen when breeding occurs at induced estrus or at 72 and 96 hours post treatment. Conception rates may be lower than expected in those fixed time breeding programs which omit the second insemination (ie, the insemination at or near 96 hours). This is especially true if a fixed time insemination is used following a single Estrumate injection. As with all parenteral products, careful aseptic techniques should be employed to decrease the possibility of post injection bacterial infection. Antibiotic therapy should be employed at the first sign of infection.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Two mL of Estrumate (500 mcg of cloprostenol) should be administered by INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION for all indications in both beef and dairy cattle.
Do not puncture stopper more than 12 times.
WARNINGS
For veterinary use only.
Women of childbearing age, asthmatics, and persons with bronchial and other respiratory problems should exercise extreme caution when handling this product. In the early stages, women may be unaware of their pregnancies. Estrumate is readily absorbed through the skin and may cause abortion and/or bronchiospasms; direct contact with the skin should therefore be avoided. Accidental spillage on the skin should be washed off immediately with soap and water.
STORAGE CONDITIONS:
- Protect from light.
- Store in container.
- Store at controlled room temperature 59°-86° F. (15°-30° C).
- USE WITHIN 28 DAYS OF FIRST USE.
CAUTION:
Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Made in Germany.
Copyright © 2013, Intervet Inc (d/b/a Merck Animal Health) a subsidiary of Merck & Co. Madison, NJ 07940
All rights reserved. Code No. 065502 Rev. 09/16
176042 R3
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mL Vial Label
10 Doses
20 mL
Estrumate®
(cloprostenol sodium)
Equivalent to 250 mcg cloprostenol/mL
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this
drug to use by or on the order of a
licensed veterinarian.
MERCK
Animal Health

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mL Vial Carton
NDC 0061-1266-02
20 mL
Estrumate®
(cloprostenol injection)
An Analogue of
Prostaglandin F2α for
Intramuscular Injection
in Beef and Dairy Cattle.
Equivalent to 250 mcg
cloprostenol / mL
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law
restricts this drug to use by or on
the order of a licensed veterinarian.
FOR VETERINARY USE ONLY
20 mL
10 Doses
MERCK
Animal Health

| ESTRUMATE
cloprostenol injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. (001317601) |
Trademark Results [Estrumate]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ESTRUMATE 77084378 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
INTERVET INC. 2007-01-17 |
 ESTRUMATE 73086007 1102497 Live/Registered |
IMPERIAL CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES LIMITED 1976-05-04 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
