KEVZARA- sarilumab injection, solution
KEVZARA by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
KEVZARA by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC, Sanofi Winthrop Industrie, Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Genzyme Corporation, Genzyme Ireland Limited, Nelson Laboratories, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KEVZARA® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KEVZARA.
KEVZARA (sarilumab) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS INFECTIONS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Serious infections leading to hospitalization or death including bacterial, viral, invasive fungal, and other opportunistic infections have occurred in patients receiving KEVZARA. (5.1)
- If a serious infection develops, interrupt KEVZARA until the infection is controlled. (5.1)
- Cases of tuberculosis (TB) have been reported. Prior to starting KEVZARA, test for latent TB; if positive, start treatment for TB. (5.1)
- Closely monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection during treatment with KEVZARA. (5.1)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KEVZARA® is an interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor antagonist indicated for treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- KEVZARA may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate (MTX) or other conventional DMARDs. (2.1)
- The recommended dosage of KEVZARA is 200 mg once every two weeks, administered as a subcutaneous injection. (2.1)
General Considerations for Administration
- KEVZARA initiation is not recommended in patients with ANC less than 2000/mm3, platelets less than150,000/mm3 or liver transaminases above 1.5 times ULN. (2.2)
Dosage Modifications
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
KEVZARA is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to sarilumab or any of the inactive ingredients. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serious Infections: Avoid KEVZARA use during an active infection. (5.1)
- Neutropenia, Thrombocytopenia, Elevated Liver Enzymes, Lipid Abnormalities: Monitor laboratory parameters. (5.2)
- Gastrointestinal (GI) Perforation: Risk may be increased with concurrent diverticulitis or concomitant use of NSAIDs or corticosteroids. Promptly evaluate acute abdominal signs or symptoms. (5.3)
- Hypersensitivity reactions. (5.5)
- Live vaccines: Avoid use with KEVZARA due to the risk of infection. Follow vaccination guidelines. (5.7, 7.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence at least 3%) are neutropenia, increased ALT, injection site erythema, upper respiratory infections and urinary tract infections. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact sanofi-aventis at 1-800-633-1610 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Discontinue drug or nursing taking into consideration importance of drug to mother. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 4/2018
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS INFECTIONS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 General Considerations for Administration
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Laboratory Abnormalities or Serious Infection
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Infections
5.2 Laboratory Abnormalities
5.3 Gastrointestinal Perforation
5.4 Immunosuppression
5.5 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.6 Active Hepatic Disease and Hepatic Impairment
5.7 Live Vaccines
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Immunogenicity
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Use with Other Drugs for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
7.2 Interactions with CYP450 Substrates
7.3 Live Vaccines
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS INFECTIONS
Patients treated with KEVZARA are at increased risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Opportunistic infections have also been reported in patients receiving KEVZARA. Most patients who developed infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids.
Avoid use of KEVZARA in patients with an active infection.
Reported infections include:
- Active tuberculosis, which may present with pulmonary or extrapulmonary disease. Patients should be tested for latent tuberculosis before KEVZARA use and during therapy. Treatment for latent infection should be initiated prior to KEVZARA use.
- Invasive fungal infections, such as candidiasis, and pneumocystis. Patients with invasive fungal infections may present with disseminated, rather than localized, disease.
- Bacterial, viral and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens.
Closely monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection during treatment with KEVZARA. If a serious infection develops, interrupt KEVZARA until the infection is controlled.
Consider the risks and benefits of treatment with KEVZARA prior to initiating therapy in patients with chronic or recurrent infection.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
KEVZARA may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate (MTX) or other conventional DMARDs.
The recommended dosage of KEVZARA is 200 mg once every two weeks given as a subcutaneous injection.
Reduce dose to 150 mg once every two weeks for management of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia and elevated liver enzymes [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
2.2 General Considerations for Administration
- KEVZARA initiation is not recommended in patients with an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) less than 2000 per mm3, platelet count less than 150,000 per mm3, or who have ALT or AST above 1.5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Prior to initiating KEVZARA, test patients for latent tuberculosis (TB). If positive, consider treating for TB prior to KEVZARA use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Avoid using KEVZARA with biological DMARDs because of the possibility of increased immunosuppression and increased risk of infection. The concurrent use of KEVZARA with biological DMARDs such as TNF antagonists, IL-1R antagonists, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies and selective co-stimulation modulators has not been studied.
- Avoid KEVZARA use in patients with active infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
- KEVZARA is intended for use under the guidance of a healthcare professional. A patient may self-inject KEVZARA or the patient's caregiver may administer KEVZARA. Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the preparation and administration of KEVZARA prior to use according to the Instructions for Use (IFU).
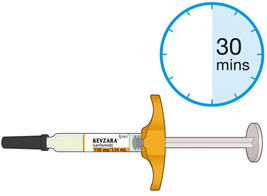
- Allow the pre-filled syringe to sit at room temperature for 30 minutes prior to subcutaneous injection. Do not warm KEVZARA in any other way.
- If using a pre-filled pen, allow the pre-filled pen to sit at room temperature for 60 minutes prior to subcutaneous injection. Do not warm KEVZARA in any other way.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. KEVZARA solution should be clear and colorless to pale yellow. Do not use if the solution is cloudy, discolored or contains particles, or if any part of the pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen appears to be damaged.
- Instruct patients to inject the full amount in the syringe or pen (1.14 mL), which provides 200 mg or 150 mg of KEVZARA, according to the directions provided in the IFU.
- Rotate injection sites with each injection. Do not inject into skin that is tender, damaged, or has bruises or scars.
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Laboratory Abnormalities or Serious Infection
If a patient develops a serious infection, hold treatment with KEVZARA until the infection is controlled.
Modify dosage in case of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia or liver enzyme elevations (see Table 1). For treatment initiation criteria, see Dosage and Administration (2.2).
Table 1: KEVZARA Dosage Modification for Neutropenia, Thrombocytopenia, or Elevated Liver Enzymes Low Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC)
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]Lab Value (cells/mm3) Recommendation ANC greater than 1000 Maintain current dosage of KEVZARA. ANC 500–1000 Hold treatment with KEVZARA until ANC greater than 1000.
KEVZARA can then be resumed at 150 mg every two weeks and increased to 200 mg every two weeks as clinically appropriate.ANC less than 500 Discontinue KEVZARA. Low Platelet Count
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]Lab Value (cells/mm3) Recommendation 50,000–100,000 Hold treatment with KEVZARA until platelets greater than 100,000.
KEVZARA can then be resumed at 150 mg every two weeks and increased to 200 mg every two weeks as clinically appropriate.Less than 50,000 If confirmed by repeat testing, discontinue KEVZARA. Liver Enzyme Abnormalities
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]Lab Value Recommendation ALT greater than ULN to 3 times ULN or less Consider dosage modification of concomitant DMARDs as clinically appropriate. ALT greater than 3 times ULN to 5 times ULN or less Hold treatment with KEVZARA until ALT less than 3 times ULN.
KEVZARA can then be resumed at 150 mg every two weeks and increased to 200 mg every two weeks as clinically appropriate.ALT greater than 5 times ULN Discontinue KEVZARA. - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
KEVZARA is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to sarilumab or any of the inactive ingredients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Infections
Serious and sometimes fatal infections due to bacterial, mycobacterial, invasive fungal, viral, or other opportunistic pathogens have been reported in patients receiving immunosuppressive agents including KEVZARA for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The most frequently observed serious infections with KEVZARA included pneumonia and cellulitis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Among opportunistic infections, tuberculosis, candidiasis, and pneumocystis were reported with KEVZARA. Some patients presented with disseminated rather than localized disease and were often taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids, which in addition to RA may predispose them to infections. While not reported in KEVZARA clinical studies, other serious infections (e.g., histoplasmosis, cryptococcus, aspergillosis) have been reported in patients receiving other immunosuppressive agents for the treatment of RA.
Avoid use of KEVZARA in patients with an active infection, including localized infections. Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating KEVZARA in patients who have:
- chronic or recurrent infection;
- a history of serious or opportunistic infections;
- underlying conditions, in addition to RA, that may predispose them to infection;
- been exposed to tuberculosis; or
- lived in or traveled to areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses.
Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during treatment with KEVZARA, as signs and symptoms of acute inflammation may be lessened due to suppression of the acute phase reactants [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Hold treatment with KEVZARA if a patient develops a serious infection or an opportunistic infection.
Perform prompt and complete diagnostic testing appropriate for an immunocompromised patient who develops a new infection during treatment with KEVZARA; initiate appropriate antimicrobial therapy, and closely monitor the patient.
Tuberculosis
Evaluate patients for tuberculosis (TB) risk factors and test for latent infection prior to initiating treatment with KEVZARA. Treat patients with latent TB with standard antimycobacterial therapy before initiating KEVZARA. Consider anti-TB therapy prior to initiation of KEVZARA in patients with a past history of latent or active TB in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed, and for patients with a negative test for latent TB but having risk factors for TB infection. When considering anti-TB therapy, consultation with a physician with expertise in TB may be appropriate.
Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of TB including patients who tested negative for latent TB infection prior to initiating therapy.
Viral Reactivation
Viral reactivation has been reported with immunosuppressive biologic therapies. Cases of herpes zoster were observed in clinical studies with KEVZARA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The risk of Hepatitis B reactivation with KEVZARA is unknown since patients who were at risk for reactivation were excluded.
5.2 Laboratory Abnormalities
Neutropenia
Treatment with KEVZARA was associated with a higher incidence of decrease in absolute neutrophil count (ANC), including neutropenia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- Assess neutrophil count prior to initiation of KEVZARA and monitor neutrophil count 4 to 8 weeks after start of therapy and every 3 months thereafter [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. For recommendations regarding initiating KEVZARA therapy and dosage modifications based on ANC results see Dosage and Administration (2.2 and 2.4).
- Based on the pharmacodynamics of the changes in ANC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)], use results obtained at the end of the dosing interval when considering dose modification.
Thrombocytopenia
Treatment with KEVZARA was associated with a reduction in platelet counts in clinical studies [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- Assess platelet count prior to initiation of KEVZARA and monitor platelets 4 to 8 weeks after start of therapy and every 3 months thereafter. For recommendations regarding initiating KEVZARA therapy and dosage modifications based on platelet counts see Dosage and Administration (2.2 and 2.4).
Elevated Liver Enzymes
Treatment with KEVZARA was associated with a higher incidence of transaminase elevations. These elevations were transient and did not result in any clinically evident hepatic injury in clinical studies [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Increased frequency and magnitude of these elevations were observed when potentially hepatotoxic drugs (e.g., MTX) were used in combination with KEVZARA.
- Assess ALT/AST levels prior to initiation of KEVZARA and monitor ALT and AST levels 4 to 8 weeks after start of therapy and every 3 months thereafter. When clinically indicated, consider other liver function tests such as bilirubin. For recommendations regarding initiating KEVZARA therapy and dosage modifications based on transaminase elevations see Dosage and Administration (2.2 and 2.4).
Lipid Abnormalities
Treatment with KEVZARA was associated with increases in lipid parameters such as LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and/or triglycerides [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- Assess lipid parameters approximately 4 to 8 weeks following initiation of treatment with KEVZARA, then at approximately 6 month intervals.
- Manage patients according to clinical guidelines for the management of hyperlipidemia.
5.3 Gastrointestinal Perforation
Gastrointestinal perforations have been reported in clinical studies, primarily as complications of diverticulitis. GI perforation risk may be increased with concurrent diverticulitis or concomitant use of NSAIDs or corticosteroids. Promptly evaluate patients presenting with new onset abdominal symptoms [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.4 Immunosuppression
Treatment with immunosuppressants may result in an increased risk of malignancies. The impact of treatment with KEVZARA on the development of malignancies is not known but malignancies were reported in clinical studies [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.5 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in association with KEVZARA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Hypersensitivity reactions that required treatment discontinuation were reported in 0.3% of patients in controlled RA trials. Injection site rash, rash, and urticaria were the most frequent hypersensitivity reactions. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction. If anaphylaxis or other hypersensitivity reaction occurs, stop administration of KEVZARA immediately. Do not administer KEVZARA to patients with known hypersensitivity to sarilumab [see Contraindications (4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.6 Active Hepatic Disease and Hepatic Impairment
Treatment with KEVZARA is not recommended in patients with active hepatic disease or hepatic impairment, as treatment with KEVZARA was associated with transaminase elevations [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.7 Live Vaccines
Avoid concurrent use of live vaccines during treatment with KEVZARA due to potentially increased risk of infections; clinical safety of live vaccines during KEVZARA treatment has not been established. No data are available on the secondary transmission of infection from persons receiving live vaccines to patients receiving KEVZARA. The interval between live vaccinations and initiation of KEVZARA therapy should be in accordance with current vaccination guidelines regarding immunosuppressive agents [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
- Serious infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, elevated liver enzymes, lipid abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Gastrointestinal perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Immunosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
All patients in the safety data described below had moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis.
The safety of KEVZARA in combination with conventional DMARDs was evaluated based on data from seven studies, of which two were placebo-controlled, consisting of 2887 patients (long-term safety population). Of these, 2170 patients received KEVZARA for at least 24 weeks, 1546 for at least 48 weeks, 1020 for at least 96 weeks, and 624 for at least 144 weeks.
The pre-rescue placebo-controlled population includes patients from the two Phase 3 efficacy studies (Studies 1 and 2) from weeks 0 to 16 for Study 1 and weeks 0 to 12 for Study 2, and was used to assess common adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities prior to patients being permitted to switch from placebo to KEVZARA. In this population, 582 patients, 579 patients, and 579 patients received KEVZARA 200 mg, KEVZARA 150 mg, or placebo once every two weeks, respectively, in combination with conventional DMARDs.
The 52-week placebo-controlled population includes patients from one Phase 2 study of 12 week duration and two Phase 3 efficacy studies (one of 24 week duration and the other of 52 week duration). This placebo-controlled population includes all subjects from the double-blind, placebo-controlled periods from each study and was analyzed under their original randomization assignment. In this population, 661 patients, 660 patients, and 661 patients received KEVZARA 200 mg, KEVZARA 150 mg, or placebo once every two weeks, respectively, in combination with conventional DMARDs.
Most safety data are described for the pre-rescue population. For rarer events, the 52-week placebo-controlled population is used.
The most common serious adverse reactions were infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
The most frequent adverse reactions (occurring in at least 3% of patients treated with KEVZARA in combination with DMARDs) observed with KEVZARA in the clinical studies were neutropenia, increased ALT, injection site erythema, upper respiratory infections, and urinary tract infections.
In the pre-rescue placebo-controlled population, premature discontinuation due to adverse reactions occurred in 8%, 6% and 3% of patients treated with KEVZARA 200 mg, KEVZARA 150 mg, and placebo, respectively.
The most common adverse reaction (greater than 1%) that resulted in discontinuation of therapy with KEVZARA was neutropenia.
The use of KEVZARA as monotherapy was assessed in 132 patients, of which 67 received KEVZARA 200 mg and 65 patients received KEVZARA 150 mg without concomitant DMARDs. The safety profile was generally consistent with that in the population receiving concomitant DMARDs.
Overall Infections
In the pre-rescue placebo-controlled population, the rate of infections in the 200 mg and 150 mg KEVZARA + DMARD group was 110 and 105 events per 100 patient-years, respectively, compared to 81 events per 100 patient-years in the placebo + DMARD group. The most commonly reported infections (2% to 4% of patients) were upper respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, and nasopharyngitis.
In the 52-week placebo-controlled population, 0.8% of patients (5 patients) treated with KEVZARA 200 mg + DMARD, 0.6% (4 patients) treated with KEVZARA 150 mg + DMARD and 0.5% (3 patients) treated with placebo + DMARD had an event of herpes zoster [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
The overall rate of infections with KEVZARA + DMARD in the long-term safety population was consistent with rates in the controlled periods of the studies.
Serious Infections
In the pre-rescue population, the rate of serious infections in the 200 mg and 150 mg KEVZARA + DMARD group was 3.8 and 4.4 events per 100 patient-years, respectively, compared to 2.5 events per 100 patient-years in the placebo + DMARD group. In the 52-week placebo-controlled population, the rate of serious infections in the 200 mg and 150 mg KEVZARA + DMARD group was 4.3 and 3.0 events per 100 patient-years, respectively, compared to 3.1 events per 100 patient-years in the placebo + DMARD group.
In the long-term safety population, the overall rate of serious infections was consistent with rates in the controlled periods of the studies. The most frequently observed serious infections included pneumonia and cellulitis. Cases of opportunistic infection have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Gastrointestinal Perforation
In the 52-week placebo-controlled population, one patient on KEVZARA therapy experienced a gastrointestinal (GI) perforation (0.11 events per 100 patient-years).
In the long-term safety population, the overall rate of GI perforation was consistent with rates in the controlled periods of the studies. Reports of GI perforation were primarily reported as complications of diverticulitis including lower GI perforation and abscess. Most patients who developed GI perforations were taking concomitant nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids. The contribution of these concomitant medications relative to KEVZARA in the development of GI perforations is not known [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
In the pre-rescue placebo-controlled population, the proportion of patients who discontinued treatment due to hypersensitivity reactions was higher among those treated with KEVZARA (0.3% in 200 mg, 0.2% in 150 mg) than placebo (0%). The rate of discontinuations due to hypersensitivity in the long-term safety population was consistent with the placebo-controlled period.
Injection Site Reactions
In the pre-rescue placebo-controlled population, injection site reactions were reported in 7% of patients receiving KEVZARA 200 mg, 6% receiving KEVZARA 150 mg, and 1% receiving placebo. These injection site reactions (including erythema and pruritus) were mild in severity for the majority of patients and necessitated drug discontinuation in 2 (0.2%) patients receiving KEVZARA.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Decreased neutrophil count
In the pre-rescue placebo-controlled population, decreases in neutrophil counts less than 1000 per mm3 occurred in 6% and 4% of patients in the 200 mg KEVZARA + DMARD and 150 mg KEVZARA + DMARD group, respectively, compared to no patients in the placebo + DMARD groups. Decreases in neutrophil counts less than 500 per mm3 occurred in 0.7% of patients in both the 200 mg KEVZARA + DMARD and 150 mg KEVZARA + DMARD groups. Decrease in ANC was not associated with the occurrence of infections, including serious infections.
In the long-term safety population, the observations on neutrophil counts were consistent with what was seen in the placebo-controlled clinical studies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Decreased platelet count
In the pre-rescue placebo-controlled population, decreases in platelet counts less than 100,000 per mm3 occurred in 1% and 0.7% of patients on 200 mg and 150 mg KEVZARA + DMARD, respectively, compared to no patients on placebo + DMARD, without associated bleeding events.
In the long-term safety population, the observations on platelet counts were consistent with what was seen in the placebo-controlled clinical studies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Elevated liver enzymes
Liver enzyme elevations in the pre-rescue placebo-controlled population (KEVZARA + DMARD or placebo + DMARD) are summarized in Table 2. In patients experiencing liver enzyme elevation, modification of treatment regimen, such as interruption of KEVZARA or reduction in dose, resulted in decrease or normalization of liver enzymes [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. These elevations were not associated with clinically relevant increases in direct bilirubin, nor were they associated with clinical evidence of hepatitis or hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Table 2: Incidence of Liver Enzyme Elevations in Adults with Moderately to Severely Active Rheumatoid Arthritis* Placebo + DMARD
N=579KEVZARA 150 mg + DMARD
N=579KEVZARA 200 mg + DMARD
N=582ULN = Upper Limit of Normal - * Phase 3 placebo-controlled safety population through the pre-rescue period
AST Greater than ULN to 3 times ULN or less 15% 27% 30% Greater than 3 times ULN to 5 times ULN 0% 1% 1% Greater than 5 times ULN 0% 0.7% 0.2% ALT Greater than ULN to 3 times ULN or less 25% 38% 43% Greater than 3 times ULN to 5 times ULN 1% 4% 3% Greater than 5 times ULN 0% 1% 0.7% Lipid Abnormalities
Lipid parameters (LDL, HDL, and triglycerides) were first assessed at 4 weeks following initiation of KEVZARA + DMARDs in the placebo-controlled population. Increases were observed at this time point with no additional increases observed thereafter. Changes in lipid parameters from baseline to Week 4 are summarized below:
- Mean LDL increased by 12 mg/dL in the KEVZARA 150 mg every two weeks + DMARD group and 16 mg/dL in the KEVZARA 200 mg every two weeks + DMARD group.
- Mean triglycerides increased by 20 mg/dL in the KEVZARA 150 mg every two weeks + DMARD group and 27 mg/dL in the KEVZARA 200 mg every two weeks + DMARD group.
- Mean HDL increased by 3 mg/dL in both the KEVZARA 150 mg every two weeks + DMARD and KEVZARA 200 mg every two weeks + DMARD groups.
In the long-term safety population, the observations in lipid parameters were consistent with what was observed in the placebo-controlled clinical studies.
Malignancies
In the 52-week placebo-controlled population, 9 malignancies (exposure-adjusted event rate of 1.0 event per 100 patient-years) were diagnosed in patients receiving KEVZARA+ DMARD compared to 4 malignancies in patients in the control group (exposure-adjusted event rate of 1.0 event per 100 patient-years).
In the long-term safety population, the rate of malignancies was consistent with the rate observed in the placebo-controlled period [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Other Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions occurring in 2% or more of patients on KEVZARA + DMARD and greater than those observed in patients on placebo + DMARD are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3: Common Adverse Reactions* in Adults with Moderately to Severely Active Rheumatoid Arthritis † Preferred Term Placebo + DMARD
(N=579)KEVZARA 150 mg + DMARD
(N=579)KEVZARA 200 mg + DMARD
(N=582)- * Adverse reactions occurring in 2% or more in the 150 mg KEVZARA + DMARD or 200 mg KEVZARA + DMARD groups and greater than observed in Placebo + DMARD
- † Pre-rescue, placebo-controlled population
Neutropenia 0.2% 7% 10% Alanine aminotransferase increased 2% 5% 5% Injection site erythema 0.9% 5% 4% Injection site pruritus 0.2% 2% 2% Upper respiratory tract infection 2% 4% 3% Urinary tract infection 2% 3% 3% Hypertriglyceridemia 0.5% 3% 1% Leukopenia 0% 0.9% 2% Medically relevant adverse reactions occurring at an incidence less than 2% in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with KEVZARA in controlled studies was oral herpes.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to sarilumab in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
In the pre-rescue population, 4.0% of patients treated with KEVZARA 200 mg + DMARD, 5.7% of patients treated with KEVZARA 150 mg + DMARD and 1.9% of patients treated with placebo + DMARD, exhibited an anti-drug antibody (ADA) response. Neutralizing antibodies (NAb) were detected in 1.0% of patients on KEVZARA 200 mg + DMARD, 1.6% of patients on KEVZARA 150 mg + DMARD, and 0.2% of patients on placebo + DMARD.
In patients treated with KEVZARA monotherapy, 9.2% of patients exhibited an ADA response with 6.9% of patients also exhibiting NAbs. Prior to administration of KEVZARA, 2.3% of patients exhibited an ADA response.
No correlation was observed between ADA development and either loss of efficacy or adverse reactions.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Use with Other Drugs for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Population pharmacokinetic analyses did not detect any effect of methotrexate (MTX) on sarilumab clearance. KEVZARA has not been investigated in combination with JAK inhibitors or biological DMARDs such as TNF antagonists [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
7.2 Interactions with CYP450 Substrates
Various in vitro and limited in vivo human studies have shown that cytokines and cytokine modulators can influence the expression and activity of specific cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes and therefore have the potential to alter the pharmacokinetics of concomitantly administered drugs that are substrates of these enzymes. Elevated interleukin-6 (IL-6) concentration may down-regulate CYP activity such as in patients with RA and hence increase drug levels compared to subjects without RA. Blockade of IL-6 signaling by IL-6Rα antagonists such as KEVZARA might reverse the inhibitory effect of IL-6 and restore CYP activity, leading to altered drug concentrations.
The modulation of IL-6 effect on CYP enzymes by KEVZARA may be clinically relevant for CYP substrates with a narrow therapeutic index, where the dose is individually adjusted. Upon initiation or discontinuation of KEVZARA, in patients being treated with CYP substrate medicinal products, perform therapeutic monitoring of effect (e.g., warfarin) or drug concentration (e.g., theophylline) and adjust the individual dose of the medicinal product as needed.
Exercise caution when coadministering KEVZARA with CYP3A4 substrate drugs where decrease in effectiveness is undesirable, e.g., oral contraceptives, lovastatin, atorvastatin, etc. The effect of KEVZARA on CYP450 enzyme activity may persist for several weeks after stopping therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Live Vaccines
Avoid concurrent use of live vaccines during treatment with KEVZARA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to KEVZARA during pregnancy. Physicians are encouraged to register patients and pregnant women are encouraged to register themselves by calling 1-877-311-8972.
Risk Summary
The limited human data with KEVZARA in pregnant women are not sufficient to inform drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. Monoclonal antibodies, such as sarilumab, are actively transported across the placenta during the third trimester of pregnancy and may affect immune response in the in utero exposed infant [see Clinical Considerations]. From animal data, and consistent with the mechanism of action, levels of IgG, in response to antigen challenge, may be reduced in the fetus/infant of treated mothers [see Clinical Considerations and Data]. In an animal reproduction study, consisting of a combined embryo-fetal and pre- and postnatal development study with monkeys that received intravenous administration of sarilumab, there was no evidence of embryotoxicity or fetal malformations with exposures up to approximately 84 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) [see Data]. The literature suggests that inhibition of IL-6 signaling may interfere with cervical ripening and dilatation and myometrial contractile activity leading to potential delays of parturition [see Data].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively. KEVZARA should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Monoclonal antibodies are increasingly transported across the placenta as pregnancy progresses, with the largest amount transferred during the third trimester. Risks and benefits should be considered prior to administering live or live-attenuated vaccines to infants exposed to KEVZARA in utero [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. From the animal data, and consistent with the mechanism of action, levels of IgG, in response to antigen challenge, may be reduced in the fetus/infant of treated mothers [see Data].
Data
Animal Data
In a combined embryo-fetal and pre- and postnatal development study, pregnant cynomolgus monkeys received sarilumab at intravenous doses of 0, 5, 15, or 50 mg/kg/week from confirmation of pregnancy at gestation day (GD) 20, throughout the period of organogenesis (up to approximately GD 50), and continuing to natural birth of infants at around GD 165. Maintenance of pregnancy was not affected at any doses. Sarilumab was not embryotoxic or teratogenic with exposures up to approximately 84 times the MRHD (based on AUC with maternal intravenous doses up to 50 mg/kg/week). Sarilumab had no effect on neonatal growth and development evaluated up to one month after birth. Sarilumab was detected in the serum of neonates up to one month after birth, suggesting that the antibody had crossed the placenta.
Following antigen challenge, decreased IgG titers attributed to the immunosuppressive action of sarilumab were evident in studies with older monkeys, with exposures up to approximately 80 times the MRHD (based on AUC with intravenous doses up to 50 mg/kg/week) and juvenile mice treated with an analogous antibody, which binds to murine IL-6Rα to inhibit IL-6 mediated signaling, at subcutaneous doses up to 200 mg/kg/week. These findings suggest the potential for decreased IgG titers, following antigen challenge, in infants of mothers treated with KEVZARA.
Parturition is associated with significant increases of IL-6 in the cervix and myometrium. The literature suggests that inhibition of IL-6 signaling may interfere with cervical ripening and dilatation and myometrial contractile activity leading to potential delays of parturition. For mice deficient in IL-6 (ll6-/- null mice), parturition was delayed relative to wild-type (ll6+/+) mice. Administration of recombinant IL-6 to ll6-/- null mice restored the normal timing of delivery.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
No information is available on the presence of sarilumab in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Maternal IgG is present in human milk. If sarilumab is transferred into human milk, the effects of local exposure in the gastrointestinal tract and potential limited systemic exposure in the infant to sarilumab are unknown. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes clear determination of the risk of KEVZARA to an infant during lactation; therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for KEVZARA and the potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from KEVZARA or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients in clinical studies of KEVZARA [see Clinical Studies (14)], 15% were 65 years of age and over, while 1.6% were 75 years and over. In clinical studies, no overall differences in safety and efficacy were observed between older and younger patients. The frequency of serious infection among KEVZARA and placebo-treated patients 65 years of age and older was higher than those under the age of 65. As there is a higher incidence of infections in the elderly population in general, caution should be used when treating the elderly.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
The safety and efficacy of KEVZARA have not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment, including patients with positive HBV or HCV serology [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. KEVZARA has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Sarilumab is a human recombinant monoclonal antibody of the IgG1 subclass that binds to the IL-6 receptor and has an approximate molecular weight of 150 kDa. Sarilumab is produced by recombinant DNA technology in Chinese Hamster Ovary cell suspension culture.
KEVZARA (sarilumab) injection for subcutaneous administration is supplied as a sterile, colorless to pale yellow, preservative-free solution of approximately pH 6.0. KEVZARA is supplied in a single-dose pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen. Each syringe or pen delivers 1.14 mL of solution containing 150 mg or 200 mg of sarilumab, arginine (8.94 mg), histidine (3.71 mg), polysorbate 20 (2.28 mg), sucrose (57 mg) and Water for Injection, USP.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sarilumab binds to both soluble and membrane-bound IL-6 receptors (sIL-6R and mIL-6R), and has been shown to inhibit IL-6-mediated signaling through these receptors. IL-6 is a pleiotropic pro-inflammatory cytokine produced by a variety of cell types including T- and B-cells, lymphocytes, monocytes, and fibroblasts. IL-6 has been shown to be involved in diverse physiological processes such as T-cell activation, induction of immunoglobulin secretion, initiation of hepatic acute phase protein synthesis, and stimulation of hematopoietic precursor cell proliferation and differentiation. IL-6 is also produced by synovial and endothelial cells leading to local production of IL-6 in joints affected by inflammatory processes such as rheumatoid arthritis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Following single-dose subcutaneous administration of sarilumab 200-mg and 150-mg in patients with RA, rapid reduction of CRP levels was observed. Levels were reduced to normal within 2 weeks after treatment initiation. Following single-dose sarilumab administration, in patients with RA, absolute neutrophil counts decreased to the nadir between 3 to 4 days and thereafter recovered towards baseline [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Treatment with sarilumab resulted in decreases in fibrinogen and serum amyloid A, and increases in hemoglobin and serum albumin.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The pharmacokinetics of sarilumab were characterized in 1770 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treated with sarilumab which included 631 patients treated with 150 mg and 682 patients treated with 200 mg doses by subcutaneous injection every two weeks for up to 52 weeks. The median tmax was observed in 2 to 4 days.
At steady state, exposure over the dosing interval measured by area under curve (AUC) increased 2-fold with an increase in dose from 150 to 200 mg every two weeks. Steady state was reached in 14 to 16 weeks with a 2- to 3-fold accumulation compared to single dose exposure.
For the 150 mg every two weeks dose regimen, the estimated mean (± SD) steady-state AUC, Cmin and Cmax of sarilumab were 202 ± 120 mg.day/L, 6.35 ± 7.54 mg/L, and 20.0 ± 9.20 mg/L, respectively.
For the 200 mg every two weeks dose regimen, the estimated mean (± SD) steady-state AUC, Cmin and Cmax of sarilumab were 395 ± 207 mg.day/L, 16.5 ± 14.1 mg/L, and 35.6 ± 15.2 mg/L, respectively.
Elimination
Sarilumab is eliminated by parallel linear and non-linear pathways. At higher concentrations, the elimination is predominantly through the linear, non-saturable proteolytic pathway, while at lower concentrations, non-linear saturable target-mediated elimination predominates. The half-life of sarilumab is concentration-dependent. At 200 mg every 2 weeks, the concentration-dependent half-life is up to 10 days in patients with RA at steady state. At 150 mg every 2 weeks, the concentration-dependent half-life is up to 8 days in patients with RA at steady state.
After the last steady state dose of 150 mg and 200 mg sarilumab, the median times to non-detectable concentration are 28 and 43 days, respectively.
Population pharmacokinetic analyses in patients with RA revealed that there was a trend toward higher apparent clearance of sarilumab in the presence of anti-sarilumab antibodies.
Metabolism
The metabolic pathway of sarilumab has not been characterized. As a monoclonal antibody sarilumab is expected to be degraded into small peptides and amino acids via catabolic pathways in the same manner as endogenous IgG.
Excretion
Monoclonal antibodies, including sarilumab, are not eliminated via renal or hepatic pathways.
Specific Populations
Population pharmacokinetic analyses in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis showed that age, gender and race did not meaningfully influence the pharmacokinetics of sarilumab. Although body weight influenced the pharmacokinetics of sarilumab, no dose adjustments are recommended for any of these demographics.
Hepatic impairment
No formal study of the effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of sarilumab was conducted.
Renal impairment
No formal study of the effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of sarilumab was conducted. Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis of data from 1770 patients with RA, including patients with mild (creatinine clearance (CLcr): 60 to 90 mL/min; N=471 at baseline) or moderate (CLcr: 30 to 60 mL/min; N=74 at baseline) renal impairment, CLcr was correlated with sarilumab exposure. However, the effect of CLcr on exposure is not sufficient to warrant a dose adjustment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)]. Patients with severe renal impairment were not studied.
Drug-Drug Interactions
CYP450 substrates
Simvastatin is a CYP3A4 and OATP1B1 substrate. In 17 patients with RA, one week following a single 200-mg subcutaneous administration of sarilumab, exposure of simvastatin and simvastatin acid decreased by 45% and 36%, respectively [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term animal studies have been performed to establish the carcinogenicity potential of sarilumab. Literature indicates that the IL-6 pathway can mediate anti-tumor responses by promoting increased immune cell surveillance of the tumor microenvironment. However, available published evidence also supports that IL-6 signaling through the IL-6 receptor may be involved in pathways that lead to tumorigenesis. The malignancy risk in humans from an antibody that disrupts signaling through the IL-6 receptor, such as sarilumab, is presently unknown.
Fertility and reproductive performance were unaffected in male and female mice treated with an analogous antibody, which binds to murine IL-6Rα to inhibit IL-6 mediated signaling, at subcutaneous doses of 10, 25, and 100 mg/kg twice per week.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Design of Clinical Studies in Adults with Moderately to Severely Active RA
The efficacy and safety of KEVZARA were assessed in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter studies (Study 1 and Study 2) in patients older than 18 years with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) diagnosed according to American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria. Patients had at least 8 tender and 6 swollen joints at baseline.
Study 1 evaluated 1197 patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who had inadequate clinical response to methotrexate (MTX). Patients received subcutaneous KEVZARA 200 mg, KEVZARA 150 mg, or placebo every two weeks with concomitant MTX. After Week 16 in Study 1, patients with an inadequate response could have been rescued with KEVZARA 200 mg every two weeks.
Study 2 evaluated 546 patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who had an inadequate clinical response or were intolerant to one or more TNF-α antagonists. Patients received subcutaneous KEVZARA 200 mg, KEVZARA 150 mg, or placebo every two weeks with concomitant conventional DMARDs (MTX, sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and/or hydroxychloroquine). After Week 12 in Study 2, patients with an inadequate response could have been rescued with KEVZARA 200 mg every two weeks.
In Studies 1 and 2, the primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who achieved an ACR20 response at Week 24. Other key endpoints evaluated included change from baseline in HAQ-DI at Week 16 in Study 1 and at Week 12 in Study 2, and change from baseline in van der Heijde-modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS) at Week 52 in Study 1.
Clinical Response
The percentages of KEVZARA every two weeks + MTX/DMARD-treated patients achieving ACR20, ACR50 and ACR70 responses in Studies 1 and 2 are shown Table 4. In both studies, patients treated with either 200 mg or 150 mg of KEVZARA every two weeks + MTX/DMARD had higher ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 response rates versus placebo + MTX/DMARD-treated patients at Week 24.
In Studies 1 and 2, a greater proportion of patients treated with KEVZARA 200 mg or 150 mg every two weeks plus MTX/DMARD achieved a low level of disease activity as measured by a Disease Activity Score 28-C-Reactive Protein (DAS28-CRP) <2.6 compared with placebo + MTX/DMARD at the end of the studies (Table 4). In Study 1, the proportion of patients achieving DAS28-CRP <2.6 who had at least 3 or more active joints at the end of Week 24 was 33.1%, 37.8% and 20%, in the KEVZARA 200 mg + MTX/DMARD arm, KEVZARA 150 mg + MTX/DMARD arm, and placebo arm respectively.
Table 4: Clinical Response in Placebo-Controlled Studies 1 and 2 in Adults with Moderately to Severely Active RA* Percentage of Patients Study 1 Study 2 Placebo + MTX
N=398KEVZARA 150 mg + MTX
N=400KEVZARA 200 mg + MTX
N=399
Placebo + DMARD(s)†
N=181KEVZARA 150 mg + DMARD(s)†
N=181KEVZARA 200 mg + DMARD(s)†
N=184- * Patients who were rescued or discontinued were considered non-responders for the analyses included in this table. In Study 1, at week 52, 196, 270, and 270 patients remained on placebo, KEVZARA 150 mg, and KEVZARA 200 mg respectively.
- † DMARDs in Study 2 included MTX, sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and/or hydroxychloroquine
- ‡ Weighted estimate of the rate difference; CI=confidence interval
- § Primary end point
- ¶ NA=Not Applicable as Study 2 was a 24-week study
- # Major clinical response = ACR70 for at least 24 consecutive weeks during the 52-week period.
- Þ Patients with DAS28-CRP <2.6 may have active joints
ACR20 Week 12 34.7% 54.0% 64.9% 37.6% 54.1% 62.5% Difference from placebo, (95% CI)‡ 19.4%
(12.6%, 26.1%)
30.2%
(23.6%, 36.8%)
16.6%
(6.7%, 26.5%)
25.3%
(15.7%, 34.8%)
Week 24§ 33.4% 58.0% 66.4% 33.7% 55.8% 60.9% Difference from placebo, (95% CI)‡ 24.6%
(18.0%, 31.3%)33.0%
(26.5%, 39.5%)22.1%
(12.6%, 31.6%)
27.4%
(17.7%, 37.0%)Week 52 31.7% 53.5% 58.6% Difference from placebo, (95% CI)‡ 21.9%
(15.2%, 28.5%)
27.0%
(20.5%, 33.6%)
NA¶ NA¶ NA¶ ACR50 Week 12 12.3% 26.5% 36.3% 13.3% 30.4% 33.2% Difference from placebo, (95% CI)‡ 14.2%
(8.9%, 19.6%)24.1%
(18.4%, 29.8%)17.1%
(9.2%, 25.1%)20.1%
(12.0%, 28.3%)Week 24 16.6% 37.0% 45.6% 18.2% 37.0% 40.8% Difference from placebo, (95% CI)‡ 20.4%
(14.5%, 26.3%)
29.1%
(23.0%, 35.1%)
18.8%
(10.2%, 27.4%)
22.8%
(14.0%, 31.6%)
Week 52 18.1% 40.0% 42.9% Difference from placebo, (95% CI)‡ 21.9%
(15.8%, 28.0%)
24.8%
(18.7%, 30.9%)
NA¶ NA¶ NA¶ ACR70 Week 12 4.0% 11.0% 17.5% 2.2% 13.8% 14.7% Difference from placebo, (95% CI)‡ 7.0%
(3.4%, 10.6%)
13.5%
(9.4%, 17.7%)
11.6%
(6.2%, 17.0%)
12.5%
(7.1%, 17.9%)
Week 24 7.3% 19.8% 24.8% 7.2% 19.9% 16.3% Difference from placebo, (95% CI)‡ 12.5%
(7.8%, 17.1%)
17.5%
(12.6%, 22.5%)
12.7%
(6.1%, 19.3%)
9.2%
(2.8%, 15.7%)
Week 52 9.0% 24.8% 26.8% Difference from placebo, (95% CI)‡ 15.7%
(10.6%, 20.8%)
17.8%
(12.6%, 23.0%)
NA¶ NA¶ NA¶ Major clinical response# Responders
3.0% 12.8% 14.8% NA¶ NA¶ NA¶ Difference from placebo, (95% CI)‡ 9.7%
(6.1%, 13.4%)
11.8%
(7.9%, 15.6%)
DAS28-CRP < 2.6Þ Week 12 Percentage of patients 4.8% 18.0% 23.1% 3.9% 17.1% 17.9% Difference from placebo
(95% CI)‡13.3%
(9.0%, 17.5%)18.3%
(13.7%, 23.0%)13.3%
(7.3%, 19.3%)14.1%
(8.0%, 20.3%)Week 24 Percentage of patients 10.1% 27.8% 34.1% 7.2% 24.9% 28.8% Difference from placebo
(95% CI)‡17.7%
(12.5%, 23.0%)24.0%
(18.5%, 29.5%)17.7%
(10.5%, 24.9%)21.7%
(14.3%, 29.1%)The percent ACR20 response by visit in Study 1 is shown in Figure 1. A similar response curve was observed in Study 2.
Figure 1: Percent of ACR20 Response by Visit for Study 1 (Adults with Moderately to Severely Active RA) 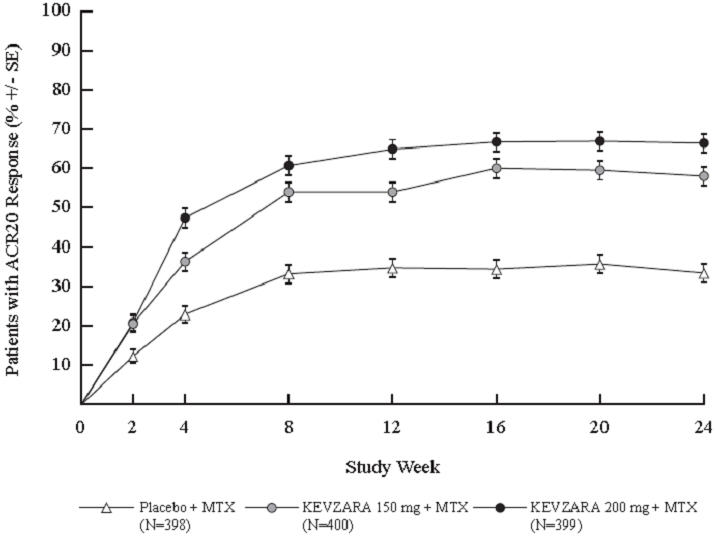
The results of the components of the ACR response criteria at Week 12 for Studies 1 and 2 are shown in Table 5.
Table 5: Mean Change from Baseline in Components of ACR Score at Week 12 (Prior to Rescue) in Adults with Moderately to Severely Active RA Study 1 Study 2 Component means (range/units) Placebo + MTX
(N=398)KEVZARA 150 mg + MTX
(N=400)KEVZARA 200 mg + MTX
(N=399)Placebo + DMARD(s)
(N=181)KEVZARA 150 mg + DMARD(s)
(N=181)KEVZARA 200 mg + DMARD(s)
(N=184)- * VAS=visual analog scale
Tender Joints (0–68) Baseline 26.80 27.21 26.50 29.42 27.66 29.55 Week 12 16.25 12.88 11.78 19.18 13.38 13.10 Change from baseline -10.51 -14.42 -14.94 -9.79 -14.11 -15.92 Swollen Joints (0–66) Baseline 16.68 16.60 16.77 20.21 19.60 19.97 Week 12 9.66 7.50 6.79 12.50 8.82 8.28 Change from baseline -7.02 -9.03 -10.12 -7.25 -10.77 -10.89 Pain VAS* (0–100 mm) Baseline 63.71 65.48 66.71 71.57 71.02 74.86 Week 12 49.25 41.47 36.93 54.77 43.45 41.66 Change from baseline -14.45 -23.73 -29.77 -16.12 -27.95 -32.77 Physician global VAS* (0–100 mm) Baseline 62.86 63.43 63.59 68.39 68.10 67.76 Week 12 39.25 31.32 28.47 43.73 33.65 30.18 Change from baseline -23.63 -31.85 -34.84 -24.60 -34.92 -36.92 Patient global VAS* (0–100 mm) Baseline 63.70 64.43 66.49 68.77 67.71 70.89 Week 12 49.37 41.52 38.05 53.67 41.99 41.74 Change from baseline -13.92 -22.88 -28.39 -15.05 -26.05 -28.83 HAQ-DI (0–3) Baseline 1.61 1.63 1.69 1.80 1.72 1.82 Week 12 1.34 1.15 1.13 1.49 1.23 1.33 Change from baseline -0.27 -0.47 -0.57 -0.29 -0.50 -0.49 CRP (mg/L) Baseline 20.46 22.57 22.23 26.02 23.60 30.77 Week 12 19.61 9.24 3.30 21.72 9.21 4.58 Change from baseline -0.58 -13.59 -18.31 -3.39 -14.24 -25.91 Radiographic Response
In Study 1, structural joint damage was assessed radiographically and expressed as the van der Heijde-modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS) and its components, the erosion score and joint space narrowing score. Radiographs of hands and feet were obtained at baseline, 24 weeks, and 52 weeks and scored independently by at least two well-trained readers who were blinded to treatment group and visit number.
Both doses of KEVZARA + MTX were superior to placebo + MTX in the change from baseline in mTSS over 52 weeks (see Table 6). Less progression of both erosion and joint space narrowing scores over 52 weeks was reported in the KEVZARA + MTX treatment groups compared to the placebo + MTX group.
Treatment with KEVZARA + MTX was associated with significantly less radiographic progression of structural damage as compared with placebo + MTX. At Week 52, 55.6% of patients receiving KEVZARA 200 mg + MTX and 47.8% of patients receiving KEVZARA 150 mg + MTX had no progression of structural damage (as defined by a change in the Total Sharp Score of zero or less) compared with 38.7% of patients receiving placebo.
Table 6: Mean Radiographic Change from Baseline at Week 52 in Study 1 in Adults with Moderately to Severely Active RA* Study 1 Placebo + MTX
(N=398)KEVZARA 150 mg + MTX
(N=400)KEVZARA 200 mg + MTX
(N=399)- * Week 52 analysis employs linear extrapolation method to impute missing or post-rescue data
- † LS=least squares
- ‡ CI=confidence interval
Modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS) Mean change 2.78 0.90 0.25 LS† mean difference (95% CI‡) -1.88 (-2.74, -1.01) -2.52 (-3.38, -1.66) Erosion score Mean change 1.46 0.42 0.05 LS† mean difference (95% CI‡) -1.03 (-1.53, -0.53) -1.40 (-1.90, -0.90) Joint space narrowing score Mean change 1.32 0.47 0.20 LS† mean difference (95% CI‡) -0.85 (-1.34, -0.35) -1.12 (-1.61, -0.63) Physical Function Response
In Studies 1 and 2, physical function and disability were assessed by the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI). Patients receiving KEVZARA 200 mg every two weeks + MTX/DMARD and KEVZARA 150 mg every two weeks + MTX/DMARD demonstrated greater improvement from baseline in physical function compared to placebo + MTX/DMARD at Week 16 and Week 12 in Studies 1 and 2, respectively (Table 7).
Table 7: Physical function in Studies 1 and 2 in Adults with Moderately to Severely Active RA Study 1 Study 2 Week 16 Week 12 Placebo + MTX
(N=398)KEVZARA 150 mg + MTX
(N=400)KEVZARA 200 mg + MTX
(N=399)Placebo + DMARD(s)
(N=181)KEVZARA 150 mg + DMARD(s)
(N=181)KEVZARA 200 mg + DMARD(s)
(N=184)- * Difference in adjusted mean change from baseline compared with placebo + DMARD at Week 16 (Study 1) or Week 12 (Study 2) and 95% confidence interval for that difference.
- † Change from baseline greater than 0.3 units
HAQ-DI Change from baseline -0.30 -0.54 -0.58 -0.29 -0.50 -0.49 Difference from placebo (95% CI)* -0.24
(-0.31, -0.16)-0.26
(-0.34, -0.18)-0.20
(-0.32, -0.09)-0.21
(-0.33, -0.10)% of patients with clinically meaningful improvement† 42.5% 53.8% 57.4% 35.9% 47% 51.1% Other Health Related Outcomes
General health status was assessed by the Short Form health survey (SF-36) in Studies 1 and 2. Patients receiving KEVZARA 200 mg every two weeks + MTX/DMARD demonstrated greater improvement from baseline compared to placebo + MTX/DMARD in the physical component summary (PCS) at Week 24, but there was no evidence of a difference between the treatment groups in the mental component summary (MCS) at Week 24. Patients receiving KEVZARA 200 mg + MTX/DMARD reported greater improvement relative to placebo in the domains of Physical Functioning, Role Physical, Bodily Pain, General Health Perception, Vitality, Social Functioning and Mental Health, but not in the Role Emotional domain.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
KEVZARA (sarilumab) injection is supplied as a colorless to pale yellow solution in a single-dose pre-filled syringes and single-dose pre-filled pens.
Strength Package Size NDC Number 150 mg/1.14 mL 2 syringes per pack 0024-5908-01 200 mg/1.14 mL 2 syringes per pack 0024-5910-01 Strength Package Size NDC Number 150 mg/1.14 mL 2 pre-filled pens per pack 0024-5920-01 200 mg/1.14 mL 2 pre-filled pens per pack 0024-5922-01 Storage and Stability
Refrigerate at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze. Do not shake.
If needed, patients/caregivers may store KEVZARA at room temperature up to 77°F (25°C) up to 14 days in the outer carton. Do not store above 77°F (25°C). After removal from the refrigerator, use KEVZARA within 14 days or discard.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Infections
Inform patients that KEVZARA may lower their resistance to infections. Instruct patients to contact their physician immediately when symptoms suggesting infection appear, to ensure rapid evaluation and appropriate treatment [see Warning and Precautions (5.1)].
Gastrointestinal Perforation
Inform patients that some patients, particularly those also taking NSAIDS, and/or steroids, have had tears (perforations) of the stomach or intestines. Inform patients that gastrointestinal perforations have been reported in KEVZARA-treated patients in clinical studies, primarily as a complication of diverticulitis. Instruct patients to contact their physician immediately when symptoms of severe, persistent abdominal pain appear to ensure rapid evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Hypersensitivity and Serious Allergic Reaction
Assess patient suitability for home use for SC injection. Inform patients that some patients who have been treated with KEVZARA have developed serious allergic reactions. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any symptom of serious allergic reactions.
Pregnancy Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to KEVZARA during pregnancy. Encourage participation in the registry [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Instruction on Injection Technique
Instruct patients and caregivers to read the Instructions for Use before the patient starts using KEVZARA, and each time the patient gets a refill as there may be new information they need to know.
Provide guidance to patients and caregivers on proper subcutaneous injection technique, including aseptic technique, and how to use the pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen correctly (see Instructions for Use).
The pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen should be left at room temperature for 30 minutes or 60 minutes respectively (see the Instructions for Use) prior to use. The syringe or pen should be used within 14 days after being taken out of the refrigerator. A puncture-resistant container should be used to dispose the used pre-filled syringes or pre-filled pens and should be kept out of the reach of children. Instruct patients or caregivers in the technique as well as proper pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen disposal, and caution against reuse of these items.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
REGENERON
SANOFI GENZYMEManufactured by:
sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807
A SANOFI COMPANY
U.S. License # 1752Marketed by:
sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC (Bridgewater, NJ 08807) and
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Tarrytown, NY 10591)
KEVZARA® is a registered trademark of Sanofi Biotechnology
©2018 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. / sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC
Issue Date: April 2018
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
KEVZARA® (KEV-za-ra)
(sarilumab)
injection, for subcutaneous useThis Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: April 2018 What is the most important information I should know about KEVZARA?
KEVZARA can cause serious side effects including:- 1.
Serious Infections. KEVZARA is a prescription medicine that affects your immune system. KEVZARA can lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections. Some people have serious infections while using KEVZARA, including tuberculosis (TB), and infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses that can spread throughout the body. Some people have died from these infections.
Your healthcare provider should test you for TB before starting KEVZARA.- Your healthcare provider should monitor you closely for signs and symptoms of TB during treatment with KEVZARA.
Before starting KEVZARA, tell your healthcare provider if you:- think you have an infection or have symptoms of an infection, with or without a fever:
- sweats or chills
- muscle aches
- cough
- shortness of breath
- blood in your phlegm
- weight loss
- warm, red or painful skin or sores on your body
- diarrhea or stomach pain
- burning when you urinate or urinating more often than normal
- feeling very tired
-
- are being treated for an infection.
- get a lot of infections or have infections that keep coming back.
- have diabetes, HIV, or a weak immune system. People with these conditions have a higher chance of getting infections.
- have TB, or have been in close contact with someone with TB.
- live or have lived, or have traveled to certain parts of the country (such as the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys and the Southwest) where there is an increased chance of getting certain fungal infections (histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, or blastomycosis). These infections may happen more often or become more severe if you use KEVZARA. Ask your healthcare provider if you do not know if you have lived in an area where these infections are common.
- have or have had hepatitis.
- 2.
Changes in certain laboratory test results.
Your healthcare provider should do blood tests before you start KEVZARA, 4 to 8 weeks after starting KEVZARA, and then every 3 months during treatment to check for:- low neutrophil count. Neutrophils are white blood cells that help the body fight off bacterial infections. A low neutrophil count is common with KEVZARA, and can be severe.
- low platelet count. Platelets are blood cells that help with blood clotting and stop bleeding.
- increase in certain liver function tests. An increase in certain liver function tests is common with KEVZARA, and can be severe.
Your healthcare provider should do blood tests 4 to 8 weeks after starting KEVZARA and then every 6 months during treatment to check for an:- increase in blood cholesterol levels.
- 3. Tears (perforation) of the stomach or intestines. Tell your healthcare provider if you have had a condition known as diverticulitis (inflammation in parts of the large intestine) or ulcers in your stomach or intestines. Some people using KEVZARA get tears in their stomach or intestine. This happens most often in people who also take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or methotrexate. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have fever and stomach (abdominal) pain that does not go away.
- 4. Cancer. KEVZARA may increase your risk of certain cancers by changing the way your immune system works. Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had any type of cancer.
See "What are the possible side effects with KEVZARA?" for more information about side effects.
What is KEVZARA?
KEVZARA is an injectable prescription medicine called an Interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor blocker. KEVZARA is used to treat adults with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) after at least one other medicine called a disease modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) has been used and did not work well or could not be tolerated.
It is not known if KEVZARA is safe and effective in children.Who should not use KEVZARA?
Do not use KEVZARA if you are allergic to sarilumab or any of the ingredients in KEVZARA. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in KEVZARA.Before using KEVZARA, talk to your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have an infection. See "What is the most important information I should know about KEVZARA?"
- have liver problems.
- have had stomach (abdominal) pain or been diagnosed with diverticulitis or ulcers in your stomach or intestines.
- have recently received or are scheduled to receive a vaccine. People who take KEVZARA should not receive live vaccines.
- plan to have surgery or a medical procedure.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if KEVZARA will harm your unborn baby.
Pregnancy Registry: Sanofi has a registry for pregnant women who use KEVZARA. The purpose of this registry is to gather information about the health of the pregnant mother and her baby. If you are pregnant or become pregnant while using KEVZARA, talk to your healthcare provider about how you can join this pregnancy registry or call 1-877-311-8972 to enroll. - are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if KEVZARA passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you use KEVZARA.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you use:- any other medicines to treat your RA. You should not take rituximab (Rituxan®), etanercept (Enbrel®), infliximab (Remicade®), anakinra (Kineret®), adalimumab (Humira®), abatacept (Orencia®), certolizumab (Cimzia®), golimumab (Simponi®), tocilizumab (Actemra®), or tofacitinib (Xeljanz®) while you are using KEVZARA. Using KEVZARA with these medicines may increase your risk of infection.
- medicines that affect the way certain liver enzymes work. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if your medicine is one of these.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use KEVZARA? - See the detailed Instructions for Use that come with this Medication Guide for instructions about the right way to prepare and give your KEVZARA injections at home.
- KEVZARA is given as an injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection).
- KEVZARA is available as a single-use pre-filled syringe or single-use pre-filled pen. Your healthcare provider will prescribe the dose and type of KEVZARA that is best for you.
- If your healthcare provider decides that you or a caregiver can give the injections of KEVZARA at home, you or your caregiver should receive training on the right way to prepare and inject KEVZARA. Do not try to inject KEVZARA until you have been shown the right way to give the injections by your healthcare provider.
- Inject 1 dose of KEVZARA every 2 weeks.
What are the possible side effects of KEVZARA?
KEVZARA can cause serious side effects, including:- See "What is the most important information I should know about KEVZARA?"
- Serious allergic reactions. Serious allergic reactions can happen with KEVZARA. Get medical attention right away if you have any of the following signs of a serious allergic reaction:
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- swelling of the lips, tongue, or face
- chest pain
- feeling dizzy or faint
- moderate or severe stomach (abdominal) pain or vomiting
Common side effects of KEVZARA include: - injection site redness
- upper respiratory tract infection
- urinary tract infection
- nasal congestion, sore throat, and runny nose
These are not all of the possible side effects of KEVZARA.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to sanofi-aventis at 1-800-633-1610.How should I store KEVZARA? - Store KEVZARA in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Store KEVZARA in the original carton until use to protect it from light.
- Do not freeze KEVZARA.
- Do not shake KEVZARA.
- KEVZARA may be stored at room temperature up to 77°F (25°C) for up to 14 days in the original outer carton.
- Throw away KEVZARA if it has been kept at room temperature and not been used within 14 days.
General Information about the safe and effective use of KEVZARA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use KEVZARA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give KEVZARA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about KEVZARA that was written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in KEVZARA?
Active Ingredient: sarilumab
Inactive Ingredients: arginine, histidine, polysorbate 20, sucrose, and Water for Injection, USP.
REGENERON
SANOFI GENZYME
Manufactured by: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC Bridgewater, NJ 08807, A SANOFI COMPANY U.S. License # 1752. Marketed by: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC (Bridgewater, NJ 08807) and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Tarrytown, NY 10591) KEVZARA® is a registered trademark of Sanofi Biotechnology ©2018 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. / sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC
For more information, go to www.KEVZARA.com or call 1-844-KEVZARA (1-844-538-9272). - 1.
Serious Infections. KEVZARA is a prescription medicine that affects your immune system. KEVZARA can lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections. Some people have serious infections while using KEVZARA, including tuberculosis (TB), and infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses that can spread throughout the body. Some people have died from these infections.
-
Instructions For UseKEVZARA® (KEV-za-ra)(sarilumab)injection, for subcutaneous useSingle-dose Pre-filled Syringe (150 mg/1.14 mL)
Important information:
KEVZARA is available as a single-dose pre-filled syringe (called "syringe" in these instructions). The pre-filled syringe contains 150 mg of KEVZARA for injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection) 1 time every 2 weeks.
Do not try to inject KEVZARA until you have been shown the right way to give the injections by your healthcare provider.
Do Do not - Read all of the instructions carefully before using the syringe.
- Keep unused syringes in the original carton and store in the refrigerator between 36°F and 46°F (2°C and 8°C).
- Keep the carton in an insulated bag with an ice pack when traveling.
- Let the syringe warm up at room temperature for at least 30 minutes before using.
- Use the syringe within 14 days after taking it out of the refrigerator or insulated bag.
- Keep the syringe and all medicines out of the reach of children.
- Do not use the syringe if it has been damaged or the needle cap is missing or not attached. Return the syringe and the package it came in to your pharmacy.
- Do not remove the needle cap until just before you are ready to inject.
- Do not touch the needle.
- Do not re-use the syringe or try to put the cap back on the syringe.
- Do not freeze or heat up the syringe.
- Do not expose the syringe to direct sunlight.
- Do not inject through your clothes.
Keep these instructions for future use.
If you have any further questions, ask your healthcare provider or call 1-844-KEVZARA (1-844-538-9272).
KEVZARA pre-filled syringe parts
What you will need for your injection:
- A new KEVZARA 150 mg/1.14 mL pre-filled syringe
- Alcohol wipe
- Cotton ball or gauze
- Sharps disposal container. See "How should I dispose of (throw away) KEVZARA pre-filled syringes?" at the end of this Instructions for Use.
Step A: Get ready for an injection
1. Prepare all of the equipment you will need on a clean, flat working surface. - Take 1 syringe out of the package by holding the middle of the syringe body. Do not hold the syringe by the plunger, finger grip or needle cap. Do not pull off the needle cap until you are ready to inject.
- Keep the remaining syringe in the carton in the refrigerator.
2. Look at the label. - Check that you have the correct medicine and the correct dose.
- Check the expiration date.
- Do not use the syringe if the expiration date has passed.

3. Look at the medicine. - Check to see if the liquid in the syringe is clear and colorless to pale yellow.
- You may see air bubbles. This is normal.
- Do not inject if the liquid is cloudy, discolored or contains particles. Safely dispose of the syringe in a sharps container and get a new one.
4. Lay the syringe on a flat surface and allow it to warm up at room temperature for at least 30 minutes. - Using the syringe at room temperature may make the injection more comfortable.
- Do not use the syringe if it has been out of the refrigerator for more than 14 days.
- Do not try to warm the syringe in any other way.
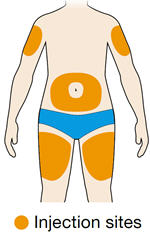
5. Select the injection site. - You can inject into the front of your thigh or your belly (abdomen), but not the area 2 inches (5 cm) around your belly button (navel).
- If somebody else gives you the injection, you can also use the upper arm.
- Change the injection site each time you inject.
- Do not inject into skin that is tender, damaged or has bruises or scars.
6. Prepare the injection site. - Wash your hands.
- Clean the skin at the injection site with an alcohol wipe and let it air dry before injecting.
- Do not touch the injection site again before the injection.
Step B: Give the injection
Complete Step B after completing all steps in Step A "Get ready for an injection".
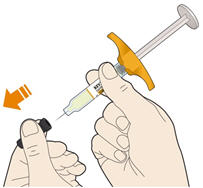
1. Pull off the needle cap. - Hold the syringe in the middle of the syringe body with the needle pointing away from you.
- Keep your hand away from the plunger.
- Do not get rid of any air bubbles in the syringe.
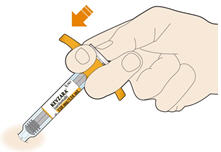
- Do not pull off the needle cap until you are ready to inject.
- Do not put the needle cap back on.
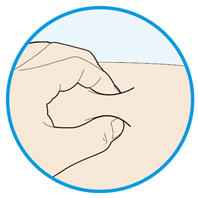
2. Pinch the skin. - Use your thumb and first (index) finger to pinch a fold of skin at the cleaned injection site.
3. Insert the needle into the fold of skin at about a 45 degree angle. 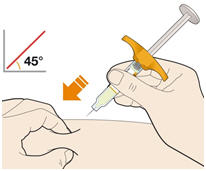
4. Push the plunger down. - Slowly push the plunger down as far as it will go until the syringe is empty.
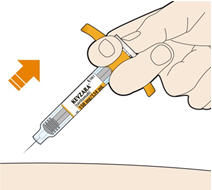
5. Before you remove the needle, check that the syringe is empty. - Pull the needle out at the same angle as inserted.
- If you see any blood at the injection site, press a cotton ball or gauze on the injection site.
- Do not rub the injection site.
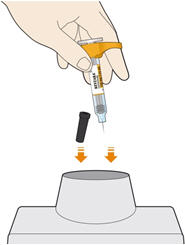
6. Dispose of the syringe. - The KEVZARA syringe should not be reused.
- Put the used syringe into your FDA-cleared sharps disposal container or a puncture resistant container (see "How should I dispose of (throw away) KEVZARA pre-filled syringes?").
- Do not put the needle cap back on.
How should I dispose of (throw away) KEVZARA pre-filled syringes?
- Put the used syringe in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) the syringe in your household trash.
- If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
- Do not reuse the syringe.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Important: Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
REGENERON
SANOFI GENZYMEManufactured by:
sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807
A SANOFI COMPANY
U.S. License # 1752Marketed by: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC (Bridgewater, NJ 08807)
and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Tarrytown, NY 10591)KEVZARA® is a registered trademark of Sanofi Biotechnology
©2017 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. / sanofi-aventis U.S. LLCIssued: May 2017
-
Instructions For UseKEVZARA® (KEV-za-ra)(sarilumab)injection, for subcutaneous useSingle-dose Pre-filled Syringe (200 mg/1.14 mL)
Important information:
KEVZARA is available as a single-dose pre-filled syringe (called "syringe" in these instructions). The pre-filled syringe contains 200 mg of KEVZARA for injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection) 1 time every 2 weeks.
Do not try to inject KEVZARA until you have been shown the right way to give the injections by your healthcare provider.
Do Do not - Read all of the instructions carefully before using the syringe.
- Keep unused syringes in the original carton and store in the refrigerator between 36°F and 46°F (2°C and 8°C).
- Keep the carton in an insulated bag with an ice pack when traveling.
- Let the syringe warm up at room temperature for at least 30 minutes before using.
- Use the syringe within 14 days after taking it out of the refrigerator or insulated bag.
- Keep the syringe and all medicines out of the reach of children.
- Do not use the syringe if it has been damaged or the needle cap is missing or not attached. Return the syringe and the package it came in to your pharmacy.
- Do not remove the needle cap until just before you are ready to inject.
- Do not touch the needle.
- Do not re-use the syringe or try to put the cap back on the syringe.
- Do not freeze or heat up the syringe.
- Do not expose the syringe to direct sunlight.
- Do not inject through your clothes.
Keep these instructions for future use.
If you have any further questions, ask your healthcare provider or call 1-844-KEVZARA (1-844-538-9272).
KEVZARA pre-filled syringe parts
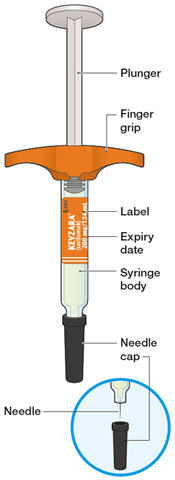
What you will need for your injection:
- A new KEVZARA 200 mg/1.14 mL pre-filled syringe
- Alcohol wipe
- Cotton ball or gauze
- Sharps disposal container. See "How should I dispose of (throw away) KEVZARA pre-filled syringes?" at the end of this Instructions for Use.
Step A: Get ready for an injection
1. Prepare all of the equipment you will need on a clean, flat working surface. - Take 1 syringe out of the package by holding the middle of the syringe body. Do not hold the syringe by the plunger, finger grip or needle cap. Do not pull off the needle cap until you are ready to inject.
- Keep the remaining syringe in the carton in the refrigerator.
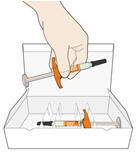
2. Look at the label. - Check that you have the correct medicine and the correct dose.
- Check the expiration date.
- Do not use the syringe if the expiration date has passed.
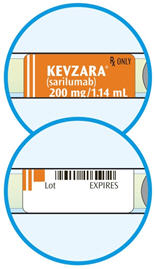
3. Look at the medicine. - Check to see if the liquid in the syringe is clear and colorless to pale yellow.
- You may see air bubbles. This is normal.
- Do not inject if the liquid is cloudy, discolored or contains particles. Safely dispose of the syringe in a sharps container and get a new one.
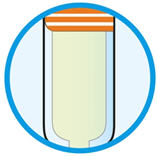
4. Lay the syringe on a flat surface and allow it to warm up at room temperature for at least 30 minutes. - Using the syringe at room temperature may make the injection more comfortable.
- Do not use the syringe if it has been out of the refrigerator for more than 14 days.
- Do not try to warm the syringe in any other way.
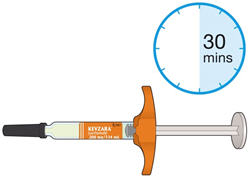
5. Select the injection site. - You can inject into the front of your thigh or your belly (abdomen), but not the area 2 inches (5 cm) around your belly button (navel).
- If somebody else gives you the injection, you can also use the upper arm.
- Change the injection site each time you inject.
- Do not inject into skin that is tender, damaged or has bruises or scars.
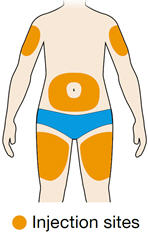
6. Prepare the injection site. - Wash your hands.
- Clean the skin at the injection site with an alcohol wipe and let it air dry before injecting.
- Do not touch the injection site again before the injection.
Step B: Give the injection
Complete Step B after completing all steps in Step A "Get ready for an injection"
1. Pull off the needle cap. - Hold the syringe in the middle of the syringe body with the needle pointing away from you.
- Keep your hand away from the plunger.
- Do not get rid of any air bubbles in the syringe.
- Do not pull off the needle cap until you are ready to inject.
- Do not put the needle cap back on.
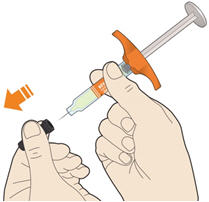
2. Pinch the skin. - Use your thumb and first (index) finger to pinch a fold of skin at the cleaned injection site.
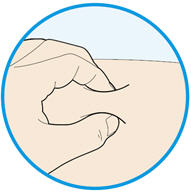
3. Insert the needle into the fold of skin at about a 45 degree angle. 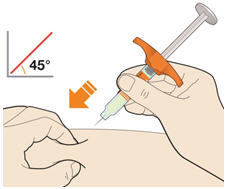
4. Push the plunger down. - Slowly push the plunger down as far as it will go until the syringe is empty.
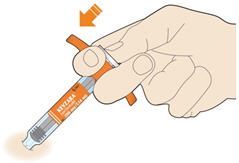
5. Before you remove the needle, check that the syringe is empty. - Pull the needle out at the same angle as inserted.
- If you see any blood at the injection site, press a cotton ball or gauze on the site.
- Do not rub the injection site.
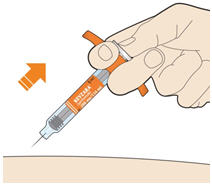
6. Dispose of the syringe. - The KEVZARA syringe should not be reused.
- Put the used syringe into your FDA-cleared sharps disposal container of a puncture resistant container (see "How should I dispose of (throw away) KEVZARA pre-filled syringes?").
- Do not put the needle cap back on.
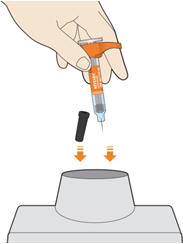
How should I dispose of (throw away) KEVZARA pre-filled syringes?
- Put the used syringe in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) the syringe in your household trash.
- If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
- Do not reuse the syringe.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Important: Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
REGENERON
SANOFI GENZYMEManufactured by:
sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807
A SANOFI COMPANY
U.S. License # 1752Marketed by: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC, (Bridgewater, NJ 08807)
and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Tarrytown, NY 10591)KEVZARA® is a registered trademark of Sanofi Biotechnology
©2017 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. / sanofi-aventis U.S. LLCIssued: May 2017
-
Instructions For UseKEVZARA® (KEV-za-ra)(sarilumab)injection, for subcutaneous useSingle-dose pre-filled pen (150 mg/1.14 mL)
Important information:
KEVZARA is available as a single-dose pre-filled pen (called "pen" in these instructions). The pre-filled pen contains 150 mg of KEVZARA for injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection) 1 time every 2 weeks.
Do not try to inject KEVZARA until you have been shown the right way to give the injections by your healthcare provider.
Do Do not - Read all of the instructions carefully before using the pre-filled pen.
- Keep unused pens in the original carton and store in the refrigerator between 36°F and 46°F (2°C and 8°C).
- Keep the carton in an insulated bag with an ice pack when traveling.
- Let the pen warm up at room temperature for at least 60 minutes before using.
- Use the pen within 14 days after taking it out of the refrigerator or insulated bag.
- Keep the pen and all medicines out of the reach of children.
- Do not use the pre-filled pen if it has been damaged or the orange cap is missing or not attached. Return the pen and the package it came in to your pharmacy.
- Do not remove the orange cap until just before you are ready to inject.
- Do not touch the yellow needle cover.
- Do not try to put the orange cap back on the pen.
- Do not re-use the pen.
- Do not freeze or heat up the pen.
- Do not expose the pen to direct sunlight.
- Do not inject through your clothes.
Keep these instructions for future use.
If you have any further questions, ask your healthcare provider or call 1-844-KEVZARA (1-844-538-9272).
KEVZARA pre-filled pen parts
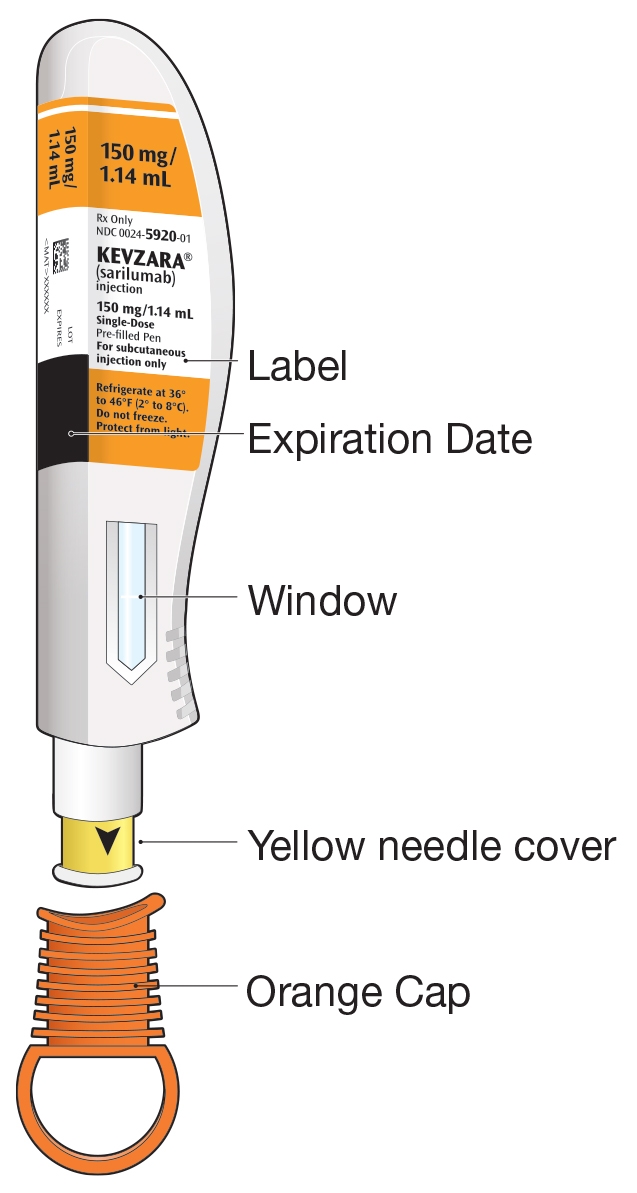
What you will need for your injection:
- An unused KEVZARA 150 mg/1.14 mL pre-filled pen
- Alcohol wipe
- Cotton ball or gauze
- Sharps disposal container. See "How should I throw away (dispose of) KEVZARA pre-filled pens?" at the end of this Instructions for Use.
Step A: Get ready for an injection
1. Prepare all of the equipment you will need on a clean, flat working surface. - Take 1 pen out of the packaging by holding the middle of the pen body. Do not remove the orange cap until you are ready to inject.
- Keep the remaining pen in the carton in the refrigerator.
2. Look at the label. - Check that you have the correct medicine and the correct dose.
- Check the expiration date. This is shown on the side of the pen.
- Do not use the pen if the expiration date has passed.
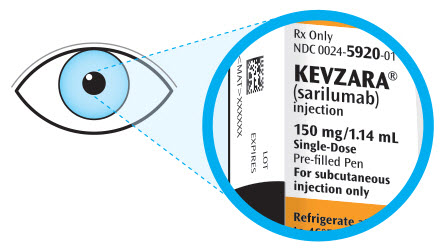
3. Look at the window. - Check to see that the liquid in the window is clear and colorless to pale yellow.
- You may see air bubbles. This is normal.
- Do not inject if the liquid is cloudy, discolored or contains particles. Safely throw away (dispose of) the pen in a sharps container and get a new one.
- The window is clear when the pen is unused. The window will turn solid yellow after the pen has been used.
- Do not use if the window is solid yellow. Safely dispose of the pen in a sharps container and get a new one.
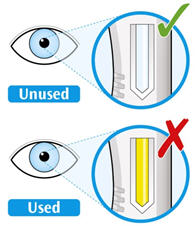
4. Lay the pen on a flat surface and allow it to warm up at room temperature for at least 60 minutes. - Using the pen at room temperature may make the injection more comfortable.
- Do not use the pen if it has been out of the refrigerator for more than 14 days.
- Do not try to warm the pen in any other way.
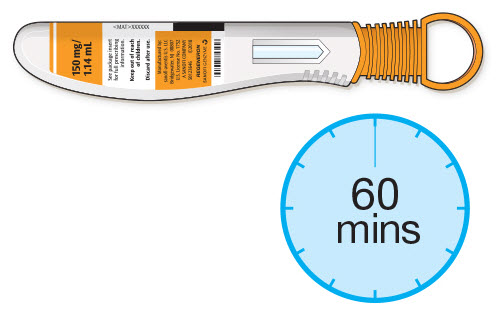
5. Select the injection site. - You can inject into your thigh or belly (abdomen), but not the area 2 inches (5 cm) around your belly button (navel).
- If somebody else gives you the injection, you can also use the outer area of the upper arm.
- Change the injection site each time you inject.
- Do not inject into skin that is tender, damaged or has bruises or scars.
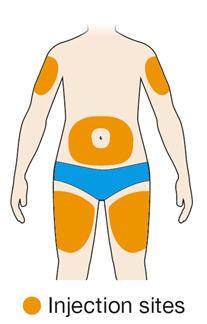
6. Prepare the injection site. - Wash your hands.
- Clean the skin at the injection site with an alcohol wipe and let it air dry before injecting.
- Do not touch the injection site again before the injection.
Step B: Give the injection
Complete Step B after completing all steps in Step A "Get ready for an injection"
1. Twist or pull off the orange cap. - Do not remove the orange cap until you are ready to inject.
- Do not touch the yellow needle cover.
- Do not put the orange cap back on.
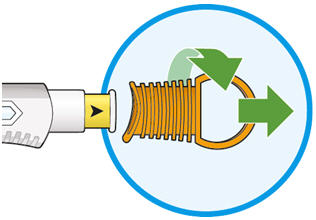
2. Put the yellow needle cover on your skin at about a 90 degree angle. - Make sure you can see the window.
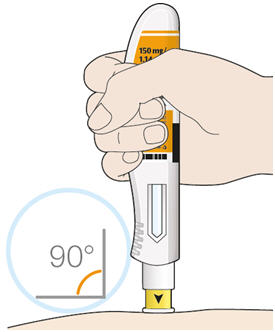
3. Press down and hold the pen firmly against your skin. - There will be a "click" when the injection starts.
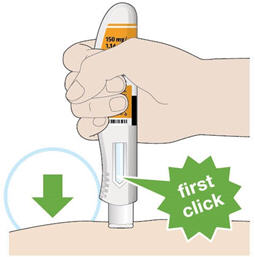
4. Keep holding the pen firmly against your skin. - The window will start to turn solid yellow.
- The injection can take up to 15 seconds.
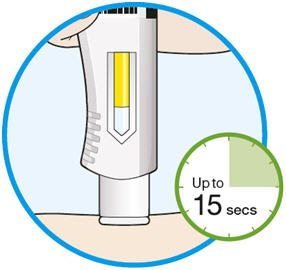
5. There will be a second click when the injection is complete. Check to see if the entire window has turned solid yellow before you remove the pen. - If you do not hear the second click, you should still check to see if the entire window has turned solid yellow.
- If the entire window does not turn solid yellow, this means that you may not have received your full dose of medicine. Call your healthcare provider right away.
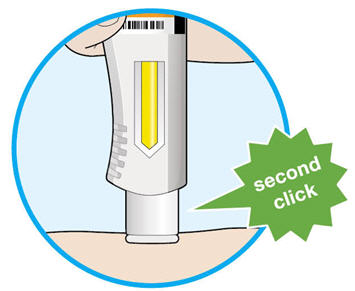
6. Remove the pen from your skin. - After you remove the pen from your skin, the needle will be covered automatically.
- If you see any blood at the injection site, press a cotton ball or gauze on the site.
- Do not rub the injection site.
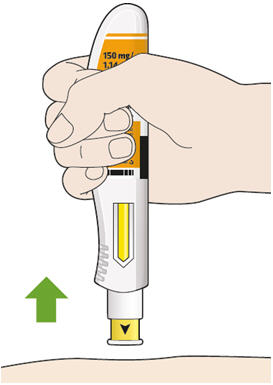
7. Dispose of the pen - The KEVZARA pre-filled pen should not be reused.
- Put the used pen into your FDA-cleared sharps disposal container or a puncture-resistant container (see "How should I throw away (dispose of) KEVZARA pre-filled pens?").
- Do not put the orange cap back on.
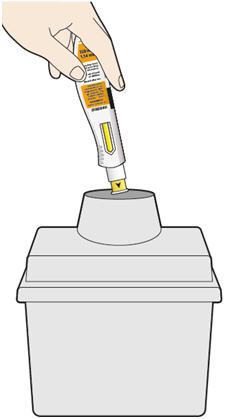
How should I throw away (dispose of) KEVZARA pre-filled pens?
- Put the used pen in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) the pen in your household trash.
- If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
- Do not reuse the pen.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Important: Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
REGENERON
SANOFI GENZYMEManufactured by:
sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807
A SANOFI COMPANY
U.S. License # 1752Marketed by: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC (Bridgewater, NJ 08807)
and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Tarrytown, NY 10591)KEVZARA® is a registered trademark of Sanofi Biotechnology
©2018 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. / sanofi-aventis U.S. LLCIssued: April 2018a
-
Instructions For UseKEVZARA® (KEV-za-ra)(sarilumab)injection, for subcutaneous useSingle-dose pre-filled pen (200 mg/1.14 mL)
Important information:
KEVZARA is available as a single-dose pre-filled pen (called "pen" in these instructions). The pre-filled pen contains 200 mg of KEVZARA for injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection) 1 time every 2 weeks.
Do not try to inject KEVZARA until you have been shown the right way to give the injections by your healthcare provider.
Do Do not - Read all of the instructions carefully before using the pre-filled pen.
- Keep unused pens in the original carton and store in the refrigerator between 36°F and 46°F (2°C and 8°C).
- Keep the carton in an insulated bag with an ice pack when traveling.
- Let the pen warm up at room temperature for at least 60 minutes before using.
- Use the pen within 14 days after taking it out of the refrigerator or insulated bag.
- Keep the pen and all medicines out of the reach of children.
- Do not use the pre-filled pen if it has been damaged or the orange cap is missing or not attached. Return the pen and the package it came in to your pharmacy.
- Do not remove the orange cap until just before you are ready to inject.
- Do not touch the yellow needle cover.
- Do not try to put the orange cap back on the pen.
- Do not re-use the pen.
- Do not freeze or heat up the pen.
- Do not expose the pen to direct sunlight.
- Do not inject through your clothes.
Keep these instructions for future use.
If you have any further questions, ask your healthcare provider or call 1-844-KEVZARA (1-844-538-9272).
KEVZARA pre-filled pen parts

What you will need for your injection:
- An unused KEVZARA 200 mg/1.14 mL pre-filled pen
- Alcohol wipe
- Cotton ball or gauze
- Sharps disposal container. See "How should I throw away (dispose of) KEVZARA pre-filled pens?" at the end of this Instructions for Use.
Step A: Get ready for an injection
1. Prepare all of the equipment you will need on a clean, flat working surface. - Take 1 pen out of the packaging by holding the middle of the pen body. Do not remove the orange cap until you are ready to inject.
- Keep the remaining pen in the carton in the refrigerator.
2. Look at the label. - Check that you have the correct medicine and the correct dose.
- Check the expiration date. This is shown on the side of the pen.
- Do not use the pen if the expiration date has passed.
3. Look at the window. - Check to see that the liquid in the window is clear and colorless to pale yellow.
- You may see air bubbles. This is normal.
- Do not inject if the liquid is cloudy, discolored or contains particles. Safely throw away (dispose of) the pen in a sharps container and get a new one.
- The window is clear when the pen is unused. The window will turn solid yellow after the pen has been used.
- Do not use if the window is solid yellow. Safely dispose of the pen in a sharps container and get a new one.
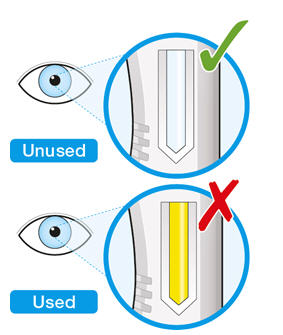
4. Lay the pen on a flat surface and allow it to warm up at room temperature for at least 60 minutes. - Using the pen at room temperature may make the injection more comfortable.
- Do not use the pen if it has been out of the refrigerator for more than 14 days.
- Do not try to warm the pen in any other way.
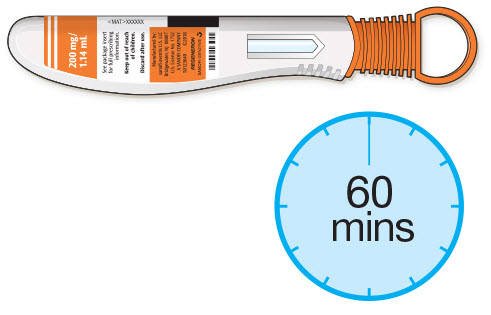
5. Select the injection site. - You can inject into your thigh or belly (abdomen), but not the area 2 inches (5 cm) around your belly button (navel).
- If somebody else gives you the injection, you can also use the outer area of the upper arm.
- Change the injection site each time you inject.
- Do not inject into skin that is tender, damaged or has bruises or scars.
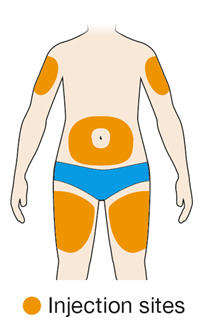
6. Prepare the injection site. - Wash your hands.
- Clean the skin at the injection site with an alcohol wipe and let it air dry before injecting.
- Do not touch the injection site again before the injection
Step B: Give the injection
Complete Step B after completing all steps in Step A "Get ready for an injection"
1. Twist or pull off the orange cap. - Do not remove the orange cap until you are ready to inject.
- Do not touch the yellow needle cover.
- Do not put the orange cap back on.
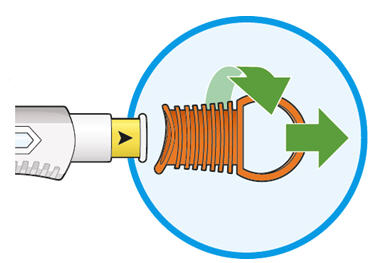
2. Put the yellow needle cover on your skin at about a 90 degree angle. - Make sure you can see the window.
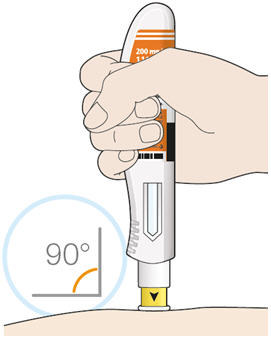
3. Press down and hold the pen firmly against your skin. - There will be a "click" when the injection starts.
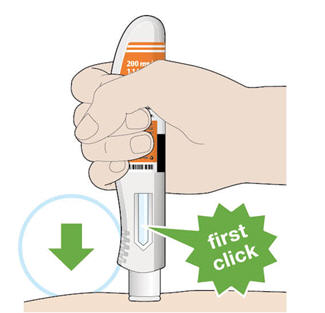
4. Keep holding the pen firmly against your skin. - The window will start to turn solid yellow.
- The injection can take up to 15 seconds.
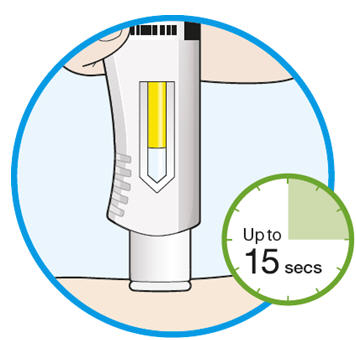
5. There will be a second click when the injection is complete. Check to see if the entire window has turned solid yellow before you remove the pen. - If you do not hear the second click, you should still check to see if the entire window has turned solid yellow.
- If the entire window does not turn solid yellow, this means that you may not have received your full dose of medicine. Call your healthcare provider right away.
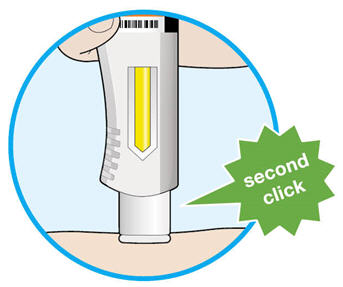
6. Remove the pen from your skin. - After you remove the pen from your skin, the needle will be covered automatically.
- If you see any blood at the injection site, press a cotton ball or gauze on the site.
- Do not rub the injection site.
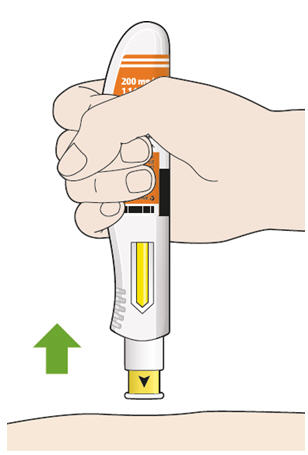
7. Dispose of the pen - The KEVZARA pre-filled pen should not be reused.
- Put the used pen into your FDA-cleared sharps disposal container or a puncture-resistant container (see "How should I throw away (dispose of) KEVZARA pre-filled pens?").
- Do not put the orange cap back on.
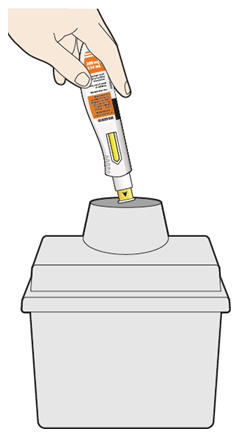
How should I throw away (dispose of) KEVZARA pre-filled pens?
- Put the used pen in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) the pen in your household trash.
- If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
- Do not reuse the pen.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Important: Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
REGENERON
SANOFI GENZYMEManufactured by:
sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807
A SANOFI COMPANY
U.S. License # 1752Marketed by: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC (Bridgewater, NJ 08807)
and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Tarrytown, NY 10591)KEVZARA® is a registered trademark of Sanofi Biotechnology
©2018 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. / sanofi-aventis U.S. LLCIssued: April 2018a
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mg/1.14 mL Syringe Carton
NDC: 0024-5908-01
Rx OnlyKEVZARA®
(sarilumab)
injection150 mg/1.14 mL (131.6 mg/mL)
2 Single-Dose Pre-filled Syringes
For Subcutaneous Injection Use OnlyREGENERON
SANOFI GENZYMEStore in a refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in the original
carton to protect from light. Do NOT freeze. Do NOT shake.If needed, patients/caregivers may store KEVZARA at room
temperature up to 77°F (25°C) up to 14 days in the outer carton.
Do not store above 77°F (25°C). After removal from the
refrigerator, use KEVZARA within 14 days or discard.Date removed from the refrigerator ____/____/____
ATTENTION: Enclosed Medication Guide is required for each patient
150 mg/1.14 mL

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 200 mg/1.14 mL Syringe Carton
NDC: 0024-5910-01
Rx OnlyKEVZARA®
(sarilumab)
injection200 mg/1.14 mL (175.4 mg/mL)
2 Single-Dose Pre-filled Syringes
For Subcutaneous Injection Use OnlyREGENERON
SANOFI GENZYMEStore in a refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in the original
carton to protect from light. Do NOT freeze. Do NOT shake.If needed, patients/caregivers may store KEVZARA at room
temperature up to 77°F (25°C) up to 14 days in the outer carton.
Do not store above 77°F (25°C). After removal from the
refrigerator, use KEVZARA within 14 days or discard.Date removed from the refrigerator ____/____/____
ATTENTION: Enclosed Medication Guide is required for each patient
200 mg/1.14 mL

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mg/1.14 mL Pen Carton
NDC: 0024-5920-01
Rx OnlyKEVZARA®
(sarilumab)
injection150 mg/1.14 mL (131.6 mg/mL)
2 Single-Dose Pre-filled Pens
For Subcutaneous Injection Use OnlyREGENERON
SANOFI GENZYMEStore in a refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in the original
carton to protect from light. Do NOT freeze. Do NOT shake.If needed, patients/caregivers may store KEVZARA at room
temperature up to 77°F (25°C) up to 14 days in the outer carton.
Do not store above 77°F (25°C). After removal from the
refrigerator, use KEVZARA within 14 days or discard.Date removed from the refrigerator ____/____/____
ATTENTION: Enclosed Medication Guide is required for each patient
150 mg/1.14 mL

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 200 mg/1.14 mL Pen Carton
NDC: 0024-5922-01
Rx OnlyKEVZARA®
(sarilumab)
injection200 mg/1.14 mL (175.4 mg/mL)
2 Single-Dose Pre-filled Pens
For Subcutaneous Injection Use OnlyREGENERON
SANOFI GENZYMEStore in a refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in the original
carton to protect from light. Do NOT freeze. Do NOT shake.If needed, patients/caregivers may store KEVZARA at room
temperature up to 77°F (25°C) up to 14 days in the outer carton.
Do not store above 77°F (25°C). After removal from the
refrigerator, use KEVZARA within 14 days or discard.Date removed from the refrigerator ____/____/____
ATTENTION: Enclosed Medication Guide is required for each patient
200 mg/1.14 mL

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
KEVZARA
sarilumab injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0024-5908 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength sarilumab (UNII: NU90V55F8I) (sarilumab - UNII:NU90V55F8I) sarilumab 150 mg in 1.14 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ARGININE (UNII: 94ZLA3W45F) 8.94 mg in 1.14 mL HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) 3.71 mg in 1.14 mL POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) 2.28 mg in 1.14 mL SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 57 mg in 1.14 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0024-5908-01 2 in 1 PACKAGE 05/22/2017 1 1.14 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 0024-5908-02 2 in 1 PACKAGE 05/22/2017 2 1.14 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761037 05/22/2017 KEVZARA
sarilumab injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0024-5910 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength sarilumab (UNII: NU90V55F8I) (sarilumab - UNII:NU90V55F8I) sarilumab 200 mg in 1.14 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ARGININE (UNII: 94ZLA3W45F) 8.94 mg in 1.14 mL HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) 3.71 mg in 1.14 mL POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) 2.28 mg in 1.14 mL SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 57 mg in 1.14 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0024-5910-01 2 in 1 PACKAGE 05/22/2017 1 1.14 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 0024-5910-02 2 in 1 PACKAGE 05/22/2017 2 1.14 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761037 05/22/2017 KEVZARA
sarilumab injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0024-5920 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength sarilumab (UNII: NU90V55F8I) (sarilumab - UNII:NU90V55F8I) sarilumab 150 mg in 1.14 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ARGININE (UNII: 94ZLA3W45F) 8.94 mg in 1.14 mL HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) 3.71 mg in 1.14 mL POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) 2.28 mg in 1.14 mL SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 57 mg in 1.14 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0024-5920-01 2 in 1 PACKAGE 04/13/2018 1 1.14 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 0024-5920-02 2 in 1 PACKAGE 04/13/2018 2 1.14 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761037 05/22/2017 KEVZARA
sarilumab injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0024-5922 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength sarilumab (UNII: NU90V55F8I) (sarilumab - UNII:NU90V55F8I) sarilumab 200 mg in 1.14 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ARGININE (UNII: 94ZLA3W45F) 8.94 mg in 1.14 mL HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) 3.71 mg in 1.14 mL POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) 2.28 mg in 1.14 mL SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 57 mg in 1.14 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0024-5922-01 2 in 1 PACKAGE 04/13/2018 1 1.14 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 0024-5922-02 2 in 1 PACKAGE 04/13/2018 2 1.14 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761037 05/22/2017 Labeler - sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC (824676584) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sanofi Winthrop Industrie 297730488 MANUFACTURE(0024-5908, 0024-5910, 0024-5920, 0024-5922) , ANALYSIS(0024-5908, 0024-5910, 0024-5920, 0024-5922) , LABEL(0024-5908, 0024-5910, 0024-5920, 0024-5922) , PACK(0024-5908, 0024-5910, 0024-5920, 0024-5922) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH 313218430 MANUFACTURE(0024-5920, 0024-5922) , ANALYSIS(0024-5920, 0024-5922) , LABEL(0024-5920, 0024-5922) , PACK(0024-5920, 0024-5922) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 945589711 API MANUFACTURE(0024-5908, 0024-5910, 0024-5920, 0024-5922) , ANALYSIS(0024-5908, 0024-5910, 0024-5920, 0024-5922) , MANUFACTURE(0024-5908, 0024-5910, 0024-5920, 0024-5922) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Genzyme Corporation 050424395 LABEL(0024-5908, 0024-5910, 0024-5920, 0024-5922) , PACK(0024-5908, 0024-5910, 0024-5920, 0024-5922) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Genzyme Ireland Limited 985127419 MANUFACTURE(0024-5908, 0024-5910) , ANALYSIS(0024-5908, 0024-5910) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Nelson Laboratories, Inc. 151663234 ANALYSIS(0024-5908, 0024-5910)
Trademark Results [KEVZARA]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 KEVZARA 87275074 5274968 Live/Registered |
Sanofi Biotechnology 2016-12-20 |
 KEVZARA 86394577 4780600 Live/Registered |
SANOFI BIOTECHNOLOGY 2014-09-15 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.