Nitroglycerin by Rebel Distributors Corp NITROGLYCERIN tablet
Nitroglycerin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Nitroglycerin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Rebel Distributors Corp. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Nitroglycerin, an organic nitrate, is a vasodilating agent. The chemical name for nitroglycerin is 1,2,3-propanetriol trinitrate. The chemical structure is:
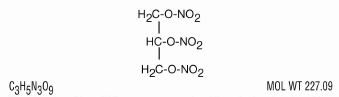
Nitroglycerin tablets USP are compressed sublingual nitroglycerin tablets containing the non-volatile nitroglycerin fixing agent polyethylene glycol. The tablets contain 0.3 mg (1/200 grain), 0.4 mg (1/150 grain), and 0.6 mg (1/100 grain) nitroglycerin. Also contains lactose NF, polyethylene glycol 3350 NF, microcrystalline cellulose NF, colloidal silicon dioxide NF, and magnesium stearate NF.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Relaxation of vascular smooth muscle is the principal pharmacologic action of nitroglycerin. The mechanism by which nitroglycerin produces relaxation of smooth muscle is unknown. Although venous effects predominate, nitroglycerin produces, in a dose-related manner, dilation of both arterial and venous beds. Dilation of the postcapillary vessels, including large veins, promotes peripheral pooling of blood and decreases venous return to the heart, reducing left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (preload). Arteriolar relaxation reduces systemic vascular resistance and arterial pressure (afterload). Myocardial oxygen consumption or demand (as measured by the pressure-rate product, tension-time index and stroke-work index) is decreased by both the arterial and venous effects of nitroglycerin, and amore favorable supply-demand ratio can be achieved.
Nitroglycerin also dilates large epicardial coronary arteries; however, the extent to which this effect contributes to the relief of exertional angina is unclear.
Therapeutic doses of nitroglycerin may reduce systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial blood pressure. Effective coronary perfusion pressure is usually maintained, but can be compromised if blood pressure falls excessively or increased heart rate decreases diastolic filling time.
Elevated central venous and pulmonary capillary wedge pressures, pulmonary vascular resistance and systemic vascular resistance are also reduced by nitroglycerin therapy. Heart rate is usually slightly increased, presumably a reflex response to the fall in blood pressure. Cardiac index may be increased, decreased, or unchanged. Patients with elevated left ventricular filling pressure and systemic vascular resistance values in conjunction with a depressed cardiac index are likely to experience an improvement in cardiac index. On the other hand, when filling pressures and cardiac index are normal, cardiac index may be slightly reduced by intravenous nitroglycerin.
Mechanism of Action
Nitroglycerin forms free radical nitric oxide (NO) which activates guanylate cyclase, resulting in an increase of guanosine 3'5' monophosphate (cyclic GMP) in smooth muscle and other tissues. This eventually leads to dephosphorylation of the light chain of myosin, which regulates the contractile state in smooth muscle, resulting in vasodilation.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Nitroglycerin is rapidly absorbed following sublingual administration. Its onset of action is approximately one to three minutes. Significant pharmacologic effects are present for 30 to 60 minutes following administration by the above route.
Nitroglycerin is rapidly metabolized to dinitrates and mononitrates, with a short half-life, estimated at 1 to 4 minutes. A liver reductase enzyme is of primary importance in the metabolism of nitroglycerin to glycerol nitrate metabolites and organic nitrate. Two active major metabolites 1,2- and 1,3-dinitroglycerols are less potent vasodilators and have longer half-lives than the parent compound. Dinitrates are metabolized to mononitrates and ultimately glycerol. The monohydrate is not considered biologically active with respect to cardiovascular effects.
At plasma concentrations of between 50 and 500 ng/mL, the binding of nitroglycerin to plasma proteins is approximately 60%, while that of 1,2dinitroglycerin and 1,3-dinitroglycerin is 60% and 30%, respectively. The activity and half-life of 1,2-dinitroglycerin and 1,3-dinitroglycerin are not well characterized. The mononitrate is not active.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sublingual nitroglycerin therapy is contraindicated in patients with early myocardial infarction, severe anemia, increased intracranial pressure and those with a known hypersensitivity to nitroglycerin.
Administration of Nitroglycerin tablets USP is contraindicated in patients who are using Viagra® (sildenafil citrate). Viagra® has been shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of organic nitrates.
- WARNINGS
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Only the smallest dose required for effective relief of the acute anginal attack should be used. Excessive use may lead to the development of tolerance. Nitroglycerin USP tablets are intended for sublingual or buccal administration and should not be swallowed. Severe hypotension, particularly with upright posture, may occur even with small doses of nitroglycerin. The drug should be used cautiously in patients with volume depletion or low systolic blood pressure.
Paradoxical bradycardia and increased angina pectoris may accompany nitroglycerin-induced hypotension.
Nitrate therapy may aggravate angina caused by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Tolerance to the vascular and antianginal effects of nitroglycerin and cross-tolerance to other nitrates and nitrites may occur.
The drug should be discontinued if blurring of vision or drying of the mouth occurs. Excessive dosage of nitroglycerin may produce severe headaches.
Information for patients
If possible, patients should sit down when taking Nitroglycerin tablets USP. This eliminates the possibility of falling due to lightheadedness or dizziness.
Nitroglycerin may produce a burning or tingling sensation when administered sublingually; however, the ability to produce a burning or tingling sensation should not be considered a reliable method for determining the potency of the tablets.
Nitroglycerin should be kept in the original glass container, tightly capped. The cotton should be discarded once the bottle is opened.
Administration of Nitroglycerin tablets USP is contraindicated in patients who are using Viagra® (sildenafil citrate). Viagra® has been shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of organic nitrates (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Interactions
Drug interactions
Concomitant use of nitrates and alcohol may cause hypotension. Patients receiving antihypertensive drugs, beta-adrenergic blockers or phenothiazines and nitrates should be observed for possible additive hypotensive effects. Marked orthostatic hypotension has been reported when calcium channel blockers and organic nitrates were used concomitantly. Dose adjustment of either class of agent may be necessary.
Aspirin may decrease the clearance and enhance the hemodynamic effects of sublingual nitroglycerin. A decrease in the therapeutic effect of sublingual nitroglycerin may result from use of long-acting nitrates.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility
No long-term studies in animals were performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of nitroglycerin.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with nitroglycerin. It is also not known whether nitroglycerin can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Nitroglycerin should be given to apregnant woman only if clearly needed.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Headache which may be severe and persistent may occur immediately after use. Vertigo, weakness, palpitation and other manifestations of postural hypotension may develop occasionally, particularly in erect, immobile patients. Marked sensitivity to the hypotensive effects of nitrates (manifested by nausea, vomiting, weakness, diaphoresis, pallor and collapse) may occur at therapeutic doses. Syncope due to nitrate vasodilation has been reported. Flushing, drug rash, and exfoliative dermatitis have been reported in patients receiving nitrate therapy.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Nitrate overdose may result in: severe hypotension, tachycardia, bradycardia, heart block, palpitation, death due to circulatory collapse, syncope, persistent throbbing headache, vertigo, visual disturbance, increased intracranial pressure, paralysis, and coma followed by convulsions, flushing and diaphoresis, nausea and vomiting, colic and diarrhea, dyspnea, methemoglobinemia.
Since hypotension from nitroglycerin overdosage results from venodilation and arterial hypovolemia, therapy should be directed toward central volume expansion. Elevation of extremities may be sufficient, but intravenous infusion may also be necessary. Use of arterial vasoconstrictors may do more harm than good. Management of nitroglycerin overdose in patients with renal disease or congestive heart failure may require invasive monitoring.
If methemoglobinemia is present, intravenous administration of methylene blue 1-2 mg/kg of body weight may be required.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
One tablet should be dissolved under the tongue or in the buccal pouch at the first sign of an acute anginal attack. The dose may be repeated approximately every five minutes, until relief is obtained. If the pain persists after a total of 3 tablets in a 15-minute period, prompt medical attention is recommended. Nitroglycerin tablets USP may be used prophylactically 5 to 10 minutes prior to engaging in activities which might precipitate an acute attack.
During administration the patient should rest, preferably in the sitting position.
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with renal failure.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Nitroglycerin Tablets, USP are supplied as follows:
0.4 mg - White tablet embossed with a "4".
4 x Bottles of 25: NDC: 21695-697-25
Bottle of 100: NDC: 21695-810-00 - STORAGE AND HANDLING
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured By:
Konec, Inc,
Tucson, AZ 65713Manufactured For:

Glenmark Generics Inc., USA
Mahwah, NJ 07430Questions? 1 (888) 721-7115
www.glenmarkgenerics.comRepackaged by:
Rebel Distributors Corp
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
-
NITROGLYCERIN TABLETS USPPatient Information Booklet
This booklet provides general guidance and instruction on the use of Nitroglycerin Tablet USP. You should use this booklet as a handy reminder of your doctor's instructions. Remember to always follow the directions your doctor gave you, and ask your doctor if you have any questions about Nitroglycerin Tablets therapy.
Nitroglycerin Tablets should not be used if you are severely anemic, have been diagnosed with increased pressure on the brain, or are sensitive/allergic to Nitroglycerin. If you are taking Nitroglycerin Tablets, you should not take Viagra® (sildenafil citrate).
While using Nitroglycerin Tablets, if you experience blurring of vision or drying of the mouth, discontinue use and let your doctor know. Nitroglycerin Tablets may cause anotable drop in blood pressure if you are taking blood pressure medication, consuming alcohol, or taking nitrates or antipsychotics.
Excessive use of Nitroglycerin Tablets may lead to tolerance. Headache may occur immediately after Nitroglycerin Tablets use. Dizziness, weakness, and fainting may develop occasionally, especially in patients who are not lying down. The cancer-causing potential of Nitroglycerin Tablets is unknown. Unless specifically prescribed by a physician, Nitroglycerin Tablets should not be used in pregnant or nursing women or in children.
What is angina?
Angina is a medical condition that causes you to feel temporary pain in your chest. The pain may range from adull ache to a severe, crushing sensation. Attacks can occur several times a day or every few weeks, months, or years.
What causes angina?
Angina occurs when your heart muscle needs more oxygen than it can get. This can happen at almost any time, especially during or following physical exertion, stress, or exposure to cold air.
What happens if angina is not treated?
Angina is serious, and, if left untreated, it can lead to additional medical problems such as heart attack. Your angina therapy could save your life. Please read this booklet and make sure to follow your doctor's directions for your angina therapy. Be sure to carry your Nitroglycerin Tablets with you at all times because you never know when you will need them.
How is angina treated?
In addition to having patients modify their activities, one of the most commonly prescribed medications for angina is nitroglycerin. Nitroglycerin Tablets USP and the nitroglycerin patches are nitrates, a form of nitroglycerin. Nitroglycerin Tablets can be used immediately prior to activities that may bring on an angina attack and to treat an angina attack that has already started.
What are Nitroglycerin Tablets USP and how do they work?
Nitroglycerin Tablets USP are a form of nitroglycerin used to relieve or prevent episodes of acute angina. The drug is taken sublingually, meaning it is placed under the tongue to dissolve. Nitroglycerin Tablets can relieve angina by dilating the arteries of the heart so that more oxygen-carrying blood can reach the heart muscle.
How should I use Nitroglycerin Tablets USP when I am having an angina attack?
You may use up to three Nitroglycerin Tablets USP in a 15 minute period. If you continue to feel pain after 15 minutes, call your doctor or seek medical attention immediately. Stay calm and be aware that this unrelieved pain does not necessarily mean you are having a heart attack.
Always follow your doctors directions for use. In general, the following schedule should be followed:
ONSET:
At the first sign of an attack, sit down and then place one Nitroglycerin Tablet under your tongue. You should take Nitroglycerin Tablets while sitting because your blood pressure may drop and cause lightheadedness and dizziness.
5 MIN:
If after waiting 5 minutes, your pain is still present, take a second Nitroglycerin Tablet.
10 MIN:
Again, if after waiting another 5 minutes, the pain is still present, you should take a third Nitroglycerin Tablet.
15 MIN:
If the pain continues 5 minutes or longer after your third Nitroglycerin Tablet, call your doctor or seek medical attention immediately to find out what to do next.
Can I use Nitroglycerin Tablets USP to prevent an angina attack?
Nitroglycerin Tablets may also be used immediately before activities that you feel might cause an angina attack, such as exercise or sexual intercourse. Since you are the best judge of what may set off an attack, be sure to have a bottle of Nitroglycerin Tablets on hand for those times in those places where you would most expect an attack. Take one Nitroglycerin Tablet 5 to 10 minutes before you begin these activities, or follow your doctor's recommendations.
Can I swallow Nitroglycerin Tablets USP?
No. It is very important that each Nitroglycerin Tablet be placed under the tongue until it has fully dissolved. Nitroglycerin Tablets should not be chewed, crushed or swallowed.
Can I eat, drink, or smoke while using Nitroglycerin Tablets USP?
No, do not eat, drink any beverages (including alcohol), smoke, or use chewing tobacco while a tablet is dissolving and/or when you are experiencing acute chest pain.
Should I expect any side effects when I take Nitroglycerin Tablets USP?
Some patients may feel a slight stinging sensation while the tablet is dissolving under the tongue. You also might experience warmth and flushing of the face or lightheadedness and dizziness. Sometimes, patients experience mild to severe headaches with their first few Nitroglycerin Tablets. These side effects usually are not signs of other problems, but you should let your doctor know if you have any concerns.
Why does this package contain four bottles of Nitroglycerin Tablets USP?
Instead of one bottle of 100 tablets, each bottle of Nitroglycerin Tablets USP in the 4-by-25 pack contains 25 tablets. Therefore, you can place the bottles in locations where you might have an angina attack, such as your bedroom, workroom, kitchen, or office. Also, you should always keep a bottle in a jacket or coat pocket (not a shirt or trouser pocket) or purse. By keeping Nitroglycerin Tablets in multiple locations, you will be sure to have your Nitroglycerin Tablets nearby when you need it.
What are the advantages of the 4-by-25 pack?
When purchasing just one 100-tablet bottle, patients cannot keep the drug in different locations without removing tablets from the original container. This is a problem since only the original containers protect Nitroglycerin Tablets from air, heat, moisture, and light. Exposure to these elements can reduce the strength of Nitroglycerin Tablets. Use of the 4-by-25 pack is a convenient way to properly store Nitroglycerin Tablets.
Why isn't there cotton in the Nitroglycerin Tablets USP?
The cotton has been left out of these bottles to make it as easy as possible for you to get a tablet when you need one.
How should I store Nitroglycerin Tablets USP?
Keep bottles where you are likely to have an angina attack, and remember to always keep one bottle with you - for example, in a pocketbook, tote bag, or overcoat. Keep the bottle loose and away from your body to protect the medication from body heat. Nitroglycerin Tablets bottles should not be kept in trouser or shirt pockets. To protect against loss of potency, Nitroglycerin Tablets should be stored in the original bottle and the bottle kept tightly closed. Nitroglycerin Tablets should not be placed in a pillbox or any other container. Do not place other medication in the Nitroglycerin Tablets bottle. Do not refrigerate Nitroglycerin Tablets; room temperature is best. As with all medications, keep Nitroglycerin Tablets out of the reach of children.
How do I know when to replace a bottle of Nitroglycerin Tablets USP?
If the medication has been exposed to ahigh temperature or if the date on the bottle has expired, it should be discarded. Your pharmacist can help determine if your Nitroglycerin Tablets should be replaced.
Manufactured By:
Konec, Inc,
Tucson, AZ 65713Manufactured For:

Glenmark Generics Inc., USA
Mahwah, NJ 07430Questions? 1 (888) 721-7115
www.glenmarkgenerics.comRepackaged by:
Rebel Distributors Corp
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
- Principal Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
NITROGLYCERIN
nitroglycerin tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 21695-810(NDC: 68462-146) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NITROGLYCERIN (UNII: G59M7S0WS3) (NITROGLYCERIN - UNII:G59M7S0WS3) NITROGLYCERIN 0.4 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE (UNII: J2B2A4N98G) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3350 (UNII: G2M7P15E5P) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 4mm Flavor Imprint Code 4 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 21695-810-00 100 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date Unapproved drug other 03/03/2005 Labeler - Rebel Distributors Corp (118802834) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Rebel Distributors Corp 118802834 RELABEL, REPACK
Trademark Results [Nitroglycerin]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 NITROGLYCERIN 76482982 2851735 Dead/Cancelled |
J. Richard Industries, Inc. 2003-01-17 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
