VALRUBICIN INTRAVESICAL SOLUTION solution, concentrate
Valrubicin Intravesical Solution by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Valrubicin Intravesical Solution by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VALRUBICIN INTRAVESICAL SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VALRUBICIN INTRAVESICAL SOLUTION.
VALRUBICIN intravesical solution, for intravesical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1981INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Valrubicin intravesical solution is an anthracycline topoisomerase inhibitor indicated for intravesical therapy of BCG-refractory carcinoma in situ (CIS) of the urinary bladder in patients for whom immediate cystectomy would be associated with unacceptable morbidity or mortality. ( 1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For Intravesical Use Only. ( 2.1)
- Valrubicin intravesical solution is recommended at a dose of 800 mg administered intravesically once a week for six weeks. ( 2.1)
- Delay administration at least two weeks after transurethral resection and/or fulguration. ( 2.1)
- Warm valrubicin intravesical solution slowly to room temperature, but do not heat. ( 2.1)
- Use caution when handling and preparing the solution of valrubicin intravesical solution. ( 2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Injection: 200 mg/5 mL in single-use vials ( 3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Delaying cystectomy can lead to development of metastatic bladder cancer, which is lethal. ( 5.1)
- Do not administer valrubicin intravesical solution to patients with a perforated bladder or to those in whom the integrity of the bladder mucosa has been compromised. ( 5.2, 12.3)
- Evaluate the status of the bladder before the intravesical instillation of valrubicin intravesical solution. ( 5.3)
- Use with caution in patients with severe irritable bladder symptoms. ( 5.4)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Valrubicin intravesical solution can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. ( 5.5, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently reported adverse reactions ( >5%) after administration of valrubicin intravesical solution are urinary frequency, dysuria, urinary urgency, bladder spasm, hematuria, bladder pain, urinary incontinence, cystitis, urinary tract infection, nocturia, local burning symptoms, abdominal pain, and nausea. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Leucadia Pharmaceuticals at 1-877-411-9681 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. ( 8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 1/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
2.2 Preparation, Handling, and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Metastatic Bladder Cancer with Delayed Cystectomy
5.2 Risks in Patients with Perforated Bladder
5.3 Risk in Patients Undergoing Transurethral Resection of the Bladder (TURB)
5.4 Risk in Patients with Irritable Bladder Symptoms
5.5 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproduction Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
For Intravesical Use Only. Do NOT administer by intravenous or intramuscular routes.
Valrubicin intravesical solution is recommended at a dose of 800 mg administered intravesically once a week for six weeks. Delay administration at least two weeks after transurethral resection and/or fulguration [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2, 5.3)].
2.2 Preparation, Handling, and Administration
Handle and dispose of valrubicin intravesical solution in a manner consistent with other cytotoxic drugs. 1 The use of goggles, gloves, and protective gowns is recommended during preparation and administration of the drug.
Valrubicin intravesical solution contains polyoxyl castor oil, which has been known to cause leaching of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) a hepatotoxic plasticizer, from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) bags and intravenous tubing. Valrubicin intravesical solution should be prepared and stored in glass, polypropylene, or polyolefin containers and tubing. It is recommended that non-DEHP containing administration sets, such as those that are polyethylene-lined, be used.
Valrubicin intravesical solution is a sterile, clear red solution. Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. At temperatures below 4°C (39°F), polyoxyl castor oil may begin to form a waxy precipitate. If this happens, the vial should be warmed in the hand until the solution is clear. If particulate matter is still seen, do not administer valrubicin intravesical solution.
For each instillation, slowly allow four 5 mL vials (200 mg valrubicin/5 mL vial) to warm to room temperature, but do not heat. Withdraw 20 mL of valrubicin intravesical solution from the four vials and dilute with 55 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP to provide 75 mL of a diluted valrubicin intravesical solution. Valrubicin intravesical solution diluted in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP for administration is stable for 12 hours at temperatures up to 25°C (77°F). Since compatibility data are not available, do not mix valrubicin intravesical solution with other drugs.
Insert a urethral catheter into the patient's bladder under aseptic conditions, drain the bladder, and instill the diluted 75 mL valrubicin intravesical solution slowly via gravity flow over a period of several minutes. Withdraw the catheter and retain valrubicin intravesical solution in the bladder for two hours before voiding. At the end of two hours, all patients should void. Some patients may be unable to retain the drug for the full two hours. Instruct patients to maintain adequate hydration following valrubicin intravesical solution treatment [see Patient Counseling Information ( 17)] .
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Valrubicin intravesical solution is contraindicated in patients with:
- Perforated bladder [ see Warnings and Precautions( 5.2)]
- Known hypersensitivity to anthracyclines or polyoxyl castor oil
- Active urinary tract infection
- Small bladder capacity and unable to tolerate a 75 mL instillation
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Metastatic Bladder Cancer with Delayed Cystectomy
Inform patients that valrubicin intravesical solution has been shown to induce complete response in only about 1 in 5 patients with BCG-refractory CIS, and that delaying cystectomy could lead to development of metastatic bladder cancer, which is lethal. The exact risk of developing metastatic bladder cancer from such a delay may be difficult to assess [see Clinical Studies ( 14)] but increases the longer cystectomy is delayed in the presence of persisting CIS. If there is not a complete response of CIS to treatment after 3 months or if CIS recurs, reconsider cystectomy.
5.2 Risks in Patients with Perforated Bladder
Evaluate the bladder before the intravesical instillation of drug and do not administer valrubicin intravesical solution to patients with a perforated bladder or to those in whom the integrity of the bladder mucosa has been compromised [see Contraindications ( 4)] . In case of bladder perforation, delay the administration of valrubicin intravesical solution until bladder integrity has been restored. One patient with a perforated bladder who received 800 mg of valrubicin intravesical solution intravesically developed severe leukopenia and neutropenia approximately two weeks after drug administration [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)] .
5.3 Risk in Patients Undergoing Transurethral Resection of the Bladder (TURB)
To avoid systemic exposure to valrubicin intravesical solution for the patients undergoing TURB, evaluate the status of the bladder before the intravesical instillation of drug. Delay administration at least two weeks after transurethral resection and/or fulguration.
5.4 Risk in Patients with Irritable Bladder Symptoms
Use valrubicin intravesical solution with caution in patients with severe irritable bladder symptoms. Bladder spasm and spontaneous discharge of the intravesical instillate may occur; clamping of the urinary catheter is not advised.
5.5 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animal studies and its mechanism of action, valrubicin intravesical solution can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.1 and 12.3)] . In animal reproduction studies, intravenous administration of valrubicin to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at a dose about 0.2 times the recommended human intravesical dose caused embryo-fetal malformations and increased resorptions. Advise females who might become pregnant of the potential risk to a fetus.
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with valrubicin intravesical solution and for 6 months following the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1 and 8.3)] .
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of valrubicin intravesical solution was assessed in 230 patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder, including 205 patients who received multiple weekly doses. One hundred seventy-nine of the 205 patients received the approved dose and schedule of 800 mg weekly for multiple weeks.
Approximately 84% of patients who received intravesical valrubicin intravesical solution in clinical studies experienced local adverse reactions. The local adverse reactions associated with valrubicin intravesical solution usually occur during or shortly after instillation and resolve within 1 to 7 days after the instillate is removed from the bladder. Seven out of 143 patients (5%) who were scheduled to receive six doses of valrubicin intravesical solution failed to receive all of the planned doses because of the occurrence of local bladder symptoms.
TABLE 1 displays the frequency of the local adverse reactions at baseline and during treatment among 179 patients who received 800 mg doses of valrubicin intravesical solution in a multiple-cycle treatment regimen.
TABLE 1 Local Adverse Reactions Before and During Treatment with Valrubicin Intravesical Solution (N=179) Adverse Reaction
Before Treatment
During 6-week
Course of Treatment
ANY LOCAL
BLADDER SYMPTOM
45%
88%
Urinary Frequency
30%
61%
Dysuria
11%
56%
Urinary Urgency
27%
57%
Bladder Spasm
3%
31%
Hematuria
11%
29%
Bladder Pain
6%
28%
Urinary Incontinence
7%
22%
Cystitis
4%
15%
Nocturia
2%
7%
Local Burning Symptoms –
Procedure Related
0%
5%
Urethral Pain
0%
3%
Pelvic Pain
1%
1%
Hematuria (Gross)
0%
1%
TABLE 2 displays the adverse reactions other than local bladder symptoms that occurred in 1% or more of the 230 patients who received at least one dose of valrubicin intravesical solution in a clinical trial.
TABLE 2 Systemic Adverse Reactions (> 1%) Following Intravesical Administration of Valrubicin Intravesical Solution (N=230) Body System
Preferred Term
Body as a Whole
Abdominal Pain
5%
Asthenia
4%
Headache
4%
Malaise
4%
Back Pain
3%
Chest Pain
3%
Fever
2%
Cardiovascular
Vasodilation
2%
Digestive
Nausea
5%
Diarrhea
3%
Vomiting
2%
Flatulence
1%
Hemic and Lymphatic
Anemia
2%
Metabolic and Nutritional
Hyperglycemia
1%
Peripheral Edema
1%
Musculoskeletal
Myalgia
1%
Nervous
Dizziness
3%
Respiratory
Pneumonia
1%
Skin and Appendages
Rash
3%
Urogenital
Urinary Tract Infection
15%
Urinary Retention
4%
Hematuria (miscroscopic)
3%
Adverse reactions other than local reactions that occurred in less than 1% of the patients who received valrubicin intravesical solution intravesically in clinical trials are listed below.
Digestive System: Tenesmus
Metabolic and Nutritional: Nonprotein nitrogen increased
Skin and Appendages: Pruritus
Special Senses: Taste loss
Urogenital System: Local skin irritation, poor urine flow, and urethritis - 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animal studies and its mechanism of action, valrubicin intravesical solution can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant females [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.1 and 12.3)] . There are no available data in pregnant females to inform the drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, intravenous administration of valrubicin to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at a dose about 0.2 times the recommended human intravesical dose caused embryo-fetal malformations and increased resorptions [see Data]. Advise females who are or might become pregnant of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically-recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Daily intravenous administration of valrubicin to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at doses ≥ 12 mg/kg (about 0.2 times the recommended human intravesical dose on a mg/m 2 basis) was embryo-fetal toxic and teratogenic. Administration of 12 mg/kg resulted in fetal malformations. A dose of 24 mg/kg (about 0.3 times the recommended human intravesical dose on a mg/m 2 basis) caused numerous, severe alterations in the skull and skeleton of the developing fetuses. This dose also caused an increase in fetal resorptions and a decrease in viable fetuses.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of valrubicin or its metabolites in human milk, the effects of valrubicin on the breast-fed infant, or its effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breast-fed infants from valrubicin, advise a lactating female not to breastfeed during treatment with valrubicin intravesical solution and for 2 weeks after the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproduction Potential
Contraception
Females
Valrubicin intravesical solution can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with valrubicin intravesical solution and for 6 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1)] .
Males
Based on genotoxicity findings, advise men with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with valrubicin intravesical solution and for 3 months following the final dose [see Non Clinical Toxicology ( 13.1)]
Infertility
Males
Studies of the effects of valrubicin intravesical solution on human male or female fertility have not been done. Based on findings in animal studies, Valrubicin intravesical solution may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology ( 13.1)] .
8.5 Geriatric Use
Because carcinoma in situ of the bladder generally occurs in older individuals, 85% of the patients enrolled in the clinical studies of valrubicin intravesical solution were more than 60 years of age (49% of the patients were more than 70 years of age). In the primary efficacy studies, the mean age of the population was 69.5 years. There are no specific precautions regarding use of valrubicin intravesical solution in geriatric patients who are otherwise in good health.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no known antidote for overdoses of valrubicin intravesical solution. The primary anticipated complications of overdosage associated with intravesical administration would be consistent with irritable bladder symptoms.
Myelosuppression is possible if valrubicin intravesical solution is inadvertently administered systemically or if significant systemic exposure occurs following intravesical administration (e.g., in patients with bladder rupture/perforation). Under such inadvertent exposures in the peritoneal cavity, the expected toxicities include leukopenia and neutropenia, beginning within 1 week of dose administration, with nadirs by the second week, and recovery generally by the third week. If valrubicin intravesical solution is administered when bladder rupture or perforation is suspected, weekly monitoring of complete blood counts should be performed for 3 weeks.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Valrubicin Intravesical Solution, USP contains valrubicin (N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin-14-valerate), which is a semisynthetic analog of the anthracycline doxorubicin as a cytotoxic agent. The chemical name of valrubicin is (2 S- cis)-2-[1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-[[2,3,6-trideoxy-3-[(trifluoroacetyl)amino]-α-L- lyxo-hexopyranosyl]oxyl]-2-naphthacenyl]-2-oxoethylpentanoate. Valrubicin is an orange or orange-red powder that is highly lipophilic, soluble in methylene chloride, ethanol, methanol and acetone, and relatively insoluble in water. Its chemical formula is C 34H 36F 3NO 13 and its molecular weight is 723.65. The chemical structure is shown in FIGURE 1.
FIGURE 1. Chemical Structure of Valrubicin
Valrubicin Intravesical Solution, USP is intended for intravesical administration in the urinary bladder. It is supplied as a nonaqueous solution that should be diluted before intravesical administration. Each vial of Valrubicin Intravesical Solution, USP contains 200 mg valrubicin at a concentration of 40 mg/mL in 5 mL of 50% polyoxyl castor oil/50% v/v dehydrated alcohol, USP without preservatives or other additives. The solution is sterile and nonpyrogenic.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Valrubicin is an anthracycline that affects a variety of interrelated biological functions, most of which involve nucleic acid metabolism. In cells, it inhibits the incorporation of nucleosides into nucleic acids, causes chromosomal damage, and arrests the cell cycle in G 2. Although valrubicin does not bind strongly to DNA, valrubicin metabolites interfere with the normal DNA breaking-resealing action of DNA topoisomerase II.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
When 800 mg valrubicin intravesical solution was administered intravesically to patients with carcinoma in situ, valrubicin intravesical solution penetrated into the bladder wall. The mean total anthracycline concentration measured in bladder tissue exceeded the levels causing 90% cytotoxicity to human bladder cells cultured in vitro. During the two-hour dose-retention period, the metabolism of valrubicin intravesical solution to its major metabolites N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin and N-trifluoroacetyladriamycinol in bladder tissue was negligible. After retention, the drug was almost completely excreted by voiding the instillate. Mean percent recovery of valrubicin intravesical solution, N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin, and total anthracyclines in 14 urine samples from six patients was 98.6%, 0.4%, and 99.0% of the total administered drug, respectively. During the two-hour dose-retention period, only nanogram quantities of valrubicin intravesical solution were absorbed into the plasma. N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin and N-trifluoroacetyladriamycinol were measured in blood.
Total systemic exposure to anthracyclines during and after intravesical administration of valrubicin intravesical solution is dependent upon the condition of the bladder wall. The mean AUC 0-6hours (total anthracyclines exposure) for an intravesical dose of 900 mg of valrubicin intravesical solution administered 2 weeks after transurethral resection of bladder tumors (n=6) was 78 nmol/Lhr. In patients receiving 800 mg of valrubicin intravesical solution 5 to 51 minutes after typical (n=8) and extensive (n=5) TURB tumors, the mean AUC 0-6hours values for total anthracyclines were 409 and 788 nmol/Lhr, respectively. The AUC 0-6hours total exposure to anthracyclines was 18,382 nmol/Lhr in one patient who experienced a perforated bladder following a transurethral resection that occurred 5 minutes before administration of an intravesical dose of 800 mg of valrubicin intravesical solution. Administration of a comparable intravenous dose of valrubicin intravesical solution (600 mg/m 2; n=2) as a 24-hour infusion resulted in an AUC 0-6hours for total anthracyclines of 11,975 nmol/Lhr. These results are shown in FIGURE 2.
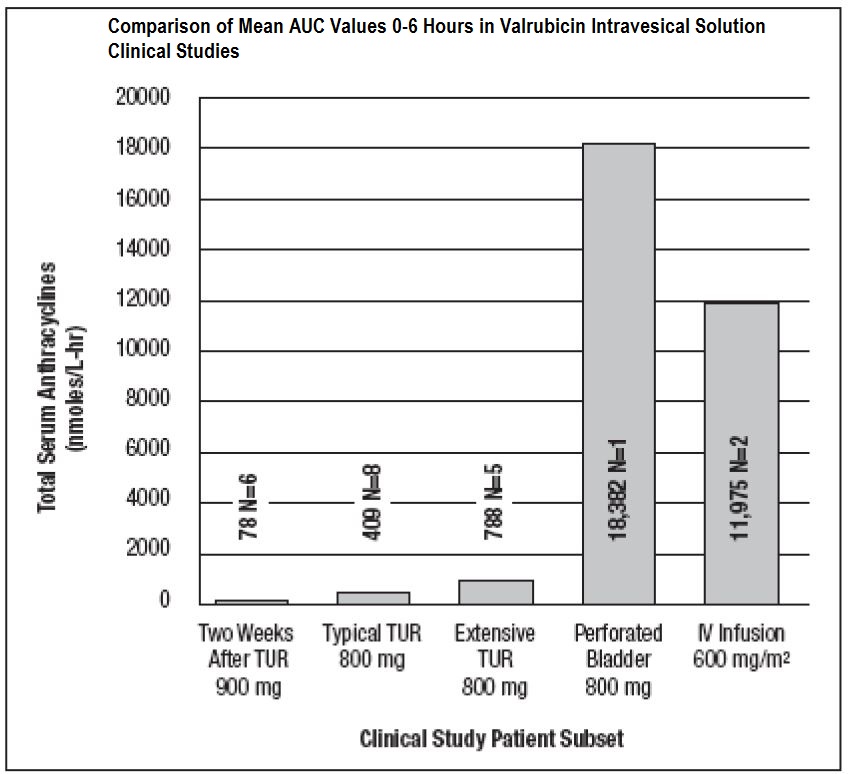
FIGURE 2. Comparison of Mean AUC0-6 hours in Valrubicin Intravesical Solution Clinical Studies (N=number of patients)
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of valrubicin has not been evaluated.
In vitro, valrubicin was mutagenic in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assayand clastogenic in the chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells.
Studies in animals evaluating the effects of valrubicin on male or female fertility have not been conducted. Based on effects on male reproductive organs in general toxicology studies in dogs with intravesical instillation, valrubicin may impair fertility in male patients. When instilled into the bladder of male dogs weekly for 6 weeks, valrubicin caused mild to moderate atrophy of the prostate with inflammation, diffuse decrease in acinar size, epithelial changes. It also caused testicular degeneration, marked germ cell depletion, spermatid giant cells and karyomegaly.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Valrubicin intravesical solution was administered intravesically to a total of 230 patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder, including 205 patients who received multiple weekly doses ranging from 200 to 900 mg. One hundred seventy-nine of the 205 patients received the approved dose and schedule of 800 mg weekly for multiple weeks. Patients receiving Valrubicin intravesical solution for refractory carcinoma in situ were monitored for disease recurrence or progression with cystoscopy, biopsy, and urine cytology every 3 months.
In the 90 study patients with BCG-refractory carcinoma in situ (CIS), 70% had received at least 2 courses of BCG and 30% had received one course of BCG and at least one additional course of treatment with another agent(s) - e.g., mitomycin, thiotepa, or interferon. Valrubicin intravesical solution was administered beginning at least two weeks after transurethral resection and/or fulguration.
After intravesical administration of valrubicin intravesical solution, 16 patients (18%) had a complete response documented by bladder biopsies and cytology at 6 months following initiation of therapy. Median duration of response from start of treatment varied according to the method of analysis (13.5 months if measured to last bladder biopsy without tumor and 21 months if measured until time of documented recurrence). A retrospective analysis in the 16 patients with complete response to valrubicin intravesical solution demonstrated that time to recurrence of their disease after treatment with valrubicin intravesical solution was longer than time to recurrence after previous courses of intravesical therapy.
Of the 90 patients with BCG-refractory CIS, 11% (10 patients) developed metastatic or deeply-invasive bladder cancer during follow-up; four of these patients, none who underwent cystectomy, died with metastatic bladder cancer and six were found to have developed stage progression to deeply-invasive disease (T3), with lymph node involvement in one patient, at the time of cystectomy. It is uncertain to what extent the development of advanced bladder cancer in these patients was due to the delay in cystectomy required to receive treatment with valrubicin intravesical solution (3 months was the time of follow-up to determine response), as cystectomy was often delayed or was never performed despite failure of treatment with valrubicin intravesical solution. In the 10 patients documented to have invasive bladder cancer or metastatic disease, the delay between the time of treatment failure (when cystectomy should have been performed) and cystectomy or documentation of advanced bladder cancer was a median of 17.5 months.
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED
Valrubicin Intravesical Solution, USP is a sterile, clear red solution in polyoxyl castor oil/dehydrated alcohol, USP, containing 40 mg valrubicin per mL. Valrubicin Intravesical Solution, USP is available in single-use, clear glass vials, individually packaged in the following sizes:
NDC 24201-101-04 Carton of four 200 mg/5 mL single-use vials
Store vials under refrigeration at 2°-8°C (36°-46°F) in the carton. DO NOT FREEZE.
The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Risk of Metastatic Bladder Cancer with Delayed Cystectomy
- Inform patients that valrubicin intravesical solution has been shown to induce complete responses in only about 1 in 5 patients, and that delaying cystectomy could lead to development of metastatic bladder cancer, which is lethal. Discuss the relative risk of cystectomy versus the risk of metastatic bladder cancer [see Clinical Trials ( 14)] and that the risk increases the longer cystectomy is delayed in the presence of persisting CIS.
Local Adverse Reactions Before and During Treatment
- Inform patients that the major acute toxicities from valrubicin intravesical solution are related to irritable bladder symptoms that may occur during instillation and retention of valrubicin intravesical solution and for a limited period following voiding [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.1)] .
- Inform patients that for the first 24 hours following administration, red-tinged urine is typical.
- Advise patients to report prolonged irritable bladder symptoms or prolonged passage of red-colored urine immediately to their physician.
- Instruct patients to maintain adequate hydration following valrubicin intravesical solution treatment.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception during treatment with valrubicin intravesical solution and for 6 months after the last dose. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1 and 8.3)] .
- Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with valrubicin intravesical solution and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.3)] .
Lactation
- Advise females not to breastfeed during treatment with valrubicin intravesical solution and for 2 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.2)] .
Healthcare professionals can telephone Leucadia Pharmaceuticals (1-877-411-9681) for information on this product.
Manufactured by:
The University of Iowa Pharmaceuticals
Iowa City, Iowa 52242Manufactured for:
Leucadia Pharmaceuticals
Carlsbad, CA 92011Rev. January 2019
- Package Label – Principle Display Panel – Vial Label
- Package Label – Principle Display Panel – Carton – 4 Vials
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VALRUBICIN INTRAVESICAL SOLUTION
valrubicin intravesical solution solution, concentrateProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 24201-101 Route of Administration INTRAVESICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VALRUBICIN (UNII: 2C6NUM6878) (VALRUBICIN - UNII:2C6NUM6878) VALRUBICIN 40 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) 0.5 mL in 1 mL POLYOXYL 35 CASTOR OIL (UNII: 6D4M1DAL6O) 0.5 mL in 1 mL NITROGEN (UNII: N762921K75) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 24201-101-04 4 in 1 CARTON 04/23/2019 1 5 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA206430 04/23/2019 Labeler - Leucadia Pharmaceuticals (013663107)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

