IMAAVY- nipocalimab injection, solution, concentrate
IMAAVY by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
IMAAVY by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Janssen Biotech, Inc., Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg Mooswiesen), Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg Schuetzenstrasse), Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg Helmut-Vetter-Strasse), Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Langenargen Eisenbahnstrasse), Janssen Biologics B.V., WuXi Biologics Co., Ltd., Eurofins Biolab Srl, Cilag AG, WuXi Biologics Biosafety Testing (Suzhou) Co., Ltd., WuXi Biologics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd, Janssen Sciences Ireland UC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use IMAAVY safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for IMAAVY.
IMAAVY™ (nipocalimab-aahu) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025INDICATIONS AND USAGE
IMAAVY is a neonatal Fc receptor blocker indicated for the treatment of generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older who are anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR) or anti-muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK) antibody positive. ( 1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on dosage, preparation, and administration. ( 2.1, 2.2, 2.3)
- Evaluate the need to administer age-appropriate vaccines according to immunization guidelines before initiation of IMAAVY. ( 2.1)
- Administer via intravenous infusion only. ( 2.2)
- The recommended initial dosage is 30 mg/kg once via intravenous infusion over at least 30 minutes. Two weeks after the initial dosage, administer a maintenance dosage of 15 mg/kg via intravenous infusion over at least 15 minutes, and continue every two weeks thereafter. ( 2.2)
- Must be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride injection prior to administration. ( 2.3)
- Administer as an intravenous infusion via a 0.2 micron in-line or add-on filter. ( 2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
IMAAVY is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity reaction to nipocalimab or to any of the excipients in IMAAVY. ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Infections: Delay administration of IMAAVY to patients with an active infection. Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection in patients treated with IMAAVY. If serious infection occurs, administer appropriate treatment and consider withholding IMAAVY until the infection has resolved. ( 5.1)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Angioedema, anaphylaxis, rash, urticaria, and eczema have occurred in patients treated with IMAAVY. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue the infusion and institute appropriate therapy. ( 5.2)
- Infusion-Related Reactions: If a severe infusion-related reaction occurs, discontinue the infusion and initiate appropriate therapy; consider the risks and benefits of readministering. If a mild to moderate infusion-related reaction occurs, may rechallenge with close clinical observation, slower infusion rates, and pre-medication. ( 5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) in patients with gMG treated with IMAAVY were respiratory tract infections, peripheral edema, and muscle spasms. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen Biotech, Inc. at 1-800-526-7736 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Closely monitor for reduced effectiveness of medications that bind to the human neonatal Fc receptor. When concomitant long-term use of such medications is essential for patient care, consider discontinuing IMAAVY and using alternative therapies. ( 7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Vaccination
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Preparation and Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infections
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.3 Infusion-Related Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of IMAAVY on Other Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Vaccination
Evaluate the need to administer age-appropriate vaccines according to immunization guidelines before initiation of IMAAVY. Because IMAAVY causes transient reduction in IgG levels, vaccination with live vaccines is not recommended during treatment with IMAAVY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Dilute IMAAVY prior to administration. Administer via intravenous infusion only [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
The recommended initial dosage of IMAAVY is 30 mg/kg administered once via intravenous infusion over at least 30 minutes. Two weeks after the initial dosage administer a maintenance dosage of 15 mg/kg via intravenous infusion over at least 15 minutes. Continue the maintenance dosage every two weeks thereafter.
If a scheduled infusion appointment is missed, the maintenance dosage of IMAAVY should be administered as soon as possible. Resume dosing every two weeks thereafter.
2.3 Preparation and Administration Instructions
Prior to administration, dilute IMAAVY single-dose vials with only 0.9% sodium chloride injection using the instructions below. For patients who weigh 40 kg or more, the total volume to be administered is 250 mL; for patients who are 12 years or older and weigh less than 40 kg, the total volume to be administered is 100 mL (see Preparation) .
Preparation
Prepare the solution for infusion using aseptic technique as follows:
- Calculate the dosage (mg), total drug volume (mL) of IMAAVY solution required, and the number of IMAAVY vials needed, based on the patient's current weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] . Each single-dose vial of IMAAVY is at a concentration of 185 mg/mL.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Check that the solution in each vial is colorless to slightly brownish, clear to slightly opalescent, and free of visible particles. Do not use if visible particles are present or if the solution is discolored (other than colorless to slightly brownish).
- Gently withdraw the calculated volume of IMAAVY from the vial(s). Discard any unused portion of the vials.
- Dilute total volume withdrawn of IMAAVY by adding to an infusion container containing 0.9% sodium chloride injection to a final volume of:
- 250 mL for patients who weigh 40 kg or more, or
- 100 mL for patients who weigh less than 40 kg.
- Gently invert the infusion container at least 10 times to mix the solution. Do not shake.
- Verify that a uniform solution has been achieved by visual inspection. Do not use if particulate matter or discoloration is present.
Storage Conditions of the Diluted Solution
- Administer the diluted IMAAVY solution immediately after preparation.
- If the diluted IMAAVY solution is not used immediately:
- Protect from light.
- Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 24 hours.
- Do not freeze.
- After preparation or removal from the refrigerator, use or discard the IMAAVY diluted solution within 12 hours, including infusion time. During these 12 hours, store under ambient light at 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
Administration
- If the diluted solution is refrigerated prior to administration, allow to warm to room temperature. Do not use external heat sources to warm IMAAVY.
- Administer the diluted solution by intravenous infusion only using an infusion set with an in-line or add-on, sterile, non-pyrogenic, low protein-binding filter made of polyethersulfone or polysulfone (pore size 0.2 micrometer or less). Administration sets must be made of either polybutadiene, polyethylene, polyurethane, polypropylene, or polyvinylchloride.
- Do not infuse IMAAVY concomitantly in the same intravenous line with other agents.
- Administer IMAAVY infusion intravenously over at least 30 minutes for the initial dose (30 mg/kg) and at least 15 minutes for subsequent doses (15 mg/kg).
- If an adverse reaction occurs during administration of IMAAVY, the infusion may be slowed or stopped at the discretion of the healthcare professional.
- Monitor the patient for 30 minutes after each infusion for signs or symptoms of an infusion-related or hypersensitivity reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
IMAAVY is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity reaction to nipocalimab or any of the excipients in IMAAVY. Reactions have included anaphylaxis and angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infections
IMAAVY may increase the risk of infection [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . In Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)] , 42 (43%) out of 98 patients treated with IMAAVY reported 71 events of infection. Across Study 1 (double blind period) and its extension study (open label-period), out of 186 patients treated with IMAAVY, 132 (71%) patients reported 360 events of infection. Serious infections were reported in 7% of patients treated with IMAAVY. Delay IMAAVY administration in patients with an active infection until the infection is resolved. During treatment with IMAAVY, monitor for clinical signs and symptoms of infection. If serious infection occurs, administer appropriate treatment and consider withholding IMAAVY until the infection has resolved.
Latent Viral Infections
Patients treated with IMAAVY may be at an increased risk of activation of latent viral infections, such as herpes zoster [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . In the extension period of Study 1, there were 2 patients with serious adverse reactions related to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, and 1 of these patients had fatal complications. Patients who screened positive for hepatitis were excluded from Study 1. Follow standard vaccination guidelines [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Immunization
The safety of immunization with live vaccines and the immune response to vaccination during treatment with IMAAVY are unknown. Because IMAAVY causes a reduction in IgG levels, vaccination with live vaccines is not recommended during treatment with IMAAVY.
Evaluate the need to administer age-appropriate vaccines according to immunization guidelines before initiation of treatment with IMAAVY.
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
In clinical trials, hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema, anaphylaxis, rash, urticaria, and eczema were observed in patients treated with IMAAVY. In Study 1, hypersensitivity reactions were mild or moderate, occurred within one hour to 2 weeks of administration [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . One patient experienced a hypersensitivity reaction (urticaria) that led to treatment discontinuation.
Management of hypersensitivity reactions depends on the type and severity of the reaction. Monitor the patient during treatment with IMAAVY and for 30 minutes after the administration is complete for clinical signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] . If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs during administration, discontinue IMAAVY infusion and institute appropriate supportive measures if needed. IMAAVY is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity to nipocalimab or any of the excipients of IMAAVY [see Contraindications (4)] .
5.3 Infusion-Related Reactions
In clinical trials, infusion-related reactions, including headache, influenza-like illness, rash, nausea, fatigue, dizziness, chills, and erythema were observed in patients treated with IMAAVY. In Study 1, infusion-related reactions were mild to moderate in severity and occurred within one hour to 2 days of administration [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
Monitor patients during treatment with IMAAVY and for 30 minutes after each infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] . If a severe infusion-related reaction occurs, discontinue IMAAVY infusion and initiate appropriate therapy. Consider the risks and benefits of readministering IMAAVY following a severe infusion-related reaction. If a mild to moderate infusion related reaction occurs, patients may be rechallenged with close clinical observation, slower infusion rates, and pre-medication.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Infusion-related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adults
In Study 1 and its extension study the safety of IMAAVY was evaluated in 186 patients with gMG who received at least one dose of IMAAVY. Of those patients, 168 patients were exposed to IMAAVY every 2 weeks for at least 6 months, and 140 patients were exposed for at least 12 months.
In Study 1, 98 adult patients with gMG received IMAAVY 15 mg/kg every two weeks (after 30 mg/kg initial dose) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Of these 98 patients, approximately 67% were female, 67% were White, 29% were Asian, and 10% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean age at study entry was 53 years (range 20 to 81).
Adverse reactions reported in at least 5% of patients treated with IMAAVY and more frequently than placebo, are summarized in Table 1. The most common adverse reactions (reported in at least 10% of patients treated with IMAAVY) were respiratory tract infection, peripheral edema, and muscle spasms.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions (≥ 5%) of Patients Treated with IMAAVY and More Frequently than in Placebo in Study 1 Adverse Reaction IMAAVY
N=98
%Placebo
N=98
%Includes the following reported in patients treated with IMAAVY: - * COVID-19 (and other related terms), pneumonia, bronchitis, pneumonia bacteria
- † other related terms
- ‡ glossitis, oral candidiasis, pericoronitis, pulpitis dental, tooth abscess, tooth infection
- § angioedema, dermatitis atopic, eczema, gingival swelling, rash (and other related terms), urticaria
Infection Respiratory tract infection * 18 13 Urinary tract infection † 6 3 Herpes zoster and Herpes simplex 6 2 Oral infection ‡ 5 3 Peripheral edema 12 2 Muscle spasm 12 3 Hypersensitivity reaction § 8 7 Abdominal pain 8 3 Back pain 8 5 Pyrexia 7 1 Diarrhea 7 3 Cough 7 3 Anemia † 6 4 Dizziness 5 1 Nausea 5 2 Hypertension 5 2 Insomnia 5 2 Infections
In Study 1 and its extension study, infections that occurred in patients treated with IMAAVY (n=186) included upper respiratory tract infection (46%), respiratory tract infection (28%; including pneumonia, bronchitis, COVID-19), urinary tract infection (15%), herpes (8%; including herpes simplex, herpes zoster, herpes zoster oticus), influenza (8%), oral infection (8%; including candidiasis and dental infections), and skin infection (7%; including cellulitis). Two (1%) cases of infections (cellulitis and urinary tract infection) led to discontinuation of IMAAVY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
Hypersensitivity Reactions
In Study 1 and its extension study, out of 186 patients treated with IMAAVY, 30 (16%) patients experienced hypersensitivity reactions, which occurred within one hour to two weeks of administration. One patient experienced hypersensitivity reaction (urticaria) that required discontinuation of IMAAVY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
Infusion-Related Reactions
In Study 1 and its extension study, out of 186 patients treated with IMAAVY, 20 (11%) patients experienced infusion-related reactions, which occurred within one hour to 2 days of administration. No patients experienced infusion-related reaction that required discontinuation of IMAAVY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
Laboratory Findings
Lipids
In Study 1 (N=98), patients treated with IMAAVY had elevations from normal to high of fasting total cholesterol ( ≥240 mg/dL) and LDL cholesterol ( ≥160 mg/dL) (24% and 11% of patients, respectively). In Study 1, these changes from baseline peaked at Week 4, then decreased and plateaued by Week 24 to mean increases of 14 mg/dL and 7 mg/dL, respectively. Five percent of patients treated with IMAAVY had decreases from normal to low (<40 mg/dL of fasting HDL cholesterol).
Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older
In a 24-week, single arm study evaluating the safety of IMAAVY in 7 pediatric patients age 12 to 16 years with gMG who were AChR positive, adverse reactions were consistent with those observed in adult patients with gMG [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] .
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of IMAAVY on Other Drugs
Concomitant use of IMAAVY with medications that bind to the human neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) (e.g., immunoglobulin products, monoclonal antibodies, or antibody derivates containing the human Fc domain of the IgG subclass) may lower systemic exposures and reduce effectiveness of such medications. Closely monitor for reduced effectiveness of medications that bind to the human neonatal Fc receptor. When concomitant long-term use of such medications is essential for patient care, consider discontinuing IMAAVY, and using alternative therapies [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are limited data on the use of IMAAVY in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
There was no evidence of direct adverse effects on fetal development following administration of nipocalimab-aahu to pregnant monkeys; however, adverse effects on the placenta were associated with fetal loss at both doses tested (see Data) .
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background rate of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
There is a pregnancy safety study for IMAAVY. If IMAAVY is administered during pregnancy, or if a patient becomes pregnant while receiving IMAAVY, healthcare providers should report IMAAVY exposure by contacting Janssen at 1-800-526-7736 or www.IMAAVY.com
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Monoclonal antibodies are increasingly transported across the placenta as pregnancy progresses, with the largest amount transferred during the third trimester. Because IMAAVY reduces maternal serum IgG concentration and impedes placental IgG transfer to the fetus, passive immunity in the infant may be reduced for 6 months or more; therefore:
- Monitor for the development of serious infection.
- Effectiveness of vaccines may be reduced.
- Consider the risks and benefits prior to administering live vaccines to infants exposed to IMAAVY in utero.
Animal Data
Intravenous administration of nipocalimab-aahu (0, 100, or 300 mg/kg) to pregnant monkeys weekly from the end of organogenesis (gestation day 45) through parturition resulted in placental ischemia, associated with fetal loss and decreased levels of IgG in the offspring at both doses tested. IgG levels in offspring returned to normal levels and no adverse effects on immune function were evident by 6 months after birth. The doses tested are 6 and 20 times the recommended human maintenance dose (15 mg/kg) on a mg/kg basis.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Nipocalimab-aahu is excreted in human colostrum and breastmilk based on limited data from an investigational study of 13 pregnant women administered nipocalimab-aahu during pregnancy where colostrum and breastmilk was assessed in the first 8 days after birth. There are insufficient data on the effect of IMAAVY in the breastfed infant. There are no data on the effect of nipocalimab on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for IMAAVY, and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from IMAAVY, or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of IMAAVY for the treatment of gMG have been established in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older. Use of IMAAVY in pediatric patients for this indication is supported by evidence from an adequate and well-controlled trial in adults with additional pharmacokinetic and safety data in pediatric patients who are 12 years of age and older [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14)] .
Safety and effectiveness of IMAAVY for the treatment of gMG in pediatric patients below the age of 12 years have not been established.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Nipocalimab-aahu, a neonatal Fc receptor blocker, is a recombinant human immunoglobulin G1 lambda (IgG1λ) monoclonal antibody, expressed in a genetically engineered Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Nipocalimab-aahu has an aglycosylated Fc region, therefore it lacks effector functions. Nipocalimab-aahu has an approximate molecular weight of 142 kilodaltons (kDa).
IMAAVY™ (nipocalimab-aahu) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly brownish, clear to slightly opalescent solution, supplied in a single-dose vial for intravenous infusion after dilution.
Each single-dose vial contains either 300 mg/1.62 mL or 1,200 mg/6.5 mL of nipocalimab-aahu at a concentration of 185 mg/mL. In addition, each mL of solution contains arginine hydrochloride (25.35 mg), histidine (0.77 mg), L-histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate (1.07 mg), methionine (1.0 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.60 mg), sucrose (64.3 mg), and water for injection, USP, at a pH of 6.0.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Nipocalimab-aahu is a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds to neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), resulting in the reduction of circulating IgG levels.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)], the pharmacological effect of nipocalimab-aahu was assessed by measuring the decrease in serum IgG levels and anti-AChR and anti-MuSK autoantibody levels. In patients positive for AChR and MuSK autoantibodies who were treated with IMAAVY, there was a reduction in AChR and MuSK autoantibodies relative to baseline. Decreases in total IgG levels followed a similar pattern. A similar reduction in AChR autoantibodies was observed in adolescent patients with gMG compared to adults.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Nipocalimab exhibits nonlinear pharmacokinetics. Following a single intravenous infusion of IMAAVY at doses ranging from 0.3 to 60 mg/kg (4 times the recommended maintenance dosage) in healthy participants, C max of nipocalimab-aahu increased in a dose-proportional manner while AUC increased in a greater than dose-proportional manner.
Metabolism
Nipocalimab is expected to be degraded by proteolytic enzymes into small peptides and amino acids.
Elimination
Nipocalimab exhibits concentration-dependent pharmacokinetics. After a single intravenous administration of 15 mg/kg nipocalimab-aahu, the mean clearance is 0.0627 L/h and half-life is 29.3 hours.
Specific Populations
Age, Sex, and Race
The pharmacokinetics of nipocalimab were not affected by age, sex, or race based on a population pharmacokinetics analysis.
Pediatric Patients
Following the recommended intravenous doses of IMAAVY in adolescent patients 12 to 16 years of age with gMG (N=7), the observed steady-state serum nipocalimab-aahu concentrations were within the range of those observed for adult patients with gMG [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] .
Patients with Renal Impairment
No dedicated pharmacokinetic study has been conducted in patients with renal impairment. Renal impairment is not expected to affect the pharmacokinetics of nipocalimab. Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, which included healthy volunteers and patients with gMG with mild to moderate renal impairment, renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] 30–89 mL/min/1.73 m 2) had no clinically significant effect on nipocalimab-aahu clearance. No dose adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dedicated pharmacokinetic study has been performed in patients with hepatic impairment. Nipocalimab is not metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes, and hepatic impairment is not expected to affect the pharmacokinetics of nipocalimab. Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, which included healthy volunteers and patients with gMG with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, there was no clinically significant effect on nipocalimab-aahu clearance. No dose adjustment is required in patients with hepatic impairment.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of nipocalimab-aahu or of other nipocalimab products.
In clinical trials, antibodies to nipocalimab-aahu were detected in 49/102 (48%) adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older during 24-week treatment period.
Out of the 49 patients who were positive for antibodies to nipocalimab-aahu, 19 (38.8%) patients had neutralizing antibodies to nipocalimab-aahu. There was no identified clinically relevant effect of antibodies, including neutralizing antibodies, to nipocalimab-aahu on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, or effectiveness of IMAAVY.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Studies to assess the carcinogenic potential of nipocalimab-aahu have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
Studies to assess the genotoxic potential of nipocalimab-aahu have not been conducted. As an antibody, nipocalimab-aahu is not expected to interact directly with DNA.
Impairment of Fertility
Once or twice weekly intravenous administration of nipocalimab-aahu (0, 20, 50, 100, or 300 mg/kg) to male and female monkeys for 26 weeks resulted in no adverse effects on reproductive organs upon histopathological examination. The highest dose tested was 20 times the recommended human maintenance dose (15 mg/kg) on a mg/kg basis.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of IMAAVY for the treatment of gMG in adults who are anti-AChR or anti-MuSK antibody positive was established in a 24-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (Study 1; NCT04951622). Patients were treated with IMAAVY with the recommended dosage regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] .
Study 1 enrolled patients with gMG who met the following criteria:
- Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America (MGFA) Clinical Classification Class II to IV
- Myasthenia Gravis-Activities of Daily Living (MG-ADL) total score of at least 6
- On stable dose of standard of care MG therapy prior to baseline that included acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors, steroids or non-steroidal immunosuppressive therapies (NSISTs), either in combination or alone.
In Study 1, a total of 196 patients were randomized 1:1 to receive IMAAVY (n=98) or placebo (n=98). Baseline characteristics were similar between treatment groups. For the primary efficacy analysis population (n=153), patients had a median age of 52 years at screening (range 20 to 81 years) and a median time since diagnosis of 6 years. Sixty percent of patients were female; 63% were White; 32% were Asian; 1% were Black or African-American; and <1% were American Indian or Alaskan Native. At baseline, median MG-ADL total score was 9, and median Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis (QMG) total score was 15. Eighty-eight percent (n=134) of patients were positive for AChR antibodies and 10% (n=16) were positive for MuSK antibodies.
At baseline, in each group, 85% of patients received AChE inhibitors, 66% of patients received steroids, and 54% of patients received NSISTs at stable doses.
The efficacy of IMAAVY was measured using the MG-ADL scale, which assesses the impact of gMG on daily functions of 8 signs and symptoms that are typically affected in gMG. Each item is assessed on a 4-point scale, where a score of 0 represents normal function and a score of 3 represents loss of ability to perform that function. A total score ranges from 0 to 24, with the higher scores indicating more impairment.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the comparison of the mean change from baseline to Weeks 22, 23, and 24 between treatment groups in the MG-ADL total score. A statistically significant difference favoring IMAAVY was observed in MG-ADL total score change from baseline (p=0.002; see Table 2 and Figure 1).
The efficacy of IMAAVY was also measured using the QMG total score, which is a 13-item categorial grading system that assesses muscle weakness. Each item is assessed on a 4 -point scale, where a score of 0 represents no weakness, and a score of 3 represents severe weakness. A total possible score ranges from 0 to 39, where higher scores indicate more severe impairment.
The secondary endpoint was the comparison of the mean change from baseline to Weeks 22 and 24 between treatment groups in the QMG total score. A statistically significant difference favoring IMAAVY was observed in the QMG total score change from baseline (p<0.001; see Table 2).
The results are presented shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Least Squares Mean Change from Baseline to Week 24 in MG-ADL and QMG Total Scores in Study 1 Efficacy Endpoints IMAAVY
N = 77
LS Mean (SE)Placebo
N = 76
LS Mean (SE)IMAAVY Change Relative to Placebo
LS Mean Difference (95% CI)p-value Key: CI=confidence interval; MG-ADL = Myasthenia Gravis – Activities of Daily Living; QMG = Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis; LS mean = Least squares mean; SE = standard error - * Mean change from baseline over weeks 22, 23, and 24
- † Mean change from baseline over weeks 22 and 24
Primary Endpoint MG-ADL Total Score * -4.7 (0.33) -3.3 (0.34) -1.5 (-2.4, -0.5) 0.002 Secondary Endpoint QMG
Total Score †-4.9 (0.5) -2.1 (0.5) -2.8 (-4.2, -1.4) <0.001 Figure 1 shows the mean change from baseline to Week 24 in MG-ADL total score in Study 1, and Figure 2 shows the mean change from baseline to Week 24 in QMG total score in Study 1.
Figure 1: Least Squares Mean Change from Baseline in MG-ADL Total Score Over 24 Weeks in Study 1
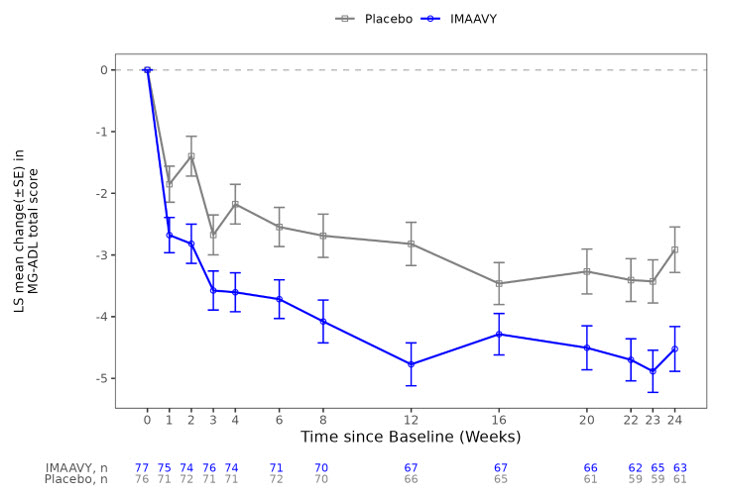
LS = least squares, SE = standard error, MG-ADL = Myasthenia Gravis Activities of Daily Living
Figure 2: Least Squares Mean Change from Baseline in QMG Total Score Over 24 Weeks in Study 1
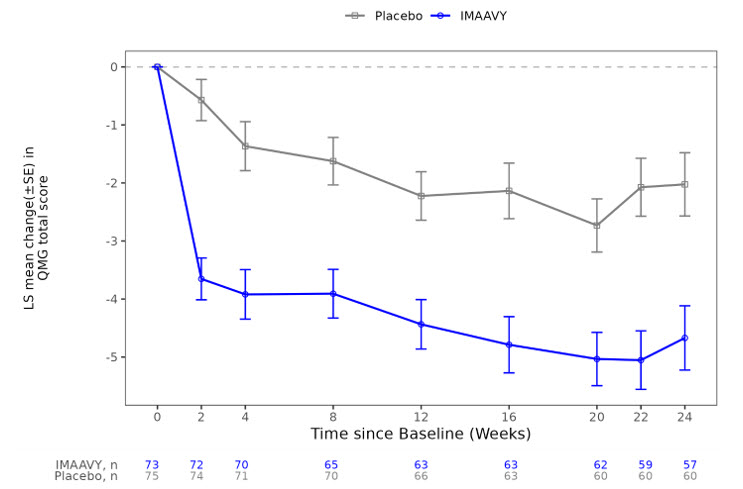
LS = least squares, SE = standard error, QMG = Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
IMAAVY™ (nipocalimab-aahu) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly brownish, clear to slightly opalescent solution for intravenous use after dilution.
IMAAVY is supplied in cartons containing a single-dose vial per carton as:
- 300 mg/1.62 mL (185 mg/mL)
NDC: 57894-800-01 - 1,200 mg/6.5 mL (185 mg/mL)
NDC: 57894-801-01 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient and/or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Infections
Instruct patients to communicate any history of infections to the healthcare provider and to contact their healthcare provider if they develop any symptoms of an infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
Administration of Vaccines
Advise patients to complete all age-appropriate vaccines according to immunization guidelines prior to initiation of treatment with IMAAVY. Administration of live vaccines is not recommended during treatment with IMAAVY. Instruct patients to inform the healthcare provider that they are being treated with IMAAVY prior to a potential vaccination [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, urticaria, and eczema have occurred in patients treated with IMAAVY. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately if these occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
Infusion-Related Reactions
Advise patients that administration of IMAAVY may result in infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
Pregnancy
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy safety study that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to IMAAVY during pregnancy, and they can be enrolled by calling 1-800-526-7736 or www.IMAAVY.com [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
IMAAVY™ [im-AH-vee]
(nipocalimab-aahu)
injection, for intravenous useThis Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Issued: 4/2025 What is IMAAVY?
IMAAVY is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children 12 years of age and older with a disease called generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) who are anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR) or anti-muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK) antibody positive.
It is not known if IMAAVY is safe and effective in children under 12 years of age.Do not receive IMAAVY if you: - have a history of a severe allergic reactions to nipocalimab or any of the ingredients in IMAAVY. Reactions have included angioedema and anaphylaxis. See the end of this Patient Information leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in IMAAVY.
Before receiving IMAAVY, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - ever had an allergic reaction to IMAAVY. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure.
- have or have had any recent infections or have any symptoms of infection.
- have recently received or are scheduled to receive an immunization (vaccine). People who are being treated with IMAAVY should not receive live vaccines.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known whether IMAAVY will harm your unborn baby.
- Pregnancy Safety Study. There is a pregnancy safety study for IMAAVY if IMAAVY is given during pregnancy or you become pregnant while receiving IMAAVY. Your healthcare provider should report IMAAVY exposure by contacting Janssen at 1-800-526-7736 or www.IMAAVY.com.
- IMAAVY can pass into your breastmilk and it is not known whether IMAAVY will harm your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you receive IMAAVY.
How will I receive IMAAVY? - IMAAVY will be given to you by your healthcare provider through a needle placed into your vein (intravenous [IV] infusion).
- You will receive a starting dose of IMAAVY infusion lasting at least 30 minutes. Two weeks later you will receive your next dose of IMAAVY infusion lasting at least 15 minutes. Your following doses will be given every two weeks.
- If you have a reaction during your IMAAVY infusion, your healthcare provider may decide to give IMAAVY more slowly or to stop your infusion.
- If you miss a scheduled IMAAVY infusion, you should receive your next dose as soon as possible.
What should I avoid while receiving IMAAVY? - You should not be given live vaccines while receiving IMAAVY.
What are the possible side effects of IMAAVY?
IMAAVY may cause serious side effects, including:- Infections. Infections are a common side effect of IMAAVY that can be serious. Receiving IMAAVY may increase your risk of infection. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms of infection:
- fever
- chills
- shivering
- cough
- sore throat
- fever blisters
- burning when you urinate
- Allergic (hypersensitivity) reactions. Allergic reactions may happen during or up to a few weeks after your IMAAVY infusion. Get emergency medical help right away if you get any of these symptoms during or after your IMAAVY infusion, which may be part of a serious allergic reaction:
- swelling of your face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat
- difficulty swallowing or breathing
- itchy rash (hives)
- chest pain or tightness
- Infusion-related reactions. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms during or a few days after your infusion of IMAAVY:
- headache
- rash
- nausea
- fatigue
- dizziness
- chills
- flu-like symptoms
- redness of skin
The most common side effects in people with gMG treated with IMAAVY include: - infection in parts of your body that you use for breathing (respiratory tract infection)
- swelling in your hands, ankles, or feet (peripheral edema)
- muscle spasms
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.General information about the safe and effective use of IMAAVY.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet.
You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about IMAAVY that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients of IMAAVY?
Active ingredient : nipocalimab-aahu
Inactive ingredients: arginine hydrochloride, histidine, L-histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate, methionine, polysorbate 80, sucrose, and water for injection.Manufactured by: Janssen Biotech, Inc., Horsham, PA 19044, USA
U.S. License Number 1864
For patent information: www.janssenpatents.com
© 2025 Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies
For more information, call 1-800-526-7736 or go to www.IMAAVY.com -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 mg / 1.62 mL Vial Box
NDC: 57894-800-01
imaavy™
(nipocalimab-aahu)
Injection300 mg / 1.62 mL
(185 mg / mL)For Intravenous Infusion
After DilutionRx only
One single-dose vial.
Discard unused portion.Johnson
& Johnson
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1,200 mg / 6.5 mL Vial Box
NDC: 57894-801-01
imaavy™
(nipocalimab-aahu)
Injection1,200 mg / 6.5 mL
(185 mg / mL)For Intravenous Infusion
After DilutionRx only
One single-dose vial.
Discard unused portion.Johnson
& Johnson
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
IMAAVY
nipocalimab injection, solution, concentrateProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 57894-801 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NIPOCALIMAB (UNII: 87M90CV8NC) (NIPOCALIMAB - UNII:87M90CV8NC) NIPOCALIMAB 185 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ARGININE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: F7LTH1E20Y) HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) HISTIDINE MONOHYDROCHLORIDE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: X573657P6P) METHIONINE (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color brown (colorless to slightly brownish) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 57894-801-01 1 in 1 BOX 04/29/2025 1 6.5 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761430 04/29/2025 IMAAVY
nipocalimab injection, solution, concentrateProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 57894-800 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NIPOCALIMAB (UNII: 87M90CV8NC) (NIPOCALIMAB - UNII:87M90CV8NC) NIPOCALIMAB 185 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ARGININE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: F7LTH1E20Y) HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) HISTIDINE MONOHYDROCHLORIDE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: X573657P6P) METHIONINE (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color brown (colorless to slightly brownish) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 57894-800-01 1 in 1 BOX 04/29/2025 1 1.62 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761430 04/29/2025 Labeler - Janssen Biotech, Inc. (099091753) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Janssen Biotech, Inc. 038978363 api manufacture(57894-801, 57894-800) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg Mooswiesen) 312670654 analysis(57894-800, 57894-801) , manufacture(57894-800, 57894-801) , pack(57894-800, 57894-801) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg Schuetzenstrasse) 316126754 analysis(57894-800, 57894-801) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg Helmut-Vetter-Strasse) 341629292 analysis(57894-800, 57894-801) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Langenargen Eisenbahnstrasse) 344217323 manufacture(57894-800, 57894-801) , analysis(57894-800, 57894-801) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Janssen Biologics B.V. 409612918 analysis(57894-800, 57894-801) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations WuXi Biologics Co., Ltd. 421298354 api manufacture(57894-800, 57894-801) , analysis(57894-800, 57894-801) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Eurofins Biolab Srl 429117112 analysis(57894-800, 57894-801) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Cilag AG 483237103 analysis(57894-800, 57894-801) , pack(57894-800, 57894-801) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations WuXi Biologics Biosafety Testing (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. 544312968 analysis(57894-800, 57894-801) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations WuXi Biologics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd 544367368 api manufacture(57894-800, 57894-801) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Janssen Sciences Ireland UC 986030167 analysis(57894-800, 57894-801)
Trademark Results [IMAAVY]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 IMAAVY 98087543 not registered Live/Pending |
Johnson & Johnson 2023-07-17 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.