BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE AND TIMOLOL MALEATE- brimonidine tartrate, timolol maleate solution/ drops
BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE and TIMOLOL MALEATE by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE and TIMOLOL MALEATE by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Pacific Pharma, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE and TIMOLOL MALEATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE and TIMOLOL MALEATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION.
BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE and TIMOLOL MALEATE Ophthalmic solution 0.2%/0.5%
For topical administration
Initial U.S. Approval: 2007
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is an alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist with a beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitor indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension who require adjunctive or replacement therapy due to inadequately controlled IOP; the IOP-lowering of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution dosed twice a day was slightly less than that seen with the concomitant administration of timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, 0.5% dosed twice a day and brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution, 0.2% dosed three times per day. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
One drop in the affected eye(s), twice daily approximately 12 hours apart. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Solution containing 2 mg/mL brimonidine tartrate and 5 mg/mL timolol. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Bronchial asthma, a history of bronchial asthma, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. (4.1, 5.1, 5.3)
- Sinus bradycardia, atrioventricular block, overt cardiac failure, cardiogenic shock. (4.2, 5.2)
- Neonates and infants (under the age of 2 years). (4.3)
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this product. (4.4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Potential for Severe Respiratory or Cardiac Reactions (5.1)
- Cardiac Failure (5.2)
- Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (5.3)
- Potentiation of Vascular Insufficiency (5.4)
- Increased Reactivity to Allergens (5.5)
- Potentiation of Muscle Weakness (5.6)
- Masking of Hypoglycemic Symptoms in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus (5.7)
- Masking of Thyrotoxicosis (5.8)
- Ocular Hypersensitivity (5.9)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions occurring in approximately 5 to 15% of patients included allergic conjunctivitis, conjunctival folliculosis, conjunctival hyperemia, eye pruritus, ocular burning, and stinging. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie at 1-800-678-1605 or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Antihypertensives/cardiac glycosides may lower blood pressure. (7.1)
- Concomitant use with systemic beta-blockers may potentiate systemic beta-blockade. (7.2)
- Oral or intravenous calcium antagonists may cause atrioventricular conduction disturbances, left ventricular failure, and hypotension. (7.3)
- Catecholamine-depleting drugs may have additive effects and produce hypotension and/or marked bradycardia. (7.4)
- Use with CNS depressants may result in an additive or potentiating effect. (7.5)
- Digitalis and calcium antagonists may have additive effects in prolonging atrioventricular conduction time. (7.6)
- CYP2D6 inhibitors may potentiate systemic beta-blockade. (7.7)
- Tricyclic antidepressants may potentially blunt the hypotensive effect of systemic clonidine. (7.8)
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors may result in increased hypotension. (7.9)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Not for use in children below the age of 2 years. Use with caution in children ≥ 2 years of age. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2024
- Bronchial asthma, a history of bronchial asthma, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. (4.1, 5.1, 5.3)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Reactive Airway Disease Including Asthma, COPD
4.2 Sinus Bradycardia, AV Block, Cardiac Failure, Cardiogenic Shock
4.3 Neonates and Infants (Under the Age of 2 Years)
4.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potential for Severe Respiratory or Cardiac Reactions
5.2 Cardiac Failure
5.3 Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
5.4 Potentiation of Vascular Insufficiency
5.5 Increased Reactivity to Allergens
5.6 Potentiation of Muscle Weakness
5.7 Masking of Hypoglycemic Symptoms in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
5.8 Masking of Thyrotoxicosis
5.9 Ocular Hypersensitivity
5.10 Contamination of Topical Ophthalmic Products After Use
5.11 Impairment of Beta-adrenergically Mediated Reflexes During Surgery
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antihypertensives/Cardiac Glycosides
7.2 Beta-adrenergic Blocking Agents
7.3 Calcium Antagonists
7.4 Catecholamine-depleting Drugs
7.5 CNS Depressants
7.6 Digitalis and Calcium Antagonists
7.7 CYP2D6 Inhibitors
7.8 Tricyclic Antidepressants
7.9 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.2%/0.5% is an alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist with a beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitor indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension who require adjunctive or replacement therapy due to inadequately controlled IOP; the IOP-lowering of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution dosed twice a day was slightly less than that seen with the concomitant administration of 0.5% timolol maleate ophthalmic solution dosed twice a day and 0.2% brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution dosed three times per day.
- 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4
CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Reactive Airway Disease Including Asthma, COPD
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in patients with reactive airway disease including bronchial asthma; a history of bronchial asthma; severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3)].
4.2 Sinus Bradycardia, AV Block, Cardiac Failure, Cardiogenic Shock
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in patients with sinus bradycardia; second or third degree atrioventricular block; overt cardiac failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]; cardiogenic shock.
4.3 Neonates and Infants (Under the Age of 2 Years)
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in neonates and infants (under the age of 2 years).
4.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Local hypersensitivity reactions have occurred following the use of different components of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in patients who have exhibited a hypersensitivity reaction to any component of this medication in the past.
-
5
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potential for Severe Respiratory or Cardiac Reactions
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution contains timolol maleate; and although administered topically can be absorbed systemically. Therefore, the same types of adverse reactions found with systemic administration of beta-adrenergic blocking agents may occur with topical administration. For example, severe respiratory reactions and cardiac reactions including death due to bronchospasm in patients with asthma, and rarely death in association with cardiac failure have been reported following systemic or ophthalmic administration of timolol maleate [see Contraindications (4.1)]. Additionally, ophthalmic beta-blockers may impair compensatory tachycardia and increase risk of hypotension.
5.2 Cardiac Failure
Sympathetic stimulation may be essential for support of the circulation in individuals with diminished myocardial contractility, and its inhibition by beta-adrenergic receptor blockade may precipitate more severe failure.
In patients without a history of cardiac failure, continued depression of the myocardium with beta-blocking agents over a period of time can, in some cases, lead to cardiac failure. At the first sign or symptom of cardiac failure, brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution should be discontinued [see Contraindications (4.2)].
5.3 Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (e.g., chronic bronchitis, emphysema) of mild or moderate severity, bronchospastic disease, or a history of bronchospastic disease (other than bronchial asthma or a history of bronchial asthma, in which brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4.1)] should, in general, not receive beta-blocking agents, including brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
5.4 Potentiation of Vascular Insufficiency
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution may potentiate syndromes associated with vascular insufficiency. Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution should be used with caution in patients with depression, cerebral or coronary insufficiency, Raynaud’s phenomenon, orthostatic hypotension, or thromboangiitis obliterans.
5.5 Increased Reactivity to Allergens
While taking beta-blockers, patients with a history of atopy or a history of severe anaphylactic reactions to a variety of allergens may be more reactive to repeated accidental, diagnostic, or therapeutic challenge with such allergens. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat anaphylactic reactions.
5.6 Potentiation of Muscle Weakness
Beta-adrenergic blockade has been reported to potentiate muscle weakness consistent with certain myasthenic symptoms (e.g., diplopia, ptosis, and generalized weakness). Timolol has been reported rarely to increase muscle weakness in some patients with myasthenia gravis or myasthenic symptoms.
5.7 Masking of Hypoglycemic Symptoms in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents should be administered with caution in patients subject to spontaneous hypoglycemia or to diabetic patients (especially those with labile diabetes) who are receiving insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents may mask the signs and symptoms of acute hypoglycemia.
5.8 Masking of Thyrotoxicosis
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents may mask certain clinical signs (e.g., tachycardia) of hyperthyroidism. Patients suspected of developing thyrotoxicosis should be managed carefully to avoid abrupt withdrawal of beta-adrenergic blocking agents that might precipitate a thyroid storm.
5.9 Ocular Hypersensitivity
Ocular hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solutions 0.2%, with some reported to be associated with an increase in intraocular pressure [see Contraindications (4.4)].
5.10 Contamination of Topical Ophthalmic Products After Use
There have been reports of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multiple-dose containers of topical ophthalmic products. These containers had been inadvertently contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had a concurrent corneal disease or a disruption of the ocular epithelial surface [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.11 Impairment of Beta-adrenergically Mediated Reflexes During Surgery
The necessity or desirability of withdrawal of beta-adrenergic blocking agents prior to major surgery is controversial. Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade impairs the ability of the heart to respond to beta-adrenergically mediated reflex stimuli. This may augment the risk of general anesthesia in surgical procedures. Some patients receiving beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents have experienced protracted severe hypotension during anesthesia. Difficulty in restarting and maintaining the heartbeat has also been reported. For these reasons, in patients undergoing elective surgery, some authorities recommend gradual withdrawal of beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents.
If necessary during surgery, the effects of beta-adrenergic blocking agents may be reversed by sufficient doses of adrenergic agonists.
-
6
ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Brimonidine Tartrate and Timolol Maleate Ophthalmic Solution
In clinical trials of 12 months duration with brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, the most frequent reactions associated with its use occurring in approximately 5% to 15% of the patients included: allergic conjunctivitis, conjunctival folliculosis, conjunctival hyperemia, eye pruritus, ocular burning, and stinging. The following adverse reactions were reported in 1% to 5% of patients: asthenia, blepharitis, corneal erosion, depression, epiphora, eye discharge, eye dryness, eye irritation, eye pain, eyelid edema, eyelid erythema, eyelid pruritus, foreign body sensation, headache, hypertension, oral dryness, somnolence, superficial punctate keratitis, and visual disturbance.
Other adverse reactions that have been reported with the individual components are listed below.
Brimonidine Tartrate (0.1%-0.2%)
Abnormal taste, allergic reaction, blepharoconjunctivitis, blurred vision, bronchitis, cataract, conjunctival blanching, conjunctival edema, conjunctival hemorrhage, conjunctivitis, cough, dizziness, dyspepsia, dyspnea, fatigue, flu syndrome, follicular conjunctivitis, gastrointestinal disorder, hypercholesterolemia, hypotension, infection (primarily colds and respiratory infections), hordeolum, insomnia, keratitis, lid crusting, lid disorder, muscular pain, nasal dryness, ocular allergic reaction, pharyngitis, photophobia, rash, rhinitis, sinus infection, sinusitis, superficial punctate keratopathy, tearing, upper respiratory symptoms, visual field defect, vitreous detachment, vitreous disorder, vitreous floaters, and worsened visual acuity.
Timolol (Ocular Administration)
Body as a whole: chest pain; Cardiovascular: Arrhythmia, bradycardia, cardiac arrest, cardiac failure, cerebral ischemia, cerebral vascular accident, claudication, cold hands and feet, edema, heart block, palpitation, pulmonary edema, Raynaud’s phenomenon, syncope, and worsening of angina pectoris; Digestive: anorexia, diarrhea, nausea; Immunologic: Systemic lupus erythematosus; Nervous System/Psychiatric: Increase in signs and symptoms of myasthenia gravis, insomnia, nightmares, paresthesia, behavioral changes and psychic disturbances including confusion, hallucinations, anxiety, disorientation, nervousness, and memory loss; Skin: Alopecia, psoriasiform rash or exacerbation of psoriasis; Hypersensitivity: Signs and symptoms of systemic allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria, and generalized and localized rash; Respiratory: Bronchospasm (predominantly in patients with pre-existing bronchospastic disease) [see Contraindications (4.1)], dyspnea, nasal congestion, respiratory failure, upper respiratory infections; Endocrine: Masked symptoms of hypoglycemia in diabetes patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]; Special Senses: diplopia, choroidal detachment following filtration surgery, cystoid macular edema, decreased corneal sensitivity, pseudopemphigoid, ptosis, refractive changes, tinnitus; Urogenital: Decreased libido, impotence, Peyronie’s disease, retroperitoneal fibrosis.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following reactions have been identified during post-marketing use of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solutions, timolol ophthalmic solutions, or both in combination, in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The reactions, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solutions, timolol ophthalmic solutions, or a combination of these factors, include: eyelid erythema extending to the cheek or forehead, hypersensitivity, iritis, keratoconjunctivitis sicca, miosis, nausea, skin reactions (including erythema, rash, and vasodilation), and tachycardia. In infants, apnea, bradycardia, coma, hypothermia, hypotonia, lethargy, pallor, respiratory depression, and somnolence have been reported [see Contraindications (4.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Oral Timolol/Oral Beta-blockers
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported in clinical experience with ORAL timolol maleate or other ORAL beta-blocking agents and may be considered potential effects of ophthalmic timolol maleate: Allergic: Erythematous rash, fever combined with aching and sore throat, laryngospasm with respiratory distress; Body as a whole: Decreased exercise tolerance, extremity pain, weight loss; Cardiovascular: Vasodilatation, worsening of arterial insufficiency; Digestive: Gastrointestinal pain, hepatomegaly, ischemic colitis, mesenteric arterial thrombosis, vomiting; Hematologic: Agranulocytosis, nonthrombocytopenic purpura, thrombocytopenic purpura; Endocrine: Hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia; Skin: Increased pigmentation, pruritus, skin irritation, sweating; Musculoskeletal: Arthralgia; Nervous System/Psychiatric: An acute reversible syndrome characterized by disorientation for time and place, decreased performance on neuropsychometrics, diminished concentration, emotional lability, local weakness, reversible mental depression progressing to catatonia, slightly clouded sensorium, vertigo; Respiratory: Bronchial obstruction, rales; Urogenital: Urination difficulties.
-
7
DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antihypertensives/Cardiac Glycosides
Because brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution may reduce blood pressure, caution in using drugs such as antihypertensives and/or cardiac glycosides with brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is advised.
7.2 Beta-adrenergic Blocking Agents
Patients who are receiving a beta-adrenergic blocking agent either orally or intravenously and brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution should be observed for potential additive effects of beta-blockade, both systemic and on intraocular pressure. The concomitant use of two topical beta-adrenergic blocking agents is not recommended.
7.3 Calcium Antagonists
Caution should be used in the co-administration of beta-adrenergic blocking agents, such as brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, and oral or intravenous calcium antagonists because of possible atrioventricular conduction disturbances, left ventricular failure, and hypotension. In patients with impaired cardiac function, co-administration should be avoided.
7.4 Catecholamine-depleting Drugs
Close observation of the patient is recommended when a beta blocker is administered to patients receiving catecholamine-depleting drugs such as reserpine, because of possible additive effects and the production of hypotension and/or marked bradycardia, which may result in vertigo, syncope, or postural hypotension.
7.5 CNS Depressants
Although specific drug interaction studies have not been conducted with brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, the possibility of an additive or potentiating effect with CNS depressants (alcohol, barbiturates, opiates, sedatives, or anesthetics) should be considered.
7.6 Digitalis and Calcium Antagonists
The concomitant use of beta-adrenergic blocking agents with digitalis and calcium antagonists may have additive effects in prolonging atrioventricular conduction time.
7.7 CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Potentiated systemic beta-blockade (e.g., decreased heart rate, depression) has been reported during combined treatment with CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., quinidine, SSRIs) and timolol.
7.8 Tricyclic Antidepressants
Tricyclic antidepressants have been reported to blunt the hypotensive effect of systemic clonidine. It is not known whether the concurrent use of these agents with brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution in humans can lead to resulting interference with the IOP-lowering effect. Caution, however, is advised in patients taking tricyclic antidepressants which can affect the metabolism and uptake of circulating amines.
7.9 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors may theoretically interfere with the metabolism of brimonidine and potentially result in an increased systemic side effect such as hypotension. Caution, however, is advised in patients taking MAO inhibitors which can affect the metabolism and uptake of circulating amines.
-
8
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenicity studies have been performed in animals. Brimonidine tartrate was not teratogenic when given orally during gestation days 6 through 15 in rats and days 6 through 18 in rabbits. The highest doses of brimonidine tartrate in rats (2.5 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (5 mg/kg/day) achieved AUC exposure values 580 and 37-fold higher, respectively, than similar values estimated in humans treated with brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, 1 drop in both eyes twice daily.
Teratogenicity studies with timolol in mice, rats, and rabbits at oral doses up to 50 mg/kg/day [4,200 times the maximum recommended human ocular dose of 0.012 mg/kg/day on a mg/kg basis (MRHOD)] demonstrated no evidence of fetal malformations. Although delayed fetal ossification was observed at this dose in rats, there were no adverse effects on postnatal development of offspring. Doses of 1,000 mg/kg/day (83,000 times the MRHOD) were maternotoxic in mice and resulted in an increased number of fetal resorptions. Increased fetal resorptions were also seen in rabbits at doses 8,300 times the MRHOD without apparent maternotoxicity.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women; however, in animal studies, brimonidine crossed the placenta and entered into the fetal circulation to a limited extent. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Timolol has been detected in human milk following oral and ophthalmic drug administration. It is not known whether brimonidine tartrate is excreted in human milk, although in animal studies, brimonidine tartrate has been shown to be excreted in breast milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in children under the age of 2 years [see Contraindications (4.3)]. During post-marketing surveillance, apnea, bradycardia, coma, hypotension, hypothermia, hypotonia, lethargy, pallor, respiratory depression, and somnolence have been reported in infants receiving brimonidine. The safety and effectiveness of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate have not been studied in children below the age of 2 years.
The safety and effectiveness of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution have been established in the age groups 2 – 16 years of age. Use of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution in these age groups is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution in adults with additional data from a study of the concomitant use of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution in pediatric glaucoma patients (ages 2 to 7 years). In this study, brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% was dosed three times a day as adjunctive therapy to beta-blockers. The most commonly observed adverse reactions were somnolence (50%-83% in patients 2 to 6 years) and decreased alertness. In pediatric patients 7 years of age or older (>20 kg), somnolence appears to occur less frequently (25%). Approximately 16% of patients on brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution discontinued from the study due to somnolence.
-
10
OVERDOSAGE
There have been reports of inadvertent overdosage with timolol ophthalmic solution resulting in systemic effects similar to those seen with systemic beta-adrenergic blocking agents such as dizziness, headache, shortness of breath, bradycardia, bronchospasm, and cardiac arrest. With the exception of hypotension, very limited information exists on accidental ingestion of brimonidine in adults. Symptoms of brimonidine overdose have been reported in neonates, infants, and children receiving brimonidine ophthalmic solutions as part of medical treatment of congenital glaucoma or by accidental oral ingestion [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Treatment of an oral overdose includes supportive and symptomatic therapy; a patent airway should be maintained.
-
11
DESCRIPTION
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.2%/0.5%, sterile, is a relatively selective alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist with a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitor (topical intraocular pressure lowering agent).
The structural formulae are:
Brimonidine tartrate:
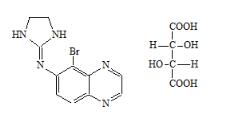
5-bromo-6-(2-imidazolidinylideneamino) quinoxaline L-tartrate; MW= 442.24
Timolol maleate:
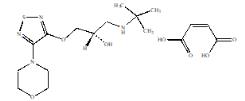
(-)-1-(tert-butylamino)-3-[(4-morpholino-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-oxy]-2-propanol maleate (1:1) (salt); MW= 432.50 as the maleate salt
In solution, brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.2%/0.5% has a clear, greenish-yellow color. It has an osmolality of 260-330 mOsmol/kg and a pH during its shelf life of 6.5-7.3.
Brimonidine tartrate appears as an off-white, or white to pale-yellow powder and is soluble in both water (1.5 mg/mL) and in the product vehicle (3 mg/mL) at pH 7.2. Timolol maleate appears as a white, odorless, crystalline powder and is soluble in water, methanol, and alcohol.
Each mL of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution contains the active ingredients brimonidine tartrate 0.2% and timolol 0.5% with the inactive ingredients benzalkonium chloride 0.005%; sodium phosphate, monobasic; sodium phosphate, dibasic; purified water; and hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust pH.
-
12
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is comprised of two components: brimonidine tartrate and timolol. Each of these two components decreases elevated intraocular pressure, whether or not associated with glaucoma. Elevated intraocular pressure is a major risk factor in the pathogenesis of optic nerve damage and glaucomatous visual field loss. The higher the level of intraocular pressure, the greater the likelihood of glaucomatous field loss and optic nerve damage.
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is a relatively selective alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist with a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitor. Both brimonidine and timolol have a rapid onset of action, with peak ocular hypotensive effect seen at two hours post-dosing for brimonidine and one to two hours for timolol.
Fluorophotometric studies in animals and humans suggest that brimonidine tartrate has a dual mechanism of action by reducing aqueous humor production and increasing uveoscleral outflow.
Timolol maleate is a beta1 and beta2 adrenergic receptor inhibitor that does not have significant intrinsic sympathomimetic, direct myocardial depressant, or local anesthetic (membrane-stabilizing) activity.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Systemic absorption of brimonidine and timolol was assessed in healthy volunteers and patients following topical dosing with brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. Normal volunteers dosed with one drop of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution twice daily in both eyes for seven days showed peak plasma brimonidine and timolol concentrations of 30 pg/mL and 400 pg/mL, respectively. Plasma concentrations of brimonidine peaked at 1 to 4 hours after ocular dosing. Peak plasma concentrations of timolol occurred approximately 1 to 3 hours post-dose.
In a crossover study of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, brimonidine tartrate 0.2%, and timolol 0.5% administered twice daily for 7 days in healthy volunteers, the mean brimonidine area-under-the-plasma-concentration-time curve (AUC) for brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution was 128 ± 61 pghr/mL versus 141 ± 106 pghr/mL for the respective monotherapy treatments; mean Cmax values of brimonidine were comparable following brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution treatment versus monotherapy (32.7 ± 15 pg/mL versus 34.7 ± 22.6 pg/mL, respectively). Mean timolol AUC for brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution was similar to that of the respective monotherapy treatment (2919 ± 1679 pghr/mL versus 2909 ± 1231 pghr/mL, respectively); mean Cmax of timolol was approximately 20% lower following brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution treatment versus monotherapy.
In a parallel study in patients dosed twice daily with brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, twice daily with timolol 0.5%, or three times daily with brimonidine tartrate 0.2%, one-hour post dose plasma concentrations of timolol and brimonidine were approximately 30-40% lower with brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution than their respective monotherapy values. The lower plasma brimonidine concentrations with brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution appears to be due to twice-daily dosing for brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution versus three-times dosing with brimonidine tartrate 0.2%.
Distribution
The protein binding of timolol is approximately 60%. The protein binding of brimonidine has not been studied.
Metabolism
In humans, brimonidine is extensively metabolized by the liver. Timolol is partially metabolized by the liver.
Excretion
In the crossover study in healthy volunteers, the plasma concentration of brimonidine declined with a systemic half-life of approximately 3 hours. The apparent systemic half-life of timolol was about 7 hours after ocular administration.
Urinary excretion is the major route of elimination of brimonidine and its metabolites. Approximately 87% of an orally-administered radioactive dose of brimonidine was eliminated within 120 hours, with 74% found in the urine. Unchanged timolol and its metabolites are excreted by the kidney.
Special Populations
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment.
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution has not been studied in patients with renal impairment.
A study of patients with renal failure showed that timolol was not readily removed by dialysis. The effect of dialysis on brimonidine pharmacokinetics in patients with renal failure is not known.
Following oral administration of timolol maleate, the plasma half-life of timolol is essentially unchanged in patients with moderate renal insufficiency.
-
13
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
With brimonidine tartrate, no compound-related carcinogenic effects were observed in either mice or rats following a 21-month and 24-month study, respectively. In these studies, dietary administration of brimonidine tartrate at doses up to 2.5 mg/kg/day in mice and 1 mg/kg/day in rats achieved 150 and 210 times, respectively, the plasma Cmax drug concentration in humans treated with one drop of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution into both eyes twice daily, the recommended daily human dose.
In a two-year study of timolol maleate administered orally to rats, there was a statistically significant increase in the incidence of adrenal pheochromocytomas in male rats administered 300 mg/kg/day [approximately 25,000 times the maximum recommended human ocular dose of 0.012 mg/kg/day on a mg/kg basis (MRHOD)]. Similar differences were not observed in rats administered oral doses equivalent to approximately 8,300 times the daily dose of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution in humans.
In a lifetime oral study of timolol maleate in mice, there were statistically significant increases in the incidence of benign and malignant pulmonary tumors, benign uterine polyps and mammary adenocarcinomas in female mice at 500 mg/kg/day, (approximately 42,000 times the MRHOD), but not at 5 or 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 420 to 4,200 times higher, respectively, than the MRHOD). In a subsequent study in female mice, in which post-mortem examinations were limited to the uterus and the lungs, a statistically significant increase in the incidence of pulmonary tumors was again observed at 500 mg/kg/day.
The increased occurrence of mammary adenocarcinomas was associated with elevations in serum prolactin which occurred in female mice administered oral timolol at 500 mg/kg/day, but not at doses of 5 or 50 mg/kg/day. An increased incidence of mammary adenocarcinomas in rodents has been associated with administration of several other therapeutic agents that elevate serum prolactin, but no correlation between serum prolactin levels and mammary tumors has been established in humans. Furthermore, in adult human female subjects who received oral dosages of up to 60 mg of timolol maleate (the maximum recommended human oral dosage), there were no clinically meaningful changes in serum prolactin.
Brimonidine tartrate was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a series of in vitro and in vivo studies including the Ames bacterial reversion test, chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells, and three in vivo studies in CD-1 mice: a host-mediated assay, cytogenetic study, and dominant lethal assay.
Timolol maleate was devoid of mutagenic potential when tested in vivo (mouse) in the micronucleus test and cytogenetic assay (doses up to 800 mg/kg) and in vitro in a neoplastic cell transformation assay (up to 100 mcg/mL). In Ames tests the highest concentrations of timolol employed, 5,000 or 10,000 mcg/plate, were associated with statistically significant elevations of revertants observed with tester strain TA100 (in seven replicate assays), but not in the remaining three strains. In the assays with tester strain TA100, no consistent dose response relationship was observed, and the ratio of test to control revertants did not reach 2. A ratio of 2 is usually considered the criterion for a positive Ames test.
Reproduction and fertility studies in rats with timolol maleate and in rats with brimonidine tartrate demonstrated no adverse effect on male or female fertility at doses up to approximately 100 times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
-
14
CLINICAL STUDIES
Clinical studies were conducted to compare the IOP-lowering effect over the course of the day of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution administered twice a day (BID) to individually-administered brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution, 0.2% administered three times per day (TID) and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, 0.5% BID in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution BID provided an additional 1 to 3 mm Hg decrease in IOP over brimonidine treatment TID and an additional 1 to 2 mm Hg decrease over timolol treatment BID during the first 7 hours post dosing. However, the IOP-lowering of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution BID was less (approximately 1-2 mm Hg) than that seen with the concomitant administration of 0.5% timolol BID and 0.2% brimonidine tartrate TID. Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution administered BID had a favorable safety profile versus concurrently administered brimonidine TID and timolol BID in the self-reported level of severity of sleepiness for patients over age 40.
-
16
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is supplied sterile, in white opaque plastic LDPE bottles and tips, with blue high impact polystyrene (HIPS) caps as follows:
5 mL in 10 mL bottle NDC: 82182-455-05
10 mL in 10 mL bottle NDC: 82182-455-10
15 mL in 15 mL bottle NDC: 82182-455-15
Storage: Store at 15°-25°C (59°-77°F). Protect from light.
-
17
PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Patients with bronchial asthma, a history of bronchial asthma, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sinus bradycardia, second or third degree atrioventricular block, or cardiac failure should be advised not to take this product [see Contraindications (4.1, 4.2)].
Patients should be instructed that ocular solutions, if handled improperly or if the tip of the dispensing container contacts the eye or surrounding structures, can become contaminated by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions or by inadvertent contact with the dropper tip [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. Always replace the cap after using. If solution changes color or becomes cloudy, do not use. Do not use the product after the expiration date marked on the bottle.
Patients also should be advised that if they have ocular surgery or develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection), they should immediately seek their physician's advice concerning the continued use of the present multidose container.
If more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least five minutes apart.
Patients should be advised that brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution contains benzalkonium chloride which may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Contact lenses should be removed prior to administration of the solution. Lenses may be reinserted 15 minutes following administration of brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
As with other similar medications, brimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution may cause fatigue and/or drowsiness in some patients. Patients who engage in hazardous activities should be cautioned of the potential for a decrease in mental alertness.
Distributed by:
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, IL 60064
© 2024 AbbVie. All rights reserved.
PACIFIC PHARMA and its design are trademarks of Allergan, Inc., an AbbVie company.20087220
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 82182-455-05
Brimonidine Tartrate/Timolol Maleate
Ophthalmic Solution 0.2%/0.5%
5 mL
STERILE
Rx Only
PACIFIC PHARMA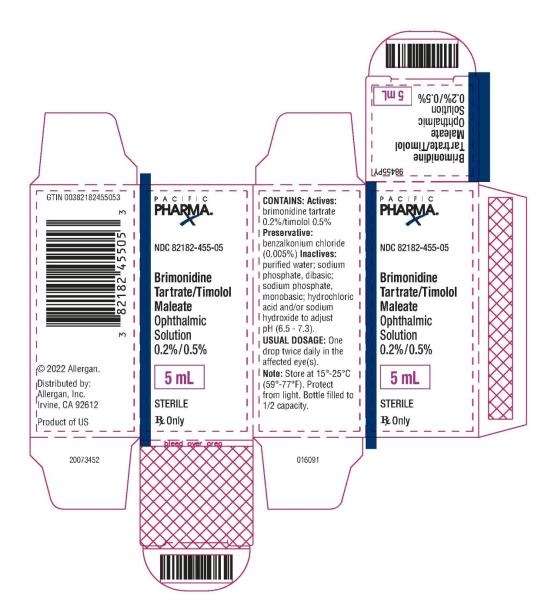
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 82182-455-10
Brimonidine Tartrate/Timolol Maleate
Ophthalmic Solution 0.2%/0.5%
10 mL
STERILE
Rx Only
PACIFIC PHARMA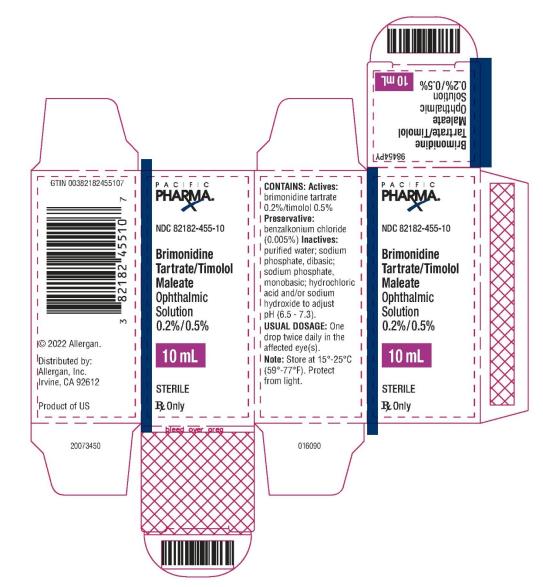
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 82182-455-15
Brimonidine Tartrate/Timolol Maleate
Ophthalmic Solution 0.2%/0.5%
15 mL
STERILE
Rx Only
PACIFIC PHARMA
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE AND TIMOLOL MALEATE
brimonidine tartrate, timolol maleate solution/ dropsProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 82182-455 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE (UNII: 4S9CL2DY2H) (BRIMONIDINE - UNII:E6GNX3HHTE) BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE 2 mg in 1 mL TIMOLOL MALEATE (UNII: P8Y54F701R) (TIMOLOL ANHYDROUS - UNII:5JKY92S7BR) TIMOLOL ANHYDROUS 5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: GR686LBA74) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC (UNII: 3980JIH2SW) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 82182-455-05 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/21/2022 2 NDC: 82182-455-10 10 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/21/2022 3 NDC: 82182-455-15 15 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/21/2022 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA authorized generic NDA021398 10/21/2022 Labeler - Pacific Pharma, Inc. (877645267)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.