SAVELLA- milnacipran hydrochloride tablet, film coated
Savella by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Savella by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Cardinal Health 107, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Savella safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Savella.
Savella® (milnacipran HCl) Tablets
Initial U.S. Approval: 2009WARNING: SUICIDALITY AND ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer Savella in two divided doses per day (2.1).
- Based on efficacy and tolerability, dosing may be titrated according to the following schedule (2.1):
- Day 1: 12.5 mg once
- Days 2-3: 25 mg/day (12.5 mg twice daily)
- Days 4-7: 50 mg/day (25 mg twice daily)
- After Day 7: 100 mg/day (50 mg twice daily)
- Recommended dose is 100 mg/day (2.1).
- May be increased to 200 mg/day based on individual patient response (2.1).
- Dose should be adjusted in patients with severe renal impairment (2.2).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Tablets: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Serotonin Syndrome and MAOIs: Do not use MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders with Savella or within 5 days of stopping treatment with Savella. Do not use Savella within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders. In addition, do not start Savella in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue (4.1, 5.2).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Suicidality: Monitor for worsening of depressive symptoms and suicide risk (5.1).
- Serotonin Syndrome: Serotonin syndrome has been reported with SSRIs and SNRIs, including Savella, both when taken alone, but especially when co-administered with other serotonergic agents (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines and St. John's Wort). If such symptoms occur, discontinue Savella and initiate supportive treatment. If concomitant use of Savella with other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, patients should be made aware of a potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during treatment and dose increases (5.2).
- Elevated blood pressure and heart rate: Savella may increase blood pressure and heart rate. In an ambulatory blood pressure monitoring study, a substantially higher proportion of Savella-treated patients experienced clinically significant blood pressure and heart rate elevations as compared with placebo-treated patients. Measure blood pressure and heart rate prior to initiating treatment with Savella and monitor periodically throughout treatment (5.3, 5.4).
- Seizures: Cases have been reported with Savella therapy. Prescribe Savella with care in patients with a history of seizure disorder (5.5).
- Hepatotoxicity: More patients treated with Savella than with placebo experienced mild elevations of ALT and AST. Rarely, fulminant hepatitis has been reported in patients treated with Savella. Avoid concomitant use of Savella in patients with substantial alcohol use or chronic liver disease (5.6).
- Discontinuation: Withdrawal symptoms have been reported in patients when discontinuing treatment with Savella. A gradual dose reduction is recommended (5.7).
- Abnormal Bleeding: Savella may increase the risk of bleeding events. Caution patients about the risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of Savella and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation (5.9).
- Male patients with a history of obstructive uropathies may experience higher rates of genitourinary adverse events (5.11).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently occurring adverse reactions (≥ 5% and greater than placebo) were nausea, headache, constipation, dizziness, insomnia, hot flush, hyperhidrosis, vomiting, palpitations, heart rate increased, dry mouth, and hypertension (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Allergan at 1-800-678-1605 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 6/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: SUICIDALITY AND ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
2.2 Patients with Renal Insufficiency
2.3 Patients with Hepatic Insufficiency
2.4 Discontinuing Savella
2.5 Switching a Patient to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) Intended to Treat Psychiatric Disorders
2.6 Use of Savella with other MAOIs such as Linezolid or Methylene Blue
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Suicide Risk
5.2 Serotonin Syndrome
5.3 Elevated Blood Pressure
5.4 Elevated Heart Rate
5.5 Seizures
5.6 Hepatotoxicity
5.7 Discontinuation of Treatment with Savella
5.8 Hyponatremia
5.9 Abnormal Bleeding
5.10 Activation of Mania
5.11 Patients with a History of Dysuria
5.12 Angle Closure Glaucoma
5.13 Concomitant Use with Alcohol
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
7.2 Serotonergic Drugs
7.3 Triptans
7.4 Catecholamines
7.5 CNS-active drugs
7.6 Clinically Important Interactions with Select Cardiovascular Agents
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
9.3 Dependence
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: SUICIDALITY AND ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS
Savella is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), similar to some drugs used for the treatment of depression and other psychiatric disorders. Antidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Anyone considering the use of such drugs in a child, adolescent, or young adult must balance this risk with the clinical need. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older. Depression and certain other psychiatric disorders are themselves associated with increases in the risk of suicide. Patients of all ages who are started on Savella should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Families and caregivers should be advised of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Savella is not approved for use in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Savella is not approved for use in pediatric patients [see Indications and Usage (1), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Savella is indicated for the management of fibromyalgia.
Savella is not approved for use in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Savella is given orally with or without food.
Taking Savella with food may improve the tolerability of the drug.
2.1 Recommended Dosing
The recommended dose of Savella is 100 mg/day (50 mg twice daily).
Based on efficacy and tolerability dosing may be titrated according to the following schedule:
Day 1: 12.5 mg once
Days 2-3: 25 mg/day (12.5 mg twice daily)
Days 4-7: 50 mg/day (25 mg twice daily)
After Day 7: 100 mg/day (50 mg twice daily)
Based on individual patient response, the dose may be increased to 200 mg/day (100 mg twice daily).
Doses above 200 mg/day have not been studied.
Savella should be tapered and not abruptly discontinued after extended use [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
2.2 Patients with Renal Insufficiency
No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with mild renal impairment.
Savella should be used with caution in patients with moderate renal impairment.
For patients with severe renal impairment (indicated by an estimated creatinine clearance of 5-29 mL/min), the maintenance dose should be reduced by 50% to 50 mg/day (25 mg twice daily).
Based on individual patient response, the dose may be increased to 100 mg/day (50 mg twice daily).
Savella is not recommended for patients with end-stage renal disease.
2.3 Patients with Hepatic Insufficiency
No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with hepatic impairment.
As with any drug, caution should be exercised in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
2.4 Discontinuing Savella
Withdrawal symptoms have been observed in clinical trials following discontinuation of milnacipran, as with other serotonin and norepinephrine re-uptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Patients should be monitored for these symptoms when discontinuing treatment. Savella should be tapered and not abruptly discontinued after extended use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
2.5 Switching a Patient to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) Intended to Treat Psychiatric Disorders
At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of a MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders and initiation of therapy with Savella. Conversely, at least 5 days should be allowed after stopping Savella before starting a MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders [see Contraindications (4.1)].
2.6 Use of Savella with other MAOIs such as Linezolid or Methylene Blue
Do not start Savella in a patient being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue because there is increased risk of serotonin syndrome. In a patient who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition, other interventions, including hospitalization, should be considered [see Contraindications (4.1)].
In some cases, a patient already receiving Savella therapy may require urgent treatment with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. If acceptable alternatives to linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are not available and the potential benefits of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are judged to outweigh the risks of serotonin syndrome in a particular patient, Savella should be stopped promptly, and linezolid or intravenous methylene blue can be administered. The patient should be monitored for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for 5 days or until 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, whichever comes first. Therapy with Savella may be resumed 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
The risk of administering methylene blue by non-intravenous routes (such as oral tablets or by local injection) or in intravenous doses much lower than 1 mg/kg with Savella is unclear. The clinician should nevertheless be aware of the possibility of emergent symptoms of serotonin syndrome with such use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Film-coated, immediate-release tablets in four strengths: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg of milnacipran hydrochloride.
12.5 mg tablets are round, blue, "F" on one side, "L" on the reverse;
25 mg tablets are round, white, "FL" on one side, "25" on the reverse;
50 mg tablets are oval, white, "FL" on one side, "50" on the reverse;
100 mg tablets are oval, pink, "FL" on one side, "100" on the reverse
[see Description (11) and How Supplied/ Storage and Handling (16)].
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
The use of MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders with Savella or within 5 days of stopping treatment with Savella is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. The use of Savella within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders is also contraindicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Starting Savella in a patient who is being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Suicide Risk
Savella is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine re-uptake inhibitor (SNRI), similar to some drugs used for the treatment of depression and other psychiatric disorders.
Patients, both adult and pediatric, with depression or other psychiatric disorders may experience worsening of their depression and/or the emergence of suicidal ideation and behavior (suicidality) or unusual changes in behavior, whether or not they are taking these medications, and this risk may persist until significant remission occurs. Suicide is a known risk of depression and certain other psychiatric disorders, and these disorders themselves are the strongest predictors of suicide. There has been a long-standing concern, however, that antidepressants, including drugs that inhibit the reuptake of norepinephrine and/or serotonin, may have a role in inducing worsening of depression and the emergence of suicidality in certain patients during the early phases of treatment.
In the placebo-controlled clinical trials of adults with fibromyalgia, among the patients who had a history of depression at treatment initiation, the incidence of suicidal ideation was 0.5% in patients treated with placebo, 0% in patients treated with Savella 100 mg/day, and 1.3% in patients treated with Savella 200 mg/day. No suicides occurred in the short-term or longer-term (up to 1 year) fibromyalgia trials.
Pooled analyses of short-term placebo-controlled trials of drugs used to treat depression (SSRIs and others) showed that these drugs increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults (ages 18-24) with major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with these drugs compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction in suicidality risk with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults age 65 and older.
The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in children and adolescents with MDD, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 24 short-term trials of 9 drugs used to treat depression in over 4400 patients. The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in adults with MDD or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 295 short-term trials (median duration of 2 months) of 11 antidepressant drugs in over 77,000 patients.
There was considerable variation in risk of suicidality among drugs, but a tendency toward an increase in the younger patients for almost all drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidality across the different indications, with the highest incidence in MDD. The risk of differences (drug versus placebo), however, were relatively stable within age strata and across indications. These risk differences (drug-placebo difference in the number of cases of suicidality per 1000 patients treated) are provided in Table 1.
Table 1: Risk Differences (Drug – Placebo) in the number of Cases of Suicidality, per 1000 patients treated Age Range
Drug-Placebo Difference in Number of Cases of Suicidality per 1000 Patients Treated
< 18
14 additional cases
18-24
5 additional cases
Decreases Compared to Placebo
25-64
1 fewer case
≥ 65
6 fewer cases
No suicides occurred in any of the pediatric trials. There were suicides in the adult trials, but the number was not sufficient to reach any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
It is unknown whether the suicidality risk extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond several months.
However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with depression that the use of antidepressants can delay the recurrence of depression.
All patients being treated with drugs inhibiting the reuptake of norepinephrine and/or serotonin for any indication should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, and unusual changes in behavior, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases.
The following symptoms, anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, mania, have been reported in adult and pediatric patients being treated with drugs inhibiting the reuptake of norepinephrine and/or serotonin for major depressive disorder as well as for other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric. Although a causal link between the emergence of such symptoms and either the worsening of depression and/or the emergence of suicidal impulses has not been established, there is concern that such symptoms may represent precursors to emerging suicidality.
Consideration should be given to changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing the medication, in patients who may experience worsening depressive symptoms, or who are experiencing emergent suicidality or symptoms that might be precursors to worsening depression or suicidality, especially if these symptoms are severe or abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms.
If the decision has been made to discontinue treatment due to worsening depressive symptoms or emergent suicidality, medication should be tapered, as rapidly as is feasible, but with recognition that abrupt discontinuation can produce withdrawal symptoms [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.4), and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Families and caregivers of patients being treated with drugs inhibiting the reuptake of norepinephrine and/or serotonin for major depressive disorder or other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric, should be alerted about the need to monitor patients for the emergence of agitation, irritability, unusual changes in behavior, and the other symptoms described above, as well as the emergence of suicidality, and to report such symptoms immediately to health care providers. Such monitoring should include daily observation by families and caregivers. Prescriptions for Savella should be written for the smallest quantity of tablets consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
5.2 Serotonin Syndrome
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with SNRIs and SSRIs, including Savella, alone but particularly with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines, and St. John's Wort) and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular MAOIs, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue).
Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for the emergence of serotonin syndrome.
The concomitant use of Savella with MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders is contraindicated. Savella should also not be started in a patient who is being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. All reports with methylene blue that provided information on the route of administration involved intravenous administration in the dose range of 1 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg. No reports involved the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection) or at lower doses. There may be circumstances when it is necessary to initiate treatment with an MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking Savella. Savella should be discontinued before initiating treatment with the MAOI [see Contraindications (4.1), Dosage and Administration (2.5, 2.6)].
If concomitant use of Savella with other serotonergic drugs including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, buspirone, tryptophan, amphetamines, and St. John's Wort is clinically warranted, patients should be made aware of a potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases.
Treatment with Savella and any concomitant serotonergic agents should be discontinued immediately if the above events occur, and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
5.3 Elevated Blood Pressure
A double-blind, placebo-controlled ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) study was conducted to evaluate the effects of milnacipran (up to 200 mg/day) on blood pressure in 321 fibromyalgia patients. Among fibromyalgia patients who were normotensive at baseline, an analysis of the blood pressure findings demonstrated a substantially higher proportion of Savella-treated patients had a hypertensive blood pressure measurement at the Week 4, 50 mg BID steady state visit (17.7% [n=21/119]) and the Week 7, 100 mg BID steady state visit (14.3% [n=15/105]) as compared to placebo-treated patients (3.7% [n=2/54] and 0% [0/49] at the Week 4 and Week 7 visits, respectively). Hypertension was defined as mean systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mmHg and change from baseline in mean SBP ≥10 mmHg or mean diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥90 mmHg and change from baseline in mean DBP ≥5 mmHg for the 12-hour period post AM study drug measurement at that visit. Furthermore, 1.9% (4/210) of Savella-treated and 0.9% (1/111) of placebo patients discontinued treatment for increases in blood pressure.
The increased risk of blood pressure measurements in the hypertensive range in Savella-treated patients is supported by substantial increases in mean SBP and DBP measurements observed in the ABPM study. Table 2 shows that, following treatment with Savella 50 mg BID for three weeks in patients who were normotensive at baseline, the mean increase from baseline was 5 mmHg in systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP). After further treatment with Savella 100 mg BID for two weeks, the mean increase from baseline in SBP and DBP was 6 mmHg. Similar elevations occurred in Savella-treated patients who were hypertensive at baseline.
Table 2: Mean (Standard Error) Change from Baseline in Mean 24-hour Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) of Milnacipran or Placebo following 4 Weeks of Treatment (50mg BID) and a Subsequent 2 Weeks of Treatment (100mg BID) *Blood pressure measurements made after 3 weeks of milnacipran 50mg BID ^Blood pressure measurements made after 2 weeks of milnacipran 100mg BID Normotensive
Hypertensive
n
Systolic
Diastolic
n
Systolic
Diastolic
Placebo
39
0(2)
-1(1)
50
0(2)
0(2)
50 mg BID*
92
5(1)
5(1)
84
5(2)
4(1)
Placebo
37
0(2)
-1(1)
47
-1(2)
0(1)
100 mg BID^
82
6(1)
6(1)
80
5(2)
4(1)
Similar patterns of treatment-emergent blood pressure elevations were observed in Phase 3 and clinical pharmacology studies as manifested by an increased risk of new onset hypertension or substantial increases in end of study blood pressure measurements in patients with hypertension at baseline (Table 3).
Table 3: Blood pressure changes in Phase 3 randomized controlled trials Milnacipran
50 mg BIDMilnacipran
100 mg BIDPlacebo
FM patients normotensive at baseline who became hypertensive (defined as SBP ≥ 140 mmHg or DBP ≥ 90 mmHg on three consecutive post-baseline visits)
20%
17%
7%
FM patients with sustained increases in SBP (increase of ≥ 15 mmHg on three consecutive post-baseline visits)
9%
6%
2%
FM patients with sustained increases in DBP (increase of ≥ 10 mmHg on three consecutive post-baseline visits)
13%
10 %
4%
FM patients hypertensive at baseline who had increases in SBP ≥ 15 mmHg at end of study
10%
7%
4%
FM patients hypertensive at baseline who had increases in DBP ≥ 10 mmHg at end of study
8%
6%
3%
Sustained increases in blood pressure may have adverse consequences. Cases of elevated blood pressure requiring immediate treatment have been reported.
Concomitant use of Savella with drugs that increase blood pressure and heart rate has not been evaluated and such combinations should be used with caution [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Effects of Savella on blood pressure in patients with significant hypertension or cardiac disease have not been systematically evaluated. Savella should be used with caution in these patients.
Measure blood pressure prior to initiating treatment and periodically monitor blood pressure throughout Savella treatment. Treat pre-existing hypertension and other cardiovascular disease before starting therapy with Savella. For patients who experience a sustained increase in blood pressure while receiving Savella, either reduce the dose or discontinue treatment with Savella if clinically warranted.
5.4 Elevated Heart Rate
A double-blind, placebo-controlled ABPM study was conducted to evaluate the effects of milnacipran (up to 200 mg/day) on blood pressure in 321 fibromyalgia patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Information on heart rate was also collected. Following treatment with Savella 50mg BID for three weeks in patients who were normotensive at baseline, the mean increase in mean 24-hour heart rate from baseline was 13 beats per minute. After further treatment with Savella 100 mg BID for two weeks, the mean increase from baseline in heart rate was 13 beats per minute.
Similar trends were observed in the clinical trials where Savella treatment was associated with mean increases in heart rate of approximately 7 to 8 beats per minute [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Increases in heart rate ≥ 20 beats per minute occurred more frequently in Savella-treated patients when compared to placebo (8% in the Savella 50 mg BID and 100 mg BID treatment arms versus 0.3% in the placebo arm).
Savella has not been systematically evaluated in patients with a cardiac rhythm disorder.
Measure heart rate prior to initiating treatment and periodically monitor the heart rate throughout Savella treatment. Treat pre-existing tachyarrhythmias and other cardiac disease before starting therapy with Savella. For patients who experience a sustained increase in heart rate while receiving Savella, either reduce the dose or discontinue treatment with Savella if clinically warranted.
5.5 Seizures
Savella has not been systematically evaluated in patients with a seizure disorder. In clinical trials evaluating Savella in patients with fibromyalgia, seizures/convulsions have not been reported. However, seizures have been reported infrequently in patients treated with Savella for disorders other than fibromyalgia. Savella should be prescribed with care in patients with a history of a seizure disorder.
5.6 Hepatotoxicity
In the placebo-controlled fibromyalgia trials, increases in the number of patients treated with Savella with mild elevations of ALT or AST (1-3 times the upper limit of normal, ULN) were observed. Increases in ALT were more frequently observed in the patients treated with Savella 100 mg/day (6%) and Savella 200 mg/day (7%), compared to the patients treated with placebo (3%). One patient receiving Savella 100 mg/day (0.2%) had an increase in ALT greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal but did not exceed 10 times the upper limit of normal. Increases in AST were more frequently observed in the patients treated with Savella 100 mg/day (3%) and Savella 200 mg/day (5%) compared to the patients treated with placebo (2%).
The increases of bilirubin observed in the fibromyalgia clinical trials were not clinically significant.
No case met the criteria of elevated ALT > 3x ULN and associated with an increase in bilirubin ≥ 2x ULN.
There have been cases of increased liver enzymes and reports of severe liver injury, including fulminant hepatitis with milnacipran from foreign postmarketing experience. In the cases of severe liver injury, there were significant underlying clinical conditions and/or the use of multiple concomitant medications. Because of underreporting, it is impossible to provide an accurate estimate of the true incidence of these reactions.
Savella should be discontinued in patients who develop jaundice or other evidence of liver dysfunction. Treatment with Savella should not be resumed unless another cause can be established.
Savella should ordinarily not be prescribed to patients with substantial alcohol use or evidence of chronic liver disease.
5.7 Discontinuation of Treatment with Savella
Withdrawal symptoms have been observed in clinical trials following discontinuation of milnacipran, as with other SNRIs and SSRIs.
During marketing of milnacipran, and other SNRIs and SSRIs, there have been spontaneous reports of adverse events indicative of withdrawal and physical dependence occurring upon discontinuation of these drugs, particularly when discontinuation is abrupt. The adverse events include the following: dysphoric mood, irritability, agitation, dizziness, sensory disturbances (e.g., paresthesias such as electric shock sensations), anxiety, confusion, headache, lethargy, emotional lability, insomnia, hypomania, tinnitus, and seizures. Although these events are generally self-limiting, some have been reported to be severe.
Patients should be monitored for these symptoms when discontinuing treatment with Savella. Savella should be tapered and not abruptly discontinued after extended use. If intolerable symptoms occur following a decrease in the dose or upon discontinuation of treatment, then resuming the previously prescribed dose may be considered. Subsequently, the physician may continue decreasing the dose but at a more gradual rate [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.8 Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia may occur as a result of treatment with SSRIs and SNRIs, including Savella. In many cases, this hyponatremia appears to be the result of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). Cases with serum sodium lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported. Elderly patients may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia with SNRIs, SSRIs, or Savella. Also, patients taking diuretics or who are otherwise volume-depleted may be at greater risk [see Geriatric Use (8.5)]. Discontinuation of Savella should be considered in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia.
Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls. Signs and symptoms associated with more severe and/or acute cases have included hallucination, syncope, seizure, coma, respiratory arrest, and death.
5.9 Abnormal Bleeding
SSRIs and SNRIs, including Savella, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Concomitant use of aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), warfarin, and other anti-coagulants may add to this risk. Case reports and epidemiological studies (case-control and cohort design) have demonstrated an association between use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding. Bleeding events related to SSRIs and SNRIs use have ranged from ecchymoses, hematomas, epistaxis, and petechiae to life-threatening hemorrhages.
Patients should be cautioned about the risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of Savella and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation.
5.10 Activation of Mania
No activation of mania or hypomania was reported in the clinical trials evaluating effects of Savella in patients with fibromyalgia. However those clinical trials excluded patients with current major depressive episode. Activation of mania and hypomania have been reported in patients with mood disorders who were treated with other similar drugs for major depressive disorder. As with these other agents, Savella should be used cautiously in patients with a history of mania.
5.11 Patients with a History of Dysuria
Because of their noradrenergic effect, SNRIs including Savella, can affect urethral resistance and micturition. In the controlled fibromyalgia trials, dysuria occurred more frequently in patients treated with Savella (1%) than in placebo-treated patients (0.5%). Caution is advised in use of Savella in patients with a history of dysuria, notably in male patients with prostatic hypertrophy, prostatitis, and other lower urinary tract obstructive disorders. Male patients are more prone to genitourinary adverse effects, such as dysuria or urinary retention, and may experience testicular pain or ejaculation disorders.
5.12 Angle Closure Glaucoma
The pupillary dilation that occurs following use of SNRI drugs including Savella may trigger an angle closure attack in a patient with anatomically narrow angles who does not have a patent iridectomy.
5.13 Concomitant Use with Alcohol
In clinical trials, more patients treated with Savella developed elevated transaminases than did placebo treated patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. Because it is possible that milnacipran may aggravate pre-existing liver disease, Savella should not be prescribed to patients with substantial alcohol use or evidence of chronic liver disease.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Patient Exposure
Savella was evaluated in three double-blind placebo-controlled trials involving 2209 fibromyalgia patients (1557 patients treated with Savella and 652 patients treated with placebo) for a treatment period up to 29 weeks.
The stated frequencies of adverse reactions represent the proportion of individuals who experienced, at least once, a treatment-emergent adverse reaction of the type listed. A reaction was considered treatment emergent if it occurred for the first time or worsened while receiving therapy following baseline evaluation.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
In placebo-controlled trials in patients with fibromyalgia, 23% of patients treated with Savella
100 mg/day, 26% of patients treated with Savella 200 mg/day discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions, compared to 12% of patients treated with placebo. The adverse reactions that led to withdrawal in ≥ 1% of patients in the Savella treatment group and with an incidence rate greater than that in the placebo treatment group were nausea (milnacipran 6%, placebo 1%), palpitations (milnacipran 3%, placebo 1%), headache (milnacipran 2%, placebo 0%), constipation (milnacipran 1%, placebo 0%), heart rate increased (milnacipran 1%, placebo 0%), hyperhidrosis (milnacipran 1%, placebo 0%), vomiting (milnacipran 1%, placebo 0%), and dizziness (milnacipran 1% and placebo 0.5%). Discontinuation due to adverse reactions was generally more common among patients treated with Savella 200 mg/day compared to Savella 100 mg/day.
Most Common Adverse Reactions in Placebo Controlled Trials
In the placebo-controlled fibromyalgia patient trials, the most frequently occurring adverse reaction in clinical trials was nausea. The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5% and twice placebo) in patients treated with Savella were constipation, hot flush, hyperhidrosis, vomiting, palpitations, heart rate increased, dry mouth, and hypertension.
Table 4 lists all adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% of patients treated with Savella at either 100 or 200 mg/day and at an incidence greater than that of placebo.
Table 4: Treatment-Emergent Adverse Reaction Incidence in Placebo Controlled Trials in Fibromyalgia Patients (Events Occurring in at Least 2% of All Savella-Treated Patients and Occurring More Frequently in Either Savella Treatment Group Than in the Placebo Treatment Group) System Organ Class–
Preferred TermSavella
100 mg/day
(n = 623) %Savella
200 mg/day
(n = 934) %All Savella
(n = 1557) %Placebo
(n = 652) %Cardiac Disorders
Palpitations
8
7
7
2
Tachycardia
3
2
2
1
Eye Disorders
Vision blurred
1
2
2
1
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Nausea
35
39
37
20
Constipation
16
15
16
4
Vomiting
6
7
7
2
Dry mouth
5
5
5
2
Abdominal pain
3
3
3
2
General Disorders
Chest pain
3
2
2
2
Chills
1
2
2
0
Chest discomfort
2
1
1
1
Infections
Upper respiratory tract infection
7
6
6
6
Investigations
Heart rate increased
5
6
6
1
Blood pressure increased
3
3
3
1
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders
Decreased appetite
1
2
2
0
Nervous System Disorders
Headache
19
17
18
14
Dizziness
11
10
10
6
Migraine
6
4
5
3
Paresthesia
2
3
2
2
Tremor
2
2
2
1
Hypoesthesia
1
2
1
1
Tension headache
2
1
1
1
Psychiatric Disorders
Insomnia
12
12
12
10
Anxiety
5
3
4
4
Respiratory Disorders
Dyspnea
2
2
2
1
Skin Disorders
Hyperhidrosis
8
9
9
2
Rash
3
4
3
2
Pruritus
3
2
2
2
Vascular Disorders
Hot flush
11
12
12
2
Hypertension
7
4
5
2
Flushing
2
3
3
1
Weight Changes
In placebo-controlled fibromyalgia clinical trials, patients treated with Savella for up to 3 months experienced a mean weight loss of approximately 0.8 kg in both the Savella 100 mg/day and the Savella 200 mg/day treatment groups, compared with a mean weight loss of approximately 0.2 kg in placebo-treated patients.
Genitourinary Adverse Reactions in Males
In the placebo-controlled fibromyalgia studies, the following treatment-emergent adverse reactions related to the genitourinary system were observed in at least 2% of male patients treated with Savella, and occurred at a rate greater than in placebo-treated male patients: dysuria, ejaculation disorder, erectile dysfunction, ejaculation failure, libido decreased, prostatitis, scrotal pain, testicular pain, testicular swelling, urinary hesitation, urinary retention, urethral pain, and urine flow decreased.
Other Adverse Reactions Observed During Clinical Trials of Savella in Fibromyalgia
Following is a list of frequent (those occurring on one or more occasions in at least 1/100 patients) treatment-emergent adverse reactions reported from 1824 fibromyalgia patients treated with Savella for periods up to 68 weeks. The listing does not include those events already listed in Table 4, those events for which a drug cause was remote, those events which were so general as to be uninformative, and those events reported only once which did not have a substantial probability of being acutely life threatening.
Adverse reactions are categorized by body system and listed in order of decreasing frequency. Adverse reactions of major clinical importance are described in the Warnings and Precautions section (5).
Gastrointestinal Disorders — diarrhea, dyspepsia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, flatulence, abdominal distension
General Disorders — fatigue, peripheral edema, irritability, pyrexia
Infections — urinary tract infection, cystitis
Injury, Poisoning, and Procedural Complications — contusion, fall
Investigations — weight decreased or increased
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders — hypercholesterolemia
Nervous System Disorders — somnolence, dysgeusia
Psychiatric Disorders — depression, stress
Skin Disorders — night sweats
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified from spontaneous reports of Savella received worldwide. These adverse reactions have been chosen for inclusion because of a combination of seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal connection to Savella. However, because these adverse reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These events include:
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders — leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia
Cardiac Disorders — supraventricular tachycardia, Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
Eye Disorders — accommodation disorder
Endocrine Disorders — hyperprolactinemia
Gastrointestinal Disorders — acute pancreatitis
Hepatobiliary Disorders — hepatitis
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders — anorexia, hyponatremia
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders — rhabdomyolysis
Nervous System Disorders — convulsions (including grand mal), loss of consciousness, Parkinsonism
Psychiatric Disorders — aggression, anger, delirium, hallucination, homicidal ideation
Renal and Urinary Disorders — acute renal failure
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders — galactorrhea
Skin Disorders — erythema multiforme, Stevens Johnson syndrome
Vascular Disorders — hypertensive crisis
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Milnacipran undergoes minimal CYP450 related metabolism, with the majority of the dose excreted unchanged in urine (55%), and has a low binding to plasma proteins (13%). In vitro and in vivo studies showed that Savella is unlikely to be involved in clinically significant pharmacokinetic drug interactions [see Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations (12.3)].
7.1 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
[See Dosage and Administration (2.5 and 2.6), Contraindications (4.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.2 Serotonergic Drugs
[See Dosage and Administration (2.5 and 2.6), Contraindications (4.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.3 Triptans
There have been rare postmarketing reports of serotonin syndrome with use of an SSRI and a triptan. If concomitant treatment of Savella with a triptan is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.4 Catecholamines
Savella inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine. Therefore concomitant use of Savella with epinephrine and norepinephrine may be associated with paroxysmal hypertension and possible arrhythmia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4)].
7.5 CNS-active drugs
Given the primary CNS effects of Savella, caution should be used when it is taken in combination with other centrally acting drugs, including those with a similar mechanism of action.
Clomipramine: In a drug-drug interaction study, an increase in euphoria and postural hypotension was observed in patients who switched from clomipramine to Savella.
7.6 Clinically Important Interactions with Select Cardiovascular Agents
Digoxin: Use of Savella concomitantly with digoxin may be associated with potentiation of adverse hemodynamic effects. Postural hypotension and tachycardia have been reported in combination therapy with intravenously administered digoxin (1 mg). Co-administration of Savella and intravenous digoxin should be avoided [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4)].
Clonidine: Because Savella inhibits norepinephrine reuptake, co-administration with clonidine may inhibit clonidine's anti-hypertensive effect.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Risk Summary
There are no adequate or well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Neonates exposed to dual reuptake inhibitors of serotonin and norepinephrine (such as Savella), or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors late in the third trimester have developed complications that can arise immediately upon delivery. Reproduction studies have been performed in rats, rabbits and mice. Milnacipran was shown to increase embryo fetal and perinatal lethality in rats and the incidence of a minor skeletal variation in rabbits at doses below (rat) or approximately equal to (rabbit) the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 200 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis. No effects were seen in mice when treated with milnacipran during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 3 times the MHRD on a mg/m2 basis. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, Savella should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Pregnancy Registry
Physicians are advised to recommend that pregnant patients taking Savella enroll in the Savella Pregnancy Registry. Enrollment is voluntary and may be initiated by pregnant patients or their healthcare providers by contacting the registry at 1-877-643-3010 or by email at pregnancyregistries@incresearch.com. Data forms may also be downloaded from the registry website at www.savellapregnancyregistry.com.
Clinical Consideration
Neonates exposed to dual reuptake inhibitors of serotonin and norepinephrine, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors late in the third trimester have developed complications that can arise immediately upon delivery and require prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding. Such complications can arise immediately upon delivery. Monitor neonates for reported clinical findings such as respiratory distress, cyanosis, apnea, seizures, temperature instability, feeding difficulty, vomiting, hypoglycemia, hypotonia, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, tremor, jitteriness, irritability, and constant crying. These features are consistent with either a direct toxic effect of these classes of drugs or, possibly, a drug discontinuation syndrome. It should be noted that, in some cases, the clinical picture is consistent with serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Animal Data
Studies were conducted in rats, rabbits and mice with dosing of milnacipran during the period of organogenesis. In rats, milnacipran was shown to increase embryo fetal lethality at doses of 5 mg/kg/day (0.25 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). In rabbits, dose-dependent increases in the incidence of the skeletal variation of an extra single rib were observed in several pups from multiple litters in the absence of maternal toxicity at 15 mg/kg/day (1.5 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). The clinical significance of this finding is unknown. In mice, no embryotoxic or teratogenic effects were seen at doses up to 125 mg/kg/day (3 times the MHRD on a mg/m2 basis).
With peri- and postnatal exposure to oral milnacipran in rats, decreases in viability and body weight were observed on Postpartum Day 4 at a dose of 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.25 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). The no-effect dose for maternal and offspring toxicity was 2.5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.1 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis).
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Milnacipran is present in the milk of lactating women treated with Savella. In a pharmacokinetic study, a single, oral dose of 50 mg milnacipran HCl tablet was administered to 8 lactating women who were at least 12 weeks postpartum and weaning their infants. The maximum estimated daily infant dose for milnacipran from breast milk (assuming mean milk consumption of 150 mL/kg/day) was 5% of the maternal dose based on peak plasma concentrations. In most patients, peak concentrations of milnacipran in breast milk were seen within 4 hours after the maternal dose. Because of the limited data regarding infant exposure to Savella, caution should be exercised when Savella is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of Savella in a fibromyalgia pediatric population below the age of 18 have not been established [see Boxed Warning, Indications and Usage (1), and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. The use of Savella is not recommended in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In controlled clinical studies of Savella, 402 patients were 60 years or older, and no overall differences in safety and efficacy were observed between these patients and younger patients.
In view of the predominant excretion of unchanged milnacipran via kidneys and the expected decrease in renal function with age, renal function should be considered prior to use of Savella in the elderly [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
SNRIs, SSRIs, and Savella, have been associated with cases of clinically significant hyponatremia in elderly patients, who may be at greater risk for this adverse event [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
-
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.2 Abuse
Milnacipran did not produce behavioral signs indicative of abuse potential in animal or human studies.
9.3 Dependence
Milnacipran produces physical dependence, as evidenced by the emergence of withdrawal symptoms following drug discontinuation, similar to other SNRIs and SSRIs. These withdrawal symptoms can be severe. Thus, Savella should be tapered and not abruptly discontinued after extended use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is limited clinical experience with Savella overdose in humans. In clinical trials, cases of acute ingestions up to 1000 mg, alone or in combination with other drugs, were reported with none being fatal.
In postmarketing experience, fatal outcomes have been reported for acute overdoses primarily involving multiple drugs but also with Savella only. The most common signs and symptoms included increased blood pressure, cardio-respiratory arrest, changes in the level of consciousness (ranging from somnolence to coma), confusional state, dizziness, and increased hepatic enzymes.
Management of Overdose
There is no specific antidote to Savella, but if serotonin syndrome ensues, specific treatment (such as with cyproheptadine and/or temperature control) may be considered. In case of acute overdose, treatment should consist of those general measures employed in the management of overdose with any drug.
An adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation should be assured and cardiac rhythm and vital signs should be monitored. Induction of emesis is not recommended. Gastric lavage with a large-bore orogastric tube with appropriate airway protection, if needed, may be indicated if performed soon after ingestion or in symptomatic patients. Because there is no specific antidote for Savella, symptomatic care and treatment with gastric lavage and activated charcoal should be considered as soon as possible for patients who experience a Savella overdose.
Due to the large volume of distribution of this drug, forced diuresis, dialysis, hemoperfusion, and exchange transfusion are unlikely to be beneficial.
In managing overdose, the possibility of multiple drug involvement should be considered. The physician should consider contacting a poison control center for additional information on the treatment of any overdose. Telephone numbers for certified poison control centers are listed in the Physicians' Desk Reference (PDR).
-
11 DESCRIPTION
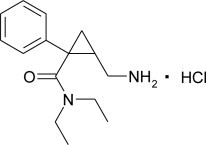
Milnacipran hydrochloride is a selective norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitor; it inhibits norepinephrine uptake with greater potency than serotonin. It is a racemic mixture with the chemical name: (±)-[1R(S),2S(R)]-2-(aminomethyl)-N,N-diethyl-1-phenylcyclopropanecarboxamide hydrochloride. The structural formula is:
Milnacipran hydrochloride is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a melting point of 179°C.
It is freely soluble in water, methanol, ethanol, chloroform, and methylene chloride and sparingly soluble in diethyl ether. It has an empirical formula of C15H23ClN2O and a molecular weight of 282.8 g/mol.
Savella is available for oral administration as film-coated tablets containing 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg milnacipran hydrochloride. Each tablet also contains dibasic calcium phosphate, povidone, carboxymethylcellulose calcium, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, and talc as inactive ingredients. The film coat contains the following additional inactive ingredients:
12.5 mg:
FD&C Blue #2 Aluminum Lake, polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide
25 mg:
Polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide
50 mg:
Polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide
100 mg:
FD&C Red #40 Aluminum Lake, polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The exact mechanism of the central pain inhibitory action of milnacipran and its ability to improve the symptoms of fibromyalgia in humans are unknown. Preclinical studies have shown that milnacipran is a potent inhibitor of neuronal norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake; milnacipran inhibits norepinephrine uptake with approximately 3-fold higher potency in vitro than serotonin without directly affecting the uptake of dopamine or other neurotransmitters. Milnacipran has no significant affinity for serotonergic (5-HT1-7), α- and β-adrenergic, muscarinic (M1-5), histamine (H1-4), dopamine (D1-5), opiate, benzodiazepine, and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in vitro. Pharmacologic activity at these receptors is hypothesized to be associated with the various anticholinergic, sedative, and cardiovascular effects seen with other psychotropic drugs.
Milnacipran has no significant affinity for Ca++, K+, Na+ and Cl– channels and does not inhibit the activity of human monoamine oxidases (MAO-A and MAO-B) or acetylcholinesterase.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiovascular Electrophysiology-The effect of Savella on the QTcF interval was measured in a double-blind placebo- and positive-controlled parallel study in 88 healthy subjects using 600 mg/day Savella (3 to 6 times the recommended therapeutic dose for fibromyalgia). After baseline and placebo adjustment, the maximum mean QTcF change was 8 ms (2-sided 90% CI, 3-12 ms). This increase is not considered to be clinically significant.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Milnacipran is well absorbed after oral administration with an absolute bioavailability of approximately 85% to 90%. The exposure to milnacipran increased proportionally within the therapeutic dose range. It is excreted predominantly unchanged in urine (55%) and has a terminal elimination half-life of about 6 to 8 hours. Steady-state levels are reached within 36 to 48 hours and can be predicted from single-dose data. The active enantiomer, d-milnacipran, has a longer elimination half-life (8-10 hours) than the l-enantiomer (4-6 hours). There is no interconversion between the enantiomers.
Absorption and Distribution
Savella is absorbed following oral administration with maximum concentrations (Cmax) reached within 2 to 4 hours post dose. Absorption of Savella is not affected by food. The absolute bioavailability is approximately 85% to 90%. The mean volume of distribution of milnacipran following a single intravenous dose to healthy subjects is approximately 400 L.
Plasma protein binding is 13%.
Metabolism and Elimination
Milnacipran and its metabolites are eliminated primarily by renal excretion. Following oral administration of 14C-milnacipran hydrochloride, approximately 55% of the dose was excreted in urine as unchanged milnacipran (24% as l-milnacipran and 31% as d-milnacipran). The l-milnacipran carbamoyl-O-glucuronide was the major metabolite excreted in urine and accounted for approximately 17% of the dose; approximately 2% of the dose was excreted in urine as d-milnacipran carbamoyl-O-glucuronide. Approximately 8% of the dose was excreted in urine as the N-desethyl milnacipran metabolite.
Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations
Renal Impairment-Milnacipran pharmacokinetics were evaluated following single oral administration of 50 mg Savella to subjects with mild (creatinine clearance [CLcr] 50-80 mL/min), moderate (CLcr 30-49 mL/min), and severe (CLcr 5-29 mL/min) renal impairment and to healthy subjects (CLcr > 80 mL/min). The mean AUC0-∞ increased by 16%, 52%, and 199%, and terminal elimination half-life increased by 38%, 41%, and 122% in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively, compared with healthy subjects.
No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with mild renal impairment. Caution should be exercised in patients with moderate renal impairment. Dose adjustment is necessary in severe renal impairment patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Hepatic Impairment-Milnacipran pharmacokinetics were evaluated following single oral administration of 50 mg Savella to subjects with mild (Child-Pugh A), moderate (Child-Pugh B), and severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment and to healthy subjects. AUC0-∞ and T½ were similar in healthy subjects and subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment. However, subjects with severe hepatic impairment had a 31% higher AUC0-∞ and a 55% higher T½ than healthy subjects. Caution should be exercised in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Elderly-Cmax and AUC parameters of milnacipran were about 30% higher in elderly (> 65 years) subjects compared with young subjects due to age-related decreases in renal function.
No dosage adjustment is necessary based on age unless renal function is severely impaired [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Gender-Cmax and AUC parameters of milnacipran were about 20% higher in female subjects compared with male subjects. Dosage adjustment based on gender is not necessary.
Lactation study- In a pharmacokinetic study, a single, oral dose of 50 mg milnacipran HCl tablet was administered to 8 lactating women who were at least 12 weeks postpartum and weaning their infants. The maximum estimated daily infant dose for milnacipran from breast milk (assuming mean milk consumption of 150 mL/kg/day) was 5% of the maternal dose based on peak plasma concentrations. In most patients, peak concentrations of milnacipran in breast milk were seen within 4 hours after the maternal dose. Because of the limited data regarding infant exposure to Savella, caution should be exercised when Savella is administered to a nursing woman.
Drug-Drug Interactions
In Vitro Studies
In general, milnacipran, at concentrations that were at least 25 times those attained in clinical trials, did not inhibit human CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4 or induce human CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4/5 enzyme systems, indicating a low potential of interactions with drugs metabolized by these enzymes.
In vitro studies have shown that the biotransformation rate of milnacipran by human hepatic microsomes and hepatocytes was low. A low biotransformation was also observed following incubation of milnacipran with cDNA-expressed human CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4 isozymes.
In Vivo Studies
The drug interaction studies described in this section were conducted in healthy adult subjects.
Carbamazepine-There were no clinically significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of milnacipran following co-administration of Savella (100 mg/day) and carbamazepine (200 mg twice a day). No changes were observed in the pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine or its epoxide metabolite due to co-administration with Savella.
Clomipramine-Switching from clomipramine (75 mg once a day) to milnacipran (100 mg/day) without a washout period did not lead to clinically significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of milnacipran. Because an increase in adverse events (eg, euphoria and postural hypotension) was observed after switching from clomipramine to milnacipran, monitoring of patients during treatment switch is recommended.
Digoxin-There was no pharmacokinetic interaction between Savella (200 mg/day) and digoxin
(0.2 mg/day Lanoxicaps) following multiple-dose administration to healthy subjects.
Fluoxetine-Switching from fluoxetine (20 mg once a day), a strong inhibitor of CYP2D6 and a moderate inhibitor of CYP2C19, to milnacipran (100 mg/day) without a washout period did not affect the pharmacokinetics of milnacipran.
Lithium-Multiple doses of Savella (100 mg/day) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of lithium.
Lorazepam-There was no pharmacokinetic interaction between a single dose of Savella (50 mg) and lorazepam (1.5 mg).
Pregabalin-There were no clinically significant changes in the steady-state pharmacokinetics of milnacipran or pregabalin following twice a day co-administration of 50 mg milnacipran and 150 mg pregabalin.
Warfarin-Steady-state milnacipran (200 mg/day) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of R-warfarin and S-warfarin or the pharmacodynamics (as assessed by measurement of prothrombin INR) of a single dose of 25 mg warfarin. The pharmacokinetics of Savella were not altered by warfarin.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Dietary administration of milnacipran to rats at doses of 50 mg/kg/day (2 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) for 2 years caused a statistically significant increase in the incidence of thyroid C-cell adenomas and combined adenomas and carcinomas in males. A carcinogenicity study was conducted in Tg.rasH2 mice for 6 months at oral gavage doses of up to 125 mg/kg/day.
Milnacipran did not induce tumors in Tg.rasH2 mice at any dose tested.
Mutagenesis
Milnacipran was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) or in the L5178Y TK +/- mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay. Milnacipran was also not clastogenic in an in vitro chromosomal aberration test in human lymphocytes or in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
Although administration of milnacipran to male and female rats had no statistically significant effect on mating or fertility at doses up to 80 mg/kg/day (4 times the MRHD on an mg/m2 basis), there was an apparent dose-related decrease in the fertility index at clinically relevant doses based on body surface area.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Hepatic Effects
Chronic administration (2 years) of milnacipran to rats at 15 mg/kg (0.6 times the MRHD on an mg/m2 basis) and higher doses showed increased incidences of centrilobular vacuolation of the liver in male rats and eosinophilic foci in male and female rats in the absence of any change in hepatic enzymes. The clinical significance of the finding is not known. Chronic (1 year) administration in the primate at doses up to 25 mg/kg (2 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) did not demonstrate similar evidence of hepatic changes.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Management of Fibromyalgia
The efficacy of Savella for the management of fibromyalgia was established in two double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies in adult patients (18-74 years of age). Enrolled patients met the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria for fibromyalgia (a history of widespread pain for 3 months and pain present at 11 or more of the 18 specific tender point sites). Approximately 35% of patients had a history of depression. Study 1 was six months in duration and Study 2 was three months in duration.
A larger proportion of patients treated with Savella than with placebo experienced a simultaneous reduction in pain from baseline of at least 30% (VAS) and also rated themselves as much improved or very much improved based on the patient global assessment (PGIC). In addition, a larger proportion of patients treated with Savella met the criteria for treatment response, as measured by the composite endpoint that concurrently evaluated improvement in pain (VAS), physical function (SF-36 PCS), and patient global assessment (PGIC), in fibromyalgia as compared to placebo.
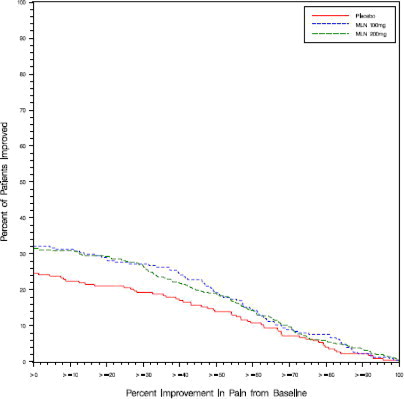
Study 1: This 6-month study compared total daily doses of Savella 100 mg and 200 mg to placebo. Patients were enrolled with a minimum mean baseline pain score of ≥ 50 mm on a 100 mm visual analog scale (VAS) ranging from 0 (“no pain”) to 100 (“worst possible pain”). The mean baseline pain score in this trial was 69. The efficacy results for Study 1 are summarized in Figure 1.
Figure 1 shows the proportion of patients achieving various degrees of improvement in pain from baseline to the 3-month time point and who concurrently rated themselves globally improved (PGIC score of 1 or 2). Patients who did not complete the 3-month assessment were assigned 0% improvement. More patients in the Savella treatment arms experienced at least a 30% reduction in pain from baseline (VAS) and considered themselves globally improved (PGIC) than did patients in the placebo arm. Treatment with Savella 200 mg/day did not confer greater benefit than treatment with Savella 100 mg/day.
Figure 1: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief with Concurrent Ratings of Being Much or Very Much Improved on the PGIC — Study 1
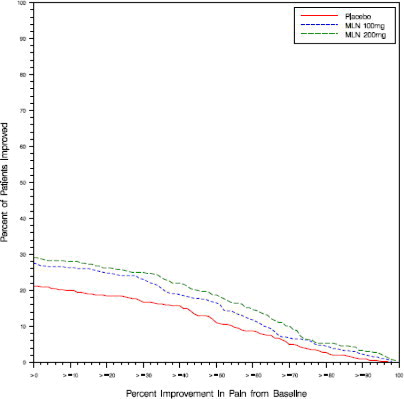
Study 2: This 3-month study compared total daily doses of Savella 100 mg and 200 mg to placebo. Patients were enrolled with a minimum mean baseline pain score of ≥ 40 mm on a 100-mm VAS ranging from 0 (“no pain”) to 100 (“worst possible pain”). The mean baseline pain score in this trial was 65. The efficacy results for Study 2 are summarized in Figure 2.
Figure 2 shows the proportion of patients achieving various degrees of improvement in pain from baseline to the 3-month time point and who concurrently rated themselves globally improved (PGIC score of 1 or 2). Patients who did not complete the 3-month assessment were assigned 0% improvement. More patients in the Savella treatment arms experienced at least a 30% reduction in pain from baseline (VAS) and considered themselves globally improved (PGIC) than did patients in the placebo arm. Treatment with Savella 200 mg/day did not confer greater benefit than treatment with Savella 100 mg/day.
Figure 2: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief with Concurrent Ratings of Being Much or Very Much Improved on the PGIC — Study 2
In both studies, some patients who rated themselves as globally “much” or “very much” improved experienced a decrease in pain as early as week 1 of treatment with a stable dose of Savella that persisted throughout these studies.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
50-mg tablets:
White, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets, debossed with “FL” on one side and “50” on the reverse
Available with approximately 1920 Tablets per bottle, NDC: 55154-4626-8
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See Medication Guide
Information for Patients
Prescribers or other health professionals should inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with Savella and should counsel them in its appropriate use. A patient Medication Guide is available for Savella. The prescriber or health professional should instruct patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide and should assist them in understanding its contents. Patients should be given the opportunity to discuss the contents of the Medication Guide and to obtain answers to any questions they may have. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of this document.
Patients should be advised of the following issues and asked to alert their prescriber if these occur while taking Savella:
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
Patients and their families and caregivers should be advised that Savella is a selective norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitor and therefore belongs to the same class of drugs as antidepressants. Patients, their families, and their caregivers should be advised that patients with depression may be at increased risk for clinical worsening and/or suicidal ideation if they stop taking anti-depressant medication, change the dose, or start a new medication.
Patients, their families, and their caregivers should be encouraged to be alert to the emergence of anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, or other unusual changes in behavior, worsening of depression, and suicidal ideation, especially early during treatment with Savella or other drugs that inhibit the reuptake of norepinephrine and/or serotonin, and when the dose is adjusted up or down. Families and caregivers of patients should be advised to observe for the emergence of such symptoms on a day-to-day basis, since changes may be abrupt. Such symptoms should be reported to the patient's prescriber or health professional, especially if they are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Patients should be cautioned about the risk of serotonin syndrome with concomitant use of Savella with other serotonergic drugs including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines and St. John's Wort, and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular MAOIs, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Patients should be advised of the signs and symptoms associated with serotonin syndrome that may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular changes (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be cautioned to seek medical care immediately if they experience these symptoms.
Elevated Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
Patients should be advised that Savella may increase their blood pressure and heart rate and that they should have their blood pressure and heart rate monitored at regular intervals when receiving treatment with Savella [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4)].
Abnormal Bleeding
Patients should be cautioned about the concomitant use of Savella and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation, since the combined use of agents that interfere with serotonin reuptake and these agents has been associated with an increased risk of abnormal bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Angle Closure Glaucoma
Patients should be advised that taking Savella can cause mild pupillary dilation, which in susceptible individuals, can lead to an episode of angle closure glaucoma. Pre-existing glaucoma is almost always open-angle glaucoma because angle closure glaucoma, when diagnosed, can be treated definitively with iridectomy. Open-angle glaucoma is not a risk factor for angle closure glaucoma. Patients may wish to be examined to determine whether they are susceptible to angle closure, and have a prophylactic procedure (e.g., iridectomy), if they are susceptible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Ability to Drive and Use Machinery
Savella might diminish mental and physical capacities necessary to perform certain tasks such as operating machinery, including motor vehicles. Patients should be cautioned about operating machinery or driving motor vehicles until they are reasonably certain that Savella treatment does not affect their ability to engage in such activities.
Alcohol
Patients should talk to their healthcare provider about their alcohol intake prior to initiating treatment with Savella [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.13)].
Discontinuation
Patients should be advised that withdrawal symptoms can occur when discontinuing treatment with Savella, particularly when discontinuation is abrupt [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Missing a Dose
Patients should be advised that if they miss a dose, they should skip the missed dose and take the next dose at their regular time.
Pregnancy
Patients should be advised to notify their physician if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during Savella therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Patients should be encouraged to enroll in the Savella Pregnancy Registry if they become pregnant, preferably before any prenatal testing is done. This registry is collecting information about the safety of milnacipran during pregnancy. To enroll, patients or their healthcare providers may call the toll-free number 1-877-643-3010 [see Use In Specific Populations (8.1)], download data forms from our website, www.savellapregnancyregistry.com, or email the registry for further information at pregnancyregistries@incresearch.com.
Nursing
Advise patients to notify their physician if they are breast feeding [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
FDA-Approved Medication Guide
MEDICATION GUIDE
Savella® (Sa-vel-la)
(milnacipran HCl)
Tablets
Savella is not used to treat depression, but it acts like medicines that are used to treat depression (antidepressants) and other psychiatric disorders.
Read the Medication Guide that comes with Savella® before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. Talk with your healthcare provider if there is something you do not understand or want to learn more about.
What is the most important information I should know about Savella?
Savella and antidepressant medicines may cause serious side effects, including:
- 1.
Suicidal thoughts or actions:
- Savella and antidepressant medicines may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, teenagers, and young adults within the first few months of treatment or when the dose is changed.
-
Depression or other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts or actions. Watch for these changes and call your healthcare provider right away if you notice:
- New or sudden changes, in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings, especially if severe.
- Pay particular attention to such changes when Savella is started or when the dose is changed.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider and call between visits if you are worried about symptoms.
- Call your healthcare provider right away or go to the nearest hospital emergency room if you have any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- attempts to commit suicide
- acting on dangerous impulses
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety or panic attacks
- feeling agitated, restless, angry or irritable
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- an increase in activity or talking more than what is normal for you
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
- Call your healthcare provider right away or go to the nearest hospital emergency room if you have any symptoms of the serious side effects listed below:
- 2.
Serotonin Syndrome. This condition can be life-threatening, symptoms may include:
- agitation, hallucinations, coma or other changes in mental status
- coordination problems or muscle twitching (overactive reflexes)
- sweating or fever
- diarrhea
- muscle rigidity
- dizziness
- tremor
- Symptoms such as racing heartbeat, high or low blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, and flushing are common with Savella. Call your healthcare provider right away if you get these symptoms and they are severe or if they happen with any of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome listed above.
- 3. Increase in blood pressure or heart rate: Savella may increase your blood pressure or heart rate. Your blood pressure and heart rate should be checked before you start and during treatment with Savella. Before taking Savella, tell your healthcare provider if you have high blood pressure or problems with your heart or blood vessels (cardiovascular disease).
- 4. Seizures or convulsions.
- 5.
Liver problems. Symptoms of liver problems may include:
- itching
- right upper abdominal pain
- dark urine
- yellowing of your skin or eyes
- enlarged liver
- increased liver enzymes
- 6.
Low salt (sodium) levels in the blood. Elderly people may be at greater risk for this. Symptoms may include:
- headache
- weakness or feeling unsteady
- confusion, problems concentrating or thinking or memory problems
- 7. Abnormal bleeding: Savella and other similar medicines (antidepressants) may increase your risk of bleeding or bruising, especially if you take the blood thinner warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), or aspirin.
- 8.
Manic episodes
- greatly increased energy
- severe trouble sleeping
- racing thoughts
- reckless behavior
- unusually grand ideas
- excessive happiness or irritability
- talking more or faster than usual
- 9.
Problems with urination
- decreased urine flow
-
unable to pass any urine
Men may be more likely to have these symptoms, and may develop pain in their testicles or have problems with ejaculation.
- 10.
Visual problems
- eye pain
- changes in vision
- swelling or redness in or around eye
- Only some people are at risk for these problems. You may want to undergo an eye examination to see if you are at risk and receive preventative treatment if you are.
Do not stop Savella without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping Savella too quickly may cause symptoms, some serious, including:
- anxiety, irritability, or confusion
- feeling tired or problems sleeping
- headache, dizziness, seizures
- electric shock-like sensations, ringing in ears
What is Savella?
Savella is a prescription medicine used to manage fibromyalgia. It is important to talk with your healthcare provider about the risks of treating fibromyalgia and also the risks of not treating it. You should discuss all treatment choices with your healthcare provider.
It is not known if Savella is safe and effective in children.
Who should not take Savella?
Do not take Savella if you:
-
take a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI). Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take an MAOI, including the antibiotic linezolid.
- Do not take an MAOI within 5 days of stopping Savella unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Do not start Savella if you stopped taking an MAOI in the last 14 days unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
-
People who take Savella close in time to an MAOI may have serious or even life-threatening side effects. Get medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- high fever
- uncontrolled muscle spasms
- stiff muscles
- rapid changes in heart rate or blood pressure
- confusion
- loss of consciousness (pass out)
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Savella?
Before starting Savella, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have heart problems or high blood pressure
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems
- have or had seizures or convulsions
- have bipolar disorder or mania
- have low sodium levels in your blood
- have or had bleeding problems
- drink alcohol. Talk to your healthcare provider about how often and how much alcohol you drink.
- have any other medical conditions
-
are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Savella will harm your unborn baby.
Pregnancy registry: There is a pregnancy registry for women who take Savella during pregnancy. The purpose of the registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. You may talk to your healthcare provider about how you can take part in this registry, or you may call the Registry directly at 1-877-643-3010 or go to www.savellapregnancyregistry.com. - are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Savella can pass into your breast milk and may harm your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby while taking Savella.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines that you take, including prescription and over-the counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Savella and some medicines may interact with each other, may not work as well, or may cause serious side effects when taken together.
Your healthcare provider or pharmacist can tell you if it is safe to take Savella with your other medicines. Do not start or stop any medicine while taking Savella without talking to your healthcare provider first.
How should I take Savella?
- Take Savella exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
-
Your healthcare provider will slowly increase your dose to find the dose that is right for you.
- On the first day of treatment, you will take 1 dose of Savella as prescribed.
- After your first dose, your healthcare provider will tell you how much Savella to take and when to take it, usually 2 times each day.
- You may take Savella with or without food. Taking Savella with food may help you tolerate it better.
- If you miss a dose, skip the missed dose and take the next dose at your regular time.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you feel that your condition is not improving during treatment with Savella.
- If you take too much Savella, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking Savella?
- Do not drive or operate machinery until you know how Savella affects you. Savella may make you less alert and affect your reaction time.
What are the possible side effects of Savella?
Savella may cause side effects, some serious, including:
The most common side effects of Savella include:
- nausea
- headache
- constipation
- dizziness
- trouble sleeping
- hot flush
- increased sweating
- vomiting
- irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- heart rate increased
- dry mouth
- high blood pressure (hypertension)
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Savella. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Savella?
- Store at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep Savella and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of Savella
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Savella for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Savella to other people, even if they have the same condition. It may harm them.
You may ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Savella that is written for health professionals.
For more information call 1-800-678-1605 or go to www.savella.com.
What are the ingredients in Savella?
Active ingredient: milnacipran hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: dibasic calcium phosphate, povidone, carboxymethylcellulose calcium, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, and talc.
The film coat contains the inactive ingredients:
12.5 mg tablets: FD&C Blue #2 Aluminum Lake, polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide
25 mg tablets: Polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide
50 mg tablets: Polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide
100 mg tablets: FD&C Red #40 Aluminum Lake, polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Allergan USA, Inc.
Irvine, CA 92612Distributed by:
Cardinal HealthDublin, OH 43017
L78001118
Revised: August 2016
Licensed from Pierre Fabre Medicament
SAVELLA® is a registered trademark of Allergan Pharmaceuticals International Limited
© 2017 Allergan. All rights reserved.
- 1.
Suicidal thoughts or actions:
- Package/Label Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SAVELLA
milnacipran hydrochloride tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 55154-4626(NDC:0456-1550) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength milnacipran hydrochloride (UNII: RNZ43O5WW5) (milnacipran - UNII:G56VK1HF36) milnacipran hydrochloride 50 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DIBASIC CALCIUM PHOSPHATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: O7TSZ97GEP) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) carboxymethylcellulose calcium (UNII: UTY7PDF93L) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) Product Characteristics Color white (white) Score no score Shape OVAL (OVAL) Size 11mm Flavor Imprint Code FL;50 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 55154-4626-8 1920 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 04/17/2009 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA022256 04/17/2009 Labeler - Cardinal Health (603638201)
Trademark Results [Savella]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 SAVELLA 88940367 not registered Live/Pending |
ALLERGAN SALES, LLC 2020-05-29 |
 SAVELLA 78234983 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Forest Laboratories, Inc 2003-04-08 |
 SAVELLA 78084676 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Forest Laboratories, Inc. 2001-09-20 |
 SAVELLA 77795756 3761078 Live/Registered |
ALLERGAN SALES, LLC 2009-08-03 |
 SAVELLA 77660515 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Forest Laboratories, Inc. 2009-01-30 |
 SAVELLA 77211766 3658661 Live/Registered |
ALLERGAN SALES, LLC 2007-06-21 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.