GASTROGRAFIN- diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium liquid
Gastrografin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Gastrografin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Bracco Diagnostics Inc, E-Z-EM Canada Inc, Justesa Imagen, S.A.U, Merck SL. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Gastrografin (Diatrizoate Meglumine and Diatrizoate Sodium Solution) is a palatable lemon-flavored water-soluble iodinated radiopaque contrast medium for oral or rectal administration only. Each mL contains 660 mg diatrizoate meglumine and 100 mg diatrizoate sodium; pH has been adjusted to 6.0 to 7.6 with sodium hydroxide. Each mL contains approximately 4.8 mg (0.21 mEq) sodium and 367 mg organically bound iodine. Inactive ingredients: edetate disodium, flavor, polysorbate 80, purified water, saccharin sodium, simethicone, and sodium citrate.
Diatrizoate meglumine is designated chemically as 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-D-glucitol 3,5-diacetamido-2,4,6-triiodo-benzoate (salt); diatrizoate sodium is monosodium 3, 5-diacetamido-2,4,6-triiodobenzoate. Structural formulas:
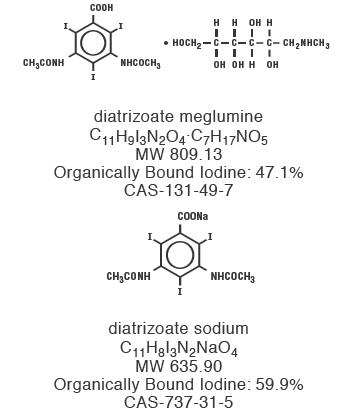
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The most important characteristic of contrast media is the iodine content. The relatively high atomic weight of iodine contributes sufficient radiodensity for radiographic contrast with surrounding tissues.
Diagnostic enteral radiopaque agents have few known pharmacological effects. Diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium exert a mild laxative effect attributable to their high osmolarity.
Diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium are sparingly absorbed from the intact gastrointestinal tract, and therefore permit gastrointestinal opacification and delineation after oral or rectal administration. Oral administration is used for radiographic evaluation of the esophagus, stomach and proximal small intestine. Rectal administration is used for examination of the colon; however, visualization of the distal small bowel is generally unsatisfactory, since the hypertonicity of the medium causes intraluminal diffusion of water with subsequent dilution of the medium. Enough absorption from the gastrointestinal tract to permit incidental visualization of the urinary tract has been reported; this should also be considered when thyroid testing is being contemplated, since iodine-mediated thyrotropic effects may occur (see PRECAUTIONS).
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Gastrografin (Diatrizoate Meglumine and Diatrizoate Sodium Solution) is indicated for radiographic examination of segments of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, proximal small intestine, and colon). The preparation is particularly indicated when a more viscous agent such as barium sulfate, which is not water-soluble, is not feasible or is potentially dangerous.
Gastrografin may also be used as an adjunct to contrast enhancement in computed tomography of the torso (body imaging); the preparation is indicated, in conjunction with intravenous administration of a radiopaque contrast agent, when unenhanced imaging may not provide sufficient definition in distinguishing normal loops of bowel from adjacent organs or areas of suspected pathology.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Dehydration: Administration of hypertonic Gastrografin solutions may lead to hypovolemia and hypotension due to fluid loss from the intestine. A 1 in 4.6 (1:4.6) dilution of Gastrografin yields an approximately isotonic 16.5 percent diatrizoate salts solution; less dilute solutions are hypertonic and may lead to intraluminal movement of fluid with resulting hypovolemia. In young or debilitated children and in elderly cachectic persons, the loss of plasma fluid may be sufficient to cause a shock-like state. If Gastrografin is used in infants and children (under 10 kg) or in dehydrated or debilitated patients, the solution must be prepared using the specific dilutions described in DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION. In debilitated patients and in patients with electrolyte imbalances, postprocedural monitoring of hydration, serum osmolarity, electrolytes and clinical status is essential. In pediatric or severely debilitated patients, the maintenance of an open intravenous fluid line for rehydration may be advisable should hypotension or shock supervene. Electrolyte disturbances must be corrected prior to the administration of any hypertonic Gastrografin solutions.
Aspiration: Aspiration of Gastrografin into the trachea and airways may result in serious pulmonary complications including, pulmonary edema, pneumonitis or death Bronchial entry of any orally administered contrast medium causes a copious osmotic effusion. Therefore, avoid use of Gastrografin in patients with esophagotracheal fistula and minimize risks for pulmonary aspiration in all patients. If Gastrografin is given by nasogastric tube, the position of the tube in the stomach must be verified before administration.
Anaphylactic reactions: Anaphylactic reactions, including fatalities, have been reported with the use of Gastrografin. Patients at increased risk include those with a history of a previous reaction to a contrast medium, patients with a known sensitivity to iodine, and patients with a known clinical hypersensitivity (bronchial asthma, hay fever, and food allergies). Medical personnel trained in the treatment of anaphylactic reactions and the necessary drugs and medical equipment should always be readily available when Gastrografin is used.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Diagnostic procedures which involve the use of radiopaque contrast agents should be carried out under the direction of personnel with the prerequisite training and with a thorough knowledge of the particular procedure to be performed. Appropriate facilities should be available for coping with any complication of administration, as well as for treatment of reaction to the contrast medium (see ADVERSE REACTIONS, and PRECAUTIONS, Information for the Patient).
Rectal administration of undiluted Gastrografin (Diatrizoate Meglumine and Diatrizoate Sodium Solution) in any patient, particularly with large doses and/or in those with overdistention, has been reported to be associated with mucosal irritation.
Cases of hyperthyroidism have been reported with the use of oral contrast media. Some of these patients reportedly had multinodular goiters which may have been responsible for the increased hormone synthesis in response to excess iodine. Administration of an intravascular iodinated radiopaque diagnostic agent to a hyperthyroid patient precipitated thyroid storm; a similar situation could follow administration of oral preparations of iodides. Therefore, caution should be exercised when administering enteral gastrointestinal radiopaque agents to hyperthyroid and euthyroid goiterous patients.
Consideration should be given to the potential for precipitation of water-soluble contrast agents under conditions that may promote hyperacidity (i.e., fasting, emotional upset, or stress). Harmful effects directly attributable to precipitate formation have not been reported. However, the possibility of interpreting the precipitate radiologically as an anatomical abnormality (i.e., ulceration of the stomach or small intestine) or injury, should be kept in mind.
Information for the Patient
Patients should receive the following information and instructions:
- This drug has been prescribed to perform an x-ray of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Inform the physician if pregnant or if allergic to iodine, any foods, or x-ray materials.
- The iodine in diatrizoate salts may interfere with some thyroid tests if these are needed in the future. Inform the attending physician at that time about this gastrointestinal study.
- This drug may cause abdominal cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, skin rashes, itching, heartburn, dizziness, or headache in some patients, but most reactions are mild and pass quickly.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Thyroid Function Tests
The results of protein bound iodine (PBI) and radioactive iodine uptake studies, which depend on iodine estimations, will not accurately reflect thyroid function for six months, and possibly as long as one year, following the administration of diagnostic enteral radiopaque media.
Thyroid function tests, if indicated, generally should be performed prior to the administration of any iodinated agent. However, thyroid function can be evaluated after use of these agents by using T3 resin uptake and total or free thyroxine (T4) assays which are not dependent on iodine estimations.
Pancreatic Tests
Small quantities of contrast medium in the intestinal tract may cause false low trypsin values when determined spectrophotometrically. Therefore, duodenal instillation should not precede pancreatic function tests involving spectrophotometric trypsin assays.
Any test which might be affected by contrast media should be performed prior to administration of the contrast medium.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic or mutagenic potential, or possible impairment of fertility in males or females.
Pregnancy
When administered intravenously, diatrizoate salts cross the placenta and are evenly distributed in fetal tissues.
No teratogenic effects attributable to diatrizoate meglumine or diatrizoate sodium have been observed in teratology studies performed in animals. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because small amounts of these agents may be absorbed, and animal teratology studies are not always predictive of human response, these agents should be used during pregnancy only when clearly needed.
Procedures including radiation involve a certain risk related to the exposure of the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Diatrizoate meglumine is excreted in breast milk following intravascular administration.
Because small amounts of enteral gastrointestinal radiopaque agents may be absorbed following oral or rectal administration, caution should be exercised when they are administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
See WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS, General.
Local injury to the colonic mucosa, particularly in the presence of underlying disease which interferes with intestinal viability, has been reported in cases where recommended doses and dilutions (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION) were not used; when extemporaneous dosage is elected, the polysorbate 80 level in the dose may be a contributing factor to injury.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most adverse reactions to enteral diagnostic radiopaque agents are mild and transitory. Nausea, vomiting and/or diarrhea, urticaria with erythema, hypoxia, acute dyspnea, tachyarrhythmia, and anaphylaxis have occurred following ingestion of the contrast medium, particularly when high concentrations of large volumes of solution are administered. Severe changes in serum osmolarity and electrolyte concentrations may produce shock-like states (see WARNINGS). It should be kept in mind that serious or anaphylactoid reactions that may occur with intravascular administration of radiopaque contrast agents are theoretically possible following administration by other routes.
-
OVERDOSAGE
See WARNINGS regarding potential hypovolemia, hypotension, or shock. The maintenance of an open intravenous fluid line for rehydration may be advisable. See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for appropriate doses and dilutions. Treatment of an overdose should be directed toward the support of all vital functions, and prompt institution of symptomatic therapy.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
General
This medium is not to be used for the preparation of solutions for parenteral administration. Oral or rectal administration only. Discard any unused portion after procedure.
The routine preparatory measures employed for barium studies are also appropriate for this agent.
For pediatric and severely cachectic patients the maintenance of an intravenous fluid line may be advisable.
Radiographic Examination of Segments of the Gastrointestinal Tract
Oral Administration: Adult oral dosage may range from 30 to 90 mL (11 to 33 g iodine), depending on the nature of the examination and the size of the patient. For infants and children less than 5 years of age, 30 mL (11 g iodine) are usually adequate; for children 5 to 10 years of age, the suggested dose is 60 mL (22 g iodine). These pediatric doses may be diluted 1:1, if desired, with water, carbonated beverage, milk, or mineral oil. When used in infants, the solution may be given in a nursing bottle. Pediatric doses may also be used in dehydrated and/or debilitated adult patients. A 1:1 dilution is also recommended when the contrast medium is used in elderly cachectic individuals.
For very young (under 10 kg) and debilitated children the dose should be diluted: 1 part Gastrografin (Diatrizoate Meglumine and Diatrizoate Sodium Solution) in 3 parts water is recommended.
For Enemas or Enterostomy Instillations: Gastrografin should be diluted when it is used for enemas and enterostomy instillations. When used as an enema, the suggested dilution for adults is 240 mL (88 g iodine) in 1,000 mL of tap water. For children under 5 years of age, a 1:5 dilution in tap water is suggested; for children over 5 years of age, 90 mL (33 g iodine) in 500 mL of tap water is a suitable dilution.
Tomography (Body Imaging)
A usual adult dose is 240 mL of a dilute Gastrografin solution prepared by diluting 25 mL (9.17 g iodine) to one liter with tap water. Less dilute solutions [up to 77 mL (28.26 g iodine) diluted to one liter with tap water] may be used when indicated. The dose is administered orally about 15 to 30 minutes prior to imaging in order to permit the contrast medium to reach the pelvic loops.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Gastrografin (Diatrizoate Meglumine and Diatrizoate Sodium Solution USP) is available in packages of:
Twenty-four 30 mL single dose bottles (NDC: 0270-0445-35).
Twelve 120 mL single dose bottles (NDC: 0270-0445-40). - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
GASTROGRAFIN
diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium liquidProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0270-0445 Route of Administration ORAL, RECTAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength diatrizoate meglumine (UNII: 3X9MR4N98U) (DIATRIZOIC ACID - UNII:5UVC90J1LK) diatrizoate meglumine 660 mg in 1 mL diatrizoate sodium (UNII: V5403H8VG7) (DIATRIZOIC ACID - UNII:5UVC90J1LK) diatrizoate sodium 100 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CITRATE (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) 3.22 mg in 1 mL EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) 0.403 mg in 1 mL SACCHARIN SODIUM (UNII: SB8ZUX40TY) 2.77 mg in 1 mL Product Characteristics Color Score Shape Size Flavor LEMON Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0270-0445-35 24 in 1 BOX 04/01/2005 1 30 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 0270-0445-40 12 in 1 BOX 02/26/1958 2 120 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA011245 02/26/1958 Labeler - Bracco Diagnostics Inc (849234661) Registrant - Bracco Diagnostics Inc (849234661) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations E-Z-EM Canada Inc 204211163 MANUFACTURE(0270-0445) , ANALYSIS(0270-0445) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Justesa Imagen, S.A.U 477020325 LABEL(0270-0445) , PACK(0270-0445) , API MANUFACTURE(0270-0445) , ANALYSIS(0270-0445) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Merck SLU 460082644 LABEL(0270-0445) , PACK(0270-0445) , ANALYSIS(0270-0445) , API MANUFACTURE(0270-0445)
Trademark Results [Gastrografin]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 GASTROGRAFIN 72047137 0676883 Live/Registered |
OLIN MATHIESON CHEMICAL CORPORATION 1958-03-05 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

