GLUCAGON- glucagon injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution GLUCAGON kit
Glucagon by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Glucagon by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GLUCAGON FOR INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GLUCAGON FOR INJECTION.
GLUCAGON for injection, for intravenous or intramuscular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1998INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Glucagon for Injection is a gastrointestinal motility inhibitor indicated for use as a diagnostic aid during radiologic examinations to temporarily inhibit movement of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract ( 1)
Limitations of Use:
Glucagon for Injection is not indicated for the emergency treatment of hypoglycemia ( 1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Reconstitute lyophilized powder with Sterile Water for Injection before use ( 2.2, 2.3)
- Determine dose based on diagnostic procedure, route of administration and procedure duration (
2.1):
- To inhibit stomach and small bowel motility the dose is 0.2 mg to 0.5 mg given intravenously or 1 mg given intramuscularly
- To inhibit colon motility the dose is 0.5 mg to 0.75 mg given intravenously or 1 mg to 2 mg given intramuscularly
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For Injection: 1 mg lyophilized powder in single dose vial for reconstitution ( 3)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes: Monitor blood glucose and treat with insulin if indicated ( 5.3)
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate in patients with cardiac disease: Monitor patients with known cardiac disease ( 5.4)
- Allergic reactions including anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties, and hypotension, generalized rash: Discontinue and treat as indicated ( 5.5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions seen with glucagon are transient changes in blood pressure, increase in heart rate, hypersensitivity reactions, nausea and vomiting, and hypoglycemia ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC at 1-800-551-7176 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Beta-blockers: May cause a greater increase in both heart rate and blood pressure ( 7)
- Insulin: Reacts antagonistically towards glucagon; monitor glucose ( 7)
- Indomethacin: May produce hypoglycemia; monitor glucose ( 7)
- Anticholinergic Drugs: Concomitant use not recommended due to increased gastrointestinal adverse reactions ( 7)
- Warfarin: May increase anticoagulant effect of warfarin; may require an adjustment in warfarin dosage ( 7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 4/2016
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose
2.2 Reconstitution of the Lyophilized Powder
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypertension in Patients with Pheochromocytoma
5.2 Hypoglycemia in Patients with Insulinoma or Glucagonoma
5.3 Hyperglycemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
5.4 Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increase in Patients with Cardiac Disease
5.5 Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Recommended Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Glucagon for Injection is indicated for use as a diagnostic aid during radiologic examinations to temporarily inhibit movement of the gastrointestinal tract.
Limitations of Use:
Glucagon for Injection is not indicated for the emergency treatment of hypoglycemia because it is not packaged with a syringe and diluent necessary for rapid preparation and administration during an emergency outside of a healthcare facility.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose
Determine the dose based on the type of diagnostic procedure, the route of administration and expected procedure duration [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.2)] .
The usual dose to inhibit movement of the:
- Stomach and small bowel is 0.2 mg to 0.5 mg given intravenously or 1 mg given intramuscularly.
- Colon is 0.5 mg to 0.75 mg given intravenously or 1 mg to 2 mg given intramuscularly.
Bolus doses above 1 mg administered intravenously have caused nausea and vomiting and are not recommended [see Adverse Reactions ( 6)] .
2.2 Reconstitution of the Lyophilized Powder
Glucagon for Injection is a lyophilized powder, which requires reconstitution with Sterile Water for Injection prior to intravenous or intramuscular use.
- Using a syringe, withdraw 1 mL of Sterile Water for Injection and inject into the vial containing Glucagon for Injection lyophilized powder.
- Shake the vial gently until the powder is completely dissolved and no particles remain in the reconstituted solution.
- Visually inspect the reconstituted solution for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The reconstituted solution should be clear and of water-like consistency. Discard the reconstituted solution if there are signs of gel formation or particles.
- The reconstituted solution has a concentration of approximately 1 mg of glucagon per mL.
- Use the reconstituted glucagon immediately after reconstitution.
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
- Glucagon for Injection must be administered by medical personnel.
- The timing of administration of Glucagon for Injection depends upon the organ under examination and route of administration [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.2)] .
- If given intravenously, administer Glucagon for Injection as a bolus over a time period of 1 minute.
- Discard any unused portion.
- After the end of the diagnostic procedure, give oral carbohydrates to patients who have been fasting, if this is compatible with the diagnostic procedure.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypertension in Patients with Pheochromocytoma
Glucagon for Injection is contraindicated in patients with pheochromocytoma because glucagon may stimulate the release of catecholamines from the tumor, which may result in a sudden and marked increase in blood pressure.
5.2 Hypoglycemia in Patients with Insulinoma or Glucagonoma
Glucagon for Injection is contraindicated in patients with insulinoma or glucagonoma as it may cause secondary hypoglycemia. Test patients suspected of having glucagonoma for blood levels of glucagon prior to treatment, and monitor for changes in blood glucose levels during treatment. If a patient develops symptoms of hypoglycemia after a dose of Glucagon for Injection, administer glucose orally or intravenously.
5.3 Hyperglycemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Treatment with Glucagon for Injection in patients with diabetes mellitus may cause hyperglycemia. Monitor diabetic patients for changes in blood glucose levels during treatment. If patients develop symptoms of hyperglycemia after a dose of Glucagon for Injection, administer insulin.
5.4 Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increase in Patients with Cardiac Disease
Glucagon for Injection may increase myocardial oxygen demand, blood pressure, and pulse rate which may be life-threatening in patients with cardiac disease. Cardiac monitoring is recommended in patients with cardiac disease during glucagon treatment, and an increase in blood pressure and pulse rate may require therapy.
5.5 Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions
Generalized allergic reactions and hypersensitivity, including generalized rash, and anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties, and hypotension, have been reported with glucagon treatment or lactose. Discontinue Glucagon for Injection and administer standard treatment for anaphylaxis if needed.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypertension in patients with Pheochromocytoma [see Contraindications ( 4) and Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)]
- Hypoglycemia in Patients with Insulinoma and Glucagonoma [see Contraindications ( 4) and Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)]
- Hyperglycemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3)]
- Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions; generalized allergic reactions including generalized rash, and in some cases anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties, and hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5)]
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trials
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In an open-label clinical study of Glucagon for Injection, 29 healthy volunteers received a single dose of 1 mg Glucagon for Injection intramuscularly. Table 1 shows the most common adverse reactions that were not present at baseline and occurred in at least 5% of patients.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions in Healthy Volunteers Who Received Glucagon for Injection, 1 mg Administered Intramuscularly
(N=29)
% of Patients
Vomiting
17
Nausea
7
Adverse Reactions from the Literature and Other Clinical Studies
The following adverse reactions have been identified from the literature and clinical studies with the use of glucagon. Therefore, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency.
- Nausea and vomiting occurred with doses above 1 mg administered by rapid intravenous injection (within 1 to 2 seconds) . Doses above 1 mg are not recommended for intravenous use [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1)].
- Hypotension was reported up to 2 hours after administration in patients receiving glucagon as premedication for upper GI endoscopy procedures.
- A temporary increase in both blood pressure and pulse rate occurred following the administration of glucagon. Patients taking beta-blockers experienced a temporary increase in both pulse and blood pressure that was greater than normal [see Drug Interactions ( 7)] .
- Other adverse reactions included hypoglycemia and hypoglycemic coma, as described in postmarketing reports. Patients taking indomethacin may be more likely to experience hypoglycemia following glucagon administration [see Drug Interactions ( 7)] .
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 2 includes clinically significant drug interactions with Glucagon for Injection.
Table 2: Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with Glucagon for Injection
Beta-Blockers
Clinical Impact:
The concomitant use of beta-blockers and Glucagon for Injection may increase the risk of a temporary increase in heart rate and blood pressure.
Intervention:
The increase in blood pressure and heart rate may require therapy in patients with coronary artery disease.
Insulin
Clinical Impact:
Insulin reacts antagonistically towards glucagon.
Intervention:
Monitor blood glucose when Glucagon for Injection is used as a diagnostic aid in diabetes patients.
Indomethacin
Clinical Impact:
The concomitant use of indomethacin and Glucagon for Injection may lead to hypoglycemia.
Intervention:
Monitor blood glucose levels during glucagon treatment of patients taking indomethacin.
Anticholinergic Drugs
Clinical Impact:
The concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs and Glucagon for Injection increase the risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions due to additive effects on inhibition of gastrointestinal motility.
Intervention:
Concomitant use is not recommended.
Warfarin
Clinical Impact:
Glucagon may increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin.
Intervention:
Monitor patients for unusual bruising or bleeding, as adjustments in warfarin dosage may be required.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B.
Reproduction studies were performed in rats and rabbits with another glucagon product at doses of 0.4, 2, and 10 mg per kg. These doses represent exposures of up to 100 and 200 times the human dose based on mg/m 2 for rats and rabbits, respectively, and revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Glucagon does not cross the human placental barrier.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether glucagon is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when glucagon is administered to a nursing woman. No clinical studies have been performed in nursing mothers, however, glucagon is a peptide and intact glucagon is not absorbed from the GI tract. Therefore, even if the infant ingested glucagon it would be unlikely to have any effect on the infant. Additionally, glucagon has a short plasma half-life thus limiting amounts available to the child.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
If overdosage occurs, the patient may experience nausea, vomiting, inhibition of GI tract motility, increase in blood pressure and heart rate, and decrease in serum potassium. In case of suspected overdosage, monitor and correct hypokalemia. If the patient develops a severe increase in blood pressure, phentolamine mesylate may be effective in lowering blood pressure for the short time that control would be needed.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Glucagon for Injection, for intravenous or intramuscular use, is a gastrointestinal motility inhibitor that is produced by solid phase peptide synthesis. Glucagon is a single-chain polypeptide containing 29 amino acid residues. The chemical structure of the glucagon polypeptide is identical to human glucagon and to glucagon extracted from beef and pork pancreas. The structure of glucagon is:

C 153H 225N 43O 49S Molecular Weight = 3483
Glucagon for Injection is a sterile, lyophilized white powder in a 3 mL vial. The reconstituted solution contains 1 mg of glucagon as hydrochloride per mL and lactose monohydrate (107 mg). Glucagon for Injection is supplied at pH 2.5 to 3.5 and is soluble in water.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Extra hepatic effects of glucagon include relaxation of the smooth muscle of the stomach, small bowel, and colon.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Table 3 displays the pharmacodynamics properties of Glucagon for Injection as a diagnostic aid during radiologic examination.
Table 3: Pharmacodynamic Properties of Glucagon for Injection as a Diagnostic Aid
Route of Administration
Dose a
Time of Onset of Action for GI Smooth Muscle Relaxation
Duration of Smooth Muscle Relaxation
Intravenous
0.25 to 0.5 mg
45 seconds
9 to 17 minutes
Intramuscular
1 mg
8 to 10 minutes
12 to 27 minutes
2 mg
4 to 7 minutes
21 to 32 minutes
a Select from these doses based on type of diagnostic procedure, route of administration and procedure duration.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following intramuscular administration of 1 mg dose, the maximum plasma glucagon concentrations of 3391 pg/mL were attained approximately 10 minutes after dosing.
Metabolism
The mean apparent half-life of glucagon was 26 minutes after intramuscular administration.
Glucagon is degraded in the liver, kidney, and plasma.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been performed.
Mutagenesis
Synthetic glucagon was negative in the bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test). The clastogenic potential of synthetic glucagon in the Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) assay was positive in the absence of metabolic activation. Doses of 100 and 200 mg/kg of glucagon of both pancreatic and recombinant origins gave slightly higher incidences of micronucleus formation in male mice but there was no effect in females. The weight of evidence indicates that synthetic and recombinant glucagon are not different and do not pose a genotoxic risk to humans.
Impairment of Fertility
Glucagon (rDNA and synthetic origin) was not tested in animal fertility studies. Studies in rats have shown that pancreatic glucagon does not cause impaired fertility.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Glucagon for Injection is supplied as a sterile, lyophilized white powder in a vial.
Product #
NDC #
NP509613
63323-596-16
Glucagon for Injection, 1 mg per vial,
in packages of 10.
Glucagon for Injection is also available as a Diagnostic Kit, it is supplied as follows:
Product #
NDC #
NP509603
63323-594-03
One carton containing one 1 mg of Glucagon for Injection, and one 1 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP (NDC: 63323-185-03) for reconstitution.
The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
16.2 Recommended Storage
Before Reconstitution
The package containing Glucagon for Injection vials may be stored up to 24 months at 20° to 25° C (68° to 77° F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] prior to reconstitution. Do not freeze. Keep in the original package to protect from light.
After Reconstitution
The Glucagon for Injection must be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection prior to use. Use reconstituted glucagon solution immediately. Discard any unused portion [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.3)] .
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Inform patients that generalized allergic reactions have been reported with glucagon treatment including generalized rash, and in some cases anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties, and hypotension. Advise patients to monitor and report any signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5)] .
- Inform patients that hypoglycemia has occurred with treatment with glucagon. Inform patients of the symptoms of hypoglycemia and how to treat it. Advise patients to avoid driving or operating machinery until ingesting a meal. Advise patients to inform their health care provider if hypoglycemia occurs so that treatment may be given if necessary [see Adverse Reactions ( 6)] .
- Inform patients with diabetes mellitus that treatment with Glucagon for Injection may increase their risk of hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3)].
- Inform patients with cardiac disease that treatment with Glucagon for Injection may increase their risk of a transient increase in blood pressure and heart rate [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Glucagon 1 mg Vial Label
NP509613
Glucagon for Injection
1 mg per vial
For intramuscular or intravenous injection.
For diagnostic use only.
Reconstitute with Sterile Water for Injection, USP Rx only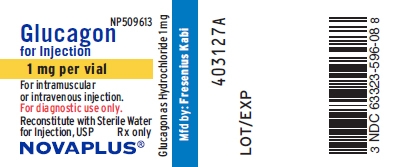
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Glucagon 1 mg Vial Tray Label
63323-596-16Glucagon for Injection
For intramuscular or intravenous injection only.
1 mg per vial
For diagnostic use only.
10 Single Dose Vials Rx only
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Glucagon Kit 1 mg Vial Label
NP509603
Glucagon for Injection
1 mg per vial
For intramuscular or intravenous injection.
For diagnostic use only.
Reconstitute with Sterile Water for Injection, USP Rx only

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Glucagon Kit 1 mL Diluent Vial Label
Sterile Water for Injection, USP
1 mL per vial
FOR DRUG DILUENT USE ONLYContains no antimicrobial or other added substance.
Do not give intravenously unless rendered nearly Isotonic.
Discard unused portion.
1 mL Single Dose Vial Rx only

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Glucagon Kit 1 mg Vial Carton Panel
Glucagon for Injection
For intramuscular or intravenous injection only.
1 mg per vial
FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE ONLY.
Reconstitute with Sterile Water for Injection, USP immediately
before use.
Each Kit contains:- One single dose vial with 1 mg of Glucagon for Injection
- One single dose vial with 1 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP
Single Dose Vials
Rx only
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
GLUCAGON
glucagon injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63323-596 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR, INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength GLUCAGON HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 1H87NVF4DB) (GLUCAGON - UNII:76LA80IG2G) GLUCAGON 1 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63323-596-16 10 in 1 TRAY 05/08/2015 1 NDC: 63323-596-08 1 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-USE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA201849 05/08/2015 GLUCAGON
glucagon kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63323-594 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63323-594-03 1 in 1 CARTON; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package 12/01/2015 Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 VIAL, SINGLE-USE 1 mL Part 2 1 VIAL, SINGLE-USE 1 mL Part 1 of 2 GLUCAGON
glucagon injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 63323-596 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS, INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength GLUCAGON HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 1H87NVF4DB) (GLUCAGON - UNII:76LA80IG2G) GLUCAGON 1 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63323-596-06 1 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-USE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA201849 05/08/2015 Part 2 of 2 WATER
sterile water injectionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 63323-185 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS, INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) (WATER - UNII:059QF0KO0R) WATER 1 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63323-185-03 1 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-USE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA088400 11/23/2015 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA201849 12/01/2015 Labeler - Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC (608775388) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC 023648251 manufacture(63323-594, 63323-596)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
