DEXTROSE- dextrose monohydrate injection, solution
Dextrose by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Dextrose by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Becton Dickinson and Company , Fresenius Kabi Deutschland GmbH. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION:
10% Dextrose Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for fluid replenishment and caloric supply in single dose containers for intravenous administration. It contains no antimicrobial agents. Composition, osmolarity, pH, and caloric content are shown in Table 1.
Size
(mL)*Dextrose
Monohydrate,
USP (g/L)Osmolarity
(mOsmol/L)
(calc.)pH nominal
(range)Caloric
Content
(kcal/L)10% Dextrose Injection, USP 250
500
1,000100 505 4.5
(3.2 to 6.5)340 The flexible container is fabricated from a specially formulated non-plasticized, film containing polypropylene and thermoplastic elastomers (freeflex® bag). For example, the flexible container system is compatible with and appropriate for use in the admixture and administration of paclitaxel. The amount of water that can permeate from the container into the overwrap is insufficient to affect the solution significantly. Solutions in contact with the flexible container can leach out certain of the container's chemical components in very small amounts within the expiration period. The suitability of the container material has been confirmed by tests in animals according to USP biological tests for plastic containers.
The flexible container is a closed system, and air is prefilled in the container to facilitate drainage. The container does not require entry of external air during administration.
The container has two ports: one is the administration outlet port for attachment of an intravenous administration set and the other port has a medication site for addition of supplemental medication (see INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE). The primary function of the overwrap is to protect the container from the physical environment.
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
- CONTRAINDICATIONS:
-
WARNINGS:
10% Dextrose injection should not be administered simultaneously with blood through the same administration set because of the possibility of Psuedo agglutination or hemolysis.
The intravenous administration of these solutions can cause fluid and/or solute overloading resulting in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations, overhydration, congested states, or pulmonary edema. The risk of dilutive states is inversely proportional to the electrolyte concentrations of the injections. The risk of solute overload causing congested states with peripheral and pulmonary edema is directly proportional to the electrolyte concentrations of the injections.
Excessive administration of dextrose injections may result in significant hypokalemia.
In very low birth weight infants, excessive or rapid administration of dextrose injection may result in increased serum osmolality and possible intracerebral hemorrhage.
Clinical evaluation and periodic laboratory determinations are necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid base balance during prolonged parenteral therapy or whenever the condition of the patient warrants such evaluation.
-
PRECAUTIONS:
General
Do not connect flexible plastic containers in series in order to avoid air embolism due to possible residual air contained in the primary container. Such use could result in air embolism due to residual air being drawn from the primary container before administration of the fluid from a secondary container is completed.
Pressurizing intravenous solutions contained in flexible plastic containers to increase flow rates can result in air embolism if the residual air in the container is not fully evacuated prior to administration.
Use of a vented intravenous administration set with the vent in the open position could result in air embolism. Vented intravenous administration sets with the vent in the open position should not be used with flexible plastic containers.
10% Dextrose injection should be used with caution in patients with overt or subclinical diabetes mellitus.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well controlled studies with 10% Dextrose injection in pregnant women and animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with this drug. Therefore, it is not known whether 10% Dextrose injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. 10% Dextrose injection should be given during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Labor and Delivery
Intrapartum maternal intravenous infusion of glucose-containing solutions may produce maternal hyperglycemia with subsequent fetal hyperglycemia and fetal metabolic acidosis. Fetal hyperglycemia can result in increased fetal insulin levels which may result in neonatal hypoglycemia following delivery. Consider the potential risks and benefits for each specific patient before administering 10% Dextrose injection.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is present in human milk. Because many drugs are present in human milk, caution should be exercised when 10% Dextrose injection is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
The use of 10% Dextrose injection in pediatric patients is based on clinical practice (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Newborns – especially those born premature and with low birth weight - are at increased risk of developing hypo- or hyperglycemia and therefore need close monitoring during treatment with intravenous glucose solutions to ensure adequate glycemic control in order to avoid potential long term adverse effects. Hypoglycemia in the newborn can cause prolonged seizures, coma and brain damage. Hyperglycemia has been associated with intraventricular hemorrhage, late onset bacterial and fungal infection, retinopathy of prematurity, necrotizing enterocolitis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, prolonged length of hospital stay, and death.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of 10% Dextrose injection did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and chills.
Reactions which may occur because of the injection or the technique of administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation and hypervolemia.
If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures and save the remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
As directed by a physician. Dosage is dependent upon the age, weight and clinical condition of the patient as well as laboratory determinations.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. Use of a final filter is recommended during administration of all parenteral solutions, where possible.
Do not administer unless solution is clear and seal is intact.
All injections in flexible plastic containers are intended for intravenous administration using sterile equipment.
The dosage selection and constant infusion rate of intravenous dextrose must be selected with caution in pediatric patients, particularly neonates and low birth weight infants, because of the increased risk of hyperglycemia/hypoglycemia. Frequent monitoring of serum glucose concentrations is required when dextrose is prescribed to pediatric patients, particularly neonates and low birth weight infants. The infusion rate and volume depends on the age, weight, clinical and metabolic conditions of the patient, concomitant therapy and should be determined by the consulting physician experienced in pediatric intravenous fluid therapy.
Additives may be incompatible. Complete information is not available. Those additives known to be incompatible should not be used. Consult with pharmacist, if available. If, in the informed judgment of the physician, it is deemed advisable to introduce additives, use aseptic technique. Mix thoroughly when additives have been introduced. Do not store solutions containing additives.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
10% Dextrose Injection, USP is supplied in single dose flexible plastic containers as follows:
Product Number Unit of Sale Strength Each 1727172105 NDC: 17271-721-05 Package of 30 freeflex® bag 25 grams per 250 mL
(100 mg per mL)NDC: 17271-721-05 One 250 mL freeflex® bag 1727172106 NDC: 17271-721-06 Package of 20 freeflex® bag 50 grams per 500 mL
(100 mg per mL)NDC: 17271-721-06 One 500 mL freeflex® bag 1727172107 NDC: 17271-721-07 Package of 10 freeflex® bag 100 grams per 1,000 mL (100 mg per mL) NDC: 17271-721-07 One 1000 mL freeflex® bag Exposure of pharmaceutical products to heat should be minimized. Avoid excessive heat.
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE:
Check flexible container solution composition, lot number, and expiry date.
Do not remove solution container from its overwrap until immediately before use. Use sterile equipment and aseptic technique.
To Open
- Turn solution container over so that the text is face down. Using the pre-cut corner tabs, peel open the overwrap and remove solution container.
- Check the solution container for leaks by squeezing firmly. If leaks are found, or if the seal is not intact, discard the solution.
- Do not use if the solution is cloudy or a precipitate is present.
To Add Medication
- Identify WHITE Additive Port with arrow pointing toward container.
- Immediately before injecting additives, break off WHITE Additive Port Cap with the arrow pointing toward container.
- Hold base of WHITE Additive Port horizontally.
- Insert needle horizontally through the center of WHITE Additive Port's septum and inject additives.
- Mix container contents thoroughly. For high density medication such as potassium chloride, squeeze ports while ports are upright and mix thoroughly.
Preparation for Administration
- Immediately before inserting the infusion set, break off BLUE Infusion Port Cap with the arrow pointing away from container.
- Use a non-vented infusion set or close the air-inlet on a vented set.
- Close the roller clamp of the infusion set.
- Hold the base of BLUE Infusion Port.
- Insert spike through BLUE Infusion Port by rotating wrist slightly until the spike is inserted.
NOTE: See full directions accompanying administration set.
WARNING: Do not use flexible container in series connections.
Manufactured for:
Becton, Dickinson and Company
1 Becton Drive
Franklin Lakes, NJ 07417 USA
For product inquiry: 1-800-523-0502
Distributed by BD. Manufactured by Fresenius Kabi.Made in Germany
www.fresenius-kabi.com/us
451636
Issued: May 2019 -
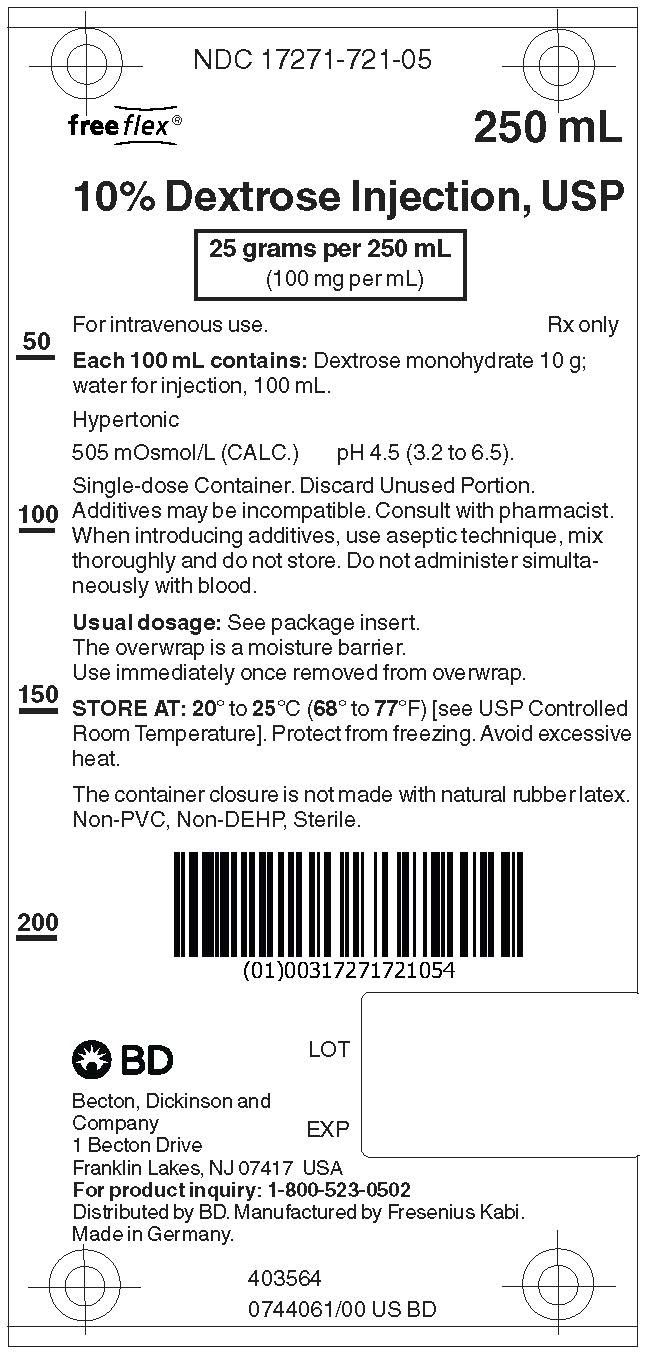
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY – 10% Dextrose Bag Label
NDC: 17271-721-05
freeflex® 250 mL10% Dextrose Injection, USP
25 grams per 250 mL (100 mg per mL)
For intravenous use. Rx only
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY – 10% Dextrose Case Label
NDC: 17271-721-05
10% Dextrose Injection, USP250 mL x 30
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10% Dextrose Bag Label
NDC: 17271-721-06
freeflex® 500 mL
10% Dextrose Injection, USP
50 grams per 500 mL (100 mg per mL)
For intravenous use. Rx only
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10% Dextrose Case Label
NDC: 17271-721-06
10% Dextrose Injection, USP
500 mL x 20
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10% Dextrose Bag Label
NDC: 17271-721-07
freeflex® 1,000 mL
10% Dextrose Injection, USP
100 grams per 1,000 mL (100 mg per mL)
For intravenous use. Rx only
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10% Dextrose Case Label
NDC: 17271-721-07
10% Dextrose Injection, USP
1,000 mL x 10
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DEXTROSE
dextrose monohydrate injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 17271-721 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: LX22YL083G) (ANHYDROUS DEXTROSE - UNII:5SL0G7R0OK) DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE 100 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 17271-721-05 30 in 1 CASE 02/05/2020 1 250 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 17271-721-06 20 in 1 CASE 02/05/2020 2 500 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 17271-721-07 10 in 1 CASE 02/05/2020 3 1000 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA209448 02/05/2020 Labeler - Becton Dickinson and Company (124987988) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Fresenius Kabi Deutschland GmbH 506719546 ANALYSIS(17271-721) , MANUFACTURE(17271-721)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.