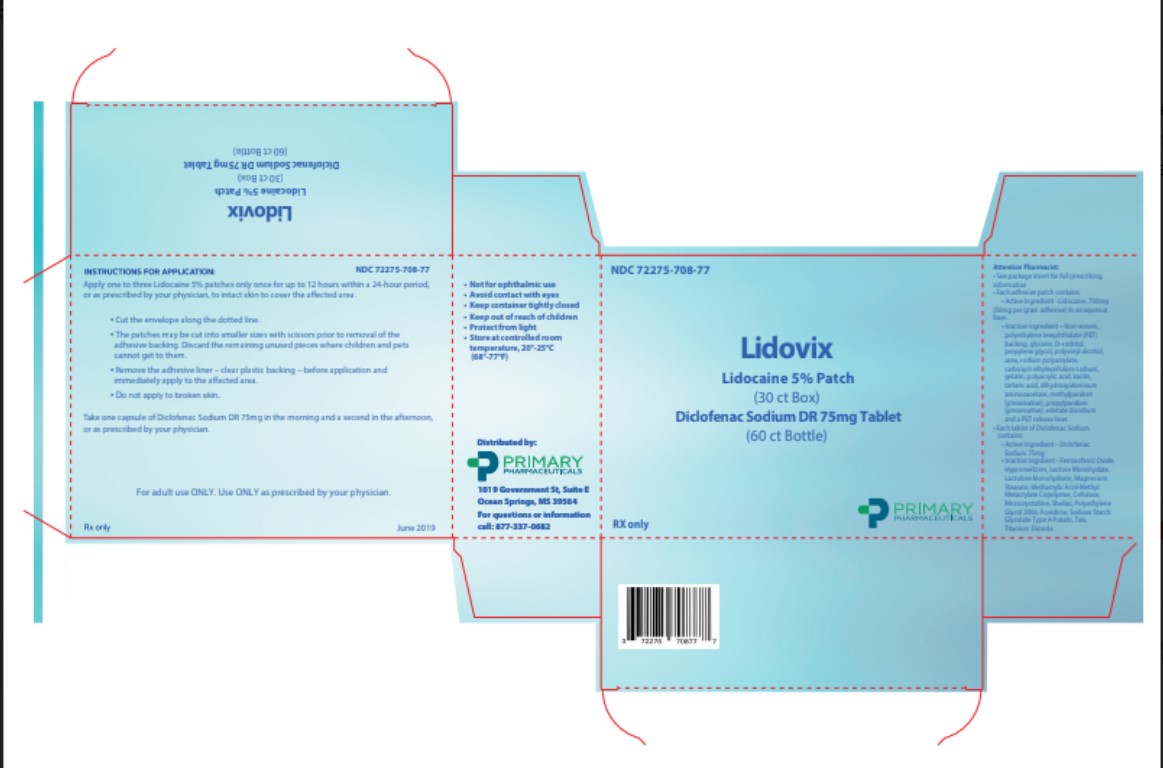
LIDOVIX DELAYED RELEASE- lidocaine, diclofenac sodium kit
Lidovix by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Lidovix by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Primary Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Actavis Laboratories UT, Inc, Rainbow Gold. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use (see WARNINGS).
- Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS).
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, And Perforation
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events (see WARNINGS).
-
DESCRIPTION
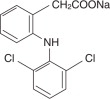
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets is a benzene-acetic acid derivative. Diclofenac sodium is a white or slightly yellowish crystalline powder and is sparingly soluble in water at 25°C. The chemical name is 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino] benzeneacetic acid, monosodium salt. The molecular weight is 318.14. Its molecular formula is C 14H 10Cl 2NNaO 2, and it has the following structural formula
The inactive ingredients in diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets include: hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, methacrylic acid copolymer, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, propylene glycol, sodium starch glycolate, talc, titanium dioxide, triethyl citrate.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Diclofenac has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
The mechanism of action of diclofenac, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Diclofenac is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Diclofenac concentrations reached during therapy have produced in vivo effects. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because diclofenac is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Diclofenac is 100% absorbed after oral administration compared to IV administration as measured by urine recovery. However, due to first-pass metabolism, only about 50% of the absorbed dose is systemically available (see Table 1). Food has no significant effect on the extent of diclofenac absorption. However, there is usually a delay in the onset of absorption of 1 to 4.5 hours and a reduction in peak plasma levels of <20%.
Table 1. Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Diclofenac PK Parameter Normal Healthy Adults (20-48 years)
MeanCoefficient of Mean Variation (%) Absolute
Bioavailability (%)
[N = 7]55 40 T max (hr) [N = 56] 2.3 69 Oral Clearance (CL/F;
mL/min) [N = 56]582 23 Renal Clearance
(% unchanged drug in
urine) [N = 7]<1 — Apparent Volume of
Distribution (V/F; L/kg)
[N = 56]1.4 58 Terminal Half-life (hr)
[N = 56]2.3 48 Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of diclofenac sodium is 1.4 L/kg.
Diclofenac is more than 99% bound to human serum proteins, primarily to albumin. Serum protein binding is constant over the concentration range (0.15-105 mcg/ml) achieved with recommended doses.
Diclofenac diffuses into and out of the synovial fluid. Diffusion into the joint occurs when plasma levels are higher than those in the synovial fluid, after which the process reverses and synovial fluid levels are higher than plasma levels. It is not known whether diffusion into the joint plays a role in the effectiveness of diclofenac.
Elimination
Metabolism
Five diclofenac metabolites have been identified in human plasma and urine. The metabolites include 4'-hydroxy-, 5-hydroxy-, 3'-hydroxy-, 4',5-dihydroxy- and 3'-hydroxy-4'-methoxy-diclofenac. The major diclofenac metabolite, 4'-hydroxy-diclofenac, has very weak pharmacologic activity. The formation of 4'-hydroxy- diclofenac is primarily mediated by CYP2C9.
Both diclofenac and its oxidative metabolites undergo glucuronidation or sulfation followed by biliary excretion. Acylglucuronidation mediated by UGT2B7 and oxidation mediated by CYP2C8 may also play a role in diclofenac metabolism. CYP3A4 is responsible for the formation of minor metabolites, 5-hydroxy- and 3'-hydroxy-diclofenac. In patients with renal dysfunction, peak concentrations of metabolites 4'-hydroxy- and 5-hydroxydiclofenac were approximately 50% and 4% of the parent compound after single oral dosing compared to 27% and 1% in normal healthy subjects.
Excretion
Diclofenac is eliminated through metabolism and subsequent urinary and biliary excretion of the glucuronide and the sulfate conjugates of the metabolites. Little or no free unchanged diclofenac is excreted in the urine. Approximately 65% of the dose is excreted in the urine and approximately 35% in the bile as conjugates of unchanged diclofenac plus metabolites. Because renal elimination is not a significant pathway of elimination for unchanged diclofenac, dosing adjustment in patients with mild to moderate renal dysfunction is not necessary. The terminal half-life of unchanged diclofenac is approximately 2 hours.
Special Populations
Hepatic Impairment: Hepatic metabolism accounts for almost 100% of diclofenac elimination, so patients with hepatic disease may require reduced doses of diclofenac compared to patients with normal hepatic function.
Renal Impairment: Diclofenac pharmacokinetics has been investigated in subjects with renal insufficiency. No differences in the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac have been detected in studies of patients with renal impairment. In patients with renal impairment (inulin clearance 60-90, 30-60, and <30 mL/min; N=6 in each group), AUC values and elimination rate were comparable to those in healthy subjects.
Drug Interactions Studies
Voriconazole: When co-administered with voriconazole (inhibitor of CYP2C9, 2C19 and 3A4 enzyme), the C max and AUC of diclofenac increased by 114% and 78%, respectively ( see PRECAUTIONS; Drug Interactions).
Aspirin: When NSAIDs were administered with aspirin, the protein binding of NSAIDs were reduced, although the clearance of free NSAID was not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known. See Table 2 for clinically significant drug interactions of NSAIDs with aspirin ( see PRECAUTIONS; Drug Interactions).
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use diclofenac. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals ( see WARNINGS; Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation).
Diclofenac is indicated:
- For relief of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis
- For relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
- For acute or long-term use in the relief of signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are contraindicated in the following patients:
- Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to diclofenac or any components of the drug product ( see WARNINGS; Anaphylactic Reactions, Serious Skin Reactions).
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients ( see WARNINGS; Anaphylactic Reaction, Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity).
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery ( see Warnings; Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events).
-
WARNINGS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke, which can be fatal. Based on available data, it is unclear that the risk for CV thrombotic events is similar for all NSAIDs. The relative increase in serious CV thrombotic events over baseline conferred by NSAID use appears to be similar in those with and without known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. However, patients with known CV disease or risk factors had a higher absolute incidence of excess serious CV thrombotic events, due to their increased baseline rate. Some observational studies found that this increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events began as early as the first weeks of treatment. The increase in CV thrombotic risk has been observed most consistently at higher doses.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in NSAID-treated patients, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, throughout the entire treatment course, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID, such as diclofenac, increases the risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) events ( see WARNINGS; Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation).
Status Post Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery
Two large, controlled, clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10 -14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke. NSAIDs are contraindicated in the setting of CABG ( see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Post-MI Patients
Observational studies conducted in the Danish National Registry have demonstrated that patients treated with NSAIDs in the post-MI period were at increased risk of reinfection, CV-related death, and all-cause mortality beginning in the first week of treatment. In this same cohort, the incidence of death in the first year post-MI was 20 per 100 person years in NSAID treated patients compared to 12 per 100 person years in non-NSAID exposed patients. Although the absolute rate of death declined somewhat after the first year post-MI, the increased relative risk of death in NSAID users persisted over at least the next four years of follow-up.
Avoid the use of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets in patients with a recent MI unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of recurrent CV thrombotic events. If diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are used in patients with a recent MI, monitor patients for signs of cardiac ischemia.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including diclofenac, cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients, who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy, is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occurred in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months, and in about 2%-4% of patients treated for one year. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk.
Risk Factors for GI Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding who use NSAIDs had a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients without these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk of GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include longer duration of NSAID therapy, concomitant use of oral corticosteroids, aspirin, anticoagulants, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs):, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status. Most postmarketing reports of fatal GI events occurred in elderly or debilitated patients. Additionally, patients with advanced liver disease and/or coagulopathy are at increased risk for GI bleeding.
Strategies to Minimize the GI Risks in NSAID-treated patients:
- Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest possible duration.
- Avoid administration of more than one NSAID at a time
- Avoid use in patients at higher risk unless benefits are expected to outweigh the increased risk of bleeding. For such patients, as well as those with active GI bleeding, consider alternate therapies other than NSAIDs.
- Remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy.
- If a serious GI adverse event is suspected, promptly initiate evaluation and treatment, and discontinue diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out.
- In the setting of concomitant use of low-dose aspirin for cardiac prophylaxis, monitor patients more closely for evidence of GI bleeding (see PRECAUTIONS; Drug Interactions).
Hepatotoxicity
In clinical trials of diclofenac- containing products, meaningful elevations (i.e., more than 3 times the ULN) of AST (SGOT) were observed in about 2% of approximately 5,700 patients at some time during diclofenac treatment (ALT was not measured in all studies).
In a large, open-label, controlled trial of 3,700 patients treated with oral diclofenac sodium for 2-6 months, patients were monitored first at 8 weeks and 1,200 patients were monitored again at 24 weeks. Meaningful elevations of ALT and/or AST occurred in about 4% of patients and included marked elevations (greater than 8 times the ULN) in about 1% of the 3,700 patients. In that open-label study, a higher incidence of borderline (less than 3 times the ULN), moderate (3-8 times the ULN), and marked (greater than 8 times the ULN) elevations of ALT or AST was observed in patients receiving diclofenac when compared to other NSAIDs. Elevations in transaminases were seen more frequently in patients with osteoarthritis than in those with rheumatoid arthritis.
Almost all meaningful elevations in transaminases were detected before patients became symptomatic. Abnormal tests occurred during the first 2 months of therapy with diclofenac in 42 of the 51 patients in all trials who developed marked transaminase elevations.
In postmarketing reports, cases of drug-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported in the first month, and in some cases, the first 2 months of therapy, but can occur at any time during treatment with diclofenac. Postmarketing surveillance has reported cases of severe hepatic reactions, including liver necrosis, jaundice, fulminant hepatitis with and without jaundice, and liver failure. Some of these reported cases resulted in fatalities or liver transplantation.
In a European retrospective population-based, case-controlled study, 10 cases of diclofenac associated drug-induced liver injury with current use compared with non-use of diclofenac were associated with a statistically significant 4-fold adjusted odds ratio of liver injury. In this particular study, based on an overall number of 10 cases of liver injury associated with diclofenac, the adjusted odds ratio increased further with female gender, doses of 150 mg or more, and duration of use for more than 90 days.
Physicians should measure transaminases at baseline and periodically in patients receiving long-term therapy with diclofenac, because severe hepatotoxicity may develop without a prodrome of distinguishing symptoms. The optimum times for making the first and subsequent transaminase measurements are not known. Based on clinical trial data and postmarketing experiences, transaminases should be monitored within 4 to 8 weeks after initiating treatment with diclofenac. However, severe hepatic reactions can occur at any time during treatment with diclofenac.
If abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, if clinical signs and/or symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dark urine, etc.), diclofenac should be discontinued immediately.
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and “flu-like” symptoms). If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), discontinue diclofenac immediately, and perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse liver related event in patients treated with diclofenac, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Exercise caution when prescribing diclofenac with concomitant drugs that are known to be potentially hepatotoxic (e.g., acetaminophen, antibiotics, anti-epileptics).
Hypertension
NSAIDs, including diclofenac, can lead to new onset of hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, thiazides diuretics, or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. (see PRECAUTIONS; Drug Interactions) .
Monitor blood pressure (BP) during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
Heart Failure and Edema
The Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists' Collaboration meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials demonstrated an approximately two-fold increase in hospitalizations for heart failure in COX-2 selective-treated patients and nonselective NSAID-treated patients compared to placebo treated patients. In a Danish National Registry study of patients with heart failure, NSAID use increased the risk of MI, hospitalization for heart failure, and death.
Additionally, fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients treated with NSAIDs. Use of diclofenac may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions [e.g, diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)] (see PRECAUTIONS; Drug Interactions).
Avoid the use of diclofenac in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If diclofenac is used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure.
Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia
Renal Toxicity
Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury.
Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of a NSAID may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, dehydration, hypovolemia, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors or ARBs, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of diclofenac in patients with advanced renal disease. The renal effects of diclofenac may hasten the progression of renal dysfunction in patients with pre-existing renal disease.
Correct volume status in dehydrated or hypovolemic patients prior to initiating diclofenac. Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia during use of diclofenac (see PRECAUTIONS; Drug Interactions). Avoid the use of diclofenac in patients with advanced renal disease unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening renal function. If diclofenac is used in patients with advanced renal disease, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function.
Anaphylactic Reactions
Diclofenac has been associated with anaphylactic reactions in patients with and without known hypersensitivity to diclofenac and in patients with aspirin sensitive asthma (see CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS; Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity).
Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
A subpopulation of patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma which may include chronic rhinosinusitis complicated by nasal polyps; severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm; and/or intolerance to aspirin and other NSAIDs. Because cross-reactivity between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, diclofenac is contraindicated in patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). When diclofenac is used in patients with preexisting asthma (without known aspirin sensitivity), monitor patients for changes in the signs and symptoms of asthma.
Serious Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including diclofenac, can cause serious skin adverse reactions such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin reactions and to discontinue the use of diclofenac at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity. Diclofenac is contraindicated in patients with previous serious skin reactions to NSAIDs (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Diclofenac may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Avoid use of NSAIDs, including diclofenac, in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks of gestation (third trimester) (see PRECAUTIONS; Pregnancy).
Hematologic Toxicity
Anemia has occurred in NSAID-treated patients. This may be due to occult or gross blood loss, fluid retention, or an incompletely described effect on erythropoiesis. If a patient treated with diclofenac, has any signs or symptoms of anemia, monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit.
NSAIDs, including diclofenac, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Co-morbid conditions such as coagulation disorders, concomitant use of warfarin, other anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may increase this risk. Monitor these patients for signs of bleeding (see PRECAUTIONS; Drug Interactions).
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids and the patient should be observed closely for any evidence of adverse effects, including adrenal insufficiency and exacerbation of symptoms of arthritis.
The pharmacological activity of diclofenac in reducing fever and inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
Information for Patients
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide) that accompanies each prescription dispensed. Inform patients, families, or their caregivers of the following information before initiating therapy with diclofenac and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy.
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events:
Advise patients to be alert for the symptoms of cardiovascular thrombotic events, including chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, or slurring of speech, and to report any of these symptoms to their healthcare provider immediately (see WARNINGS; Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events).
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
Advise patients to report symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis to their health care provider. In the setting of concomitant use of low-dose aspirin for cardiac prophylaxis, inform patients of the increased risk for the signs and symptoms of GI bleeding (see WARNING; Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation).
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, diarrhea, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and “flu-like” symptoms). If these occur, instruct patients to stop diclofenac and seek immediate medical therapy (see WARNINGS; Hepatotoxicity).
Heart Failure and Edema:
Advise patients to be alert for the symptoms of congestive heart failure including shortness of breath, unexplained weight gain, or edema and to contact their healthcare provider if such symptoms occur (see WARNINGS; Heart Failure and Edema).
Anaphylactic Reactions
Inform patients of the signs of an anaphylactic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). Instruct patients to seek immediate emergency help if these occur (see WARNINGS; Anaphylactic Reactions).
Serious Skin Reactions
Advise patients to stop diclofenac immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their healthcare provider as soon as possible (see WARNINGS; Serious Skin Reactions).
Female Fertility
Advise females of reproductive potential who desire pregnancy that NSAIDs, including diclofenac, may be associated with a reversible delay in ovulation (see PRECAUTIONS; Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility).
Fetal Toxicity
Inform pregnant women to avoid use of diclofenac and other NSAIDs, starting at 30 weeks gestation because of the risk of the premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus (see WARNINGS; Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus).
Avoid Concomitant Use of NSAIDs
Inform patients that the concomitant use of diclofenac with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) is not recommended due to the increased risk of gastrointestinal toxicity, and little or no increase in efficacy (see WARNINGS; Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation and Drug Interactions). Alert patients that NSAIDs may be present in “over the counter” medications for treatment of colds, fever, or insomnia.
Use of NSAIDS and Low-Dose Aspirin
Inform patients not to use low-dose aspirin concomitantly with diclofenac until they talk to their healthcare provider (see PRECAUTIONS; Drug Interactions).
Masking of Inflammation and Fever
The pharmacological activity of diclofenac in reducing inflammation, and possibly fever, may diminish the utility of diagnostic signs in detecting infections.
Laboratory Monitoring
Because serious GI bleeding, hepatotoxicity, and renal injury can occur without warning symptoms or signs, consider monitoring patients on long term NSAID treatment with a CBC and a chemistry profile periodically (see WARNINGS; Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforation, and Hepatotoxicity).
Drug Interactions
See Table 2 for clinically significant drug interactions with diclofenac.
Table 2: Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with Diclofenac Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis Clinical Impact: - Diclofenac and anticoagulants such as warfarin have a synergistic effect on bleeding. The concomitant use of diclofenac and anticoagulants have an increased risk of serious bleeding compared to the use of either drug alone.
- Serotonin release by platelets plays an important role in hemostasis. Case-control and cohort epidemiological studies showed that concomitant use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and an NSAID may potentiate the risk of bleeding more than an NSAID alone.
Intervention: Monitor patients with concomitant use of diclofenac with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelet agents
(e.g., aspirin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for signs of bleeding ( see PRECAUTIONS; Hematological Toxicity).Aspirin Clinical Impact: Controlled clinical studies showed that the concomitant use of NSAIDs and analgesic doses of aspirin does not produce any greater therapeutic effect than the use of NSAIDs alone. In a clinical study, the concomitant use of an NSAID and aspirin was associated with a significantly increased incidence of GI adverse reactions as compared to use of the NSAID alone (see
WARNINGS; Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation) .Intervention: Concomitant use of diclofenac and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended because of the increased risk of bleeding ( see PRECAUTIONS: Hematological Toxicity).
Diclofenac is not a substitute for low dose aspirin for cardiovascular protection.ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers, and Beta-Blockers Clinical Impact: - NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), or beta-blockers (including propranolol).
- In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or have renal impairment, co-administration of an NSAID with ACE inhibitors or ARBs may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. These effects are usually reversible
Intervention: - During concomitant use of diclofenac and
- ACE-inhibitors, ARBs, or betablockers, monitor blood pressure to ensure that the desired blood pressure is obtained.
- During concomitant use of diclofenac and ACE-inhibitors or ARBs in patients who are elderly, volume-depleted, or have impaired renal function, monitor for signs of worsening renal function ( see WARNINGS; Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia).
- When these drugs are administered concomitantly, patients should be adequately hydrated. Assess renal function at the beginning of the concomitant treatment and periodically thereafter.
Diuretics Clinical Impact: Clinical studies, as well as post-marketing observations, showed that NSAIDs reduced the natriuretic effect of loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) and thiazide diuretics in some patients. This effect has been attributed to the NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. Intervention: During concomitant use of diclofenac with diuretics, observe patients for signs of worsening renal function, in addition to assuring diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects ( see WARNINGS; Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia). Digoxin Clinical Impact: The concomitant use of diclofenac with digoxin has been reported to increase the serum concentration and prolong the half-life of digoxin. Intervention: During concomitant use of diclofenac and digoxin, monitor serum digoxin levels. Lithium Clinical Impact: NSAIDs have produced elevations in plasma lithium levels and reductions in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15%, and the renal clearance decreased by approximately 20%. This effect has been attributed to NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. Intervention: During concomitant use of diclofenac and lithium, monitor patients for signs of lithium toxicity. Methotrexate Clinical Impact: Concomitant use of NSAIDs and methotrexate may increase the risk for methotrexate toxicity (e.g., neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunction). Intervention: During concomitant use of diclofenac and methotrexate, monitor patients for methotrexate toxicity. Cyclosporine Clinical Impact: Concomitant use of diclofenac and cyclosporine may increase cyclosporine's nephrotoxicity. Intervention: During concomitant use of diclofenac and cyclosporine, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function. NSAIDs and Salicylates Clinical Impact: Concomitant use of diclofenac with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) increases the risk of GI toxicity, with little or no increase in efficacy ( see WARNINGS; Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation). Intervention: The concomitant use of diclofenac with other NSAIDs or salicylates is not recommended. Pemetrexed Clinical Impact: Concomitant use of diclofenac and pemetrexed may increase the risk of pemetrexedassociated myelosuppression, renal, and GI toxicity (see the pemetrexed prescribing information). Intervention: During concomitant use of diclofenac and pemetrexed, in patients with renal impairment whose creatinine clearance ranges from 45 to 79 mL/min, monitor for myelosuppression, renal and GI toxicity.
NSAIDs with short elimination half-lives (e.g., diclofenac, indomethacin) should be avoided for a period of two days before, the day of, and two days following administration of pemetrexed.
In the absence of data regarding potential interaction between pemetrexed and NSAIDs with longer half-lives (e.g., meloxicam, nabumetone), patients taking these NSAIDs should interrupt dosing for at least five days before, the day of, and two days following pemetrexed administration.CYP2C9 Inhibitors or Inducers: Clinical Impact: Diclofenac is metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes, predominantly by CYP2C9. Co-administration of diclofenac with CYP2C9 inhibitors (e.g. voriconazole) may enhance the exposure and toxicity of diclofenac whereas co-administration with CYP2C9 inducers (e.g. rifampin) may lead to compromised efficacy of diclofenac. Intervention: A dosage adjustment may be warranted when diclofenac is administered with CYP2C9 inhibitors or inducers ( see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY; Pharmacokinetics). Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in rats given diclofenac sodium up to 2 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.1 times maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of diclofenac, 200 mg/day, based on body surface area (BSA) comparison ) have revealed no significant increases in tumor incidence. A 2-year carcinogenicity study conducted in mice employing diclofenac sodium at doses up to 0.3 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.007 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison) in males and 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.02 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison) in females did not reveal any oncogenic potential.
Mutagenesis
Diclofenac sodium did not show mutagenic activity in in vitro point mutation assays in mammalian (mouse lymphoma) and microbial (yeast, Ames) test systems and was nonmutagenic in several mammalian in vitro and in vivo tests, including dominant lethal and male germinal epithelial chromosomal studies in mice, and nucleus anomaly and chromosomal aberration studies in Chinese hamsters.
Impairment of Fertility
Diclofenac sodium administered to male and female rats at 4 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.2 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison) did not affect fertility.
Based on the mechanism of action, the use of prostaglandin-mediated NSAIDs, including diclofenac, may delay or prevent rupture of ovarian follicles, which has been associated with reversible infertility in some women. Published animal studies have shown that administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors has the potential to disrupt prostaglandin mediated follicular rupture required for ovulation. Small studies in women treated with NSAIDs have also shown a reversible delay in ovulation. Consider withdrawal of NSAIDs, including diclofenac, in women who have difficulties conceiving or who are undergoing investigation of infertility.
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Use of NSAIDs, including diclofenac, during the third trimester of pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Avoid use of NSAIDs, including diclofenac, in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks of gestation (third trimester) (see WARNINGS; Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arterious).
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of diclofenac in pregnant women. Data from observational studies regarding potential embryofetal risks of NSAID use in women in the first or second trimesters of pregnancy are inconclusive. In the general U.S. population, all clinically recognized pregnancies, regardless of drug exposure, have a background rate of 2-4% for major malformations, and 15-20% for pregnancy loss. In animal reproduction studies, no evidence of teratogenicity was observed in mice, rats, or rabbits given diclofenac during the period of organogenesis at doses up to approximately 0.5, 0.5, and 1 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of diclofenac, 200 mg/day, despite the presence of maternal and fetal toxicity at these doses [see Data] . Based on animal data, prostaglandins have been shown to have an important role in endometrial vascular permeability, blastocyst implantation, and decasualization. In animal studies, administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors such as diclofenac, resulted in increased pre- and post-implantation loss.
Data
Animal Data
Reproductive and developmental studies in animals demonstrated that diclofenac sodium administration during organogenesis did not produce teratogenicity despite the induction of maternal toxicity and fetal toxicity in mice at oral doses up to 20 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.5 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of diclofenac, 200 mg/day, based on body surface area (BSA) comparison), and in rats and rabbits at oral doses up to 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.5 and 1 times, respectively, the MRHD based on BSA comparison). In a study in which pregnant rats were orally administered 2 or 4 mg/kg diclofenac (0.1 and 0.2 times the MRHD based on BSA) from Gestation Day 15 through Lactation Day 21, significant maternal toxicity (peritonitis, mortality) was noted. These maternally toxic doses were associated with dystocia, prolonged gestation, reduced fetal weights and growth, and reduced fetal survival. Diclofenac has been shown to cross the placental barrier in mice, rats, and humans.
Labor or Delivery
There are no studies on the effects of diclofenac during labor or delivery. In animal studies, NSAIDS, including diclofenac, inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, cause delayed parturition, and increase the incidence of stillbirth.
Nursing Mothers
Risk Summary
Based on available data, diclofenac may be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for diclofenac and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from the diclofenac or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
One woman treated orally with a diclofenac salt, 150 mg/day, had a milk diclofenac level of 100 mcg/L, equivalent to an infant dose of about 0.03 mg/ kg/day. Diclofenac was not detectable in breast milk in 12 women using diclofenac (after either 100 mg/day orally for 7 days or a single 50 mg intramuscular dose administered in the immediate postpartum period).
Geriatric Use
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID-associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions. If the anticipated benefit for the elderly patient outweighs these potential risks, start dosing at the low end of the dosing range, and monitor patients for adverse effects (see WARNINGS; Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events, Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation, Hepatotoxicity, Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia, PRECAUTIONS; Laboratory Monitoring ) .
Diclofenac is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, ADVERSE REACTIONS).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events (see WARNINGS)
- GI Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforation (see WARNINGS)
- Hepatotoxicity (see WARNINGS)
- Hypertension (see WARNINGS)
- Heart Failure and Edema (see WARNINGS)
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia (see WARNINGS)
- Anaphylactic Reactions (see WARNINGS)
- Serious Skin Reactions (see WARNINGS)
- Hematologic Toxicity (see WARNINGS)
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In patients taking diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, or other NSAIDs, the most frequently reported adverse experiences occurring in approximately 1%-10% of patients are:
Gastrointestinal experiences including: abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, gross bleeding/perforation, heartburn, nausea, GI ulcers (gastric/duodenal) and vomiting.
Abnormal renal function, anemia, dizziness, edema, elevated liver enzymes, headaches, increased bleeding time, pruritus, rashes and tinnitus.
Additional adverse experiences reported occasionally include:
Body as a Whole: fever, infection, sepsis
Cardiovascular System: congestive heart failure, hypertension, tachycardia, syncope
Digestive System: dry mouth, esophagitis, gastric/peptic ulcers, gastritis, gastrointestinal bleeding, glossitis, hematemesis, hepatitis, jaundice
Hemic and Lymphatic System: ecchymosis, eosinophilia, leukopenia,
melena, purpura, rectal bleeding, stomatitis, thrombocytopenia
Metabolic and Nutritional: weight changes
Nervous System: anxiety, asthenia, confusion, depression, dream abnormalities, drowsiness, insomnia, malaise, nervousness, paresthesia, somnolence, tremors, vertigo
Respiratory System: asthma, dyspnea
Skin and Appendages: alopecia, photosensitivity, sweating increased
Special Senses: blurred vision
Urogenital System: cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, oliguria/polyuria, proteinuria, renal failure
Other adverse reactions, which occur rarely are:
Body as a Whole: anaphylactic reactions, appetite changes, death
Cardiovascular System: arrhythmia, hypotension, myocardial infarction, palpitations, vasculitis
Digestive System: colitis, eructation, fulminant hepatitis with and without jaundice, liver failure, liver necrosis, pancreatitis
Hemic and Lymphatic System: agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia
Metabolic and Nutritional: hyperglycemia
Nervous System: convulsions, coma, hallucinations, meningitis
Respiratory System: respiratory depression, pneumonia
Skin and Appendages: angioedema, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, urticaria
Special Senses: conjunctivitis, hearing impairment
-
OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdosages have been typically limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which have been generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding has occurred. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression and coma have occurred, but were rare. (see WARNINGS; Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events, Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation, Hypertension, Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia) .
Manage patients with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdosage. There are no specific antidotes. Consider emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 grams in adults, 1 to 2 grams per kg of body weight in pediatric patients) and/or osmotic cathartic in symptomatic patients seen within four hours of ingestion or in patients with a large overdose (5 to 10 times the recommended dosage). Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
For additional information about overdosage treatment contact a poison control center (1-800-222-1222).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use diclofenac. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS; Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation) .
After observing the response to initial therapy with diclofenac, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient's needs.
For the relief of osteoarthritis, the recommended dosage is 100-150 mg/day in divided doses (50 mg twice a day or three times a day, or 75 mg twice a day).
For the relief of rheumatoid arthritis, the recommended dosage is 150-200 mg/day in divided doses (50 mg three times a day. or four times a day, or 75 mg twice a day.).
For the relief of ankylosing spondylitis, the recommended dosage is 100-125 mg/day, administered as 25 mg four times a day, with an extra 25-mg dose at bedtime if necessary.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets
75 mg -– white to off-white, biconvex, round shaped, unscored (imprinted
 on one side), supplied in bottles of 60
on one side), supplied in bottles of 60
Bottles of 60 ..................................................................NDC: 61442-103-60
Store at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from moisture.
Dispense in tight container (USP).
Manufactured by:
Carlsbad Tech
Carlsbad, CA 92008 USARevised: 05/2016
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
Medication Guide for Nonsteroidal
Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including:
-
Increased risk of heart attack or stroke that can lead to death.This risk may happen early in treatment and may increase:
- with increasing doses of NSAIDS
- with longer use of NSAIDs
Do not take NSAIDs right before or after a heart surgery called a “coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).” Avoid taking NSAIDs after a recent heart attack, unless your healthcare provider tells you to. You may have an increased risk of another heart attack if you take NSAIDs after a recent heart attack.
-
Increased risk of bleeding, ulcers, and tears (perforation) of the esophagus (tube leading from the mouth to the stomach), stomach and intestines:
- anytime during use
- without warning symptoms
- that may cause death
The risk of getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
- past history of stomach ulcers, or intestinal bleeding with use of NSAIDs
- taking medicines called “corticosteroids”, “anticoagulants”, “SSRIs” or “SNRIs”
- increasing doses of NSAIDs
- longer use of NSAIDs
- smoking
- drinking alcohol
- older age
- poor health
- advanced liver disease
- bleeding problems
NSAIDs should only be used:
- exactly as prescribed
- at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
- for the shortest time needed
What are NSAIDs?
NSAIDs are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as different types of arthritis, menstrual cramps, and other types of short-term pain.
Who should not take NSAIDs?
Do not take NSAIDs:
- if you have had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAIDs.
- right before or after heart bypass surgery.
Before taking NSAIDs, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver or kidney problems
- have high blood pressure
- have asthma
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are considering taking NSAIDs during pregnancy.
You should not take NSAIDs after 29 weeks of pregnancy. - are breastfeeding or plan to breast feed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Do not start taking any new medicine without talking to your healthcare provider first.
What are the possible side effects of NSAIDs?
NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including: See “ What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?”
- new or worse high blood pressure
- heart failure
- liver problems including liver failure
- kidney problems including kidney failure
- low red blood cells (anemia)
- life-threatening skin reactions
- life-threatening allergic reactions
- Other side effects of NSAIDs include: stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
Get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath
- chest pain
- slurred speech or trouble breathing
- swelling of the face or throat
- weakness in one part or side of your body
Stop taking your NSAID and call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
- nausea
- more tired or weaker than usual
- diarrhea
- itching
- your skin or eyes look yellow
- indigestion or stomach pain
- flu-like symptoms
- vomit blood
- there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar
- unusual weight gain
- skin rash or blisters with fever
- swelling of the arms, legs, hands and feet
If you take too much of your NSAID, call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away.
These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Other information about NSAIDs
- Aspirin is an NSAID medicine but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
- Some NSAIDs are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.
General information about the safe and effective use of NSAIDs
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use NSAIDs for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NSAIDs to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
If you would like more information about NSAIDs, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about NSAIDs that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.carlsbadtech. com or call 1-855-397-9777
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
CTI-1 MG Rev. G 05/2016
-
Increased risk of heart attack or stroke that can lead to death.This risk may happen early in treatment and may increase:
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Lidocaine Description
Lidocaine patch 5% is comprised of an adhesive material containing 5% lidocaine, which is applied to a white non-woven polyethylene terephthalate (PET) material backing and covered with a transparent PET release liner. The release liner is removed prior to application to the skin. The size of the patch is 10 cm x 14 cm.
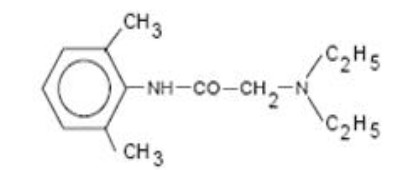
Lidocaine is chemically designated as acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl), has an octanol:water partition ratio of 43 at pH 7.4, and has the following structure:
Each adhesive patch contains 700 mg of lidocaine (50 mg per gram adhesive) in an aqueous base. It also contains the following inactive ingredients: glycerin, D-sorbitol, propylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, urea, sodium polyacrylate, carboxymethylcellulose sodium, gelatin, polyacrylic acid, kaolin, tartaric acid, dihydroxyaluminum aminoacetate, methylparaben, propylparaben, and edetate disodium.
-
Lidocaine Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Lidocaine is an amide-type local anesthetic agent and is suggested to stabilize neuronal membranes by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses.
The penetration of lidocaine into intact skin after application of lidocaine patch is sufficient to produce an analgesic effect, but less than the amount necessary to produce a complete sensory block.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption:
The amount of lidocaine systemically absorbed from lidocaine patch is directly related to both the duration of application and the surface area over which it is applied. In a pharmacokinetic study, three lidocaine patches were applied over an area of 420 cm2 of intact skin on the back of normal volunteers for 12 hours. Blood samples were withdrawn for determination of lidocaine concentration during the application and for 12 hours after removal of patches. The results are summarized in Table 1.
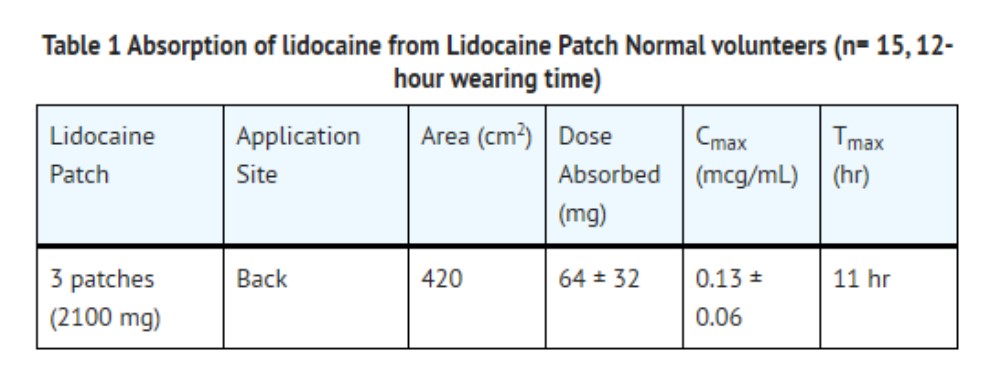
When lidocaine patch is used according to the recommended dosing instructions, only 3 ± 2% of the dose applied is expected to be absorbed. At least 95% (665 mg) of lidocaine will remain in a used patch. Mean peak blood concentration of lidocaine is about 0.13 mcg/mL (about 1/10 of the therapeutic concentration required to treat cardiac arrhythmias). Repeated application of three patches simultaneously for 12 hours (recommended maximum daily dose), once per day for three days, indicated that the lidocaine concentration does not increase with daily use. The mean plasma pharmacokinetic profile for the 15 healthy volunteers is shown in Figure 1.
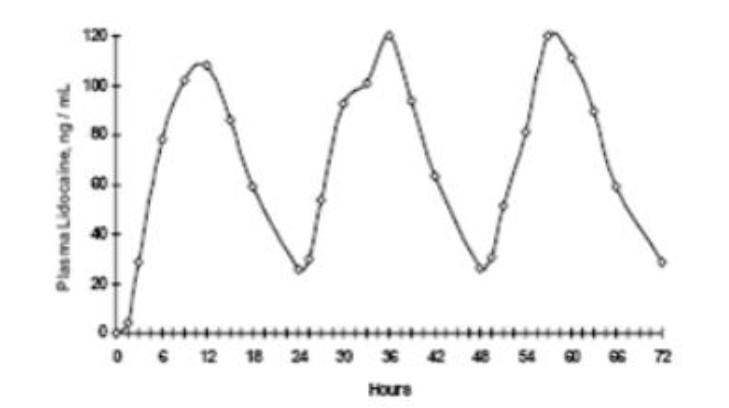
Figure 1 Mean lidocaine blood concentrations after three consecutive daily applications of three lidocaine patches simultaneously for 12 hours per day in healthy volunteers (n = 15).
Distribution:
When lidocaine is administered intravenously to healthy volunteers, the volume of distribution is 0.7 to 2.7 L/kg (mean 1.5 ± 0.6 SD, n=15). At concentrations produced by application of lidocaine patch, lidocaine is approximately 70% bound to plasma proteins, primarily alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. At much higher plasma concentrations (1 to 4 mcg/mL of free base), the plasma protein binding of lidocaine is concentration dependent. Lidocaine crosses the placental and blood brain barriers, presumably by passive diffusion.
Metabolism:
It is not known if lidocaine is metabolized in the skin. Lidocaine is metabolized rapidly by the liver to a number of metabolites, including monoethylglycinexylidide (MEGX) and glycinexylidide (GX), both of which have pharmacologic activity similar to, but less potent than that of lidocaine. A minor metabolite, 2, 6-xylidine, has unknown pharmacologic activity but is carcinogenic in rats. The blood concentration of this metabolite is negligible following application of lidocaine patch 5%. Following intravenous administration, MEGX and GX concentrations in serum range from 11 to 36% and from 5 to 11% of lidocaine concentrations, respectively.
Excretion:
Lidocaine and its metabolites are excreted by the kidneys. Less than 10% of lidocaine is excreted unchanged. The half-life of lidocaine elimination from the plasma following IV administration is 81 to 149 minutes (mean 107 ± 22 SD, n = 15). The systemic clearance is 0.33 to 0.90 L/min (mean 0.64 ± 0.18 SD, n = 15).
-
Lidocaine Clinical Trials
Single-dose treatment with lidocaine patch was compared to treatment with vehicle patch (without lidocaine), and to no treatment (observation only) in a double-blind, crossover clinical trial with 35 post-herpetic neuralgia patients. Pain intensity and pain relief scores were evaluated periodically for 12 hours. Lidocaine patch performed statistically better than vehicle patch in terms of pain intensity from 4 to 12 hours.
Multiple-dose, two-week treatment with lidocaine patch was compared to vehicle patch (without lidocaine) in a double-blind, crossover clinical trial of withdrawal-type design conducted in 32 patients, who were considered as responders to the open-label use of lidocaine patch prior to the study. The constant type of pain was evaluated but not the pain induced by sensory stimuli (dysesthesia). Statistically significant differences favoring lidocaine patch were observed in terms of time to exit from the trial (14 versus 3.8 days at p-value <0.001), daily average pain relief, and patient’s preference of treatment. About half of the patients also took oral medication commonly used in the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia. The extent of use of concomitant medication was similar in the two treatment groups.
- Lidocaine Indications and Usage
- Contraindications
-
Lidoacaine Warnings
Accidental Exposure in Children
Even a used lidocaine patch contains a large amount of lidocaine (at least 665 mg). The potential exists for a small child or a pet to suffer serious adverse effects from chewing or ingesting a new or used lidocaine patch, although the risk with this formulation has not been evaluated. It is important for patients to store and dispose of lidocaine patch 5% out of the reach of children, pets and others. (See HANDLING AND DISPOSAL)
Excessive Dosing
Excessive dosing by applying lidocaine patch 5% to larger areas or for longer than the recommended wearing time could result in increased absorption of lidocaine and high blood concentrations, leading to serious adverse effects (see ADVERSE REACTIONS, Systemic Reactions). Lidocaine toxicity could be expected at lidocaine blood concentrations above 5 mcg/mL. The blood concentration of lidocaine is determined by the rate of systemic absorption and elimination. Longer duration of application, application of more than the recommended number of patches, smaller patients, or impaired elimination may all contribute to increasing the blood concentration of lidocaine. With recommended dosing of lidocaine patch 5%, the average peak blood concentration is about 0.13 mcg/mL, but concentrations higher than 0.25 mcg/mL have been observed in some individuals.
-
Lidocaine Precaution
General
Hepatic Disease: Patients with severe hepatic disease are at greater risk of developing toxic blood concentrations of lidocaine, because of their inability to metabolize lidocaine normally.
Allergic Reactions: Patients allergic to para-aminobenzoic acid derivatives (procaine, tetracaine, benzocaine, etc.) have not shown cross sensitivity to lidocaine. However, lidocaine patch 5% should be used with caution in patients with a history of drug sensitivities, especially if the etiologic agent is uncertain.
Non-intact Skin: Application to broken or inflamed skin, although not tested, may result in higher blood concentrations of lidocaine from increased absorption. Lidocaine patch 5% is only recommended for use on intact skin.
External Heat Sources: Placement of external heat sources, such as heating pads or electric blankets, over lidocaine patch 5% is not recommended as this has not been evaluated and may increase plasma lidocaine levels.
Eye Exposure: The contact of lidocaine patch 5% with eyes, although not studied, should be avoided based on the findings of severe eye irritation with the use of similar products in animals. If eye contact occurs, immediately wash out the eye with water or saline and protect the eye until sensation returns.
Drug Interactions
Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Lidocaine patch 5% should be used with caution in patients receiving Class I antiarrhythmic drugs (such as tocainide and mexiletine) since the toxic effects are additive and potentially synergistic.
Local Anesthetics: When lidocaine patch 5% is used concomitantly with other products containing local anesthetic agents, the amount absorbed from all formulations must be considered.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: A minor metabolite, 2,6-xylidine, has been found to be carcinogenic in rats. The blood concentration of this metabolite is negligible following application of lidocaine patch 5%.
Mutagenesis: Lidocaine HCl is not mutagenic in Salmonella/mammalian microsome test nor clastogenic in chromosome aberration assay with human lymphocytes and mouse micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility: The effect of lidocaine patch 5% on fertility has not been studied.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category B. Lidocaine patch 5% has not been studied in pregnancy. Reproduction studies with lidocaine have been performed in rats at doses up to 30 mg/kg subcutaneously and have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to lidocaine. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, lidocaine patch 5% should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Labor and Delivery
Lidocaine patch 5% has not been studied in labor and delivery. Lidocaine is not contraindicated in labor and delivery. Should lidocaine patch 5% be used concomitantly with other products containing lidocaine, total doses contributed by all formulations must be considered.
Nursing Mothers
Lidocaine patch 5% has not been studied in nursing mothers. Lidocaine is excreted in human milk, and the milk:plasma ratio of lidocaine is 0.4. Caution should be exercised when lidocaine patch 5% is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
-
Lidocaine Adverse Reactions
Application Site Reactions
During or immediately after treatment with lidocaine patch 5%, the skin at the site of application may develop blisters, bruising, burning sensation, depigmentation, dermatitis, discoloration, edema, erythema, exfoliation, irritation, papules, petechia, pruritus, vesicles, or may be the locus of abnormal sensation. These reactions are generally mild and transient, resolving spontaneously within a few minutes to hours.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic and anaphylactoid reactions associated with lidocaine, although rare, can occur. They are characterized by angioedema, bronchospasm, dermatitis, dyspnea, hypersensitivity, laryngospasm, pruritus, shock, and urticaria. If they occur, they should be managed by conventional means. The detection of sensitivity by skin testing is of doubtful value.
Other Adverse Events
Due to the nature and limitation of spontaneous reports in postmarketing surveillance, causality has not been established for additional reported adverse events including:
Asthenia, confusion, disorientation, dizziness, headache, hyperesthesia, hypoesthesia, lightheadedness, metallic taste, nausea, nervousness, pain exacerbated, paresthesia, somnolence, taste alteration, vomiting, visual disturbances such as blurred vision, flushing, tinnitus, and tremor.
Systemic (Dose-Related) Reactions
Systemic adverse reactions following appropriate use of lidocaine patch 5% are unlikely, due to the small dose absorbed (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics). Systemic adverse effects of lidocaine are similar in nature to those observed with other amide local anesthetic agents, including CNS excitation and/or depression (light-headedness, nervousness, apprehension, euphoria, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, tinnitus, blurred or double vision, vomiting, sensations of heat, cold or numbness, twitching, tremors, convulsions, unconsciousness, respiratory depression and arrest). Excitatory CNS reactions may be brief or not occur at all, in which case the first manifestation may be drowsiness merging into unconsciousness. Cardiovascular manifestations may include bradycardia, hypotension and cardiovascular collapse leading to arrest.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Actavis at 1-800-272-5525 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch for voluntary reporting of adverse reactions.
-
Lidocaine Overdose
Lidocaine overdose from cutaneous absorption is rare, but could occur. If there is any suspicion of lidocaine overdose (see ADVERSE REACTIONS, Systemic Reactions), drug blood concentration should be checked. The management of overdose includes close monitoring, supportive care, and symptomatic treatment. Dialysis is of negligible value in the treatment of acute overdose with lidocaine.
In the absence of massive topical overdose or oral ingestion, evaluation of symptoms of toxicity should include consideration of other etiologies for the clinical effects, or overdosage from other sources of lidocaine or other local anesthetics.
The oral LD50 of lidocaine HCl is 459 (346 to 773) mg/kg (as the salt) in non-fasted female rats and 214 (159 to 324) mg/kg (as the salt) in fasted female rats, which are equivalent to roughly 4000 mg and 2000 mg, respectively, in a 60 to 70 kg man based on the equivalent surface area dosage conversion factors between species.
-
Lidocaine Dosage & Administration
Apply lidocaine patch 5% to intact skin to cover the most painful area. Apply the prescribed number of patches (maximum of 3), only once for up to 12 hours within a 24-hour period. Patches may be cut into smaller sizes with scissors prior to removal of the release liner. (See HANDLING AND DISPOSAL) Clothing may be worn over the area of application. Smaller areas of treatment are recommended in a debilitated patient, or a patient with impaired elimination.
If irritation or a burning sensation occurs during application, remove the patch(es) and do not reapply until the irritation subsides.
When lidocaine patch 5% is used concomitantly with other products containing local anesthetic agents, the amount absorbed from all formulations must be considered.
Lidocaine patch 5% may not stick if it gets wet. Avoid contact with water, such as bathing, swimming or showering.
-
Handling and Disposal
Hands should be washed after the handling of lidocaine patch 5%, and eye contact with lidocaine patch 5% should be avoided. Do not store patch outside the sealed envelope. Apply immediately after removal from the protective envelope. Fold used patches so that the adhesive side sticks to itself and safely discard used patches or pieces of cut patches where children and pets cannot get to them. Lidocaine patch 5% should be kept out of the reach of children.
-
Lidocaine How Supplied
Lidocaine patch 5% is available as the following:
Carton of 30 patches, packaged into individual child-resistant envelopes.
NDC: 0591-3525-30
Store at 20o to 25oC (68o to 77oF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
For more information, call Actavis at 1-800-272-5525.
Manufactured by:
Actavis Laboratories UT, Inc.
Salt Lake City, UT 84108 USA - Principal Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LIDOVIX DELAYED RELEASE
lidocaine, diclofenac sodium kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72275-708 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72275-708-77 1 in 1 CARTON 08/01/2019 1 1 in 1 BOX 1 1 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 BOTTLE 60 Part 2 1 POUCH 1 g Part 1 of 2 DICLOFENAC SODIUM DELAYED RELEASE
diclofenac sodium tablet, delayed releaseProduct Information Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DICLOFENAC SODIUM (UNII: QTG126297Q) (DICLOFENAC - UNII:144O8QL0L1) DICLOFENAC SODIUM 75 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SHELLAC (UNII: 46N107B71O) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO (UNII: 5856J3G2A2) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) METHACRYLIC ACID - METHYL METHACRYLATE COPOLYMER (1:1) (UNII: 74G4R6TH13) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 2000 (UNII: HAF0412YIT) Product Characteristics Color white Score no score Shape ROUND Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code CTI;102 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA075185 11/13/1998 Part 2 of 2 LIDOCAINE
lidocaine patchProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 0591-3525 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LIDOCAINE (UNII: 98PI200987) (LIDOCAINE - UNII:98PI200987) LIDOCAINE 50 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) UREA (UNII: 8W8T17847W) SORBITOL (UNII: 506T60A25R) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) GELATIN, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2G86QN327L) TARTARIC ACID (UNII: W4888I119H) DIHYDROXYALUMINUM AMINOACETATE (UNII: DO250MG0W6) METHYLPARABEN (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) KAOLIN (UNII: 24H4NWX5CO) PROPYLPARABEN (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE SODIUM (UNII: K679OBS311) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0591-3525-30 30 in 1 CARTON 1 1 g in 1 POUCH; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA200675 09/15/2013 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date unapproved drug other 08/01/2019 Labeler - Primary Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (066126126) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Actavis Laboratories UT, Inc 079589880 manufacture(0591-3525) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Rainbow Gold 800695152 repack(72275-708)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.