ONSIOR- robenacoxib tablet
Onsior by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Onsior by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Elanco US Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Description:
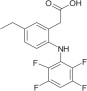
ONSIOR (robenacoxib) is a non-narcotic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the coxib class. Tablets are round, beige to brown in color, not scored, flavored and contain 6 mg robenacoxib. The molecular weight of robenacoxib is 327.28. The empirical formula is C16-H13-F4-NO2.
Robenacoxib is [5-Ethyl-2-(2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-phenylamino)-phenyl]-acetic acid. The structural formula is:
- Indication:
-
Dosage and Administration:
Always provide “Information for Cat Owners” Sheet with prescription. Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of ONSIOR tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use ONSIOR tablets.
Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual response.
The dose of ONSIOR tablets is 0.45 mg/lb (1 mg/kg) orally once daily, for a maximum of 3 days. See dosing chart for dosage directions.
Dosage Directions: For oral use in cats ≥ 5.5 lbs and ≥ 4 months of age; for up to a maximum of 3 days. Tablets are not scored and should not be broken.
Body weight 6 mg ONSIOR (robenacoxib) Tablet 5.5 to 13.2 lbs (2.5 to 6 kg) 1 whole tablet once daily 13.3 to 26.4 lbs (6.1 to 12 kg) 2 whole tablets once daily Do not use in cats weighing less than 5.5 lbs, as cats less than 5.5 lbs cannot be accurately dosed.
The first dose should be administered approximately 30 minutes prior to surgery, at the same time as the pre-anesthetic agents are given.
ONSIOR tablets may be given with or without food.
In cats ≥ 5.5 lbs and ≥ 4 months of age, subsequent doses can be given via the oral tablet, or interchanged with subcutaneous injection for a maximum of 3 total ONSIOR doses over 3 days, not to exceed one dose per day (see Animal Safety and the ONSIOR injection package insert).
Note the dose of ONSIOR tablets and ONSIOR injection are different.
If a second and third tablet dose is dispensed to the client to administer at home, doses should be dispensed in the dispensing envelope with the attached Information for Owner Sheet intact. Do not remove Information for Cat Owner Sheet. Record when the first dose was administered on the dispensing envelope. Cats weighing ≥ 13.3 lbs may require two blister cards, each dispensed in an individual dispensing envelope.
- Contraindications:
-
Warnings:
Not for use in humans. Keep this and all medications out of reach of children. Consult a physician in case of accidental ingestion by humans. For oral use in cats only.
All cats should undergo a thorough history and physical examination before the initiation of NSAID therapy. Appropriate laboratory tests should be conducted to establish hematological and serum biochemical baseline data prior to administration of an NSAID.
Owners should be advised to observe for signs of potential drug toxicity (see Adverse Reactions and Animal Safety) and be given an “Information for Cat Owners” Sheet about ONSIOR tablets.
Do not administer ONSIOR tablets or injection in conjunction with any other oral or injectable NSAID or corticosteroid.
-
Precautions:
When using NSAIDS such as ONSIOR, the use of fluid therapy during surgery is recommended to decrease potential renal complications (see Adverse Reactions, Post-Approval Experience).
Appetite should be monitored in cats receiving ONSIOR.
Stop administration of ONSIOR if appetite decreases or if the cat becomes lethargic.
The use of ONSIOR tablets has not been evaluated in cats younger than 4 months of age and weighing less than 5.5 lbs, cats used for breeding, or in pregnant or lactating cats. Cats receiving ONSIOR should weigh at least 5.5 lbs.
The use of ONSIOR in cats with cardiac disease has not been studied. ONSIOR has been shown to prolong the QT interval.
As a class, cyclo-oxygenase inhibitory NSAIDs may be associated with gastrointestinal, renal, and hepatic toxicity. Sensitivity to drug-associated adverse events varies with the individual patient. Cats that have experienced adverse reactions from one NSAID may experience adverse reactions from another NSAID. Patients at greatest risk for adverse events are those that are dehydrated, on concomitant diuretic therapy, or those with existing renal, cardiovascular, and/or hepatic dysfunction. Anesthetic drugs may affect renal perfusion; approach concomitant use of anesthetics and NSAIDs cautiously. Appropriate monitoring procedures (including ECG, blood pressure, and temperature regulation) should be employed during all surgical procedures. The use of parenteral fluids during surgery is recommended to decrease potential renal complications when using NSAIDs perioperatively.
If additional pain medication is needed after a daily dose of ONSIOR, a non-NSAID/non-corticosteroid class of analgesic may be necessary. Concurrent administration of potentially nephrotoxic drugs should be carefully approached and monitored. NSAIDs may inhibit prostaglandins which maintain normal homeostatic function. Such anti-prostaglandin effects may result in clinically significant disease in patients with underlying or pre-existing disease that has not been previously diagnosed. NSAIDs possess the potential to produce gastrointestinal ulcerations and/ or gastrointestinal perforations. Do not use ONSIOR concomitantly with other anti-inflammatory drugs, such as NSAIDs or corticosteroids. Consider appropriate washout times when switching from one NSAID to another or when switching from corticosteroid use to NSAID use. ONSIOR tablets and ONSIOR injection are safe to use interchangeably when given once a day for a maximum of 3 days in cats ≥ 4 months of age and ≥ 5.5 lbs. Note the dose of ONSIOR tablets and ONSIOR injection are different.
The use of concomitantly protein-bound drugs with ONSIOR has not been studied in cats. Commonly used protein-bound drugs include cardiac, anticonvulsant and behavioral medications. The influence of concomitant drugs that may inhibit metabolism of ONSIOR has not been evaluated. Drug compatibility should be monitored in patients requiring adjunctive therapy. Concurrent medications used during the field study with ONSIOR tablets included antiparasiticides, anesthetics, pre-anesthetic medications, and antibiotics.
The effect of cyclo-oxygenase inhibition and the potential for thromboembolic occurrence or a hypercoagulable state has not been evaluated. It is unknown whether cats with a history of hypersensitivity to ß lactam drugs will exhibit hypersensitivity to ONSIOR. Robenacoxib is poorly soluble in water and in acid solutions readily degrades to form γ-lactam. In cats, lactam is a metabolite of robenacoxib. Additionally, lactam is a degradation product that increases over the shelf-life of the tablets. Neurologic signs have been associated with the use of ß lactam drugs; it is unknown if the lactam in robenacoxib may cause similar neurologic signs (see Animal Safety). Occurrences of seizures, ataxia, and nystagmus have been associated with the use of ONSIOR.
Robenacoxib may prolong the QT interval; the associated risk of developing ventricular arrhythmia is unknown. The use of robenacoxib with other drugs shown to prolong the QT interval is not recommended. Commonly used drugs that prolong the QT interval include antihistamines, prokinetic drugs, and certain anesthetic drugs. As a class, it is unknown if the use of NSAIDs in asthmatic cats can cause acute exacerbations, as seen in some humans.
-
Adverse Reactions:
In a controlled field study, a total of 249 male and female cats representing 6 breeds, 6 months to 13 years old, weighing 5.5 – 15 lbs were included in the field safety analysis. The following table shows the number of cats exhibiting each observation.
1 Cats may have experienced more than one of these signs during the study.
Adverse Reactions in the Postoperative Pain Field Study1 ONSIOR 6 mg
Tablets for CatsPlacebo
Adverse Reaction (robenacoxib) n = 167 (vehicle control) n = 82 Incision site bleeding 7 1 Incision site infection 6 2 Inappetance, weight loss 4 2 Decreased activity, lethargy 4 1 Vomiting 4 1 Cystitis, hematuria 3 0 Hematachezia, diarrhea 3 1 Hair loss, excoriation, bruising 2 0 Respiratory, cardiac arrest 1 0 Incoordination, weakness 1 1 Death 0 1 The most commonly reported adverse reactions were surgical site bleeding, infected surgery sites, lethargy, vomiting and inappetance. Changes in the clinical pathology values were not considered clinically significant.
Post Approval Experience (2015)
The following adverse events are based on voluntary, post approval reporting. Not all adverse events are reported to FDA/CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using these data. The signs reported are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency:
Anorexia, depression/ lethargy, vomiting, elevated BUN, elevated creatinine, renal insufficiency/ failure, diarrhea, weight loss, dehydration.
In some cases, death has been reported. Some of these cases involved patients that developed renal failure/renal insufficiency.
To report suspected adverse drug events and for technical assistance, contact Elanco US Inc. at 1-888-545-5973.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth.
Information for Cat Owners:
ONSIOR, like other drugs of its class, is not free from adverse reactions. Owners should be advised of the potential for adverse reactions and be informed of the clinical signs associated with drug intolerance. Adverse reactions may include vomiting, diarrhea, decreased appetite, dark or tarry stools, increased water consumption, increased urination, anemia, yellowing of gums, skin or white of the eye due to jaundice, lethargy, incoordination, seizure, or behavioral changes. Serious adverse reactions associated with this drug class can occur without warning and may result in death (see Warnings and Adverse Reactions). Owners should be advised to discontinue ONSIOR tablets and contact their veterinarian immediately if signs of intolerance are observed. The vast majority of patients with drug related adverse reactions have recovered when the signs are recognized, the drug is withdrawn, and veterinary care, if appropriate, is initiated.
Clinical Pharmacology:
In an inflammation model in cats, robenacoxib had analgesic, antiinflammatory and anti-pyretic actions with a rapid onset of action (0.5 h).1 In an in vitro whole blood assay in cats, robenacoxib demonstrated selective COX-2 inhibition.2 The clinical relevance of this data has not been shown. Robenacoxib is an analog of diclofenac.
Absorption
After oral administration of robenacoxib tablets at 1 mg/kg without food, peak blood concentrations are attained rapidly with a median Tmax of 0.5 h, a mean Cmax of 1159 ng/ml and a mean AUC of 1337 ng.h/ml.
Co-administration of robenacoxib tablets with one third of the daily food ration produced no change in median Tmax (0.5 h), mean Cmax (1201 ng/ml) or mean AUC (1383 ng.h/ml). Co-administration of robenacoxib tablets with the entire daily food ration produced no delay in median Tmax (0.5 h), but a lower mean Cmax (691 ng/ml) and a lower mean AUC (1069 ng.h/ml). The systemic mean bioavailability of robenacoxib tablets was 49% without food. The pharmacokinetics of robenacoxib does not differ between male and female cats.
Distribution
Robenacoxib has a relatively small volume of distribution (mean Vss = 190 ml/kg) and is highly bound to plasma proteins (>99%). Robenacoxib persists longer in the inflammatory exudate of a tissue cage model than in blood. The median robenacoxib elimination half-life in exudate was about 27 hours versus 2.5 hours for blood.
Metabolism
Robenacoxib is extensively metabolized by the liver in cats. The systemic exposure of lactam metabolite is about 25% of robenacoxib exposure following oral administration to fed cats. Further, the systemic exposure to lactam appears to be two-fold greater in fed cats than fasted cats. Apart from one lactam metabolite, the identity of other metabolites is not known in cats.
Elimination
Robenacoxib is rapidly cleared from blood (mean clearance [CL] = 0.44 L kg/h) with an elimination mean half-life (t1/2) of 1.1 hours after intravenous administration. After oral administration of tablets, the terminal mean t1/2 from blood was 1.7 hours. Elimination, occurs predominantly through the biliary route (fecal and urinary excretion are 60 and 16.5% respectively).
Animal Safety:
21 Day Target Animal Safety Study: In a 21-day laboratory tolerance study, 8 month-old healthy, DSH cats (4/sex/group) were administered robenacoxib at a dose of 0 mg/kg or 24 mg/kg/day (10X the maximum exposure based on the single, 6 mg tablet size). All cats survived to study termination. Vomiting and decreased activity was noted in some of the treated cats. Two cats in the 10X group exhibited abnormal rear limb neurologic function. One of these cats also exhibited a head tilt and nystagmus at the end of the study. Mean food consumption was less in the 10X group. The mean kidney weights were lower in the 10X group compared to the control group; and the mean thymus weights were also lower in the 10X group compared to the controls. Two cats in the 10X group had chronic interstitial nephritis on histopathology. One 10X cat had a focal cecal/large intestinal erosion. One 10X cat and one control cat had periportal, multifocal necrosis in one lobe of the liver. There were four 10X cats and 2 control cats with renal tubular degeneration. Under the conditions of this study, robenacoxib was well tolerated when administered at 24 mg/kg/day for 21 days, except for 2 cats in the 10X group with neurologic signs.
42 Day Target Animal Safety Study:
In a 42 day study, 8 month-old, healthy cats were administered robenacoxib at 0, 2, 6 or 10 mg/kg/twice daily. Small thymuses were noted in all robenacoxib- treated groups with corresponding organ weight decreases and/or atrophic changes on histopathology. There was a decrease in the kidney weights in the 10 mg/kg/twice daily-group compared to the controls. Vomiting was the most common adverse reaction noted in the treated cats. An adequate safety margin was demonstrated for ONSIOR tablets when administered under the conditions of this 42-day study.
6 Month Target Animal Safety Study:
In a 6 month study, 8 month-old, healthy cats (4/sex/group) were administered robenacoxib at 0, 1X (2.4 mg/kg), 3X (7.2 mg/kg) or 5X (12 mg/kg) once daily. One 5X cat had clonic seizures on Day 115 and was ataxic on Day 175. One 5X cat had skin cold to the touch on Day 106. One cat in the 1X group experienced urethral obstruction/FLUTD. Vomiting, decreased activity, injected sclera and soft stools were the most common adverse reactions observed in the treated groups. Soft stools and injected sclera were also observed in the control group.
The mean body weights in the 1X and 3X groups were lower than the controls from Day 21 – Day 182; and lower in the 5X group from Day 28 – Day 182. There was a clear dose-related and possibly time-related increase in the QTc interval at Day 41 and Day 175, particularly in the 3X and 5X groups, no other ECG abnormalities were noted.
There was no obvious accumulation in Cmax or AUC between Days 1, 31 and 171, and there was no apparent difference in parameters between males and females. The following parameters were calculated for the 1X dosage: Tmax was 0.5 h (median), the dose-normalized mean Cmax was 668 ng/mL and the dose-normalized mean area under the curve (AUC(0-inf)) was 902 h*ng/mL. Similarly, the following parameters were calculated for the 3X dosage: Tmax was 0.5 h (median), the dose-normalized mean Cmax was 1019 ng/mL and the dose-normalized mean area under the curve (AUC(0-inf)) was 1394 h*ng/mL. For the 5X dosage the following parameters were calculated: Tmax was 1.0 h (median), the dose-normalized mean Cmax was 1198 ng/mL and the dose-normalized mean area under the curve (AUC(0-inf)) was 1884 h*ng/mL. A post hoc analysis of PK parameters revealed that dose normalized Cmax and AUC were greater than dose proportional.
The mean kidney weights were lower in all robenacoxib-treated groups. One 5X cat with decreased kidney weight and size also had transient increases in BUN and creatinine. There were transient increases in AST, amylase, and ALT in the 3X and 5X cats from Day 30 – Day 183. There was an increased severity of the tubular degeneration/regeneration in the kidneys of two 1X and two 5X cats with inflammation, papillary necrosis and papillary mineralization.
An increased incidence of minimal to mild Kupffer cell pigmentation was observed in the livers of all robenacoxib-treated cats; however, no hepatocellular damage was noted on histopathology. One 5X cat had a focal, minimal ulcer of the gastric fundus (peptic and parietal cells).
This 6 month safety study supports the safe use of ONSIOR tablets for the control of postoperative pain and inflammation associated with orthopedic surgery, ovariohysterectomy and castration in cats for a maximum of 3 days.
-
Interchangeable Use Safety Study:
ONSIOR was administered orally (6 mg tablets) and subcutaneously (20 mg/mL solution) to 4-month old healthy cats at 0, 1, 2, and 3 times the labeled doses (1X = 2.4 mg/kg/day orally based on the inherent tablet dose band or 2.0 mg/kg/day subcutaneously). Interchangeable use was evaluated by alternating three 7-day oral tablet/3-day subcutaneous injection cycles followed by one final 7-day oral tablet dosing cycle. All cats survived until study termination. Findings included: elevated creatine kinase levels on Days 13 and 37, soft stools, histologic observation of a minimal oral (tongue) ulceration in a 1X cat, injection site edema for up to 120 hours prior to resolution, and a prolonged QT interval in treated cats as compared to the controls on Day 36. There was a dose dependent and statistically significant increase in the QT interval at all three ONSIOR tablets/ONSIOR injection treatment levels. It is unknown if the increased QT interval suggests an elevated risk of ventricular arrhythmia or torsade de pointes in cats. In addition, a longer PR interval was noted in 1X group females on Day 36 compared to the controls. One 2X cat vomited twice during the last 2 dosing days. Histologically, the injection sites had minimal or mild, subacute/chronic inflammation. Inflammation at the injection sites was observed in both treated and control animals with a greater frequency in the higher dose groups than in the control and 1X groups.
Dose-normalized AUC and concentration levels were higher following the oral route than the subcutaneous route. There was no significant accumulation following once daily administration. One 2X-treated cat had a 7-fold increase in buccal mucosal bleeding time (BMBT) during the treatment period compared to the pre-treatment value.
-
Effectiveness:
Effectiveness was demonstrated using ONSIOR tablets in a masked, placebo-controlled, multi-site field study involving client-owned cats. In this study, 249 cats presenting for ovariohysterectomy or castration in conjunction with an onychectomy (forelimbs only) were randomly administered ONSIOR tablets, or a placebo. Drug was administered approximately 30 minutes prior to surgery along with pre-anesthetic medications and continued once daily for two additional treatments. Effectiveness was evaluated in 244 cats and field safety was evaluated in 249 cats. A statistically significant difference in the proportion of treatment successes in the ONSIOR tablets treatment group (137/164 or 83.5%) compared to the placebo, vehicle control group (43/80 or 53.8%) was observed. Twenty-seven out of 164 robenacoxib cases (16.5%) and 37 out of 80 placebo cases (46.2%) were treatment failures. Statistically significant differences for pain elicited on palpation at the spay or castration incision site, behavior following social interaction and posture score at various post-surgical time points were also observed. The results of the field study demonstrate that ONSIOR tablets, when administered for a maximum of three days, are effective and well-tolerated for the control of postoperative pain associated with onychectomy, ovariohysterectomy and castration in cats.
-
How Supplied:
ONSIOR tablets are available as 6 mg round flavored tablets in blisters and are supplied in blister cards containing 3 tablets. The blister cards are supplied in a veterinary carton containing 10 blister cards and are to be dispensed 1 card per patient in an ONSIOR tablets dispensing envelope containing veterinary insert and owner information sheet, supplied with the product.
-
Storage Conditions:
Store at controlled room temperature, between 59° and 77°F (15-25°C).
Manufactured for: Elanco US Inc. Greenfield, IN 46140, USA
References:
1Giraudel, J.M., King J.N., Jeunesse, E.C., Lees, P. & Toutain, P.L. (2008). Use of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic approach in the cat to determine a dosage regimen for the COX-2 selective drug robenacoxib. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 2009;32:18-30.
2Giraudel, J.M., Toutain, P.L., King J.N., & Lees, P. Differential inhibition of cyclooxygenase isoenzymes in the cat by the COX-2 selective drug robenacoxib. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 2009;32:31-40.
NADA # 141-320, Approved by FDA
Elanco, Onsior and the diagonal bar are trademarks owned or licensed by Eli Lilly and Company, its subsidiaries or affiliates.
-
INFORMATION FOR OWNERS/CAREGIVERS
onsior™
(robenacoxib)
6 mg Tablets for CatsFor Oral Use In Cats Only
Information for Cat Owners – You should read this information before starting your cat on ONSIOR tablets.
What is ONSIOR?
ONSIOR (robenacoxib) is a prescription non-narcotic, non-steroidal antiinflammatory (NSAID) of the coxib class. ONSIOR (robenacoxib) is for the control of postoperative pain and inflammation associated with orthopedic surgery (declaw), ovariohysterectomy (spay) and castration (neuter) in cats greater than or equal to 5.5 pounds (2.5 kg) and greater than or equal to 4 months of age; for a maximum of 3 days. Do not use in cats less than 5.5 lbs.
Your cat may have received one or more doses of ONSIOR tablets or injection in the hospital. Your cat should not receive more than one dose a day, for a maximum of 3 total doses. Follow the instructions given to you by your veterinarian.
This summary contains important information about ONSIOR but does not take the place of instructions from your veterinarian. Talk to your veterinarian if you do not understand any of this information or if you want to know more about ONSIOR for cats.
What kind of results can I expect when my cat takes ONSIOR for postoperative pain and inflammation?
ONSIOR may help your cat to recover more comfortably by controlling postoperative pain and inflammation following orthopedic (declaw), ovariohysterectomy (spay), or castration surgery (neuter).
- Control of postoperative pain and inflammation may vary from cat to cat.
- Administer ONSIOR tablets according to your veterinarian‘s directions, for a maximum of 3 days.
- Consult your veterinarian if your cat appears to be uncomfortable.
What cats should not take ONSIOR?
Your cat should not be given ONSIOR if s/he:
- Has had an allergic reaction to robenacoxib, the active ingredient in ONSIOR for cats
- Has had an allergic reaction (such as hives, facial swelling, or red or itchy skin) to aspirin or other NSAIDs
- Is less than 5.5 lbs or less than 4 months of age
- Has a loss of appetite/decreased appetite
- Has bloody stool or vomit
- Is presently taking aspirin, other NSAIDs, or corticosteroids
- Has a pre-existing kidney or liver condition Has any condition predisposing to dehydration
ONSIOR tablets should only be given to cats.
People should not take ONSIOR tablets. Keep ONSIOR tablets and all medication out of reach of children. Call your physician immediately if you accidentally take ONSIOR tablets.
Tell your veterinarian about:
- Any side effects your cat has previously experienced from ONSIOR or other NSAIDs
- Any digestive upset (vomiting or diarrhea) your cat has had
- Any cardiovascular, kidney or liver disease your cat has had
- Any other medical problems or allergies that your cat has now or has had in the past
- All medications that you are giving your cat or plan to give your cat, including those you can get without prescription and any dietary supplements If you plan to breed your cat, or if your cat is pregnant or nursing
Talk to your veterinarian about:
- The surgery procedure performed on your cat
- What tests should be done before surgery and prior to administering ONSIOR
- The signs of postoperative pain or inflammation that may occur following surgery
- Normal events that can be expected after your cat undergoes surgery
- How often your cat may need to be examined by your veterinarian
- The risks and benefits of using ONSIOR
How to give ONSIOR tablets to your cat.
ONSIOR tablets should be given according to your veterinarian‘s instructions. Your veterinarian will tell you what amount of ONSIOR tablets is right for your cat. ONSIOR tablets should only be given once a day and for no longer than 3 days. ONSIOR tablets should not be broken. ONSIOR tablets should be given by mouth and may be given with or without food.
What are the possible side effects that may occur in my cat during therapy with ONSIOR tablets?
ONSIOR tablets may cause some side effects in individual cats. These are normally mild, but serious side effects have been reported in cats taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) including ONSIOR tablets. Serious side effects can result in death. It is important to stop the medication and contact your veterinarian immediately if you think your cat may have a medical problem or side effect while on ONSIOR tablets. If you have additional questions about possible side effects, talk with your veterinarian or call Elanco US Inc. at 1-888-545-5973.
Look for the possible following side effects that may indicate that your cat is having a problem: Decrease in appetite
- Vomiting
- Change in bowel movements such as diarrhea or change in stool color
- Change in drinking or urination
- Change in behavior, such as depression or restlessness
If any of the above signs are noticed in your cat, stop administering ONSIOR tablets and call your veterinarian.
Can ONSIOR tablets be given with other medications?
ONSIOR tablets should not be given with other non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs – i.e. aspirin, meloxicam) or corticosteroids (i.e. prednisone).
Always tell your veterinarian about all medications that you have given your cat in the past, and any medications that you are planning to give with ONSIOR tablets.
What can I do in case my cat eats more than the prescribed amount of ONSIOR tablets?
Contact your veterinarian immediately if your cat eats more than the prescribed amount of ONSIOR tablets.
What else should I know about ONSIOR tablets?
This sheet provides a summary of information about ONSIOR tablets. If you have any questions or concerns about ONSIOR or postoperative pain and inflammation, talk to your veterinarian.
As with all prescribed medications, ONSIOR tablets should only be given to the cat for which they are prescribed. They should be given to your cat only for the condition for which they were prescribed, at the prescribed dose, as directed by your veterinarian.
NADA 141-320, Approved by FDA
Elanco, Onsior and the diagonal bar are trademarks owned or licensed by Eli Lilly and Company, its subsidiaries or affiliates.
Rev. 03/2015
- Principal Display Panel - Onsior Cat 6 mg Blister Label
-
Principal Display Panel - Onsior Cat 6 mg Carton Label
Indication: For the control of postoperative pain and inflammation associated
with orthopedic surgery, ovariohysterectomy and castration, in cats ≥
5.5 lbs (2.5 kg) and ≥ 4 months of age; for up to a maximum of 3 days.See product insert for complete information.
onsior™
(robenacoxib)
6 mg
6 mg per
tabletKeep this and all drugs out
of the reach of children.Elanco™
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ONSIOR
robenacoxib tabletProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 58198-4875 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength robenacoxib (UNII: Z588009C7C) (robenacoxib - UNII:Z588009C7C) robenacoxib 6 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POVIDONES (UNII: FZ989GH94E) CROSPOVIDONE (15 MPA.S AT 5%) (UNII: 68401960MK) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color BROWN (speckled brown, white or tan) Score no score Shape ROUND (ROUND) Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code NA;AK Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58198-4875-1 10 in 1 CARTON 1 3 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141320 04/01/2012 Labeler - Elanco US Inc, (966985624)
Trademark Results [Onsior]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ONSIOR 87234459 5214181 Live/Registered |
ELANCO US INC. 2016-11-11 |
 ONSIOR 79024304 3223362 Dead/Cancelled |
Novartis Tiergesundheit AG 2006-04-20 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.