PYRIDOSTIGMINE BROMIDE tablet, extended release
Pyridostigmine Bromide by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Pyridostigmine Bromide by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Alvogen, Inc., Norwich Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Pyridostigmine bromide is an orally active cholinesterase inhibitor. Chemically, pyridostigmine bromide is 3-hydroxy-1-methylpyridinium bromide dimethylcarbamate. Its chemical formula is C9H13BrN2O2, molecular weight 261.12. Its structural formula is:
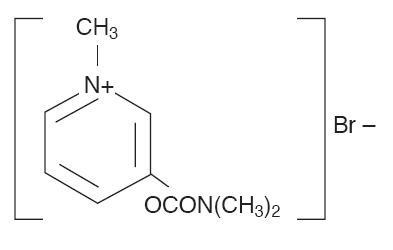
Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets contain 180 mg pyridostigmine bromide. Inactive Ingredients: carnuba wax, zein, calcium phosphate, colloidal silicon dioxide, and magnesium stearate.
-
ACTIONS
Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets inhibits the destruction of acetylcholine by cholinesterase and thereby permits freer transmission of nerve impulses across the neuromuscular junction. Pyridostigmine is an analog of neostigmine, but differs from it in certain clinically significant respects; for example, pyridostigmine is characterized by a longer duration of action and fewer gastrointestinal side effects.
- INDICATION
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets is contraindicated in mechanical intestinal or urinary obstruction, and particular caution should be used in its administration to patients with bronchial asthma. Care should be observed in the use of atropine for counteracting side effects, as discussed below.
-
WARNINGS
Although failure of patients to show clinical improvement may reflect underdosage, it can also be indicative of overdosage. As is true of all cholinergic drugs, overdosage of Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets may result in cholinergic crisis, a state characterized by increasing muscle weakness which, through involvement of the muscles of respiration, may lead to death. Myasthenic crisis due to an increase in the severity of the disease is also accompanied by extreme muscle weakness, and thus may be difficult to distinguish from cholinergic crisis on a symptomatic basis. Such differentiation is extremely important, since increases in doses of Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets or other drugs of this class in the presence of cholinergic crisis or of a refractory or "insensitive" state could have grave consequences. Osserman and Genkins1 indicate that the differential diagnosis of the two types of crisis may require the use of edrophonium chloride as well as clinical judgment. The treatment of the two conditions obviously differs radically. Whereas the presence of myasthenic crisis suggests the need for more intensive anticholinesterase therapy, the diagnosis of cholinergic crisis, according to Osserman and Genkins,1 calls for the prompt withdrawal of all drugs of this type. The immediate use of atropine in cholinergic crisis is also recommended. Atropine may also be used to abolish or obtund gastrointestinal side effects or other muscarinic reactions; but such use, by masking signs of overdosage, can lead to inadvertent induction of cholinergic crisis.
For detailed information on the management of patients with myasthenia gravis, the physician is referred to one of the excellent reviews such as those by Osserman and Genkins,2 Grob3 or Schwab.4,5
Usage in Pregnancy
The safety of Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets during pregnancy or lactation in humans has not been established. Therefore, use of Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets in women who may become pregnant requires weighing the drug's potential benefits against its possible hazards to mother and child.
- PRECAUTION
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The side effects of Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets are most commonly related to overdosage and generally are of two varieties, muscarinic and nicotinic. Among those in the former group are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, increased peristalsis, increased salivation, increased bronchial secretions, miosis and diaphoresis. Nicotinic side effects are comprised chiefly of muscle cramps, fasciculation and weakness. Muscarinic side effects can usually be counteracted by atropine, but for reasons shown in the preceding section the expedient is not without danger. As with any compound containing the bromide radical, a skin rash may be seen in an occasional patient. Such reactions usually subside promptly upon discontinuance of the medication.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Each Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablet contains 180 mg pyridostigmine bromide. This form provides uniformly slow release, hence prolonged duration of drug action; it facilitates control of myasthenic symptoms with fewer individual doses daily. The immediate effect of a 180 mg Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablet is about equal to that of a 60 mg pyridostigmine bromide tablet; however, its duration of effectiveness, although varying in individual patients, averages 2½ times that of a 60 mg dose.
Dosage
The size and frequency of the dosage must be adjusted to the needs of the individual patient. One to three Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets, 180 mg, once or twice daily, will usually be sufficient to control symptoms; however, the needs of certain individuals may vary markedly from this average. The interval between doses should be at least 6 hours. For optimum control, it may be necessary to use the more rapidly acting tablets or syrup in conjunction with Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets therapy.Note: For information on a diagnostic test for myasthenia gravis, and for the evaluation and stabilization of therapy, please see product literature on edrophonium chloride.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets, 180 mg, are supplied in bottles of 30 tablets, NDC: 47781-335-30.
Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets are available as a cream to yellow, capsule-shaped tablet, containing 180 mg pyridostigmine bromide, debossed “335” on one side and has functional scoring on the other side.
Storage
Store Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C-30°C (59°F-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets in a dry place with the silica gel (desiccant) enclosed.
Note: Because of the hygroscopic nature of the Pyridostigmine Bromide Extended release Tablets, mottling may occur. This does not affect their efficacy.
-
REFERENCES
1 Osserman KE, Genkins G. Studies in myasthenia gravis: Reduction in mortality rate after crisis. JAMA. Jan 1963; 183:97-101.
2 Osserman KE, Genkins G. Studies in myasthenia gravis. NY State J Med. June 1961; 61:2076-2085.
3 Grob D. Myasthenia gravis. A review of patho-genesis and treatment. Arch Intern Med. Oct 1961; 108:615-638.
4 Schwab RS. Management of myasthenia gravis. New Eng J Med. Mar 1963; 268:596-597.
5 Schwab RS. Management of myasthenia gravis. New Eng J Med. Mar 1963; 268:717-719.
6 Cronnelly R, Stanski DR, Miller RD, Sheiner LB. Pyridostigmine kinetics with and without renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980; 28:No. 1, 78-81.
7 Miller RD. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of anticholinesterase. In: Ruegheimer E, Zindler M, ed. Anaesthesiology. (Hamburg, Germany: Congress; Sep 14-21, 1980; 222-223.) (Int Congr. No. 538), Amsterdam, Netherlands: Excerpta Medica; 1981.
8 Breyer-Pfaff U, Maier U, Brinkmann AM, Schumm F. Pyridostigmine kinetics in healthy subjects and patients with myasthenia gravis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985;5:495-501.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PYRIDOSTIGMINE BROMIDE
pyridostigmine bromide tablet, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 47781-335 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PYRIDOSTIGMINE BROMIDE (UNII: KVI301NA53) (PYRIDOSTIGMINE - UNII:19QM69HH21) PYRIDOSTIGMINE BROMIDE 180 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CARNAUBA WAX (UNII: R12CBM0EIZ) ZEIN (UNII: 80N308T1NN) CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 97Z1WI3NDX) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color YELLOW Score 2 pieces Shape CAPSULE Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code 335 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 47781-335-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/29/2015 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA204737 06/29/2015 Labeler - Alvogen, Inc. (008057330) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Norwich Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 132218731 analysis(47781-335) , manufacture(47781-335) , pack(47781-335)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
