PILOCARPINE HYDROCHLORIDE OPHTHALMIC- pilocarpine hydrochloride solution/ drops
Pilocarpine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Pilocarpine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Amneal Pharmaceuticals NY LLC, Amneal Pharmaceuticals Private Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PILOCARPINE HYDROCHLORIDE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION 1.25% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PILOCARPINE HYDROCHLORIDE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION 1.25%.
PILOCARPINE HYDROCHLORIDE ophthalmic solution 1.25%, for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1974
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Pilocarpine hydrochloride is a cholinergic muscarinic receptor agonist indicated for the treatment of presbyopia in adults. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Instill one drop of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution 1.25% in each eye once daily. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Ophthalmic solution containing pilocarpine hydrochloride USP, 1.25%. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Blurred Vision: Patients should be advised not to drive or operate machinery if vision is not clear (e.g., blurred vision). Exercise caution in night driving and other hazardous activities in poor illumination. (5.1)
Risk of Retinal Detachment: Rare cases of retinal detachment and retinal tear have been reported with miotics, including pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. Individuals with pre-existing retinal disease are at increased risk. Therefore, examination of the retina is advised in all patients prior to initiation of therapy. Patients should be advised to seek immediate medical care with sudden onset of flashing lights, floaters or vision loss. (5.2)
Iritis: Caution is advised in patients with iritis. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (> 5%) are headache, conjunctival hyperemia and eye irritation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC at 1-877-835-5472 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Blurred Vision
5.2 Risk of Retinal Detachment
5.3 Iritis
5.4 Use with Contact Lenses
5.5 Potential for Eye Injury or Contamination
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Blurred Vision
Miotics, including pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, may cause accommodative spasm. Patients should be advised not to drive or operate machinery if vision is not clear (e.g., blurred vision).
In addition, patients may experience temporary dim or dark vision with miotics, including pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. Patients should be advised to exercise caution in night driving and other hazardous activities in poor illumination.
5.2 Risk of Retinal Detachment
Rare cases of retinal detachment and retinal tear have been reported with miotics, including pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution.
Individuals with pre-existing retinal disease are at increased risk. Therefore, examination of the retina is advised in all patients prior to the initiation of therapy.
Patients should be advised to seek immediate medical care with sudden onset of flashing lights, floaters or vision loss.
5.3 Iritis
Pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution is not recommended to be used when iritis is present because adhesions (synechiae) may form between the iris and the lens.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
- Hypersensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution dosed once daily was evaluated in 375 participants with presbyopia in two randomized, double-masked, vehicle-controlled studies (GEMINI 1 and GEMINI 2) of 30 days duration. The most common adverse reactions reported in > 5% of participants were headache and conjunctival hyperemia. Ocular adverse reactions reported in 1% to 5% of participants were blurred vision, eye pain, visual impairment, eye irritation and increased lacrimation.
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution exposure.
Eye disorders: vitreous detachment, vitreomacular traction, retinal tear, retinal detachment.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution administration in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. Oral administration of pilocarpine to pregnant rats throughout organogenesis and lactation did not produce adverse effects at clinically relevant doses.
Data
Human Data
No adequate and well-controlled trials of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution have been conducted in pregnant women. In a retrospective case series of 15 women with glaucoma, 4 patients used ophthalmic pilocarpine either pre-pregnancy, during pregnancy or postpartum. There were no adverse effects observed in patients or in their infants.
Animal Data
In embryofetal development studies, oral administration of pilocarpine to pregnant rats throughout organogenesis produced maternal toxicity, skeletal anomalies and reduction in fetal body weight at 90 mg/kg/day (approximately 485-fold higher than the maximum human ophthalmic dose [MHOD] of 0.015 mg/kg/day, on a mg/m2 basis).
In a peri-/postnatal study in rats, oral administration of pilocarpine during late gestation through lactation increased stillbirths at a dose of 36 mg/kg/day (approximately 195-fold higher than the MHOD). Decreased neonatal survival and reduced mean body weight of pups were observed at ≥ 18 mg/kg/day (approximately 100 times the maximum human ophthalmic dose of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of pilocarpine in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infants or the effects on milk production to inform risk of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution to an infant during lactation.
Pilocarpine and/or its metabolites are excreted in the milk of lactating rats. Systemic levels of pilocarpine following topical ocular administration are low [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] and it is not known whether measurable levels of pilocarpine would be present in maternal milk following topical ocular administration.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution.
Data
Animal Data
Following a single oral administration of 14C-pilocarpine to lactating rats, the radioactivity concentrations in milk were similar to those in plasma.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution did not include participants aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger participants. Other reported clinical experience with ophthalmic pilocarpine solutions have not identified overall differences in safety between elderly and younger participants.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Systemic toxicity following topical ocular administration of pilocarpine is rare, but occasionally patients who are sensitive may develop sweating and gastrointestinal overactivity. Accidental ingestion can produce sweating, salivation, nausea, tremors and slowing of the pulse and a decrease in blood pressure. In moderate overdosage, spontaneous recovery is to be expected and is aided by intravenous fluids to compensate for dehydration. For patients demonstrating severe poisoning, atropine, the pharmacologic antagonist to pilocarpine, should be used.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution USP, 1.25% is a cholinergic muscarinic receptor agonist prepared as an isotonic, clear, colorless, sterile ophthalmic solution containing 1.25% of pilocarpine hydrochloride, USP. The chemical name for pilocarpine hydrochloride, USP is (3S,4R)-3-ethyl-4-[(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]-oxolan-2-one hydrochloride. Its molecular weight is 244.72 g/mol and its molecular formula is C11H16N2O2 · HCl. Its structural formula is:
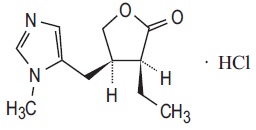
Pilocarpine hydrochloride, USP is a white or almost white, crystalline powder or colorless crystals hygroscopic. It is very soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol, slightly soluble in chloroform and insoluble in ether.
Each mL of Pilocarpine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution, USP contains:
Active: Pilocarpine hydrochloride USP, 1.25% (12.5 mg) equivalent to 1.06% (10.6 mg) pilocarpine free-base.
Preservative: Benzalkonium chloride, 0.0075%.
Inactives: Boric acid, sodium citrate dihydrate, sodium chloride, water for injection and may also include hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment to between 3.5 and 5.5, if necessary.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Pilocarpine hydrochloride is a cholinergic muscarinic agonist which activates muscarinic receptors located at smooth muscles such as the iris sphincter muscle and ciliary muscle. Pilocarpine hydrochloride contracts the iris sphincter muscle, constricting the pupil to improve near and intermediate visual acuity while maintaining some pupillary response to light. Pilocarpine hydrochloride also contracts the ciliary muscle and may shift the eye to a more myopic state.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Systemic exposure to pilocarpine was evaluated in 22 participants with presbyopia who were administered 1 drop of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution in each eye once daily for 30 days (GEMINI 1). The mean (SD) Cmax and AUC values from time 0 to last measurable concentration over 10-hour period post-last dose on Day 30 were 1.95 (0.98) ng/mL and 4.14 (2.16) ng·hr/mL, respectively. The median Tmax value on Day 30 was 0.3 hours post-dose with a range from 0.2 hours to 0.5 hours post-dose.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Pilocarpine did not induce tumors in mice at any dosage level studied (up to 30 mg/kg/day; approximately 80-times the MHOD). In rats, an oral dose of 18 mg/kg/day (approximately 100 times the MHOD), resulted in a statistically significant increase in the incidence of benign pheochromocytomas in both male and female rats and a statistically significant increase in the incidence of hepatocellular adenomas in female rats.
Mutagenesis
Pilocarpine did not show any potential to cause genetic toxicity in a series of studies that included:
1) bacterial assays (Salmonella and E. coli) for reverse gene mutations.
2) an in vitro chromosome aberration assay in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line.
3) an in vivo chromosome aberration assay (micronucleus test) in mice; and
4) a primary DNA damage assay (unscheduled DNA synthesis) in rat hepatocyte primary cultures.
Impairment of Fertility
Pilocarpine oral administration to male and female rats at a dosage of 18 mg/kg/day (100 times the MHOD) resulted in impaired reproductive function, including reduced fertility, decreased sperm motility and morphologic evidence of abnormal sperm. It is unclear whether the reduction in fertility was due to effects on males, females or both. In dogs, exposure to pilocarpine at a dosage of 3 mg/kg/day for 6 months resulted in evidence of impaired spermatogenesis (approximately 55 times the MHOD).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution dosed once daily for the treatment of presbyopia was demonstrated in two 30-Day Phase 3, randomized, double-masked, vehicle-controlled studies, namely GEMINI 1 (NCT03804268) and GEMINI 2 (NCT03857542). A total of 750 participants aged 40 years to 55 years old with presbyopia were randomized (375 to pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution group) in two studies and participants were instructed to administer one drop of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution or vehicle once daily in each eye.
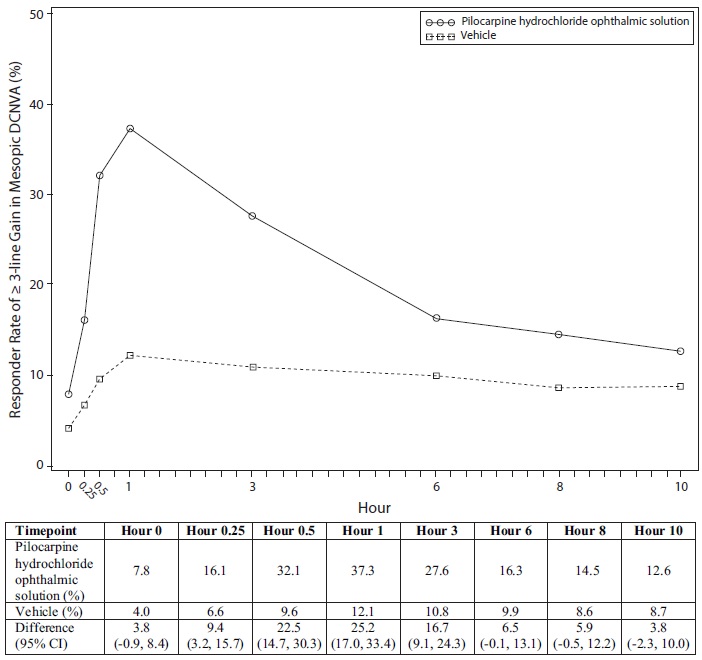
In both studies, the proportion of participants gaining 3 lines or more in mesopic, high contrast, binocular distance corrected near visual acuity (DCNVA), without losing more than 1 line (5 letters) of corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA) with the same refractive correction was statistically significantly greater in the pilocarpine hydrochloride group compared to the vehicle group at Day 30, Hour 3 (see Table 1).
Table 1: Primary Efficacy Results from GEMINI 1 and GEMINI 2 Studies (Intent-to-Treat Population)
GEMINI 1
GEMINI 2
Pilocarpine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution
N=163
Vehicle
N=160
p-value
Pilocarpine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution
N=212
Vehicle
N=215
p-value
Proportion of participants gaining 3-lines or more in mesopic DCNVA, without losing more than 1 line (5 letters) of CDVA at Day 30, Hour 3
31%
8%
p < 0.01
26%
11%
p < 0.01
Figures 1 and 2 present the proportion of participants who gained 3-lines or more in mesopic DCNVA at Day 30.
Figure 1: Proportion of Participants Achieving 3-Lines or More Improvement in Mesopic, High Contrast, Binocular DCNVA at Day 30 in GEMINI 1 (Intent-to-Treat Population)
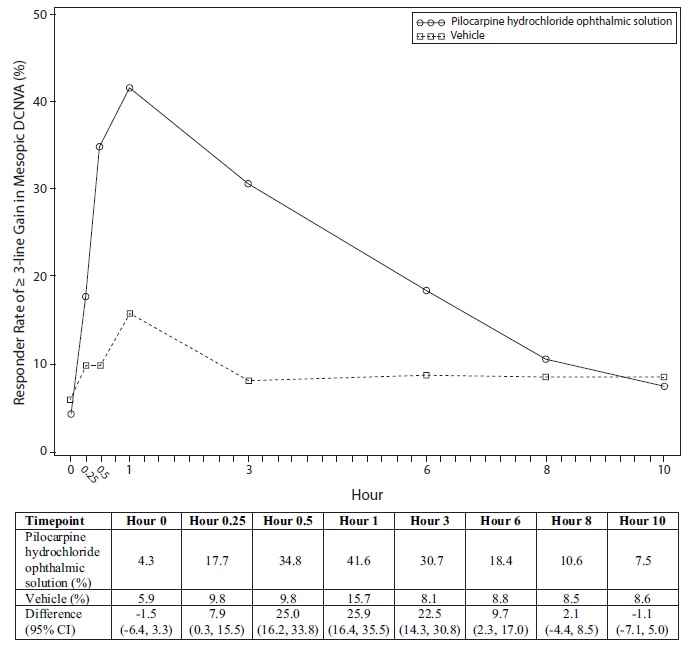
Figure 2: Proportion of Participants Achieving 3-lines or More Improvement in Mesopic, High Contrast, Binocular DCNVA at Day 30 in GEMINI 2 (Intent-to-Treat Population)
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Pilocarpine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution USP, 1.25% is supplied as a sterile, clear, colorless solution filled in low density polyethylene white opaque bottle and low density polyethylene white opaque nozzle with, dark green colored high density polyethylene cap. It is available as follows:
2.5 mL in 5 mL Bottle (Filled to 1/2 Capacity): NDC: 60219-2366-2
5 mL in 5 mL Bottle: NDC: 60219-2649-1
Storage
Store at 15° to 25°C (59° to 77°F). After opening, pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, USP can be used until the expiration date on the bottle.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Night Driving
Pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution may cause temporary dim or dark vision. Advise patients to exercise caution with night driving and when hazardous activities are undertaken in poor illumination [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Accommodative Spasm
Temporary problems when changing focus between near and distant objects may occur. Advise patients not to drive or use machinery if vision is not clear (e.g., blurred vision) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
When to Seek Physician Advice
Advise patients to seek immediate medical care with sudden onset of flashing lights, floaters or vision loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Contact Lens Wear
Contact lens should be removed prior to the instillation of pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. Wait 10 minutes after dosing before reinserting contact lenses [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Avoiding Contamination of the Product
Do not touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the contents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Concomitant Topical Ocular Therapy
If more than one topical ophthalmic medication is being used, the medicines must be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
Manufactured by:
Amneal Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
Ahmedabad 382213, INDIA
Distributed by:
Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807
Rev. 06-2025-01
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 60219-2366-2
Pilocarpine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution USP, 1.25% (2.5 mL)
Rx only
Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC


NDC: 60219-2649-1
Pilocarpine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution USP, 1.25% (5 mL)
Rx only
Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC


-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PILOCARPINE HYDROCHLORIDE OPHTHALMIC
pilocarpine hydrochloride solution/ dropsProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60219-2366 Route of Administration OPHTHALMIC Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PILOCARPINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 0WW6D218XJ) (PILOCARPINE - UNII:01MI4Q9DI3) PILOCARPINE HYDROCHLORIDE 12.5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BORIC ACID (UNII: R57ZHV85D4) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60219-2366-2 1 in 1 CARTON 05/01/2025 1 2.5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA217733 05/01/2025 PILOCARPINE HYDROCHLORIDE OPHTHALMIC
pilocarpine hydrochloride solution/ dropsProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60219-2649 Route of Administration OPHTHALMIC Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PILOCARPINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 0WW6D218XJ) (PILOCARPINE - UNII:01MI4Q9DI3) PILOCARPINE HYDROCHLORIDE 12.5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BORIC ACID (UNII: R57ZHV85D4) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60219-2649-1 1 in 1 CARTON 09/01/2025 1 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA217733 09/01/2025 Labeler - Amneal Pharmaceuticals NY LLC (123797875) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Amneal Pharmaceuticals Private Limited 860156658 analysis(60219-2366, 60219-2649) , manufacture(60219-2366, 60219-2649) , pack(60219-2366, 60219-2649) , sterilize(60219-2366, 60219-2649)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.