NITROGLYCERIN by Natco Pharma USA LLC / Natco Pharma Limited-Pharma Division NITROGLYCERIN tablet
NITROGLYCERIN by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
NITROGLYCERIN by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Natco Pharma USA LLC, Natco Pharma Limited-Pharma Division. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NITROGLYCERIN SUBLINGUAL TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NITROGLYCERIN SUBLINGUAL TABLETS.
NITROGLYCERIN sublingual tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1981
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets are a nitrate vasodilator indicated for relief of an attack or prophylaxis of angina pectoris due to coronary artery disease. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- At the onset of an attack, administer one tablet under the tongue or buccal pouch. One additional tablet may be administered every 5 minutes as needed. No more than 3 total tablets are recommended within a 15 minute period. (2)
- If chest pain persists after three tablets, seek prompt medical attention. (2)
- May be used prophylactically 5 to 10 minutes prior to engaging in activities that might precipitate an acute attack. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Sublingual tablets, 0.3 mg; 0.4 mg; 0.6 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Use of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors, such as avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil, or soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulators. (4.1, 7.1)
- Severe anemia (4.2)
- Increased intracranial pressure (4.3)
- Hypersensitivity to nitroglycerin sublingual tablets or to other nitrates or nitrites or any excipient (4.4)
- Circulatory failure and shock (4.5)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions occurring at a frequency greater than 2% are headache, dizziness and paresthesia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact NATCO PHARMA USA LLC at 1-201-786-6500 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Ergotamine: increased bioavailability of ergotamine. Avoid concomitant use. (7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2023
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 PDE-5-Inhibitors and sGC-Stimulators
4.2 Severe Anemia
4.3 Increased Intracranial Pressure
4.4 Hypersensitivity
4.5 Circulatory Failure and Shock
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Tolerance
5.2 Hypotension
5.3 Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy
5.4 Headache
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 PDE-5-Inhibitors and sGC-Stimulators
7.2 Ergotamine
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Signs and Symptoms, Methemoglobinemia
10.2 Treatment of Overdosage
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
PATIENT INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Administer one tablet under the tongue or in the buccal pouch at the first sign of an acute anginal attack. Allow tablet to dissolve without swallowing. One additional tablet may be administered every 5 minutes until relief is obtained. No more than three tablets are recommended within a 15-minute period. If the pain persists after a total of 3 tablets in a 15-minute period, or if the pain is different than is typically experienced, seek prompt medical attention.
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets may be used prophylactically 5 minutes to 10 minutes prior to engaging in activities that might precipitate an acute attack.
For patients with xerostomia, a small sip of water prior to placing the tablet under the tongue may help maintain mucosal hydration and aid dissolution of the tablet.
Administer nitroglycerin sublingual tablets at rest, preferably in the sitting position. - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 PDE-5-Inhibitors and sGC-Stimulators
Do not use nitroglycerin sublingual tablets in patients who are taking PDE-5 Inhibitors, such as avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil hydrochloride. Concomitant use can cause severe hypotension, syncope, or myocardial ischemia [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Do not use nitroglycerin sublingual tablets in patients who are taking the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators, such as riociguat. Concomitant use can cause hypotension.4.2 Severe Anemia
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets are contraindicated in patients with severe anemia (large doses of nitroglycerin may cause oxidation of hemoglobin to methemoglobin and could exacerbate anemia).
4.3 Increased Intracranial Pressure
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets may precipitate or aggravate increased intracranial pressure and thus should not be used in patients with possible increased intracranial pressure (e.g., cerebral hemorrhage or traumatic brain injury).
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Tolerance
Excessive use may lead to the development of tolerance. Only the smallest dose required for effective relief of the acute angina attack should be used. A decrease in therapeutic effect of sublingual nitroglycerin may result from use of long-acting nitrates.
5.2 Hypotension
Severe hypotension, particularly with upright posture, may occur with small doses of nitroglycerin particularly in patients with constrictive pericarditis, aortic or mitral stenosis, patients who may be volume-depleted, or are already hypotensive. Hypotension induced by nitroglycerin may be accompanied by paradoxical bradycardia and increased angina pectoris. Symptoms of severe hypotension (nausea, vomiting, weakness, pallor, perspiration and collapse/syncope) may occur even with therapeutic doses.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail elsewhere in the label:
- Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Headache [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hypersensitivity [see Contraindications (4.4)]
Vertigo, dizziness, weakness, palpitation, and other manifestations of postural hypotension may develop occasionally, particularly in erect, immobile patients. Marked sensitivity to the hypotensive effects of nitrates (manifested by nausea, vomiting, weakness, diaphoresis, pallor, and collapse) may occur at therapeutic doses. Syncope due to nitrate vasodilatation has been reported.
Flushing, drug rash, and exfoliative dermatitis have been reported in patients receiving nitrate therapy.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 PDE-5-Inhibitors and sGC-Stimulators
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets are contraindicated in patients who are using a selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5). PDE-5-Inhibitors such as avanafil, sildenafil, vardenafil, and tadalafil have been shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of organic nitrates.
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets are contraindicated in patients who are taking soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulators. Concomitant use can cause hypotension.
The time course and dose dependence of these interactions have not been studied, and use within a few days of one another is not recommended. Appropriate supportive care for the severe hypotension has not been studied, but it seems reasonable to treat this as a nitrate overdose, with elevation of the extremities and with central volume expansion.
7.2 Ergotamine
Oral administration of nitroglycerin markedly decreases the first-pass metabolism of dihydroergotamine and subsequently increases its oral bioavailability. Ergotamine is known to precipitate angina pectoris. Therefore, patients receiving sublingual nitroglycerin should avoid ergotamine and related drugs or be monitored for symptoms of ergotism if this is not possible.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk summary
Limited published data on the use of nitroglycerin are insufficient to determine a drug associated risk of major birth defects or miscarriage. In animal reproduction studies, there were no adverse developmental effects when nitroglycerin was administered intravenously to rabbits or intraperitoneally to rats during organogenesis at doses greater than 64-times the human dose (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
No embryotoxic or postnatal development effects were observed with transdermal application in pregnant rabbits and rats at doses up to 80 mg/kg/day and 240 mg/kg/day, respectively, at intraperitoneal doses in pregnant rats up to 20 mg/kg/day from gestation day 7 to 17, and at intravenous doses in pregnant rabbits up to 4 mg/kg/day from gestation day 6 to 18.
8.2 Lactation
Risk summary
Sublingual nitroglycerin has not been studied in lactating women. It is not known if nitroglycerin is present in human milk or if nitroglycerin has effects on milk production.8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of nitroglycerin in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of nitroglycerin sublingual tablets did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Signs and Symptoms, Methemoglobinemia
Nitrate overdosage may result in: severe hypotension, persistent throbbing headache, vertigo, palpitation, visual disturbance, flushing and perspiring skin (later becoming cold and cyanotic), nausea and vomiting (possibly with colic and even bloody diarrhea), syncope (especially in the upright posture), methemoglobinemia with cyanosis and anorexia, initial hyperpnea, dyspnea and slow breathing, slow pulse (dicrotic and intermittent), heart block, increased intracranial pressure with cerebral symptoms of confusion and moderate fever, paralysis and coma followed by clonic convulsions, and possibly death due to circulatory collapse.
Case reports of clinically significant methemoglobinemia are rare at conventional doses of organic nitrates. The formation of methemoglobin is dose-related and in the case of genetic abnormalities of hemoglobin that favor methemoglobin formation, even conventional doses of organic nitrates could produce harmful concentrations of methemoglobin.10.2 Treatment of Overdosage
As hypotension associated with nitroglycerin overdose is the result of venodilatation and arterial hypovolemia, prudent therapy in this situation should be directed toward increase in central fluid volume. No specific antagonist to the vasodilator effects of nitroglycerin is known. Keep the patient recumbent in a shock position and comfortably warm. Passive movement of the extremities may aid venous return. Intravenous infusion of normal saline or similar fluid may also be necessary. Administer oxygen and artificial ventilation, if necessary. If methemoglobinemia is present, administration of methylene blue (1% solution), 1-2 mg per kilogram of body weight intravenously, may be required unless the patient is known to have G-6-PD deficiency. If an excessive quantity of nitroglycerin has been recently swallowed gastric lavage may be of use.
As epinephrine is ineffective in reversing the severe hypotensive events associated with overdosage, it is not recommended for resuscitation. -
11 DESCRIPTION
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets USP, are a stabilized sublingual compressed nitroglycerin tablet that contains 0.3 mg, 0.4 mg, or 0.6 mg nitroglycerin. The sublingual tablets also contain the inactive ingredients lactose monohydrate, glyceryl monostearate, pregelatinized corn starch, calcium stearate, and hydrophobic colloidal silica.
Nitroglycerin, an organic nitrate, is a vasodilating agent. The chemical name for nitroglycerin is 1, 2, 3 propanetriol trinitrate and the chemical structure is: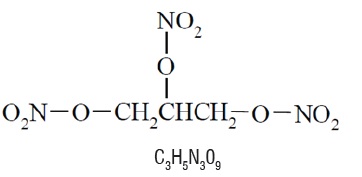
Molecular weight: 227.09
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Nitroglycerin forms free radical nitric oxide (NO) which activates guanylate cyclase, resulting in an increase of guanosine 3’5’ monophosphate (cyclic GMP) in smooth muscle and other tissues. These events lead to dephosphorylation of myosin light chains, which regulate the contractile state in smooth muscle, and result in vasodilatation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The principal pharmacological action of nitroglycerin is relaxation of vascular smooth muscle. Although venous effects predominate, nitroglycerin produces, in a dose-related manner, dilation of both arterial and venous beds. Dilation of postcapillary vessels, including large veins, promotes peripheral pooling of blood, decreases venous return to the heart, and reduces left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (preload).
Nitroglycerin also produces arteriolar relaxation, thereby reducing peripheral vascular resistance and arterial pressure (afterload), and dilates large epicardial coronary arteries; however, the extent to which this latter effect contributes to the relief of exertional angina is unclear.
Therapeutic doses of nitroglycerin may reduce systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial blood pressure. Effective coronary perfusion pressure is usually maintained, but can be compromised if blood pressure falls excessively, or increased heart rate decreases diastolic filling time.
Elevated central venous and pulmonary capillary wedge pressures, and pulmonary and systemic vascular resistance are also reduced by nitroglycerin therapy. Heart rate is usually slightly increased, presumably due to a compensatory response to the fall in blood pressure. Cardiac index may be increased, decreased, or unchanged. Myocardial oxygen consumption or demand (as measured by the pressure-rate product, tension-time index, and stroke-work index) is decreased and a more favorable supply-demand ratio can be achieved. Patients with elevated left ventricular filling pressures and increased systemic vascular resistance in association with a depressed cardiac index are likely to experience an improvement in cardiac index. In contrast, when filling pressures and cardiac index are normal, cardiac index may be slightly reduced following nitroglycerin administration.
Consistent with the symptomatic relief of angina, digital plethysmography indicates that onset of the vasodilatory effect occurs approximately 1 to 3 minutes after sublingual nitroglycerin administration and reaches a maximum by 5 minutes postdose. Effects persist for at least 25 minutes following nitroglycerin sublingual tablets administration.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Nitroglycerin is rapidly absorbed following sublingual administration of nitroglycerin sublingual tablets. Mean peak nitroglycerin plasma concentrations occur at a mean time of approximately 6 to 7 minutes postdose (Table 1). Maximum plasma nitroglycerin concentrations (Cmax) and area under the plasma concentration-time curves (AUC) increase dose-proportionally following 0.3 mg to 0.6 mg nitroglycerin sublingual tablets. The absolute bioavailability of nitroglycerin from nitroglycerin sublingual tablets is approximately 40% but tends to be variable due to factors influencing drug absorption, such as sublingual hydration and mucosal metabolism.
Table 1
Mean Nitroglycerin (SD) Values Parameter 2 × 0.3 mg
Nitroglycerin Sublingual Tablets1 × 0.6 mg
Nitroglycerin Sublingual TabletsCmax, ng/mL 2.3 (1.7) 2.1 (1.5) Tmax, min 6.4 (2.5) 7.2 (3.2) AUC(0–∞), min 14.9 (8.2) 14.9 (11.4) t½, min 2.8 (1.1) 2.6 (0.6) Distribution
The volume of distribution (VArea) of nitroglycerin following intravenous administration is 3.3 L/kg. At plasma concentrations between 50 ng/mL and 500 ng/mL, the binding of nitroglycerin to plasma proteins is approximately 60%, while that of 1,2-and 1,3-dinitroglycerin is 60% and 30%, respectively
Metabolism
A liver reductase enzyme is of primary importance in the metabolism of nitroglycerin to glycerol di-and mononitrate metabolites and ultimately to glycerol and organic nitrate. Known sites of extrahepatic metabolism include red blood cells and vascular walls. In addition to nitroglycerin, 2 major metabolites 1,2- and 1,3-dinitroglycerin, are found in plasma. Mean peak 1,2-and 1,3-dinitroglycerin plasma concentrations occur at approximately 15 minutes postdose. The elimination half-life of 1,2-and 1,3-dinitroglycerin is 36 and 32 minutes, respectively. The 1,2- and 1,3-dinitroglycerin metabolites have been reported to possess approximately 2% and 10%, respectively, of the pharmacological activity of nitroglycerin. Higher plasma concentrations of the dinitro metabolites, along with their nearly 10-fold longer elimination half-lives, may contribute significantly to the duration of pharmacologic effect. Glycerol mononitrate metabolites of nitroglycerin are biologically inactive.
Elimination
Nitroglycerin plasma concentrations decrease rapidly, with a mean elimination half-life of 2 to 3 minutes. Half-life values range from 1.5 to 7.5 minutes. Clearance (13.6 L/min) greatly exceeds hepatic blood flow. Metabolism is the primary route of drug elimination.
Drug interactions
Aspirin: Coadministration of nitroglycerin with high dose aspirin (1,000 mg) results in increased exposure to nitroglycerin. The vasodilatory and hemodynamic effects of nitroglycerin may be enhanced by concomitant administration of nitroglycerin with high dose aspirin.
Tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA): Concomitant administration of t-PA and intravenous nitroglycerin has been shown to reduce plasma levels of t-PA and its thrombolytic effect.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
Animal carcinogenesis studies with sublingually administered nitroglycerin have not been performed.
Carcinogenicity potential of nitroglycerin was evaluated in rats receiving up to 434 mg/kg/day of dietary nitroglycerin for 2 years. Rats developed dose-related fibrotic and neoplastic changes in liver, including carcinomas, and interstitial cell tumors in testes. At high dose, the incidences of hepatocellular carcinomas in males was 48% and in females was 33%, compared to 0% in untreated controls. Incidences of testicular tumors were 52% vs. 8% in controls. Lifetime dietary administration of up to 1,058 mg/kg/day of nitroglycerin was not tumorigenic in mice.
Nitroglycerin was mutagenic in Ames tests performed in 2 different laboratories. Nevertheless, there was no evidence of mutagenicity in an in vivo dominant lethal assay with male rats treated with doses up to about 363 mg/kg/day, PO, or in ex vivo cytogenetic tests in rat and dog cells.
In a 3-generation reproduction study, rats received dietary nitroglycerin at doses up to about 434 mg/kg/day for 6 months prior to mating of the F0 generation, with treatment continuing through successive F1 and F2 generations. The high dose was associated with decreased feed intake and body weight gain in both sexes at all matings. No specific effect on the fertility of the F0 generation was seen. Infertility noted in subsequent generations, however, was attributed to increased interstitial cell tissue and aspermatogenesis in the high-dose males. In this 3-generation study, there was no clear evidence of teratogenicity.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets, USP are supplied in 3 strengths in color-coded labeled bottles containing 100 tablets each (0.3 mg, 0.4 mg, and 0.6 mg), and in one strength in color-coded Patient Convenience Packages of 4 bottles of 25 tablets each (0.4 mg).
The 0.3 mg sublingual tablets are a white, round, flat faced tablet debossed with “3” on one side and “V” on other side. They are supplied as:NDC: 69339-173-01 Bottle of 100 tablets
The 0.4 mg sublingual tablets are a white, round, flat faced tablet debossed with “4” on one side and “V” on other side. They are supplied as:
NDC: 69339-174-01 Bottle of 100 tablets
NDC: 69339-174-41 Patient Convenience Package of 4 bottles of 25 tablets (NDC: 69339-174-02)The 0.6 mg sublingual tablets are a white, round, flat faced tablet debossed with "6" on one side and "V" on other side. They are supplied as:
NDC: 69339-175-01 Bottle of 100 tablets
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Nitroglycerin should be kept in the original glass container and must be tightly capped after each use to prevent loss of tablet potency.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Product of USA
Manufactured by:
NATCO PHARMA LIMITED
Kothur- 509 228, Telangana, India
Manufactured for:
NATCO Pharma USA LLC,
Parsippany, NJ 07054, USA
Revised: 07/2023
PATIENT INFORMATION
Nitroglycerin (nye” troe glis’ er in)
Sublingual Tablets, USP
Read this information carefully before you start nitroglycerin sublingual tablets and each time you refill your prescription. There may be new information. This information does not replace talking with your doctor. If you have any questions about nitroglycerin sublingual tablets, ask your doctor. Your doctor will know if nitroglycerin sublingual tablets are right for you.
What is Nitroglycerin?
Nitroglycerin is a type of medicine known as an organic nitrate and is a vasodilating agent. It is used to treat a type of chest pain called angina.
What is Angina?
Angina is a pain or discomfort that keeps coming back when part of your heart does not get enough blood. Angina feels like a pressing or squeezing pain, usually in your chest under the breastbone. Sometimes you can feel it in your shoulders, arms, neck, jaws, or back. Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets can relieve this pain.
Who should not use nitroglycerin sublingual tablets?
Do not use nitroglycerin sublingual tablets if you are allergic to organic nitrates (like the active ingredient in nitroglycerin sublingual tablets).
You should not take nitroglycerin sublingual tablets if you have the following conditions:
- very recent heart attack
- severe anemia
- increased pressure in the head
Do not take nitroglycerin sublingual tablets with drugs for erectile dysfunction, like VIAGRA® (sildenafil citrate), CIALIS® (tadalafil), or LEVITRA® (vardenafil hydrochloride), as this may lead to extreme lowering of your blood pressure.
Do not take nitroglycerin sublingual tablets if you take medicines called guanylate cyclase stimulators which include riociguat, a medicine that treats pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic-thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension.
What should I tell my doctor before taking nitroglycerin sublingual tablets?
Before using nitroglycerin sublingual tablets, tell your doctor if:
- You are taking any medicines that are used to treat angina, heart failure, or an irregular heartbeat.
- You are taking any medicines that reduce blood pressure.
- You are taking any diuretics (water pills).
- You are taking medicines that can cause dry mouth such as tricyclic antidepressants (e.g. amitriptyline, desipramine, doxepin), anticholinergic drugs, or any antimuscarinic drugs (e.g. atropine).
- You are taking ergotamine or similar drugs for migraine headaches.
- You are taking aspirin.
- You are taking any medicines for erectile dysfunction.
- You are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- You are breastfeeding.
How should I take nitroglycerin sublingual tablets?
- Do not chew, crush, or swallow nitroglycerin sublingual tablets.
- You should sit down when taking nitroglycerin sublingual tablets and use caution when you stand up. This eliminates the possibility of falling due to lightheadedness or dizziness.
- One tablet should be dissolved under the tongue or in the oral cavity at the first sign of chest pain.
- The dose may be repeated approximately every 5 minutes, until the chest pain is relieved.
- If the pain persists after a total of 3 tablets in a 15-minute period, or is different than you typically experience, call your doctor or seek emergency help.
- Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets may be used 5 minutes to 10 minutes prior to activities that might cause chest pain.
- You may feel a burning or tingling sensation in your mouth when you take nitroglycerin sublingual tablets.
What should I avoid while taking nitroglycerin sublingual tablets?
- Do not breastfeed. It is not known if nitroglycerin will pass through your milk.
- Do not consume alcohol while taking nitroglycerin sublingual tablets, as this can lower your blood pressure.
- Do not start any new prescription or non-prescription medicines or supplements, unless you check with your doctor first.
What are the possible side effects of nitroglycerin sublingual tablets?
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets may cause the following side effects:
- headache
- vertigo (a major symptom of balance disorder)
- dizziness
- weakness
- heart palpitations (unusual awareness of the heartbeat)
- low blood pressure upon rising from a seated position
- nausea and vomiting
- sweating
- paleness
- fainting
- flushing (warm or red condition of your skin)
- other skin reactions that may be severe
Tell your doctor if you are concerned about any side effects you experience. These are not all the possible side effects of nitroglycerin sublingual tablets. For a complete list, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How do I store nitroglycerin sublingual tablets?
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets should be kept in the original glass container and tightly capped after each use to prevent loss of tablet potency.
Store nitroglycerin sublingual tablets at room temperature (between 68° and 77°F).General advice about nitroglycerin sublingual tablets
Sometimes doctors will prescribe a medicine for a condition that is not included in the patient information leaflets. Only use nitroglycerin sublingual tablets the way your doctor told you to. Do not give nitroglycerin sublingual tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about nitroglycerin sublingual tablets, or you can call NATCO Pharma USA LLC at 201-786-6500.
Product of USA
Manufactured by:
NATCO PHARMA LIMITED
Kothur- 509 228, Telangana, India
Manufactured for:
NATCO Pharma USA LLC,
Parsippany, NJ 07054, USA
Revised: 07/2023
- BOTTLE LABEL OF 0.3MG 100 TABLETS
- BOTTLE CARTON OF 0.3MG 100 TABLETS
- BOTTLE LABEL OF 0.4MG 100 TABELTS
- BOTTLE CARTON OF 0.4MG 100 TABLETS
- BOTTLE LABEL OF 0.4MG 4X25 TABLETS
- BOTTLE CARTON OF 0.4MG 4X25 TABLETS
- BOTTLE LABEL OF 0.6MG 100 TABLETS
- BOTTLE CARTON OF 0.6MG 100 TABLETS
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
NITROGLYCERIN
nitroglycerin tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69339-173 Route of Administration SUBLINGUAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NITROGLYCERIN (UNII: G59M7S0WS3) (NITROGLYCERIN - UNII:G59M7S0WS3) NITROGLYCERIN 0.3 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) CALCIUM STEARATE (UNII: 776XM7047L) SILICA DIMETHYL SILYLATE (UNII: EU2PSP0G0W) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 4mm Flavor Imprint Code 3;V Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69339-173-01 1 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/03/2022 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA211604 10/03/2022 NITROGLYCERIN
nitroglycerin tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69339-174 Route of Administration SUBLINGUAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NITROGLYCERIN (UNII: G59M7S0WS3) (NITROGLYCERIN - UNII:G59M7S0WS3) NITROGLYCERIN 0.4 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) CALCIUM STEARATE (UNII: 776XM7047L) SILICA DIMETHYL SILYLATE (UNII: EU2PSP0G0W) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 4mm Flavor Imprint Code 4;V Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69339-174-01 1 in 1 CARTON 10/03/2022 1 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 69339-174-41 4 in 1 CARTON 10/03/2022 2 NDC: 69339-174-02 25 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA211604 10/03/2022 NITROGLYCERIN
nitroglycerin tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69339-175 Route of Administration SUBLINGUAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NITROGLYCERIN (UNII: G59M7S0WS3) (NITROGLYCERIN - UNII:G59M7S0WS3) NITROGLYCERIN 0.6 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) CALCIUM STEARATE (UNII: 776XM7047L) SILICA DIMETHYL SILYLATE (UNII: EU2PSP0G0W) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 4mm Flavor Imprint Code 6;V Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69339-175-01 1 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/03/2022 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA211604 10/03/2022 Labeler - Natco Pharma USA LLC (079590418) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Natco Pharma Limited-Pharma Division 918588174 MANUFACTURE(69339-173, 69339-174, 69339-175)
Trademark Results [NITROGLYCERIN]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 NITROGLYCERIN 76482982 2851735 Dead/Cancelled |
J. Richard Industries, Inc. 2003-01-17 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.







