FOLLISTIM AQ- follitropin injection, solution
Follistim AQ by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Follistim AQ by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Organon USA Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FOLLISTIM® AQ Cartridge safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FOLLISTIM® AQ Cartridge.
FOLLISTIM® AQ Cartridge (follitropin beta injection) for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Dosage and Administration Recommended Dosing in Anovulatory Women Undergoing Ovulation Induction (2.2) 09/2019 Recommended Dosing in Normal Ovulatory Women Undergoing Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) Cycle (2.3) 09/2019 Warnings and Precautions Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement (5.1) 09/2019 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) (5.2) 09/2019 Pulmonary and Vascular Complications (5.3) 09/2019 Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth (5.5) 09/2019 Ectopic Pregnancy (5.7) 09/2019 Spontaneous Abortion (5.8) 09/2019 Ovarian and Other Reproductive System Neoplasms (5.9) 09/2019 Laboratory Tests (5.10) (removed) 09/2019 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Follistim AQ Cartridge is a gonadotropin indicated:
In Women for:
- Induction of Ovulation and Pregnancy in Anovulatory Infertile Women in Whom the Cause of Infertility is Functional and Not Due to Primary Ovarian Failure (1.1)
- Pregnancy in Normal Ovulatory Women Undergoing Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) Cycle (1.2)
In Men for:
- Induction of Spermatogenesis in Men with Primary and Secondary Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism (HH) in Whom the Cause of Infertility is Not Due to Primary Testicular Failure (1.3)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
See Dose Conversion Table 1 for Follistim AQ Cartridge with Pen Injector (2.1)
In Anovulatory Women Undergoing Ovulation Induction (2.2):
- Starting daily dose of 50 international units of Follistim AQ Cartridge is administered subcutaneously for at least the first 7 days. The dose is increased by 25 or 50 international units at weekly intervals until follicular growth indicate an adequate response.
- When an acceptable pre-ovulatory state is achieved, final oocyte maturation is achieved with 5,000 to 10,000 international units of urinary human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
- The woman and her partner should have intercourse daily, beginning on the day prior to the administration of hCG and until ovulation becomes apparent.
In Normal Ovulatory Women Undergoing Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection Cycle (2.3):
- Starting dose of 200 international units (actual cartridge doses) of Follistim AQ Cartridge is administered subcutaneously for at least the first 7 days of treatment. Subsequent doses can be adjusted down or up based upon ovarian response as determined by ultrasound evaluation of follicular growth. Dosage reduction in high responders can be considered from the 6th day of treatment onward according to individual response.
- Final oocyte maturation is induced with a dose of 5,000-10,000 international units of urinary hCG.
- Oocyte (egg) retrieval is performed 34 to 36 hours later.
Induction of Spermatogenesis in Men (2.4):
- Pretreatment with urinary hCG alone (1,500 international units twice weekly) is required. If serum testosterone levels have not normalized after 8 weeks of hCG treatment, the dose may be increased to 3,000 international units twice a week.
- After normalization of serum testosterone levels, administer 450 international units per week (225 international units twice weekly or 150 international units three times weekly) of Follistim AQ Cartridge subcutaneously with the same pre-treatment hCG dose used to normalize testosterone levels.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Women and men who exhibit:
- Prior hypersensitivity to recombinant hFSH products (4)
- High levels of FSH indicating primary gonadal failure (4)
- Presence of uncontrolled non-gonadal endocrinopathies (4)
- Hypersensitivity reactions related to streptomycin or neomycin (4)
- Tumors of the ovary, breast, uterus, testis, hypothalamus or pituitary gland (4)
Women who exhibit:
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Treatment with Follistim AQ may result in:
- Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement: Monitor ovarian response carefully. (5.1)
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): Follow current clinical practice for reducing the risk of OHSS during IVF or ICSI. Adherence to recommended dose and treatment regimen and careful monitoring of ovarian response is important to reduce the risk. The OHSS risk increases with 18 or more follicles of 11 mm or more in diameter. If OHSS develops, standard management should be implemented. (5.2)
- Pulmonary and Vascular Complications: Before treatment with Follistim AQ Cartridge, weigh benefits versus risk in women with generally recognized risk factors for thromboembolic events. Pregnancy itself may increase this risk. (5.3)
- Ovarian Torsion: Diagnose and treat immediately. (5.4)
- Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth: Advise patients of the potential risks associated with multiple births. (5.5)
- Congenital Anomalies: Slightly higher incidence after IVF or ICSI than spontaneous conception that may be due to parental characteristics or multiple pregnancies. (5.6)
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Monitor for possible extrauterine pregnancy. (5.7)
- Spontaneous Abortion: Reported for all gonadotropin treatments, including Follistim AQ Cartridge. (5.8)
- Ovarian and Other Reproductive System Neoplasms: Reported for all gonadotropin treatments, including Follistim AQ Cartridge. Increased risk of these tumors in women undergoing infertility treatment has not been established. (5.9)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥2%) in women undergoing ovulation induction are ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, ovarian cyst, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain and lower abdominal pain. (6.1)
The most common adverse reactions (≥2%) in women undergoing controlled ovarian stimulation as part of an IVF or ICSI cycle are pelvic discomfort, headache, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, pelvic pain, nausea and fatigue. (6.1)
The most common (≥2%) adverse reactions in men undergoing induction of spermatogenesis are headache, acne, injection site reaction, injection site pain, gynecomastia, rash and dermoid cyst. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., at 1-877-888-4231 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Nursing Mothers: It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 9/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Induction of Ovulation and Pregnancy in Anovulatory Infertile Women in Whom the Cause of Infertility is Functional and Not Due to Primary Ovarian Failure
1.2 Pregnancy in Normal Ovulatory Women Undergoing Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) Cycle
1.3 Induction of Spermatogenesis in Men with Primary and Secondary Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism (HH) in Whom the Cause of Infertility is Not Due to Primary Testicular Failure
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
2.2 Recommended Dosing in Anovulatory Women Undergoing Ovulation Induction
2.3 Recommended Dosing in Normal Ovulatory Women Undergoing Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) Cycle
2.4 Recommended Dosing for Induction of Spermatogenesis in Men
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement
5.2 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
5.3 Pulmonary and Vascular Complications
5.4 Ovarian Torsion
5.5 Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth
5.6 Congenital Anomalies
5.7 Ectopic Pregnancy
5.8 Spontaneous Abortion
5.9 Ovarian and Other Reproductive System Neoplasms
5.10 Follistim Pen
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Study Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Ovulation Induction
14.2 Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) Cycle
14.3 Induction of Spermatogenesis
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Dosing and Use of Follistim AQ Cartridge with Pen
17.2 Therapy Duration and Necessary Monitoring in Women and Men Undergoing Treatment
17.3 Instructions on a Missed Dose
17.4 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
17.5 Ovarian Torsion
17.6 Adverse Events Reported During the Course of Treatment with IVF or ICSI
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Follistim® AQ (follitropin beta injection) Cartridge is indicated:
In Women for:
1.1 Induction of Ovulation and Pregnancy in Anovulatory Infertile Women in Whom the Cause of Infertility is Functional and Not Due to Primary Ovarian Failure
Prior to initiation of treatment with Follistim AQ Cartridge:
- Women should have a complete gynecologic and endocrinologic evaluation.
- Primary ovarian failure should be excluded.
- The possibility of pregnancy should be excluded.
- Tubal patency should be demonstrated.
- The fertility status of the male partner should be evaluated.
1.2 Pregnancy in Normal Ovulatory Women Undergoing Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) Cycle
Prior to initiation of treatment with Follistim AQ Cartridge:
- Women should have a complete gynecologic and endocrinologic evaluation and diagnosis of cause of infertility.
- The possibility of pregnancy should be excluded.
- The fertility status of the male partner should be evaluated.
In Men for:
1.3 Induction of Spermatogenesis in Men with Primary and Secondary Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism (HH) in Whom the Cause of Infertility is Not Due to Primary Testicular Failure
Prior to initiation of treatment with Follistim AQ Cartridge:
- Men should have a complete medical and endocrinologic evaluation.
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism should be confirmed and primary testicular failure should be excluded.
- Serum testosterone levels should be normalized with human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) treatment.
- The fertility status of the female partner should be evaluated.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. If the solution is not clear and colorless or has particles in it, the solution should not be used.
- Do not add any other medicines into the Follistim AQ Cartridge.
- Follistim AQ Cartridge with the pen injector device delivers on average an 18% higher amount of follitropin beta when compared to reconstituted Follistim delivered with a conventional syringe and needle. When administering Follistim AQ Cartridge, a lower starting dose and lower dose adjustments (as compared to reconstituted Follistim) should be considered. For that purpose the following Dose Conversion Table is provided:
Table 1: Follistim AQ Cartridge Administered Subcutaneously With the Follistim Pen Dose Conversion Table* Lyophilized recombinant FSH dosing with
ampules or vials, using conventional syringeFollistim AQ Cartridge
dosing with the Follistim Pen- * Each value represents an 18% difference rounded to the nearest 25 IU increment.
75 IU 50 IU 150 IU 125 IU 225 IU 175 IU 300 IU 250 IU 375 IU 300 IU 450 IU 375 IU 2.2 Recommended Dosing in Anovulatory Women Undergoing Ovulation Induction
The dosing scheme is stepwise and is individualized for each woman [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
- A starting daily dose of 50 international units of Follistim AQ Cartridge is administered [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] subcutaneously daily for at least the first 7 days.
-
Subsequent dosage adjustments are made at weekly intervals based upon ovarian response. If an increase in dose is indicated by the ovarian response, the increase should be made by 25 or 50 international units of Follistim AQ Cartridge at weekly intervals until follicular growth monitored by transvaginal ultrasound indicates an adequate ovarian response. The concurrent determination of serum estradiol levels may also be useful.
The following should be considered when planning the woman's individualized dose:- Appropriate Follistim AQ Cartridge dose adjustment(s) should be used to prevent multiple follicular growth and cycle cancellation.
- The maximum, individualized, daily dose of Follistim AQ Cartridge is 250 international units.
- Treatment should continue until ultrasonic visualizations approximate the pre-ovulatory conditions based on follicular development.
- When pre-ovulatory conditions are reached, 5,000 to 10,000 international units of urinary hCG are used to induce final oocyte maturation and ovulation.
If the ovarian monitoring suggests an increased risk of OHSS on the last day of Follistim AQ Cartridge therapy, follow current clinical practice for reducing the risk of OHSS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]. - The woman and her partner should be encouraged to have intercourse daily, beginning on the day prior to the administration of hCG and until ovulation becomes apparent.
-
During treatment with Follistim AQ Cartridge and during a two-week post-treatment period, the woman should be assessed at least every other day for signs of excessive ovarian stimulation.
It is recommended that Follistim AQ Cartridge administration be stopped if the ovarian monitoring suggests an increased risk of OHSS or abdominal pain occurs. Most OHSS occurs after treatment has been discontinued and reaches its maximum at about seven to ten days post-ovulation. Follow current clinical practice for reducing the risk of OHSS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
2.3 Recommended Dosing in Normal Ovulatory Women Undergoing Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) Cycle
The dosing scheme follows a stepwise approach and is individualized for each woman.
- A starting dose of 200 international units (actual cartridge doses) of Follistim AQ Cartridge is administered [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] subcutaneously daily for at least the first 7 days of treatment.
-
Subsequent to the first 7 days of treatment, the dose can be adjusted down or up based upon the woman's ovarian response as determined by ultrasound evaluation of follicular growth. The concurrent determination of serum estradiol levels may also be useful. Dosage reduction in high responders can be considered from the 6th day of treatment onward according to individual response.
The following should be considered when planning the woman's individualized dose:- For most normal responding women, the daily starting dose can be continued until pre-ovulatory conditions are achieved (seven to twelve days).
- For low or poor responding women, the daily dose should be increased according to the ovarian response. The maximum, individualized, daily dose of Follistim AQ Cartridge is 500 international units.
- For high responding women [those at particular risk of abnormal ovarian enlargement and/or ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)], decrease or temporarily stop the daily dose, or discontinue the cycle according to individual response. Follow current clinical practice for reducing the risk of OHSS. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2).]
- When a sufficient number of follicles of adequate size are present, dosing of Follistim AQ Cartridge is stopped and final maturation of the oocytes is induced by administering urinary hCG at a dose of 5,000 to 10,000 international units. If the ovarian monitoring suggests an increased risk of OHSS on the last day of Follistim AQ Cartridge therapy, follow current clinical practice for reducing the risk of OHSS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
- Oocyte (egg) retrieval should be performed 34 to 36 hours following the administration of hCG.
2.4 Recommended Dosing for Induction of Spermatogenesis in Men
- Pretreatment with hCG is required prior to concomitant therapy with Follistim AQ Cartridge and hCG. An initial dosage of 1,500 international units of urinary hCG should be administered at twice weekly intervals to normalize serum testosterone levels. If serum testosterone levels have not normalized after 8 weeks of hCG treatment, the urinary hCG dose can be increased to 3,000 international units twice weekly [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
- After normal serum testosterone levels have been reached, Follistim AQ Cartridge should be administered by subcutaneous injection concomitantly with hCG treatment. Follistim is given at a dosage of 450 international units per week, as either 225 international units twice weekly or 150 international units three times per week, in combination with the same hCG dose used to normalize testosterone levels. Based on delivery of a higher dose of follitropin beta with the Follistim AQ Cartridge and pen injector [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)], a lower dose of Follistim AQ Cartridge may be considered.
The concomitant therapy should be continued for at least 3 to 4 months before any improvement in spermatogenesis can be expected. If a man has not responded after this period, the combination therapy may be continued. Treatment response has been noted at up to 12 months.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Follistim AQ Cartridge is contraindicated in women and men who exhibit:
- Prior hypersensitivity to recombinant hFSH products
- High levels of FSH indicating primary gonadal failure
- Presence of uncontrolled non-gonadal endocrinopathies (e.g., thyroid, adrenal, or pituitary disorders) [see Indications and Usage (1.1, 1.2, 1.3)]
- Hypersensitivity reactions to streptomycin or neomycin. Follistim AQ may contain traces of these antibiotics
- Tumors of the ovary, breast, uterus, testis, hypothalamus or pituitary gland
Follistim AQ Cartridge is also contraindicated in women who exhibit:
- Pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
- Heavy or irregular vaginal bleeding of undetermined origin
- Ovarian cysts or enlargement not due to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Follistim AQ Cartridge should be used only by physicians who are experienced in infertility treatment. Follistim AQ Cartridge contains a potent gonadotropic substance capable of causing Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] with or without pulmonary or vascular complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] and multiple births [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Gonadotropin therapy requires the availability of appropriate monitoring facilities.
Careful attention should be given to the diagnosis of infertility and in the selection of candidates for Follistim AQ Cartridge therapy [see Indications and Usage (1.1, 1.2, 1.3) and Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3, 2.4)].
Switching to Follistim AQ Cartridge from other brands (manufacturer), types (recombinant, urinary), and/or methods of administration (Follistim Pen, conventional syringe) may necessitate an adjustment of the dose [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.1 Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement
In order to reduce the risks associated with abnormal ovarian enlargement that may occur with Follistim AQ therapy, treatment should be individualized and the lowest effective dose should be used [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)].
Careful monitoring, including use of ultrasound monitoring of ovarian response, is important to reduce the risk of overstimulation. The concurrent determination of serum estradiol levels may also be useful. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
If the ovaries are abnormally enlarged on the last day of Follistim AQ therapy, follow current clinical practice for reducing the risk of OHSS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
OHSS is a medical entity distinct from uncomplicated ovarian enlargement. Clinical signs and symptoms of mild and moderate OHSS are abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, mild to moderate enlargement of ovaries and ovarian cysts. Severe OHSS may be life-threatening. Clinical signs and symptoms of severe OHSS are large ovarian cysts, acute abdominal pain, ascites, pleural effusion, hydrothorax, dyspnea, oliguria, hematological abnormalities and weight gain. In rare instances, venous or arterial thromboembolism may occur in association with OHSS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Transient liver function test abnormalities suggestive of hepatic dysfunction with or without morphologic changes on liver biopsy have also been reported in association with OHSS.
OHSS may be caused by administration of human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) and by pregnancy (endogenous hCG). Early OHSS usually occurs within 10 days after hCG administration and may be associated with an excessive ovarian response to gonadotropin stimulation. Late OHSS occurs more than 10 days after hCG administration, as a consequence of the hormonal changes with pregnancy. Because of the risk of developing OHSS, patients should be monitored for at least two weeks after hCG administration.
Women with known risk factors for a high ovarian response may be especially prone to the development of OHSS during or following treatment with Follistim AQ Cartridge. For women having their first cycle of ovarian stimulation, for whom risk factors are only partially known, close observation for early signs and symptoms of OHSS is recommended.
Follow current clinical practice for reducing the risk of OHSS during IVF or ICSI. Adherence to the recommended Follistim AQ Cartridge dose and treatment regimen and careful monitoring of ovarian response is important to reduce the risk of OHSS. To monitor the risk of OHSS, ultrasound assessments of follicular development should be performed prior to treatment and at regular intervals during treatment; the concurrent determination of serum estradiol levels may also be useful. In IVF or ICSI there is an increased risk of OHSS with 18 or more follicles of 11 mm or more in diameter.
If OHSS develops, standard and appropriate management of OHSS should be implemented and followed.
During clinical trials with Follistim or Follistim AQ Cartridge therapy, OHSS occurred in 7.6% of 105 women (OI) and 6.4% of 751 women (IVF or ICSI) treated with Follistim and Follistim AQ Cartridge, respectively.
5.3 Pulmonary and Vascular Complications
Serious pulmonary conditions, including acute respiratory distress syndrome, have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins.
Thromboembolic events, both in association with and separate from OHSS, have been reported following therapy with gonadotropins, including Follistim AQ Cartridge. Intravascular thrombosis, which may originate in venous or arterial vessels, can result in reduced blood flow to vital organs or the extremities. In women with generally recognized risk factors for thromboembolic events, such as a personal or family history, severe obesity, or thrombophilia, may have an increased risk of venous or arterial thromboembolic events, during or following treatment with gonadotropins, including Follistim AQ Cartridge. Sequelae of such reactions have included venous thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, cerebral vascular occlusion (stroke), and arterial occlusion resulting in loss of limb and rarely in myocardial infarction. In rare cases, pulmonary complications and/or thromboembolic reactions have resulted in death. In women with recognized risk factors, the benefits of ovulation induction, in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) treatment need to be weighed against the risks. It should be noted that pregnancy itself also carries an increased risk of thrombosis.
5.4 Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian torsion has been reported after treatment with gonadotropins including Follistim AQ Cartridge. Ovarian torsion may be related to OHSS, pregnancy, previous abdominal surgery, past history of ovarian torsion, previous or current ovarian cysts and polycystic ovaries. Damage to the ovary due to reduced blood supply can be limited by early diagnosis and immediate detorsion.
5.5 Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth
Multi-fetal gestation and births have been reported with all gonadotropin treatments including Follistim AQ Cartridge treatment. The woman and her partner should be advised of the potential risks for the mother (pregnancy and delivery complications) and the neonate (low birth weight) before starting treatment. For anovulatory women undergoing ovulation induction, monitoring follicular development with transvaginal ultrasonography may aid in determining whether or not to continue the cycle in order to reduce the risk of multi-fetal gestations. The concurrent determination of serum estradiol levels may also be useful. In women undergoing IVF or ICSI procedures, the risk of multiple pregnancy is mainly related to the number of embryos transferred.
5.6 Congenital Anomalies
The incidence of congenital malformations after IVF or ICSI may be slightly higher than after spontaneous conception. This slightly higher incidence is thought to be related to differences in parental characteristics (e.g., maternal age, sperm characteristics) and to the higher incidence of multi-fetal gestations after IVF or ICSI. There are no indications that the use of gonadotropins during IVF or ICSI is associated with an increased risk of congenital malformations.
5.7 Ectopic Pregnancy
Infertile women undergoing IVF or ICSI have an increased incidence of ectopic pregnancies. Early confirmation of an intrauterine pregnancy should be determined by transvaginal ultrasound.
5.8 Spontaneous Abortion
Spontaneous abortions (miscarriage) have been reported for all gonadotropin products, including Follistim AQ Cartridge. However, causality has not been established, but may be related to a number of factors, including the underlying infertility.
5.9 Ovarian and Other Reproductive System Neoplasms
There have been infrequent reports of ovarian and other reproductive system neoplasms, both benign and malignant, in women who have undergone multiple drug regimens for controlled ovarian stimulation; however, a causal relationship has not been established.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Pulmonary and Vascular Complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Ovarian Torsion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Congenital Anomalies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Ectopic Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Spontaneous Abortion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Ovarian and Other Reproductive System Neoplasms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.1 Clinical Study Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reactions rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trial of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Ovulation Induction
In a single cycle, multi-center, assessor-blind, parallel group, comparative study, a total of 172 chronic anovulatory women who had failed to ovulate and/or conceive with clomiphene citrate therapy, were randomized and treated with Follistim (105) or a urofollitropin comparator. Adverse reactions with an incidence of greater than 2% in either treatment group are listed in Table 2.
Table 2: Common Adverse Reactions Reported at a Frequency of ≥2% in an Assessor-Blind, Comparative Study of Anovulatory Women Receiving Ovulation Induction System Organ Class/Adverse Reactions Treatment
Number (%) of WomenFollistim
N=105
n (%)Comparator
N=67
n (%)Gastrointestinal disorders Abdominal discomfort 3 (2.9) 1 (1.5) Abdominal pain 3 (2.9) 2 (3.0) Abdominal pain lower 3 (2.9) 1 (1.5) Reproductive system and breast disorders Ovarian cyst 3 (2.9) 2 (3.0) Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome 8 (7.6) 3 (4.5) General disorders and administration site conditions Pyrexia 0 (0.0) 2 (3.0) Adverse reactions reported commonly (greater than or equal to 2% of women treated with Follistim) in other ovulation induction clinical trials were headache, abdominal distension, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, pelvic pain, uterine enlargement, vaginal hemorrhage and injection site reaction.
In Vitro Fertilization/Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
In a single cycle, multi-center, double-blind, parallel group, comparative study, a total of 1509 women were randomized to receive controlled ovarian stimulation with either Follistim AQ Cartridge (751 women were treated with Follistim AQ Cartridge) or a comparator and pituitary suppression with a gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist as part of an in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) cycle. Table 3 lists adverse reactions with an incidence of greater than 2% in the group of women treated with Follistim AQ Cartridge.
Table 3: Common Adverse Reactions Reported at a Frequency of ≥2% in a Randomized, Double-blind, Active-controlled, Comparative Study of Normal Ovulatory Women Undergoing Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection Cycle System Organ Class/Adverse Reactions Follistim AQ Cartridge Treatment
N = 751
n* (%)- * n = number of women with the adverse reaction
Nervous System disorders Headache 55 (7.3%) Gastrointestinal disorders Nausea 29 (3.9%) Reproductive system and breast disorders Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome 48 (6.4%) Pelvic discomfort 62 (8.3%) Pelvic Pain 41 (5.5%) General disorders and Administration site conditions Fatigue 17 (2.3%) Induction of Spermatogenesis
In an open-label, non-comparative clinical trial, 49 men with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism were enrolled to receive pretreatment with hCG, followed by combination therapy with hCG and Follistim for induction of spermatogenesis. Of the 49 men, 30 received weekly Follistim doses of 450 international units; 24 of these 30 men received a total of 48 weeks of treatment with Follistim. Adverse reactions occurring with an incidence of greater than 2% in the 30 men treated with Follistim are listed in Table 4.
Table 4: Common Adverse Reactions Reported at a Frequency of ≥2% in an Open-Label Clinical Trial in Men with Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism System Organ Class/Adverse Reactions Follistim Treatment
N=30
n (%)Nervous system disorders Headache 2 (6.7) General disorders and administration site disorders Injection site reaction 2 (6.7) Injection site pain 2 (6.7) Skin and cutaneous tissue disorders Acne 2 (6.7) Rash 1 (3.3) Reproductive system and breast disorders Gynecomastia 1 (3.3) Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified Dermoid cyst 1 (3.3) 6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Follistim and/or Follistim AQ Cartridge. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Abdominal distension, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrheaGeneral disorders and administration site conditions
Injection site reactionReproductive system and breast disorders
Breast tenderness, metrorrhagia, ovarian enlargement, vaginal hemorrhageSkin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
RashVascular disorders
Thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] - 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category X: Follistim AQ Cartridge should not be used during pregnancy [see Contraindications (4)].
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the nursing infant from Follistim AQ Cartridge, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Aside from the possibility of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)] and multiple gestations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)], there is no additional information concerning the consequences of acute overdosage with Follistim AQ Cartridge.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Follistim AQ Cartridge contains human follicle-stimulating hormone (hFSH), a glycoprotein hormone which is manufactured by recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology. The active drug substance, follitropin beta, has a dimeric structure containing two glycoprotein subunits (alpha and beta). Both the 92 amino acid alpha-chain and the 111 amino acid beta-chain have complex heterogeneous structures arising from two N-linked oligosaccharide chains. Follitropin beta is synthesized in a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line that has been transfected with a plasmid containing the two subunit DNA sequences encoding for hFSH. The purification process results in a highly purified preparation with a consistent hFSH isoform profile and high specific activity [as determined by the Ph. Eur. test for FSH in vivo bioactivity and on the basis of the molar extinction coefficient at 277 nm (εs:mg-1cm-1) = 1.066].
The biological activity is determined by measuring the increase in ovary weight in female rats. The intrinsic luteinizing hormone (LH) activity in follitropin beta is less than 1 international unit per 40,000 international units FSH. The compound is considered to contain no LH activity.
The amino acid sequence and tertiary structure of the product are indistinguishable from that of hFSH of urinary source. Also, based on available data derived from physico-chemical tests and bioassay, follitropin beta and follitropin alfa, another recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone product, are indistinguishable.
Follistim AQ Cartridge is a ready for use, prefilled with solution, disposable cartridge containing either 175 IU of follitropin beta in 0.210 mL (833 IU/mL), 350 IU in 0.420 mL (833 IU/mL), 650 IU in 0.780 mL (833 IU/mL) or 975 IU in 1.170 mL (833 IU/mL) of aqueous solution for multiple dose use, with a maximal deliverable dose of either 150 IU, 300 IU, 600 IU or 900 IU, respectively. Inactive ingredients in the cartridges include: benzyl alcohol NF 10 mg/mL; L-methionine USP 0.5 mg/mL; polysorbate 20 NF 0.2 mg/mL; sodium citrate (dihydrate) USP 14.7 mg/mL; sucrose NF 50 mg/mL; and water for injection USP. Hydrochloric acid NF and/or sodium hydroxide NF are used to adjust the pH to 7.
Follistim AQ Cartridge is for use only with the Follistim Pen, which features an adjustable dosing system for administering the drug in a microvolume of solution. The Follistim Pen with Follistim AQ Cartridge is intended for SUBCUTANEOUS USE ONLY. The recombinant protein in Follistim AQ Cartridge has been standardized for FSH in vivo bioactivity in terms of the WHO International Standard for Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Recombinant, Human for Bioassay (code 92/642), issued by the World Health Organization Expert Committee on Biological Standardization (1995). Under current storage conditions, Follistim AQ may contain up to 11% of oxidized follitropin beta.
In clinical trials with Follistim, serum antibodies to FSH or anti-CHO cell derived proteins were not detected in any of the treated patients after exposure to Follistim for up to three cycles.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Women:
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), the active component in Follistim AQ Cartridge, is required for normal follicular growth, maturation, and gonadal steroid production.
In women, the level of FSH is critical for the onset and duration of follicular development, and consequently for the timing and number of follicles reaching maturity. Follistim AQ Cartridge stimulates ovarian follicular growth in women who do not have primary ovarian failure. In order to effect the final phase of follicle maturation, resumption of meiosis and rupture of the follicle in the absence of an endogenous LH surge, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) must be given following treatment with Follistim AQ Cartridge when patient monitoring indicates appropriate follicular development parameters have been reached.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic parameters for Follistim AQ Cartridge were evaluated in an open-label, single-center, randomized study in 20 healthy women. Serum FSH values from a single subcutaneous injection of reconstituted Follistim lyophilized powder administered by conventional syringe were compared to those values following a single subcutaneous injection of Follistim AQ Cartridge administered with the Follistim Pen injector. Administration of follitropin beta with the Follistim Pen resulted an 18% increase in AUC0–∞ and Cmax. The 18% difference in serum FSH concentrations resulting from administration of the two formulations was due to differences between the anticipated and actual volume delivered with the conventional syringe. The pharmacokinetic parameters for Follistim AQ Cartridge are as follows:
Table 5: Mean (SD) Pharmacokinetic Parameters of a Single Subcutaneous Injection of 150 IU of Follistim AQ Cartridge (n=20) AUC0–∞
(IU/L*h)Cmax
(IU/L)tmax
(h)t1/2
(h)CLapp
(L/h/kg)AUC0–∞ Area under the curve
Cmax Maximum concentration
tmax Time to maximum concentration
t1/2 Elimination half-life
CLapp ClearanceFollistim AQ 215.1 3.4 12.9 33.4 0.01 Cartridge (45.8) (0.7) (6.2) (4.2) (0.003) Absorption:
Women:
The bioavailability of Follistim following subcutaneous and intramuscular administration was investigated in healthy, pituitary-suppressed women given a single 300 international units dose. In these women, the area under the curve (AUC), expressed as the mean ± SD, was equivalent between the subcutaneous (455.6 ± 141.4 IU*h/L) and intramuscular (445.7 ± 135.7 IU*h/L) routes of administration. However, equivalence could not be established with respect to the peak serum FSH levels (Cmax). The Cmax achieved after subcutaneous administration and intramuscular administration was 5.41 ± 0.72 international units/L and 6.86 ± 2.90 international units/L, respectively. After subcutaneous or intramuscular injection the apparent dose absorbed was 77.8% and 76.4%, respectively.
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a single, intramuscular dose (300 international units) of Follistim were also investigated in a group (n=8) of gonadotropin-deficient, but otherwise healthy women. In these women, FSH (mean ± SD) AUC was 339 ± 105 international units*h/L, Cmax was 4.3 ± 1.7 international units/L. Cmax occurred at approximately 27 ± 5.4 hours after intramuscular administration.
A multiple dose, dose proportionality, pharmacokinetic study of Follistim was completed in healthy, pituitary-suppressed, female subjects given subcutaneous doses of 75, 150, or 225 international units for 7 days. Steady-state blood concentrations of FSH were reached with all doses after 5 days of treatment based on the trough concentrations of FSH just prior to dosing (Ctrough). Peak blood concentrations with the 75, 150, and 225 international units dose were 4.30 ± 0.60 international units/L, 8.51 ± 1.16 international units/L and 13.92 ± 1.81 international units/L, respectively.
Men:
No PK studies were conducted using Follistim AQ Cartridge in men. Exposures of follitropin beta from Follistim AQ Cartridge and Follistim are expected to be equivalent after adjusting for the 18% difference in dose [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Serum levels of FSH were measured in a clinical study that compared the effects of two different dosing schedules of Follistim (150 international units three times a week or 225 international units twice a week) administered by subcutaneous injection concurrently with chorionic gonadotropin for induction of spermatogenesis in hypogonadotropic hypogonadal men. Administration of Follistim was started at Week 17. Mean serum trough concentrations of FSH remained fairly constant over the treatment period. At the end of treatment (Week 64), the mean serum trough concentrations of FSH were 2.09 international units/L in the 150 international units group and 3.22 international units/L in the 225 international units group. Serum trough concentrations of FSH measured prior to the first Follistim injection on the Mondays of active treatment period (Weeks 17 to 64) and one week after the end of treatment period are presented in Figure 1.
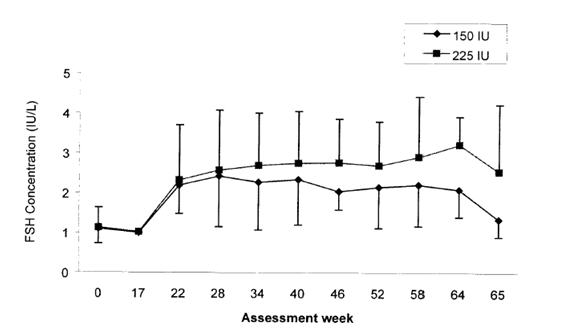
Figure 1: Mean (SD) Serum Trough Concentrations of FSH in Men Following Subcutaneous Administration of Follistim Using Two Different Dosing Schedules (150 International Units Three Times a Week or 225 International Units Twice a Week)
Distribution:
The volume of distribution of Follistim in healthy, pituitary-suppressed, women following intravenous administration of a 300 international units dose was approximately 8 L.
Metabolism:
The recombinant FSH in Follistim AQ Cartridge is biochemically very similar to urinary FSH and it is therefore anticipated that it is metabolized in the same manner.
Elimination:
The elimination half-life (t1/2) following a single subcutaneous injection of 150 IU of Follistim AQ Cartridge in women was 33.4 (4.2) hours. The clearance was 0.01 (0.003) L/h/kg.
Use in Specific Populations:
Body weight: The effect of body weight on the pharmacokinetics of Follistim was evaluated in a group of European and Japanese women who were significantly different in terms of body weight. The European women had a body weight of (mean ± SD) 67.4 ± 13.5 kg and the Japanese subjects were 46.8 ± 11.6 kg. Following a single intramuscular dose of 300 international units of Follistim, the AUC was significantly smaller in European women (339 ± 105 international units*h/L) than in Japanese women (544 ± 201 international units*h/L). However, clearance per kg of body weight was essentially the same for the respective groups (0.014 and 0.013 L/hr/kg).
Geriatric Use: The pharmacokinetics of Follistim has not been studied in geriatric subjects.
Pediatric Use: The pharmacokinetics of Follistim has not been studied in pediatric subjects.
Renal Impairment: The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Follistim has not been studied.
Hepatic Impairment: The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Follistim has not been studied.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term toxicity studies in animals have not been performed with Follistim to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of the drug. Follistim was not mutagenic in the Ames test using S. typhimurium and E. coli tester strains and did not produce chromosomal aberrations in an in vitro assay using human lymphocytes.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Ovulation Induction
The efficacy of Follistim for ovulation induction was evaluated in a randomized, assessor-blind, parallel-group comparative, multicenter safety and efficacy study of 172 chronic anovulatory women (105 subjects on Follistim) who had previously failed to ovulate and/or conceive during clomiphene citrate treatment. The study results for ovulation rates are summarized in Table 6 and those for pregnancy rates are summarized in Table 7.
Table 6: Cumulative Ovulation Rates Cycle Follistim
(n=105)First treatment cycle 72% Second treatment cycle 82% Third treatment cycle 85% 14.2 Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) Cycle
The efficacy of Follistim AQ Cartridge was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study of 1,509 healthy normal ovulatory women (mean age, body weight, and body mass index of 32 years, 68 kg and 25 kg/m2, respectively) treated for one cycle with controlled ovarian stimulation and pituitary suppression with a GnRH antagonist as part of an in vitro fertilization or intracytoplasmic sperm injection cycle. This 2008 study was conducted in Europe and North America (United States and Canada). Approximately 54% of the subjects were from North America. The overall results, as well as the results from North America only, for clinical pregnancy are summarized in Table 8.
Table 8: Pregnancy Results from Treatment With Follistim AQ Cartridge and a GnRH Antagonist in Normal Ovulatory Women Undergoing Controlled Ovarian Stimulation as Part of an In Vitro Fertilization or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection Cycle.* Intent-to-Treat Population (ITT) Parameter Follistim AQ Cartridge
Overall data
(n=750)Follistim AQ Cartridge
North American data
(n=403)- * Single treatment cycle results
- † Clinical pregnancy was assessed ≥6 weeks after transfer of one or two embryos.
Clinical pregnancy rate/cycle initiation† 41.1% 48.9% 14.3 Induction of Spermatogenesis
The safety and efficacy of Follistim administered by subcutaneous injection concomitantly with chorionic gonadotropin for injection (hCG) has been examined in a multicenter, open-label, non-comparator clinical study for induction of spermatogenesis in hypogonadotropic hypogonadal men. The study compared the effects of two different Follistim dosing schedules on semen parameters and serum levels of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). The multicenter study involved a 16-week pretreatment phase with urinary hCG at a dosage of 1,500 international units twice a week to normalize serum testosterone levels. If serum testosterone levels did not normalize after 8 weeks of hCG treatment, the urinary hCG dose could have been increased to 3,000 international units twice a week. This phase was followed by a 48-week treatment phase. Men who were still azoospermic after the pretreatment phase were randomized to receive either 225 international units Follistim together with 1,500 international units urinary hCG twice a week or 150 international units Follistim three times a week together with 1,500 international units urinary hCG twice weekly. Men who required 3,000 international units of urinary hCG twice a week in the pretreatment phase were continued on that dosage during the treatment phase. The mean age of patients in both treatment groups was approximately 30 years (range 18 to 47 years). At baseline, mean left and right testis volumes were 4.61 ± 2.94 mL and 4.57 ± 3.00 mL, respectively, in the group receiving three weekly injections of Follistim. For the group receiving two weekly injections of Follistim, the mean left and right testis volumes were 6.54 ± 2.45 mL and 7.21 ± 2.94 mL, respectively, at baseline. The primary efficacy endpoint was the percentage of patients with a mean sperm density of ≥1 × 106/mL on their last two treatment assessments. The outcomes of treatment in the 30 men enrolled in the treatment phase are summarized in Table 9.
Table 9: Number of Men Receiving Follistim Who Achieved a Mean Sperm Density of ≥106/mL on Their Last Two Treatment Assessments Follistim 150 international units three times a week
(n=15)Follistim 225 international units twice a week
(n=15)Overall
(n=30)Sperm Density of ≥106/mL n % n % n % Yes 6 40 7 47 13 43 No 9 60 8 53 17 57 Overall, the median time to reach a sperm concentration of 106 per mL was 165 days (range 25 to 327 days) in patients who demonstrated a sperm concentration of at least 106 per mL. The median time to reach a sperm concentration of at least 106 per mL was 186 days (range 25 to 327 days) for the 150 international units group and 141 days (range 43 to 204 days) for the 225 international units group. No pregnancy data were collected during the trial.
The local tolerance data were comparable between the two treatment groups. The mean percentage of days without pain calculated for all subjects in the treatment period was 91.3% for patients in the 150 international units (three times a week) and 76.0% for patients in the 225 international units (two times a week) Follistim treatment groups. In the 225 international units (twice per week) group, local symptoms judged as severe by the investigator were: itching in 1 patient (7%), pain in 2 patients (13%), bruising in 2 patients (13%), swelling in 2 patients (13%), and redness in 1 patient (7%). In the 150 international units (three times per week) group, 1 event in 1 patient (bruising, 7%) was judged as severe. No patient discontinued treatment due to injection site reaction or injection site pain.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Follistim AQ Cartridge is supplied in a box containing disposable, 29 gauge, ultra-fine, ½-inch, sterile BD Micro-Fine™ Pen Needles (for use with Follistim Pen available separately) packaged with one disposable prefilled 1.5 mL colorless glass cartridge, with grey rubber piston and an aluminum crimp-cap with black rubber inlay and in the following presentations:
NDC: 0052-0303-01 Follistim AQ Cartridge 175 international units per 0.210 mL (delivering 150 international units) with orange crimp-caps and 3 BD Micro-Fine Pen Needles
NDC: 0052-0313-01 Follistim AQ Cartridge 350 international units per 0.420 mL (delivering 300 international units) with silver crimp-caps and 5 BD Micro-Fine Pen Needles
NDC: 0052-0316-01 Follistim AQ Cartridge 650 international units per 0.780 mL (delivering 600 international units) with gold crimp-caps and 7 BD Micro-Fine Pen Needles
NDC: 0052-0326-01 Follistim AQ Cartridge 975 international units per 1.170 mL (delivering 900 international units) with blue crimp-caps and 10 BD Micro-Fine Pen Needles
Store refrigerated 2°-8°C (36°-46°F) until dispensed. Upon dispensing, the product may be stored by the patient at 2°-8°C (36°-46°F) until the expiration date, or at 25°C (77°F) for 3 months or until expiration date, whichever occurs first. Once the rubber inlay of the Follistim AQ Cartridge has been pierced by a needle, the product can only be stored for a maximum of 28 days at 2°-25°C (36°-77°F). Protect from light. Do not freeze.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
17.1 Dosing and Use of Follistim AQ Cartridge with Pen
Instruct women and men on the correct usage and dosing of Follistim AQ Cartridge in conjunction with the Follistim Pen. Make sure that individuals who have used other gonadotropin products delivered by a syringe are aware of differences arising from use of the pen. Women and men should read and follow all instructions in the Follistim Pen "Instructions for Use" Manual prior to administration of Follistim AQ Cartridge.
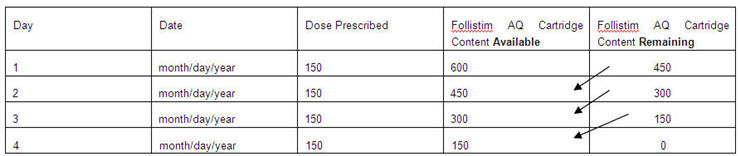
Advise women and men of the number of doses which can be extracted from the full unused Follistim AQ Cartridge that you have prescribed.
17.2 Therapy Duration and Necessary Monitoring in Women and Men Undergoing Treatment
Prior to beginning therapy with Follistim AQ Cartridge, inform women and men about the time commitment and monitoring procedures necessary to undergo treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
17.3 Instructions on a Missed Dose
Inform women and men that if they miss or forget to take a dose of Follistim AQ Cartridge, the next dose should not be doubled and they should call the healthcare provider for further dosing instructions.
17.4 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
Inform women regarding the risks with use of Follistim AQ Cartridge of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome. Instruct women to call their healthcare provider immediately if they have pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, vomiting, sudden weight gain, diarrhea, decreased urine output, or trouble breathing. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.2).]
17.5 Ovarian Torsion
Inform women regarding the risks of ovarian torsion with use of Follistim AQ Cartridge. Instruct women to call their healthcare provider immediately if they have pain in the lower abdomen. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.4).]
17.6 Adverse Events Reported During the Course of Treatment with IVF or ICSI
Inform women that the following have been reported during the course of treatment with IVF or ICSI:
- pulmonary and vascular complications [See Warnings and Precautions (5.3).]
- risk of multi-fetal gestation and birth [See Warnings and Precautions (5.5).]
- congenital anomalies [See Warnings and Precautions (5.6).]
- ectopic pregnancy [See Warnings and Precautions (5.7).]
- spontaneous abortion [See Warnings and Precautions (5.8).]
- ovarian and other reproductive system neoplasms [See Warnings and Precautions (5.9).]
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured for: Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of
MERCK & CO., INC., Whitehouse Station, NJ 08889, USAManufactured by: Vetter Pharma-Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG, Ravensburg, Germany
BD, BD Logo and BD Micro-Fine are trademarks of Becton, Dickinson and Company
For patent information: www.merck.com/product/patent/home.html
Copyright © 2004-2019 Merck Sharp & Dohme B.V., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc.
All rights reserved.Revised: 09/2019
uspi-mk8328-SOi-1909r013
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
Follistim® (Fol'-lis-tim) AQ Cartridge
(follitropin beta injection)Read the Patient Information that comes with Follistim® AQ Cartridge before you start using it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
What is Follistim AQ Cartridge?
Follistim AQ is a prescription medicine that contains follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). The medicine is taken with the Follistim Pen®.
Follistim AQ Cartridge is used:
In women:
- to help healthy ovaries to develop (mature) and release eggs
- as part of treatment programs that use special techniques (skills) to help women get pregnant by causing their ovaries to produce more mature eggs
In men:
- to help bring about the production and development of sperm
Who should not take Follistim AQ Cartridge?
Do not take Follistim AQ Cartridge if you are a Woman or Man who:
- is allergic to recombinant human FSH products
- has a high level of FSH in your blood indicating that your ovaries (women only) or testes (men only) may be permanently damaged and do not work at all
- has uncontrolled thyroid, pituitary, or adrenal gland problems
- is allergic to streptomycin or neomycin (types of antibiotics)
- has a tumor of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, breast, uterus (women only), ovary (women only), or testis (men only)
Do not take Follistim AQ Cartridge if you are a Woman who:
- is pregnant or think you may be pregnant
- has heavy or irregular vaginal bleeding and the cause is not known
- has ovarian cysts or enlarged ovaries, not due to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Talk to your healthcare provider before taking this medicine if you have any of the conditions listed above.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Follistim AQ Cartridge?
Before you take Follistim AQ, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have ever had Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS).
- are pregnant or think you may be pregnant. Follistim AQ Cartridge should not be used in pregnant women.
- have an increased risk of blood clots (thrombosis).
- have ever had a blood clot (thrombosis), or anyone in your immediate family has ever had a blood clot (thrombosis).
- have ever had stomach (abdominal) surgery.
- have ever had twisting of your ovary (ovarian torsion).
- have or have had a cyst in your ovary.
- have polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS).
- have any other medical conditions (for example, diabetes, heart disease, or any other long-term disease).
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if the medicine in Follistim AQ Cartridge passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take Follistim AQ Cartridge or breastfeed. You should not do both at the same time.
- have been told by a doctor that pregnancy would be dangerous for you.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use Follistim AQ Cartridge?
- Be sure that you read, understand, and follow the "Patient Instructions for Use" that come with Follistim AQ Cartridge.
- Use Follistim AQ Cartridge exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how much Follistim AQ Cartridge to use, how to inject it, and how often it should be injected.
- Do not inject Follistim AQ Cartridge at home until your healthcare provider has taught you the right way to put the cartridge and pen device together and to inject yourself.
- Do not mix any other medicines into the cartridge.
- Do not change your dose of Follistim AQ Cartridge unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Call your healthcare provider immediately if you use too much Follistim AQ Cartridge.
- If you miss or forget to take a dose, do not double your next dose. Ask your healthcare provider for instructions.
- Use Follistim AQ Cartridge only with the Follistim Pen.
- Do not use the Follistim Pen if you are blind or visually impaired unless you have assistance from an individual with good vision who is trained in the right way to use the pen.
- Do not re-use the BD Micro-Fine™ Pen Needle.
- Your healthcare provider may do blood hormone tests while you are taking Follistim AQ Cartridge. Make sure you follow-up with your healthcare provider to have your blood tested when told to do so.
Women:
- Your healthcare provider will do ultrasound scans of your ovaries to monitor how the follicles are growing. Make sure you follow-up with your healthcare provider to have your ultrasound scans.
Men:
- Your healthcare provider may test your semen while you are taking Follistim AQ Cartridge. Make sure you follow-up with your healthcare provider to give a semen sample for testing.
What are the possible side effects of Follistim AQ Cartridge?
Follistim AQ Cartridge may cause serious side effects.
Serious side effects in women include:
- Ovarian enlargement. Your ovaries may become very large at the end of your fertility treatment cycle. Therefore, close supervision by your healthcare provider is very important. To check the effects of your fertility treatment, your healthcare provider will take ultrasound scans of your ovaries and may also check blood hormone levels.
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). OHSS is a serious medical problem that can happen when the ovaries are over stimulated. In rare cases, OHSS may be life-threatening and has caused death. OHSS causes fluid to build up suddenly in your stomach and chest areas and can cause blood clots to form. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
- pain in your lower stomach area.
- nausea.
- vomiting.
- sudden weight gain due to fluid buildup.
- diarrhea.
- decreased urine output.
- trouble breathing.
- Lung problems. Treatment with gonadotropic hormones like Follistim AQ Cartridge can cause you to have trouble breathing (acute respiratory distress syndrome).
- Blood clots. Treatment with gonadotropic hormones like Follistim AQ Cartridge may (just as with pregnancy) increase your chance of having blood clots (thrombosis) in your blood vessels. Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in a blood vessel. Blood clots can lead to:
- blockage in your lungs (pulmonary embolus).
- stroke.
- heart attack.
- blood vessel problems (thrombophlebitis).
- a lack of blood flow (deep venous thrombosis) that may result in a loss of your arm or leg.
- Ovarian torsion. Follistim AQ Cartridge may increase the chance of twisting of the ovaries in women with certain conditions such as OHSS, pregnancy and previous stomach (abdominal) surgery, past history of a twisting of an ovary, past or current cysts in your ovary or ovaries, or polycystic ovaries. Twisting of the ovary could cause the blood flow to the ovary to be cut off.
- Pregnancy and birth of multiple babies. There is an increased chance of having twins or more than two babies, even when only one embryo is transferred into the uterus. Having a pregnancy with more than one baby at a time increases the health risk for you and your babies. Discuss your chances of multiple births with your healthcare provider.
- Birth defects. A woman's age, certain sperm problems, genetic background of both parents and a pregnancy with multiple babies can increase the chance that your baby might have a birth defect.
- Ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside of the uterus). If treatment with Follistim AQ Cartridge results in pregnancy, there is a higher chance of pregnancy outside the uterus. Therefore, your healthcare provider should perform an early ultrasound examination to exclude the possibility of pregnancy occurring outside of the uterus.
- Miscarriage. Miscarriages have been reported for all gonadotropin treatments, including Follistim AQ Cartridge. However, it is not known if miscarriages are related to treatment with fertility medicines or the underlying infertility.
- Ovarian and Other Reproductive System Tumors. There have been reports of ovarian and other reproductive system tumors in women who have had infertility treatment. It is not known if treatment with fertility medicines increases the risk of these tumors in infertile women.
The most common side effects of Follistim AQ Cartridge include:
In women:
- headache
- nausea
- stomach pain
- discomfort or pain in the lower stomach area
- cyst (closed sac) in the ovary
- feeling tired
In men:
- headache
- pain at the injection site
- bruising, swelling or redness at the injection site
- breast enlargement
- acne
These are not all the possible side effects of Follistim AQ Cartridge. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your healthcare provider immediately if you get worsening or strong pain in the lower stomach area (abdomen). Also, call your healthcare provider immediately if this happens some days after the last injection has been given.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Follistim AQ Cartridge?
- Store Follistim AQ Cartridge in the refrigerator between 2°-8°C (36°-46°F) until the expiration date.
- Follistim AQ can be stored at or below 25°C (77°F) for 3 months or until the expiration date, whichever comes first. Once the rubber inlay of the Follistim AQ Cartridge has been pierced by a needle, the product may be stored only for a maximum of 28 days at 2°-25°C (36°-77°F).
- Keep Follistim AQ Cartridge away from light.
- Do not freeze.
Keep Follistim AQ Cartridge and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about Follistim AQ Cartridge
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in the Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Follistim AQ for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Follistim AQ Cartridge to other people, even if they have the same condition that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about Follistim AQ Cartridge. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for more information about Follistim AQ Cartridge that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information, go to www.follistim.com or call 1-866-836-5633.
What are the ingredients in Follistim AQ Cartridge?
Active ingredient: follitropin beta
Inactive ingredients: sucrose, sodium citrate, benzyl alcohol NF-10 mg/mL, L-methionine, polysorbate 20, water for injection, hydrochloric acid, and/or sodium hydroxide.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured for: Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of
MERCK & CO., INC., Whitehouse Station, NJ 08889, USAManufactured by: Vetter Pharma-Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG, Ravensburg, Germany
BD, BD Logo and BD Micro-Fine are trademarks of Becton, Dickinson and Company.
For patent information: www.merck.com/product/patent/home.html
Copyright © 2004-2019 Merck Sharp & Dohme B.V., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc.
All rights reserved.Revised: 09/2019
usppi-mk8328-SOi-1909r014
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
PATIENT INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Follistim® (Fol΄-lis-tim) AQ Cartridge
(follitropin beta injection)Read the Patient Instructions for Use that comes with Follistim® AQ Cartridge before you start using it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
- A.
Getting Ready
- Follistim Pen is not recommended for the blind or visually impaired user without the assistance of an individual with good vision, trained in the proper use of the injection device.
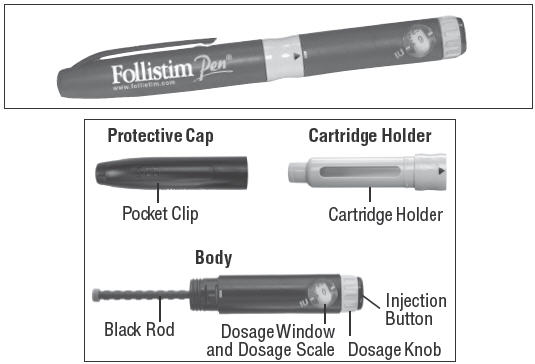
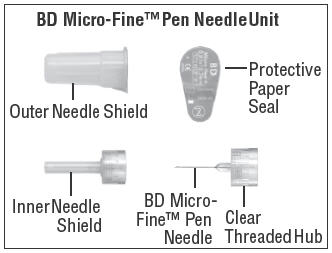
- Learn about all of the parts of the Follistim Pen (See Figure 1), Follistim AQ Cartridge (See Figure 2) and the BD Micro-Fine™ Pen Needle (See Figure 3). You will need to recognize these parts to follow the directions.
- Remove the Cartridge out of the refrigerator.
- Injecting cold drug is likely to cause discomfort. Therefore, it is recommended you allow the drug to reach room temperature before taking the injection.
- Check the liquid in the cartridge. It should appear clear and colorless. If the solution is not clear and colorless or has particles in it, do not use it.
-
Gather the supplies you will need for your injection. You will need:
- a clean dry surface
- alcohol
- cotton balls or alcohol pads
- sterile gauze
- a puncture-proof container to throw away the used syringe and needle
- Wash your hands with soap and water and dry them before you use Follistim Pen or when you replace the cartridge.
- B. Loading the Follistim Pen with the Follistim AQ Cartridge
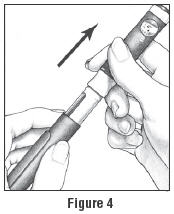
- Holding the Pen Body firmly with one hand, pull off the Protective Cap with your other hand (See Figure 4). Put the cap aside on a clean, dry surface.
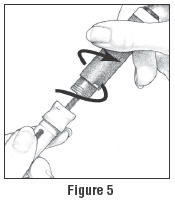
- Unscrew the entire Pen Body from the Cartridge Holder (See Figure 5). Place the Cartridge Holder and the Pen Body aside on a clean, dry surface.
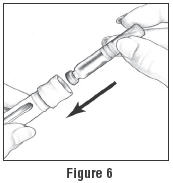
- Take the Follistim AQ Cartridge out of its package. Clean the rubber inlay on the cartridge with an alcohol pad. Pick up the Cartridge Holder. Put the Cartridge into the Cartridge Holder (See Figure 6). The metal rimmed cap goes in first.
-
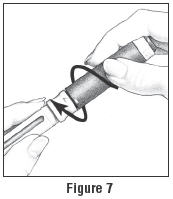
Pick up the Pen Body and lower it into the Cartridge Holder. The black rod must press against the Rubber Piston on the cartridge. Screw the Pen Body fully onto the Cartridge Holder (See Figure 7). Make sure there is no gap between the Pen Body and the Cartridge Holder. The arrow
 on the Cartridge Holder should point to the middle of the yellow alignment mark
on the Cartridge Holder should point to the middle of the yellow alignment mark  on the blue Pen Body.
on the blue Pen Body.
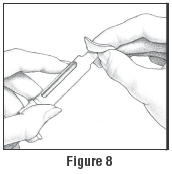
- Clean the open end of the Cartridge Holder with an alcohol pad (See Figure 8).
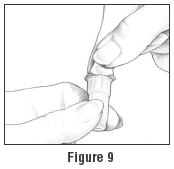
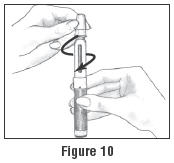
- Pick up a new BD Micro-Fine Pen Needle that is in its Outer Needle Shield. Peel off the protective paper seal (See Figure 9). Do not touch the needle. Do not place the open needle on any surface. Use Only the BD Micro-Fine 0.33 mm × 12.7 mm (29G) Pen Needles as supplied with the Follistim AQ Cartridge.
- You must use a new BD Micro-Fine Pen Needle with each injection. Never reuse a needle. Attach a new BD Micro-Fine Pen Needle after you make sure there is a Follistim AQ Cartridge in the Cartridge.
- Hold the Outer Needle Shield firmly in one hand while holding the Cartridge Holder firmly in the other hand. Push the end of the Cartridge Holder into the Outer Needle Shield. Screw them tightly together (See Figure 10). Place your Follistim Pen with the loaded cartridge and attached needle, flat on a clean, dry surface.
- C. Preparing the Injection Site
- Follistim AQ Cartridge can be injected directly into a layer of fat under your skin (subcutaneously).
- When giving a subcutaneous injection, follow your healthcare provider's instructions about changing the site for each injection. This will help lower your chances of having a skin reaction.
- Do not inject Follistim AQ Cartridge into an area that is tender, red, bruised, or hard.
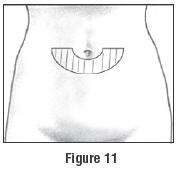
- The recommended site for injecting Follistim AQ Cartridge subcutaneously is:
- Clean the skin with an alcohol wipe where the injection is to be made. Clean about two inches around the injection site where the needle will be inserted. Do not touch the cleaned area of skin.
- D. Dialing the Dose Before You Give the Injection
- Your healthcare provider will decide on the dose of Follistim AQ Cartridge to be given. This dose may be increased or decreased as your treatment progresses depending on your individual type of treatment.
- Follistim AQ Cartridge using Follistim Pen can be administered subcutaneously (beneath the skin) in prescribed doses from 50 International Units (IU) up to 450 IU, in marked 25 IU increments. The Dosage Scale on the Pen has numbers and audible clicks to help you set the correct dose.
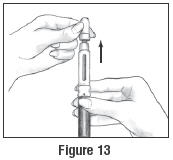
- Pull off the outer needle shield. Leave the Inner Needle Shield in place over the needle attached to the Pen (See Figure 13). Do not throw the Outer Needle Shield away, you will need it later when you throw the needle away.
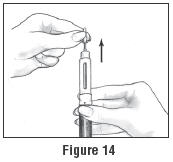
- Carefully remove the Inner Needle Shield and discard it (See Figure 14). Do not touch the needle or let it touch any surface while uncapped.
- Hold the Follistim Pen with the needle pointing upwards. Tap the Cartridge Holder gently with your finger to help air bubbles rise to the top of the needle. The small amount of air bubble will not affect the amount of medicine you receive.
- With a loaded new, unused cartridge:
- Dial the Dosage Knob until you hear one click. With the needle pointing upwards, push in the Injection Button.
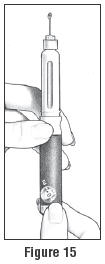
- Look for a droplet at the tip of the needle (See Figure 15). If you see the droplet, then you can dial in your dose.
- If you do not see a droplet, repeat Step 1 (as above) until you see droplet.
You must make sure you see a droplet of medicine (check the flow of medicine) or you may not inject the correct amount of medicine.
- With a partially used cartridge, to give yourself another dose of medicine you will need to attach a new BD Micro-Fine Pen Needle and look for a droplet forming at the tip of the needle (See Figure 15 above). If you see a droplet, then you can dial in your dose.
If no droplet:- 1. Dial the Dosage Knob until you hear one click. With the needle pointing upwards, push in the Injection Button.
- 2. Look for a droplet at the tip of the needle. If you see the droplet, then you can dial in your dose.
- Your Follistim AQ Cartridge should be one of the following:
- Orange Metal Cap – 150 international units
- Silver Metal Cap – 300 international units
- Gold Metal Cap – 600 international units
- Blue Metal Cap – 900 international units
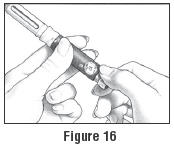
If you did not understand that you should have one of the cartridges above, please contact your healthcare provider. - For doses of 50 IU up to 450 IU, turn the Dosage Knob until the correct dosage aligns with the dosage markers on each side of the Dosage Window (see Figure 16).
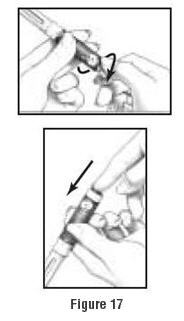
- If by mistake you dial past the correct number, do not try to turn the Dosage Knob backward to fix the mistake. Continue to turn the Dosage Knob in the same direction past the 450 IU mark, as far as it will turn. The Dosage Scale must move freely. Push the Injection Button in all the way. See Figure 17. Start to dial again starting from "0" upwards. By following these directions, you will not lose any medicine from the Follistim AQ Cartridge (See "Checking the Medicine Level Remaining").
- If you turn the Dosage Knob backward to correct the mistake, it will not damage the Pen, but you will lose some medication from the Follistim AQ Cartridge.
- Never dial your dose or try to correct a dialing mistake when the needle is still in your skin as this may result in your receiving an incorrect dose.
- If your prescribed dose exceeds the deliverable dose of Follistim Pen or exceeds the amount remaining in the cartridge, you will need to give yourself more than one injection.
- E. Giving Yourself an Injection
- Pinch a fold of skin at the cleaned injection site. Do not touch the cleaned area of skin.
- With the other hand hold the entire Pen with Cartridge loaded and Needle on like you would a pencil. Use a quick "dart-like" motion to insert the needle straight up and down (90-degree angle).
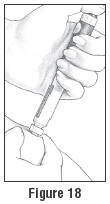
- Press the injection button all the way in to make sure you give yourself a full injection. (See Figure 18). Wait for five seconds before pulling the needle out of the skin. The middle of the Dosage Window should display a dot next to the "0".
If the injection button does not push in all the way, and the number in the Dosage Window does not read "0", it means there is not enough medication left in the cartridge to complete your prescribed dose. The number in the Dosage Window will give you the amount of medicine needed to complete your dose. Write this number down. This will be the number you dial for the completion of your dose. Start over with a new Follistim AQ Cartridge and a new needle and follow all the instructions up to this step. Make sure you choose a different injection site to complete your dose of Follistim AQ Cartridge. - Pull out the BD Micro-Fine Needle and firmly press down on the injection site with an alcohol swab. Use the BD Micro-Fine Pen Needle for one injection only.
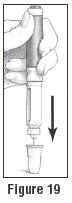
- Place the Outer Needle Shield on a flat table surface with the opening pointing up. The opening of the Outer Needle Shield is the wider end with the rim. Without holding on to the Outer Needle Shield, carefully insert the needle (attached to the Follistim Pen) into the opening of the Outer Needle Shield and push down firmly. The Outer Needle Shield should now be attached to the Cartridge Holder and covering the needle (See Figure 19).
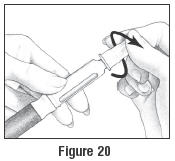
- Grip the Outer Needle Shield and use it to unscrew the needle from the Cartridge Holder (See Figure 20). If there is Follistim AQ Cartridge medicine left for more injections, put the Pen Cap back on the Pen Body and store your Follistim Pen in a safe place in the refrigerator (not in the freezer) or at room temperature. Never store the Follistim Pen with a needle attached to it. If you are giving an injection to another person, be very careful when removing the needle from the skin. Accidental needle sticks can transmit potentially serious or grave infectious diseases.
- Throw away the Outer Needle Shield with the used needle right away. Do not throw away in a trash can. Place it in a "special" container. (See "How Do I Throw Away Used Cartridges and Needles?")
- If there is Follistim AQ Cartridge medicine left for more injections, put the Pen Cap back on the Pen Body and store your Follistim Pen in a safe place in the refrigerator (not in the freezer) or at room temperature. Never store the Follistim Pen with a needle attached to it. If you are giving an injection to another person, be very careful when removing the needle from the skin. Accidental needle sticks can lead to serious infections.
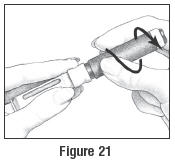
- Unscrew the Pen Body from the Cartridge Holder with the empty Follistim AQ Cartridge (See Figure 21).
- Put the Pen Body down on a clean, dry surface and remove the empty Follistim AQ Cartridge from the Cartridge Holder (See Figure 22). Safely, dispose of the empty Follistim AQ Cartridge right away in the same "special" container that you used for the needle disposal. Do not put the cartridge in a trash can. At the end of your treatment cycle, your doctor can advise you on how to properly dispose of the container. (See "How Do I Throw Away Used Cartridges and Needles?")
- F. Checking the Medicine Level Remaining
For women and men:
Your healthcare provider should advise you of the number of prescribed doses which can be extracted from the full unused Follistim AQ Cartridge.- Do not use the cartridge beyond the advised number of doses. Otherwise, you will run the risk that there will not be enough volume of drug for your prescribed dose.
For women only:- Keep a Follistim Pen Treatment Diary as follows:
- 1. Record the Follistim AQ Cartridge content on Day 1. This will either be 150, 300, 600 or 900 international units depending on what your healthcare provider has prescribed for you.
- 2. Record the dose you have been prescribed for your injection.
- 3. Subtract your Day 1 dose from the Follistim AQ Cartridge content (150, 300, 600 or 900 international units). (See example – Figure 23.) This will give you the remaining Follistim AQ Cartridge content after the Day 1 dose is taken.
- 4. Place the number determined as the content after Day 1 (see number 3) in the box as the Follistim AQ Cartridge content available for Day 2. (See example – Figure 23.)
- 5. Subtract your Day 2 dose from the Follistim AQ Cartridge content you recorded in Step 4. This will give you the remaining Follistim AQ Cartridge content after Day 2. Record this number of units. (See example – Figure 23.)
- 6.
Repeat the steps to determine the Follistim AQ Cartridge content available and Follistim AQ Cartridge remaining for each day of use.
- G. If There is Not Enough Follistim AQ in the Cartridge
- 1.
If you realize before you inject that you do not have enough medicine remaining in your Follistim AQ Cartridge for your complete dose, follow either Option 1 or Option 2, but not both.
- Option 1:
- Dial your dose and inject the remaining content in the Follistim AQ Cartridge. The Dosage Knob Injection Button will not push in all the way (do not try to force down the button) and the Dosage Window number will not read "0" but will read the number of units you will need to complete your prescribed dose.
- Write down the number of units needed to complete your dose.
- Remove the needle and dispose of it properly (see "How Do I Throw Away Used Cartridges and Needles?").
- Using the Dosage Knob, reset the Dial Window to "0" by turning the Dosage Knob past the 450 IU mark as far as it will turn and push the Injection Button in all the way.
- Before attempting to replace a Follistim AQ Cartridge, be sure that a BD Micro-Fine Pen Needle is not attached to the Follistim Pen.
- Insert a new cartridge into the Follistim Pen and attach a new BD Micro-Fine needle.
- Dial to the number of units you have written down to complete your prescribed dose.
- Prepare a different injection site and inject the remaining drug to complete your dose (See "Giving Yourself an Injection").
- Option 2
- Remove the Follistim AQ Cartridge.
- Start over with a new Follistim AQ Cartridge and Insert into the Follistim Pen.
- Follow the instructions for "Dialing the Dose" and "Giving Yourself an Injection."
- Option 1:
- 2.
If you realize after you have inserted the needle at the injection site that you do not have enough medicine remaining in your Follistim AQ Cartridge for your complete dose:
- Inject the remaining content in the Follistim AQ Cartridge. The Injection Button will not push in all the way and the number in the Dosage Window will not read "0" but will read the number of units you will need to complete your prescribed dose.
- Wait 5 seconds before withdrawing the needle from your skin and gently apply pressure to the injection site with an alcohol pad.
- Dispose of the used needle (See "How Do I Throw Away Used Cartridges and Needles?").
- Write down the number of units needed to complete your dose.
- Using the Dosage Knob, reset the Dial Window to "0" by turning the Dosage Knob past the 450 IU mark as far as it will turn and push the Injection Button in all the way.
- Insert a new cartridge into the Follistim Pen and attach a new BD Micro-Fine needle.
- Dial to the number you have recorded to complete your prescribed dose.
- Prepare a different injection site and inject the remaining drug to complete your dose (See "Giving Yourself an Injection").
- H. How to Solve Problems with Follistim AQ Cartridge and Follistim Pen
If you have problems with using the Follistim AQ Cartridge and the Follistim Pen, see the following chart. If you still have problems after following the chart or if your problem is not on the chart, contact your healthcare provider.
PROBLEM POSSIBLE CAUSES WHAT TO DO The Pen Body will not screw tightly into the Cartridge Holder. Is something in the way? Take out the Follistim Cartridge and check the Cartridge Holder to see if anything is in the way. Follow the instructions in this pamphlet to Screw the Pen Body fully onto the Cartridge Holder. No drug is coming out while checking the flow. The Cartridge Holder and the Pen Body are not properly screwed together. Remove the current needle; tighten the Pen Body to the Cartridge Holder ensuring the arrow on the Cartridge Holder is pointing to the middle of the yellow alignment mark on the blue Pen Body. Attach a new needle to the Pen.
Recheck the flow as follows:- Dial the Dosage Knob until you hear one click. With needle pointing upwards, push in the Injection Button.
- Look for a droplet at the tip of the needle.
Is the Follistim Cartridge empty? Change to a new cartridge. Has the needle been properly attached to the Follistim Pen? Remove needle and replace with a new one, ensuring that the needle is screwed on tightly to the Pen.
Recheck the flow as follows:- Dial the Dosage Knob until you hear one click. With needle pointing upwards, push in the Injection Button.
- Look for a droplet at the tip of the needle.
You are concerned that you can turn the Dosage Knob to the next number without clicking and the injection button spins freely. This is not a problem. The system is in the reset mode. The Injection Button and Dosage Knob must be pushed all the way down to '0' to re-engage the mechanism and the correct dose can now be set. A click will be heard for each setting in the viewing window. The Dosage Knob does not go back to '0' while you are injecting. Is the Follistim Cartridge empty? Change to a new cartridge. Is the needle blocked? - Remove the needle from the skin and dispose of safely.
- Check the Dosage Window and note how much remaining drug to inject.
- Attach a new needle.
- Dial the Dosage Knob until you hear one click. With needle pointing upwards, push in the Injection Button.
- Look for a droplet at the tip of the needle.
- Dial remaining dose.
Some of the drug is dripping out of the needle when you withdraw it from your skin. Did you take the needle out of your skin before waiting 5 seconds as directed in Step 15? If this happens you should inform your doctor. To avoid this problem again, you should always wait 5 seconds after you push the Injection Button before you withdraw the needle from your skin. The needle is left on the Follistim Pen. Have you missed any of the instructions? Dispose of the needle in a properly secured container as instructed by your doctor. Change to a new Follistim Cartridge and a new needle. After your last injection, a remaining volume may be left in the cartridge in addition to the normal quantity of drug dispensed. The cartridge contains extra volume for checking the drug flow. This is not a problem. You cannot get the cartridge out of the Follistim Pen. Is the needle attached? Remove the needle from the Follistim Pen and dispose of properly.
(Unscrew the Cartridge Holder from the Pen Body and take out the cartridge.)You are not sure how much drug is left in the cartridge and you do not want to start an injection and then find out that there is not enough drug. Have you kept good records of your doses? In case of any doubt, you should load a new, unused Follistim Cartridge into the Follistim Pen. See "If There is Not Enough Follistim AQ in the Cartridge."
To avoid this problem again, you should record your injections. (Women should use a treatment diary.)Important: If you have a question, always mention the Lot number of your Follistim Pen as printed on the Pen Body. If you have a complaint, please do not discard any product or packaging.
For questions on information contained in this leaflet, call 1-866-836-5633.
www.follistim.com
How Do I Throw Away Used Cartridges and Needles?
-
Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist for instructions about the right way to throw away used cartridges and needles. There may be special local or state laws about how to throw away used syringes and needles.
- Do not throw away used cartridges and needles in the household trash and do not recycle them.
- Put used and empty cartridges and needles in a closeable, puncture-resistant container. You may use a sharps container (such as a red bio-hazard container), a hard plastic container with a screw-on cap (such as an empty detergent bottle) or in a metal container with a plastic lid, (such as a coffee can).
- When the container is full, tape around the cap or lid to make sure the cap or lid does not come off.
- When your injection is given by another person, this person must also be careful when removing the cartridge and needle and disposing of the cartridge and needle to prevent accidental needle stick injury and passing infection.
How Do I Care for the Follistim Pen?
- 1. Clean all exposed surfaces of the Follistim Pen with a clean, damp cloth such as a paper towel. Never wash it in water, detergent or strong medical cleaners.
- 2. Handle the Follistim Pen carefully to avoid causing damage. You could damage the Follistim Pen by dropping it or handling it roughly.
- 3. Keep the Follistim Pen away from dust and dirt.
- 4. Never store the Follistim Pen with a needle attached to it. If you store the Follistim Pen with the needle attached, the drug could leak out and there is risk of contamination.
- 5. If the Follistim Pen breaks or is damaged, do not try to fix it yourself. Contact your healthcare provider.
- 6. Do not share your Follistim Pen with another person.
How should I store Follistim AQ Cartridge?
- Store Follistim AQ Cartridge in the refrigerator between 2°-8°C (36°-46°F) until the expiration date.
- Follistim AQ can be stored at or below 25°C (77°F) for 3 months or until the expiration date, whichever comes first. Once the rubber inlay of the Follistim AQ Cartridge has been pierced by a needle, the product may be stored only for a maximum of 28 days at 2°-25°C (36°-77°F).
- Keep Follistim AQ Cartridge away from light.
- Do not freeze.
Keep Follistim AQ Cartridge, needles, and the disposal container, out of the reach of children.
- A.
Getting Ready
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured for: Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of
MERCK & CO., INC., Whitehouse Station, NJ 08889, USAManufactured by: Vetter Pharma-Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG, Ravensburg, Germany
BD, BD Logo and BD Micro-Fine are trademarks of Becton, Dickinson and Company.
For patent information: www.merck.com/product/patent/home.html
Copyright © 2004-2019 Merck Sharp & Dohme B.V., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc.
All rights reserved.Revised: 09/2019
usppi-mk8328-SOi-1909r014
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 IU Kit Carton
NDC: 0052-0313-01
1 Sterile Prefilled 1.5 mL Cartridge
containing 0.420 mL and
5 BD Micro-Fine™ Pen Needles
Follistim® AQ Cartridge 300 IU
(follitropin beta injection)For use only with Follistim Pen®,
available separatelyFor Subcutaneous Use
Rx only

- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 600 IU Kit Carton
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 900 IU Kit Carton
NDC: 0052-0326-01
1 Sterile Prefilled 1.5 mL Cartridge
containing 1.170 mL and
10 BD Micro-Fine™ Pen NeedlesFollistim® AQ Cartridge 900 IU
(follitropin beta injection)For use only with Follistim Pen®,
available separatelyFor Subcutaneous Use
Rx only

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FOLLISTIM AQ
follitropin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0052-0313 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength follitropin (UNII: 076WHW89TW) (follitropin - UNII:076WHW89TW) follitropin 350 [iU] in 0.42 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength benzyl alcohol (UNII: LKG8494WBH) methionine (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) polysorbate 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) trisodium citrate dihydrate (UNII: B22547B95K) sucrose (UNII: C151H8M554) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) hydrochloric acid (UNII: QTT17582CB) sodium hydroxide (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0052-0313-01 1 in 1 CARTON 03/24/2004 1 1 in 1 KIT 1 0.42 mL in 1 CARTRIDGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 0052-0313-81 1 in 1 CARTON 03/24/2004 2 1 in 1 KIT 2 0.42 mL in 1 CARTRIDGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021211 03/24/2004 FOLLISTIM AQ
follitropin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0052-0316 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength follitropin (UNII: 076WHW89TW) (follitropin - UNII:076WHW89TW) follitropin 650 [iU] in 0.78 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength benzyl alcohol (UNII: LKG8494WBH) methionine (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) polysorbate 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) trisodium citrate dihydrate (UNII: B22547B95K) sucrose (UNII: C151H8M554) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) hydrochloric acid (UNII: QTT17582CB) sodium hydroxide (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0052-0316-01 1 in 1 CARTON 03/24/2004 1 1 in 1 KIT 1 0.78 mL in 1 CARTRIDGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 0052-0316-81 1 in 1 CARTON 03/24/2004 2 1 in 1 KIT 2 0.78 mL in 1 CARTRIDGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021211 03/24/2004 FOLLISTIM AQ
follitropin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0052-0326 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength follitropin (UNII: 076WHW89TW) (follitropin - UNII:076WHW89TW) follitropin 975 [iU] in 1.17 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength benzyl alcohol (UNII: LKG8494WBH) methionine (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) polysorbate 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) trisodium citrate dihydrate (UNII: B22547B95K) sucrose (UNII: C151H8M554) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) hydrochloric acid (UNII: QTT17582CB) sodium hydroxide (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0052-0326-01 1 in 1 CARTON 03/24/2004 1 1 in 1 KIT 1 1.17 mL in 1 CARTRIDGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021211 03/24/2004 Labeler - Organon USA Inc. (078796541)
Trademark Results [Follistim AQ]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 FOLLISTIM AQ 78584155 3166497 Live/Registered |
MERCK SHARP & DOHME B.V. 2005-03-10 |
 FOLLISTIM AQ 76170241 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
N.V. Organon 2000-11-22 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.