TRUXIMA- rituximab-abbs injection, solution
Truxima by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Truxima by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Cephalon, Inc., CELLTRION, Inc., SGS Vitrology Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRUXIMA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRUXIMA.
TRUXIMA® (rituximab-abbs) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
TRUXIMA (rituximab-abbs) is biosimilar* to RITUXAN® (rituximab) for the indications listed. (1)WARNING: FATAL INFUSION-RELATED REACTIONS, SEVERE MUCOCUTANEOUS REACTIONS, HEPATITIS B VIRUS REACTIVATION and PROGRESSIVE MULTIFOCAL LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Fatal infusion-related reactions within 24 hours of rituximab infusion; approximately 80% of fatal reactions occurred with first infusion. Monitor patients and discontinue TRUXIMA infusion for severe reactions (5.1).
- Severe mucocutaneous reactions, some with fatal outcomes (5.2).
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation, in some cases resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death (5.3).
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) resulting in death (5.4).
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TRUXIMA (rituximab-abbs) is a CD20-directed cytolytic antibody indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) (1.1).
- Relapsed or refractory, low grade or follicular, CD20-positive B-cell NHL as a single agent.
- Previously untreated follicular, CD20-positive, B-cell NHL in combination with first line chemotherapy and, in patients achieving a complete or partial response to a rituximab product in combination with chemotherapy, as single-agent maintenance therapy.
- Non-progressing (including stable disease), low-grade, CD20-positive, B-cell NHL as a single agent after first-line cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (CVP) chemotherapy.
-
Previously untreated diffuse large B-cell, CD20-positive NHL in combination with (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) (CHOP) or other anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) (1.2).
- Previously untreated and previously treated CD20-positive CLL in combination with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide (FC).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer only as an intravenous infusion.
- Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus.
- TRUXIMA should only be administered by a healthcare professional with appropriate medical support to manage severe infusion-related reactions that can be fatal if they occur.
- The dose for NHL is 375 mg/m2 (2.2).
- The dose for CLL is 375 mg/m2 in the first cycle and 500 mg/m2 in cycles 2-6, in combination with FC, administered every 28 days (2.3).
- The dose as a component of Zevalin® (ibritumomab tiuxetan) Therapeutic Regimen is 250 mg/m2 (2.4).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Injection: 100 mg/10 mL (10 mg/mL) and 500 mg/50 mL (10 mg/mL) solution in single dose vials (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Tumor lysis syndrome: Administer aggressive intravenous hydration, anti-hyperuricemic agents, monitor renal function (5.5).
- Infections: Withhold TRUXIMA and institute appropriate anti-infective therapy (5.6).
- Cardiac adverse reactions: Discontinue infusions in case of serious or life-threatening events (5.7).
- Renal toxicity: Discontinue in patients with rising serum creatinine or oliguria (5.8).
- Bowel obstruction and perforation: Consider and evaluate for abdominal pain, vomiting, or related symptoms (5.9).
- Immunizations: Live virus vaccinations prior to or during TRUXIMA treatment not recommended (5.10).
- Embryo-Fetal toxicity: Can cause neonatal harm. Advise of potential risk to neonates and use of effective contraception (5.11).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions in clinical trials were:
- NHL (≥ 25%): infusion-related reactions, fever, lymphopenia, chills, infection and asthenia (6.1).
- CLL (≥ 25%): infusion-related reactions and neutropenia (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact TEVA Pharmaceuticals at 1-888-483-8279 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Renal toxicity when used in combination with cisplatin (5.8).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
- * Biosimilar means that the biological product is approved based on data demonstrating that it is highly similar to an FDA-approved biological product, known as a reference product, and that there are no clinically meaningful differences between the biosimilar product and the reference product. Biosimilarity of TRUXIMA has been demonstrated for the condition(s) of use (e.g. indication(s), dosing regimen(s)), strength(s), dosage form(s), and route(s) of administration described in its Full Prescribing Information.
Revised: 11/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: FATAL INFUSION-RELATED REACTIONS, SEVERE MUCOCUTANEOUS REACTIONS, HEPATITIS B VIRUS REACTIVATION and PROGRESSIVE MULTIFOCAL LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY (PML)
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Non–Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
1.2 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosing Information
2.2 Recommended Dose for Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
2.3 Recommended Dose for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
2.4 Recommended Dose as a Component of Zevalin® for treatment of NHL
2.5 Recommended Dose for Premedication and Prophylactic Medications
2.6 Administration and Storage
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infusion-Related Reactions
5.2 Severe Mucocutaneous Reactions
5.3 Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation (HBV)
5.4 Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
5.5 Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS)
5.6 Infections
5.7 Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
5.8 Renal Toxicity
5.9 Bowel Obstruction and Perforation
5.10 Immunization
5.11 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience in Lymphoid Malignancies
6.2 Immunogenicity
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Relapsed or Refractory, Low-Grade or Follicular, CD20-Positive, B-Cell NHL
14.2 Previously Untreated, Low-Grade or Follicular, CD20-Positive, B-Cell NHL
14.3 Diffuse Large B-Cell NHL (DLBCL)
14.4 Ninety-Minute Infusions in Previously Untreated Follicular NHL and DLBCL
14.5 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: FATAL INFUSION-RELATED REACTIONS, SEVERE MUCOCUTANEOUS REACTIONS, HEPATITIS B VIRUS REACTIVATION and PROGRESSIVE MULTIFOCAL LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY (PML)
Infusion-Related Reactions
Administration of rituximab products, including TRUXIMA, can result in serious, including fatal, infusion-related reactions. Deaths within 24 hours of rituximab infusion have occurred. Approximately 80% of fatal infusion-related reactions occurred in association with the first infusion. Monitor patients closely. Discontinue TRUXIMA infusion for severe reactions and provide medical treatment for Grade 3 or 4 infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Severe Mucocutaneous Reactions
Severe, including fatal, mucocutaneous reactions can occur in patients receiving rituximab products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Reactivation
HBV reactivation can occur in patients treated with rituximab products, in some cases resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death. Screen all patients for HBV infection before treatment initiation, and monitor patients during and after treatment with TRUXIMA. Discontinue TRUXIMA and concomitant medications in the event of HBV reactivation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML), including fatal PML, can occur in patients receiving rituximab products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Non–Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
TRUXIMA (rituximab-abbs) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Relapsed or refractory, low-grade or follicular, CD20-positive, B-cell NHL as a single agent.
- Previously untreated follicular, CD20-positive, B-cell NHL in combination with first line chemotherapy and, in patients achieving a complete or partial response to a rituximab product in combination with chemotherapy, as single-agent maintenance therapy.
- Non-progressing (including stable disease), low-grade, CD20-positive, B-cell NHL as a single agent after first-line cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (CVP) chemotherapy.
- Previously untreated diffuse large B-cell, CD20-positive NHL in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone (CHOP) or other anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosing Information
Administer only as an Intravenous Infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus. TRUXIMA should only be administered by a healthcare professional with appropriate medical support to manage severe infusion-related reactions that can be fatal if they occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Premedicate before each infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Prior to First Infusion: Screen all patients for HBV infection by measuring HBsAg and anti-HBc before initiating treatment with TRUXIMA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Obtain complete blood counts including platelets (CBC) prior to the first dose.
During TRUXIMA Therapy: In patients with lymphoid malignancies, during treatment with TRUXIMA monotherapy, obtain complete blood counts (CBC) with differential and platelet counts prior to each TRUXIMA course. During treatment with TRUXIMA and chemotherapy, obtain CBC with differential and platelet counts at weekly to monthly intervals and more frequently in patients who develop cytopenias [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- First Infusion: Initiate infusion at a rate of 50 mg/hr. In the absence of infusion toxicity, increase infusion rate by 50 mg/hr increments every 30 minutes, to a maximum of 400 mg/hr.
-
Subsequent Infusions:
Standard Infusion: Initiate infusion at a rate of 100 mg/hr. In the absence of infusion toxicity, increase rate by 100 mg/hr increments at 30-minute intervals, to a maximum of 400 mg/hr.
For previously untreated follicular NHL and DLBCL patients:
If patients did not experience a Grade 3 or 4 infusion related adverse event during Cycle 1, a 90-minute infusion can be administered in Cycle 2 with a glucocorticoid-containing chemotherapy regimen.
Initiate at a rate of 20% of the total dose given in the first 30 minutes and the remaining 80% of the total dose given over the next 60 minutes. If the 90-minute infusion is tolerated in Cycle 2, the same rate can be used when administering the remainder of the treatment regimen (through Cycle 6 or 8).
Patients who have clinically significant cardiovascular disease or who have a circulating lymphocyte count ≥5000/mm3 before Cycle 2 should not be administered the 90-minute infusion [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
- Interrupt the infusion or slow the infusion rate for infusion-related reactions [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Continue the infusion at one-half the previous rate upon improvement of symptoms.
2.2 Recommended Dose for Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
The recommended dose is 375 mg/m2 as an intravenous infusion according to the following schedules:
-
Relapsed or Refractory, Low-Grade or Follicular, CD20-Positive, B-Cell NHL
Administer once weekly for 4 or 8 doses. -
Retreatment for Relapsed or Refractory, Low-Grade or Follicular, CD20-Positive, B-Cell NHL
Administer once weekly for 4 doses. -
Previously Untreated, Follicular, CD20-Positive, B-Cell NHL
Administer on Day 1 of each cycle of chemotherapy, for up to 8 doses. In patients with complete or partial response, initiate TRUXIMA maintenance eight weeks following completion of a rituximab product in combination with chemotherapy. Administer TRUXIMA as a single-agent every 8 weeks for 12 doses. -
Non-progressing, Low-Grade, CD20-Positive, B-Cell NHL, after first-line CVP chemotherapy
Following completion of 6–8 cycles of CVP chemotherapy, administer once weekly for 4 doses at 6-month intervals to a maximum of 16 doses. -
Diffuse Large B-Cell NHL
Administer on Day 1 of each cycle of chemotherapy for up to 8 infusions.
2.3 Recommended Dose for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
The recommended dose is:
- 375 mg/m2 the day prior to the initiation of FC chemotherapy, then 500 mg/m2 on Day 1 of cycles 2-6 (every 28 days).
2.4 Recommended Dose as a Component of Zevalin® for treatment of NHL
- Infuse TRUXIMA 250 mg/m2 within 4 hours prior to the administration of Indium-111-(In-111-) Zevalin and within 4 hours prior to the administration of Yttrium-90-(Y-90-) Zevalin.
- Administer TRUXIMA and In-111-Zevalin 7-9 days prior to TRUXIMA and Y-90-Zevalin.
- Refer to the Zevalin package insert for full prescribing information regarding the Zevalin therapeutic regimen.
2.5 Recommended Dose for Premedication and Prophylactic Medications
Premedicate with acetaminophen and an antihistamine before each infusion of TRUXIMA. For patients administered TRUXIMA according to the 90-minute infusion rate, the glucocorticoid component of their chemotherapy regimen should be administered prior to infusion [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
Provide prophylaxis treatment for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) and herpes virus infections for patients with CLL during treatment and for up to 12 months following treatment as appropriate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
2.6 Administration and Storage
- Use appropriate aseptic technique. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. TRUXIMA should be a clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution. Do not use vial if particulates or discoloration is present.
Administration
Withdraw the necessary amount of TRUXIMA and dilute to a final concentration of 1 mg/mL to 4 mg/mL in an infusion bag containing either 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP. Gently invert the bag to mix the solution. Do not mix or dilute with other drugs. Discard any unused portion left in the vial.
Storage
Diluted TRUXIMA solutions for infusion may be stored at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for 24 hours.
Diluted TRUXIMA solutions for infusion have been shown to be stable for an additional 24 hours at room temperature. However, since TRUXIMA solutions do not contain a preservative, diluted solutions should be stored refrigerated (2°C to 8°C). No incompatibilities between TRUXIMA and polyvinylchloride or polyethylene bags have been observed.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infusion-Related Reactions
Rituximab products can cause severe, including fatal, infusion-related reactions. Severe reactions typically occurred during the first infusion with time to onset of 30–120 minutes. Rituximab product-induced infusion-related reactions and sequelae include urticaria, hypotension, angioedema, hypoxia, bronchospasm, pulmonary infiltrates, acute respiratory distress syndrome, myocardial infarction, ventricular fibrillation, cardiogenic shock, anaphylactoid events, or death.
Premedicate patients with an antihistamine and acetaminophen prior to dosing. Institute medical management (e.g. glucocorticoids, epinephrine, bronchodilators, or oxygen) for infusion-related reactions as needed. Depending on the severity of the infusion-related reaction and the required interventions, temporarily or permanently discontinue TRUXIMA. Resume infusion at a minimum 50% reduction in rate after symptoms have resolved. Closely monitor the following patients: those with pre-existing cardiac or pulmonary conditions, those who experienced prior cardiopulmonary adverse reactions, and those with high numbers of circulating malignant cells ( ≥ 25,000/mm3). [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Severe Mucocutaneous Reactions
Mucocutaneous reactions, some with fatal outcome, can occur in patients treated with rituximab products. These reactions include paraneoplastic pemphigus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, lichenoid dermatitis, vesiculobullous dermatitis, and toxic epidermal necrolysis. The onset of these reactions has been variable and includes reports with onset on the first day of rituximab exposure. Discontinue TRUXIMA in patients who experience a severe mucocutaneous reaction. The safety of re-administration of rituximab products to patients with severe mucocutaneous reactions has not been determined.
5.3 Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation (HBV)
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation, in some cases resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure and death, can occur in patients treated with drugs classified as CD20-directed cytolytic antibodies, including rituximab products. Cases have been reported in patients who are hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) positive and also in patients who are HBsAg negative but are hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) positive. Reactivation also has occurred in patients who appear to have resolved hepatitis B infection (i.e., HBsAg negative, anti-HBc positive and hepatitis B surface antibody [anti-HBs] positive).
HBV reactivation is defined as an abrupt increase in HBV replication manifesting as a rapid increase in serum HBV DNA levels or detection of HBsAg in a person who was previously HBsAg negative and anti-HBc positive. Reactivation of HBV replication is often followed by hepatitis, i.e., increase in transaminase levels. In severe cases increase in bilirubin levels, liver failure, and death can occur.
Screen all patients for HBV infection by measuring HBsAg and anti-HBc before initiating treatment with TRUXIMA. For patients who show evidence of prior hepatitis B infection (HBsAg positive [regardless of antibody status] or HBsAg negative but anti-HBc positive), consult with physicians with expertise in managing hepatitis B regarding monitoring and consideration for HBV antiviral therapy before and/or during TRUXIMA treatment.
Monitor patients with evidence of current or prior HBV infection for clinical and laboratory signs of hepatitis or HBV reactivation during and for several months following rituximab therapy. HBV reactivation has been reported up to 24 months following completion of TRUXIMA therapy.
In patients who develop reactivation of HBV while on TRUXIMA, immediately discontinue TRUXIMA and any concomitant chemotherapy, and institute appropriate treatment. Insufficient data exist regarding the safety of resuming TRUXIMA treatment in patients who develop HBV reactivation. Resumption of TRUXIMA treatment in patients whose HBV reactivation resolves should be discussed with physicians with expertise in managing HBV.
5.4 Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
JC virus infection resulting in PML and death can occur in rituximab product-treated patients with hematologic malignancies. The majority of patients with hematologic malignancies diagnosed with PML received rituximab in combination with chemotherapy or as part of a hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Most cases of PML were diagnosed within 12 months of their last infusion of rituximab.
Consider the diagnosis of PML in any patient presenting with new-onset neurologic manifestations. Evaluation of PML includes, but is not limited to, consultation with a neurologist, brain MRI, and lumbar puncture.
Discontinue TRUXIMA and consider discontinuation or reduction of any concomitant chemotherapy or immunosuppressive therapy in patients who develop PML.
5.5 Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS)
Acute renal failure, hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, hyperuricemia, or hyperphosphatemia from tumor lysis, sometimes fatal, can occur within 12-24 hours after the first infusion of rituximab products in patients with NHL. A high number of circulating malignant cells ( ≥25,000/mm3) or high tumor burden, confers a greater risk of TLS.
Administer aggressive intravenous hydration and anti-hyperuricemic therapy in patients at high risk for TLS. Correct electrolyte abnormalities, monitor renal function and fluid balance, and administer supportive care, including dialysis as indicated. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].5.6 Infections
Serious, including fatal, bacterial, fungal, and new or reactivated viral infections can occur during and following the completion of rituximab product-based therapy. Infections have been reported in some patients with prolonged hypogammaglobulinemia (defined as hypogammaglobulinemia >11 months after rituximab exposure). New or reactivated viral infections included cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, parvovirus B19, varicella zoster virus, West Nile virus, and hepatitis B and C. Discontinue TRUXIMA for serious infections and institute appropriate anti-infective therapy.[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. TRUXIMA is not recommended for use in patients with severe, active infections.
5.7 Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
Cardiac adverse reactions, including ventricular fibrillation, myocardial infarction, and cardiogenic shock may occur in patients receiving rituximab products. Discontinue infusions for serious or life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias. Perform cardiac monitoring during and after all infusions of TRUXIMA for patients who develop clinically significant arrhythmias, or who have a history of arrhythmia or angina.
5.8 Renal Toxicity
Severe, including fatal, renal toxicity can occur after rituximab product administration in patients with NHL. Renal toxicity has occurred in patients who experience tumor lysis syndrome and in patients with NHL administered concomitant cisplatin therapy during clinical trials. The combination of cisplatin and TRUXIMA is not an approved treatment regimen. Monitor closely for signs of renal failure and discontinue TRUXIMA in patients with a rising serum creatinine or oliguria. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
5.9 Bowel Obstruction and Perforation
Abdominal pain, bowel obstruction and perforation, in some cases leading to death, can occur in patients receiving rituximab products in combination with chemotherapy. In postmarketing reports, the mean time to documented gastrointestinal perforation was 6 (range 1-77) days in patients with NHL. Evaluate if symptoms of obstruction such as abdominal pain or repeated vomiting occur.
5.10 Immunization
The safety of immunization with live viral vaccines following rituximab product therapy has not been studied and vaccination with live virus vaccines is not recommended before or during treatment.
5.11 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on human data, rituximab products can cause fetal harm due to B-cell lymphocytopenia in infants exposed in-utero. Advise pregnant women of the risk to a fetus. Females of childbearing potential should use effective contraception while receiving TRUXIMA and for 12 months following the last dose of TRUXIMA.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Severe mucocutaneous reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatitis B reactivation with fulminant hepatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Tumor lysis syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Cardiovascular adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Renal toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Bowel obstruction and perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience in Lymphoid Malignancies
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.The data described below reflect exposure to rituximab in 2783 patients, with exposures ranging from a single infusion up to 2 years. Rituximab was studied in both single-arm and controlled trials (n=356 and n=2427). The population included 1180 patients with low grade or follicular lymphoma, 927 patients with DLBCL, and 676 patients with CLL. Most NHL patients received rituximab as an infusion of 375 mg/m2 per infusion, given as a single agent weekly for up to 8 doses, in combination with chemotherapy for up to 8 doses, or following chemotherapy for up to 16 doses. CLL patients received rituximab 375 mg/m2 as an initial infusion followed by 500 mg/m2 for up to 5 doses, in combination with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide. Seventy-one percent of CLL patients received 6 cycles and 90% received at least 3 cycles of rituximab-based therapy.
The most common adverse reactions of rituximab (incidence ≥25%) observed in clinical trials of patients with NHL were infusion-related reactions, fever, lymphopenia, chills, infection, and asthenia.
The most common adverse reactions of rituximab (incidence ≥25%) observed in clinical trials of patients with CLL were: infusion-related reactions and neutropenia.
Infusion-Related Reactions
In the majority of patients with NHL, infusion-related reactions consisting of fever, chills/rigors, nausea, pruritus, angioedema, hypotension, headache, bronchospasm, urticaria, rash, vomiting, myalgia, dizziness, or hypertension occurred during the first rituximab infusion. Infusion-related reactions typically occurred within 30 to 120 minutes of beginning the first infusion and resolved with slowing or interruption of the rituximab infusion and with supportive care (diphenhydramine, acetaminophen, and intravenous saline). The incidence of infusion-related reactions was highest during the first infusion (77%) and decreased with each subsequent infusion. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. In patients with previously untreated follicular NHL or previously untreated DLBCL, who did not experience a Grade 3 or 4 infusion-related reaction in Cycle 1 and received a 90-minute infusion of rituximab at Cycle 2, the incidence of Grade 3-4 infusion-related reactions on the day of, or day after the infusion was 1.1% (95% CI [0.3%, 2.8%]). For Cycles 2-8, the incidence of Grade 3-4 infusion-related reactions on the day of or day after the 90-minute infusion, was 2.8% (95% CI [1.3%, 5.0%]). [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Clinical Studies (14.4)].
Infections
Serious infections (NCI CTCAE Grade 3 or 4), including sepsis, occurred in less than 5% of patients with NHL in the single-arm studies. The overall incidence of infections was 31% (bacterial 19%, viral 10%, unknown 6%, and fungal 1%). [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
In randomized, controlled studies where rituximab was administered following chemotherapy for the treatment of follicular or low-grade NHL, the rate of infection was higher among patients who received rituximab. In diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients, viral infections occurred more frequently in those who received rituximab.
Cytopenias and hypogammaglobulinemia
In patients with NHL receiving rituximab monotherapy, NCI-CTC Grade 3 and 4 cytopenias were reported in 48% of patients. These included lymphopenia (40%), neutropenia (6%), leukopenia (4%), anemia (3%), and thrombocytopenia (2%). The median duration of lymphopenia was 14 days (range, 1-588 days) and of neutropenia was 13 days (range, 2-116 days). A single occurrence of transient aplastic anemia (pure red cell aplasia) and two occurrences of hemolytic anemia following rituximab therapy occurred during the single-arm studies.
In studies of monotherapy, rituximab -induced B-cell depletion occurred in 70% to 80% of patients with NHL. Decreased IgM and IgG serum levels occurred in 14% of these patients.
In CLL trials, the frequency of prolonged neutropenia and late-onset neutropenia was higher in patients treated with R-FC compared to patients treated with FC. Prolonged neutropenia is defined as Grade 3-4 neutropenia that has not resolved between 24 and 42 days after the last dose of study treatment. Late-onset neutropenia is defined as Grade 3-4 neutropenia starting at least 42 days after the last treatment dose.
In patients with previously untreated CLL, the frequency of prolonged neutropenia was 8.5% for patients who received R-FC (n=402) and 5.8% for patients who received FC (n=398). In patients who did not have prolonged neutropenia, the frequency of late-onset neutropenia was 14.8% of 209 patients who received R-FC and 4.3% of 230 patients who received FC.
For patients with previously treated CLL, the frequency of prolonged neutropenia was 24.8% for patients who received R-FC (n=274) and 19.1% for patients who received FC (n=274). In patients who did not have prolonged neutropenia, the frequency of late-onset neutropenia was 38.7% in 160 patients who received R-FC and 13.6% of 147 patients who received FC.
Relapsed or Refractory, Low-Grade NHL
Adverse reactions presented in Table 1 occurred in 356 patients with relapsed or refractory, low-grade or follicular, CD20-positive, B-cell NHL treated in single-arm studies of rituximab administered as a single agent [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Most patients received rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 doses.
Table 1 Incidence of Adverse Reactions in ≥5% of Patients with Relapsed or Refractory, Low-Grade or Follicular NHL, Receiving Single-agent Rituximab (N=356)*,† All Grades (%) Grade 3 and 4 (%) - * Adverse reactions observed up to 12 months following rituximab products.
- † Adverse reactions graded for severity by NCI-CTC criteria.
Any Adverse Reactions 99 57 Body as a Whole 86 10 Fever 53 1 Chills 33 3 Infection 31 4 Asthenia 26 1 Headache 19 1 Abdominal Pain 14 1 Pain 12 1 Back Pain 10 1 Throat Irritation 9 0 Flushing 5 0 Heme and Lymphatic System 67 48 Lymphopenia 48 40 Leukopenia 14 4 Neutropenia 14 6 Thrombocytopenia 12 2 Anemia 8 3 Skin and Appendages 44 2 Night Sweats 15 1 Rash 15 1 Pruritus 14 1 Urticaria 8 1 Respiratory System 38 4 Increased Cough 13 1 Rhinitis 12 1 Bronchospasm 8 1 Dyspnea 7 1 Sinusitis 6 0 Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders 38 3 Angioedema 11 1 Hyperglycemia 9 1 Peripheral Edema 8 0 LDH Increase 7 0 Digestive System 37 2 Nausea 23 1 Diarrhea 10 1 Vomiting 10 1 Nervous System 32 1 Dizziness 10 1 Anxiety 5 1 Musculoskeletal System 26 3 Myalgia 10 1 Arthralgia 10 1 Cardiovascular System 25 3 Hypotension 10 1 Hypertension 6 1 In these single-arm rituximab studies, bronchiolitis obliterans occurred during and up to 6 months after rituximab infusion.
Previously Untreated, Low-Grade or Follicular, NHL
In NHL Study 4, patients in the R-CVP arm experienced a higher incidence of infusional toxicity and neutropenia compared to patients in the CVP arm. The following adverse reactions occurred more frequently ( ≥5%) in patients receiving R-CVP compared to CVP alone: rash (17% vs. 5%), cough (15% vs. 6%), flushing (14% vs. 3%), rigors (10% vs. 2%), pruritus (10% vs. 1%), neutropenia (8% vs. 3%), and chest tightness (7% vs. 1%). [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
In NHL Study 5, detailed safety data collection was limited to serious adverse reactions, Grade ≥ 2 infections, and Grade ≥ 3 adverse reactions. In patients receiving rituximab as single-agent maintenance therapy following rituximab plus chemotherapy, infections were reported more frequently compared to the observation arm (37% vs. 22%). Grade 3-4 adverse reactions occurring at a higher incidence (≥ 2%) in the rituximab group were infections (4% vs. 1%) and neutropenia (4% vs. <1%).
In NHL Study 6, the following adverse reactions were reported more frequently (≥5%) in patients receiving rituximab following CVP compared to patients who received no further therapy: fatigue (39% vs. 14%), anemia (35% vs. 20%), peripheral sensory neuropathy (30% vs. 18%), infections (19% vs. 9%), pulmonary toxicity (18% vs. 10%), hepato-biliary toxicity (17% vs. 7%), rash and/or pruritus (17% vs. 5%), arthralgia (12% vs. 3%), and weight gain (11% vs. 4%). Neutropenia was the only Grade 3 or 4 adverse reaction that occurred more frequently (≥2%) in the rituximab arm compared with those who received no further therapy (4% vs. 1%). [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
DLBCL
In NHL Studies 7 (NCT00003150) and 8, [see Clinical Studies (14.3)], the following adverse reactions, regardless of severity, were reported more frequently (≥5%) in patients age ≥60 years receiving R-CHOP as compared to CHOP alone: pyrexia (56% vs. 46%), lung disorder (31% vs. 24%), cardiac disorder (29% vs. 21%), and chills (13% vs. 4%). Detailed safety data collection in these studies was primarily limited to Grade 3 and 4 adverse reactions and serious adverse reactions.
In NHL Study 8, a review of cardiac toxicity determined that supraventricular arrhythmias or tachycardia accounted for most of the difference in cardiac disorders (4.5% for R-CHOP vs. 1.0% for CHOP).
The following Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions occurred more frequently among patients in the R-CHOP arm compared with those in the CHOP arm: thrombocytopenia (9% vs. 7%) and lung disorder (6% vs. 3%). Other Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions occurring more frequently among patients receiving R-CHOP were viral infection (NHL Study 8), neutropenia (NHL Studies 8 and 9 (NCT00064116)), and anemia (NHL Study 9).
CLL
The data below reflect exposure to rituximab in combination with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in 676 patients with CLL in CLL Study 11 (NCT00281918) or CLL Study 12 (NCT00090051) [see Clinical Studies (14.5)]. The age range was 30-83 years and 71% were men. Detailed safety data collection in CLL Study 11 was limited to Grade 3 and 4 adverse reactions and serious adverse reactions.
Infusion-related adverse reactions were defined by any of the following adverse events occurring during or within 24 hours of the start of infusion: nausea, pyrexia, chills, hypotension, vomiting, and dyspnea.
In CLL Study 11, the following Grade 3 and 4 adverse reactions occurred more frequently in R-FC-treated patients compared to FC-treated patients: infusion-related reactions (9% in R-FC arm), neutropenia (30% vs. 19%), febrile neutropenia (9% vs. 6%), leukopenia (23% vs. 12%), and pancytopenia (3% vs. 1%).
In CLL Study 12, the following Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions occurred more frequently in R-FC-treated patients compared to FC-treated patients: infusion-related reactions (7% in R-FC arm), neutropenia (49% vs. 44%), febrile neutropenia (15% vs. 12%), thrombocytopenia (11% vs. 9%), hypotension (2% vs. 0%), and hepatitis B (2% vs. <1%). Fifty-nine percent of R-FC-treated patients experienced an infusion-related reaction of any severity.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to rituximab in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
Using an ELISA assay, anti-rituximab antibody was detected in 4 of 356 (1.1%) patients with low-grade or follicular NHL receiving single-agent rituximab. Three of the four patients had an objective clinical response.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of rituximab. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Hematologic: prolonged pancytopenia, marrow hypoplasia, Grade 3-4 prolonged or late-onset neutropenia, hyperviscosity syndrome in Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia, prolonged hypogammaglobulinemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- Cardiac: fatal cardiac failure.
- Immune/Autoimmune Events: uveitis, optic neuritis, systemic vasculitis, pleuritis, lupus-like syndrome, serum sickness, polyarticular arthritis, and vasculitis with rash.
- Infection: viral infections, including progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), increase in fatal infections in HIV-associated lymphoma, and a reported increased incidence of Grade 3 and 4 infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- Neoplasia: disease progression of Kaposi's sarcoma.
- Skin: severe mucocutaneous reactions.
- Gastrointestinal: bowel obstruction and perforation.
- Pulmonary: fatal bronchiolitis obliterans and fatal interstitial lung disease.
- Nervous system: Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) / Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS).
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on human data, rituximab products can cause adverse developmental outcomes including B-cell lymphocytopenia in infants exposed in-utero (see Clinical Considerations). In animal reproduction studies, intravenous administration of rituximab to pregnant cynomolgus monkeys during the period of organogenesis caused lymphoid B-cell depletion in the newborn offspring at doses resulting in 80% of the exposure (based on AUC) of those achieved following a dose of 2 grams in humans. Advise pregnant women of the risk to a fetus.
Adverse outcomes in pregnancy occur regardless of the health of the mother or the use of medications. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. The estimated background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2%-4% and of miscarriage is 15%-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Human data
Postmarketing data indicate that B-cell lymphocytopenia generally lasting less than six months can occur in infants exposed to rituximab in-utero. Rituximab was detected postnatally in the serum of infants exposed in-utero.
Animal Data
An embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study was performed on pregnant cynomolgus monkeys. Pregnant animals received rituximab via the intravenous route during early gestation (organogenesis period; post coitum days 20 through 50). Rituximab was administered as loading doses on post coitum (PC) Days 20, 21 and 22, at 15, 37.5 or 75 mg/kg/day, and then weekly on PC Days 29, 36, 43 and 50, at 20, 50 or 100 mg/kg/week. The 100 mg/kg/week dose resulted in 80% of the exposure (based on AUC) of those achieved following a dose of 2 grams in humans. Rituximab crosses the monkey placenta. Exposed offspring did not exhibit any teratogenic effects but did have decreased lymphoid tissue B cells.
A subsequent pre-and postnatal reproductive toxicity study in cynomolgus monkeys was completed to assess developmental effects including the recovery of B cells and immune function in infants exposed to rituximab in utero. Animals were treated with a loading dose of 0, 15, or 75 mg/kg every day for 3 days, followed by weekly dosing with 0, 20, or 100 mg/kg dose. Subsets of pregnant females were treated from PC Day 20 through postpartum Day 78, PC Day 76 through PC Day 134, and from PC Day 132 through delivery and postpartum Day 28. Regardless of the timing of treatment, decreased B cells and immunosuppression were noted in the offspring of rituximab-treated pregnant animals. The B-cell counts returned to normal levels, and immunologic function was restored within 6 months postpartum.
8.2 Lactation
There are no data on the presence of rituximab products in human milk, the effect on the breastfed child, or the effect on milk production. However, rituximab is detected in the milk of lactating cynomolgus monkeys, and IgG is present in human milk. Since many drugs including antibodies are present in human milk, advise a lactating woman not to breastfeed during treatment and for at least 6 months after the last dose of TRUXIMA due to the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Rituximab products can cause fetal harm [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of rituximab in pediatric patients have not been established.
Hypogammaglobulinemia has been observed in pediatric patients treated with rituximab.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Diffuse Large B-Cell NHL
Among patients with DLBCL evaluated in three randomized, active-controlled trials, 927 patients received rituximab in combination with chemotherapy. Of these, 396 (43%) were age 65 or greater and 123 (13%) were age 75 or greater. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients. Cardiac adverse reactions, mostly supraventricular arrhythmias, occurred more frequently among elderly patients. Serious pulmonary adverse reactions were also more common among the elderly, including pneumonia and pneumonitis.
Low-Grade or Follicular Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Patients with previously untreated follicular NHL evaluated in NHL Study 5 were randomized to rituximab as single-agent maintenance therapy (n=505) or observation (n=513) after achieving a response to rituximab in combination with chemotherapy. Of these, 123 (24%) patients in the rituximab arm were age 65 or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients. Other clinical studies of rituximab in low-grade or follicular, CD20-positive, B-cell NHL did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Among patients with CLL evaluated in two randomized active-controlled trials, 243 of 676 rituximab-treated patients (36%) were 65 years of age or older; of these, 100 rituximab-treated patients (15%) were 70 years of age or older.
In exploratory analyses defined by age, there was no observed benefit from the addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide among patients 70 years of age or older in CLL Study 11 or in CLL Study 12; there was also no observed benefit from the addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide among patients 65 years of age or older in Study 12 [see Clinical Studies (14.5)]. Patients 70 years or older received lower dose intensity of fludarabine and cyclophosphamide compared to younger patients, regardless of the addition of rituximab. In CLL Study 11, the dose intensity of rituximab was similar in older and younger patients, however in CLL Study 12 older patients received a lower dose intensity of rituximab.
The incidence of Grade 3 and 4 adverse reactions was higher among patients receiving R-FC who were 70 years or older compared to younger patients for neutropenia [44% vs. 31% (CLL Study 11); 56% vs. 39% (CLL Study 12)], febrile neutropenia [16% vs. 6% (NHL Study 10 (NCT00719472))], anemia [5% vs. 2% (CLL Study 11); 21% vs. 10% (CLL Study 12)], thrombocytopenia [19% vs. 8% (CLL Study 12)], pancytopenia [7% vs. 2% (CLL Study 11); 7% vs. 2% (CLL Study 12)] and infections [30% vs. 14% (CLL Study 12)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Rituximab-abbs is a genetically engineered chimeric murine/human monoclonal IgG1 kappa antibody directed against the CD20 antigen. Rituximab-abbs has an approximate molecular weight of 145 kD.
Rituximab-abbs is produced by mammalian cell (Chinese Hamster Ovary) suspension culture in a nutrient medium that may contain the antibiotic gentamicin. Gentamicin is not detectable in the final product.
TRUXIMA (rituximab-abbs) injection is a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow, preservative-free solution for intravenous infusion. TRUXIMA is supplied at a concentration of 10 mg/mL in either 100 mg/10 mL or 500 mg/50 mL single-dose vials. Each mL of solution contains 10 mg rituximab-abbs, polysorbate 80 (0.7 mg), sodium chloride (9 mg), tri-sodium citrate dihydrate (7.35 mg), and Water for Injection, USP. The pH is 6.5.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Rituximab-abbs is a monoclonal antibody. Rituximab products target the CD20 antigen expressed on the surface of pre-B and mature B-lymphocytes. Upon binding to CD20, rituximab products mediate B-cell lysis. Possible mechanisms of cell lysis include complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
In NHL patients, administration of rituximab resulted in depletion of circulating and tissue-based B cells. Among 166 patients in NHL Study 1 (NCT000168740), circulating CD19-positive B cells were depleted within the first three weeks with sustained depletion for up to 6 to 9 months post treatment in 83% of patients.
B-cell recovery began at approximately 6 months and median B-cell levels returned to normal by 12 months following completion of treatment.
There were sustained and statistically significant reductions in both IgM and IgG serum levels observed from 5 through 11 months following rituximab administration; 14% of patients had IgM and/or IgG serum levels below the normal range.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
Pharmacokinetics were characterized in 203 NHL patients receiving 375 mg/m2 rituximab weekly by intravenous infusion for 4 doses. Rituximab was detectable in the serum of patients 3 to 6 months after completion of treatment.
The pharmacokinetic profile of rituximab when administered as 6 infusions of 375 mg/m2 in combination with 6 cycles of CHOP chemotherapy was similar to that seen with rituximab alone.
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis of data from 298 NHL patients who received rituximab once weekly or once every three weeks, the estimated median terminal elimination half-life was 22 days (range, 6.1 to 52 days). Patients with higher CD19-positive cell counts or larger measurable tumor lesions at pretreatment had a higher clearance. However, dose adjustment for pretreatment CD19 count or size of tumor lesion is not necessary. Age and gender had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of rituximab.
Pharmacokinetics were characterized in 21 patients with CLL receiving rituximab according to the recommended dose and schedule. The estimated median terminal half-life of rituximab was 32 days (range, 14 to 62 days).
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Relapsed or Refractory, Low-Grade or Follicular, CD20-Positive, B-Cell NHL
The safety and effectiveness of rituximab in relapsed, refractory CD20+ NHL were demonstrated in 3 single-arm studies enrolling 296 patients.
NHL Study 1
A multicenter, open-label, single-arm study was conducted in 166 patients with relapsed or refractory, low-grade or follicular, B-cell NHL who received 375 mg/m2 of rituximab given as an intravenous infusion weekly for 4 doses. Patients with tumor masses > 10 cm or with > 5000 lymphocytes/µL in the peripheral blood were excluded from the study.
Results are summarized in Table 2. The median time to onset of response was 50 days. Disease-related signs and symptoms (including B-symptoms) resolved in 64% (25/39) of those patients with such symptoms at study entry.
NHL Study 2
In a multicenter, single-arm study, 37 patients with relapsed or refractory, low-grade NHL received 375 mg/m2 of rituximab weekly for 8 doses. Results are summarized in Table 2.
NHL Study 3
In a multicenter, single-arm study, 60 patients received 375 mg/m2 of rituximab weekly for 4 doses. All patients had relapsed or refractory, low-grade or follicular, B-cell NHL and had achieved an objective clinical response to rituximab administered 3.8–35.6 months (median 14.5 months) prior to retreatment with rituximab. Of these 60 patients, 5 received more than one additional course of rituximab. Results are summarized in Table 2.
Bulky Disease
In pooled data from studies 1 and 3, 39 patients with bulky (single lesion > 10 cm in diameter) and relapsed or refractory, low-grade NHL received rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 doses. Results are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2 Summary of Rituximab NHL Efficacy Data by Schedule and Clinical Setting NHL Study 1
Weekly × 4
N=166NHL Study 2
Weekly × 8
N=37NHL Study 1 and NHL Study 3
Bulky disease,
Weekly × 4
N=39*NHL Study 3
Retreatment,
Weekly × 4
N=60- * Six of these patients are included in the first column. Thus, data from 296 intent-to-treat patients are provided in this table.
- † Kaplan-Meier projected with observed range.
- ‡ "+" indicates an ongoing response.
- § Duration of response: interval from the onset of response to disease progression.
Overall Response Rate 48% 57% 36% 38% Complete Response Rate 6% 14% 3% 10% Median Duration of Response†, ‡, § 11.2
[1.9 to 42.1+]13.4
[2.5 to 36.5+]6.9
[2.8 to 25.0+]15.0
[3.0 to 25.1+](Months) [Range] 14.2 Previously Untreated, Low-Grade or Follicular, CD20-Positive, B-Cell NHL
The safety and effectiveness of rituximab in previously untreated, low-grade or follicular, CD20+ NHL were demonstrated in 3 randomized, controlled trials enrolling 1,662 patients.
NHL Study 4
A total of 322 patients with previously untreated follicular NHL were randomized (1:1) to receive up to eight 3-week cycles of CVP chemotherapy alone (CVP) or in combination with rituximab 375 mg/m2 on Day 1 of each cycle (R-CVP) in an open-label, multicenter study. The main outcome measure of the study was progression-free survival (PFS) defined as the time from randomization to the first of progression, relapse, or death.
Twenty-six percent of the study population was >60 years of age, 99% had Stage III or IV disease, and 50% had an International Prognostic Index (IPI) score ≥2. The results for PFS as determined by a blinded, independent assessment of progression are presented in Table 3. The point estimates may be influenced by the presence of informative censoring. The PFS results based on investigator assessment of progression were similar to those obtained by the independent review assessment.
NHL Study 5
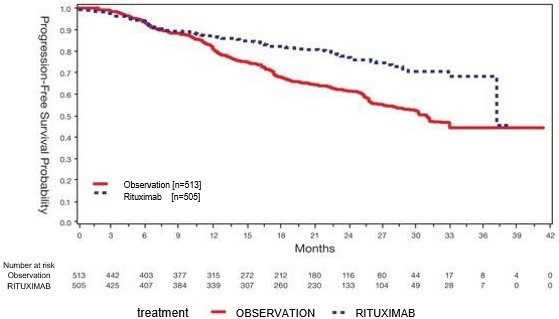
An open-label, multicenter, randomized (1:1) study was conducted in 1,018 patients with previously untreated follicular NHL who achieved a response (CR or PR) to rituximab in combination with chemotherapy. Patients were randomized to rituximab as single-agent maintenance therapy, 375 mg/m2 every 8 weeks for up to 12 doses or to observation. Rituximab was initiated at 8 weeks following completion of chemotherapy. The main outcome measure of the study was progression-free survival (PFS), defined as the time from randomization in the maintenance/observation phase to progression, relapse, or death, as determined by independent review.
Of the randomized patients, 40% were 60 years of age, 70% had Stage IV disease, 96% had ECOG performance status (PS) 01, and 42% had FLIPI scores of 35. Prior to randomization to maintenance therapy, patients had received R-CHOP (75%), R-CVP (22%), or R-FCM (3%); 71% had a complete or unconfirmed complete response and 28% had a partial response.
PFS was longer in patients randomized to rituximab as single agent maintenance therapy (HR: 0.54, 95% CI: 0.42, 0.70). The PFS results based on investigator assessment of progression were similar to those obtained by the independent review assessment.
Figure 1
Kaplan-Meier Plot of IRC Assessed PFS
NHL Study 6
A total of 322 patients with previously untreated low-grade, B-cell NHL who did not progress after 6 or 8 cycles of CVP chemotherapy were enrolled in an open-label, multicenter, randomized trial. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive rituximab, 375 mg/m2 intravenous infusion, once weekly for 4 doses every 6 months for up to 16 doses or no further therapeutic intervention. The main outcome measure of the study was progression-free survival defined as the time from randomization to progression, relapse, or death. Thirty-seven percent of the study population was >60 years of age, 99% had Stage III or IV disease, and 63% had an IPI score ≥2.
There was a reduction in the risk of progression, relapse, or death (hazard ratio estimate in the range of 0.36 to 0.49) for patients randomized to rituximab as compared to those who received no additional treatment.
14.3 Diffuse Large B-Cell NHL (DLBCL)
The safety and effectiveness of rituximab were evaluated in three randomized, active-controlled, open-label, multicenter studies with a collective enrollment of 1854 patients. Patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-cell NHL received rituximab in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) or other anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens.
NHL Study 7
A total of 632 patients age ≥60 years with DLBCL (including primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma) were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to treatment with CHOP or R-CHOP. Patients received 6 or 8 cycles of CHOP, each cycle lasting 21 days. All patients in the R-CHOP arm received 4 doses of rituximab 375 mg/m2 on Days -7 and -3 (prior to Cycle 1) and 48-72 hours prior to Cycles 3 and 5. Patients who received 8 cycles of CHOP also received rituximab prior to Cycle 7. The main outcome measure of the study was progression-free survival, defined as the time from randomization to the first of progression, relapse, or death. Responding patients underwent a second randomization to receive rituximab or no further therapy.
Among all enrolled patients, 62% had centrally confirmed DLBCL histology, 73% had Stage III-IV disease, 56% had IPI scores ≥2, 86% had ECOG performance status of <2, 57% had elevated LDH levels, and 30% had two or more extranodal disease sites involved. Efficacy results are presented in Table 4. These results reflect a statistical approach which allows for an evaluation of rituximab administered in the induction setting that excludes any potential impact of rituximab given after the second randomization.
Analysis of results after the second randomization in NHL Study 7 demonstrates that for patients randomized to R-CHOP, additional rituximab exposure beyond induction was not associated with further improvements in progression-free survival or overall survival.NHL Study 8
A total of 399 patients with DLBCL, age ≥60 years, were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive CHOP or R-CHOP. All patients received up to eight 3-week cycles of CHOP induction; patients in the R-CHOP arm received rituximab 375 mg/m2 on Day 1 of each cycle. The main outcome measure of the study was event-free survival, defined as the time from randomization to relapse, progression, change in therapy, or death from any cause. Among all enrolled patients, 80% had Stage III or IV disease, 60% of patients had an age-adjusted IPI ≥2, 80% had ECOG performance status scores <2, 66% had elevated LDH levels, and 52% had extranodal involvement in at least two sites. Efficacy results are presented in Table 4.
NHL Study 9
A total of 823 patients with DLBCL, aged 18-60 years, were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive an anthracycline-containing chemotherapy regimen alone or in combination with rituximab. The main outcome measure of the study was time to treatment failure, defined as time from randomization to the earliest of progressive disease, failure to achieve a complete response, relapse, or death. Among all enrolled patients, 28% had Stage III-IV disease, 100% had IPI scores of ≤1, 99% had ECOG performance status of <2, 29% had elevated LDH levels, 49% had bulky disease, and 34% had extranodal involvement. Efficacy results are presented in Table 4.
Table 4 Efficacy Results in NHL Studies 7, 8, and 9 NHL Study 7
(n = 632)NHL Study 8
(n = 399)NHL Study 9
(n = 823)R-CHOP CHOP R-CHOP CHOP R-Chemo Chemo Main outcome Progression-free survival
(years)Event-free survival
(years)Time to treatment failure
(years)- * NE = Not reliably estimable.
- † R-CHOP vs. CHOP.
- ‡ Significant at p < 0.05, 2-sided.
- § Kaplan-Meier estimates.
Median of main outcome measure 3.1 1.6 2.9 1.1 NE* NE* Hazard ratio† 0.69‡ 0.60‡ 0.45‡ Overall survival at 2 years§ 74% 63% 69% 58% 95% 86% Hazard ratio† 0.72‡ 0.68‡ 0.40‡ In NHL Study 8, overall survival estimates at 5 years were 58% vs. 46% for R-CHOP and CHOP, respectively.
14.4 Ninety-Minute Infusions in Previously Untreated Follicular NHL and DLBCL
In NHL Study 10, a total of 363 patients with previously untreated follicular NHL (n=113) or DLBCL (n=250) were evaluated in a prospective, open-label, multi-center, single-arm trial for the safety of 90-minute rituximab infusions. Patients with follicular NHL received rituximab 375 mg/m2 plus CVP chemotherapy. Patients with DLBCL received rituximab 375 mg/m2 plus CHOP chemotherapy. Patients with clinically significant cardiovascular disease were excluded from the study. Patients were eligible for a 90-minute infusion at Cycle 2 if they did not experience a Grade 3-4 infusion-related adverse event with Cycle 1 and had a circulating lymphocyte count ≤ 5000/mm3 before Cycle 2. All patients were pre-medicated with acetaminophen and an antihistamine and received the glucocorticoid component of their chemotherapy prior to rituximab infusion. The main outcome measure was the development of Grade 3-4 infusion-related reactions on the day of, or day after, the 90-minute infusion at Cycle 2 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Eligible patients received their Cycle 2 rituximab infusion over 90 minutes as follows: 20% of the total dose given in the first 30 minutes and the remaining 80% of the total dose given over the next 60 minutes [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Patients who tolerated the 90-minute rituximab infusion at Cycle 2 continued to receive subsequent rituximab infusions at the 90-minute infusion rate for the remainder of the treatment regimen (through Cycle 6 or Cycle 8).
The incidence of Grade 3-4 infusion-related reactions at Cycle 2 was 1.1% (95% CI [0.3%, 2.8%]) among all patients, 3.5% (95% CI [1.0%, 8.8%]) for those patients treated with R-CVP, and 0.0% (95% CI [0.0%, 1.5%]) for those patients treated with R-CHOP. For Cycles 2-8, the incidence of Grade 3-4 infusion-related reactions was 2.8% (95% CI [1.3%, 5.0%]). No acute fatal infusion-related reactions were observed.
14.5 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
The safety and effectiveness of rituximab were evaluated in two randomized (1:1) multicenter open-label studies comparing FC alone or in combination with rituximab for up to 6 cycles in patients with previously untreated CLL [CLL Study 11 (n=817)] or previously treated CLL [CLL Study 12 (n=552)]. Patients received fludarabine 25 mg/m2/day and cyclophosphamide 250 mg/m2/day on days 1, 2 and 3 of each cycle, with or without rituximab. In both studies, seventy-one percent of CLL patients received 6 cycles and 90% received at least 3 cycles of rituximab-based therapy.
In CLL Study 11, 30% of patients were 65 years or older, 31% were Binet stage C, 45% had B symptoms, more than 99% had ECOG performance status (PS) 0-1, 74% were male, and 100% were White. In CLL Study 12, 44% of patients were 65 years or older, 28% had B symptoms, 82% received a prior alkylating drug, 18% received prior fludarabine, 100% had ECOG PS 0-1, 67% were male and 98% were White.
The main outcome measure in both studies was progression-free survival (PFS), defined as the time from randomization to progression, relapse, or death, as determined by investigators (CLL Study 11) or an independent review committee (CLL Study 12). The investigator assessed results in CLL Study 12 were supportive of those obtained by the independent review committee. Efficacy results are presented in Table 5.
Table 5 Efficacy Results in CLL Studies 11 and 12 CLL Study 11*
(Previously untreated)CLL Study 12*
(Previously treated)R-FC
N = 408FC
N = 409R-FC
N = 276FC
N = 276- * As defined in 1996 National Cancer Institute Working Group guidelines.
Median PFS (months) 39.8 31.5 26.7 21.7 Hazard ratio (95% CI) 0.56 (0.43, 0.71) 0.76 (0.6, 0.96) P value (Log-Rank test) < 0.01 0.02 Response rate
(95% CI)86%
(82, 89)73%
(68, 77)54%
(48, 60)45%
(37, 51)Across both studies, 243 of 676 rituximab-treated patients (36%) were 65 years of age or older and 100 rituximab-treated patients (15%) were 70 years of age or older. The results of exploratory subset analyses in elderly patients are presented in Table 6.
Table 6 Efficacy Results in CLL Studies 11 and 12 in Subgroups Defined by Age* CLL Study 11 CLL Study 12 Age subgroup Number of Patients Hazard Ratio for PFS (95% CI) Number of Patients Hazard Ratio for PFS (95% CI) - * From exploratory analyses.
Age < 65 yrs 572 0.52 (0.39, 0.70) 313 0.61 (0.45, 0.84) Age ≥ 65 yrs 245 0.62 (0.39, 0.99) 233 0.99 (0.70, 1.40) Age < 70 yrs 736 0.51 (0.39, 0.67) 438 0.67 (0.51, 0.87) Age ≥ 70 yrs 81 1.17 (0.51, 2.66) 108 1.22 (0.73, 2.04) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
TRUXIMA (rituximab-abbs) injection is a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow, preservative-free solution for intravenous infusion supplied as a carton containing one 100 mg/10 mL (10 mg/mL) single-dose vial (NDC: 63459-103-10) or a carton containing one 500 mg/50 mL (10 mg/mL) single-dose vial (NDC: 63459-104-50).
Store TRUXIMA vials refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). TRUXIMA vials should be protected from direct sunlight. Do not freeze or shake.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Infusion-Related Reactions
Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of infusion-related reactions. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately to report symptoms of infusion-related reactions including urticaria, hypotension, angioedema, sudden cough, breathing problems, weakness, dizziness, palpitations, or chest pain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Severe Mucocutaneous Reactions
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for symptoms of severe mucocutaneous reactions, including painful sores or ulcers on the mouth, blisters, peeling skin, rash, and pustules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for symptoms of hepatitis including worsening fatigue or yellow discoloration of skin or eyes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs and symptoms of PML, including new or changes in neurological symptoms such as confusion, dizziness or loss of balance, difficulty talking or walking, decreased strength or weakness on one side of the body, or vision problems [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS)
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs and symptoms of tumor lysis syndrome such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and lethargy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Infections
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs and symptoms of infections including fever, cold symptoms (e.g., rhinorrhea or laryngitis), flu symptoms (e.g., cough, fatigue, body aches), earache or headache, dysuria, oral herpes simplex infection, and painful wounds with erythema and advise patients of the increased risk of infections during and after treatment with TRUXIMA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
Advise patients of the risk of cardiovascular adverse reactions, including ventricular fibrillation, myocardial infarction, and cardiogenic shock. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately to report chest pain and irregular heartbeats [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Renal Toxicity
Advise patients of the risk of renal toxicity. Inform patients of the need for healthcare providers to monitor kidney function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Bowel Obstruction and Perforation
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs and symptoms of bowel obstruction and perforation, including severe abdominal pain or repeated vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise a pregnant woman of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise female patients that rituximab products can cause fetal harm if taken during pregnancy and to use effective contraception during treatment with TRUXIMA and for at least 12 months after the last dose of TRUXIMA. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TRUXIMA and for 6 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: 05/2019 MEDICATION GUIDE
TRUXIMA®(trux-ee'-mah)
(rituximab-abbs)
injectionWhat is the most important information I should know about TRUXIMA?
TRUXIMA can cause serious side effects that can lead to death, including:-
Infusion-related reactions. Infusion-related reactions are very common side effects of TRUXIMA treatment. Serious infusion-related reactions can happen during your infusion or within 24 hours after your infusion of TRUXIMA. Your healthcare provider should give you medicines before your infusion of TRUXIMA to decrease your chance of having a severe infusion-related reaction.
Tell your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you get any of these symptoms during or after an infusion of TRUXIMA:
- hives (red itchy welts) or rash
- itching
- swelling of your lips, tongue, throat or face
- sudden cough
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, or wheezing
- weakness
- dizziness or feel faint
- palpitations (feel like your heart is racing or fluttering)
- chest pain
-
Severe skin and mouth reactions. Tell your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you get any of these symptoms at any time during your treatment with TRUXIMA:
- painful sores or ulcers on your skin, lips or in your mouth
- blisters
- peeling skin
- rash
- pustules
-
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation. Before you receive your TRUXIMA treatment, your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check for HBV infection. If you have had hepatitis B or are a carrier of hepatitis B virus, receiving TRUXIMA could cause the virus to become an active infection again. Hepatitis B reactivation may cause serious liver problems including liver failure, and death. You should not receive TRUXIMA if you have active hepatitis B liver disease. Your healthcare provider will monitor you for hepatitis B infection during and for several months after you stop receiving TRUXIMA.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get worsening tiredness, or yellowing of your skin or white part of your eyes, during treatment with TRUXIMA. -
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML). PML is a rare, serious brain infection caused by a virus that can happen in people who receive TRUXIMA. People with weakened immune systems can get PML. PML can result in death or severe disability. There is no known treatment, prevention, or cure for PML.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any new or worsening symptoms or if anyone close to you notices these symptoms:
- confusion
- dizziness or loss of balance
- difficulty walking or talking
- decreased strength or weakness on one side of your body
- vision problems
See "What are the possible side effects of TRUXIMA?" for more information about side effects. What is TRUXIMA?
TRUXIMA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with:- Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL): alone or with other chemotherapy medicines.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): with the chemotherapy medicines fludarabine and cyclophosphamide.
Before you receive TRUXIMA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have had a severe reaction to TRUXIMA or a rituximab product
- have a history of heart problems, irregular heart beat or chest pain
- have lung or kidney problems
- have an infection or weakened immune system.
- have or have had any severe infections including:
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV)
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
- Parvovirus B19
- Varicella zoster virus (chickenpox or shingles)
- West Nile Virus
- have had a recent vaccination or are scheduled to receive vaccinations. You should not receive certain vaccines before or during treatment with TRUXIMA.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Talk to your healthcare provider about the risks to your unborn baby if you receive TRUXIMA during pregnancy.
Females who are able to become pregnant should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with TRUXIMA and for 12 months after the last dose of TRUXIMA. Talk to your healthcare provider about effective birth control.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think that you are pregnant during treatment with TRUXIMA. - are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if TRUXIMA passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment and for at least 6 months after your last dose of TRUXIMA.
- a Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) inhibitor medicine
- a Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug (DMARD)
How will I receive TRUXIMA? - TRUXIMA is given by infusion through a needle placed in a vein (intravenous infusion), in your arm. Talk to your healthcare provider about how you will receive TRUXIMA.
- Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicines before each infusion of TRUXIMA to reduce infusion side effects such as fever and chills.
- Your healthcare provider should do blood tests regularly to check for side effects to TRUXIMA.
- Before each TRUXIMA treatment, your healthcare provider or nurse will ask you questions about your general health. Tell your healthcare provider or nurse about any new symptoms.
What are the possible side effects of TRUXIMA?
TRUXIMA can cause serious side effects, including:- See "What is the most important information I should know about TRUXIMA?"
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS). TLS is caused by the fast breakdown of cancer cells. TLS can cause you to have:
- kidney failure and the need for dialysis treatment
- abnormal heart rhythm
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following signs or symptoms of TLS:
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- lack of energy
-
Serious infections. Serious infections can happen during and after treatment with TRUXIMA, and can lead to death. TRUXIMA can increase your risk of getting infections and can lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections. Types of serious infections that can happen with TRUXIMA include bacterial, fungal, and viral infections. After receiving TRUXIMA, some people have developed low levels of certain antibodies in their blood for a long period of time (longer than 11 months). Some of these people with low antibody levels developed infections. People with serious infections should not receive TRUXIMA. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any symptoms of infection:
- fever
- cold symptoms, such as runny nose or sore throat that do not go away
- flu symptoms, such as cough, tiredness, and body aches
- earache or headache
- pain during urination
- cold sores in the mouth or throat
- cuts, scrapes or incisions that are red, warm, swollen or painful
- Heart problems. TRUXIMA may cause chest pain, irregular heartbeats, and heart attack. Your healthcare provider may monitor your heart during and after treatment with TRUXIMA if you have symptoms of heart problems or have a history of heart problems. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have chest pain or irregular heartbeats during treatment with TRUXIMA.
- Kidney problems, especially if you are receiving TRUXIMA for NHL. TRUXIMA can cause severe kidney problems that lead to death. Your healthcare provider should do blood tests to check how well your kidneys are working.
- Stomach and Serious bowel problems that can sometimes lead to death. Bowel problems, including blockage or tears in the bowel can happen if you receive TRUXIMA with chemotherapy medicines. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any severe stomach-area (abdomen) pain or repeated vomiting during treatment with TRUXIMA.
The most common side effects of TRUXIMA include:- infusion-related reactions (see "What is the most important information I should know about TRUXIMA?")
- infections (may include fever, chills)
- body aches
- tiredness
- nausea
- aching joints during or within hours of receiving an infusion
- more frequent upper respiratory tract infection
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.General information about the safe and effective use of TRUXIMA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about TRUXIMA that is written for healthcare professionals.What are the ingredients in TRUXIMA?
Active ingredient: rituximab-abbs
Inactive ingredients: polysorbate 80, sodium chloride, tri-sodium citrate dihydrate, and Water for Injection, USP.
Manufactured by: CELLTRION, Inc. 20, Academy-ro 51 beon-gil, Yeonsu-gu, Incheon, 22014 Republic of KoreaUS License Number 1996
Marketed by: Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. North Wales, PA 19454
For more information, go to www.TRUXIMA.com or call 1-888-483-8279.
-
Infusion-related reactions. Infusion-related reactions are very common side effects of TRUXIMA treatment. Serious infusion-related reactions can happen during your infusion or within 24 hours after your infusion of TRUXIMA. Your healthcare provider should give you medicines before your infusion of TRUXIMA to decrease your chance of having a severe infusion-related reaction.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100mg Vial Carton

NDC: 63459-103-10
Truxima®
(rituximiab-abbs)
Injection
100 mg/10 mL
(10 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Use
after Dilution
One single-dose vial.
Discard unused portion.
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
PROVIDE ENCLOSED
MEDICATION GUIDE
TO PATIENT.
Rx only
teva
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 500 mg Vial Carton

NDC: 63459-104-50
Truxima®
(rituximiab-abbs)
Injection
500 mg/50 mL
(10 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Use
after Dilution
One single-dose vial.
Discard unused portion.
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
PROVIDE ENCLOSED
MEDICATION GUIDE
TO PATIENT.
Rx only
teva
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
TRUXIMA
rituximab-abbs injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63459-103 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength rituximab (UNII: 4F4X42SYQ6) (rituximab - UNII:4F4X42SYQ6) rituximab 10 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Sodium Chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 9 mg in 1 mL Trisodium Citrate Dihydrate (UNII: B22547B95K) 7.35 mg in 1 mL Polysorbate 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) 0.7 mg in 1 mL Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63459-103-10 1 in 1 CARTON 11/09/2019 1 10 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-USE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761088 11/09/2019 TRUXIMA
rituximab-abbs injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63459-104 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength rituximab (UNII: 4F4X42SYQ6) (rituximab - UNII:4F4X42SYQ6) rituximab 10 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Sodium Chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 9 mg in 1 mL Trisodium Citrate Dihydrate (UNII: B22547B95K) 7.35 mg in 1 mL Polysorbate 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) 0.7 mg in 1 mL Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63459-104-50 1 in 1 CARTON 11/09/2019 1 50 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-USE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761088 11/09/2019 Labeler - Cephalon, Inc. (183236314) Registrant - CELLTRION, Inc. (688836030)
Trademark Results [Truxima]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 TRUXIMA 88452656 not registered Live/Pending |
CELLTRION, INC. 2019-05-30 |
 TRUXIMA 79168237 4962045 Live/Registered |
CELLTRION, INC. 2015-02-27 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.