SUSVIMO- ranibizumab injection, solution
Susvimo by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Susvimo by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Genentech, Inc., Roche Singapore Technical Operations Pte. Ltd., Roche Diagnostics GmbH. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SUSVIMO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SUSVIMO.
SUSVIMO® (ranibizumab injection) for intravitreal use via SUSVIMO ocular implant
Initial U.S. Approval: 2006WARNING: ENDOPHTHALMITIS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
The SUSVIMO implant has been associated with an up to 3-fold higher rate of endophthalmitis than monthly intravitreal injections of ranibizumab.
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with:
- Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a VEGF inhibitor (1.1).
- Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a VEGF inhibitor (1.2).
- Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a VEGF inhibitor (1.3).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For intravitreal use via SUSVIMO ocular implant. (2.1)
-
Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) and Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
The recommended dose of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is 2 mg (0.02 mL of 100 mg/mL solution) continuously delivered via the SUSVIMO implant with refills every 24 weeks (approximately 6 months). (2.2) -
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
The recommended dose of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is 2 mg (0.02 mL of 100 mg/mL solution) continuously delivered via the SUSVIMO implant with refills every 36 weeks (approximately 9 months). (2.3) - Supplemental treatment with 0.5 mg intravitreal ranibizumab injection may be administered in the affected eye if clinically necessary. (2.4)
- Perform the initial implantation, refill-exchange, and implant removal (if necessary) procedures under strict aseptic conditions. (2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 100 mg/mL solution in a single-dose vial (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- The SUSVIMO implant and/or implant-related procedures have been associated with endophthalmitis, rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, implant dislocation, septum dislodgement, vitreous hemorrhage, conjunctival retraction, conjunctival erosion, and conjunctival bleb. Patients should be instructed to report signs or symptoms that could be associated with these events without delay. Additional surgical and/or medical management may be required. (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.7)
- Vitreous Hemorrhage: Temporarily discontinue antithrombotic medication prior to the implant insertion procedure to reduce the risk of vitreous hemorrhage. Vitrectomy may be needed. (5.5)
- Postoperative Decrease in Visual Acuity: A decrease in visual acuity usually occurs over the first two postoperative months. (5.8)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) were conjunctival hemorrhage, conjunctival hyperemia, iritis, eye pain, conjunctival disorder, cataract and vitreous hemorrhage. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Genentech at 1-888-835-2555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 9/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: ENDOPHTHALMITIS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
1.2 Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
1.3 Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Information
2.2 Neovascular (Wet) Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) and Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
2.3 Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
2.4 Supplemental Treatment with Intravitreal Ranibizumab Injection
2.5 Ocular Implant Initial Fill
2.6 Ocular Implant Insertion
2.7 Ocular Implant Removal
2.8 Ocular Implant Refill-Exchange Procedure
2.9 Delayed or Missed Doses
2.10 Dosage (Refill-Exchange) Modifications for Adverse Reactions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Ocular or Periocular Infections
4.2 Active Intraocular Inflammation
4.3 Hypersensitivity
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Endophthalmitis
5.2 Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
5.3 Implant Dislocation
5.4 Septum Dislodgement
5.5 Vitreous Hemorrhage
5.6 Conjunctival Erosion or Retraction
5.7 Conjunctival Bleb
5.8 Postoperative Decrease in Visual Acuity
5.9 Postoperative Intraocular Inflammation
5.10 Air Bubbles Causing Improper Filling of the Implant
5.11 Deflection or Movement of the Implant
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
14.2 Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
14.3 Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage
16.3 Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: ENDOPHTHALMITIS
The SUSVIMO implant has been associated with an up to 3-fold higher rate of endophthalmitis than monthly intravitreal injections of ranibizumab. Many of these events were associated with conjunctival retractions or erosions. Appropriate conjunctiva management and early detection with surgical repair of conjunctival retractions or erosions may reduce the risk of endophthalmitis. [see Contraindications (4.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is indicated for the treatment of patients with Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) inhibitor medication.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Information
For Intravitreal Use via SUSVIMO ocular implant.
The SUSVIMO initial fill and ocular implant insertion and implant removal procedures must be performed under aseptic conditions by a physician experienced in vitreoretinal surgery. The SUSVIMO ocular implant must be surgically implanted in the eye or removed from the eye (if medically necessary) in an operating room using aseptic technique. See SUSVIMO Instructions for Use and the standardized steps to optimize surgical outcomes.
SUSVIMO refill-exchange procedures must be performed under aseptic conditions by a physician experienced in ophthalmic surgery [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)].
Do not administer SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) as a bolus intravitreal injection. Do not substitute SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) with other ranibizumab products.
2.2 Neovascular (Wet) Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) and Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
The recommended dose of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is 2 mg (0.02 mL of 100 mg/mL solution) continuously delivered via the SUSVIMO ocular implant with refills administered every 24 weeks (approximately 6 months).
2.3 Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
The recommended dose of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is 2 mg (0.02 mL of 100 mg/mL solution) continuously delivered via the SUSVIMO ocular implant with refills administered every 36 weeks (approximately 9 months).
2.4 Supplemental Treatment with Intravitreal Ranibizumab Injection
Supplemental treatment with 0.5 mg (0.05 mL of 10 mg/mL) intravitreal ranibizumab injection may be administered in the affected eye while the SUSVIMO implant is in place and if clinically necessary [see Clinical Studies (14)].
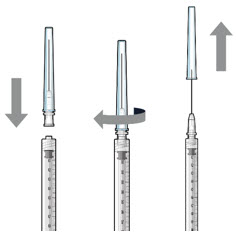
2.5 Ocular Implant Initial Fill
The implant initial fill procedure must be performed by a physician experienced in vitreoretinal surgery [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. The implant will be filled using aseptic technique with 0.02 mL of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) prior to insertion of the implant into the patient's eye [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
Refer to the complete SUSVIMO Instructions for Use for the initial fill and implant procedure included in the insertion tool assembly carton for further details.
Use aseptic technique to carry out the following preparation steps prior to insertion of the ocular implant into the patient's eye:
Step 1: Gather the supplies needed. - One SUSVIMO ocular implant with insertion tool assembly (included)
- One SUSVIMO initial fill needle (34-gauge with integrated 5 μm filter) with blue cap (included)
- One SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL vial (included)
- One sterile 5-micron filter needle (19-gauge × 1½ inch) (not included)
- One sterile 1 mL Luer Lock syringe (not included)
Step 2: Transfer Dose from Vial to Syringe Note: Use the filter needle (not included) to withdraw SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) from the vial. 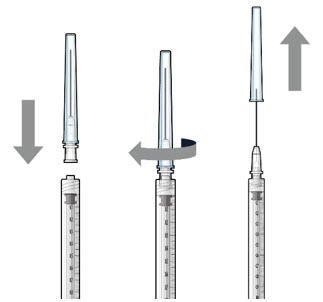
Figure 1Do not use the SUSVIMO initial fill needle for this step. - Prepare SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) vial by removing the flip-off cap and disinfecting the rubber vial septum with alcohol.
- Attach a filter needle to the syringe by screwing it tightly onto the Luer lock (see Figure 1).
- Carefully remove the needle cap by pulling it straight off.
- Using aseptic technique, withdraw all of the contents of the SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) vial through the filter needle into the syringe.
Step 3: Remove Air from Syringe - With the filter needle attached, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up.
- If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the bubbles rise to the top (Figure 2).
- Slowly push the plunger rod just until all air is expelled from the syringe and needle.
- – It is important to preserve as much drug as possible in order to completely fill the implant.
- Remove and properly dispose of the filter needle after air is removed from syringe.
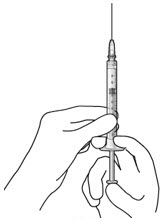
Figure2Step 4: Attach SUSVIMO Initial Fill Needle
Do not use the filter needle to fill the implant.- Attach the SUSVIMO initial fill needle (included) firmly onto the syringe by screwing it tightly onto the Luer lock (see Figure 3). Ensure that the initial fill needle is attached to the syringe.
- Carefully remove the needle cap by pulling straight off.
- Do not wipe the needle at any time.
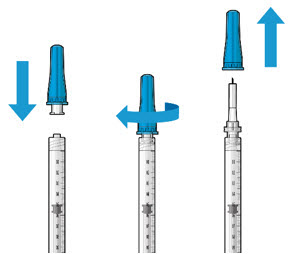
Figure 3Step 5: Remove Any Remaining Air from Syringe - With the initial fill needle attached, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up.
If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the bubbles rise to the top (see Figure 4). - Slowly push the plunger rod just until all air is expelled from the syringe and needle, and a drop of drug solution is seen at the needle tip (see Figure 5).
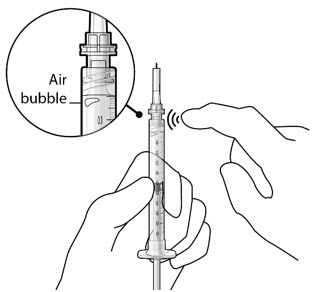
Figure 4
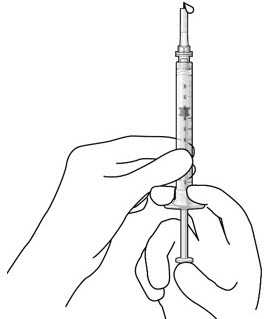
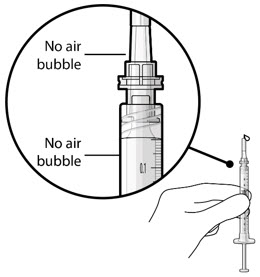
Figure 5Note: It is important to preserve as much drug as possible in order to completely fill the implant. Step 6: Inspect the Syringe for Air Bubbles - Inspect the syringe and the needle hub to ensure that no air bubbles are present (see Figure 6).
- If air bubbles are present, continue to remove air from the syringe and reinspect.
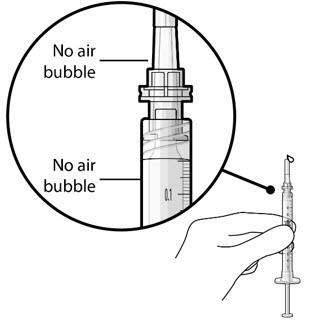
Figure 6Note: Use the syringe within 15 minutes of removing all air to avoid ranibizumab drying in the needle and impeding fluid flow.
Do not use the initial fill needle if the needle is clogged.Step 7: Load Syringe into the Carrier
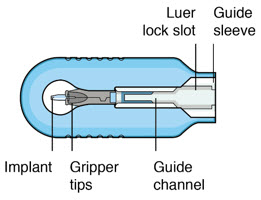
Do not hold or push on the plunger rod of the syringe while inserting the needle into the implant septum.- Retrieve insertion tool carrier with pre-positioned implant from the inner tray.
- Align the syringe Luer lock above the Luer lock slot in the carrier to protect the needle from being damaged.
- Lower the syringe into the carrier (see Figure 7).
- Push the syringe forward until it stops, taking care to avoid touching the plunger rod (see Figure 8)
- With the syringe loaded, (see Figure 9) the initial fill needle should now be penetrating the implant septum.
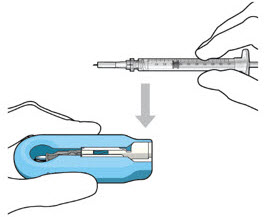
Figure 7: Align and lower the syringe into the carrier
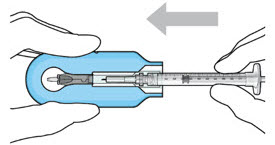
Figure 8: Push the syringe into the carrier
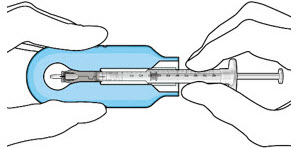
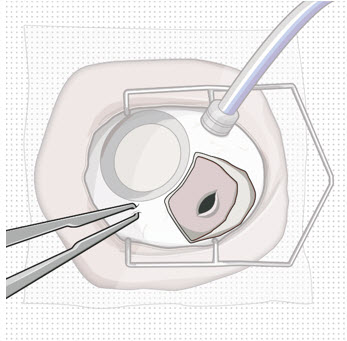
Figure 9: Syringe with initial fill needle inserted through the implant septumStep 8: Fill Ocular Implant with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) Under Microscope - Under the microscope, slowly administer SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) into the ocular implant by slightly tilting the carrier upwards (see Figure 10).
- The ocular implant should be filled over approximately 5 to 10 seconds, to help avoid air entrapment in the implant reservoir.
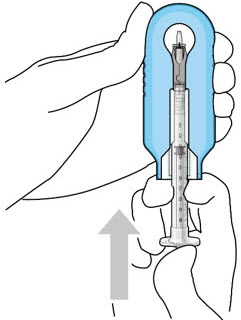
Figure 10: Administer ranibizumab into the implant
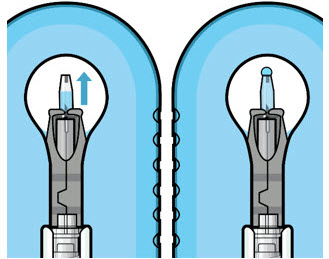
Figure 11: Dome of drug solution forms at tip of implant as viewed under magnificationNote: When filling the ocular implant, drug solution should only exit the ocular implant from the release control element. If drug solution is leaking from the implant at a different location, such as the side of the implant, do not use the ocular implant.
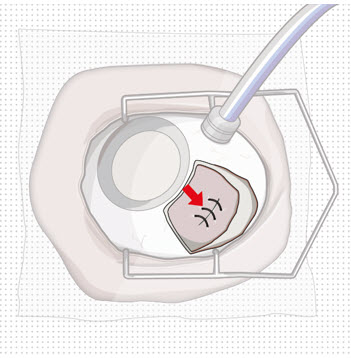
If fluid is leaking from the septum at the needle insertion site, the needle may not be fully penetrating the implant septum. Fully push the syringe forward before continuing to fill the ocular implant.- Continue filling the ocular implant until the implant is completely full of drug solution and all air has been expelled as evidenced by a dome of drug solution formed at the tip of the implant on the release control element (see Figure 11).
Step 9: Inspect the Filled Ocular Implant Under the Microscope - Inspect the ocular implant under the microscope to ensure that the ocular implant is completely full of drug solution (see Figure 12).
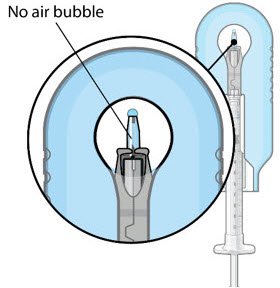
Figure 12: Proper appearance of implant after initial filling with ranibizumabNote: Minimize air bubbles within the implant reservoir as they may cause slower drug release. If an air bubble is present, it must be no larger than 1/3 of the widest diameter of the implant. If excess air is observed, do not use the ocular implant. Note: No more than 30 minutes should pass between the initial fill of the implant and the insertion into the patient's eye to ensure that the release control element remains saturated with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection). If SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) dries in the release control element, the implant may not release the drug properly into the vitreous after insertion. Step 10: Remove the Syringe and Guide Sleeve from the Carrier - Remove the syringe and guide sleeve from the carrier by pulling back on the syringe (see Figure 13). The syringe will be locked into the guide sleeve.
- Properly dispose of the used syringe together with the needle and guide sleeve in a sharps disposal container or in accordance with local requirements.
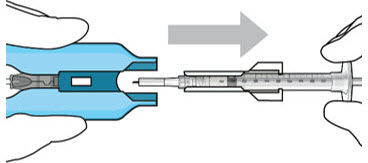
Figure 13: Remove the syringe and guide sleeve from the insertion tool carrierStep 11: Slide the Insertion Tool Handle into the Carrier 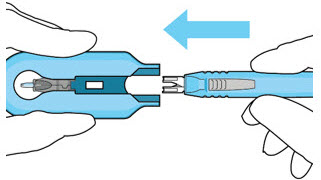
Figure 14: Insert the handle into the insertion tool carrier
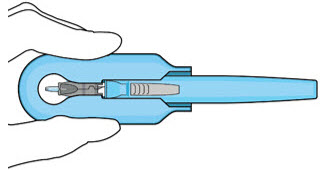
Figure 15: Fully inserted handleNote: Do not withdraw the handle and implant until the eye is ready for insertion. Contact between the implant and any surface or object – even within the sterile field – may result in the introduction of a foreign body into the vitreous. 2.6 Ocular Implant Insertion
SUSVIMO ocular implant insertion is a surgical procedure that is performed in an operating room. The procedure must be performed under aseptic conditions by a physician experienced in vitreoretinal surgery [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
The ocular implant is filled with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) immediately prior to insertion. No more than 30 minutes should pass between the initial fill of the ocular implant and the insertion into the patient's eye.
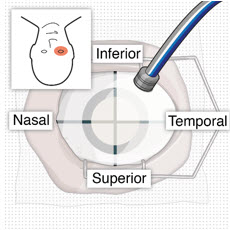
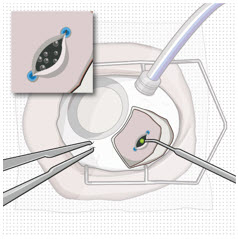
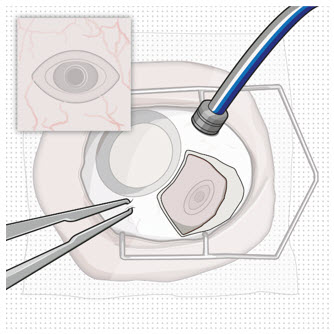
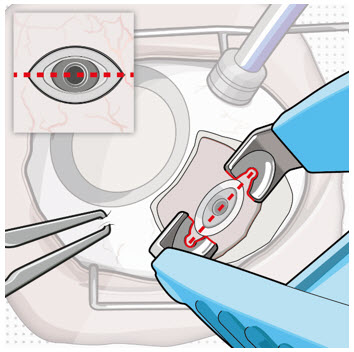
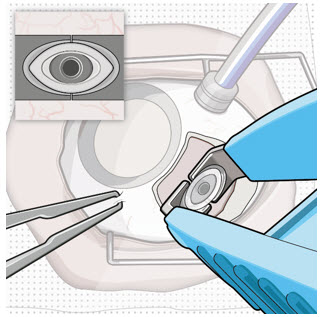
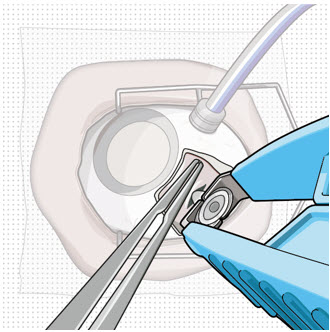
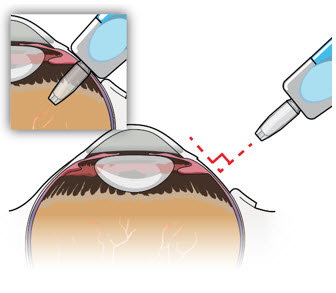
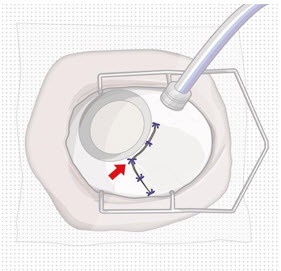
After placing an infusion line in the eye, create at least a 6×6 mm peritomy of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule centered around the selected SUSVIMO implant location in the supero-temporal quadrant. Perform careful conjunctival incision, hemostasis of the underlying sclera, and generous undermining of Tenon's capsule. Using aseptic technique, fill the ocular implant [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Using an MVR blade, create a full thickness dissection of the sclera 4 mm from the limbus until the pars plana is fully visible, with final target scleral incision length of 3.5 mm. Using a 532 nm laser endoprobe, apply contiguous, overlapping laser spots starting at 300 mW 1000 ms along the full length of the exposed pars plana and repeat until complete ablation is achieved. Pass a 3.2 mm slit knife perpendicularly through the center of the scleral dissection to open the underlying pars plana. Use the insertion tool to slowly insert the SUSVIMO implant into the sclero-pars plana incision perpendicular to the globe, ensuring that the long axis of the implant flange is properly aligned with the sclero-pars plana incision. Using the closed gripper tips of the insertion tool, seat the implant flush against the sclera. Clean any residual vitreous around the implant flange using a vitrector. Suture both Tenon's capsule and conjunctiva, using scleral anchoring at the apex of the peritomy, ensuring complete coverage of the implant flange. Refer to the complete SUSVIMO Instructions for Use for the initial fill and implant procedure included in the insertion tool assembly carton for further details.
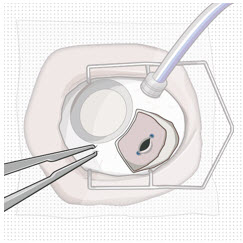
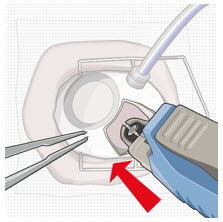
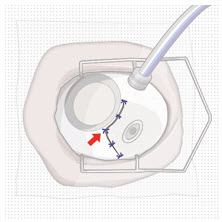
2.7 Ocular Implant Removal
Removal of the SUSVIMO ocular implant is a surgical procedure that is performed in an operating room. The procedure must be performed under aseptic conditions by a physician experienced in vitreoretinal surgery [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
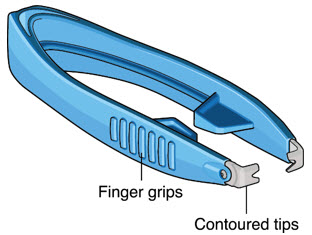
After placing an infusion line in the eye, create at least a 6×6 mm peritomy of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule around the SUSVIMO ocular implant flange. Remove any fibrous capsule or scar tissue that may have formed over the implant flange and septum using scalpel and forceps. With the explant tool oriented perpendicular to the globe, align the contoured tips with the long axis of the implant flange and grasp underneath the implant flange. Once the implant is secured in the explant tool, pull the implant from the eye in a perpendicular motion. Clear any vitreous prolapse present within or around the scleral wound using a vitrector. Completely close the scleral incision with multiple non-absorbable sutures. Close the Tenon's capsule and conjunctiva to completely cover the scleral incision. Refer to the complete Instructions for Use for the implant removal procedure included in the explant tool carton for further details.
2.8 Ocular Implant Refill-Exchange Procedure
The SUSVIMO ocular implant refill-exchange procedure must be performed under strict aseptic conditions by a physician experienced in ophthalmic surgery [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. This includes the use of a surgical mask, sterile gloves, and a lid speculum.
Prior to and after the refill-exchange procedure, perform a dilated slit lamp exam and/or dilated indirect ophthalmoscopy to inspect the implant in the vitreous cavity through the pupil to identify if dislodgement of the implant septum has occurred [see Figure 33 and Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. If the septum has dislodged, any further refill-exchange procedures should not be performed because normal device functioning cannot be assured. Discontinue treatment with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) following septum dislodgement and consider implant removal should the benefit of the removal procedure outweigh the risk.
Step 1: Gather the supplies needed. - One SUSVIMO Refill Needle (34-gauge with a 5 µm integrated filter) with clear cap (included)
- One SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL vial (included)
- One sterile 1 mL Luer Lock syringe (not included)
- One sterile 5-micron filter needle (19-gauge × 1½ inch) (not included)
- Anesthetic ophthalmic solutions
- Ophthalmic broad-spectrum microbicide solution
- Cotton tips and gauze
- Sterile powder free gloves
- Face masks
- Lid speculum
- Magnification such as visor or loupes
- Task lighting
- Indirect ophthalmoscope and lens
- Sterile drape (optional for refill-exchange procedure)
Step 2: Inspect Packaging and Components - Prior to use in the clinic, inspect the packaging of the components for damage. Do not use if the sterility has been compromised or the contents have been dropped, damaged, or tampered with.
- Check the expiration date printed on the label.
- Remove the vial from the carton. Note: the outside of the vial is not sterile.
- Use aseptic technique to open packaging and remove the sterile refill needle from the tray.
- Inspect components and place onto sterile field (see Figure 16).
 Figure 16
Figure 16Step 3: Inspect SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) - Visually inspect the contents of the SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) vial for particulate matter and discoloration.
- SUSVIMO should be colorless to slightly brownish
Step 4: Patient Preparation - Dilate the pupil of the eye.
- Perform slit lamp examination and/or indirect ophthalmoscopy to inspect the implant and its components in the vitreous cavity through the dilated pupil.
- Position the patient on exam chair in the supine position at approximately 20° to 30° angle for optimal visualization of the implant.
- Apply a broad-spectrum microbicide to the periocular skin, eyelid, and ocular surface prior to the refill-exchange procedure. The use of a sterile drape is up to the physician's discretion.
- Perform the procedure under topical anesthesia.
- If needed, subconjunctival anesthesia may be administered in the nasal quadrant, away from the implant.
Step 5: Transfer Dose from Vial to Syringe 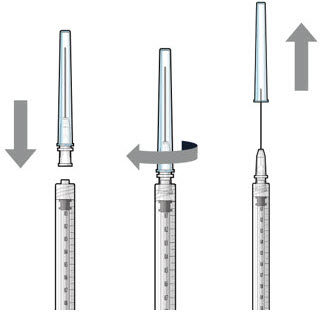
Figure 17Note: Use the filter needle to withdraw SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) from the vial. Do not use the SUSVIMO refill needle for this step. - Prepare ranibizumab vial by removing the flip-off cap and disinfecting the rubber vial septum with alcohol.
- Attach a filter needle to the syringe by screwing it tightly onto the Luer lock (see Figure 17).
- Carefully remove the needle cap by pulling it straight off.
- Using aseptic technique, withdraw all of the contents of the SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) vial through the filter needle into the syringe.
Step 6: Remove Air from Syringe - With the filter needle attached, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up.
- If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the bubbles rise to the top (Figure 18).
- Slowly push the plunger rod just until the air is expelled from the syringe and needle.
- – It is important to preserve as much drug as possible in order to completely refill the implant
- Remove and properly dispose of the filter needle after air is removed from the syringe.
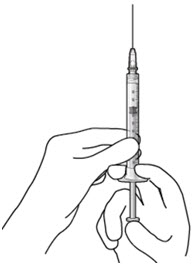
Figure 18Step 7: Attach SUSVIMO Refill Needle
Do not use the filter needle to fill the implant.- Attach the SUSVIMO refill needle firmly onto the syringe by screwing it tightly onto the Luer lock (see Figure 19). Ensure that the refill needle is attached to the syringe.
- Carefully remove the needle cap, pulling straight off to avoid damage to the needle cannula.
- Do not wipe the needle at any time.
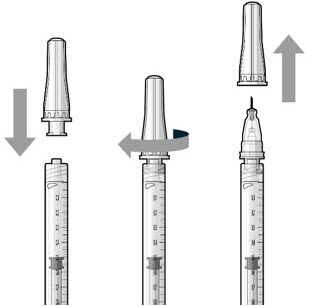 Figure 19
Figure 19Step 8: Remove Any Remaining Air from Syringe and Adjust Drug Dose - With the refill needle attached, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up.
- If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the bubbles rise to the top (see Figure 20).
- Slowly push the plunger rod until all air is expelled from the syringe and needle and the uppermost edge of the black plunger tip is aligned with the 0.1 mL dose mark (see Figure 21).
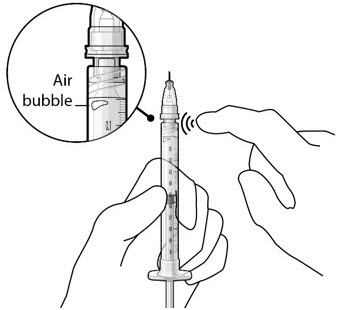
Figure 20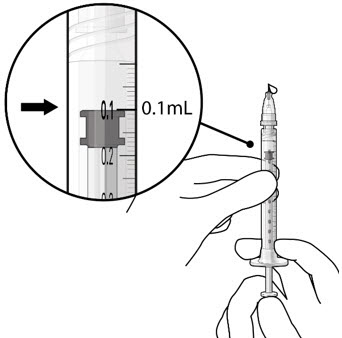
Figure 21Step 9: Inspect the Syringe for Air Bubbles 
Figure 22Note: Ensure no air bubbles are present in the syringe and needle hub. Air injected into the implant could result in slower drug release. - Inspect the syringe and the needle hub using magnification to ensure that no air bubbles are present (see Figure 22).
Note: Use the syringe within 15 minutes of removing all air and adjusting the drug dose to avoid drug solution drying in the needle and impeding fluid flow.
Do not use the refill needle or syringe if the needle is clogged.Step 10: Stabilize the globe and orient the refill needle 
Figure 23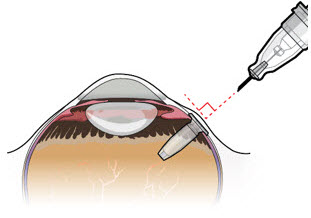 Figure 24
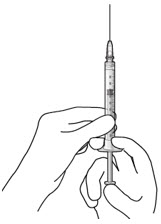
Figure 24Note: Perform the refill-exchange procedure using magnification (e.g., loupes, reading glasses, magnifiers) for visual assistance. - After placing the lid speculum in the eye, stabilize the globe with a cotton-tipped applicator to minimize eye movement (see Figure 23).
- – Recommend standing on the contralateral side of the implanted eye, with the patient looking down and toward their nose to optimally expose the implant.
- Orient the refill needle perpendicular to the globe (see Figure 24).
Step 11: Insert the Refill Needle 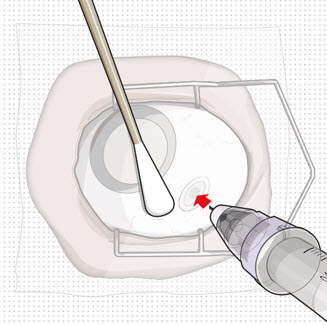
Figure 25
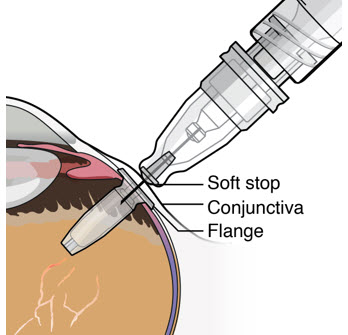 Figure 26
Figure 26Note: Insert needle at the very center of the implant septum and perpendicular to the implant to ensure the needle inserts fully. Do not maneuver if there is resistance as it will bend the needle. Do not use a bent refill needle; replace if bent or if damage is suspected. - Targeting the center of the implant septum, insert the refill needle perpendicularly through the conjunctiva and into the implant septum (see Figure 25).
- – If excessive resistance, withdraw the refill needle. Orient and insert again.
- – Do not twist when encountering conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule to gain access to the septum, as damage to the overlying tissue and to the septum of the device may result.
- Continue inserting the needle until the soft stop of the refill needle makes physical contact with the conjunctiva (see Figure 26) to provide a tactile cue that optimal contact has been made.
Step 12: Refill the SUSVIMO Implant - Refill the implant slowly, by delivering the entire contents of the syringe into the implant, over approximately 5 to 10 seconds, to avoid pressure build-up in the implant reservoir. The soft stop of the refill needle must remain in contact with the conjunctiva throughout the procedure.
- As ranibizumab is administered into the implant, existing solution from the implant should immediately begin to fill the refill needle fluid collection chamber (see Figure 27).
- If fluid is not observed collecting in the refill needle fluid collection reservoir, stop injecting and ensure the refill needle is inserted into the center of the implant septum at a perpendicular angle and the soft stop is in contact with the conjunctiva.
- Administer all of the syringe contents in order to achieve the target replacement ranibizumab concentration in the implant reservoir.
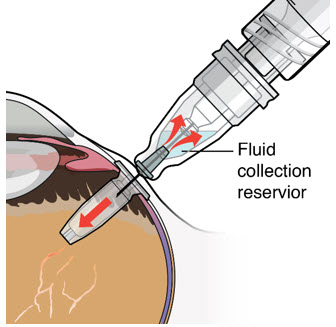
Figure 27Step 13: Withdraw the Syringe - Withdraw the syringe perpendicular to the globe to avoid damaging the septum (see Figure 28).
- A cotton-tipped applicator may be used to provide counter traction to the conjunctiva during needle withdrawal.
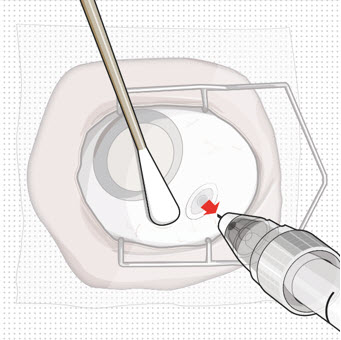
Figure 28Step 14: Dispose of the Used Components - Do not recap the needle or detach it from the syringe. Dispose of the used syringe together with the refill needle in a sharps disposal container or in accordance with local requirements.
Step 15: Perform Indirect Ophthalmoscopy - Perform dilated indirect ophthalmoscopy (and slit lamp exam as needed) to ensure continued proper position of the implant and its components (e.g., septum) in the vitreous cavity and to examine for complications.
2.9 Delayed or Missed Doses
For patients with AMD or DME, if a planned dose (refill-exchange) of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is missed, it should be administered as soon as possible and the subsequent refill-exchange procedures should be performed 24 weeks (approximately 6 months) thereafter.
For patients with DR, if a planned dose (refill-exchange) of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is missed, it should be administered as soon as possible and the subsequent refill-exchange procedures should be performed 36 weeks (approximately 9 months) thereafter.
2.10 Dosage (Refill-Exchange) Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Table 1 describes dosage modifications for specific adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]. No dosage reductions for SUSVIMO are recommended.
Table 1: Dosage (Refill-Exchange) Modifications for Adverse Reactions Adverse Reactions Dosage Modification Intraocular inflammation ≥ 1 + cells or flare Withhold dose (refill-exchange) Sight threatening events (e.g., rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, vitreous hemorrhage, unexplained vision loss, etc.) Withhold dose (refill-exchange) Local infections of either eye Withhold dose (refill-exchange) Infectious endophthalmitis Withhold dose (refill-exchange) Severe systemic infection Withhold dose (refill-exchange) Observed damage to the implant Withhold dose (refill-exchange) and consider SUSVIMO implant removal [see Dosage and Administration (2.8, 2.9)]. - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
The SUSVIMO implant and/or implant-related procedures have been associated with endophthalmitis, rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, implant dislocation, septum dislodgement, vitreous hemorrhage, conjunctival erosion, conjunctival retraction, and conjunctival blebs. Patients should be instructed to report any signs or symptoms that could be associated with these events without delay. In some cases, these events can present asymptomatically. The implant and the tissue overlying the implant flange should be monitored routinely following the implant insertion, and refill-exchange procedures to permit early medical or surgical intervention as necessary. Special precautions need to be taken when handling SUSVIMO components [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.3)].
5.1 Endophthalmitis
In the active comparator period of controlled clinical trials in AMD, the ranibizumab implant has been associated with a 3-fold higher rate of endophthalmitis than monthly intravitreal injections of ranibizumab (1.7% in the SUSVIMO arm vs 0.5% in the intravitreal arm). When including extension phases of clinical trials, 2% (11/555) of patients receiving the ranibizumab implant experienced an episode of endophthalmitis. Reports occurred between days 5 and 853, with a median of 173 days. Many, but not all, of the cases of endophthalmitis reported a preceding or concurrent conjunctival retraction or erosion event.
In the active comparator period of the controlled clinical trial in DME, 0% of patients in the SUSVIMO arm compared to 0.3% in the intravitreal arm experienced an episode of endophthalmitis. When including the extension phase of the clinical trial, 0.7% (4/556) of patients receiving the ranibizumab implant experienced an episode of endophthalmitis. Reports occurred between days 625 and 1016, with a median of 824 days.
In the period with an observational comparator arm of the clinical trial in DR, there were no patients (0/105) in the SUSVIMO arm who experienced an episode of endophthalmitis [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. When including the extension phase of the clinical trial 0.8% (1/128) patients receiving the ranibizumab implant experienced an episode of endophthalmitis, with the event reported on day 695.
Endophthalmitis should be treated promptly in an effort to reduce the risk of vision loss and maximize recovery. The SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) dose (refill-exchange) should be delayed until resolution of endophthalmitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.10) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Patients should not have an active or suspected ocular or periocular infection or severe systemic infection at the time of any SUSVIMO implant or refill procedure. Appropriate intraoperative handling followed by secure closure of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule, and early detection and surgical repair of conjunctival erosions or retractions and strict/controlled aseptic technique conditions throughout refill-exchange procedures may reduce the risk of endophthalmitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
5.2 Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachments have occurred in clinical trials of SUSVIMO and may result in vision loss. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachments should be promptly treated with an intervention (e.g., pneumatic retinopexy, vitrectomy, or laser photocoagulation). SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) dose (refill-exchange) should be delayed in the presence of a retinal detachment or retinal break [see Dosage and Administration (2.10)].
Careful evaluation of the retinal periphery is recommended to be performed, and any suspected areas of abnormal vitreo-retinal adhesion or retinal breaks should be treated before inserting the implant in the eye.
5.3 Implant Dislocation
In clinical trials, the device has dislocated/subluxated into the vitreous cavity or has extended outside the vitreous cavity into or beyond the subconjunctival space. Device dislocation requires urgent surgical intervention. Strict adherence to the scleral incision length and appropriate targeting of the pars plana during laser ablation may reduce the risk of implant dislocation.
5.4 Septum Dislodgement
In clinical trials, a type of implant damage where the septum has dislodged into the implant body has been reported. Perform a dilated slit lamp exam and/or dilated indirect ophthalmoscopy to inspect the implant in the vitreous cavity through the pupil prior to and after the refill-exchange procedure to identify if septum dislodgement has occurred. Discontinue treatment with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) following septum dislodgement and consider implant removal should the benefit of the removal procedure outweigh the risk [see Dosage and Administration (2.9)]. The benefits and risks of retaining, removing, or removing and replacing an implant with a dislodged septum are not well characterized.
Appropriate handling and insertion of the refill needle into the septum (avoid twisting and/or rotation) is required to minimize the risk of septum dislodgement [see Dosage and Administration (2.8)].
5.5 Vitreous Hemorrhage
Vitreous hemorrhages may result in temporary vision loss. Vitrectomy may be needed in the case of a non-clearing vitreous hemorrhage [see Dosage and Administration (2.10)].
In clinical trials of SUSVIMO including the extension phases in patients with AMD, vitreous hemorrhages were reported in 5.2% (23/443) of patients receiving SUSVIMO.
In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phases in patients with DME, vitreous hemorrhages were reported in 10.1% (56/556) of patients receiving SUSVIMO.
In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phase in patients with DR, vitreous hemorrhages were reported in 9.4% (12/128) of patients receiving SUSVIMO.
The majority of these hemorrhages occurred within the first post-operative month following surgical implantation and the majority of vitreous hemorrhages resolved spontaneously.
Patients on antithrombotic medication (e.g., oral anticoagulants, aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) may be at increased risk of vitreous hemorrhage. Antithrombotic medications are recommended to be temporarily interrupted prior to the implant insertion procedure. The SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) dose (refill-exchange) should be delayed in the event of sight-threatening vitreous hemorrhage.
The use of pars plana laser ablation and scleral cauterization should be performed to reduce the risk of vitreous hemorrhage.
5.6 Conjunctival Erosion or Retraction
A conjunctival erosion is a full thickness degradation or breakdown of the conjunctiva in the area of the implant flange. A conjunctival retraction is a recession or opening of the limbal and/or radial peritomy. Conjunctival erosions or retractions have been associated with an increased risk of endophthalmitis, especially if the implant becomes exposed. Surgical intervention (e.g., conjunctival/Tenon's capsule repair) is recommended to be performed in case of conjunctival erosion or retraction with or without exposure of the implant flange.
In clinical trials of SUSVIMO including the extension phases in patients with AMD, 3.6% (16/443) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival erosion and 1.6% (7/443) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival retraction in the study eye.
In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phases of patients with DME, 2.2% (12/556) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival erosion and 1.3% (7/556) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival retraction in the study eye.
In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phase in patients with DR, 2.3% (3/128) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival erosion and 1.6% (2/128) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival retraction in the study eye.
Appropriate intraoperative handling of conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule to preserve tissue integrity and secure closure of peritomy while ensuring placement of sutures away from implant edge may reduce the risk of conjunctival erosion or retraction. The implant and the tissue overlying the implant flange should be monitored routinely following the implant insertion.
5.7 Conjunctival Bleb
A conjunctival bleb is an encapsulated elevation of the conjunctiva above the implant flange, which may be secondary to subconjunctival thickening or fluid. Conjunctival blebs may require surgical management to avoid further complications, especially if the implant septum is no longer identifiable due to the conjunctival bleb.
In clinical trials of SUSVIMO including the extension phases in patients with AMD, 5.9% (26/443) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival bleb/conjunctival filtering bleb leak in the study eye.
In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phases in patients with DME, 9% (50/556) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival bleb/conjunctival filtering bleb leak in the study eye.
In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phase in patients with DR, 3.9% (5/128) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival bleb/conjunctival filtering bleb leak in the study eye.
Strict adherence to the scleral incision length, appropriate intraoperative handling of conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule to preserve tissue integrity and secure closure of peritomy, and proper seating of the refill needle during refill-exchange procedures may reduce the risk of conjunctival bleb.
5.8 Postoperative Decrease in Visual Acuity
Visual acuity was decreased by 4 letters on average in the first postoperative month and 2 letters on average in the second postoperative month following initial implantation of SUSVIMO in patients with AMD [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Visual acuity was decreased by 7 letters on average in the first postoperative month and 3 to 4 letters on average in the second postoperative month following initial implantation of SUSVIMO in patients with DME and DR [see Clinical Studies (14.2 and 14.3)].
5.9 Postoperative Intraocular Inflammation
Postoperative intraocular inflammation has occurred following SUSVIMO implantation. The majority of cases occurred during the first week following implantation and resolved within the first month.
5.10 Air Bubbles Causing Improper Filling of the Implant
Minimize air bubbles within the implant reservoir as they may cause slower drug release. During the initial fill procedure, if an air bubble is present, it must be no larger than 1/3 of the widest diameter of the implant. If excess air is observed after initial fill, do not use the implant. During the refill-exchange procedure, if excess air is present in the syringe and needle do not use the syringe and needle. If excess air bubbles are observed after the refill-exchange procedure, consider repeating the refill-exchange procedure.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Endophthalmitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Implant Dislocation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Septum Dislodgement [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Vitreous Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Conjunctival Erosion or Retraction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Conjunctival Bleb [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Postoperative Decrease in Visual Acuity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in one clinical trial of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of the same or another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data below (Table 2) reflect exposure of 248 patients with AMD in the Archway study through Week 40, 320 patients with DME in the Pagoda study up to Week 64, and 105 patients with DR in the Pavillion study through Week 52 following the SUSVIMO initial fill and implant insertion, refill, and implant removal (if necessary) procedures.
In clinical trials of SUSVIMO in AMD patients, the most common (≥ 10%) adverse reactions up to Week 40 were conjunctival hemorrhage (72%), conjunctival hyperemia (26%), iritis (23%), and eye pain (10%). Septum dislodgement was reported in 0.4% of the AMD patient population.
In clinical trials of SUSVIMO in DME patients, patient population the most common (≥ 10%) adverse reactions up to Week 64 were conjunctival hemorrhage (62%), conjunctival hyperemia (15%), iritis (14%), eye pain (13%), cataract (11%), conjunctival disorder (10%) and vitreous hemorrhage (10%).
In clinical trials of SUSVIMO in DR patients, the most common (≥ 10%) adverse reactions up to Week 52 were conjunctival hemorrhage (73%), conjunctival disorder (14%), iritis (12%) and conjunctival hyperemia (11%).
Table 2 Adverse Reactions occurring in ≥ 4% of patients in the SUSVIMO arm Adverse Reactions AMD
Week 40DME
Week 64DR
Week 52SUSVIMO
n = 248Intravitreal ranibizumab
n = 167SUSVIMO
n = 320Intravitreal ranibizumab
0.5 mg
n = 314SUSVIMO
n = 105- * Iritis includes: iritis, anterior chamber flare, anterior chamber inflammation, and anterior chamber cell.
- † Conjunctival disorder includes: conjunctival adhesion, conjunctival disorder, conjunctival edema, conjunctival erosion, conjunctival retraction, and subconjunctival fibrosis.
- ‡ Conjunctival bleb/filtering bleb leak includes: conjunctival bleb, conjunctival filtering bleb leak, conjunctival cyst, subconjunctival cyst, and implant site cyst.
- § Headache includes: headache and procedural headache.
- ¶ Cataract includes: cataract, cortical cataract, nuclear cataract, and subcapsular cataract.
- # Corneal abrasion includes: corneal abrasion and vital dye staining cornea present.
Conjunctival hemorrhage 72% 6% 62% 18% 73% Conjunctival hyperemia 26% 2% 15% 0 11% Iritis* 23% 0.6% 14% 2% 12% Eye pain 10% 5% 13% 6% 9% Conjunctival disorder† 9% 0 10% 0.3% 14% Vitreous floaters 9% 2% 4% 5% 2% Conjunctival bleb/ filtering bleb leak‡ 8% 0 8% 0 2% Foreign body sensation in eyes 7% 1% 3% 2% 9% Headache§ 6% 2% 6% 4% 9% Hypotony of eye 6% 0 3% 0 0 Vitreous detachment 6% 5% 8% 5% 9% Vitreous hemorrhage 5% 2% 10% 2% 6% Cataract¶ 4% 4% 11% 7% 7% Corneal disorder 4% 0 1% 0 1% Corneal abrasion# 4% 0.6% 4% 1% 4% Corneal edema 4% 0 4% 0.3% 4% In clinical trials of SUSVIMO, hyphema was reported in 0.4% of AMD patients, 1.9% of DME patients, and 1.9% of DR patients.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) administration in pregnant women. Administration of ranibizumab to pregnant monkeys throughout the period of organogenesis resulted in a low incidence of skeletal abnormalities at intravitreal doses up to 41 times the human exposure (based on serum levels following the recommended clinical dose). No skeletal abnormalities were observed at serum trough levels similar to the human exposure after a single eye treatment at the recommended clinical dose (see Data).
Animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, and it is not known whether ranibizumab can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Based on the anti-VEGF mechanism of action for ranibizumab [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], treatment with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) may pose a risk to human embryofetal development.
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, and other adverse outcomes. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects is 2% – 4% and of miscarriage is 15% – 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal Data
An embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study was performed on pregnant cynomolgus monkeys. Pregnant animals received intravitreal injections of ranibizumab every 14 days starting on Day 20 of gestation, until Day 62 at doses of 0, 0.125, and 1 mg/eye. Skeletal abnormalities including incomplete and/or irregular ossification of bones in the skull, vertebral column, and hindlimbs and shortened supernumerary ribs were seen at a low incidence in fetuses from animals treated with 1 mg/eye of ranibizumab. The 1 mg/eye dose resulted in trough serum ranibizumab levels up to 41 times higher than observed human Cmax levels of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) after treatment of a single eye.
No skeletal abnormalities were seen at the lower dose of 0.125 mg/eye, a dose which resulted in trough exposures similar to single eye treatment with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) in humans. No effect on the weight or structure of the placenta, maternal toxicity, or embryotoxicity was observed.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data available on the presence of ranibizumab in human milk, the effects of ranibizumab on the breastfed infant or the effects of ranibizumab on milk production/excretion. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because the potential for absorption and harm to infant growth and development exists, caution should be exercised when SUSVIMO is administered to a nursing woman.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from ranibizumab.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Females of reproductive potential should use effective contraception during treatment with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) and for at least 12 months after the last dose of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection).
Infertility
No studies on the effects of ranibizumab on fertility have been conducted and it is not known whether ranibizumab can affect reproduction capacity. Based on the anti-VEGF mechanism of action for ranibizumab, treatment with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) may pose a risk to reproductive capacity.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Ranibizumab is a recombinant humanized IgG1 kappa isotype monoclonal antibody fragment for intraocular use. Ranibizumab binds to and inhibits the biologic activity of human vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A). Ranibizumab, which lacks an Fc region, has a molecular weight of approximately 48 kilodaltons and is produced by an E. coli expression system in a nutrient medium containing the antibiotic tetracycline. Tetracycline is not detectable in the final product.
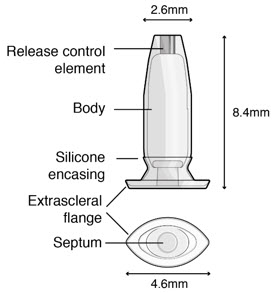
SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is supplied as a sterile, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to slightly brownish solution for intravitreal use via the SUSVIMO implant. Each single-dose vial contains 10 mg of ranibizumab, histidine HCl (0.1 mg), polysorbate 20 (0.01 mg), sucrose (8.2 mg), and Water for Injection, in 0.1 mL of solution with a pH of 5.5. The SUSVIMO implant is designed to contain approximately 0.02 mL (2 mg) of ranibizumab solution when filled. SUSVIMO does not contain an antimicrobial preservative.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ranibizumab binds to the receptor binding site of multiple biologically active forms of VEGF-A, including VEGF110. VEGF-A has been shown to cause neovascularization and leakage in models of ocular angiogenesis and vascular occlusion and is thought to contribute to pathophysiology of neovascular AMD. The binding of ranibizumab to VEGF-A prevents the interaction of VEGF-A with its receptors (VEGFR1 and VEGFR2) on the surface of endothelial cells, reducing endothelial cell proliferation, vascular leakage, and new blood vessel formation.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The SUSVIMO implant provides a continuous release of ranibizumab where the release of ranibizumab into the vitreous decreases over time as the concentration in the implant decreases. The ranibizumab serum and aqueous humor concentrations with a SUSVIMO 24-week and 36-week treatment interval are maintained below the maximum and above the minimum concentrations experienced with monthly 0.5 mg intravitreal ranibizumab.
Distribution
Ranibizumab did not accumulate in serum when administered with refills every 24 weeks or every 36 weeks.
Following implant insertion of SUSVIMO in patients with AMD, the mean (±SD) maximum ranibizumab serum concentration (Cmax) was 0.48 (±0.17) ng/mL and median (range) time to maximum serum concentration (Tmax) was 26 (1 – 89) days. Following the initial fill and refill of SUSVIMO in patients, maximum serum concentrations of ranibizumab were below the ranibizumab concentration necessary to inhibit the biological activity of VEGF by 50%.
Elimination
Specific Populations
Patients with renal impairment were included in the population pharmacokinetic analysis of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection). Across all indications, systemic clearance of ranibizumab was slightly lower in renally impaired patients but was not clinically significant. No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of ranibizumab were observed based on age in the patient population.
12.6 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immune response in patients treated with ranibizumab including SUSVIMO. The detection of an immune response is highly dependent on the sensitivity, specificity, and drug tolerance level of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies in the study described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
Prior to treatment with SUSVIMO, 2.1-3.6% of patients with AMD, DME, or DR tested positive for anti-ranibizumab antibodies. In patients with AMD, after the SUSVIMO implant insertion and treatment, 12% (29 of 247) patients tested positive for anti-ranibizumab antibodies. In patients with DME, after 4 doses of intravitreal ranibizumab, and SUSVIMO implant insertion and treatment, 13% (41 of 320) patients tested positive for anti-ranibizumab antibodies. In patients with DR, after 2 doses of intravitreal ranibizumab, and SUSVIMO implant insertion and treatment, 17% (17 of 99) patients tested positive for anti-ranibizumab antibodies. No clinically meaningful differences in the pharmacokinetics, efficacy, or safety in patients testing positive for anti-ranibizumab antibodies were observed.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No studies have been conducted to determine the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection). Based on the anti-VEGF mechanism of action for ranibizumab, treatment with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) may pose a risk to reproductive capacity [see Females and Males of Reproductive Potential (8.3)].
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
The clinical efficacy and safety of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) was assessed in a randomized, visual assessor-masked, active treatment-controlled study (Archway-NCT03677934) in patients with AMD. A total of 415 patients (248 in the SUSVIMO arm and 167 in the intravitreal ranibizumab arm) were enrolled and treated in this study. Patients were diagnosed with AMD within the 9 months prior to screening and received ≥ 3 doses of anti-VEGF intravitreal agents in the study eye within the last 6 months prior to screening. Each patient was required to have demonstrated a response to an anti-VEGF intravitreal agent prior to randomization. Patients were randomized in a 3:2 ratio to receive continuous delivery of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) via the SUSVIMO implant every 24 weeks or 0.5 mg intravitreal ranibizumab injections every 4 weeks. For patients randomized to the SUSVIMO arm, supplemental treatment with 0.5 mg intravitreal ranibizumab injections was available at Weeks 16, 20, 40, 44, 64, 68, 88, and 92, if needed. In the first 24 weeks, 1.6% of patients assessed for supplemental treatment received 1 or more supplemental treatment(s) and in the following 24 weeks, 5.4% of patients assessed for supplemental treatment received 1 or more supplemental treatment(s).
The primary efficacy endpoint of change from baseline in distance Best Corrected Visual Acuity (BCVA) score averaged over Week 36 and Week 40 demonstrated that SUSVIMO was equivalent to intravitreal ranibizumab injections administered every 4 weeks. Detailed efficacy results are shown in Table 3 and Figure 29 below.
Table 3 Visual Acuity outcomes at Week 40 in Archway (GR40548) Study Outcome Measure* SUSVIMO (100 mg/mL)
n=248Intravitreal ranibizumab 0.5 mg (10 mg/mL)
n=167Difference
(95% CI)†BCVA = Best corrected visual acuity - * BCVA measured using the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) visual acuity chart at a starting distance of 4 meters.
- † All estimates are adjusted estimates based on a mixed-effect model with repeated measures. SUSVIMO arm - intravitreal ranibizumab arm. 95% is a rounding of 95.03% CI; The type 1 error was adjusted for interim safety monitoring.
- ‡ Equivalence margins were ±4.5 letters.
Adjusted Mean change from baseline in BCVA score averaged over Weeks 36 and 40 0.2 0.5 -0.3
(-1.7, 1.1)‡Q24W = every 24 weeks; Q4W = every 4 weeks - * Prior to study treatment, a median of 4 doses of anti-VEGF intravitreal agents were administered in the study eye of patients in the SUSVIMO and intravitreal ranibizumab arms.
- † Decrease in BCVA at Week 4 during post-operative recovery period.
Figure 29 Adjusted Mean change from Baseline in Best Corrected Visual Acuity in study eye through Week 48 in the Archway (GR40548) study*, † 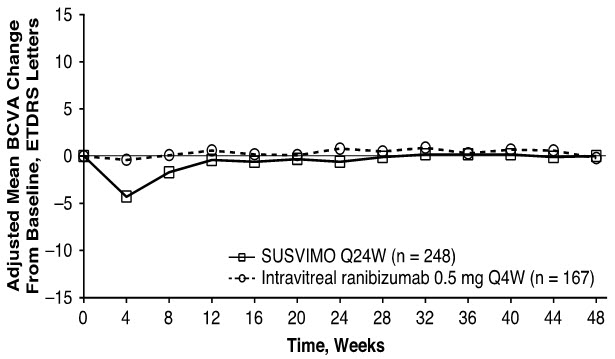
Consistent results were observed across patient subgroup analyses for mean change from baseline in BCVA score (age, gender, number of prior anti-VEGF intravitreal injections, and baseline BCVA score).
14.2 Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
The clinical efficacy and safety of SUSVIMO were assessed in a randomized, visual assessor-masked, active treatment-controlled study (Pagoda-NCT04108156) in patients with DME. A total of 634 patients (381 in the SUSVIMO arm and 253 in the intravitreal ranibizumab 0.5 mg arm) were enrolled and treated in this study. Patients were randomized in a 3:2 ratio to receive continuous delivery of SUSVIMO via the implant every 24 weeks or 0.5 mg intravitreal ranibizumab injections every 4 weeks.
Prior to study treatment, a median of 4 doses of intravitreal ranibizumab 0.5 mg were administered in the study eye of patients in the SUSVIMO and intravitreal ranibizumab arms. Patient ages ranged from 29 to 89 years with a mean of 60.7 years. A total of 21% of patients were previously treated for DME. At baseline, the overall mean visual acuity was 65.3 letters (range: 25 to 89 letters).
The primary efficacy endpoint of change from baseline in distance Best Corrected Visual Acuity (BCVA) score averaged over Week 60 and Week 64 demonstrated that SUSVIMO was non-inferior to intravitreal ranibizumab injections administered every 4 weeks. Detailed efficacy results are shown in Table 4 and Figure 30 below.
Table 4 Key efficacy outcomes at Week 60 and Week 64 in the Pagoda (GR40550) Study Outcome Measure* SUSVIMO 100 mg/mL
n=381Intravitreal ranibizumab 0.5 mg
(10 mg/mL)
n=253Difference
(95% CI)†BCVA = Best corrected visual acuity - * BCVA measured using the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) visual acuity chart at a starting distance of 4 meters.
- † All estimates are adjusted estimates based on a mixed-effect model with repeated measures. 95% is a rounding of 95.05% CI; The type 1 error was adjusted for interim safety monitoring.
Change in BCVA scores from baseline averaged over Week 60 and Week 64
Adjusted Mean9.6 9.4 0.2 (-1.2, 1.6) Figure 30 Adjusted Mean change from Baseline in Best Corrected Visual Acuity in study eye through Week 64 in the Pagoda (GR40550) study
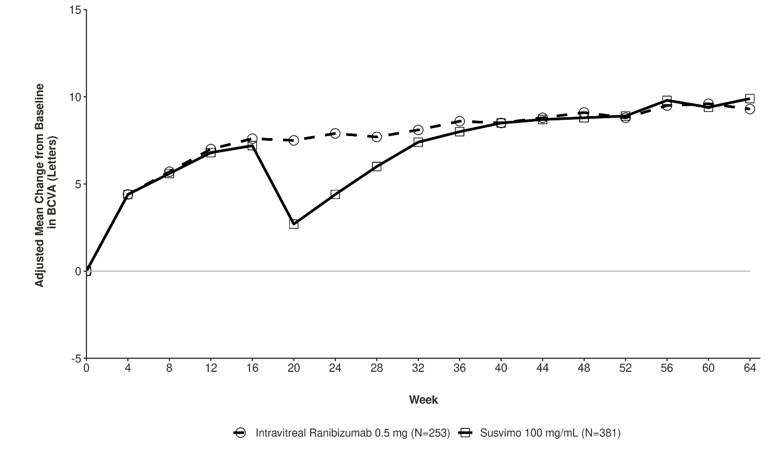
Consistent results were observed across patient subgroup analyses for mean change from baseline in BCVA score (age, ethnicity, gender, baseline HbA1c score, focal/macular laser history, baseline BCVA score, prior intravitreal anti-VEGF treatment and DR severity).
14.3 Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
The clinical efficacy and safety of SUSVIMO were assessed in a randomized, visual assessor and reading center-masked study (Pavilion-NCT04503551) in patients with moderately-severe to severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) [Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scale (ETDRS-DRSS) of 47 or 53], without center-involved DME (CI-DME), and who had not received prior treatment in the study eye for DR. A total of 174 patients (106 in the SUSVIMO arm and 68 in the observational comparator arm) were enrolled in this study.
Patients who had not received prior treatment in the study eye for DR were randomized in a 5:3 ratio to continuous delivery of SUSVIMO via the implant every 36 weeks or to clinical observation. Prior to the implant procedure, two loading doses of intravitreal ranibizumab 0.5 mg were administered in the study eye. The observational comparator arm did not receive loading doses of intravitreal ranibizumab. For patients who developed CI-DME or proliferative diabetic retinopathy/anterior segment neovascularization in either arm, supplemental treatment with intravitreal injections of 0.5 mg ranibizumab was available per investigator's clinical judgment at any non-refill-exchange study visit. Patient ages ranged from 24 to 83 years with a mean of 53.9 years. At baseline, the overall mean visual acuity was 82.4 letters (range: 69 to 97 letters).
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with a ≥ 2-step improvement on the ETDRS-DRSS from baseline at Week 52 versus clinical observation. SUSVIMO with two loading doses of intravitreal ranibizumab was superior to clinical observation at Week 52. Detailed results are shown in Table 5 and Figure 31 below.
Table 5 Efficacy Outcomes through Week 52 in the Pavilion (GR41675) Study Outcome Measure SUSVIMO
100 mg/mL
(n=106)Clinical Observation
(n=68)Difference
95% CI *ETDRS-DRSS = Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scores
CMH = Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test- * All estimates are adjusted estimates based on the CMH method. 95% is a rounding of 95.04% CI; the type 1 error was adjusted for interim safety monitoring. p<0.01 compared with clinical observation.
Adjusted proportion of patients with ≥ 2-step improvement from baseline on the ETDRS-DRSS at Week 52 80% 9% 71% (61%, 81%) Figure 31 Adjusted Proportion of Patients with a ≥ 2-Step Improvement from Baseline on ETDRS-DRSS in Study Eye over Time through Week 52 in the Pavilion (GR41675) Study
In the SUSVIMO arm, none of the patients assessed for supplemental treatment received any supplemental injections of intravitreal ranibizumab and 40% of patients in the observational comparator arm received 1 or more supplemental treatments through Week 52.
Consistent results were observed across patient subgroup analyses for ETDRS-DRSS score including age, race, ethnicity, baseline hemoglobin (HbA1c) and baseline ETDRS-DRSS score.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Each SUSVIMO initial fill needle kit (NDC: 50242-078-55) contains:
- One SUSVIMO 100 mg/mL single-dose glass vial
- One SUSVIMO initial fill needle (34-gauge needle with a 5 μm integrated filter) with a blue cap
Each SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) carton (NDC: 50242-078-12) contains one SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL that is clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to slightly brownish solution in a single-dose glass vial.
Each SUSVIMO initial fill needle carton contains a SUSVIMO initial fill needle (34-gauge needle with a 5 μm integrated filter) with a blue cap.
Each SUSVIMO refill needle carton contains a SUSVIMO refill needle (34-gauge vented needle with a 5 μm integrated filter) with a clear cap.
Device and Materials Description Components 
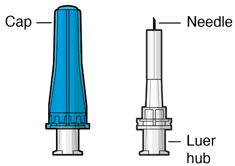
Figure 32SUSVIMO implant - SUSVIMO implant (Figure 33) is capable of holding 0.02 mL of drug, and is secured within the sclera, by the extrascleral flange that remains visible through the conjunctiva following insertion.
- The septum is a self-sealing interface through which ranibizumab is administered to fill the implant.
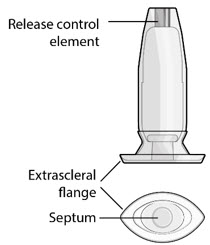
Figure 33SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL vial - SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) (Figure 34) is used to fill the implant with ranibizumab prior to insertion or during subsequent refill-exchange in an office-based setting.
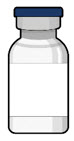
Figure 34SUSVIMO refill needle - SUSVIMO refill needle (Figure 35) consists of a 34 G vented needle assembly, silicone soft stop, and a 5 μm integrated filter within the needle hub. It is designed to simultaneously exchange the contents of the implant reservoir with replacement ranibizumab in an office-based setting. As replacement ranibizumab is administered into the implant through the stainless-steel cannula, fluid remaining in the implant flows through openings in the vented needle and is collected in the fluid collection reservoir.
- SUSVIMO refill needle is distinguished by its clear cap.
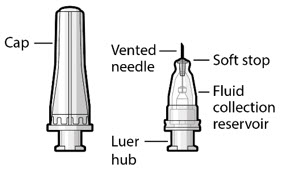
Figure 35Materials List
Materials that are required and supplied to perform the procedure are:
- SUSVIMO refill needle, 34 G, with clear cap
- SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL
Additional materials required to perform the procedure but are not provided are:
- One sterile 1 mL Luer Lock syringe (not included)
- One sterile 5-micron filter needle (19-gauge × 1½ inch) (not included)
- Anesthetic ophthalmic solutions
- Ophthalmic broad-spectrum microbicide solution
- Cotton tips and gauze
- Sterile powder free gloves
- Face masks
- Lid speculum
- Magnification such as visor or loupes
- Task lighting
- Indirect ophthalmoscope and lens
- Sterile drape (optional for refill-exchange procedure)
16.2 Storage
Store SUSVIMO initial fill needle kit at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do not freeze. Protect from light. Do not shake. The SUSVIMO initial fill needle has been sterilized with electron beam processing.
Store SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/ mL vial at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do not freeze. Protect from light. Do not shake. Prior to use, the unopened vial may be kept at 9°C to 30°C (48°F to 86°F) for up to 24 hours provided it is protected from light.
Store the SUSVIMO implant and insertion tool assembly, refill needle and explant tool at room temperature 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F). The SUSVIMO implant and insertion tool assembly has been sterilized with ethylene oxide gas. The SUSVIMO refill needle and explant tool has been sterilized with electron beam processing.
Store the SUSVIMO initial fill needle at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F). The SUSVIMO initial fill needle has been sterilized with electron beam processing.
16.3 Handling
SUSVIMO components are supplied sterile and are for single-use only. Do not reprocess, re-sterilize, or reuse SUSVIMO components. Do not use if the sterility has been compromised or the contents have been dropped, damaged or tampered with. Do not use past the expiration date printed on the label. Do not open sealed tray until time of use. Avoid contact between sharp surgical instruments and the SUSVIMO implant as the material of the septum and silicone encasing is soft and susceptible to damage.
Important Device Handling Information
- Use caution when performing ophthalmic procedures (e.g., B-scan ophthalmic ultrasound, scleral depression, or gonioscopy) that may cause deflection or movement of the implant and subsequent injury.
Ocular Implant Initial Fill Procedure
- Minimize air bubbles within the implant reservoir as they may cause slower drug release. If an air bubble is present, it must be no larger than 1/3 of the widest diameter of the implant. If excess air is observed after initial fill, do not use the implant.
Ocular Implant Insertion Procedure
- Perpendicular entry of the implant is important to avoid contact between the implant and intraocular structures such as the lens, as contact between the implant and the intraocular structures may cause adverse reactions such as traumatic cataract.
- Avoid excessive force on the globe by first ensuring that the tip of the implant has passed through the sclero-pars plana incision before slowly pushing the implant into place.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Advise patients on the following after the implant insertion procedure:
Positioning:
- Keep head above shoulder level for the rest of the day.
- Sleep with head on 3 or more pillows during the day and the night after surgery.
How to care for the treated eye after the procedure:
- Do not remove the eye shield until they are instructed to do so by their healthcare provider. At bedtime, continue to wear the eye shield for at least 7 nights following the implant surgery.
- Administer all post-operative eye medications as directed by their healthcare provider.
- Do not push on the eye, rub the eye, or touch the area of the eye where the implant is located (underneath the eyelid in the upper and outer part of the eye) for 30 days following the implant insertion.
- Do not participate in strenuous activities until 1-month after the implant insertion or after discussion with their healthcare provider.
Advise patients on the following after the Refill-Exchange procedure:
- Refrain from pushing on the treated eye, rubbing the eye, or touching the eye in the area of the implant (located underneath the eyelid in the upper and outer part of your eye) for 7 days following the refill-exchange procedure.
- Administer eye drops as directed by their healthcare provider.
Advise patients on the following after the implant removal procedure (if it is deemed medically necessary):
- Keep your head above shoulder level for the rest of the day.
- Sleep with your head on 3 or more pillows if lying down during the day and night after the implant removal.
- Wear an eye shield for at least 7 nights following the implant removal.
- Do not participate in strenuous activities until 14 days following the implant removal.
- Administer all post-operative anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drops, as directed by your healthcare provider.
Advise patients on the following throughout SUSVIMO treatment:
- Do not drive or use machinery until the eye shield can be removed and visual function has recovered sufficiently [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- The SUSVIMO implant and/or implant related procedures have been associated with conjunctival reactions (bleb, erosion, retraction), vitreous hemorrhage, endophthalmitis, rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, the dislocation of the implant, septum dislodgement, and a temporary decrease in vision.
- While the implant is in the eye, avoid rubbing the eye or touching the area as much as possible. However, if necessary to do so, make sure hands are cleaned prior to touching the eye.
- Seek immediate care from an ophthalmologist if there are sudden changes in their vision (an increase in moving spots, the appearance of "spider webs", flashing lights, or a loss in vision), increasing eye pain, progressive vision loss, sensitivity to light, redness in the white of the eye, a sudden sensation that something is in their eye, or eye discharge or watering [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: 5/2025 MEDICATION GUIDE
SUSVIMO® (suss-VIH-moh)
(ranibizumab injection)
for intravitreal use via SUSVIMO ocular implantWhat is the most important information I should know about SUSVIMO?
SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is delivered into the eye using the SUSVIMO implant. The SUSVIMO implant and the procedures to insert, fill, refill and remove the eye (ocular) implant can cause serious side effects including:- an eye infection (endophthalmitis). Endophthalmitis is an infection of the eyeball that can cause permanent damage to your eye including blindness. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have increasing eye pain, vision loss, sensitivity to light, or redness in the white of the eye. Endophthalmitis requires urgent (same day) medical or surgical treatment.
- a missing layer on top of the white part of the eye (conjunctival erosion). Conjunctival erosion is an area that becomes missing (defect) in the layer (conjunctiva) that covers the white part of the eye which may result in exposure of the implant. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have a sudden feeling that something is in your eye, if you have eye discharge, or watering of the eye. Conjunctival erosion may require surgical treatment.
- an opening of the layer that covers the white part of the eye (conjunctival retraction). Conjunctival retraction is an opening or gaping in the layer (conjunctiva) that covers the white part of the eye which may cause the implant to be exposed. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have a sudden feeling that something is in your eye, if you have eye discharge, or watering of the eye. Conjunctival retraction may require surgical treatment.
To help prevent or keep these side effects from becoming more serious follow all post-procedure instructions your healthcare provider gives you. See "How will I receive SUSVIMO?".What is SUSVIMO?
SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with:- Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) who have responded to at least two injections of a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) inhibitor in the gel-like part of the eye (intravitreal).
- Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) who have responded to at least two injections of a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) inhibitor in the gel-like part of the eye (intravitreal).
- Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) who have responded to at least two injections of a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) inhibitor in the gel-like part of the eye (intravitreal).
Do not receive SUSVIMO if you: - have an infection in or around your eye.
- have active swelling around your eye that may include pain and redness.
- are allergic to ranibizumab or any of the ingredients in SUSVIMO. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in SUSVIMO.
Before receiving SUSVIMO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - are currently taking or have recently taken medicines that lower the chance of blood clots forming in the body such as warfarin, low or regular doses of aspirin, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID).
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if SUSVIMO will harm your unborn baby. You should use birth control during your treatment with SUSVIMO and for 12 months after your last dose of SUSVIMO.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if SUSVIMO passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you receive SUSVIMO.
How will I receive SUSVIMO? - SUSVIMO is implanted through the white part of the eye (sclera) by your healthcare provider.
- Your healthcare provider will refill your implant device every 6 months (about every 24 weeks) if you have AMD or DME or every 9 months (about every 36 weeks) if you have DR.
- If you miss a scheduled refill, call your healthcare provider as soon as possible to reschedule your refill. Your next refill should be given 6 months after your last refill if you have AMD or DME, or 9 months after your last refill if you have DR.
After the Implant Insertion:-
Positioning of your head
- Keep your head above shoulder level for the rest of the day.
- Sleep with your head on 3 or more pillows during the day and night after your implant insertion.
-
How to care for your eye
- Do not remove the eye shield from your eye until you are told to by your healthcare provider. At bedtime, continue to wear an eye shield for at least 7 nights following the implant insertion.
- Take all post-operative eye medicines as your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Do not push on the eye, rub the eye, or touch the area of the eye where the implant is located (underneath the eyelid in the upper and outer part of your eye) for 30 days following the implant insertion.
- Do not participate in strenuous activities until 1 month after the implant insertion or after talking to your healthcare provider.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Implant Card
- Get your implant card from your healthcare provider after receiving the implant and keep the card in a safe place for future reference. The implant card contains important information about your SUSVIMO implant.
- Show your current and future healthcare providers your implant card. This is important if you need to have an MRI. You may only receive an MRI under very specific conditions if you have the SUSVIMO implant. Your healthcare provider will review the information on the implant card and will let you know if you should receive an MRI.
- Do not push on the eye, rub the eye, or touch the area of the eye where the implant is located (underneath the eyelid in the upper and outer part of your eye) for 7 days following the refill procedure.
- Take eye drops exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take them.
- Keep your head above shoulder level for the rest of the day.
- Sleep with your head on 3 or more pillows if lying down during the day and night after implant removal.
- Wear an eye shield for at least 7 nights following the implant removal.
- Do not participate in strenuous activities until 14 days following the implant removal.
- Give all post-operative drops, as told by your healthcare provider.
What should I avoid while receiving SUSVIMO? - Do not drive or use machinery until the eye shield can be removed and you can see.
- Avoid rubbing your eye or touching the area of your eye where the implant is located as much as possible while the implant is in place. If you have to rub or touch your eye, wash your hands first.
What are the possible side effects of SUSVIMO?
See "What is the most important information I should know about SUSVIMO?" on the first page.
In addition to those side effects listed on page one, the SUSVIMO implant and the procedures to insert, fill, refill and remove the eye (ocular) implant can cause other serious side effects including:- Tear and separation of layers of the retina (Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment). Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is a tear and separation of one of the layers of the retina in the back of the eye that senses light. Call your healthcare provider or go to the emergency room right away if you see flashing lights, see a curtain or veil covering part of your vision, have a change in your vision, or a loss of vision. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment requires surgical treatment.
- Implant movement (Implant dislocation): Tell your healthcare provider right away if you notice that the implant has moved out of place. This movement may require surgical treatment to correct.
- Implant damage: Damage to the implant that prevents continued treatment (refills) with SUSVIMO. If the implant is not able to be properly refilled, your wet AMD may be inadequately treated and your physician may remove the implant and/or change your treatment.
- Bleeding (Vitreous hemorrhage): Vitreous hemorrhage is bleeding within the gel-like substance (vitreous) inside of your eye. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have an increase in moving spots or what looks like spider webs in your vision as you may need an additional eye surgery.
- Bump on top of the white layer of the eye (Conjunctival bleb): Conjunctival bleb is a small bulge in the layer (conjunctiva) that covers the white part of the eye where the implant is inserted. This may be due to leakage of fluid from the inside of the eye. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have a sudden feeling that something is in your eye (foreign body sensation), see a bulge over the white part of your eye, if you have eye discharge, or watering in the eye. You may need medical or surgical treatment.
- Temporary decrease in vision after the SUSVIMO procedure.
- blood on the white of the eye
- eye pain
- redness in the white of the eye
- sensitivity to light
These are not all the possible side effects of SUSVIMO.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to Genentech at 1-888-835-2555.General information about the safe and effective use of SUSVIMO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about SUSVIMO that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection)?
Active ingredient: ranibizumab
Inactive ingredients: histidine HCl, polysorbate 20, sucrose.
Manufactured by: Genentech, Inc., A Member of the Roche Group, 1 DNA Way, South San Francisco, CA 94080-4990
U.S. License No.: 1048 -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Susvimo®
(ranibizumab injection)
For Susvimo ocular implant use
Instructions for UseInitial Fill and Implant Procedure Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Susvimo procedures should be performed by an ophthalmologist experienced in vitreoretinal surgery.
Refer to the Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL prescribing information for a complete list of indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, and adverse events.
Contents
Introduction
3 Device Description 4 Components 8 Intended Use/Indications for Use 8 Contraindications 8 Warnings 9 Precautions 10 How Supplied, Handling, and Storage Instructions for Use
11 Introduction and Materials 13 Preparatory Procedures 14 Infusion Line Placement Procedure 15 Conjunctival Dissection Procedure 17 Syringe Preparation and Initial Implant Fill 25 Implant Insertion 35 Disposal and Post-insertion Procedures 36 Explanation of symbols on product or package labeling Introduction
These instructions include only the procedure for filling and inserting the Susvimo implant. For more information, refer to the Susvimo prescribing information for the refill-exchange procedure and Susvimo Instructions for Use for the implant removal procedure.
Device Description
Susvimo is an intraocular drug delivery system designed to be used specifically with Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL. The system consists of an intraocular implant along with ancillary devices used to fill, insert, and explant (if needed) the implant.
The implant is a refillable drug reservoir that is inserted into the eye through the pars plana. The implant is secured within the scleral incision, with the extrascleral flange that remains visible through the conjunctiva following insertion. Once filled with ranibizumab, the implant is designed to provide continuous release of ranibizumab. The implant will be refilled with ranibizumab in an office-based setting via an administration through the conjunctiva and implant septum.
Components
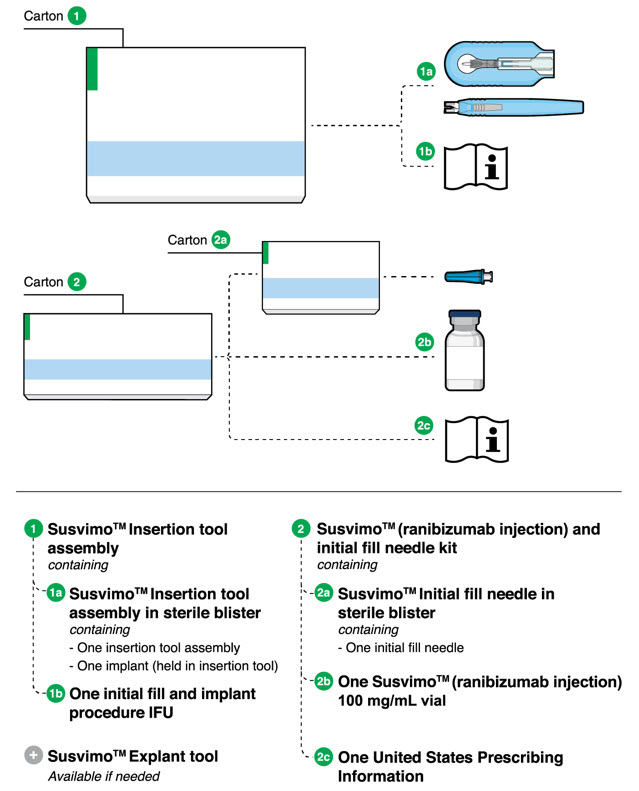
Figure 1
Susvimo components for initial fill and implant procedure
Susvimo implant (packaged with insertion tool assembly)
Susvimo implant (Figure 2 and Figure 3) is a refillable reservoir inserted into the eye through the pars plana. The body of the implant, which includes the release control element, extends into the vitreous cavity.
Table 1 Susvimo implant component description Implant components Description Extrascleral flange The extrascleral flange provides secure anchoring of the implant within the scleral incision and is encased in silicone. Septum The septum is a self-sealing interface through which ranibizumab is administered into the implant both prior to insertion and during subsequent refills in an office-based setting. Body The body of the implant contains a hollow drug reservoir, capable of holding 0.02 mL of drug. Release control element The titanium release control element controls the rate of ranibizumab diffusion from the drug reservoir into the vitreous. Susvimo insertion tool assembly
Susvimo insertion tool assembly is designed to facilitate handling of the implant during the initial fill and implant procedure. The insertion tool assembly is comprised of a carrier and handle (Figure 4 and Figure 5), described in more detail below:
Table 2 Susvimo insertion tool assembly component description Insertion tool assembly components Description Gripper tips The implant is provided pre-positioned in the insertion tool assembly gripper tips. After initial fill of the implant with ranibizumab, the implant and gripper tips are transferred from the insertion tool carrier to the insertion tool handle. Luer lock slot The syringe is loaded into the insertion tool carrier by aligning the syringe Luer lock with the insertion tool carrier Luer lock slot. Guide channel The guide channel serves to direct the syringe and initial fill needle in the insertion tool carrier during the initial fill of the implant. Release button Pressing the release button on the insertion tool handle will open the gripper tips and release the implant. Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL vial
Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) (Figure 6) is used to fill the implant prior to insertion or during subsequent refill-exchange in an office-based setting.
Figure 6
Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL vialSusvimo initial fill needle
Susvimo initial fill needle (Figure 7) is designed to fill the implant with ranibizumab prior to implant insertion. The initial fill needle is distinguished by its blue cap.
Figure 7
Susvimo initial fill needleTable 3 Susvimo initial fill needle component description Initial fill needle components Description Needle 34 G needle Integrated filter Integrated 5 µm filter within needle hub Intended Use/Indications for Use
Susvimo ocular implant is approved for use with Susvimo (ranibizumab injection). Refer to the Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) prescribing information for a complete list of indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, and adverse events.
Contraindications
Susvimo is contraindicated in patients with ocular or periocular infections, with active intraocular inflammation, or with known hypersensitivity to ranibizumab or any of the excipients in Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL. Hypersensitivity reactions may manifest as severe intraocular inflammation.
Warnings
- Do not use if the sterility has been compromised or the contents have been dropped, damaged or tampered with.
- Minimize air bubbles within the implant reservoir as they may cause slower drug release. If an air bubble is present, it must be no larger than 1/3 of the widest diameter of the implant.
If excess air is observed after initial fill, do not use the implant. - Perpendicular entry of the implant is important to avoid contact between the implant and intraocular structures such as the lens, as contact between the implant and the intraocular structures may cause adverse events such as traumatic cataract.
- Avoid excessive force on the globe by first ensuring that the tip of the implant has passed through the sclero-pars plana incision before slowly pushing the implant into place.
Precautions
- Read and follow all instructions, warnings, and cautions prior to use.
- Susvimo procedures should be performed by an ophthalmologist experienced in vitreoretinal surgery.
- Use the Susvimo components and materials as specified in these instructions to perform the implant insertion procedure including initial fill.
- Avoid contact between sharp surgical instruments and the implant as the material of the septum and silicone encasing are soft and susceptible to damage.
- The implant is MR Conditional. The Patient Implant card is provided with instructions and must be completed and given to the patient after implant insertion. For further information please refer to the 'Post-insertion patient instructions' section.
Use with Standard Procedures
Susvimo implant is compatible for use with the following standard procedures: A-scan ophthalmic ultrasound, slit lamp examination, indirect ophthalmoscopy, tonometry, optical coherence tomography (OCT), visual field (perimetry), standard lasers for ophthalmic treatments, radiography (x-ray), computed tomography (CT) scan, fluorescein/ indocyanine angiography, and fundus autofluorescence.
Use caution when performing ophthalmic procedures that may cause deflection of the implant and subsequent injury. For example, B-scan ophthalmic ultrasound, scleral depression, or gonioscopy.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Safety Information
 MR Conditional.
MR Conditional.Non-clinical testing has demonstrated that the Susvimo implant is MR Conditional. A patient with this device can be safely scanned in an MR system meeting the following conditions:
- Static magnetic field of 1.5-Tesla (1.5 T) or 3-Tesla (3 T)
- Maximum spatial field gradient of 3,000 G/cm (30 T/m)
- Maximum MR system reported, whole body averaged specific absorption rate (SAR) of 4.0 W/kg (First Level Controlled Operating Mode)
Under the scan conditions defined above, the Susvimo implant is expected to produce a maximum temperature rise of less than 1°C after 15 minutes of continuous scanning.
In non-clinical testing, the image artifact caused by the device extends approximately 4 mm from the Susvimo implant when imaged with a gradient echo pulse sequence in a 3 T MRI system.
How Supplied, Handling, and Storage
- All Susvimo components are supplied sterile.
Do not reprocess or resterilize. - All Susvimo components are for single use only.
Do not reuse Susvimo components. - Do not open sealed tray until time of use.
- Do not use if the package is damaged or broken as sterility may be compromised.
- Do not use past the expiration date printed on the label.
Susvimo ocular implant and insertion tool assembly
- The sealed tray has been sterilized with ethylene oxide gas.
- Store the Susvimo implant and insertion tool assembly at room temperature 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F).
Susvimo (ranibizumab injection)
- Susvimo should be stored at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do not freeze. Protect from light. Do not shake. Prior to use, the unopened vial may be kept at 9°C to 30°C (48°F to 86°F) for up to 24 hours.
Initial fill needle
- Susvimo initial fill needle should be stored at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F). Susvimo initial fill needle has been sterilized with electron beam processing.
See Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) prescribing information for additional information.
Instructions for Use
Introduction and Materials
Implant insertion is a surgical procedure that is performed in an operating room. The implant is filled with Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) immediately prior to insertion.
Materials List
The materials that are required in the operating room on the day of the procedure are listed in Tables 4 and 5.
Table 4 Susvimo components provided for initial fill and implant procedure Item Description Susvimo ocular implant with insertion tool assembly Susvimo initial fill needle, 34 G, with blue cap Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL Susvimo explant tool
(Refer to Susvimo implant removal Instructions for Use for information on implant removal.)Table 5 Additional materials required but not provided for initial fill and implant procedure Item Description One sterile 1 mL Luer Lock syringe (not included) One sterile 5-micron filter needle (19-gauge × 1½ inch) (not included) Surgical microscope Vitrectomy surgical control system Standard 25 G or 27 G vitrectomy set up 23 G or 25 G 532 nm Endolaser probe and associated source Standard vitrectomy tray (including adjustable caliper, 0.12 straight toothed forceps, blunt wescott scissors) Cauterization equipment (including standard fine tip diathermy and eraser tip wet-field cautery) Ophthalmic broad-spectrum microbicide solution Marking pad 3.5 mm and 4.0 mm fixed caliper or equivalent fixed tool 3.5 mm fixed width gauge or equivalent fixed tool 19 G or 20 G MVR Straight Knife Slit Knife, 3.2 mm Straight Gut or Vicryl sutures for conjunctival tissues (suggested 7-0 to 9-0: monofilament recommended) Indirect ophthalmoscope and lens Drapes Preparatory Procedures
1. Inspect packaging and components - Prior to use in the operating room, inspect the packaging of the components for damage.
- Check the expiration date printed on the label.
- Remove the vial from the carton.
NOTE: the outside of the vial is not sterile. - Open sterile packaging and using aseptic technique, remove the components from their tray.
- Inspect components and place onto sterile field (Figure 8).
 Warning
Warning
Do not use if the sterility has been compromised or the contents have been dropped, damaged, or tampered with.2. Inspect Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) - Visually inspect the contents of the ranibizumab vial for particulate matter and discoloration.
- The drug solution should be colorless to slightly brownish.
 Caution
Caution
Do not use if particulate, cloudiness or discoloration are visible.3. Patient Preparation - Dilate the pupil of the eye.
- Place the patient in a supine position on the operating table.
- Implant insertion is a surgical procedure and therefore requires sterile controls (i.e. use of broad-spectrum microbicide solution on eye including lids and lashes and draping) be in place to minimize the risk of ocular infection.
- Perform the procedure under local anesthesia using either peribulbar, retrobulbar, or sub-Tenon's technique.
- Place lid speculum.
Infusion Line Placement Procedure
1. Place infusion line - Place an infusion cannula in the inferotemporal quadrant via an angled entry wound.
- – Alternate placement is acceptable based on patient anatomy per physician discretion (superotemporal placement should be avoided).
- – Alternatively, the line may be placed after the peritomy but prior to the scleral dissection.
- Attach the infusion line. Keep the infusion line off (Figure 9).
Conjunctival Dissection Procedure
1. Identify the site of insertion 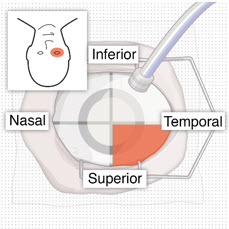
Figure 10
Superotemporal quadrant
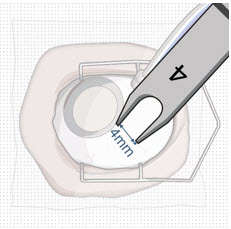
Figure 11
4 mm posterior to the limbus2. Create conjunctival peritomy  Caution
Caution
The peritomy size should be at least 6 mm by 6 mm centered around the selected implant location to ensure the proper clearance of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule from the implant flange once the implant is inserted into the eye.- Measure with adjustable caliper and create at least a 6mm by 6mm peritomy of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule around the selected implant location, using wet field cautery (eraser tip) to achieve hemostasis of the underlying episcleral tissues (Figure 12).
- – A peritomy size of at least 6 mm by 6 mm centered around the selected implant location provides proper clearance of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule for the implant flange (long axis of implant flange = 4.6 mm).
- – A peritomy size of at least 6 mm by 6 mm facilitates implant placement away from radial relaxing incision.
- – Appropriate peritomy size is vital for ease of subsequent surgery.
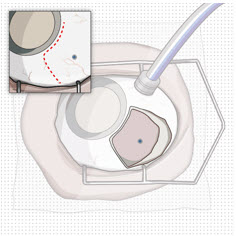
Figure 12
Conjunctival peritomy with blue dot representing selected implant location- – Only one radial incision is recommended, to avoid excessive conjunctival suturing and longer healing process.
- – Careful incision creation is key to maintain integrity of conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule. Careful and generous undermining is key to minimize mechanical tension and adequate coverage of the implant while closing the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule.
- Maintain hemostasis around the scleral incision throughout the surgery to facilitate the identification and management of incisional bleeding, to avoid post-operative vitreous hemorrhage.
Syringe Preparation and Initial Implant Fill
Using aseptic technique, the implant will be filled with 0.02 mL of ranibizumab prior to insertion of the implant into the patient's eye.
1. Transfer dose from vial to syringe
 Caution
Caution
Use the filter needle to withdraw ranibizumab from the vial.
Do not use the initial fill needle for this step.- Prepare ranibizumab vial by removing the flip-off cap and disinfecting the rubber vial septum with alcohol.
- Attach a filter needle to the syringe by screwing it tightly onto the Luer lock (Figure 13).
- Carefully remove the needle cap by pulling it straight off.
- Using aseptic technique, withdraw all of the contents of the ranibizumab vial through the filter needle into the syringe.
2. Remove air from syringe - With the filter needle attached, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up.
- If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the bubbles rise to the top (Figure 14).
- Slowly push the plunger rod just until all air is expelled from the syringe and needle.
- – It is important to preserve as much drug as possible in order to completely fill the implant.
- Remove and properly dispose of the filter needle after air is removed from syringe.
3. Attach initial fill needle - Attach the initial fill needle firmly onto the syringe by screwing it tightly onto the Luer lock (Figure 15).
- Carefully remove the needle cap by pulling straight off.
- Do not wipe the needle at any time.
 Caution
Caution
Ensure that the initial fill needle is attached to the syringe.
Do not use the filter needle to fill the implant.
Figure 15
Initial fill needle attached to syringe and cap removal4. Remove any remaining air from syringe - With the initial fill needle attached, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up.
- If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the bubbles rise to the top (Figure 16).
- Slowly push the plunger rod just until all air is expelled from the syringe and needle, and a drop of drug solution is seen at the needle tip (Figure 17).
- – It is important to preserve as much drug as possible in order to completely fill the implant.
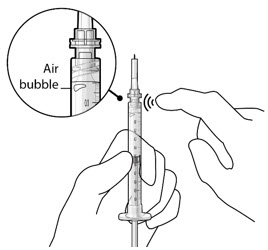
Figure 16
Gently tap the syringe to dislodge bubbles
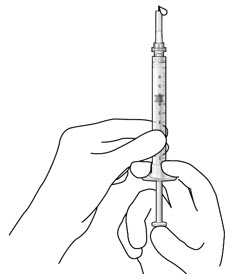
Figure 17
No air bubbles and a drop of drug at the needle tip5. Inspect the syringe for air bubbles - Inspect the syringe and the needle hub to ensure that no air bubbles are present (Figure 18).
- If air bubbles are present, continue to remove air from the syringe and reinspect.
 Caution
Caution
Use the syringe within 15 minutes of removing all air to avoid ranibizumab drying in the needle and impeding fluid flow.
Do not use the initial fill needle if the needle is clogged.6. Load syringe into the carrier
 Caution
Caution
Do not hold or push on the plunger rod of the syringe while inserting the needle into the implant septum.- Retrieve insertion tool carrier with pre-positioned implant from the inner tray.
- Align the syringe Luer lock above the Luer lock slot in the carrier to protect the needle from being damaged.
- Lower the syringe into the carrier (Figure 19).
- Push the syringe forward until it stops, taking care to avoid touching the plunger rod (Figure 20).
- With the syringe loaded, (Figure 21) the initial fill needle should now be penetrating the implant septum.
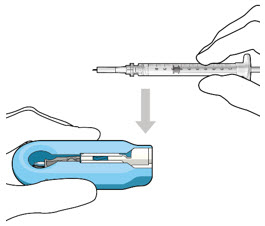
Figure 19
Align and lower the syringe into the carrier
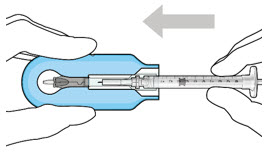
Figure 20
Push the syringe into the carrier
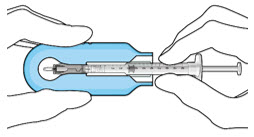
Figure 21
Syringe with initial fill needle inserted through the implant septum7. Fill implant with ranibizumab under microscope - Under the microscope, slowly administer ranibizumab into the implant by slightly tilting the carrier upwards (Figure 22).
- The implant should be filled over approximately 5 to 10 seconds, to help avoid air entrapment in the implant reservoir.
- Continue filling the implant until the implant is completely full of drug solution and all air has been expelled as evidenced by a dome of drug solution formed at the tip of the implant on the release control element (Figure 23).
 Caution
Caution
When filling the implant, fluid should only exit the implant from the release control element. If fluid is leaking from the implant at a different location, such as the side of the implant, do not use the implant.
If fluid is leaking from the septum at the needle insertion site, the needle may not be fully penetrating the implant septum. Fully push the syringe forward before continuing to fill the implant.
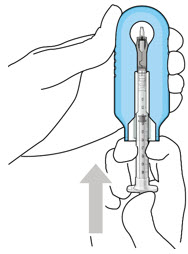
Figure 22
Administer ranibizumab into the implant
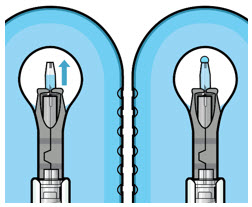
Figure 23
Dome of drug solution forms at tip of implant as viewed under magnification8. Inspect the filled implant under the microscope -
Inspect the implant under the microscope to ensure that the implant is completely full of drug solution (Figure 24).
 Warning
Warning
Minimize air bubbles within the implant reservoir as they may cause slower drug release. If an air bubble is present, it must be no larger than 1/3 of the widest diameter of the implant.
If excess air is observed, do not use the implant.
 Caution
Caution
No more than 30 minutes should pass between the initial fill of the implant and the insertion into the patient's eye to ensure that the release control element remains saturated with ranibizumab. If ranibizumab dries in the release control element, the implant may not release the drug properly into the vitreous after insertion.
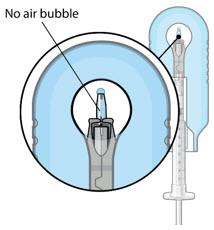
Figure 24
Proper appearance of implant after initial filling with ranibizumab9. Remove the syringe and guide sleeve from the carrier - Remove the syringe and guide sleeve from the carrier by pulling back on the syringe (Figure 25). The syringe will be locked into the guide sleeve.
- Properly dispose of the used syringe together with the needle and guide sleeve in a sharps disposal container or in accordance with local requirements.
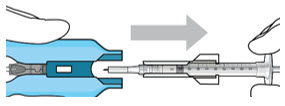
Figure 25
Remove the syringe and guide sleeve from the insertion tool carrier10. Slide the insertion tool handle into the carrier - Slide the insertion tool handle into the guide channel of the carrier, ensuring that both components are facing upwards (Figure 26).
- Push the handle forward as far as it will go into the gripper tips (Figure 27).
 Caution
Caution
Do not withdraw the handle and implant until the eye is ready for insertion. Contact between the implant and any surface or object – even within the sterile field – may result in the introduction of a foreign body into the vitreous.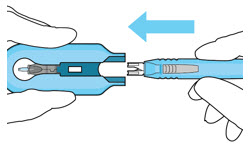
Figure 26
Insert the handle into the insertion tool carrier
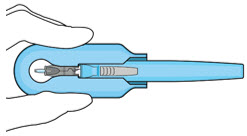
Figure 27
Fully inserted handleImplant Insertion
1. Verify hemostasis of the scleral surface
- Clear any excess blood from the scleral surface.
- Perform careful scleral wet field cauterization as needed, particularly in the area of the sclero-pars plana incision.
2. Mark incision site - Keep sclera dry and create discrete ink marks using a light touch.
- Mark a location 4 mm from the limbus using an inked fixed width caliper (or equivalent) at the selected implant location (Figure 28).
- Mark a 3.5 mm length for scleral dissection parallel to and 4 mm posterior to the limbus using an inked fixed width caliper (or equivalent) (Figure 29).
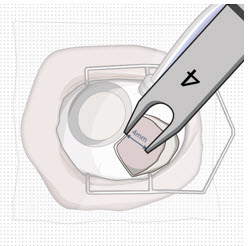
Figure 28
4 mm posterior to the limbus
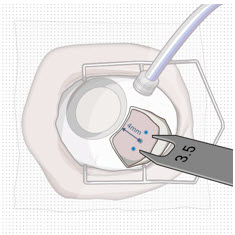
Figure 29
Fixed width caliper measurement3. Perform scleral incision - Using an MVR blade, create a full thickness dissection of the sclera until the pars plana is fully visible (Figure 30).
- – Ensure scleral dissection location is away from the radial conjunctival incision.
 Caution
Caution
The final target length for the scleral incision is 3.5 mm. Keep in mind that laser may further result in enlargement of incision and limit the secureness of the fit of the implant.- Confirm the length of the incision by using the largest width of the 3.5 mm incision gauge (Figure 31).
- If the incision is over 3.5 mm, as indicated by a loose fit/side to side motion of 3.5 mm gauge, place a suture through the wound opposite the relaxing incision to reduce the incision down to 3.5 mm, and bury the knot. After suturing, confirm the incision length is 3.5 mm (Figure 31).
- If there are any areas of visible bleeding from the wound, carefully perform diathermy.
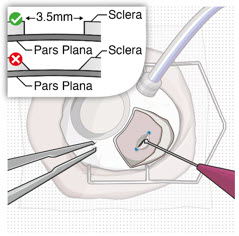
Figure 30
Stabilize the globe and perform full thickness scleral incision
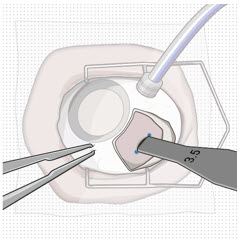
Figure 31
Confirm correct length of scleral incision4. Perform laser treatment of the pars plana
 Caution
Caution
Laser treatment may result in enlargement of the incision. Laser treatment should not be used to intentionally enlarge the length of scleral incision.
 Caution
Caution
Carefully apply the laser only to the choroidal tissue in the exposed pars plana. Minimize any laser application to the surrounding scleral tissue to avoid damaging tissue integrity.- Confirm pars plana is dry before laser treatment and keep dry throughout the procedure (with surgical sponge).
- – Consider placing a surgical sponge as a wick at one end of the incision.
- Using a 532 nm laser endoprobe, apply contiguous, overlapping laser spots starting at 300 mW 1000 ms along the full length of the exposed pars plana (Figure 32). Repeat until complete ablation is achieved.
- – Maintain focus of laser on exposed pars plana.
- – Keep foot pedal depressed to achieve full 1000 ms spots (expect smoke).
- – Ensure the pars plana at the corners of scleral incision is adequately treated.
- – Do not use painting strokes with the laser.
- – Do not contact the pars plana directly with laser probe.
- Repeat application of laser along the full length of the pars plana until full or partial split of the pars plana, or other visual endpoints are achieved, as indicated by:
- – Gray color change.
- – Uniform perforated appearance.
- – Domes of vitreous fluid percolating through pars plana.
- If visual endpoint is not achieved after several passes with the laser, increase laser power in 100 mW increments.
- Once laser ablation of pars plana is completed, remeasure the entire length (including corners) of the scleral incision with 3.5 mm gauge to confirm the final post-laser incision is 3.5 mm. If final incision is greater than 3.5 mm, as indicated by a loose fit/side to side motion of 3.5 mm gauge, place a suture through the wound opposite the relaxing incision to reduce incision down to 3.5 mm.
 Caution
Caution
A final post-laser incision length of 3.5 mm provides a secure fit for the implant.
Do not enlarge the scleral dissection beyond 3.5 mm as a final incision length greater than 3.5 mm may result in an improperly seated implant and will require additional suturing.
5. Perform pars plana incision - Pass a 3.2 mm slit knife perpendicularly through the center of the scleral incision to open the underlying pars plana (Figure 33 and Figure 34).
- Ensure widest part of the blade passes through the incision.
- Ensure adequate hemostasis.
- Carefully check for any active bleeding from the pars plana incision; if active bleeding is present, address it with fine tip diathermy within the incision before proceeding.
 Caution
Caution
Do not enlarge the pars plana incision with lateral movements. The incision width of 3.2 mm ensures that the pars plana incision is within the laser-treated area of the pars plana and reduces the risk of vitreous hemorrhage.- Aim to the center of the globe.
- Insert blade straight in and straight out.
- Avoid sideways motion.
- Avoid enlargement of the incision.
- Avoid the edges of the wound.
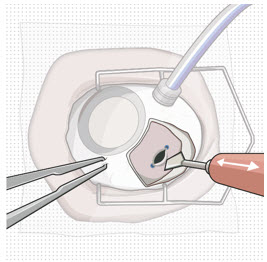
Figure 33
Pars plana incision
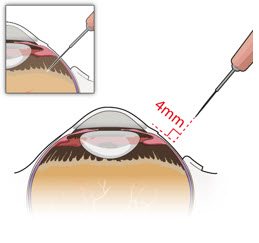
Figure 34
Perpendicular entry of slit knife6. Withdraw the insertion tool handle with filled implant - Withdraw the insertion tool handle, which is now attached to the gripper tips and implant, by slowly pulling the carrier and handle apart (Figure 35).
- Take care not to touch implant to any surface other than incision.
 Caution
Caution
When holding the insertion tool handle, take care not to touch the implant to any surface other than the sclero-pars plana incision during the insertion procedure.
Do not use the implant if it is inadvertently released or is contaminated through contact with any surface other than the exposed sclera, including objects within the surgical field.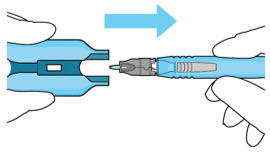
Figure 35
Withdraw the insertion tool handle with filled implant7. Stabilize the globe - Prior to inserting the implant, stabilize the globe with forceps to prevent unwanted eye movement (Figure 36).
- The forceps should remain in place until the insertion procedure is complete.
8. Orient the implant - Orient the long axis of the implant flange with the length of the sclero-pars plana incision (Figure 37).
- Aligning the implant in this direction enables the intended seating of the implant within the sclero-pars plana incision.
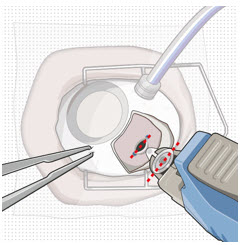
Figure 37
The long axis of the implant aligned with the length of the sclero-pars plana incision9. Insert the implant
 Warning
Warning
Perpendicular entry of the implant is important to avoid contact between the implant and intraocular structures such as the lens, as contact between the implant and the intraocular structures may cause adverse events such as traumatic cataract.
 Warning
Warning
Avoid excessive force on the globe by first ensuring that the tip of the implant has passed through the sclero-pars plana incision before slowly pushing the implant into place.- Slowly insert the implant through the sclero-pars plana incision perpendicular to the globe (Figure 38 and Figure 39).
- A slight initial twisting motion may be helpful to ease the implant through the sclero-pars plana incision (Figure 40).
- Continue pressing the implant slowly through the incision until the insertion tool handle gripper tips abut the sclera.
- Per the surgeon's discretion, the infusion line may be turned on while inserting the implant.
- If excess vitreous prolapses from the incision, use the vitrector to remove it and then place the implant.
- If a small amount of vitreous prolapse is present, place the implant first and then use the vitrector to remove the excess. Only use the vitrector to remove vitreous prolapse (do not use surgical sponge and/or scissors).
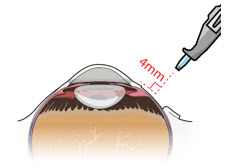
Figure 38
Perpendicular entry of the implant
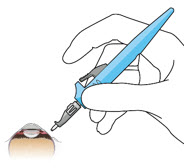
Figure 39
Implant insertion
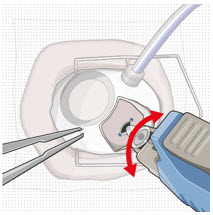
Figure 40
Implant insertion with a slight initial twisting motion10. Release the implant - Ensure that the long axis of the implant is properly aligned with the sclero-pars plana incision before releasing the implant from the insertion tool.
- The forceps that are stabilizing the globe should remain in place.
- Release the implant by depressing the release button completely (Figure 41 and Figure 42).
 Caution
Caution
If the implant flange is not parallel to the limbus after releasing, it needs to be repositioned solely using the gripper tips of the insertion tool handle. Reposition gently to avoid damage to the implant and to avoid contact between the implant and intraocular structures such as the lens. Avoid excessive manipulation of the implant flange.
Do not use any other rigid instruments to reposition.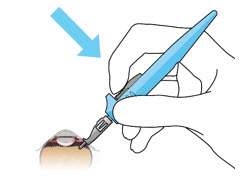
Figure 41
Release implant with the release button
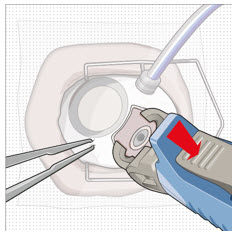
Figure 42
Implant release11. Seat the implant
 Caution
Caution
Use the insertion tool gripper tips to seat the implant.
Do not use any other rigid instruments as they may damage the implant.
 Caution
Caution
Ensure that the long axis of the implant is aligned with the length of the sclero-pars plana incision and that the implant is seated flush against the sclera.- Remove finger from the release button to close the insertion tool gripper tips.
- Gently press the closed gripper tips against the center of the implant to seat the implant flush against the sclera (Figure 43).
- Clean any residual vitreous around the implant flange using a vitrector.
12. Suture Tenon's capsule and conjunctiva
- Close both Tenon's capsule and conjunctiva, with Vicryl or gut sutures, ensuring complete coverage of the implant flange.
- Use scleral anchoring at the apex of the peritomy.
- Ensure suture placement away from the implant (Figure 44).
 Caution
Caution
Do not place a suture directly over the implant, otherwise adverse events including incomplete healing, infection, and discomfort can occur.
 Caution
Caution
Complete closure of both Tenon's capsule and conjunctiva across the surgical site is critical to minimize potential complications such as conjunctival retraction over the implant.13. Remove infusion cannula
- If the infusion was previously turned on, then set the infusion pressure to 20 mmHg before removing the infusion cannula.
- Check for persistent leaks at the infusion cannula site and suture if necessary.
14. Check Intraocular Pressure (IOP)
- Using digital palpation, check the IOP. If necessary, inject additional fluid to restore IOP.
15. Check implant placement
- Perform indirect ophthalmoscopy to confirm implant position and to examine for the presence of any complications.
Disposal and Post-insertion Procedures
1. Dispose of used Susvimo components and tools
- Do not recap the needle or detach it from the syringe. Dispose of the used Susvimo components and tools in a sharps disposal container or in accordance with local requirements.
2. Perform post-insertion procedures
- Post-insertion procedures are consistent with standard post-surgical procedures.
3. Post-insertion patient instructions
Provide the patient with the following post-operative instructions:
- Positioning:
- – Keep head above shoulder level for the rest of the day.
- – Sleep with head elevated on 3 or more pillows if lying down during the day and night after implant insertion.
- Information on caring for the eye after the procedure, including but not limited to the following:
- – Do not remove the eye shield until they are instructed to do so by their physician. At bedtime, continue to wear the eye shield for at least 7 nights following implant insertion.
- – Administer all post-operative eye medications, as directed by their physician.
- – Do not push on the eye, rub the eye, or touch the region of the eye where the implant is located (underneath the eyelid in the upper and outer part of the eye) for 30 days following implant insertion. Avoid rubbing the eye or touching the area where the implant is located as much as possible at all other times but if necessary to do so, make sure hands are cleaned prior to touching the eye.
- – Do not participate in strenuous activities until 1 month after implant insertion or after discussion with their physician.
- Monitor for symptoms that may require immediate medical attention while the implant is in place.
- MR Conditional information:
- – The surgeon should inform the patient that the implant is MR Conditional (as noted on their Susvimo implant card) and if patient needs to undergo an MRI, they should let their doctor know they have Susvimo implanted in their eye.
- – After implant insertion, the surgeon should give the patient the implant card with the appropriate information filled in, and should advise the patient to keep the card in a safe place, e.g. his or her wallet, for future reference. The surgeon should advise the patient that this implant card contains important information related to the Susvimo implant and that the card should be shown to their current and future health care providers.
Explanation of symbols on product or package labeling
Table 6 Symbols on blister tray and carton Symbol Title 
Manufacturer 
Prescription only 
Do not re-use 
Do not use if package is damaged 
Consult Instructions for Use 
Sterilized by irradiation 
Sterilized using ethylene oxide 
Temperature limit 
Expiration date/Use by date 
Lot/Batch number 
MR Conditional Manufactured by:
Genentech, Inc.
A Member of the Roche Group
1 DNA Way
South San Francisco, CA 94080-4990
U.S. License No.: 1048SUSVIMO is a registered trademark of Genentech, Inc.
©2025 Genentech, Inc. All rights reserved.This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved: 9/2025 -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Susvimo™
(ranibizumab injection)
For Susvimo ocular implant use
Instructions for UseImplant Removal Procedure Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Susvimo procedures should be performed by an ophthalmologist experienced in vitreoretinal surgery.
Refer to the Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL prescribing information for a complete list of indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, and adverse events.
Contents
Introduction
3 Device Description 3 Components 4 Intended Use/ Indications for Use 4 Warnings 4 Precautions 5 How Supplied, Handling, and Storage Instructions for Use
6 Introduction and Materials 7 Preparatory Procedures 8 Implant Removal 16 Disposal and Post-removal Procedures 17 Explanation of symbols on product or package labeling Introduction
These instructions include only the implant removal procedure for the Susvimo implant. Refer to the Susvimo Instructions for Use for the initial fill and implant procedure and prescribing information for the refill-exchange procedure.
Device Description
Susvimo is an intraocular drug delivery system designed to be used specifically with Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL.
These Instructions for Use describe the required materials and steps necessary for removal of the Susvimo implant.
Components
Susvimo explant tool
Susvimo explant tool (Figure 2) is a pair of forceps with contoured tips, which are designed to grasp underneath the implant flange to securely engage the implant during removal.
Intended Use/ Indications for Use
Susvimo explant tool is approved for use with Susvimo ocular implant. Refer to the Susvimo (ranibizumab injection) prescribing information for a complete list of indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, and adverse events.
Warnings
- Do not use if the sterility has been compromised or the contents have been dropped, damaged or tampered with.
- Do not grasp the implant by the short axis of the implant flange. Remove the implant in a gentle manner. Perpendicular exit of the implant is important to avoid contact between the implant and intraocular structures such as the lens.
Precautions
- Read and follow all instructions, warnings, and cautions prior to use.
- Susvimo procedures should be performed by an ophthalmologist experienced in vitreoretinal surgery.
- Use Susvimo components and materials as specified in these instructions to perform the implant removal procedure.
How Supplied, Handling, and Storage
- Susvimo explant tool has been electron beam sterilized. Do not reprocess or resterilize.
- Susvimo explant tool is for single-use only. Do not reuse the Susvimo explant tool.
- Do not open sealed tray until time of use.
- Do not use if the package is damaged or broken as sterility may be compromised.
- Do not use past the expiration date printed on the label.
- Susvimo explant tool should be stored at a room temperature 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F).
Instructions for Use
Introduction and Materials
Removal of the Susvimo implant requires a surgical procedure that is performed in an operating room.
Materials List
Materials that are required and provided for the procedure are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Susvimo sterile components that are provided for implant removal Item Description Susvimo explant tool Materials required but not provided are listed in Table 2.
Table 2 Additional materials required but not provided for implant removal Item Description Surgical microscope Vitrectomy surgical control system Standard 25 G or 27 G vitrectomy set up Standard vitrectomy tray (including 0.12 straight toothed forceps and blunt wescott scissors) Cauterization equipment (including standard fine tip diathermy and eraser tip wet-field cautery) Ophthalmic broad-spectrum microbicide solution Surgical scalpel blade #15 Non-absorbable sutures for sclera (suggested Nylon) Gut or Vicryl sutures for conjunctival tissues (suggested 7-0 to 9-0: monofilament recommended) Indirect ophthalmoscope and lens Drapes Preparatory Procedures
1. Inspect and open sterile packaging
- Prior to use in the operating room, inspect the sterile packaging of the explant tool for damage.
- Check the expiration date printed on the label.
- Open sterile packaging and using aseptic technique, remove the explant tool from the tray.
- Inspect the explant tool and place onto sterile surface.
 Warning
Warning
Do not use if the sterility has been compromised or the contents have been dropped, damaged, or tampered with.
2. Patient Preparation
- Dilate the pupil of the eye.
- Place the patient in a supine position on the operating table.
- Implant removal is a surgical procedure and therefore requires sterile controls (i.e. use of ophthalmic broad-spectrum microbicide solution on eye including lids and lashes and draping) be in place to minimize the risk of ocular infection.
- Perform the procedure under local anesthesia using either peribulbar, retrobulbar, or sub-Tenon's technique.
- Place lid speculum.
Implant Removal
Perform the implant removal procedure under the microscope. Consider placing a traction suture for better visualization of the superotemporal quadrant throughout the entire implant removal procedure.
1. Place infusion line
- Place an infusion cannula in the inferotemporal quadrant via an angled entry wound.
- Attach the infusion line, however keep the infusion off.
2. Perform conjunctival peritomy
- Create at least a 6 mm by 6 mm peritomy of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule around the implant flange (Figure 3).
3. Remove fibrous capsule covering implant
- Remove any fibrous capsule or scar tissue that may have formed over the implant flange and septum (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
- – To expose the implant, use a scalpel to make an incision in the tissue around the entire circumference of the implant (Figure 4).
- – Use forceps to carefully dissect the implant flange and neck from the surrounding tissue so that the edges of the flange are completely exposed and the implant is free of any adherent tissue (Figure 5).
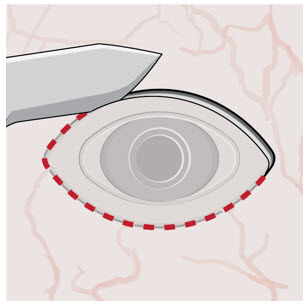
Figure 4
Incision to remove tissue that may be covering the implant flange and septum
Figure 5
Exposed implant4. Stabilize the globe and align the explant tool
- Stabilize the globe with forceps to prevent unwanted eye movement.
- With the explant tool oriented perpendicular to the globe, align the contoured tips with the long axis of the implant flange (Figure 6).
5. Grasp the implant
 Warning
Warning
Do not grasp the implant by the short axis of the implant flange. Remove the implant in a gentle manner. Perpendicular exit of the implant is important to avoid contact between the implant and intraocular structures such as the lens.
- Use the contoured tips of the explant tool to gently grasp underneath the long axis of the implant flange (Figure 7).
6. Remove the implant
- Once the implant is secured in the explant tool, in a gentle manner pull the implant from the eye in a perpendicular motion to avoid contact with adjacent intraocular structures.
- During removal, use forceps to stabilize the globe and provide counter traction to help release the surrounding tissue (Figure 8).
- During removal, continue to maintain perpendicular orientation of the implant relative to the globe (Figure 9).
- If needed per the surgeon's discretion, the infusion line on the vitrectomy surgical system can be turned on during implant removal.
- Control any scleral or conjunctival bleeding, using cauterization if needed, and clear any vitreous prolapse present within or around the scleral wound using a vitrectomy setup.
7. Suture the sclera
- Completely close the scleral incision with non-absorbable (suggested Nylon) sutures (Figure 11). More than one suture will be needed to close the wound. It is recommended to place equally spaced partial thickness interrupted sutures.
- Ensure that the knots are buried.
 Caution
Caution
Do not overtighten the scleral sutures, to minimize excessive tensions on the sclera or cornea.
8. Suture conjunctiva
- Close Tenon's capsule and conjunctiva to completely cover the scleral incision (Figure 12).
 Caution
Caution
Completely close Tenon's capsule and conjunctiva to minimize potential post-removal complications.
9. Remove infusion cannula
- If the infusion was previously turned on, then set the infusion pressure to 20 mmHg before removing the infusion cannula.
- Place suture at infusion cannula site as needed.
10. Check Intraocular Pressure (IOP) using digital palpation
11. Perform indirect ophthalmoscopy to examine for the presence of any complications
Disposal and Post-removal Procedures
1. Dispose of the used components
- Dispose of the used explant tool together with the implant in a biohazard waste container or in accordance with local requirements.
2. Perform post-removal procedures
- Post-removal procedures are consistent with standard post-surgical procedures.
3. Post-removal patient instructions
- Provide the patient with the following post-operative instructions:
- –
Positioning:
- Keep head above shoulder level for the rest of the day.
- Sleep with head elevated on 3 or more pillows if lying down during the day and night after implant removal.
- –
Information on caring for the eye after the procedure, including but not limited to:
- Monitor for symptoms that may require immediate attention.
- Wear an eye shield at bedtime for at least 7 nights.
- Do not participate in strenuous activities until 14 days following the implant removal procedure.
- Administer all post-operative anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drops, as directed by their physician.
- –
Positioning:
Explanation of symbols on product or package labeling
Table 3 Symbols on blister tray and carton Symbol Title 
Manufacturer 
Prescription only 
Do not re-use 
Do not use if package is damaged 
Consult Instructions for Use 
Sterilized by irradiation 
Temperature limit 
Expiration date/ Use by date 
Lot/Batch number Manufactured by:
Genentech, Inc.
A Member of the Roche Group
1 DNA Way
South San Francisco, CA 94080-4990U.S. License No.: 1048
SUSVIMO is a trademark of Genentech, Inc.
©2021 Genentech, Inc.
All rights reserved.This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved: 10/2021
Representative sample of labeling (see the HOW SUPPLIED section for complete listing):
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Kit Carton
NDC: 50242-078-55
Susvimo™
(ranibizumab injection)See instructions for use
included with the
Susvimo ocular implant
with insertion tool assembly100 mg/mL
Vial contains 10 mg/0.1 mL ranibizumab
For use with Susvimo ocular implant
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
Carton contents:
- One Susvimo single-dose vial
- One Susvimo initial fill needle
Rx only
Genentech
10233586
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg/mL Vial Carton
NDC: 50242-078-12
Susvimo®
(ranibizumab injection)100 mg/mL
Vial contains
10 mg/0.1 mL ranibizumabFor use with Susvimo
ocular implantDispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.Rx only
1 Single-dose vial
Genentech
11032207
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SUSVIMO
ranibizumab injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50242-078 Route of Administration INTRAVITREAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength RANIBIZUMAB (UNII: ZL1R02VT79) (RANIBIZUMAB - UNII:ZL1R02VT79) RANIBIZUMAB 100 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50242-078-12 1 in 1 CARTON 10/22/2021 1 1 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package 2 NDC: 50242-078-55 1 in 1 CARTON 10/22/2021 09/30/2027 2 1 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761197 10/22/2021 Labeler - Genentech, Inc. (080129000) Registrant - Genentech, Inc. (080129000) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Roche Singapore Technical Operations Pte. Ltd 937189173 ANALYSIS(50242-078) , API MANUFACTURE(50242-078) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Genentech, Inc. (Hillsboro) 833220176 PACK(50242-078) , LABEL(50242-078) , ANALYSIS(50242-078) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Roche Diagnostics GmbH 315028860 ANALYSIS(50242-078)
Trademark Results [Susvimo]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 SUSVIMO 90059713 not registered Live/Pending |
Genentech, Inc. 2020-07-17 |
 SUSVIMO 88460882 not registered Live/Pending |
Genentech, Inc. 2019-06-05 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.