Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder
Ceftiflex by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Ceftiflex by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Cephazone Pharma LLC, Orchid Pharma Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
CEFTIFLEX- ceftiofur sodium injection, powder, for solution
Cephazone Pharma LLC
----------
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder
For intramuscular and subcutaneous injection in cattle only. For intramuscular injection in swine, sheep, goats, and horses. For subcutaneous injection only in dogs, day-old chickens and day-old turkey poults. This product may be used in lactating dairy cattle, sheep, and goats.
CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-420
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder contains the sodium salt of ceftiofur which is a broad spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic active against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria including β-lactamase-producing strains. Like other cephalosporins, ceftiofur is bactericidal in vitro, resulting from inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
Each mL of the reconstituted drug contains ceftiofur sodium equivalent to 50 mg ceftiofur. The pH was adjusted with sodium hydroxide and monobasic potassium phosphate.
Chemical Structure of Ceftiofur Sodium:
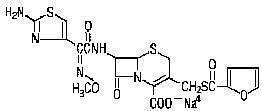
Chemical Name of Ceftiofur Sodium:
5-Thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-carboxylic acid, 7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazoly)(methoxyimino)-acetyl]amino]-3-[[(2-furanylcarbonyl)thio] methyl]-8-oxo-, monosodium salt, [6R-[6α,7β(Z)]]-
RECONSTITUTION OF THE STERILE POWDER:
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder should be reconstituted as follows:
1 gram vial- Reconstitute with 20 mL Sterile Water for Injection. Each mL of the resulting solution contains ceftiofur sodium equivalent to 50 mg ceftiofur.
4 gram vial- Reconstitute with 80 mL Sterile Water for Injection. Each mL of the resulting solution contains ceftiofur sodium equivalent to 50 mg ceftiofur.
Shake thoroughly prior to use.
Cattle
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is indicated for treatment of bovine respiratory disease (shipping fever, pneumonia) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida and Histophilus somni. Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is also indicated for treatment of acute bovine interdigital necrobacillosis (foot rot, pododermatitis) associated with Fusobacterium necrophorum and Bacteroides melaninogenicus.
Swine
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is indicated for treatment/control of swine bacterial respiratory disease (swine bacterial pneumonia) associated with Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Salmonella choleraesuis and Streptococcus suis.
Sheep
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is indicated for treatment of sheep respiratory disease (sheep pneumonia) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida.
Goat
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is indicated for treatment of caprine respiratory disease (goat pneumonia) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida.
Horses
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is indicated for treatment of respiratory infections in horses associated with Streptococcus zooepidemicus.
Dogs
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is indicated for the treatment of canine urinary tract infections associated with Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis.
Day-Old Chicks
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is indicated for the control of early mortality, associated with E. coli organisms susceptible to ceftiofur, in day-old chicks.
Day-Old Turkey Poults
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is indicated for the control of early mortality, associated with E. coli organisms susceptible to ceftiofur, in day-old turkey poults.
Cattle
Administer to cattle by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection at the dosage of 0.5 to 1.0 mg ceftiofur per pound (1.1 to 2.2 mg/kg) of body weight (1-2 mL reconstituted sterile solution per 100 lbs body weight). Treatment should be repeated at 24-hour intervals for a total of three consecutive days. Additional treatments may be given on days four and five for animals which do not show a satisfactory response (not recovered) after the initial three treatments. Selection of dosage (0.5 to 1.0 mg/lb) should be based on the practitioner's judgment of severity of disease (i.e., for respiratory disease, extent of elevated body temperature, depressed physical appearance, increased respiratory rate, coughing and /or loss of appetite; and for foot rot, extent of swelling, lesion and severity of lameness).
Swine
Administer to swine by intramuscular injection at the dosage of 1.36 to 2.27 mg ceftiofur per pound (3.0 to 5.0 mg/kg) of body weight (1 mL of reconstituted sterile solution per 22 to 37 lbs body weight). Treatment should be repeated at 24-hour intervals for a total of three consecutive days.
Sheep
Administer to sheep by intramuscular injection at the dosage of 0.5 to 1.0 mg ceftiofur per pound (1.1 to 2.2 mg/kg) of body weight (1-2 mL reconstituted sterile solution per 100 lbs body weight). Treatment should be repeated at 24-hour intervals for a total of three consecutive days. Additional treatments may be given on days four and five for animals which do not show a satisfactory response (not recovered) after the initial three treatments. Selection of dosage (0.5 to 1.0 mg/lb) should be based on the practitioner's judgment of severity of disease (i.e., extent of elevated body temperature, depressed physical appearance, increased respiratory rate, coughing and/or loss of appetite).
Goats
Administer to goats by intramuscular injection at the dosage of 0.5 to 1.0 mg ceftiofur per pound (1.1 to 2.2 mg/kg) of body weight (1-2 mL reconstituted sterile solution per 100 lbs body weight). Treatment should be repeated at 24-hour intervals for a total of three consecutive days. Additional treatments may be given on days four and five for animals which do not show a satisfactory response (not recovered) after the initial three treatments. Selection of dosage (0.5 to 1.0 mg/lb) should be based on the practitioner's judgment of severity of disease (i.e., extent of elevated body temperature, depressed physical appearance, increased respiratory rate, coughing and/or loss of appetite). Pharmacokinetic data indicate that elimination of the drug is more rapid in lactating does. For lactating does, the high end of the dose range is recommended.
Horses
Administer to horses by intramuscular injection at the dosage of 1.0 to 2.0 mg ceftiofur per pound (2.2 to 4.4 mg/kg) of body weight (2-4 mL reconstituted sterile solution per 100 lbs body weight). A maximum of 10 mL may be administered per injection site. Treatment should be repeated at 24-hour intervals, continued for 48 hours after clinical signs have disappeared and should not exceed 10 days.
Dogs
Administer to dogs by subcutaneous injection at the dosage of 1.0 mg ceftiofur per pound (2.2 mg/kg) of body weight (0.1 mL reconstituted sterile solution per 5 lbs body weight). Treatment should be repeated at 24-hour intervals for 5-14 days.
Reconstituted Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is to be administered to dogs by subcutaneous injection. No vial closure should be entered more than 20 times. Therefore, only the 1 gram vial is approved for use in dogs.
Day-Old Chicks
Administer by subcutaneous injection in the neck region of day-old chicks at the dosage of 0.08 to 0.20 mg ceftiofur/chick. One mL of the 50 mg/mL reconstituted solution will treat approximately 250 to 625 day-old chicks.
Reconstituted Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is to be administered by subcutaneous injection only. A sterile 26 gauge needle and syringe or properly cleaned automatic injection machine should be used.
Day-Old Turkey Poults
Administer by subcutaneous injection in the neck region of day-old turkey poults at the dosage of 0.17 to 0.5 mg ceftiofur/poult. One mL of the 50 mg/mL reconstituted solution will treat approximately 100 to 294 day-old turkey poults.
Reconstituted Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is to be administered by subcutaneous injection only.
As with all drugs, the use of Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is contraindicated in animals previously found to be hypersensitive to the drug.
NOT FOR HUMAN USE. KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Penicillins and cephalosporins can cause allergic reactions in sensitized individuals. Topical exposures to such antimicrobials, including ceftiofur, may elicit mild to severe allergic reactions in some individuals. Repeated or prolonged exposure may lead to sensitization. Avoid direct contact of the product with the skin, eyes, mouth, and clothing.
Persons with a known hypersensitivity to penicillin or cephalosporins should avoid exposure to this product.
In case of accidental eye exposure, flush with water for 15 minutes. In case of accidental skin exposure, wash with soap and water. Remove contaminated clothing. If allergic reaction occurs (e.g., skin rash, hives, difficult breathing), seek medical attention.
CONTACT INFORMATION:
To report suspected adverse drug events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), contact Cephazone at (800) 587-4306. For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae

PRECAUTIONS:
The effects of ceftiofur on the reproductive performance, pregnancy, and lactation of cattle, swine, sheep, and goats have not been determined.
Cattle
Following subcutaneous administration of ceftiofur sodium in the neck, small areas of discoloration at the site may persist beyond five days, potentially resulting in trim loss of edible tissues at slaughter.
As with any parenteral injection, localized post-injection bacterial infections may result in abscess formation. Attention to hygienic procedures can minimize their occurrence.
Swine
The safety of ceftiofur has not been determined for swine intended for breeding.
Horses
The safety of ceftiofur has not been determined for horses intended for breeding. The administration of antimicrobials to horses under conditions of stress may be associated with acute diarrhea that could be fatal. If acute diarrhea is observed, discontinue use of this antimicrobial and initiate appropriate therapy.
Dogs
The safety of ceftiofur has not been determined for dogs intended for breeding, or pregnant dogs.
The use of ceftiofur may result in some sign of immediate and transient local pain to the animal.
CLINCAL MICROBIOLOGY:
Summaries of MIC data are presented in Tables 1 and 2. Testing followed Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) Guidelines.
| Animal | Organism | Number Tested | Date Tested | MIC90(µg/mL)* | MIC Range (µg/mL) |
|
|
|||||
| Bovine | Mannheimia haemolytica | 461 | 1988-1992 | 0.06 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.13 |
| Mannheimia haemolytica | 42 | 1993 | 0.015 | ≤ 0.003 - 0.03 | |
| Pasteurella multocida | 318 | 1988-1992 | 0.06 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.25 | |
| Pasteurella multocida | 48 | 1993 | ≤ 0.003 | ≤ 0.003 - 0.015 | |
| Histophilus somni | 109 | 1088-1992 | 0.06 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.13 | |
| Histophilus somni | 59 | 1993 | ≤ 0.0019 | No range | |
| Fusobacterium necrophorum | 17 | 1994 | ≤ 0.06 | No range | |
| Swine | Actinobacillus pleuropn. | 83 | 1993 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.06 |
| Pasteurella multocida | 74 | 1993 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.06 | |
| Streptococcus suis | 94 | 1993 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.03 – 1.0 | |
| Salmonella choleraesuis | 50 | 1993 | 1.0 | 1.0-2.0 | |
| β-hemolyticStreptococcus spp | 24 | 1993 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.06 | |
| Actinobacillus suis | 77 | 1998 | 0.0078 | 0.0019-0.0078 | |
| Haemophilus parasuis | 76 | 1998 | 0.06 | 0.0039-0.25 | |
| Sheep | Mannheimia haemolytica | 39 | 1992 | 0.13 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.13 |
| Pasteurella multocida | 23 | 1992 | ≤ 0.03 | No range | |
| Canine | Escherichia coli | 44 | 1992 | 4.0 | 0.06-64.0 |
| Escherichia coli | 18 | 1990 | 0.25 | 0.13-0.5 | |
| Proteus mirabilis | 17 | 1990 | ≤ 0.06 | ≤ 0.06- 0.5 | |
| Proteus mirabilis | 23 | 1992 | 1.0 | ≤ 0.06- 4.0 | |
| Turkey | Escherichia coli | 1204 | 1995 | 1.0 | 0.13->32.0 |
| Animal | Organism | Number Tested | Date Tested | MIC90(µg/mL)** | MIC Range (µg/mL) |
|
*The following in vitro data are available but their clinical significance is unknown. |
|||||
|
** Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for 90% of the isolates. |
|||||
|
*** MIC50 is 32 µg/mL |
|||||
| Bovine | Mannheimia haemolytica | 110 | 1997-1998 | 0.06 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.25 |
| Mannheimia haemolytica | 139 | 1998-1999 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.5 | |
| Mannheimia haemolytica | 209 | 1999-2000 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.12 | |
| Mannheimia haemolytica | 189 | 2000-2001 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.12 | |
| Pasteurella multocida | 107 | 1997-1998 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.25 | |
| Pasteurella multocida | 181 | 1998-1999 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.5 | |
| Pasteurella multocida | 208 | 1999-2000 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.12 | |
| Pasteurella multocida | 259 | 2000-2001 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.12 | |
| Histophilus somni | 48 | 1997-1998 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03-0.25 | |
| Histophilus somni | 87 | 1998-1999 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.125 | |
| Histophilus somni | 77 | 1999-2000 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.06 | |
| Histophilus somni | 129 | 2000-2001 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.12 | |
| Bacteroides fragilis group | 29 | 1994 | 16.0 | ≤ 0.06 ->16.0 | |
| Bacteroides spp. non-fragilis group | 12 | 1994 | 16.0 | 0.13->16.0 | |
| Peptostreptocuccus anaerobius | 12 | 1994 | 2.0 | 0.13-2.0 | |
| Swine | Actinobacillus pleuropn. | 97 | 1997-1998 | ≤ 0.03 | No range |
| Actinobacillus pleuropn. | 111 | 1998-1999 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 - 0.25 | |
| Actinobacillus pleuropn. | 126 | 1999-2000 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03-0.06 | |
| Actinobacillus pleuropn. | 89 | 2000 - 2001 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.06 | |
| Pasteurella multocida | 114 | 1997-1998 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -1.0 | |
| Pasteurella multocida | 147 | 1998-1999 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.5 | |
| Pasteurella multocida | 173 | 1999-2000 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.06 | |
| Pasteurella multocida | 186 | 2000-2001 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.12 | |
| Streptococcus suis | 106 | 1997-1998 | 0.50 | ≤ 0.03 -4.0 | |
| Streptococcus suis | 142 | 1998-1999 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.03 -1.0 | |
| Streptococcus suis | 146 | 1999-2000 | 0.06 | ≤ 0.03 -4.0 | |
| Streptococcus suis | 167 | 2000-2001 | 0.06 | ≤ 0.03 -4.0 | |
| Salmonella choleraesuis | 96 | 1999-2000 | 1.0 | 0.03->4.0 | |
| Salmonella choleraesuis | 101 | 2000-2001 | 1.0 | 0.5-2.0 | |
| Equine | Streptococcus equi subsp. equi. | 12 | 1994 | ≤ 0.0019 | No range |
| Streptococcus equi subsp. equi. | 29 | 2002 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.5 | |
| Streptococcus zooepidemicus | 48 | 1994 | ≤ 0.0019 | No range | |
| Streptococcus zooepidemicus | 59 | 2002 | ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.03 -0.25 | |
| Rhodococcus equi | 66 | 1998 | 4.0 | ≤ 0.03 -16.0 | |
| Rhodococcus equi | 42 | 2002 | 8.0 | ≤ 0.03 ->32.0 | |
| Bacteroides fragilis group | 32 | 1995 | >16.0 | ≤ 0.03 ->16.0 | |
| Bacteroides spp. nonfragilis group | 12 | 1995 | 4.0 | 0.25 - 4.0 | |
| Fusobacterium necrophorum | 16 | 1995 | ≤ 0.06 | No range | |
| Canine | Escherichia coli | 26 | 2000 | 32.00 | 0.25->32 |
| Proteus mirabilis | 14 | 2000 | 0.25 | 0.06-0.25 | |
| Turkey | Escherichia coli | 17 | 1998-1999 | 1.0 | 0.25-1.0 |
| Escherichia coli | 25 | 1999-2000 | 0.50 | 0.25-1.0 | |
| Escherichia coli | 20 | 2000-20001 | 2.0 | 0.12-16.0 | |
| Citrobacter spp. | 37 | 1995 | 32.0 | 0.5->32.0 | |
| Enterobacter spp. | 51 | 1995 | >32.0 | 0.13->32.0 | |
| Klebsiella spp. | 100 | 1995 | 1.0 | 0.13 – 2.0 | |
| Proteus spp. | 19 | 1995 | 1.0 | 0.06 – 32.0 | |
| Pseudomonas spp.*** | 31 | 1995 | >32.0 | 0.06 - >32.0 | |
| Salmonella spp. | 24 | 1995 | 1.0 | 0.5 – 1.0 | |
| Staphylococcus spp.(coagulase negative) | 17 | 1995 | 2.0 | 1.0 – 2.0 | |
| Staphylococcus spp.(coagulase positive) | 26 | 1995 | 8.0 | 0.13 - >32.0 | |
| Chicken | Escherichia coli | 62 | 1997-1998 | 0.50 | 0.25 -2.0 |
| Escherichia coli | 53 | 1998-1999 | 4.0 | 0.25 ->4.0 | |
| Escherichia coli | 67 | 1999-2000 | 0.50 | 0.12 – 16.0 | |
| Escherichia coli | 90 | 2000-20001 | 1.0 | ≤ 0.03 -8.0 | |
Based on the pharmacokinetic studies of ceftiofur in swine and cattle after a single intramuscular injection of 1.36 to 2.27 mg ceftiofur equivalents/lb (3.0 to 5.0 mg/kg) BW (swine) or 0.5 to 1.0 mg ceftiofur equivalents/ lb (1.1 to 2.2 mg/kg) BW (cattle) and the MIC and disk (30 ug) diffusion data, the following breakpoints are recommended by CLSI.
Zone Diameter (mm) MIC (µg/mL) Interpretation
≥ 21 ≤2.0 (S) Susceptible
18-20 4.0 (I) Intermediate
≤ 17 ≥ 8.0 (R) Resistant
A report of "Susceptible" indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited by generally achievable blood levels. A report of "Intermediate" is a technical buffer zone and isolates falling into this category should be retested. Alternatively the organism may be successfully treated if the infection is in a body site where drug is physiologically concentrated. A report of "Resistant" indicates that the achievable drug concentrations are unlikely to be inhibitory and other therapy should be selected.
Based on the pharmacokinetic studies of ceftiofur in horses after a single intramuscular injection of 1 mg ceftiofur equivalents/lb (2.2 mg/kg) BW, clinical effectiveness data and MIC data, the following breakpoint is recommended by CLSI.
Zone Diameter (mm) MIC (µg/mL) Interpretation
≥ 22 ≤ 0.25 (S) Susceptible
The susceptible only category is used for populations of organisms (usually one species) for which regression analysis (disk vs. MIC) cannot be performed. These breakpoints will permit detection of strains with decreased susceptibility as compared to the original population.
Standardized procedures require the use of laboratory control organisms for both standardized diffusion techniques and standardized dilution techniques. The 30 µg ceftiofur sodium disk should give the following zone diameters and the ceftiofur sodium standard reference powder (or disk) should provide the following MIC values for the reference strain. Ceftiofur sodium disks or powder reference standard is appropriate for both ceftiofur salts.
| Organism Name (ATCC Number) | Zone Diameter* (mm) | MIC Range (µg/mL) |
|
*All testing performed using a 30 µg disk. |
||
|
** Quality control ranges are applicable only to tests performed by disk diffusion test using a chocolate Mueller-Hinton agar, incubated in 5-7% CO2 for 20-24 hours. |
||
|
*** MIC quality control ranges are applicable only to tests performed by broth microdilution procedures using |
||
|
Veterinary fastidious medium (VFM). |
||
| Escherichia coli (25922) | 26-31 | 0.25-1.0 |
| Staphylococcus aureus (29213) | - | 0.25-1.0 |
| Staphylococcus aureus (25923) | 27-31 | - |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (27853) | 14-18 | 16.0-64.0 |
| Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (27090) | 34-42** | 0.004-0.015*** |
| Histophilus somni (700025) | 36-46** | 0.0005-0.004*** |
HOW SUPPLIED:
Ceftiofur Sodium Sterile Powder is available in the following package sizes:
1 gram vial
4 gram vial
1. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Approved Standard - Second Edition. NCCLS document M31-A2. CLSI, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087-1898, 2002.
Manufactured by:
Cephzaone Pharma LLC
Pomona, CA 91767
Rev. July 2023
| CEFTIFLEX
ceftiofur sodium injection, powder, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Cephazone Pharma LLC (138954909) |
| Registrant - Cephazone Pharma LLC (138954909) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cephazone Pharma LLC | 138954909 | manufacture | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orchid Pharma Limited | 675829201 | api manufacture | |
Trademark Results [Ceftiflex]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 CEFTIFLEX 98711744 not registered Live/Pending |
Med-Pharmex, Inc. 2024-08-22 |
 CEFTIFLEX 87535740 5416452 Live/Registered |
Med-Pharmex, Inc. 2017-07-20 |
 CEFTIFLEX 78672853 3671000 Dead/Cancelled |
Med-Pharmex, Incorporated 2005-07-18 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

