KEBILIDI- eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq suspension
KEBILIDI by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
KEBILIDI by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by PTC Therapeutics, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KEBILIDI safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KEBILIDI.
KEBILIDI (eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq) suspension, for intraputaminal infusion
Initial U.S. Approval: 2024INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KEBILIDI is an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector-based gene therapy indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with aromatic L amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on change from baseline in gross motor milestone achievement at 48 weeks post-treatment. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory clinical trial. (1, 14)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For single-dose intraputaminal infusion only.
- Recommended dose: 1.8×1011 vector genomes (vg). (2.2)
- Brain imaging for stereotactic planning and intraoperative navigation should be done prior to the procedure. (2.4)
- Post stereotactic registration, mark the entry point on the skull. Surgical access through the skull bone and dura should be performed. (2.4)
- Administer a total dose of 1.8×1011 vg (0.32 mL total volume) delivered as four 0.08 mL (0.45×1011 vg) infusions (two sites per putamen-anterior and posterior) at a rate of 0.003 mL/minute (0.18 mL/hour) for a total of 27 minutes per site, administered in a single stereotactic surgery using a cannula that is FDA-authorized for intraparenchymal infusion. (2.2, 2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- KEBILIDI is a suspension for intraputaminal administration with a nominal concentration of 5.6×1011 vg/mL. (3)
- KEBILIDI is supplied in a single-dose vial that contains 2.8×1011 vg of eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq in an extractable volume of 0.5 mL of suspension. Each mL of suspension contains 5.6×1011 vg of eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq. (3, 16)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Patients who have not achieved skull maturity assessed by neuroimaging. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Procedural complications: Monitor patients for procedural complications for neurosurgery, including events of respiratory and cardiac arrest after administration of KEBILIDI. (5.1)
- Dyskinesia: Monitor patients for dyskinesia after treatment with KEBILIDI. The use of dopamine antagonists can be used to control dyskinesia symptoms. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥15%) were dyskinesia, pyrexia, hypotension, anemia, salivary hypersecretion, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, insomnia, hypomagnesemia, and procedural complications. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact PTC Therapeutics, Inc at toll-free phone 1 866 562 4620 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 11/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosing Information
2.2 Recommended Dose
2.3 Preparation
2.4 Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Procedural Complications
5.2 Dyskinesia
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KEBILIDI (eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq) is an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector-based gene therapy indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on the change from baseline in gross motor milestone achievement at 48 weeks post treatment [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory clinical trial.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For single-dose intraputaminal infusion only.
2.1 Important Dosing Information
- Confirm patient has AADC deficiency due to biallelic mutations in the DDC gene.
- Strictly observe aseptic technique during preparation and administration of KEBILIDI.
- KEBILIDI should be administered in a medical center which specializes in stereotactic neurosurgery.
- Administer KEBILIDI only using an FDA-authorized cannula for intraparenchymal infusion (i.e., ClearPoint SmartFlow Neuro Cannula Part Number NGS-NC-01-EE or NGS-NC-02-EE).
- Use of the syringe (i.e., connecting the syringe to the syringe pump and priming of the cannula) should begin within 6 hours of starting product thaw
- KEBILIDI is intended to be administered with an infusion pump capable of infusing at a rate of 0.003 mL/min.
2.2 Recommended Dose
KEBILIDI is administered as four intraputaminal infusions in a single stereotactic neurosurgical procedure as per the recommended dose shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended Dose of KEBILIDI
Total Recommended Dose 1.8x1011 vg (0.32 mL) Total number of infusions 4 Volume (dose) per infusion 0.08 mL (0.45x1011 vg) Location of infusions 2 in anterior putamen, 2 in posterior putamen Infusion rate at each target point 0.003 mL/min Dose duration for infusion at each target point 27 minutes 2.3 Preparation
Thawing KEBILIDI Vial
- Coordinate timing of KEBILIDI thaw and infusion. KEBILIDI should be used within 6 hours of starting product thaw. Infusion of KEBILIDI takes 4 hours. The maximum time from thaw to completion of infusion should be no more than 10 hours.
- Thaw the KEBILIDI vial upright at room temperature before use. The contents of the vial will thaw in approximately 15 minutes at room temperature. Do not thaw or warm the vial any other way. Gently invert the vial 3 times. Do not shake the vial.
- Inspect the fully thawed KEBILIDI vial after mixing. KEBILIDI should be inspected visually for particulate matter, and discoloration prior to administration. KEBILIDI is clear to slightly opaque. The color of KEBILIDI should be a colorless to faint white suspension
- Do not use if particulates, or discoloration are visible in the suspension.
Preparing KEBILIDI in Syringe
- Gather supplies listed in Table 2 for preparation:
Table 2: Supplies for KEBILIDI PreparationAbbreviations: PC=Polycarbonate; PP=Polypropylene Component Material of Construction 1mL lubricated sterile Luer-lock syringe with elastomer plunger
Or
5mL lubricated sterile Luer-lock syringe with elastomer plungerSilicone, PC; Silicone, PP
Silicone, PP18 or 19 G sterile needle with 5µm filter Stainless steel, PC hub; Stainless steel, PP hub Sterile Luer-lock syringe cap - Plastic bag for delivery into surgical unit - Secondary container for delivery into surgical unit - - Prepare KEBILIDI using sterile techniques under aseptic conditions, proper engineering controls (e.g., biological safety cabinets or isolator) as per the institutional policies.
- Open the syringe and label it as the product-filled syringe.
- Attach the filter needle to the syringe.
- Draw the full volume of the vial of KEBILIDI into the syringe. Invert the vial and syringe and partially withdraw or angle the needle as necessary to maximize recovery of product.
- Draw air into the syringe so that the needle is emptied of product. Carefully remove the needle from syringe containing KEBILIDI. Purge the air from the syringe until there is no air bubble and then cap with a syringe cap.
- Place the syringe in a plastic bag and seal the bag.
- Place the plastic bag in an appropriate secondary container for delivery to the surgical suite at room temperature.
- The filled syringe prepared under aseptic conditions for delivery to the surgical site should be used immediately.
Notes:
- Do not refreeze thawed product.
- Dispose any remaining KEBILIDI or disposable material in compliance with institutional policy
2.4 Administration
Gather supplies for administration:
- KEBILIDI [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]
- SmartFlow Neuro Cannula
- Syringe pump, capable of an infusion rate of 0.003 mL/min and compatible with 1 mL or 5 mL syringe sizes
- Stereotactic systemIdentification of the Target Points Within the Putamen
- Using standard neurosurgical stereotactic procedure, brain imaging for stereotactic planning and intraoperative navigation should be done prior to the procedure (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Four Target Points within the Putamen for Infusion Sites
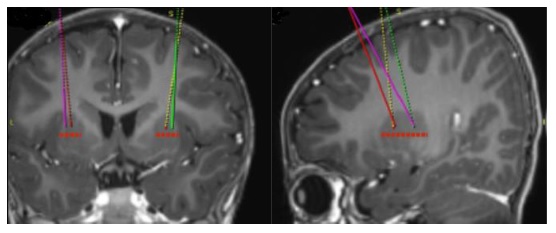
- After stereotactic registration is complete, mark the entry point on the skull. Surgical access through the skull bone and dura should be performed.
Figure 2: Infusion Delivery System
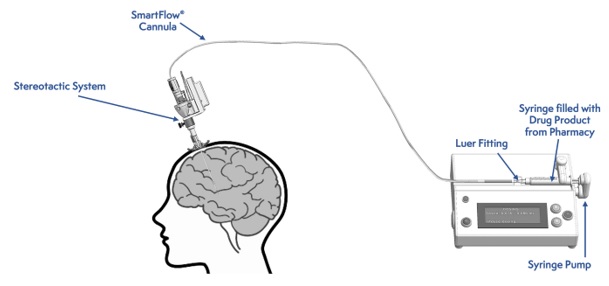
Intraputaminal Administration of KEBILIDI
Administer KEBILIDI by bilateral intraputaminal infusion using a single infusion cannula in one surgical session at two sites (anterior and posterior) per putamen. The infusion cannula is placed and infusion performed separately for each target point (see Figure 2).
- Tightly connect the syringe containing the prepared KEBILIDI to Luer Lock connector at the proximal end of the infusion cannula.
- Load syringe onto the infusion pump and secure appropriately.
- Set infusion pump occlusion limit to the highest level to prevent pump from alarming or disrupting the infusion.
- Prime KEBILIDI at the rate of up to 0.003 mL/minute (0.18 mL/hour) until the first drop of the product can be seen at the tip of the needle.
- Place sterile absorbent pad or gauze under the tip of the cannula to contain drops of the prepared product that might emerge during priming.
- Run the infusion pump prior to insertion of the cannula to ensure the prepared product is flowing from the tip immediately before insertion.
- Place the infusion SmartFlow Neuro Cannula at the designation point in the putamen using stereotactic tools based on pre-planned stereotactic trajectories.
- Starting with the first target site, insert the cannula through a burr hole into the putamen and then incrementally withdraw cannula along the intraputaminal infusion track, distributing the 0.08 mL (infused at a rate of 0.003 mL/min) of KEBILIDI per putamen across the planned trajectory to optimize distribution across the target site. The pump should run continuously throughout the 27-minute infusion, including during the repositioning to the designated sites along the infusion track.
- Once the infusion is complete, stop the pump and leave the cannula in place for 5 minutes before withdrawing. Re-zero the total delivered volume setting on the infusion pump as soon as the cannula is inserted to the target and perform infusion. Reinsert at the next target point, repeating the same procedure for the other 3 target points.
- After standard neurosurgical closure procedures, carry out a postoperative brain imaging examination of the patient to ensure there are no complications (e.g., bleeding).
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
KEBILIDI is a sterile suspension for intraputaminal infusion. Each single-dose vial contains 2.8×1011 vg/0.5 mL (nominal concentration of 5.6×1011 vg/mL) of KEBILIDI and each 2 mL vial contains an extractable volume of 0.5 mL.
Following product thaw, the suspension for infusion is a clear to slightly opaque, colorless to faint white liquid, free of visible particulates [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Procedural Complications
Procedural complications have been reported after neurosurgery required for KEBILIDI administration. These events included respiratory and cardiac arrest which occurred within 24 hours of the neurosurgical procedure and during post-surgical care [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. KEBILIDI administration has the potential risk for additional procedure related adverse events including cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak, intracranial bleeding, neuroinflammation, acute infarction, and infection.
Monitor patients for procedure related adverse events with KEBILIDI administration, including continuous cardiorespiratory monitoring during hospitalization.
5.2 Dyskinesia
Dyskinesia was reported after administration of KEBILIDI. All events were reported within 3 months of administration and 2 events required hospitalization [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of dyskinesia after KEBILIDI treatment which may include involuntary movements of face, arm, leg, or entire body. These may present as fidgeting, writhing, wriggling, head bobbing or body swaying. The use of dopamine antagonists may be considered to control dyskinesia symptoms.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data described in this section reflects exposure to KEBILIDI in 13 pediatric patients with genetically confirmed AADC deficiency who received a single dose of 1.8×1011 vg. The median duration of follow-up was 72 weeks (range 23 to 109 weeks) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥15%) are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions in ≥15% of Patients in Study 1
*Procedural complications included respiratory and cardiac arrest. Adverse Reaction Patients Treated with KEBILIDI
N=13 (%)Dyskinesia 10 (77%) Pyrexia 5 (38%) Hypotension 4 (31%) Anemia 4 (31%) Salivary hypersecretion 3 (23%) Hypokalemia 3 (23%) Hypophosphatemia 3 (23%) Insomnia 3 (23%) Hypomagnesemia 2 (15%) Procedural complications* 2 (15%) Other clinically significant adverse reaction includes worsening in duration and frequency of oculogyric crises during hospitalization following administration of KEBILIDI reported in one patient.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no clinical data from the use of KEBILIDI in pregnant women. Animal reproductive and developmental toxicity studies have not been conducted with KEBILIDI.
In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk SummaryThere is no data on the presence of KEBILIDI in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Pregnancy status of females with reproductive potential should be verified. Sexually active females of reproductive potential should have a negative pregnancy test before administering KEBILIDI.
Contraception
There are insufficient exposure data to provide a recommendation concerning duration of contraception following treatment with KEBILIDI.
Infertility
There is no data on the effects of KEBILIDI on fertility.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of KEBILIDI have been established in pediatric patients. The use of KEBILIDI was evaluated in a single-arm, open-label study that enrolled 13 pediatric patients aged 16 months to 10 years who had achieved skull maturity [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Clinical Studies (14)].
The safety and effectiveness of KEBILIDI have not been studied in pediatric patients younger than 16 months.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
KEBILIDI (eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq) is a gene therapy product that expresses the human aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase enzyme (hAADC). It is a recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 2 (rAAV2) based vector containing the complementary DNA of the human DDC gene under the control of the cytomegalovirus immediate-early promoter. Eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq is produced in human embryonic kidney cells by recombinant DNA technology.
KEBILIDI is a sterile suspension administered by bilateral intraputaminal infusion in one surgical session at two sites (anterior and posterior) per putamen. Each single-dose 2 mL vial contains 2.8×1011 vg in an extractable volume of 0.5 mL of suspension. Each mL of suspension contains 5.6×1011 vg. Patients will receive a total dose of 1.8×1011 vg delivered as four 0.08 mL (0.45×1011 vg) infusions (two per putamen).
KEBILIDI is provided in a single-dose 2 mL vial containing a clear to slightly opaque, colorless to faint white liquid, free of visible particulates following thaw from its frozen state. The excipients include potassium chloride (3 mM), sodium chloride (337 mM), potassium dihydrogen phosphate (2 mM), disodium hydrogen phosphate (8 mM), and poloxamer 188 (0.001%).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
KEBILIDI is a recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 2 (rAAV2) based gene therapy designed to deliver a copy of the DDC gene which encodes the AADC enzyme. Intraputaminal infusion of KEBILIDI results in AADC enzyme expression and subsequent production of dopamine in the putamen.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Homovanillic Acid in Cerebrospinal Fluid
In Study 1, homovanillic acid (HVA), a downstream metabolite of dopamine, in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was measured at baseline, Week 8, and Week 48 using a high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). In all patients of Study 1, an increase in CSF HVA levels from baseline was observed at Week 8 and Week 48 (Table 4).
Table 4: HVA Levels in CSF (Study 1)
Note: Lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was 2 nmol/L, and values reported as <LLOQ were imputed as 0.5*LLOQ.
Abbreviations: CSF=cerebrospinal fluid; HVA=homovanillic acid; N=number of subjects;
Max=maximum; Min=minimumTimepoint Observed Values
(nmol/L)Change from Baseline (nmol/L) Percent Change from Baseline(%) Baseline N 13 - - Median (Min, Max) 3.34 (1.00, 93.73) - - Week 8 N 12 12 12 Median (Min, Max) 35.09 (15.09, 150.48) 26.62 (12.49, 56.75) 534.7 (57.4, 2810.0) Week 48 N 9 9 9 Median (Min, Max) 29.16 (14.21, 125.84) 24.7 (13.21, 58.02) 773.1 (33.9, 3991.0) 18F-DOPA Uptake in the Putamen
18F-DOPA is a positron-emitting fluorine-labeled substrate of the AADC enzyme. Following administration of 18F-DOPA, its uptake into the putamen assessed by positron emission tomography (PET) imaging reflects AADC enzyme activity of dopaminergic neurons in the putamen. In Study 1, 18F DOPA uptake in the putamen was assessed at baseline and followed up at Week 8 in 12 out 13 patients and at Week 48 in 10 out 13 patients indicating increased AADC 18F DOPA uptake in all assessed patients. The median (range) percent increase from baseline was 259% (65% to 620%) at Week 8 and 271% (25% to 760%) at Week 48.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Biodistribution (within the body) and Vector Shedding (excretion/secretion)
KEBILIDI vector DNA levels in various tissues and secretions were determined using a validated quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay.
Nonclinical data
Biodistribution of eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq was evaluated in rats at Days 7, 30, 90, and 180 after single-dose intraputaminal infusion at dose levels up to 7.5×109 vg/animal (21-fold higher than the recommended human dose based on relative brain weight). At Day 7, vector DNA was observed in the putamen, cerebellum, cerebrum, and spinal cord. Vector DNA levels declined from Day 7 to Day 90, with DNA levels primarily sustained in the putamen at Day 180.
Clinical data
Following administration of KEBILIDI at a total dose for each patient of 1.8×1011 vg in Study 1, biodistribution and viral shedding in CSF, blood, and urine were evaluated in 13 patients. CSF was collected at Weeks 8 and 48, and blood and urine were collected from Day 3 up to Week 48. Five (38%) patients showed detectable vector DNA levels in blood at Day 3 ranging from 4.0×103 to 6.5×103 copies/mL, which became below the limit of detection (<3.1×103 copies/mL) by Week 3. No vector was detected in CSF or urine.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-AAV2 antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-AAV2 antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-AAV2 antibodies in other studies.
There is no clinical experience with KEBILIDI in patients with pre-existing anti-AAV2 neutralizing antibody at titers >1:1200.
In Study 1, anti-AAV2 total binding antibodies and anti-AAV2 neutralizing antibodies were assessed from Day 3 up to Week 48 following administration of KEBILIDI. In all patients (N=13), titers of total binding antibody and neutralizing antibody increased from Week 3 and remained elevated, as measured at Week 48 (N=9). The highest titers in each patient ranged from 1:800 to 1:204,800 for total binding antibodies and from 1:80 to 1:10,240 for neutralizing antibody. Because of the small sample size of Study 1, there is insufficient data to determine the effect of anti-AAV2 antibody on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, or effectiveness.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of KEBILIDI was evaluated in one open-label, single arm study (Study 1; NCT04903288). The study enrolled pediatric patients with genetically confirmed, severe AADC deficiency who had achieved skull maturity assessed with neuroimaging. The main efficacy outcome measure was gross motor milestone achievement evaluated at week 48 and assessed using the Peabody Developmental Motor Scale, Second Edition (PDMS-2). Patients treated with KEBILIDI were compared to an external untreated natural history cohort of 43 pediatric patients with severe AADC deficiency who had at least one motor milestone assessment after 2 years of age.
A total of 13 patients received a single total dose of 1.8×1011 vg of KEBILIDI given as four intraputaminal infusions in a single stereotactic neurosurgical procedure. The demographic characteristics of the population were as follows: the median age was 2.8 years (1.3 to 10.8 years), 7 patients (54%) were female, 10 patients (77%) were Asian, 2 patients (15%) were White, and 1 patient was of “other” race. Twelve of the 13 patients had the severe phenotype of AADC deficiency, defined as having no motor milestone achievement at baseline and no clinical response to standard of care therapies. The one remaining patient had a “variant” of the severe disease phenotype, with the ability to sit with assistance but with lack of head control.
Gross motor milestone achievement at Week 48 was assessed in 12 of the 13 patients treated in Study 1 (one patient dropped out of the study prior to Week 48).
Eight (67%) of the 12 treated patients achieved a new gross motor milestone at week 48: 3 patients achieved full head control, 2 patients achieved sitting with or without assistance, 2 patients achieved walking backwards and the patient with the “variant” severe phenotype was able to sit unassisted. The two patients who achieved walking backwards at week 48 were treated before 2 years of age. The four patients who were unable to achieve new gross motor milestones at week 48 were treated between the ages of 2.8 and 10.8 years. In comparison, none of the 43 untreated patients with the severe phenotype had documented motor milestone achievement at last assessment at a median age of 7.2 years (range 2 to 19 years).
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
KEBILIDI is supplied in a single-dose 2 mL vial containing sterile, clear to slightly opaque, colorless to faint white liquid free of visible particulates, following thaw from its frozen state. Each KEBILIDI (eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq) vial contains 2.8×1011 vg of eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq in an extractable volume of 0.5 mL of suspension. Each mL of suspension contains a nominal concentration of 5.6×1011 vg of eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq.
Package (carton): NDC Number 52856-601-01
Container (vial): NDC Number 52856-601-11
Storage and Handling
Store and transport frozen at ≤-65°C (-85°F). Keep the vial in the supplied carton.
Thaw KEBILIDI prior to administration. If not used immediately, store at room temperature (up to 25°C [77°F]) and use within 6 hours of starting product thaw [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Do not refreeze vial once thawed.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Discuss the following with patients and caregivers:
- Administration: Inform patients/caregivers that KEBILIDI administration involves an infusion into the brain that is administered during the neurosurgical procedure [see Administration 2.4)].
- Procedural Complications: Inform patients/caregivers about the complications of the neurosurgical procedure required for administration of KEBILIDI, including respiratory and cardiac arrest, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak, intracranial bleeding, neuroinflammation, acute infarction, and infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Dyskinesia: Inform patients/caregivers that they may experience dyskinesia within 3 months after treatment with KEBILIDI. Symptoms of dyskinesia may include involuntary movements of face, arm, leg, or entire body which may present as fidgeting, writhing, wriggling, head bobbing or body swaying. Advise patients and caregivers to contact their healthcare provider if these symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Vector Shedding: Inform patients/caregivers that temporary vector shedding of KEBILIDI may occur for 3 weeks after administration. Advise patients/caregivers on proper hand hygiene and appropriate handling of waste materials generated from dressings and/or any secretions (e.g., blood, nasal secretions, urine, stool, and CSF). Recommended procedures include storage of waste material in sealed bags prior to disposal and wearing gloves for dressings changes and waste disposal. Patients should not donate blood, organs, tissues, or cells for transplantation [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)].
Manufactured by: PTC Therapeutics, Inc.
Warren, NJ 07059 USA
US License No. 2168
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 52856-601-01 - Carton Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 52856-601-11 - Vial Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
KEBILIDI
eladocagene exuparvovec-tneq suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 52856-601 Route of Administration INTRACEREBRAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ELADOCAGENE EXUPARVOVEC (UNII: S51J6N56M7) (ELADOCAGENE EXUPARVOVEC - UNII:S51J6N56M7) ELADOCAGENE EXUPARVOVEC 560000000000 {GC} in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 660YQ98I10) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) MONOBASIC POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE (UNII: 4J9FJ0HL51) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, ANHYDROUS (UNII: 22ADO53M6F) POLOXAMER 188 (UNII: LQA7B6G8JG) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (Clear to slightly opaque, colorless to faint-white liquid) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 52856-601-01 1 in 1 CARTON 11/13/2024 1 NDC: 52856-601-11 0.5 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 7: Separate Products Requiring Cross Labeling Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125722 11/13/2024 Labeler - PTC Therapeutics, Inc. (124371951)
Trademark Results [KEBILIDI]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 KEBILIDI 98022361 not registered Live/Pending |
PTC Therapeutics, Inc. 2023-05-31 |
 KEBILIDI 88360989 not registered Live/Pending |
PTC THERAPEUTICS, INC. 2019-03-28 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.