PEMAZYRE- pemigatinib tablet
PEMAZYRE by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
PEMAZYRE by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Incyte Corporation. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PEMAZYRE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PEMAZYRE.
PEMAZYRE™ (pemigatinib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2020
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PEMAZYRE is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adults with previously treated, unresectable locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with a fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusion or other rearrangement as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1, 2.1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s). (1, 2.1)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Confirm the presence of an FGFR2 fusion or rearrangement prior to initiation of treatment with PEMAZYRE. (2.1)
- Recommended dose is 13.5 mg orally once daily for 14 consecutive days followed by 7 days off therapy in 21-day cycles. Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. (2.2)
- Swallow tablet whole, with or without food. (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 4.5 mg, 9 mg, and 13.5 mg. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- PEMAZYRE can cause retinal pigment epithelial detachment. Perform ophthalmological examination including optical coherence tomography (OCT) prior to initiation of therapy, every 2 months for the first 6 months of treatment and every 3 months thereafter, and urgently at any time for visual symptoms. (2.3, 5.1)
- Hyperphosphatemia: Increases in phosphate levels are a pharmacodynamic effect of PEMAZYRE. Monitor for hyperphosphatemia and withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue based on duration and severity of hyperphosphatemia. (2.3, 5.2)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus and use effective contraception. (5.3, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 20%) are hyperphosphatemia, alopecia, diarrhea, nail toxicity, fatigue, dysgeusia, nausea, constipation, stomatitis, dry eye, dry mouth, decreased appetite, vomiting, arthralgia, abdominal pain, hypophosphatemia, back pain, and dry skin. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Incyte Corporation at 1-855-463-3463 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Dosage Modification for Adverse Reactions
2.4 Dosage Modification for Concomitant Use with Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ocular Toxicity
5.2 Hyperphosphatemia
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on PEMAZYRE
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Cholangiocarcinoma
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PEMAZYRE is indicated for the treatment of adults with previously treated, unresectable locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with a fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusion or other rearrangement as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with PEMAZYRE based on the presence of an FGFR2 fusion or rearrangement as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Information on FDA-approved test(s) for the detection of an FGFR2 fusion or rearrangement in cholangiocarcinoma is available at http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of PEMAZYRE is 13.5 mg orally once daily for 14 consecutive days followed by 7 days off therapy, in 21-day cycles. Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
Take PEMAZYRE with or without food at approximately the same time every day [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Swallow tablets whole. Do not crush, chew, split, or dissolve tablets.
If the patient misses a dose of PEMAZYRE by 4 or more hours or if vomiting occurs, resume dosing with the next scheduled dose.
2.3 Dosage Modification for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reductions for adverse reactions are provided in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended Dose Reductions for PEMAZYRE for Adverse Reactions - * Permanently discontinue PEMAZYRE if unable to tolerate 4.5 mg once daily.
Dose Reduction Recommended Dosage First 9 mg once daily for first 14 days of each 21-day cycle Second* 4.5 mg once daily for first 14 days of each 21-day cycle The recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
Table 2: Recommended Dosage Modifications for PEMAZYRE Adverse Reactions - * Severity as defined by National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) version 4.03.
Adverse Reaction Severity* PEMAZYRE Dosage Modification Retinal Pigment Epithelial Detachment (RPED) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] RPED - If asymptomatic and stable on serial examination, continue PEMAZYRE.
- If symptomatic or worsening on serial examination, withhold PEMAZYRE.
- If asymptomatic and improved on subsequent examination, resume PEMAZYRE at a lower dose
- If symptoms persist or examination does not improve, consider permanent discontinuation of PEMAZYRE, based on clinical status.
Hyperphosphatemia
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]Serum phosphate
> 7 mg/dL- ≤10 mg/dL- Initiate phosphate lowering therapy and monitor serum phosphate weekly.
- Withhold PEMAZYRE if levels are not < 7 mg/dL within 2 weeks of starting phosphate lowering therapy.
- Resume PEMAZYRE at the same dose when phosphate levels are < 7 mg/dL for first occurrence; resume at a lower dose level for subsequent recurrences.
Serum phosphate >10 mg/dL
- Initiate phosphate lowering therapy and monitor serum phosphate weekly.
- Withhold PEMAZYRE if levels are not ≤ 10 mg/dL within 1 week after starting phosphate lowering therapy.
- Resume PEMAZYRE at the next lower dose level when phosphate levels are < 7 mg/dL.
- Permanently discontinue PEMAZYRE for recurrence of serum phosphate > 10mg/dL following 2 dose reductions.
Other Adverse Reactions Grade 3 - Withhold PEMAZYRE until resolves to Grade 1 or baseline.
- Resume PEMAZYRE at next lower dose if resolves within 2 weeks.
- Permanently discontinue PEMAZYRE if does not resolve within 2 weeks.
- Permanently discontinue PEMAZYRE for recurrent Grade 3 after 2 dose reductions.
Grade 4 - Permanently discontinue PEMAZYRE.
2.4 Dosage Modification for Concomitant Use with Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors with PEMAZYRE. If concomitant use with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided:
- Reduce PEMAZYRE dose from 13.5 mg to 9 mg.
- Reduce PEMAZYRE dose from 9 mg to 4.5 mg.
If concomitant use of a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor is discontinued, increase the PEMAZYRE dose (after 3 plasma half-lives of the CYP3A inhibitor) to the dose that was used before starting the strong inhibitor [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets:
- 4.5 mg: round, white to off-white tablet debossed on one side with "I" and "4.5" on the other side.
- 9 mg: oval, white to off-white tablet debossed on one side with "I" and "9" on the other side.
- 13.5 mg: round, white to off-white tablet debossed on one side with "I" and "13.5" on the other side.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ocular Toxicity
Retinal Pigment Epithelial Detachment (RPED)
PEMAZYRE can cause RPED, which may cause symptoms such as blurred vision, visual floaters, or photopsia. Clinical trials of PEMAZYRE did not conduct routine monitoring including optical coherence tomography (OCT) to detect asymptomatic RPED; therefore, the incidence of asymptomatic RPED with PEMAZYRE is unknown.
Among 466 patients who received PEMAZYRE across clinical trials, RPED occurred in 6% of patients, including Grade 3-4 RPED in 0.6%. The median time to first onset of RPED was 62 days. RPED led to dose interruption of PEMAZYRE in 1.7% of patients, and dose reduction and permanent discontinuation in 0.4% and in 0.4% of patients, respectively. RPED resolved or improved to Grade 1 levels in 87.5% of patients who required dosage modification of PEMAZYRE for RPED.
Perform a comprehensive ophthalmological examination including OCT prior to initiation of PEMAZYRE and every 2 months for the first 6 months and every 3 months thereafter during treatment. For onset of visual symptoms, refer patients for ophthalmologic evaluation urgently, with follow-up every 3 weeks until resolution or discontinuation of PEMAZYRE.
Modify the dose or permanently discontinue PEMAZYRE as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Dry Eye
Among 466 patients who received PEMAZYRE across clinical trials, dry eye occurred in 27% of patients, including Grade 3-4 in 0.6% of patients. Treat patients with ocular demulcents as needed.
5.2 Hyperphosphatemia
Increases in phosphate levels are a pharmacodynamic effect of PEMAZYRE [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Among 466 patients who received PEMAZYRE across clinical trials, hyperphosphatemia was reported in 92% of patients based on laboratory values above the upper limit of normal. The median time to onset of hyperphosphatemia was 8 days (range 1-169). Phosphate lowering therapy was required in 29% of patients receiving PEMAZYRE.
Monitor for hyperphosphatemia and initiate a low phosphate diet when serum phosphate level is > 5.5 mg/dL. For serum phosphate levels > 7 mg/dL, initiate phosphate lowering therapy and withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue PEMAZYRE based on duration and severity of hyperphosphatemia [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in an animal study and its mechanism of action, PEMAZYRE can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Oral administration of pemigatinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused fetal malformations, fetal growth retardation, and embryo-fetal death at maternal exposures lower than the human exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) at the clinical dose of 13.5 mg.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PEMAZYRE and for 1 week after the final dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PEMAZYRE and for 1 week after the final dose [see Use in Special Population (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Ocular Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hyperphosphatemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of PEMAZYRE was evaluated in FIGHT-202, which included 146 patients with previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Patients were treated orally with PEMAZYRE 13.5 mg once daily for 14 days on followed by 7 days off therapy until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The median duration of treatment was 181 days (range: 7 to 730 days).
The median age of PEMAZYRE-treated patients was 59 years (range 26-78), 58% were females, and 71% were White.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 45% of patients receiving PEMAZYRE. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 2% of patients who received PEMAZYRE included abdominal pain, pyrexia, cholangitis, pleural effusion, acute kidney injury, cholangitis infective, failure to thrive, hypercalcemia, hyponatremia, small intestinal obstruction, and urinary tract infection. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4.1% of patients, including failure to thrive, bile duct obstruction, cholangitis, sepsis, and pleural effusion.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 9% of patients who received PEMAZYRE. Adverse reactions requiring permanent discontinuation in ≥1% of patients included intestinal obstruction and acute kidney injury.
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 43% of patients who received PEMAZYRE. Adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption in ≥ 1% of patients included stomatitis, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, arthralgia, fatigue, abdominal pain, AST increased, asthenia, pyrexia, ALT increased, cholangitis, small intestinal obstruction, alkaline phosphatase increased, diarrhea, hyperbilirubinemia, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, decreased appetite, dehydration, hypercalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypophosphatemia, back pain, pain in extremity, syncope, acute kidney injury, onychomadesis, and hypotension.
Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 14% of patients who received PEMAZYRE. Adverse reactions requiring dosage reductions in ≥1% of patients who received PEMAZYRE included stomatitis, arthralgia, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, asthenia, and onychomadesis.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions in FIGHT-202. Table 4 summarizes laboratory abnormalitiesin FIGHT-202.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions (≥ 15%) in Patients Receiving PEMAZYRE in FIGHT-202 - * Graded per NCI CTCAE 4.03.
- † Only Grades 3 – 4 were identified.
- ‡ Includes hyperphosphatemia and blood phosphorous increased; graded based on clinical severity and medical interventions taken according to the "investigations-other, specify" category in NCI CTCAE v4.03.
- § Includes hypophosphatemia and blood phosphorous decreased.
- ¶ Includes nail toxicity, nail disorder, nail discoloration, nail dystrophy, nail hypertrophy, nail ridging, nail infection, onychalgia, onychoclasis, onycholysis, onychomadesis, onychomycosis, and paronychia.
- # Includes dry eye, keratitis, lacrimation increased, pinguecula, and punctate keratitis.
PEMAZYRE
(N=146)Adverse Reaction All Grades*
(%)Grades ≥ 3†
(%)Metabolism and nutrition disorders Hyperphosphatemia‡ 60 0 Decreased appetite 33 1.4 Hypophosphatemia§ 23 12 Dehydration 15 3.4 Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Alopecia 49 0 Nail toxicity¶ 43 2.1 Dry skin 20 0.7 Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome 15 4.1
Gastrointestinal disorders Diarrhea 47 2.7 Nausea 40 2.1 Constipation 35 0.7 Stomatitis 35 5 Dry mouth 34 0 Vomiting 27 1.4 Abdominal pain 23 4.8 General disorders Fatigue 42 4.8 Edema peripheral 18 0.7 Nervous system disorders Dysgeusia 40 0 Headache 16 0 Eye disorders Dry eye# 35 0.7 Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Arthralgia 25 6 Back pain 20 2.7 Pain in extremity 19 2.1 Infections and infestations Urinary tract infection 16 2.7 Investigations Weight loss 16 2.1 Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in ≤ 10% of patients included fractures (2.1%). In all patients treated with pemigatinib, 1.3% experienced pathologic fractures (which included patients with and without cholangiocarcinoma [N=466]).
Table 4: Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 10%) Worsening from Baseline in Patients Receiving PEMAZYRE in FIGHT-202 - * The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 142-146 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
- † Graded per NCI CTCAE 4.03.
- ‡ Based on CTCAE 5.0 grading.
- § Graded based on comparison to upper limit of normal.
PEMAZYRE*
(N=146)Laboratory Abnormality All Grades† (%) Grades ≥ 3 (%) Hematology Decreased hemoglobin 43 6 Decreased lymphocytes 36 8 Decreased platelets 28 3.4 Increased leukocytes 27 0.7 Decreased leukocytes 18 1.4 Chemistry Increased phosphate‡ 94 0 Decreased phosphate 68 38 Increased alanine aminotransferase 43 4.1 Increased aspartate aminotransferase 43 6 Increased calcium 43 4.1 Increased alkaline phosphatase 41 11 Increased creatinine§ 41 1.4 Decreased sodium 39 12 Increased glucose 36 0.7 Decreased albumin 34 0 Increased urate 30 10 Increased bilirubin 26 6 Decreased potassium 26 5 Decreased calcium 17 2.7 Increased potassium 12 2.1 Decreased glucose 11 1.4 Increased Creatinine
Within the first 21-day cycle of PEMAZYRE dosing, serum creatinine increased (mean increase of 0.2 mg/dL) and reached steady state by Day 8, and then decreased during the 7 days off therapy. Consider alternative markers of renal function if persistent elevations in serum creatinine are observed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on PEMAZYRE
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers
Concomitant use of PEMAZYRE with a strong or moderate CYP3A inducer decreases pemigatinib plasma concentrations, [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] which may reduce the efficacy of PEMAZYRE. Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A inducers with PEMAZYRE.
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Concomitant use of a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor with PEMAZYRE increases pemigatinib plasma concentrations, [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] which may increase the incidence and severity of adverse reactions. Reduce PEMAZYRE dose if concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors cannot be avoided [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in an animal study and its mechanism of action, PEMAZYRE can cause fetal harm or loss of pregnancy when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data on the use of PEMAZYRE in pregnant women. Oral administration of pemigatinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at maternal plasma exposures below the human exposure at the clinical dose of 13.5 mg resulted in fetal malformations, fetal growth retardation, and embryo-fetal death (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Once daily oral administration of pemigatinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in 100% embryofetal mortality due to post-implantation loss at doses ≥ 0.3 mg/kg (approximately 0.6 times the human exposure based on AUC at the clinical dose of 13.5 mg). Fetal survival was unaffected at 0.1 mg/kg per day; however, once daily oral administration of pemigatinib at the 0.1 mg/kg dose level (approximately 0.2 times the human exposure based on AUC at the clinical dose of 13.5 mg) resulted in reduced mean fetal body weight and an increase in fetal skeletal and visceral malformations, major blood vessel variations, and reduced ossification.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of pemigatinib or its metabolites in human milk or their effects on either the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children from PEMAZYRE, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment and for 1 week after the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating PEMAZYRE [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
PEMAZYRE can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PEMAZYRE and for 1 week after the final dose.
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PEMAZYRE and for 1 week after the final dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of PEMAZYRE have not been established in pediatric patients.
Animal Toxicity Data
In 4- or 13-week repeat-dose toxicology studies in rats and non-human primates, animals displayed toxicities in bone and teeth at pemigatinib exposures lower than the human exposure at the clinical dose of 13.5 mg. Physeal and cartilage dysplasia were present in multiple bones in both species, and tooth (incisor) abnormalities (complete loss of ameloblasts with associated secondary changes) occurred in rats. Six weeks after cessation of dosing, these findings did not show complete evidence of recovery, and additional tooth-related findings (mal-aligned, whitened, broken, and trimmed/thinned incisors) developed in the 13-week study.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In FIGHT-202, 32% of patients were 65 years and older, and 8% of patients were 75 years and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (glomerular filtration rate (GFR) ≥ 30 to <90 mL/min estimated by Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) equation). The recommended dose of PEMAZYRE has not been established for patients with severe renal impairment (GFR <30 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild (total bilirubin > upper limit of normal (ULN) to 1.5 × ULN or AST > ULN) or moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1.5–3 × ULN with any AST). The recommended dose of PEMAZYRE has not been established for patients with severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >3 × ULN with any AST) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Pemigatinib is a kinase inhibitor with the chemical name 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-1,3,4,7-tetrahydro-2H-pyrrolo[3',2':5,6]pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-2-one. Pemigatinib has a molecular formula of C24H27F2N5O4 and molecular mass of 487.5 g/mole. Pemigatinib has the following chemical structure:
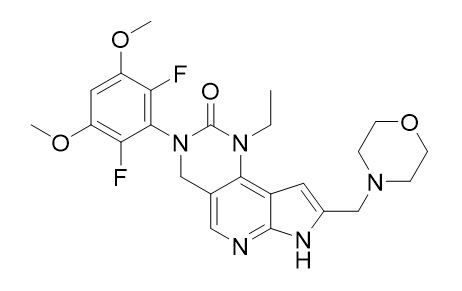
Pemigatinib is a white to off-white solid that is not hygroscopic. The solubility of pemigatinib is pH dependent with decreasing solubility observed with increasing pH. PEMAZYRE tablets are uncoated and for oral administration. Tablets are available containing 4.5 mg, 9 mg, or 13.5 mg of pemigatinib active ingredient. The inactive ingredients include magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Pemigatinib is a small molecule kinase inhibitor that targets FGFR1, 2 and 3 with IC50 values of less than 2 nM. Pemigatinib also inhibited FGFR4 in vitro at a concentration approximately 100 times higher than those that inhibit FGFR1, 2, and 3. Pemigatinib inhibited FGFR1-3 phosphorylation and signaling and decreased cell viability in cancer cell lines with activating FGFR amplifications and fusions that resulted in constitutive activation of FGFR signaling. Constitutive FGFR signaling can support the proliferation and survival of malignant cells. Pemigatinib exhibited anti-tumor activity in mouse xenograft models of human tumors with FGFR1, FGFR2, or FGFR3 alterations resulting in constitutive FGFR activation including a patient-derived xenograft model of cholangiocarcinoma that expressed an oncogenic FGFR2-Transformer-2 beta homolog (TRA2b) fusion protein.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a dose 1.5 times the maximum recommended dose, PEMAZYRE does not result in a large mean increase (i.e. >20 ms) of the QTc interval.
Serum Phosphate
Pemigatinib increased serum phosphate levels as a consequence of FGFR inhibition. In patients, the increase in serum phosphate observed after treatment with pemigatinib was exposure-dependent across the dose range of 1 to 20 mg once daily (0.07 to 1.5 times the recommended dose), with increased risk of hyperphosphatemia with higher pemigatinib exposure.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The geometric mean steady-state pemigatinib AUC0-24h was 2620 nM·h (54% CV) and Cmax was 236 nM (56% CV) for 13.5 mg orally once daily. Steady state pemigatinib concentrations increased proportionally over the dose range of 1 to 20 mg (0.07 to 1.5 times the recommended dose). Steady-state was achieved within 4 days following repeated once daily dosing. With repeated once daily dosing, pemigatinib accumulated with a median accumulation ratio of 1.63 (range 0.63 to 3.28).
Absorption
The median time to achieve peak pemigatinib plasma concentration (Tmax) was 1.13 (0.50‑6.00) hours.
Effect of Food
Administration of PEMAZYRE with a high-fat and high-calorie meal (approximately 1000 calories with 150 calories from protein, 250 calories from carbohydrate, and 500‑600 calories from fat) had no clinically meaningful effect on pemigatinib pharmacokinetics.
Distribution
The estimated apparent volume of distribution was 235 L (60.8%) following a 13.5 mg oral dose. In vitro, pemigatinib was 90.6% bound to human plasma proteins at concentrations ranging from 1 to 10 µM.
Elimination
The geometric mean elimination half-life (t½) of pemigatinib was 15.4 (51.6% CV) hours and the geometric mean apparent clearance (CL/F) was 10.6 L/h (54% CV).
Metabolism
Pemigatinib is predominantly metabolized by CYP3A4 in vitro. The major drug-related moiety in plasma was unchanged pemigatinib in a human [14C] mass balance study.
Excretion
Following a single oral 11 mg dose of radiolabeled pemigatinib, 82.4% of the dose was recovered in feces (1.4% as unchanged) and 12.6% in urine (1% as unchanged).
Specific Populations
No clinically meaningful differences in the systemic exposure of pemigatinib were observed based on age (21 ‑ 79 years), sex, race/ethnicity, body weight (39.8 ‑ 156 kg), mild to moderate renal impairment, or mild to moderate hepatic impairment. The effect of severe renal impairment, renal dialysis in end-stage renal disease, or severe hepatic impairment on pemigatinib exposure is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Based Approaches
Effect of CYP3A Inhibitors on Pemigatinib: Itraconazole, a strong CYP3A inhibitor, increased Cmax by 17% and increased AUC by 88% following a single oral PEMAZYRE dose of 4.5 mg [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Concomitant use of moderate CYP3A inhibitors is predicted to increase pemigatinib exposure by approximately 50-80% [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Effect of CYP3A Inducers on Pemigatinib: Rifampin, a strong CYP3A inducer, decreased pemigatinib Cmax by 62% and AUC by 85% following a single oral PEMAZYRE dose of 13.5 mg [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Concomitant use of a moderate CYP3A inducer is predicted to decrease pemigatinib exposure by more than 50% [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Effect of Acid-Lowering Agents on Pemigatinib: Esomeprazole, a proton pump inhibitor, decreased pemigatinib Cmax by 35% and AUC by 8% following a single oral PEMAZYRE dose of 13.5 mg; these differences are not expected to be clinically meaningful. Ranitidine, a histamine-2 antagonist, did not affect pemigatinib exposure.
Other Drugs: No clinically significant differences in glucose levels were observed when metformin (OCT2/MATE1 substrate) was co-administered with pemigatinib.
In Vitro Studies
Effect of Pemigatinib on CYP Enzymes: Pemigatinib is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or CYP3A4 or an inducer of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, or CYP3A4.
Pemigatinib as a Substrate for Transporters: Pemigatinib is a substrate of both P-gp and BCRP. P-gp or BCRP inhibitors are not expected to affect pemigatinib exposure at clinically relevant concentrations.
Effect of Pemigatinib on Transporters: Pemigatinib is an inhibitor of P-gp, OCT2, and MATE1. Pemigatinib may increase serum creatinine by decreasing renal tubular secretion of creatinine; this may occur due to inhibition of renal transporters OCT2 and MATE1 and may not affect glomerular function [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with pemigatinib.
Pemigatinib was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic in either an in vitro chromosome aberration assay or an in vivo micronucleus assay in rats.
Dedicated fertility studies with pemigatinib have not been conducted. Oral administration of pemigatinib did not result in any dose-related findings likely to result in impaired fertility in male and female reproductive organs.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Cholangiocarcinoma
FIGHT-202 (NCT02924376), a multicenter open-label single-arm trial, evaluated the efficacy of PEMAZYRE in 107 patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma whose disease had progressed on or after at least 1 prior therapy and who had an FGFR2 gene fusion or non-fusion rearrangement, as determined by a clinical trial assay performed at a central laboratory. Qualifying in-frame fusions and other rearrangements were predicted to have a breakpoint within intron 17/exon 18 of the FGFR2 gene leaving the FGFR2 kinase domain intact.
Patients received PEMAZYRE in 21-day cycles at a dosage of 13.5 mg orally once daily for 14 consecutive days, followed by 7 days off therapy. PEMAZYRE was administered until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR) as determined by an independent review committee (IRC) according to RECIST v1.1.
The median age was 56 years (range: 26 to 77 years), 61% were female, 74% were White, and 95% had a baseline Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 (42%) or 1 (53%). Ninety-eight percent of patients had intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Eighty-six percent of patients had in-frame FGFR2 gene fusions and the most commonly identified FGFR2 fusion was FGFR2-BICC1 (34%). Fourteen percent of patients had other FGFR2 rearrangements that could not be confidently predicted to be in-frame fusions, including rearrangements without an identifiable partner gene. All patients had received at least 1 prior line of systemic therapy, 27% had 2 prior lines of therapy, and 12% had 3 or more prior lines of therapy. Ninety-six percent of patients had received prior platinum-based therapy including 76% with prior gemcitabine/cisplatin.
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 5.
The median time to response was 2.7 months (range 0.7 – 6.9 months).
Table 5: Efficacy Results in FIGHT-202 - * The 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated using the Brookmeyer and Crowley's method.
Note: Data are from IRC per RECIST v1.1, and complete and partial responses are confirmed.Efficacy Parameter PEMAZYRE
N = 107ORR (95% CI) 36% (27, 45) Complete response 2.8% Partial response 33% Median DoR (months) (95% CI)* 9.1 (6.0, 14.5) Patients with DoR ≥ 6 months, n (%) 24 (63%)
Patients with DoR ≥ 12 months, n (%) 7 (18%)
- * The 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated using the Brookmeyer and Crowley's method.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
PEMAZYRE tablets are available as follows:
- 4.5 mg: Round, white to off-white debossed on one side with “I” and “4.5” on the other side in bottles of 14 with child-resistant closure, NDC: 50881-026-01
- 9 mg: Oval, white to off-white debossed on one side with “I” and “9” on the other side in bottles of 14 with child-resistant closure, NDC: 50881-027-01
- 13.5 mg: Round, white to off-white debossed on one side with “I” and “13.5” on the other side in bottles of 14 with child-resistant closure, NDC: 50881-028-01
Store PEMAZYRE tablets at room temperature 20°C ‑ 25°C (68°F ‑ 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C ‑ 30°C (59°F ‑ 86°F).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Ocular Toxicity
Advise patients that PEMAZYRE may cause ocular toxicity including RPED and to immediately inform their healthcare provider if they experience any visual changes. Also advise patients that they should use artificial tear or substitutes, hydrating or lubricating eye gels in order to prevent or treat dry eyes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hyperphosphatemia
Inform patients that they may experience increase in phosphate levels and of the need to monitor serum phosphate levels. They should immediately inform their healthcare provider of any symptoms related to acute change in phosphate levels such as muscle cramps, numbness, or tingling around the mouth [see Warnings and Precautions 5.2)].
Nail Disorders
Advise patients that PEMAZYRE may cause nail disorders [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Advise females to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or become pregnant. Inform female patients of the risk to a fetus and potential loss of pregnancy[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PEMAZYRE and for 1 week after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations(8.3)].
- Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential or who are pregnant to use effective contraception during treatment and for 1 week after receiving the final dose of PEMAZYRE[see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
- Advise patients not to breastfeed during treatment with PEMAZYRE and for 1 week after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Administration
- Instruct patients do not crush, chew, split or dissolve tablets.
- Instruct patients if they miss a dose by 4 or more hours or if they vomit after taking a dose, resume dosing with the next scheduled dose. Extra tablets should not be taken to make up for the missed dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of all concomitant medications, herbal and dietary supplements. Advise patients to avoid grapefruit products during treatment with PEMAZYRE [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Manufactured for:
Incyte Corporation
Wilmington, DE 19803PEMAZYRE is a trademark of Incyte Corporation.
U.S. Patent Nos. 9,611,267 and 10,131,667
© 2020 Incyte Corporation. All rights reserved. -
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
PEMAZYRE™ (pemah zeer)
(pemigatinib) tabletsWhat is PEMAZYRE?
PEMAZYRE is a prescription medicine that is used to treat adults with bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) that has spread or cannot be removed by surgery:- who have already received a previous treatment, and
- whose tumor has a certain type of abnormal "FGFR2” gene.
Your healthcare provider will test your cancer for a certain type of abnormal FGFR2 gene and make sure that PEMAZYRE is right for you.
It is not known if PEMAZYRE is safe and effective in children.Before you take PEMAZYRE, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have vision or eye problems
- have problems swallowing tablets
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. PEMAZYRE can harm your unborn baby or cause loss of your pregnancy (miscarriage). You should not become pregnant during treatment with PEMAZYRE.
Females who can become pregnant:
º Your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with PEMAZYRE.
º You should use an effective method of birth control during treatment and for 1 week after your final dose of PEMAZYRE. Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods that may be right for you.
º Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think that you may be pregnant.
Males with female partners who can become pregnant:
º You should use effective birth control when sexually active during treatment with PEMAZYRE and for 1 week after your final dose of PEMAZYRE.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed.Do not breastfeed during treatment and for 1 week after your final dose of PEMAZYRE.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How should I take PEMAZYRE?
- Take PEMAZYRE exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- PEMAZYRE is taken in cycles of 21 days. Take PEMAZYRE 1 time each day for 14 days, followed by 7 days off treatment, to complete a 21-day treatment cycle.
- Take PEMAZYRE 1 time each day at about the same time each day.
- Take PEMAZYRE with or without food.
- Swallow tablets whole. Do not crush, chew, split, or dissolve PEMAZYRE tablets.
- You should not eat or drink grapefruit products during treatment with PEMAZYRE.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose of PEMAZYRE, or may temporarily or completely stop treatment if you get certain side effects.
- If you miss a dose of PEMAZYRE, you can take the missed dose within 4 hours on the same day. If more than 4 hours have passed, do not make up the dose. Take your regular dose of PEMAZYRE the next day at the usual time. Do not take more PEMAZYRE than prescribed to make up for the missed dose.
- If you vomit after taking PEMAZYRE, do not take another PEMAZYRE tablet. Take your regular dose of PEMAZYRE the next day at the usual time.
What are the possible side effects of PEMAZYRE?
PEMAZYRE may cause serious side effects, including:
-
Eye problems. Certain eye problems are common with PEMAZYRE but can also be serious. Eye problems include dry eye or inflamed eyes, inflamed cornea (front part of the eye), increased tears, and a disorder of the retina (an internal part of the eye). You will need to see an eye specialist for a complete eye exam before you begin treatment with PEMAZYRE, every 2 months for the first 6 months, and then every 3 months during treatment with PEMAZYRE.
- You should use artificial tears or substitutes, hydrating or lubricating eye gels as needed, to help prevent or treat dry eyes.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any changes in your vision during treatment with PEMAZYRE, including: blurred vision, flashes of light, or see black spots. You may need to see an eye specialist right away.
-
High phosphate levels in your blood (hyperphosphatemia). Hyperphosphatemia is common with PEMAZYRE but can also be serious. Your healthcare provider will check your blood phosphate levels during treatment with PEMAZYRE.
- Your healthcare provider may prescribe changes in your diet or phosphate lowering therapy, or change, interrupt or stop PEMAZYRE if needed.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any muscle cramps, or numbness or tingling around your mouth.
The most common side effects of PEMAZYRE include:
- hair loss
- diarrhea
- nails separate from the bed or poor formation of the nail
- feeling tired
- change in sense of taste
- nausea
- constipation
- mouth sores
- dry eyes
- dry mouth
- decrease in appetite
- vomiting
- joint pain
- stomach-area (abdominal) pain
- low phosphate in blood
- back pain
- dry skin
These are not all the possible side effects of PEMAZYRE. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1‑800-FDA-1088.How should I store PEMAZYRE?
- Store PEMAZYRE at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
General information about the safe and effective use of PEMAZYRE
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use PEMAZYRE for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not give PEMAZYRE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information that is written for healthcare professionals.What are the ingredients in PEMAZYRE?
Active ingredient: pemigatinib
Inactive ingredients: magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate.
Manufactured for: Incyte Corporation, Wilmington, DE 19803
PEMAZYRE is a trademark of Incyte Corporation. All rights reserved.
© 2020 Incyte Corporation
For more information, call Incyte at 1-855-463-3463 or go to www.PEMAZYRE.com
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued:04/2020
- 4.5 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- 9 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- 13.5 mg Tablet Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PEMAZYRE
pemigatinib tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50881-026 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PEMIGATINIB (UNII: Y6BX7BL23K) (PEMIGATINIB - UNII:Y6BX7BL23K) PEMIGATINIB 4.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (White to off-white) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code I;45 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50881-026-01 14 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 04/17/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA213736 04/17/2020 PEMAZYRE
pemigatinib tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50881-027 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PEMIGATINIB (UNII: Y6BX7BL23K) (PEMIGATINIB - UNII:Y6BX7BL23K) PEMIGATINIB 9 mg Product Characteristics Color WHITE (White to off-white) Score no score Shape OVAL Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code I;9 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50881-027-01 14 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 04/17/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA213736 04/17/2020 PEMAZYRE
pemigatinib tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50881-028 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PEMIGATINIB (UNII: Y6BX7BL23K) (PEMIGATINIB - UNII:Y6BX7BL23K) PEMIGATINIB 13.5 mg Product Characteristics Color WHITE (White to off-white) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code I;135 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50881-028-01 14 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 04/17/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA213736 04/17/2020 Labeler - Incyte Corporation (556967347)
Trademark Results [PEMAZYRE]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 PEMAZYRE 88895503 not registered Live/Pending |
Incyte Holdings Corporation 2020-04-30 |
 PEMAZYRE 88616570 not registered Live/Pending |
INCYTE HOLDINGS CORPORATION 2019-09-13 |
 PEMAZYRE 87822632 not registered Live/Pending |
Incyte Holdings Corporation 2018-03-06 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.


