LOSARTAN POTASSIUM AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE tablet
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Dispensing Solutions, Inc., PSS World Medical, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
USE IN PREGNANCY
When used in pregnancy during the second and third trimesters, drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and even death to the developing fetus. When pregnancy is detected, Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets should be discontinued as soon as possible. See WARNINGS, Fetal/Neonatal Morbidity and Mortality.
-
DESCRIPTION
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg/12.5 mg, Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 100 mg/12.5 mg and Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 100 mg/25 mg combine an angiotensin II receptor (type AT1) antagonist and a diuretic, hydrochlorothiazide.
Losartan potassium, a non-peptide molecule, is chemically described as 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1H-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium salt. Its empirical formula is C22H22ClKN6O, and its structural formula is:
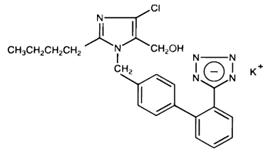
Losartan potassium, USP is a white to off-white free-flowing crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 461.01. It is freely soluble in water, soluble in alcohols, and slightly soluble in common organic solvents, such as acetonitrile and methyl ethyl ketone.
Oxidation of the 5-hydroxymethyl group on the imidazole ring results in the active metabolite of losartan.
Hydrochlorothiazide is 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide. Its empirical formula is C7H8ClN3O4S2 and its structural formula is:
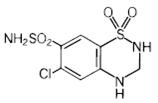
Hydrochlorothiazide, USP is a white, or practically white, crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 297.74, which is slightly soluble in water, but freely soluble in sodium hydroxide solution.
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP are available for oral administration in three tablet combinations of losartan and hydrochlorothiazide. Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 50 mg/12.5 mg contain 50 mg of losartan potassium USP and 12.5 mg of hydrochlorothiazide USP. Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 100 mg/12.5 mg contain 100 mg of losartan potassium USP and 12.5 mg of hydrochlorothiazide USP. Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 100 mg/25 mg contain 100 mg of losartan potassium USP and 25 mg of hydrochlorothiazide USP. Inactive ingredients are colloidal silicon dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, talc and titanium dioxide. Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 50 mg/12.5 mg and Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 100 mg/25 mg also contain D and C yellow No. 10 lake.
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 50 mg/12.5 mg contain 4.24 mg (0.108 mEq) of potassium, Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 100 mg/12.5 mg contain 8.48 mg (0.216 mEq) of potassium, and Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 100 mg/25 mg contain 8.48 mg (0.216 mEq) of potassium. -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hypertension
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension. This fixed dose combination is not indicated for initial therapy of hypertension, except when the hypertension is severe enough that the value of achieving prompt blood pressure control exceeds the risk of initiating combination therapy in these patients (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Hypertensive Patients with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets are indicated to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy, but there is evidence that this benefit does not apply to Black patients. (See PRECAUTIONS, Race, CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, Losartan Potassium, Reduction in the Risk of Stroke, Race, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Losartan potassium-hydrochlorothiazide has been evaluated for safety in 858 patients treated for essential hypertension and 3889 patients treated for hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy. In clinical trials with losartan potassium-hydrochlorothiazide, no adverse experiences peculiar to this combination have been observed. Adverse experiences have been limited to those that were reported previously with losartan potassium and/or hydrochlorothiazide. The overall incidence of adverse experiences reported with the combination was comparable to placebo.
In general, treatment with losartan potassium-hydrochlorothiazide was well tolerated. For the most part, adverse experiences have been mild and transient in nature and have not required discontinuation of therapy. In controlled clinical trials, discontinuation of therapy due to clinical adverse experiences was required in only 2.8% and 2.3% of patients treated with the combination and placebo, respectively.
In these double-blind controlled clinical trials, the following adverse experiences reported with losartan-hydrochlorothiazide occurred in ≥1 percent of patients, and more often on drug than placebo, regardless of drug relationship:
Losartan Potassium-
Hydrochlorothiazide
(n=858)
Placebo
(n=173)
Body as a Whole
Abdominal pain
1.2
0.6
Edema/swelling
1.3
1.2
Cardiovascular
Palpitation
1.4
0.0
Musculoskeletal
Back pain
2.1
0.6
Nervous/Psychiatric
Dizziness
5.7
2.9
Respiratory
Cough
2.6
2.3
Sinusitis
1.2
0.6
Upper respiratory infection
6.1
4.6
Skin
Rash
1.4
0.0
The following adverse events were also reported at a rate of 1% or greater, but were as, or more, common in the placebo group in studies of essential hypertension: asthenia/fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, headache, bronchitis, pharyngitis.
Adverse events occurred at about the same rates in men and women. Adverse events were somewhat more frequent in the elderly compared to non-elderly patients and somewhat more frequent in Blacks compared to non-Blacks for both the losartan-hydrochlorothiazide and the control groups.
A patient with known hypersensitivity to aspirin and penicillin, when treated with losartan potassium, was withdrawn from study due to swelling of the lips and eyelids and facial rash, reported as angioedema, which returned to normal 5 days after therapy was discontinued.
Superficial peeling of palms and hemolysis were reported in one subject treated with losartan potassium.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Losartan Potassium
Significant lethality was observed in mice and rats after oral administration of 1000 mg/kg and 2000 mg/kg, respectively, about 44 and 170 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis.
Limited data are available in regard to overdosage in humans. The most likely manifestation of overdosage would be hypotension and tachycardia; bradycardia could occur from parasympathetic (vagal) stimulation. If symptomatic hypotension should occur, supportive treatment should be instituted.
Neither losartan nor its active metabolite can be removed by hemodialysis.
Hydrochlorothiazide
The oral LD50 of hydrochlorothiazide is greater than 10 g/kg in both mice and rats. The most common signs and symptoms observed are those caused by electrolyte depletion (hypokalemia, hypochloremia, hyponatremia) and dehydration resulting from excessive diuresis. If digitalis has also been administered, hypokalemia may accentuate cardiac arrhythmias. The degree to which hydrochlorothiazide is removed by hemodialysis has not been established.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Hypertension
Dosing must be individualized. The usual starting dose of losartan is 50 mg once daily, with 25 mg recommended for patients with intravascular volume depletion (e.g., patients treated with diuretics) (see WARNINGS, Hypotension ─ Volume-Depleted Patients) and patients with a history of hepatic impairment (see WARNINGS, Impaired Hepatic Function). Losartan can be administered once or twice daily at total daily doses of 25 to 100 mg. If the antihypertensive effect measured at trough using once-a-day dosing is inadequate, a twice-a-day regimen at the same total daily dose or an increase in dose may give a more satisfactory response.
Hydrochlorothiazide is effective in doses of 12.5 to 50 mg once daily and can be given at doses of 12.5 to 25 mg as Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets.
To minimize dose-independent side effects, it is usually appropriate to begin combination therapy only after a patient has failed to achieve the desired effect with monotherapy.
The side effects (see WARNINGS) of losartan are generally rare and apparently independent of dose; those of hydrochlorothiazide are a mixture of dose-dependent (primarily hypokalemia) and dose-independent phenomena (e.g., pancreatitis), the former much more common than the latter. Therapy with any combination of losartan and hydrochlorothiazide will be associated with both sets of dose-independent side effects.
Replacement Therapy: The combination may be substituted for the titrated components.
Dose Titration by Clinical Effect: A patient whose blood pressure is not adequately controlled with losartan monotherapy (see above) or hydrochlorothiazide alone, may be switched to Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets 50 mg/12.5 mg (losartan 50 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg) once daily. If blood pressure remains uncontrolled after about 3 weeks of therapy, the dose may be increased to two tablets of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg/12.5 mg once daily or one tablet of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 100 mg/25 mg (losartan 100 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg) once daily. A patient whose blood pressure is not adequately controlled with losartan 100 mg monotherapy (see above) may be switched to Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets 100 mg/12.5 mg once daily. If blood pressure remains uncontrolled after about 3 weeks of therapy, the dose may be increased to two tablets of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg/12.5 mg once daily or one tablet of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 100 mg/25 mg (losartan 100 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg) once daily.
A patient whose blood pressure is inadequately controlled by 25 mg once daily of hydrochlorothiazide, or is controlled but who experiences hypokalemia with this regimen, may be switched to Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets 50 mg/12.5 mg (losartan 50 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg) once daily, reducing the dose of hydrochlorothiazide without reducing the overall expected antihypertensive response. The clinical response to Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets 50 mg/12.5 mg should be subsequently evaluated, and if blood pressure remains uncontrolled after about 3 weeks of therapy, the dose may be increased to two tablets of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets 50 mg/12.5 mg once daily or one tablet of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets 100 mg/25 mg (losartan 100 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg) once daily.
The usual dose of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide is one tablet of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg/12.5 mg once daily. More than two tablets of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg/12.5 mg once daily or more than one tablet of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 100 mg/25 mg once daily is not recommended. The maximal antihypertensive effect is attained about 3 weeks after initiation of therapy.
Use in Patients with Renal Impairment: The usual regimens of therapy with Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets may be followed as long as the patient's creatinine clearance is >30 mL/min. In patients with more severe renal impairment, loop diuretics are preferred to thiazides, so Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets are not recommended.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment: Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets are not recommended for titration in patients with hepatic impairment (see WARNINGS, Impaired Hepatic function) because the appropriate 25 mg starting dose of losartan cannot be given.
Severe Hypertension
The starting dose of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets for initial treatment of severe hypertension is one tablet of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg/12.5 mg once daily (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects). For patients who do not respond adequately to Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets 50 mg/12.5 mg after 2 to 4 weeks of therapy, the dosage may be increased to one tablet of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 100 mg/25 mg once daily. The maximum dose is one tablet of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide 100 mg/25 mg once daily. Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets are not recommended as initial therapy in patients with hepatic impairment (see WARNINGS, Impaired Hepatic Function) because the appropriate 25 mg starting dose of losartan cannot be given. It is also not recommended for use as initial therapy in patients with intravascular volume depletion (e.g., patients treated with diuretics, see WARNINGS, Hypotension ─ Volume-Depleted Patients).
Hypertensive Patients with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Treatment should be initiated with losartan potassium tablets 50 mg once daily. Hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg should be added or Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets 50 mg/12.5 mg substituted if the blood pressure reduction is inadequate. If additional blood pressure reduction is needed, losartan potassium tablets 100 mg and hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg or Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets 100 mg/12.5 mg may be substituted, followed by losartan potassium tablets 100 mg and hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg or Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets 100 mg/25 mg. For further blood pressure reduction other antihypertensives should be added (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, Losartan Potassium, Reduction in the Risk of Stroke).
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets may be administered with other antihypertensive agents.
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets may be administered with or without food.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 100 mg/12.5 mg are white to off white colored, oval shaped, biconvex film coated tablets, debossed with "1117" on one side and plain on other side.
Bottles of 90 NDC: 68258-6031-09
Storage
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) (See USP controlled room temperature). Protect from light.
Keep container tightly closed.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP
100 mg/12.5 mg
Rx only
Read the Patient Information that comes with Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your condition and treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets?
Do not take Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets can harm your unborn baby causing injury and even death. Stop taking Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets if you become pregnant and call your doctor right away. If you plan to become pregnant, talk to your doctor about other treatment options before taking Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets.
What are Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets?
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets contain 2 prescription medicines, an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) and a diuretic (water pill). It is used to:
- lower high blood pressure (hypertension). Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets are not usually the first medicine used to treat high blood pressure.
- lower the chance of stroke in patients with high blood pressure and a heart problem called left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets may not help Black patients with this problem.
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets have not been studied in children less than 18 years old.
High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Blood pressure is the force in your blood vessels when your heart beats and when your heart rests. You have high blood pressure when the force is too much. The losartan ingredient in Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets can help your blood vessels relax so your blood pressure is lower. The hydrochlorothiazide ingredient in Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets work by making your kidneys pass more water and salt.
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) is an enlargement of the walls of the left chamber of the heart (the heart’s main pumping chamber). LVH can happen from several things. High blood pressure is the most common cause of LVH.
Who should not take Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets?
Do not take Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets if you:
- are allergic to any ingredients in Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets. See a complete list of ingredients in Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets at the end of this leaflet.
- are allergic to any sulfonamide-containing ("sulfa") medicines. Ask your doctor if you are not sure what sulfonamide-containing ("sulfa") medicines are.
- are not passing urine.
What should I tell my doctor before taking Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets?
Tell your doctor about all your medical conditions including if you:
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. See "What is the most important information I should know about Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets?"
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets can pass into your milk and may harm your baby. You and your doctor should decide if you will take Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets or breast-feed. You should not do both.
- have been vomiting (throwing up), having diarrhea, sweating a lot, or not drinking enough fluids. These could cause you to have low blood pressure.
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems
- have systemic lupus erythematosus (Lupus; SLE)
- have diabetes
- have asthma
- have gout
- have any allergies
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets and certain other medicines may interact with each other. Especially tell your doctor if you are taking:
- potassium supplements
- salt substitutes containing potassium
- water pills (diuretics)
- lithium (a medicine used to treat a certain kind of depression)
- medicines used to treat pain and arthritis, called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including COX-2 inhibitors.
- other medicines to reduce blood pressure.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets?
- Take Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor may change your dose if needed.
- Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets can be taken with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is close to your next dose, do not take the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time.
- If you take too much Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, call your doctor or Poison Control Center, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
- Your doctor may do blood tests from time to time while you are taking Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets.
What are the possible side effects of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets?
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets may cause the following side effects that may be serious:
- injury or death of unborn babies. See "What is the most important information I should know about Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets?"
- allergic reaction. Symptoms of an allergic reaction are swelling of the face, lips, throat, or tongue. Get emergency medical help right away and stop taking Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets.
- low blood pressure (hypotension). Low blood pressure may cause you to feel faint or dizzy. Lie down if you feel faint or dizzy. Call your doctor right away.
- a new or worsening condition called systemic lupus erythematosus (Lupus; SLE)
- If you have kidney problems, you may see a worsening in how well your kidneys work. Call your doctor if you get swelling in your feet, ankles, or hands, or unexplained weight gain.
- If you have liver problems, you may see a worsening in how well your liver works. Call your doctor if you get nausea, pain in the right upper stomach area (abdomen), yellow eyes or skin (which can be itchy).
- Eye problems. One of the medicines in Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets can cause eye problems that, if left untreated, may lead to vision loss. Symptoms of eye problems can happen within hours to weeks of starting Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets.
Tell your doctor right away if you have:
○ decrease in vision
○ eye pain
The most common side effects of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets in people with high blood pressure are:
- "colds" (upper respiratory infection)
- dizziness
- stuffy nose
- back pain
- fast or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- rash
Tell your doctor if you get any side effect that bothers you or that won't go away. This is not a complete list of side effects. For a complete list, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets?
- Store Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) (See USP controlled room temperature).
- Keep Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets in a tightly closed container, and keep Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets out of the light.
- Keep Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets?
Active ingredients: losartan potassium, USP and hydrochlorothiazide, USP
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, talc and titanium dioxide. Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 50 mg/12.5 mg and Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 100 mg/25 mg also contain D and C yellow No. 10 lake. - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LOSARTAN POTASSIUM AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE
losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68258-6031(NDC:13668-117) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LOSARTAN POTASSIUM (UNII: 3ST302B24A) (LOSARTAN - UNII:JMS50MPO89) LOSARTAN POTASSIUM 100 mg HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE (UNII: 0J48LPH2TH) (HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE - UNII:0J48LPH2TH) HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE 12.5 mg Product Characteristics Color white (white to off white) Score no score Shape OVAL (oval shaped, biconvex film coated tablets) Size 16mm Flavor Imprint Code 117 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68258-6031-9 90 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA090528 04/06/2010 Labeler - Dispensing Solutions, Inc. (066070785) Registrant - PSS World Medical, Inc. (101822682) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Dispensing Solutions, Inc. 066070785 relabel, repack
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
