NURTEC ODT- rimegepant sulfate tablet, orally disintegrating
NURTEC ODT by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
NURTEC ODT by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use
See full prescribing information for
Initial U.S. ApprovalINDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The recommended dose is 75 mg taken orally, as needed. (2.1)
- The maximum dose in a 24-hour period is 75 mg. (2.1)
- The safety of treating more than 15 migraines in a 30-day period has not been established. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
NURTEC ODT orally disintegrating tablets: 75 mg (3) (4)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Patients with a history of hypersensitivity reaction to rimegepant, NURTEC ODT, or to any of its components. (4) (5)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions: If a serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue NURTEC ODT and initiate appropriate therapy. Severe hypersensitivity reactions have included dyspnea and rash, and can occur days after administration. (5.1) (6)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant administration. (7.1)
- Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Avoid another dose within 48 hours when administered with a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor. (7.1)
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Avoid concomitant administration. (7.2)
- Inhibitors of P-gp or BCRP: Avoid concomitant administration. (7.3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Exposures were significantly higher in subjects with severe hepatic impairment. Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C). (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Information
2.2 Administration Information
2.3 Concomitant Administration with Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
2.4 Concomitant Administration with Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inducers
2.5 Concomitant Administration with Inhibitors of P-gp or BCRP
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 Warning and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP3A4 Inhibitors7.2 CYP3A Inducers
7.3 Transporters
8 IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.5 Pharmacogenomics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
PATIENT INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 2.1 Dosing Information
-
2.2 Administration Information
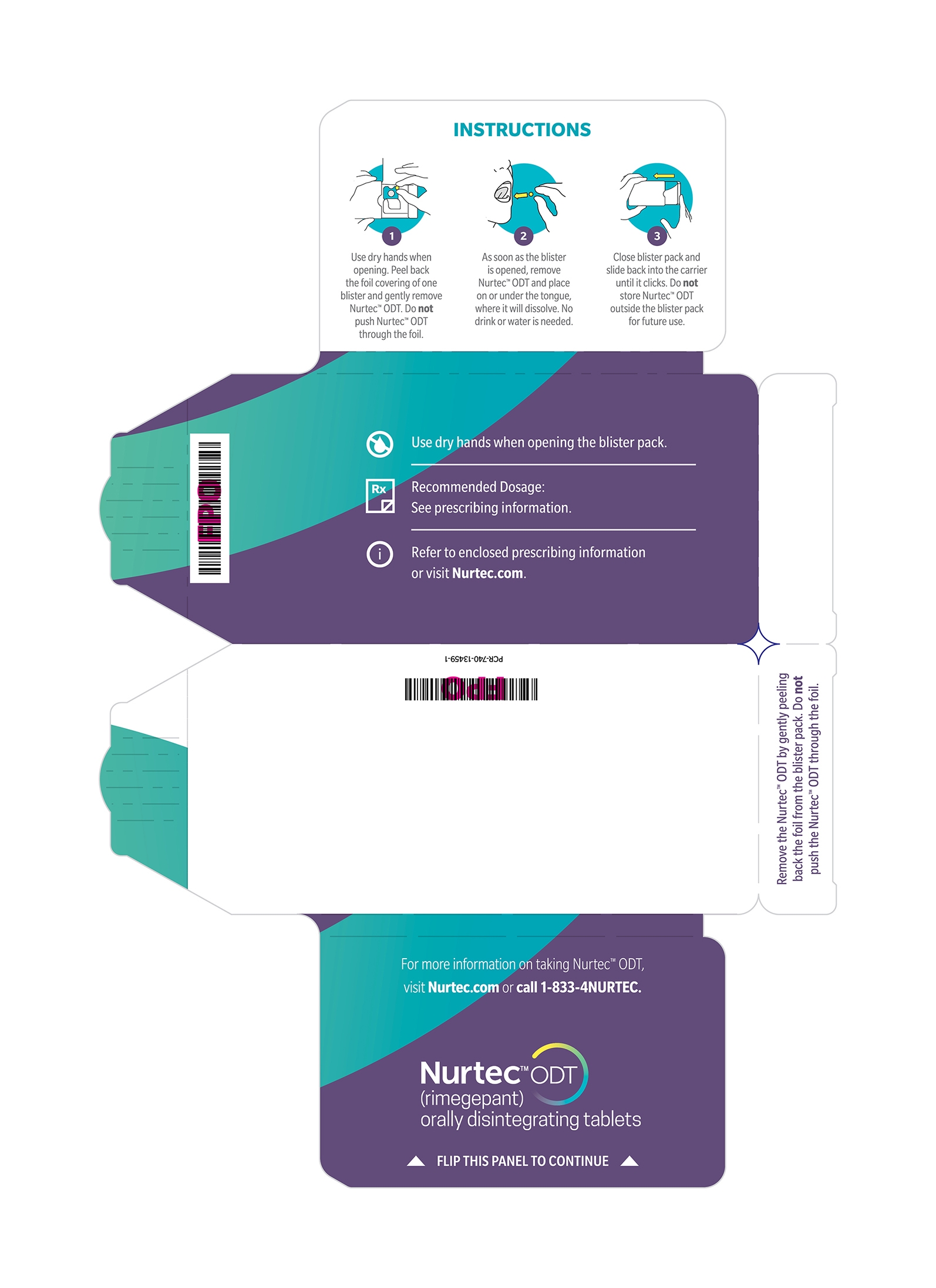
Instruct the patient on the following administration instructions:
- Use dry hands when opening the blister pack.
- Peel back the foil covering of one blister and gently remove the orally disintegrating tablet (ODT). Do not push the ODT through the foil.
- As soon as the blister is opened, remove the ODT and place on the tongue; alternatively, the ODT may be placed under the tongue.
- The ODT will disintegrate in saliva so that it can be swallowed without additional liquid.
- Take the ODT immediately after opening the blister pack. Do not store the ODT outside the blister pack for future use.
- 2.3 Concomitant Administration with Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
- 2.4 Concomitant Administration with Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inducers
- 2.5 Concomitant Administration with Inhibitors of P-gp or BCRP
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 Warning and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including dyspnea and rash, have occurred with NURTEC ODT in clinical studies. Hypersensitivity reactions can occur days after administration, and delayed serious hypersensitivity has occurred. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue NURTEC ODT and initiate appropriate therapy [ see Contraindications (4)].
- 6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
-
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of NURTEC ODT has been evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (Study 1) in 682 patients with migraine who received one 75 mg dose of NURTEC ODT [ see Clinical Studies (14)]. Approximately 85% were female, 74% were White, 21% were Black, and 17% were Hispanic or Latino. The mean age at study entry was 40 years (range 18-75 years of age).
Long-term safety was assessed in an open-label extension study using a different oral dosage form of rimegepant. That study evaluated 1,798 patients, dosing intermittently for up to one year, including 1,131 patients who were exposed to rimegepant 75 mg for at least 6 months, and 863 who were exposed for at least one year, all of whom treated an average of at least two migraine attacks per month.
The most common adverse reaction in Study 1 was nausea (2% in patients who received NURTEC ODT compared to 0.4% of patients who received placebo).
Hypersensitivity, including dyspnea and severe rash, occurred in less than 1% of patients treated with NURTEC ODT [ see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Concomitant administration of NURTEC ODT with strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 results in a significant increase in rimegepant exposure. Avoid concomitant administration of NURTEC ODT with strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Concomitant administration of NURTEC ODT with moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4 may result in increased exposure of rimegepant. Avoid another dose of NURTEC ODT within 48 hours when it is concomitantly administered with moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4 [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
7.2 CYP3A Inducers
Concomitant administration of NURTEC ODT with strong or moderate inducers of CYP3A can result in a significant reduction in rimegepant exposure, which may lead to loss of efficacy of NURTEC ODT. Avoid concomitant administration of NURTEC ODT with strong or moderate inducers of CYP3A [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 7.3 Transporters
-
8 IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of NURTEC ODT in pregnant women. In animal studies, oral administration of rimegepant during organogenesis resulted in adverse effects on development in rats (decreased fetal body weight and increased incidence of fetal variations) at exposures greater than those used clinically and which were associated with maternal toxicity. The evaluation of developmental effects following oral administration of rimegepant throughout pregnancy and lactation was inadequate (see Data).
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively. The estimated rate of major birth defects (2.2 to 2.9%) and miscarriage (17%) among deliveries to women with migraine are similar to rates reported in women without migraine.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Published data have suggested that women with migraine may be at increased risk of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension during pregnancy.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of rimegepant (0, 10, 60, or 300 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in decreased fetal body weight and an increased incidence of fetal variations at the highest dose tested (300 mg/kg/day), which was associated with maternal toxicity. Plasma exposures (AUC) at the no-effect dose (60 mg/kg/day) for adverse effects on embryofetal development were approximately 45 times that in humans at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 75 mg/day.
Oral administration of rimegepant (0, 10, 25, or 50 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in no adverse effects on embryofetal development. The highest dose tested (50 mg/kg/day) was associated with plasma exposures (AUC) approximately 10 times that in humans at the MRHD.
The prenatal and postnatal development study in rats, in which rimegepant (0, 10, 25, or 60 mg/kg/day) was orally administered throughout gestation and lactation, was inadequate to assess for adverse effects of rimegepant during these periods of development.
-
8.2 Lactation
There are no data on the presence of rimegepant or its metabolites in human milk, the effects of rimegepant on the breastfed infant, or the effects of rimegepant on milk production. There are no animal data on the excretion of rimegepant in milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for NURTEC ODT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from NURTEC ODT or from the underlying maternal condition.
- 8.4 Pediatric Use
- 8.5 Geriatric Use
-
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of NURTEC ODT is required in patients with mild (Child-Pugh A) or moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment. Plasma concentrations of rimegepant were significantly higher in subjects with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment. Avoid use of NURTEC ODT in patients with severe hepatic impairment [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8.7 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of NURTEC ODT is required in patients with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment. NURTEC ODT has not been studied in patients with end-stage renal disease and in patients on dialysis. Avoid use of NURTEC ODT in patients with end-stage renal disease (CLcr < 15 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is limited clinical experience with NURTEC ODT overdosage. Treatment of an overdose of NURTEC ODT should consist of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient. No specific antidote for the treatment of rimegepant overdose is available. Rimegepant is unlikely to be significantly removed by dialysis because of high serum protein binding [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
NURTEC ODT contains rimegepant sulfate, a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist. Rimegepant sulfate is described chemically as (5S,6S,9R)-5-amino-6-(2,3-difluorophenyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-cyclohepta[b]pyridin-9-yl 4-(2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)-1-piperidinecarboxylate hemisulfate sesquihydrate and its structural formula is:
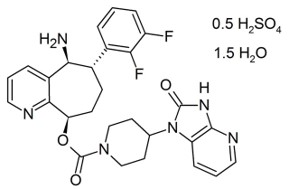
Its empirical formula is C 28H 28F 2N 6O 3 0.5 H 2SO 4 1.5 H 2O, representing a molecular weight of 610.63. Rimegepant free base has a molecular weight of 534.56. Rimegepant sulfate is a white to off-white, crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water.
NURTEC ODT (orally disintegrating tablets) is for sublingual or oral use and contains 85.65 mg rimegepant sulfate, equivalent to 75 mg rimegepant free base, and the following inactive ingredients: benzyl alcohol, eucalyptol, gelatin, limonene, mannitol, menthol, menthone, menthyl acetate, sucralose, and vanillin.
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 12.1 Mechanism of Action
-
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The relationship between pharmacodynamic activity and the mechanism(s) by which rimegepant exerts its clinical effects is unknown.
No clinically relevant differences in resting blood pressure were observed when rimegepant was concomitantly administered with sumatriptan (12 mg subcutaneous, given as two 6 mg doses separated by one hour) compared with sumatriptan alone to healthy volunteers.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a single dose 4 times the recommended dose, rimegepant does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
-
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration of NURTEC ODT, rimegepant is absorbed with the maximum concentration at 1.5 hours. The absolute oral bioavailability of rimegepant is approximately 64%.
Effects of Food
Following administration of NURTEC ODT under fed condition with a high-fat meal, T max was delayed by 1 hour and resulted in a 42 to 53% reduction in C max and a 32 to 38% reduction in AUC. NURTEC ODT was administered without regard to food in clinical safety and efficacy studies. The impact of the reduction in rimegepant exposure because of administration with food on its efficacy is unknown.
Distribution
The steady state volume of distribution of rimegepant is 120 L. Plasma protein binding of rimegepant is approximately 96%.
Elimination
Metabolism
Rimegepant is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9.
Rimegepant is primarily eliminated in unchanged form (~77% of the dose) with no major metabolites (i.e., > 10%) detected in plasma.
Excretion
The elimination half-life of rimegepant is approximately 11 hours in healthy subjects. Following oral administration of [ 14C]-rimegepant to healthy male subjects, 78% of the total radioactivity was recovered in feces and 24% in urine. Unchanged rimegepant is the major single component in excreted feces (42%) and urine (51%).
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
In a dedicated clinical study comparing the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant in subjects with mild (estimated creatinine clearance [CLcr] 60-89 mL/min), moderate (CLcr 30-59 mL/min), and severe (CLcr 15-29 mL/min) renal impairment to that with normal subjects (healthy matched control), the exposure of rimegepant following single 75 mg dose was approximately 40% higher in subjects with moderate renal impairment. However, there was no clinically meaningful difference in the exposure of rimegepant in subjects with severe renal impairment compared to subjects with normal renal function (CLcr >=90mL/min). NURTEC ODT has not been studied in patients with end-stage renal disease (CLcr < 15 mL/min) [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Hepatic Impairment
In a dedicated clinical study comparing the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment to that with normal subjects (healthy matched control), the exposure of rimegepant (C max and AUC) following single 75 mg dose was approximately 2-fold higher in subjects with severe impairment (Child-Pugh class C). There were no clinically meaningful differences in the exposure of rimegepant in subjects with mild (Child-Pugh class A) and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B) compared to subjects with normal hepatic function [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Other Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant were observed based on age, sex, race/ethnicity, body weight, or CYP2C9 genotype [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)].
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Studies
- Enzymes
Rimegepant is a substrate of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 ( see In Vivo Studies). Rimegepant is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or UGT1A1 at clinically relevant concentrations. However, rimegepant is a weak inhibitor of CYP3A4 with time-dependent inhibition. Rimegepant is not an inducer of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, or CYP3A4 at clinically relevant concentrations.
- Transporters
Rimegepant is a substrate of P-gp and BCRP. Concomitant administration of inhibitors of P-gp or BCRP may increase the exposure of rimegepant [ see Drug Interactions (7.3)]. No dedicated drug interaction study was conducted to assess their effects on the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant.
Rimegepant is not a substrate of OATP1B1 or OATP1B3. Considering its low renal clearance, rimegepant was not evaluated as a substrate of the OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, or MATE2‑K.
Rimegepant is not an inhibitor of P-gp, BCRP, OAT1, or MATE2-K at clinically relevant concentrations. It is a weak inhibitor of OATP1B1 and OAT3. Rimegepant is an inhibitor of OATP1B3, OCT2, and MATE1. No clinical drug interactions are expected for NURTEC ODT with these transporters at clinically relevant concentrations.
In Vivo Studies
CYP3A4 Inhibitors
In a dedicated drug interaction study, concomitant administration of 75 mg rimegepant (single dose) with itraconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, at steady state resulted in increased exposures of rimegepant (AUC by 4-fold and C max by ~1.5-fold) [ see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. No dedicated drug interaction study was conducted to assess the effect of concomitant administration of a weak inhibitor of CYP3A4 on the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant. The concomitant administration of rimegepant with a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4 may increase rimegepant exposures (AUC) by less than 2-fold [ see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Concomitant administration of rimegepant with a weak inhibitor of CYP3A4 is not expected to have a clinically significant impact on rimegepant exposures.
CYP3A Inducers
In a dedicated drug interaction study, concomitant administration of 75 mg rimegepant (single dose) with rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, at steady state resulted in decreased exposures of rimegepant (AUC by 80% and C max by 64%), which may lead to loss of efficacy [ see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. No dedicated drug interaction study was conducted to assess the effect of concomitant administration of a moderate or weak inducer of CYP3A4 on the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant. Since rimegepant is a moderately sensitive substrate for CYP3A4, drugs that are moderate inducers of CYP3A4 can also cause significant reduction in rimegepant exposure resulting in loss of efficacy [ see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Clinically significant interaction is not expected with concomitant administration of weak inducers of CYP3A4 and rimegepant.
CYP2C9 Inhibitors
In a dedicated drug interaction study, concomitant administration of 75 mg rimegepant (single dose) with fluconazole, a combined moderate CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 inhibitor, resulted in increased exposures of rimegepant (AUC by 1.8-fold) with no relevant effect on C max. Rimegepant is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9. Increase in the exposure of rimegepant can be attributed to combined inhibition of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 with fluconazole administration suggesting a minor contribution from CYP2C9. Thus, CYP2C9 inhibition alone is not expected to significantly affect rimegepant exposures.
Other Drugs:
No significant pharmacokinetic interactions were observed when rimegepant was concomitantly administered with oral contraceptives (norelgestromin, ethinyl estradiol), midazolam (a sensitive CY3A4 substrate), or sumatriptan [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
-
12.5 Pharmacogenomics
CYP2C9 activity is reduced in individuals with genetic variants such as the CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 alleles. Rimegepant Cmax and AUC0-inf were similar in CYP2C9 intermediate metabolizers (i.e., *1/*2, *2/*2, *1/*3, n=43) as compared to normal metabolizers (i.e., *1/*1, N=72). Adequate PK data are not available from CYP2C9 poor metabolizers (i.e., *2/*3). Since the contribution of CYP2C9 to rimegepant metabolism is considered minor, CYP2C9 polymorphism is not expected to significantly affect its exposure.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Oral administration of rimegepant to Tg.rasH2 mice (0, 10, 100, or 300 mg/k/day) for 26 weeks and to rats (0, 5, 20, or 45 mg/kg/day) for 91-100 weeks resulted in no evidence of drug-induced tumors in either species. In rats, the plasma exposure (AUC) at the highest dose tested (45 mg/kg/day) was approximately 30 times that in humans at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 75 mg/day.
Mutagenesis
Rimegepant was negative in in vitro (bacterial reverse-mutation, chromosomal aberration in Chinese hamster ovary cells) and in vivo (rat micronucleus) assays.
Impairment of Fertility
Oral administration of rimegepant (0, 30, 60, or 150 mg/kg/day) to male and female rats prior to and during mating and continuing in females to gestation day (GD) 7 resulted in uterine atrophy at all doses and reduced fertility at the highest dose tested. In a second fertility study testing lower doses (0, 5, 15, or 25 mg/kg/day), no adverse effects on fertility, uterine histopathology, or early embryonic development were observed. The no-effect dose for impairment of fertility and early embryonic development in rats (25 mg/kg/day) was associated with plasma drug exposures (AUC) approximately 15 times that in humans at the MRHD.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of NURTEC ODT for the acute treatment of migraine with and without aura in adults was demonstrated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial: Study 1 (NCT03461757). The study randomized patients to 75 mg of NURTEC ODT (N=732) or placebo (N=734). Patients were instructed to treat a migraine of moderate to severe headache pain intensity. Rescue medication (i.e., NSAIDs, acetaminophen, and/or an antiemetic) was allowed 2 hours after the initial treatment. Other forms of rescue medication such as triptans were not allowed within 48 hours of initial treatment. Approximately 14% of patients were taking preventive medications for migraine at baseline. None of the patients in Study 1 were on concomitant preventive medication that act on the CGRP pathway.
The primary efficacy analyses were conducted in patients who treated a migraine with moderate to severe pain. NURTEC ODT 75 mg demonstrated an effect on pain freedom and most bothersome symptom (MBS) freedom at two hours after dosing, compared to placebo. Pain freedom was defined as a reduction of moderate or severe headache pain to no headache pain, and MBS freedom was defined as the absence of the self-identified MBS (i.e., photophobia, phonophobia, or nausea). Among patients who selected an MBS, the most commonly selected symptom was photophobia (54%), followed by nausea (28%), and phonophobia (15%).
In Study 1, the percentage of patients achieving headache pain freedom and MBS freedom two hours after a single dose was statistically significantly greater in patients who received NURTEC ODT compared to those who received placebo (Table 1).
Table 1: Migraine Efficacy Endpoints for Study 1
Study 1 NURTEC ODT
75 mgPlacebo
Pain Free at 2 hours n/N* 142/669 74/682 % Responders 21.2 10.9 Difference from placebo (%) 10.3 p-value <0.001 MBS Free at 2 hours n/N* 235/669 183/682 % Responders 35.1 26.8 Difference from placebo (%) 8.3 p-value 0.001 *n=number of responders/N=number of patients in that treatment group
Figure 1 presents the percentage of patients achieving migraine pain freedom within 2 hours following treatment in Study 1.
Figure 1: Percentage of Patients Achieving Pain Freedom within 2 Hours in Study 1
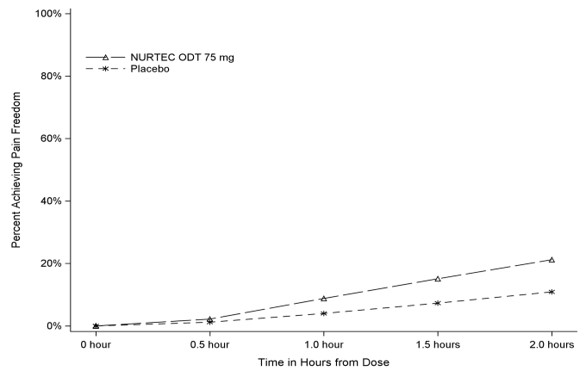
Figure 2 presents the percentage of patients achieving MBS freedom within 2 hours in Study 1.
Figure 2: Percentage of Patients Achieving MBS Freedom within 2 Hours in Study 1
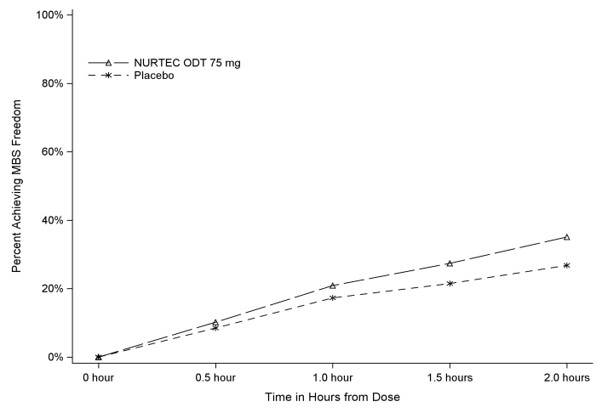
Table 2. Additional Migraine Efficacy Endpoints in Study 1
Study 1 NURTEC ODT
75 mgPlacebo Pain Relief at 2 hours n/N* 397/669 295/682 % Responders 59.3 43.3 Difference from placebo 16.1 p-value <0.001 Sustained Pain Freedom 2-48 hours
n/N* 90/669 37/682 % Responders 13.5 5.4 Difference from placebo 8.0 p-value <0.001 Use of Rescue Medication within 24 hours**
n/N* 95/669 199/682 % Responders 14.2 29.2 Difference from placebo -15.0 p-value <0.001 Percentage of Patients Reporting Normal Function at 2 hours n/N* 255/669 176/682 % Responders 38.1 25.8 Difference from placebo 12.3 p-value <0.001 *n=number of responders/N=number of patients in that treatment group
**This analysis includes only the use of NSAIDs, acetaminophen, or antiemetics, within 24 hours post-dose; the use of triptans, or other acute migraine medication, was not allowed.
The incidence of photophobia and phonophobia was reduced following administration of NURTEC ODT 75 mg as compared to placebo.
-
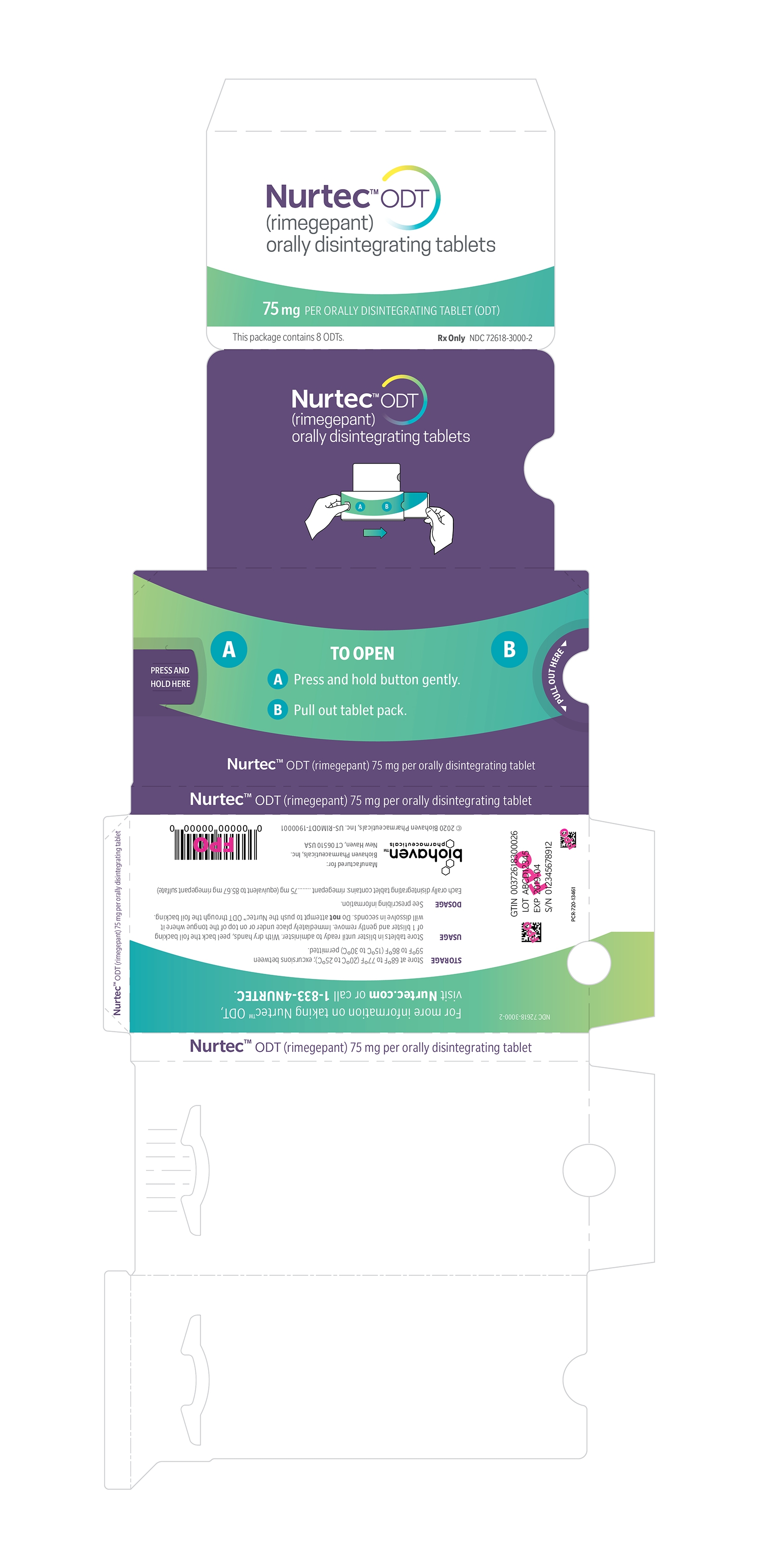
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
NURTEC ODT 75 mg orally disintegrating tablets are white to off-white, circular, debossed with the symbol
 , and supplied in cartons containing a blister pack of 8 orally disintegrating tablets. Each ODT contains 75 mg rimegepant.
, and supplied in cartons containing a blister pack of 8 orally disintegrating tablets. Each ODT contains 75 mg rimegepant.
NDC: 72618-3000-2
- 16.2 Storage and Handling
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Handling of Orally Disintegrating Tablets Packaging
Instruct patients not to remove the blister from the outer aluminum pouch until ready to use the orally disintegrating tablet inside [ see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions and that these reactions can occur days after administration of NURTEC ODT. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately if signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions occur [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT INFORMATION
PATIENT INFORMATION
NURTEC™ ODT (NUR-tek)
(rimegepant sulfate)
orally disintegrating tablets (ODT)What is NURTEC ODT?
NURTEC ODT is a prescription medicine used for the acute treatment of migraine attacks with or without aura in adults.
- NURTEC ODT is not used as a preventive treatment of migraine.
- It is not known if NURTEC ODT is safe and effective in children.
Do not take NURTEC ODT if you are:
- allergic to rimegepant or any of the ingredients in NURTEC ODT.
Before you take NURTEC ODT, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver problems.
- have kidney problems.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if NURTEC ODT will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if NURTEC ODT passes into your breast milk.
How should I take NURTEC ODT?
- Take NURTEC ODT exactly how your healthcare provider tells you to.
- NURTEC ODT can be taken 1 time each day as needed. You should not take more than 1 tablet in 24 hours.
- It is not known if it is safe to take NURTEC ODT for more than 15 migraine headaches in 30 days.
- To take NURTEC ODT:
- Use dry hands when opening the blister pack.
- Peel back the foil covering of one blister and gently remove NURTEC ODT. Do not push NURTEC ODT through the foil.
- As soon as the blister is opened, remove NURTEC ODT and place on or under the tongue.
- NURTEC ODT will dissolve and no drink or water is needed.
- Take NURTEC ODT immediately after opening the blister pack. Do not store NURTEC ODT outside the blister pack for future use.
- If you take too much NURTEC ODT, go to the nearest emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of NURTEC ODT?
NURTEC ODT may cause serious side effects including:
- Allergic reactions. Allergic reactions, including trouble breathing and rash, can happen after you take NURTEC ODT. This can happen days after you take NURTEC ODT. Call your healthcare provider or get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms, which may be part of an allergic reaction:
- Swelling of the face, mouth, tongue, or throat
- Trouble breathing
The most common side effect of NURTEC ODT is:
- nausea
This is not the only possible side effect of NURTEC ODT.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800 FDA-1088.How should I store NURTEC ODT?
- Store NURTEC ODT in the blister package that it comes in.
- Store NURTEC ODT at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
General information about the safe and effective use of NURTEC ODT:
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use NURTEC ODT for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NURTEC ODT to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about NURTEC ODT that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in NURTEC ODT?
Active ingredient in NURTEC ODT: rimegepant
Inactive ingredients in NURTEC ODT: benzyl alcohol, eucalyptol, gelatin, limonene, mannitol, menthol, menthone, menthyl acetate, sucralose, and vanillin
Manufactured for:
Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
New Haven, CT 06510 USA

NURTEC and Biohaven are trademarks of Biohaven Pharmaceutical Holding Company Ltd.
For more information, go to www.nurtec.com or call 1-833-4NURTEC.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Issued: 2/2020
- Dose pack - Outer Sleeve Label (Carton)
- Dose pack - Inner Sleeve Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
NURTEC ODT
rimegepant sulfate tablet, orally disintegratingProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72618-3000 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength RIMEGEPANT SULFATE (UNII: 1383NM3Q0H) (RIMEGEPANT - UNII:997WVV895X) RIMEGEPANT 75 mg in 75 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LIMONENE, (+)- (UNII: GFD7C86Q1W) BENZYL ALCOHOL (UNII: LKG8494WBH) MENTHYL ACETATE, (+/-)- (UNII: LF3LEI45OH) VANILLIN (UNII: CHI530446X) MENTHOL (UNII: L7T10EIP3A) MENTHONE, (+)- (UNII: 15F1B5K9A5) MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) SUCRALOSE (UNII: 96K6UQ3ZD4) EUCALYPTOL (UNII: RV6J6604TK) GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) Product Characteristics Color white (white to off-white) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 14mm Flavor MINT Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72618-3000-2 1 in 1 CARTON 03/05/2020 1 75 mg in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 
Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212728 03/05/2020 Labeler - Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, Inc (079870003)
Trademark Results [NURTEC ODT]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 NURTEC ODT 88840180 not registered Live/Pending |
Biohaven Pharmaceutical Holding CompanyLtd. 2020-03-19 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.