DEPO-MEDROL- methylprednisolone acetate injection, suspension
Depo-Medrol by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Depo-Medrol by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Zoetis Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- Caution
-
DESCRIPTION
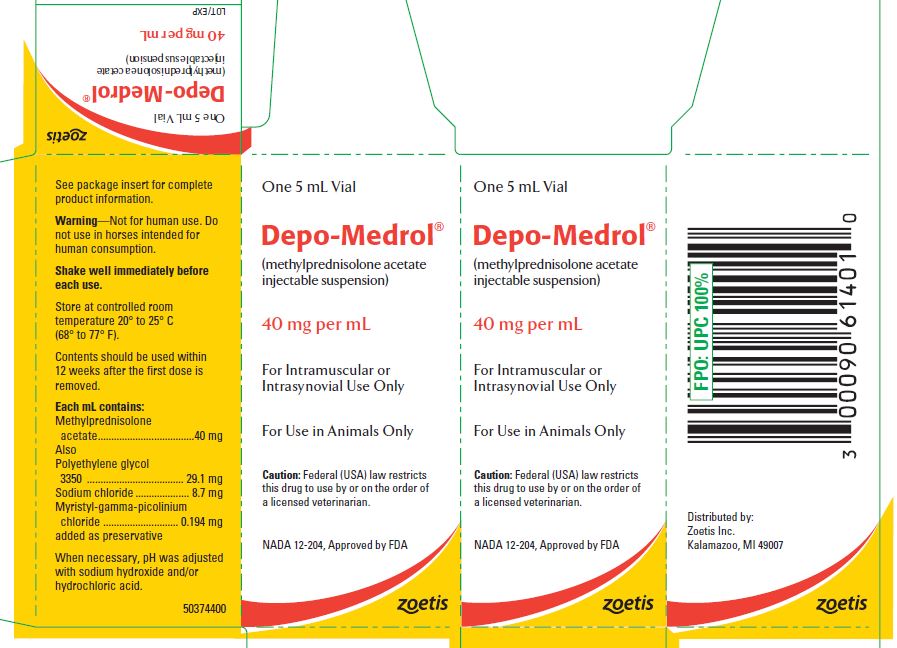
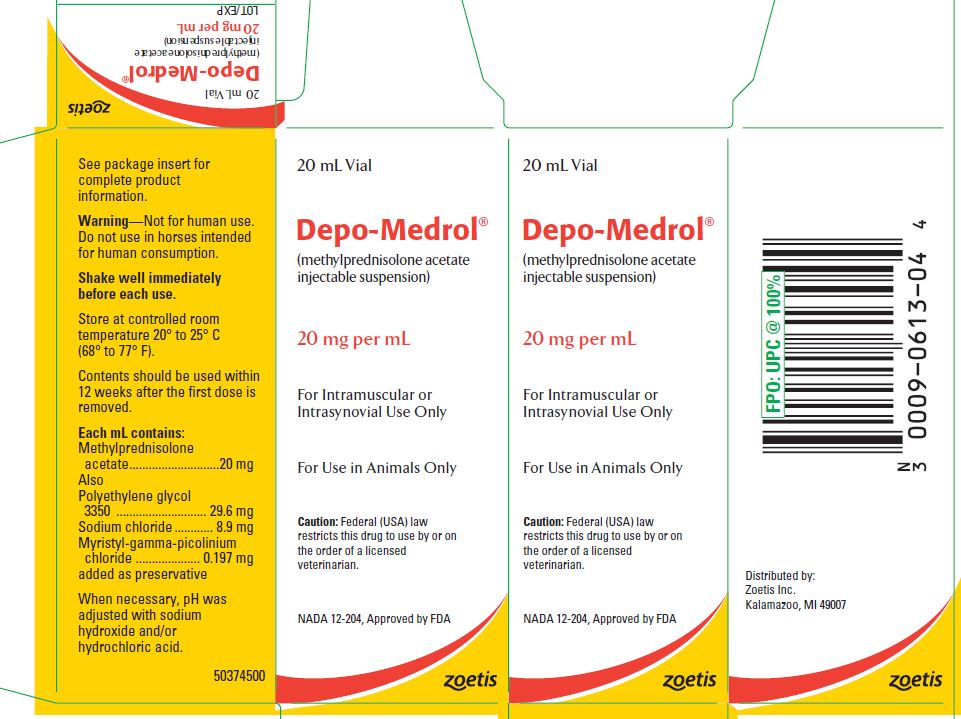
These preparations are recommended for intramuscular and intrasynovial injection in horses and dogs, and intramuscular injection in cats. DEPO-MEDROL is available in two concentrations, 20 mg per mL and 40 mg per mL. Each mL of these preparations contains:
20 mg 40 mg When necessary, pH was adjusted with sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid. The chemical name for methylprednisolone acetate is pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 21-(acetyloxy)-11,17-dihydroxy-6-methyl-, (6α,11ß)-
Methylprednisolone acetate 20 mg 40 mg Polyethylene glycol 3350 29.6 mg 29.1 mg Sodium chloride 8.9 mg 8.7 mg Myristyl-gamma-picolinium chloride added as preservative 0.197 mg 0.194 mg -
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Metabolic and Hormonal Effects
Methylprednisolone, an anti-inflammatory steroid synthesized and developed in the
Research Laboratories of The Upjohn Company, is the 6-methyl derivative of
prednisolone. Exceeding prednisolone in anti-inflammatory potency and having even
less tendency than prednisolone to induce sodium and water retention,methylprednisolone
offers the advantage over older corticosteroids of affording
equally satisfactory anti-inflammatory effect with the use of lower doses and with an
enhanced split between anti-inflammatory and mineralocorticoid activities. Estimates
of the relative potencies of methylprednisolone and prednisolone range from
1.13 to 2.1, with an average of 1.5. In anti-inflammatory activity, as measured by the
granuloma pouch assay, methylprednisolone is twice as active as prednisolone. In
mineralocorticoid activity (ie, the capacity to induce retention of sodium and water in
the adrenalectomized rat) methylprednisolone is slightly less active than prednisolone.
The duration of plasma steroid levels following rapid intravenous injection in intact
dogs is appreciably longer for methylprednisolone than for prednisolone, the
respective “half-life” value for the two steroids being 80.9 ± 7.5 minutes for methylprednisolone
and 71.3 ±1.7 minutes for prednisolone.While the effect of parenterally administered DEPO-MEDROL is prolonged, it has
the same metabolic and anti-inflammatory actions as orally administered methylprednisolone
acetate. -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Musculoskeletal Conditions
As with other adrenal steroids, DEPO-MEDROL has
been found useful in alleviating the pain and lameness associated with acute localized
arthritic conditions and generalized arthritic conditions. It has been used successfully
to treat rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic arthritis, osteoarthritis, periostitis, tendinitis,
synovitis, tenosynovitis, bursitis, and myositis of horses; traumatic arthritis,
osteoarthritis, and generalized arthritic conditions of dogs. Remission of musculoskeletal
conditions may be permanent, or symptoms may recur, depending on the cause and
extent of structural degeneration.
Allergic Conditions
This preparation is especially beneficial in relieving pruritus
and inflammation of allergic dermatitis, acute moist dermatitis, dry eczema, urticaria,
bronchial asthma, pollen sensitivities and otitis externa in dogs; allergic dermatitis and
moist and dry eczema in cats. Onset of relief may begin within a few hours to a few
days following injection and may persist for a few days to six weeks. Symptoms may
be expected to recur if the cause of the allergic reaction is still present, in which case
retreatment may be indicated. In treating acute hypersensitivity reactions, such as
anaphylactic shock, intravenous SOLU-DELTA-CORTEF® Sterile Powder containing
prednisolone sodium succinate, as well as other appropriate treatments, should be
used.Overwhelming Infections with Severe Toxicity
In dogs and cats moribund from
overwhelmingly severe infections for which antibacterial therapy is available (eg,
critical pneumonia, pyometritis), DEPO-MEDROL may be lifesaving, acting to inhibit
the inflammatory reaction, which itself may be lethal; preventing vascular collapse
and preserving the integrity of the blood vessels; modifying the patient’s reaction to
drugs; and preventing or reducing the exudative reaction which often complicates
certain infections. As supportive therapy, it improves the general attitude of the animal
being treated. All necessary procedures for the establishment of a bacterial diagnosis
should be carried out whenever possible before institution of therapy. Corticosteroid
therapy in the presence of infection should be administered for the shortest possible
time compatible with maintenance of an adequate response, and antibacterial therapy
should be continued for at least three days after the hormone has been withdrawn.
Combined hormone and antibacterial therapy does not obviate the need for indicated
surgical treatment.Other Conditions
In certain conditions where it is desired to reduce inflammation,
vascularization, fibroblastic infiltration, and scar tissue, the use of DEPO-MEDROL
should be considered. Snakebite of dogs also is an indication for the use of this
suspension because of its anti-toxemic, anti-shock, and anti-inflammatory activity. It
is particularly effective in reducing swelling and preventing sloughing. Its employment
in the treatment of such conditions is recommended as a supportive measure to
standard procedures and time-honored treatments and will give comfort to the animal
and hasten complete recovery. -
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Systemic therapy with methylprednisolone acetate, as with other corticoids, is
contraindicated in animals with arrested tuberculosis, peptic ulcer, and Cushing’s
syndrome. The presence of active tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, renal
insufficiency, predisposition to thrombophlebitis, hypertension, or congestive heart
failure necessitates carefully controlled use of corticosteroids. Intrasynovial,
intratendinous, or other injections of corticosteroids for local effect are contraindicated
in the presence of acute infectious conditions. Exacerbation of pain, further loss of
joint motion, with fever and malaise following injection may indicate that the condition
has become septic. Appropriate antibacterial therapy should be instituted immediately. -
WARNING
Clinical and experimental data have demonstrated that corticosteroids administered
orally or parenterally to animals may induce the first stage of parturition when administered
during the last trimester of pregnancy and may precipitate premature
parturition followed by dystocia, fetal death, retained placenta and metritis.Additionally, corticosteroids administered to dogs, rabbits, and rodents during
pregnancy have resulted in cleft palate in offspring. Corticosteroids administered to
dogs during pregnancy have also resulted in other congenital anomalies, including
deformed forelegs, phocomelia, and anasarca.Not for human use. Do not use in horses intended for human consumption.
-
PRECAUTIONS
DEPO-MEDROL exerts an inhibitory influence on the mechanisms and the tissue
changes associated with inflammation. Vascular permeability is decreased, exudation
diminished, and migration of the inflammatory cells markedly
inhibited. In addition, systemic manifestations such as fever and signs of toxemia may also be suppressed.
While certain aspects of this alteration of the inflammatory reaction may be beneficial,
the suppression of inflammation may mask the signs of infection and tend to facilitate
spread of microorganisms. Hence, all patients receiving this drug should be watched
for evidence of intercurrent infection. Should infection occur, it must be brought under
control by the use of appropriate antibacterial measures, or administration of this preparation
should be discontinued. However, in infections characterized by
overwhelming toxicity, methylprednisolone acetate therapy in conjunction with
appropriate antibacterial therapy is effective in reducing mortality and morbidity.
Without conjoint use of an antibiotic to which the invader-organism is sensitive,
injudicious use of the adrenal hormones in animals with infections can be hazardous.
As with other corticoids, continued or prolonged use is discouraged.While no sodium retention or potassium depletion has been observed at the doses
recommended, animals receiving methylprednisolone acetate, as with all corticoids,
should be under close observation for possible untoward effects. If symptoms of
hypopotassemia (hypokalemia) should occur, corticoid therapy should be discontinued
and potassium chloride administered by continuous intravenous drip.Since this drug lacks significant mineralocorticoid activity in usual therapeutic
doses, it is not likely to afford adequate support in states of acute adrenocortical
insufficiency. For treatment of the latter, the parent adrenocortical steroids,
hydrocortisone or cortisone, should be used. -
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
INTRAMUSCULAR
Following intramuscular injection of methylprednisolone acetate, a prolonged
systemic effect results. The dose varies with the size of the animal patient, the
severity of the condition under treatment, and the animal’s response to therapy.
Dogs and Cats
The average intramuscular dose for dogs is 20 mg. In accordance
with the size of the dog and severity of the condition under treatment, the dose may
range from 2 mg in miniature breeds to 40 mg in medium breeds, and even as high
as 120 mg in extremely large breeds or dogs with severe involvement.The average intramuscular dose for cats is 10 mg with a range up to 20 mg.
Injections may be made at weekly intervals or in accordance with the severity of the
condition and clinical response..
Horses
The usual intramuscular dose for horses is 200 mg repeated as necessary.
For maintenance therapy in chronic conditions, initial doses should be reduced
gradually until the smallest effective (ie, individualized) dose is established.
MEDROL® Tablets containing methylprednisolone may also be used for maintenance
in dogs and cats, administered according to the recommended dose.
When treatment is to be withdrawn after prolonged and intensive therapy, the dose
should be reduced gradually.If signs of stress are associated with the condition being treated, the dose should be
increased. If a rapid hormonal effect of maximum intensity is required, as in
anaphylactic shock, the intravenous administration of highly soluble SOLU-DELTACORTEF®
Sterile Powder containing prednisolone sodium succinate is indicated.INTRASYNOVIAL
Methylprednisolone acetate, a slightly soluble ester of methylprednisolone, is
capable of producing a more prolonged local anti-inflammatory effect than equimolar
doses of hydrocortisone acetate. Following intrasynovial injection, relief from pain
may be experienced within 12 to 24 hours. The duration of relief varies, but averages
three to four weeks, with a range of one to five or more weeks. Injections of
methylprednisolone acetate have been well tolerated. Intrasynovial (intra-articular)
injections may occasionally result in an increased localized inflammatory response.Intrasynovial injection is recommended as an adjuvant to general therapeutic
measures to effect suppression of inflammation in one or a few peripheral structures
when (1) the disease is limited to one or a few peripheral structures; (2) the disease
is widespread
with one or a few peripheral structures actively inflamed; (3) systemic
therapy with other corticoids or corticotropin controls all but a few of the more actively
involved structures; (4) systemic therapy with cortisone, hydrocortisone, or corticotropin
is contraindicated; (5) joints show early but actively progressing deformity (to enhance
the effect of physiotherapy and corrective procedures); and (6) surgical or other
orthopedic corrective measures are to be or have been done.The action of DEPO-MEDROL injected intrasynovially appears to be well localized
since significant metabolic effects characteristic of systemic administration of adrenal
steroids have not been observed. In a few instances mild and transient improvement
of structures other than those injected have been reported. No other systemic effects
have been noted. However, it is possible that mild systemic effects may occur
following intrasynovial administration, and this possibility is greater the larger the
number of structures injected and the higher the total dose employed.Procedure for Intrasynovial Injection
The anatomy of the area to be injected
should be reviewed in order to assure that the suspension is properly placed and to
determine that large blood vessels or nerves are avoided. The injection site is located
where the synovial cavity is most superficial. The area is prepared for aseptic injection
of the medicament by the removal of hair and cleansing of the skin with alcohol or
Mercresin® tincture. A sterile 18- to 21-gauge needle for horses, 20- to 22-gauge
needle for dogs, on a dry syringe is quickly inserted into the synovial space and a
small amount of synovial fluid withdrawn. If there is an excess of synovia and more
than 1 mL of suspension is to be injected, it is well to aspirate a volume of fluid
comparable to that which is to be injected. With the needle in place, the aspirating
syringe is removed and replaced by a second syringe containing the proper amount
of suspension which is then injected. In some animals a transient pain is elicited
immediately upon injection into the affected cavity. This pain varies from mild to
severe and may last for a few minutes up to 12 hours. After injection, the structure
may be moved gently a few times to aid mixing of the synovial fluid and the
suspension. The site may be covered with a small sterile dressing.Areas not suitable for injection are those that are anatomically inaccessible such as
spinal joints and those like the sacroiliac joints, which are devoid of synovial space.
Treatment failures are most frequently the result of failure to enter the synovial space.
If failures occur when injections into the synovial spaces are certain, as determined
by aspiration of fluid, repeated injections are usually futile. Local therapy does not
alter the underlying disease process, and whenever possible comprehensive therapy
including physiotherapy and orthopedic correction should be employed.The single intrasynovial dose depends on the size of the part, which corresponds to
the size of the animal. The interval between repeated injections depends on the
duration of relief obtained. - STORAGE AND HANDLING
- HOW SUPPLIED
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mg Vial Carton
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 40 mg Vial Carton
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DEPO-MEDROL
methylprednisolone acetate injection, suspensionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 54771-1613 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR, INTRASYNOVIAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE (UNII: 43502P7F0P) (METHYLPREDNISOLONE - UNII:X4W7ZR7023) METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE 20 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3350 (UNII: G2M7P15E5P) 29.6 mg in 1 mL SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 54771-1613-1 20 mL in 1 VIAL Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA012204 04/15/1960 DEPO-MEDROL
methylprednisolone acetate injection, suspensionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 54771-1614 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR, INTRASYNOVIAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE (UNII: 43502P7F0P) (METHYLPREDNISOLONE - UNII:X4W7ZR7023) METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE 40 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3350 (UNII: G2M7P15E5P) 29 mg in 1 mL SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 54771-1614-1 5 mL in 1 VIAL Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA012204 04/15/1960 Labeler - Zoetis Inc. (828851555)
Trademark Results [Depo-Medrol]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 DEPO-MEDROL 72078585 0694836 Live/Registered |
UPJOHN COMPANY, THE 1959-07-28 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.