ANAVIP (crotalidae immune f(ab)2- equine injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
ANAVIP by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
ANAVIP by is a Other medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Rare Disease Therapeutics, Inc, Laboratorios Silanes S.A. de C.V.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ANAVIP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ANAVIP.
ANAVIP(R)
Crotalidae Immune F(ab')2 (Equine)
Lyophilized Powder for Solution for Injection
For Intravenous Use Only
Initial U.S. Approval: 2015INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ANAVIP [Crotalidae Immune F(ab')2 (Equine)] is an equine-derived antivenin indicated for the management of adult and pediatric patients with North American rattlesnake envenomation. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Intravenous use only
Dose No. of Vials Infusion Rate Initial Dose 10 vials Infuse intravenously over 60 minutes. (2) Additional dose(s) to achieve initial control 10 vials
(as needed)Infuse intravenously over 60 minutes. (2) Observation and late dosing 4 vials Infuse intravenously over 60 minutes.(2) - Initiate administration as soon as possible after rattlesnake bite in patients who develop signs of envenomation (e.g., local injury, coagulation abnormality, or systemic signs of envenomation).
- Monitor patients in a health care setting at least 18 hours following initial control of signs and symptoms. Re-emerging symptoms including coagulapathies may be suppressed with an additional 4 vial doses of ANAVIP as needed. (2)
- Reconstitute each vial with 10 milliliters (mL) of sterile normal saline (0.9% NaCl). (2)
- Combine and further dilute to a total of 250 mL with sterile normal saline (0.9% NaCl). (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Each vial contains a sterile, lyophilized preparation containing not more than 120 milligrams total protein and not less than the indicated number of mouse LD50 neutralizing units (3):
Snake Species Used for Standardization Minimum Mouse LD50 Units per Vial Bothrops asper 780 Crotalus durissus 790 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- ANAVIP may cause allergic reactions
- Patients with known allergies to horse protein are particularly at risk for an anaphylactic reaction. If signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis or hypersensitivity reactions (including urticaria, rash, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension) occur, discontinue immediately and institute appropriate treatment.
- Monitor patients with follow-up visits for signs and symptoms of delayed allergic reactions or serum sickness (rash, fever, myalgia, arthralgia, pruritus, urticarial rash) and treat appropriately if necessary. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (>2%) in the clinical trials were: pruritus, nausea, rash, arthralgia, peripheral edema, myalgia, headache, pain in extremity, vomiting and erythema. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Rare Disease Therapeutics, Inc., at 1-877-851-1902, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: No human or animal data. Use only if clearly needed. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
5.2 Transmissible Infectious Agents
5.3 Reactions to Cresol
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For Intravenous use only.
Administer ANAVIP as soon as possible after rattlesnake bite in patients who develop any signs of envenomation (e.g., local injury, coagulation abnormality, or systemic signs of envenomation).
The amount of antivenin required to treat a snake bitten patient is highly variable owing in part to the venom burden, the potency of the venom and the time to health care presentation. Use supportive measures to treat certain manifestations of rattlesnake envenomation, such as pain, swelling, hypotension, and wound infection. Contact the local poison control centers for additional individual treatment advice.
Prior to initiating treatment perform laboratory analyses, including complete blood count, platelet count, PT, PTT, serum fibrinogen level and routine serum chemistries. Repeat testing at regular intervals to gauge response to therapy and anticipate additional dosing.
Initial Dose: 10 vials
- The initial dose of ANAVIP is 10 vials.
- Reconstitute the contents of each vial with 10 milliliters (mL) of sterile normal saline (0.9% NaCl). Reconstitution time should be less than one minute when using continuous gentle swirling.
- Inspect the solution visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The solution is expected to be clear to yellow/green and opalescent. Do not use if otherwise discolored or turbid.
- Combine the contents of the reconstituted vials promptly and further dilute to a total volume of 250 mL with sterile normal saline (0.9% NaCl). Fluid volumes may need to be adjusted for very small children or infants. Poison Control Centers are a helpful resource for individual treatment advice.
- Infuse intravenously over 60 minutes.
- For the first 10 minutes infuse at a 25-50 mL/hour rate, carefully monitoring for any allergic reactions, including any anaphylactic reactions. Discontinue the infusion if any allergic reaction occurs and institute appropriate emergency treatment. Reassess the risk to benefit before continuing the infusion.
- If no reactions occur, the infusion rate may be increased to the full 250 mL/hour rate until completion. If there is any allergic reaction at any time, stop the infusion, treat accordingly, and reassess the need to continue ANAVIP.
- Following the completion of infusion, monitor the patient for at least 60 minutes for any allergic reaction and to determine that local signs of envenomation are not progressing (leading edge of local injury not progressing), systemic symptoms are resolved and coagulation parameters have normalized or are trending toward normal.
- Discard partially or unused reconstituted and diluted product.
Additional Dosing to Achieve Initial Control
- Administer additional 10 vial doses if needed to arrest the progressive symptoms and repeat every hour. There is no known maximum dose.
- Repeat above steps for initial dose as many times as needed until local signs of envenomation are not progressing, systemic symptoms are resolved and coagulation parameters have normalized or are trending toward normal.
- Prepare as described above for initial dose.
- Once initial control has been achieved, observe the patient to determine any need for further dosing, as described below.
Observation and late Dosing
- Monitor patients in a health care setting at least 18 hours following initial control of signs and symptoms. Re-emerging symptoms including coagulopathies may be suppressed with additional 4 vial doses of ANAVIP as needed. Reconstitute each vial with 10 mL of sterile normal saline (0.9% NaCl). Combine and further dilute to a total of 250 mL. Infuse intravenously over 60 minutes.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ANAVIP is supplied as a sterile, lyophilized powder. Each vial contains not more than 120 milligrams (mg) total protein and not less than the indicated number of mouse LD50 neutralizing units:
Snake Species Used for Standardization Minimum Mouse LD50 Units per Vial Bothrops asper 780 Crotalus durissus 790 5.1 Hypersensitivity
ANAVIP may cause allergic reactions.
- Patients with known allergies to horse protein are particularly at risk for an anaphylactic reaction. If signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis or hypersensitivity reactions (including urticaria, rash, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension) occur, discontinue immediately and institute appropriate treatment.
- Monitor patients with follow-up visits for signs and symptoms of delayed allergic reactions or serum sickness (rash, fever, myalgia, arthralgia, pruritus, urticarial rash) and treat appropriately if necessary.4
5.2 Transmissible Infectious Agents
ANAVIP is made from equine (horse) plasma and may therefore carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses.
5.3 Reactions to Cresol
Trace amounts of cresol from the manufacturing process are contained in ANAVIP. Localized reactions and generalized myalgias have been reported with the use of cresol as an injectable excipient.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions observed in more than 2 percent (2%) of patients in the clinical trials for ANAVIP were: pruritus, nausea, rash, arthralgia, peripheral edema, erythema, headache, myalgia, pain in extremity, and vomiting.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
A total of 86 patients were treated with ANAVIP, ranging from 2 to 80 years old. The patient population was comprised of 60 males and 26 females. Patients were monitored for signs and symptoms of adverse reactions including acute hypersensitivity reactions and serum sickness. Follow-up interviews were conducted at 5, 8, 15 and 22 days after treatment to assess symptoms of ongoing venom effect, serum sickness, and any other adverse reactions.
Table 1 shows the adverse reactions occurring in patients across all clinical trials for ANAVIP. Seventy-six percent (65/86) of patients receiving ANAVIP reported at least one adverse reaction.Table 1: Incidence of Adverse Events in Clinical Studies of ANAVIP by Body System ANAVIP [N=86]
n (%)Patients Reporting at Least One Adverse Event 65 (76%) Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders 47 (55%) Pruritus 37 (43%) Rash 10 (12%) Blister 4 (5%) Erythema 3 (4%) Gastrointestinal disorders 28 (33%) Nausea 20 (23%) Vomiting 5 (6%) Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders 19 (22%) Arthralgia 9 (11%) Myalgia 6 (7%) Pain in extremity 5 (6%) General disorders and administration site conditions 21 (24%) Edema peripheral 7 (8%) Chills 3 (4%) Pyrexia 4 (5%) Nervous system disorders 12 (14%) Headache 5 (6%) Psychiatric disorders 4 (5%) Anxiety 2 (2%) Insomnia 2 (2%) Metabolism and nutrition disorders 4 (5%) Dehydration 2 (2%) Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders 5 (6%) Dyspnea 1 (1%) Blood and lymphatic system disorders 2 (2%) Thrombocytopenia 1 (1%) 8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with ANAVIP. It is also not known whether ANAVIP can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. ANAVIP should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether ANAVIP is excreted in human breast milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ANAVIP is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Twenty-four percent (21/86) of patients studied in clinical trials were 16 years of age or younger (6 patients were 2 years of age to 5 years of age, 15 patients ranged from at least 5 years of age to 16 years of age). None of the pediatric patients in the phase 3 study experienced a recurrent coagulopathic effect. All adverse reactions in the pediatric patients were non-serious. The most frequent adverse reactions among pediatric patients were nausea and vomiting, itching and fever. Thus, the safety and efficacy in the pediatric population was not different from adults.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ANAVIP [Crotalidae Immune F(ab')2 (Equine)] is a sterile, lyophilized, polyvalent preparation of equine immunoglobulin F(ab')2 fragments, manufactured from plasma of horses immunized with venom of Bothrops asper and Crotalus durissus. The product is obtained by pepsin digestion of horse plasma to remove the Fc portion of immunoglobulin, followed by fractionation and purification steps. The F(ab')2 content is not less than 85%, F(ab') content is not more than 7%, and the product contains less than 5% intact immunoglobulin. Each vial of ANAVIP contains 25.2-56.8 mg of sodium chloride, 18.2 - 85.8 mg of sucrose, and 16.2-51.8 mg of glycine as stabilizers. Trace amounts of pepsin (≤160 ng/vial), cresol (≤0.058 mg/vial), borates (≤1 mg/vial) and sulfates (≤1.7 mg/vial) may be present from the manufacturing process. Each vial contains no more than 120 mg of protein and will be neutralize not less than 780 times the LD50 of Bothrops asper venom and 790 times the LD50 of Crotalus durissus venom in a mouse neutralization assay.
The manufacturing procedures that contribute to the reduction of risk of viral transmission include pepsin digestion, ammonium sulfate precipitation/heat treatment and nanofiltration. -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
ANAVIP contains venom-specific F(ab')2 fragments of immunoglobulin G (IgG) that bind and neutralize venom toxins, facilitating redistribution away from target tissues and elimination from the body.1,2
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Fourteen healthy volunteers each received one vial of intravenous (IV) doses (one vial = 81.86 mg) of an antivenin comparable to ANAVIP both in composition and manufacturing. On the first day of antivenin administration, blood samples were collected from all subjects at 16 specific time points: 0 (prior to drug infusion), 5, 10, 20, 30, 45, 60, 120, and 480 minutes after drug infusion. Additional samples were drawn just prior to discharge (Day 1), and on days 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, and 21. A two-compartment model best described the concentration-time data. The pharmacokinetic parameters of the antivenin are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of ANAVIP Antivenin Following a Single IV Dose to Healthy Volunteers (n=13) Units Mean
SD Area under plasma concentration vs time curve AUC0-∞(µgh/mL) 4144 670 Steady-state volume of distribution Vss (L) 3.3 0.9 Mean residence time MRT (h) 157 40 Elimination half-life Beta-HL (h) 133 53 Total Clearance CL (mL/h) 22 7 -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
In a published non-GLP study3, ANAVIP and another licensed pit viper antivenin were tested and cross-reactivity to the venoms of multiple different pit vipers including rattlesnakes was demonstrated in rabbits and mice. Animal studies to determine an NOAEL were unsuccessful due to technical limitations that prevented determination of a systematically toxic dose.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Study 1 was a randomized, prospective, open-label, controlled, comparative, multicenter study was conducted in 12 patients aged 18 to 70 years of age with signs of pit viper envenomation.6 The subjects received either a licensed pit viper antivenin as an active control, or ANAVIP. The subjects were dosed until initial control was achieved, followed by maintenance doses. All patients in both treatment groups achieved initial control of local injury and coagulopathy following early antivenin treatment.
In the active control group, at the end of maintenance dosing, 5 of 6 subjects had platelet counts above 150,000/mm3, and all 6 had fibrinogen levels above 150 mg/dL. During the follow-up phase two patients exhibited platelets below 150,000/mm3 and fibrinogen below 150 mg/dL, leading to inpatient management with administration of additional doses (one subject received an additional 6 doses (12 vials) and one subject received an additional 4 doses (8 vials).
In the ANAVIP arm, at the end of maintenance dosing, 5 of 6 subjects had platelet counts above 150,000/mm3. One subject’s platelets were 114,000/mm3 and were trending upward and all 6 had fibrinogen levels above 150 mg/dL. During the follow-up phase, 5 of 6 subjects had platelet counts above 150,000/mm3, with no downward trend; 1 subject’s platelet counts was 127,000/mm3 on follow-up Day 1, reached 160,000/mm3 on Day 4 and continued trending upward. All 6 subjects in the ANAVIP group had fibrinogen levels above 150 mg/dL during the follow-up phase. None in the ANAVIP group required rehospitalization or retreatment with ANAVIP.
Study 2 was a randomized, prospective, blinded, controlled, comparative, multicenter study, comparing two ANAVIP regimens with a licensed pit viper antivenin (comparator) conducted in patients with pit viper envenomation at 16 sites in the United States. The study had an in-hospital Acute Treatment Phase that included screening and baseline assessments, initial and maintenance dosing, and an outpatient Follow-up Phase that included 4 follow-up visits on Days 5, 8, 15 and 22.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to one of three groups: ANAVIP with ANAVIP maintenance therapy (Group 1), ANAVIP with placebo maintenance therapy (Group 2), or Comparator product with Comparator product maintenance therapy (Group 3).
Initial dosing consisted of sequential intravenous (IV) doses infused to achieve initial control. If initial control of envenomation was not achieved, treatment was repeated until initial control was attained. Maintenance dosing (4 vials of ANAVIP or placebo [normal saline (0.9% NaCl)], or 2 vials of comparator product) was initiated 6 hours after the start of the last dose required to achieve initial control, and continued every 6 hours for 3 doses.
The Follow-up Phase began immediately after the third maintenance dose. Patients returned to the clinical site on Days 5, 8, and 15 for scheduled follow-up visits. Patients with ongoing signs of envenomation received 4 vials of ANAVIP or 2 vials of Comparator product. Dosing was provided as needed until the patient was stabilized. One hundred twenty-one (121) patients received blinded study drug and were analyzed for safety and efficacy.
The efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients experiencing coagulopathic effect as measured on Study Day 5 or 8. Patients were assessed as experiencing a coagulopathic effect if they had any one of the following: absolute platelet levels < 150,000/mm3 as measured on either Study Day 5 (±1 day) or 8 (±1 day); absolute fibrinogen levels <150 mg/dL as measured on either Study Day 5 (±1 day) or 8 (±1 day); or clinical coagulopathy between end of maintenance dosing and Study Day 5 requiring additional antivenin. The comparison of coagulopathic effect proportions between treatment groups was tested using an exact logistic regression model with terms for treatment and region. Comparisons of the proportion of coagulopathic effect for two levels of ANAVIP versus Comparator product were performed in the following order: ANAVIP with ANAVIP maintenance dose versus Comparator product; then ANAVIP with Placebo maintenance dose versus Comparator product. The number and percentage of patients who experienced coagulopathic effect is summarized by treatment group in Table 3. The efficacy analysis did not meet the pre-specified statistically defined superiority criterion. However, the percentages of subjects showing prespecified criteria for coagulopathic effect on either Day 5 and/or Day 8 were 10.3% and 5.3% in the Groups 1 and 2 when compared to 29.7% in Group 3 indicating efficacy of ANAVIP in management of coagulopathic effect in patients with North American rattlesnake envenomation.Table 3. Comparison of Coagulopathic Effect Rates on Study Day 5 or Study Day 8 Experienced Coagulopathic Effect on Either Day 5 or Day 8 Group 1 (n=39) ANAVIP/ANAVIP Group 2 (n=38) ANAVIP/Placebo Group 3 (n=37) Comparator product Yes
No4 (10.3%)
35 (89.7%)2 (5.3%)
36 (94.7%)11 (29.7%)
26 (70.3%)Treatment Group (vs. Group 3) Odds Ratio (95% Cl) 0.275(0.058, 1.048) 0.135(0.014, 0.686) Cl= confidence interval
FDA conducted a post hoc analysis to assess the outcomes of the patients who presented with or without baseline coagulopathic effect in the three treatment groups. Using the pre-specified criteria for coagulopathic effect, it was found that ANAVIP/ANAVIP (Group 1) had the highest percentage of baseline coagulopathic subjects among the three groups [41.5% compared with 17.5% and 32.5% for the ANAVIP/Placebo (Group 2) and Comparator product (Group 3), respectively]. Thirty-three percent (33%) of all baseline coagulopathic subjects also experienced coagulopathic effect on either Day 5 or 8, compared to only 6% for baseline non-coagulopathic subjects. Only 18% of the subjects with baseline coagulopathic effect in Group 1 continued to remain coagulopathic at Days 5 or 8 compared to 58% in Group 3 (Table 4).Table 4. Coagulopathy by Treatment Group and Baseline Coagulopathy Baseline coagulopathy Experienced coagulopathy on either Day 5 or 8 ANAVIP/ANAVIP ANAVIP/Placebo Comparator product Total Yes Number of subjects N=17 N=7 N=12 N=36 Yes 3 (17.65%) 2 (28.57%) 7 (58.33%) 12 (33.3%) No 14 (82.35%) 5 (71.43%) 5 (41.67%) 24 (66.7%) No Number of subjects N=22 N=31 N=25 N=78 Yes 1 (4.55%) 0 (0%) 4 (16%) 5 (6.4%) No 21 (95.45%) 31 (100%) 21 (84%) 73 (93.6%) An exact logistic regression analysis adjusting for baseline coagulopathic effect and region was conducted and showed that treatment effect for both Groups 1 and 2 is statistically significant (Table 5). This analysis provides supportive evidence of the efficacy of ANAVIP.
Table 5. Comparison Coagulopathic Effect Rates Adjusted for Baseline Coagulopathy Group 1 (N=39) ANAVIP/ANAVIP Group 2 (N=38) ANAVIP/Placebo Treatment Group (vs Comparator product)
Odds ration (95% Cl1)0.184 (0.033, 0.794) 0.121 (0.010, 0.764) 1Cl= confidence interval
Analysis by snakebite type was performed but was limited due to the number of unknown snakebite types (N=43). However, 57 subjects who were envenomated by rattlesnakes showed more severe coagulopathic effects and resolution of these effects after treatment with ANAVIP as compared to 21 subjects who were envenomated by copperhead snakes. Efficacy outcomes could not be evaluated in the copperhead snake bite subgroup due to these limited coagulopathic effects. -
15 REFERENCES
1. Seifert SA and Boyer LV: Recurrence phenomena after immunoglobulin therapy for snake envenomation: Part 1. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of immunoglobulin antivenoms and related antibodies. Annals of Emergency Medicine 37(2):189-195; 2001.
2. Boyer LV, Seifert SA and Cain JS: Recurrence phenomena after immunoglobulin therapy for snake envenomation: Part 2. Guidelines for clinical management with crotaline Fab antivenom. Annals of Emergency Medicine 37(2):196-201; 2001.
3. Sanchez EE, Galan JA, Perez JC, et al. The efficacy of two antivenoms against the venom of North American snakes, Toxicon 41: 357-365; 2003.
4. Gold BS, Dart RC and Barish RA: Bites of venomous snakes. New England Journal of Medicine 347(5):347-56; 2002.
5. Boyer LV, Seifert SA, Clark RF, et al: Recurrent and persistent coagulopathy following pit viper envenomation. Archives of Internal Medicine 159:706-710; 1999.
6. Boyer LV, Chase PB, Degan JA, et al: Subacute coagulopathy in a randomized, comparative trial of Fab and F(ab’)2 antivenoms. Toxicon 74: 101-108; 2013.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
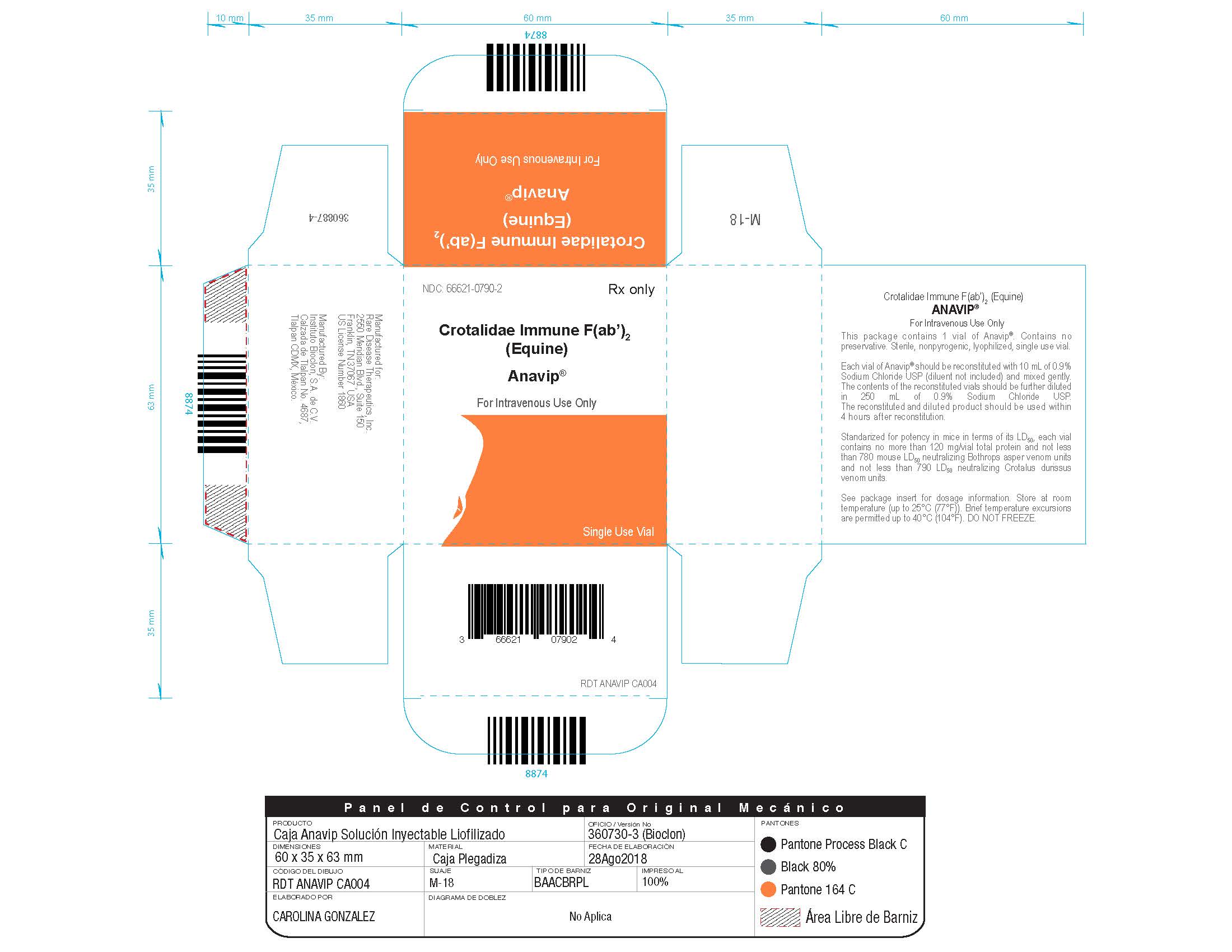
ANAVIP is supplied as a sterile lyophilized preparation in a single-use vial. When reconstituted with 10 mL of 0.9% NaCl solution, each vial contains not more than 12 mg per mL of protein, and will neutralize not less 780 times the LD50 of Bothrops asper venom and 790 times the LD50 of Crotalus durissus venom in a mouse neutralization assay.
Each carton NDC: 66621-0790-2 contains 1 vial of ANAVIP NDC: 66621-0790-1.
- Store at room temperature (up to 25 ºC (77 ºF)). Brief temperature excursions are permitted up to 40 ºC (104ºF).
- DO NOT FREEZE.
- Discard partially used vials.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Advise patients to contact their physician immediately if they experience unusual bruising or bleeding (e.g., nosebleeds, excessive bleeding after brushing teeth, the appearance of blood in stools or urine, excessive menstrual bleeding, petechiae, excessive bruising or persistent oozing from superficial injuries) after hospital discharge.5
- Serious Allergic Reactions
- Advise patients to contact their physician immediately if they experience any signs and symptoms of delayed allergic reactions or serum sickness (e.g., rash, fever, myalgias, arthralgia, pruritus, urticaria) after hospital discharge.4 [see Hypersensitivity (5.1)].4
Manufactured by:
Instituto Bioclon S.A. de C.V.
Tlalpan CDMX, Mexico
Manufactured for:
Rare Disease Therapeutics, Inc.
2550 Meridian Blvd., Suite 150
Franklin, TN 37067
www.raretx.com
U.S. License No. 1860
Part No. RDT Anavip PI004
Silanes Part number: 360893-4
PACKAGE LABEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ANAVIP
crotalidae immune f(ab)2(equine) injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type PLASMA DERIVATIVE Item Code (Source) NDC: 66621-0790 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PIT VIPER (CROTALINAE) IMMUNE GLOBULIN ANTIVENIN (EQUINE) (UNII: 92VV7G83ED) (PIT VIPER (CROTALINAE) IMMUNE GLOBULIN ANTIVENIN (EQUINE) - UNII:92VV7G83ED) PIT VIPER (CROTALINAE) IMMUNE GLOBULIN ANTIVENIN (EQUINE) 12 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 66621-0790-2 1 in 1 CARTON 1 NDC: 66621-0790-1 10 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125488 05/06/2015 Labeler - Rare Disease Therapeutics, Inc (966133100) Registrant - Rare Disease Therapeutics, Inc (966133100) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Instituto Bioclon S.A. de C.V. 811974559 manufacture(66621-0790)
Trademark Results [ANAVIP]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ANAVIP 78825625 3506545 Live/Registered |
LABORATORIOS SILANES S.A. DE C.V. 2006-02-28 |
 ANAVIP 78295398 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Pharmasil, Inc. 2003-09-03 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.