YORVIPATH- palopegteriparatide injection, solution
Yorvipath by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Yorvipath by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Ascendis Pharma, Endocrinology, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use YORVIPATH safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for YORVIPATH.
YORVIPATH® (palopegteriparatide) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2024INDICATIONS AND USAGE
YORVIPATH is a parathyroid hormone analog (PTH(1-34)) indicated for the treatment of hypoparathyroidism in adults. (1)
Limitations of Use:
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Use only one injection to achieve the once daily recommended dosage. (2.1)
- Maximum recommended YORVIPATH dosage is 30 mcg subcutaneously once daily. (2.1)
- Individualize YORVIPATH dosage based on serum calcium. (2.1)
- Refer to the Full Prescribing Information for complete dosage and administration information. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: single-patient-use prefilled pen (3)
- 168 mcg/0.56 mL pen, labeled doses of 6, 9, or 12 mcg
- 294 mcg/0.98 mL pen, labeled doses of 15, 18, or 21 mcg
- 420 mcg/1.4 mL pen, labeled doses of 24, 27, or 30 mcg
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Severe hypersensitivity to palopegteriparatide or any components of YORVIPATH. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Unintended Changes in Serum Calcium Levels Related to Number of Daily Injections: Use only one daily YORVIPATH injection. Using two YORVIPATH injections to achieve the recommended once daily dosage increases the variability of the total delivered dose. (5.1)
- Serious Hypercalcemia and Hypocalcemia: Have occurred with YORVIPATH. Periodically measure serum calcium and monitor for signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia. (5.2, 5.3)
- Potential Risk of Osteosarcoma: YORVIPATH is not recommended in patients at increased risk of osteosarcoma. (5.4)
- Orthostatic Hypotension: Has been reported with YORVIPATH. Monitor for signs and symptoms of orthostatic hypotension. (5.5)
- Digoxin Toxicity: Concomitant use with digoxin may predispose to digitalis toxicity if hypercalcemia develops. With concomitant use, frequently measure serum calcium and digoxin levels, and monitor for signs and symptoms of digoxin toxicity. (5.6, 7.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions occurring in ≥5% of patients: injection site reactions, vasodilatory signs and symptoms, headache, diarrhea, back pain, hypercalcemia, and oropharyngeal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Ascendis Pharma at 1-844-442-7236 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drugs Known to Affect Calcium: When used concomitantly with YORVIPATH, measure serum calcium levels more frequently. (7.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Monitor breastfed infants for symptoms of hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia. Consider monitoring serum calcium in the breastfed infant (8.2).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 10/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Overview of Dosage and Monitoring
2.2 Laboratory Testing Prior to Initiation of YORVIPATH
2.3 Modification of Active Vitamin D and Calcium Supplements on Day of YORVIPATH Initiation or Up-titration
2.4 Recommended Dosage, Titration Scheme, and Monitoring
2.5 Dose Delay, Interruption, or Discontinuation of YORVIPATH
2.6 Preparation of Pen and Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Unintended Changes in Serum Calcium Levels Related to Number of Daily Injections
5.2 Serious Hypercalcemia
5.3 Serious Hypocalcemia
5.4 Potential Risk of Osteosarcoma
5.5 Orthostatic Hypotension
5.6 Risk of Digoxin Toxicity with Concomitant Use of Digitalis Compounds
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs Affected by Serum Calcium
7.2 Drugs Known to Affect Serum Calcium
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Pharmacology and Toxicology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Treatment of Adults with Hypoparathyroidism
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
YORVIPATH is indicated for the treatment of hypoparathyroidism in adults.
Limitations of Use
- YORVIPATH was not studied for acute post-surgical hypoparathyroidism.
- YORVIPATH's titration scheme was only evaluated in adults who first achieved an albumin-corrected serum calcium of at least 7.8 mg/dL using calcium and active vitamin D treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4) and Clinical Studies (14)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Overview of Dosage and Monitoring
- Use only one injection to achieve the once daily recommended dosage. Using two injections to achieve the recommended once daily dosage increases the risk of unintended changes in serum calcium levels, including hypocalcemia and hypercalcemia. [see Dosage and Administration (2.4, 2.6) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- The maximum recommended dosage is 30 mcg subcutaneously once daily. If an adequate response is not achieved with a maximum YORVIPATH dosage of 30 mcg, consider adding or restarting calcium and/or active vitamin D therapy and/or seek other treatment options [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- YORVIPATH's once daily subcutaneous dosage is individualized. The recommended starting dosage is 18 mcg once daily and is titrated in 3 mcg increments or decrements with the goal of maintaining serum calcium within the normal range without the need for active vitamin D (e.g., calcitriol) or therapeutic calcium doses (elemental calcium >600 mg/day). Calcium supplementation sufficient to meet daily dietary requirements may be continued.
- Advise patients to monitor daily for clinical signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia.
- Measure serum calcium 7 to 10 days after the first YORVIPATH dose and after any dose change in YORVIPATH, active vitamin D, or calcium supplements, and monitor for clinical signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia. Once the YORVIPATH maintenance dosage is achieved, measure serum calcium levels at a minimum every 4 to 6 weeks or as indicated for symptoms of hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia.
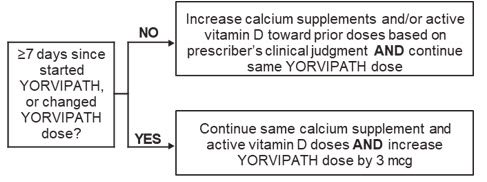
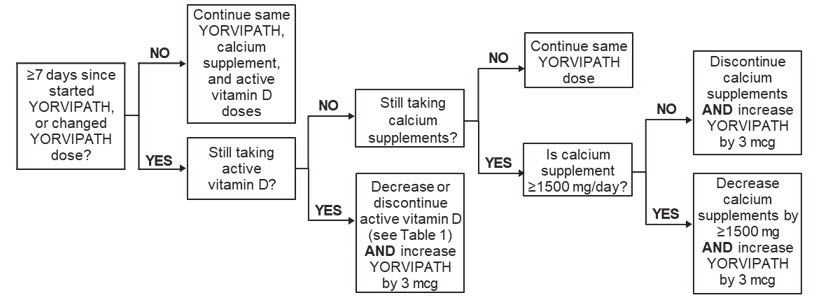
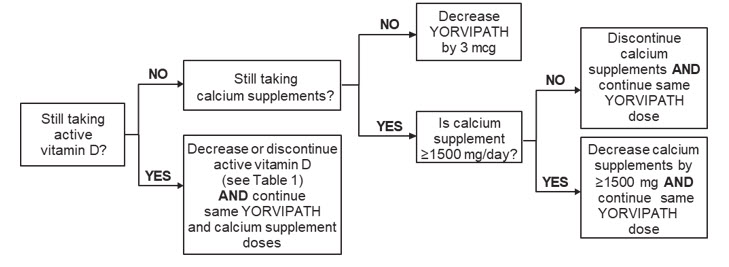
- Adjust YORVIPATH, active vitamin D, and/or calcium supplements per Figure 1. Some patients may require an increase in the YORVIPATH dose over time to maintain the same therapeutic effect [see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Refer to the Instructions for Use (IFU) for detailed instructions on the proper preparation and administration of YORVIPATH [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
2.2 Laboratory Testing Prior to Initiation of YORVIPATH
- Within two weeks before the first dose of YORVIPATH, confirm serum 25(OH) vitamin D is within the normal range and albumin-corrected serum calcium is ≥7.8 mg/dL.
2.3 Modification of Active Vitamin D and Calcium Supplements on Day of YORVIPATH Initiation or Up-titration
- On the day of initiation or up-titration of YORVIPATH, adjust the dose of active vitamin D and calcium supplements based on albumin-corrected serum calcium and current active vitamin D intake (Table 1).
Table 1: Dosage Adjustments to Active Vitamin D (calcitriol) and Calcium Supplements upon Initiation or Up-titration of YORVIPATH Treatment Albumin-Corrected Serum Calcium Current Active Vitamin D (calcitriol) Intake Adjust Active Vitamin D (calcitriol) Intake Adjust Calcium Supplements - * If calcium supplements are needed to meet dietary requirements, continuing dietary calcium supplements at elemental dosages ≤600 mg/day may be considered instead of discontinuing the calcium entirely.
≥8.3 mg/dL >1 mcg/day Reduce calcitriol dosage by ≥50% Maintain current calcium dosage ≥8.3 mg/dL ≤1 mcg/day Discontinue calcitriol Maintain current calcium dosage ≥7.8 to <8.3 mg/dL Any amount Reduce calcitriol dosage by ≥50% Maintain current calcium dosage ≥7.8 mg/dL Not currently on active vitamin D Not applicable Reduce calcium daily dosage by at least 1500 mg or discontinue* if current calcium daily dosage is ≤1500 mg/day 2.4 Recommended Dosage, Titration Scheme, and Monitoring
- The recommended starting dosage of YORVIPATH is 18 mcg once daily. Dosage adjustments should be made in 3 mcg increments or decrements. Do not increase the YORVIPATH dosage more often than every 7 days. Do not decrease the YORVIPATH dosage more often than every 3 days.
- The recommended dosage range of YORVIPATH is 6 to 30 mcg once daily.
- Measure serum calcium within 7 to 10 days after the first dose and any dose change in YORVIPATH, active vitamin D, or calcium supplements, and monitor for clinical symptoms of hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia. Adjust YORVIPATH, active vitamin D, and/or calcium supplements per Figure 1.
- The maintenance dosage is individualized and should be the YORVIPATH dose that achieves serum calcium within the normal range, without the need for active vitamin D or therapeutic doses of calcium. Calcium supplementation sufficient to meet daily dietary requirements may be continued. Once the maintenance dosage is achieved, monitor for clinical signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia and measure serum calcium levels as indicated, and at a minimum every 4 to 6 weeks, as some patients may require further dose titration. If calcium levels remain low with the maximum recommended dosage of 30 mcg once daily, consider adding or restarting calcium and/or active vitamin D therapy and/or seek other treatment.
Titration Recommendations for Albumin-Corrected Serum Calcium Less Than 12 mg/dL
Figure 1 shows dosage titration recommendations for YORVIPATH, active vitamin D, and calcium in adults with specific albumin-corrected serum calcium ranges that are less than or equal to 12 mg/dL. The maximum recommended dosage of YORVIPATH is 30 mcg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Figure 1: Titration of YORVIPATH, Active Vitamin D, and Calcium Supplements
Albumin-Corrected Serum Calcium <8.3 mg/dL:
Albumin-Corrected Serum Calcium 8.3 to 10.6 mg/dL:
Albumin-Corrected Serum Calcium 10.7 to 11.9 mg/dL:
Titration Recommendations for Albumin-Corrected Serum Calcium 12 mg/dL or Greater
Withhold YORVIPATH for 2 to 3 days and then recheck serum calcium. If albumin-corrected serum calcium remains ≥12 mg/dL, withhold YORVIPATH for an additional 2 to 3 days and then recheck serum calcium. Once the albumin-corrected serum calcium is <12 mg/dL, resume titration of YORVIPATH, active vitamin D, and calcium supplements per the applicable section of Figure 1 using the most recent serum calcium value.
2.5 Dose Delay, Interruption, or Discontinuation of YORVIPATH
Take YORVIPATH as soon as possible if a dose is missed by less than 12 hours. Skip the missed dose if the dose has been missed by more than 12 hours. Take the next dose as scheduled.
If YORVIPATH treatment is delayed or interrupted for 3 days or more, evaluate patients for signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia and consider measuring serum calcium. If indicated, resume treatment with, or increase the dose of, calcium supplements and active vitamin D. Resume YORVIPATH at the previously prescribed dose as soon as possible after an interruption then measure serum calcium within 7 to 10 days and adjust doses of YORVIPATH, active vitamin D, and/or calcium supplements per Figure 1 [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
2.6 Preparation of Pen and Administration Instructions
Patients and caregivers who will administer YORVIPATH should receive appropriate training by a healthcare professional prior to first use.
Follow the Instructions For Use to administer YORVIPATH using pen and needle:
- YORVIPATH must be refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) until first use.
- YORVIPATH should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. YORVIPATH is a clear, colorless solution. Do not use if solid particles appear or if the solution is cloudy or colored.
- When a pen is used for the first time, test pen flow.
- Click the needle straight onto the pen, then screw the needle onto the pen until secure.
- Administer YORVIPATH subcutaneously to the abdomen or front of the thigh. Rotate the injection site daily.
- YORVIPATH should be administered initially when the patient can sit or lie down because of the potential of orthostatic hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: Clear, colorless solution in single-patient-use prefilled pens in three presentations
Table 2 displays the YORVIPATH prefilled pen presentations, strengths, labeled doses, and deliverable dose ranges.
Table 2: YORVIPATH Prefilled Pen Presentations, Strengths, Labeled Doses, and Deliverable Dose Ranges Pen Type and Strength Labeled Dose (mcg) Range of Deliverable Dose*
(Minimum – Maximum) (mcg)- * Deliverable dose range at each labeled dose setting based on prefilled pen performance. Use only labeled dose for titration (refer to Figure 1).
Prefilled pen with blue push button
(168 mcg/0.56 mL)6 4.5 - 7.5 9 7.5 - 10.5 12 10.5 - 13.5 Prefilled pen with orange push button
(294 mcg/0.98 mL)15 13.1 - 16.5 18 16.1 - 19.5 21 19.1 - 22.5 Prefilled pen with burgundy push button
(420 mcg/1.4 mL)24 21.6 - 25.5 27 24.6 - 28.5 30 27.6 - 31.5 - 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Unintended Changes in Serum Calcium Levels Related to Number of Daily Injections
Use only one YORVIPATH injection to achieve the recommended once daily dosage. Using two YORVIPATH injections to achieve the recommended once daily dosage increases the variability of the total delivered dose, which can cause unintended changes in serum calcium levels, including hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warning and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
5.2 Serious Hypercalcemia
Serious events of hypercalcemia requiring hospitalization have been reported with YORVIPATH. The risk is highest when starting or increasing the dose of YORVIPATH but may occur at any time. Measure serum calcium 7 to 10 days after any dose change or if there are signs or symptoms of hypercalcemia, and at a minimum of every 4 to 6 weeks once the maintenance dose is achieved. Treat hypercalcemia if needed. If albumin-corrected serum calcium is greater than 12 mg/dL, withhold YORVIPATH for at least 2-3 days [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. For less serious hypercalcemia, adjust the dose of YORVIPATH, active vitamin D, and/or calcium supplements [see Dosage and Administration (2), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.3 Serious Hypocalcemia
Serious events of hypocalcemia have been observed with PTH products, including YORVIPATH. The risk is highest when YORVIPATH is abruptly discontinued, but may occur at any time, even in patients who have been on stable doses of YORVIPATH. Measure serum calcium 7 to 10 days after any dose change or if there are signs or symptoms of hypocalcemia, and at a minimum of every 4 to 6 weeks once the maintenance dosage is achieved. Treat hypocalcemia if needed, and adjust the dose of YORVIPATH, active vitamin D, and/or calcium supplements if hypocalcemia occurs [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.4 Potential Risk of Osteosarcoma
YORVIPATH is a PTH analog. An increased incidence of osteosarcoma (a malignant bone tumor) has been reported in male and female rats treated with PTH analogs, including teriparatide. Osteosarcoma occurrence in rats is dependent on teriparatide or PTH dose and treatment duration. Osteosarcoma has been reported in patients treated with teriparatide in the postmarketing setting; however, an increased risk of osteosarcoma has not been observed in observational studies in humans. There are limited data assessing the risk of osteosarcoma beyond 2 years of teriparatide use.
YORVIPATH is not recommended in patients who are at increased risk of osteosarcoma, such as patients with:
- Open epiphyses. YORVIPATH is not approved in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
- Metabolic bone diseases other than hypoparathyroidism, including Paget's disease of bone.
- Unexplained elevations of alkaline phosphatase.
- Bone metastases or a history of skeletal malignancies.
- History of external beam or implant radiation therapy involving the skeleton.
- Hereditary disorders predisposing to osteosarcoma.
Instruct patients to promptly report clinical symptoms (e.g., persistent localized pain) and signs (e.g., soft tissue mass tender to palpation) that could be consistent with osteosarcoma.
5.5 Orthostatic Hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension has been reported with YORVIPATH. Associated signs and symptoms may include decreased blood pressure, dizziness (including postural dizziness), palpitations, tachycardia, presyncope, or syncope. Such symptoms can be managed by dosing at bedtime, while reclining. YORVIPATH should be administered initially when the patient can sit or lie down due to the potential of orthostatic hypotension.
5.6 Risk of Digoxin Toxicity with Concomitant Use of Digitalis Compounds
YORVIPATH increases serum calcium, and therefore, concomitant use with digoxin (which has a narrow therapeutic index) may predispose patients to digitalis toxicity if hypercalcemia develops. Digoxin efficacy may be reduced if hypocalcemia is present. When YORVIPATH is used concomitantly with digoxin, measure serum calcium and digoxin levels routinely, and monitor for signs and symptoms of digoxin toxicity. Refer to the digoxin prescribing information for dose adjustments, if needed [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Risk of Unintended Changes in Serum Calcium Levels Related to Number of Daily Injections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Serious Hypercalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Serious Hypocalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Potential Risk of Osteosarcoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Orthostatic Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Risk of Digoxin Toxicity with Concomitant Use of Digitalis Compounds [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The phase 3 trial included 82 subjects with hypoparathyroidism with a median YORVIPATH treatment duration of 182 days (Study 1) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Adverse reactions associated with YORVIPATH in Study 1 during the 26-week blinded period (incidence ≥5% and occurring ≥2% more frequently than placebo) are shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions in ≥5% of Subjects with Hypoparathyroidism Treated with YORVIPATH and with ≥2% Higher Frequency Compared to Placebo in Study 1 Adverse Reaction YORVIPATH
N=61
n (%)Placebo
N=21
n (%)Abbreviations: N, total number of subjects in the treatment arm; n, number of subjects with the adverse reaction; %, percent of subjects with the adverse reaction. - * Injection site reactions includes the preferred terms injection site bruising, injection site erythema, injection site rash, and injection site reaction.
- † Vasodilatory signs and symptoms includes the preferred terms blood pressure orthostatic decreased, dizziness, dizziness postural, orthostatic hypotension, palpitations, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, presyncope, syncope, and vertigo.
- ‡ Back pain includes the preferred terms back pain, flank pain, and spinal pain.
Injection site reactions* 24 (39) 1 (5) Vasodilatory signs and symptoms† 17 (28) 0 Headache 13 (21) 2 (10) Diarrhea 6 (10) 1 (5) Back pain‡ 5 (8) 0 Hypercalcemia 5 (8) 0 Oropharyngeal pain 4 (7) 0 Description of Selected Adverse Reactions
Hypercalcemia
Table 4 summarizes the number of subjects who had at least one serum calcium measurement greater than the upper limit of the reference range at a post-baseline visit in Study 1. The incidence of hypercalcemia was greater in subjects treated with YORVIPATH.
Symptomatic hypercalcemia was reported in 8% of subjects treated with YORVIPATH, and all occurred within the first 3 months after initiation of YORVIPATH.
Table 4: Incidence of Elevated Albumin-Corrected Serum Calcium (>10.6 mg/dL or >12 mg/dL) Post-Baseline in Subjects with Hypoparathyroidism Treated with YORVIPATH or Placebo in Study 1 YORVIPATH
N=61Placebo
N=21Abbreviations: N, total number of subjects in the treatment arm; n, number of subjects meeting criteria. - * Subjects meeting albumin-corrected serum calcium >10.6 mg/dL criterion includes subjects meeting albumin-corrected serum calcium >12 mg/dL criterion.
Albumin-Corrected Serum Calcium >10.6 mg/dL, n (%)* 33 (54.1) 2 (9.5) Albumin-Corrected Serum Calcium >12 mg/dL, n (%) 8 (13.1) 0 (0) -
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs Affected by Serum Calcium
Digoxin
YORVIPATH increases serum calcium, therefore, concomitant use with digoxin (which has a narrow therapeutic index) may predispose patients to digitalis toxicity if hypercalcemia develops. Digoxin efficacy may be reduced if hypocalcemia is present. When YORVIPATH is used concomitantly with digoxin, measure serum calcium and digoxin levels, and monitor for signs and symptoms of digoxin toxicity. Adjustment of the digoxin and/or YORVIPATH dose may be needed.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from reports of pregnancies in the clinical trials from drug development are insufficient to identify a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are disease-associated risks to the mother and fetus related to hypocalcemia in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations). In animal reproduction studies, administration of palopegteriparatide to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in no significant adverse effects up to doses 16- and 13-fold, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD), based on PTH(1-34) and active metabolite PTH(1-33) exposure by area under the curve (AUC) (see Data).
The background risk of birth defects and miscarriages for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
If YORVIPATH is administered during pregnancy, or if a patient becomes pregnant while receiving YORVIPATH, healthcare providers should report YORVIPATH exposure by calling 1-844-442-7236.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and Embryo/Fetal Risk
Maternal hypocalcemia can result in an increased rate of spontaneous abortion, premature and dysfunctional labor, and possibly preeclampsia. Infants born to mothers with hypocalcemia can have associated fetal and neonatal hyperparathyroidism, which may cause fetal and neonatal skeletal demineralization, subperiosteal bone resorption, osteitis fibrosa cystica, and neonatal seizures. Infants born to mothers with hypocalcemia should be monitored for signs of hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia, including neuromuscular irritability (e.g., myotonic jerks, seizures), apnea, cyanosis, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study in rats, palopegteriparatide was administered subcutaneously during the period of organogenesis (gestation days (GD) 6 to 17) at doses of 2, 8, and 30 mcg/kg/day. In pregnant rats, there was no evidence of embryo-lethality, fetotoxicity, or fetal malformations up to the highest dose tested corresponding to 16-fold the MRHD, based on PTH(1-34) and active metabolite PTH(1-33) exposure by AUC.
In an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study in rabbits, palopegteriparatide was administered subcutaneously to pregnant female rabbits during the period of organogenesis (GD 7 to 19) at doses of 1, 3, and 6 mcg/kg/day. There was no evidence of any palopegteriparatide-related embryo-lethality, fetotoxicity, or fetal malformations at any dose level up to 13-fold the MRHD, based on PTH(1-34) exposure by AUC.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data available on the presence of palopegteriparatide or its metabolite in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Infants breastfed by females treated with YORVIPATH should be monitored for signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia. Monitoring of serum calcium in the infant should be considered.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for YORVIPATH and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from YORVIPATH or from the underlying sub-optimally treated maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of YORVIPATH have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In Study 1, 8 of 61 (13%) YORVIPATH-treated subjects were 65 years of age or over compared to 2 of 21 (10%) subjects in the placebo group. Clinical studies of YORVIPATH did not include a sufficient number of subjects 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult subjects.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥ 15 mL/min/1.73 m2).
In a dedicated renal impairment study, patients with severe renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate 15 to 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) had no clinically significant difference in total PTH compared to subjects with normal renal function upon treatment with YORVIPATH [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Accidental overdose of YORVIPATH may cause hypercalcemia that can be severe and require medical intervention. One subject in Study 1 accidentally received approximately 3-fold the prescribed dose of YORVIPATH for more than 7 consecutive days and developed albumin-corrected serum calcium as high as 16.1 mg/dL, requiring hospitalization.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
YORVIPATH (palopegteriparatide injection) is a parathyroid hormone analog (PTH(1-34)). Palopegteriparatide is a prodrug of teriparatide (PTH(1-34)) consisting of PTH(1-34) transiently conjugated to an inert carrier via a proprietary TransCon Linker. PTH(1-34) is identical to the 34 N-terminal amino acids (the biologically active region) of the 84-amino acid human parathyroid hormone. The carrier is a branched 40 kDa (2×20 kDa) methoxypolyethylene glycol (mPEG) moiety. The average molecular weight of palopegteriparatide is approximately 47.4 kDa.
The structure of palopegteriparatide drug substance is shown in Figure 2. The theoretical molecular formula is C209H340N60O59S3 + 2 × (C2H4O)n, where n is between approximately 450 and 500.
Figure 2: Structure of Palopegteriparatide
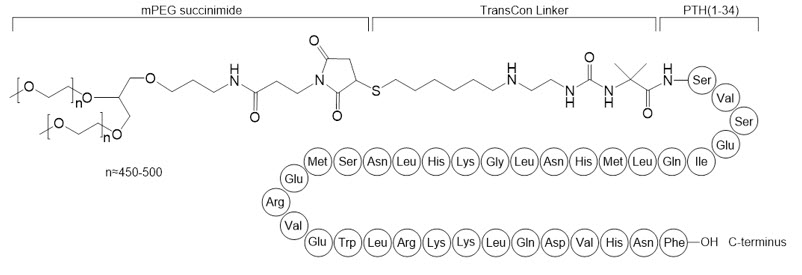
YORVIPATH is a sterile, clear, and colorless solution in a glass cartridge which is pre-assembled in a single-patient-use prefilled pen for subcutaneous administration. The prefilled pen is co-packaged with disposable needles to administer 14 doses of YORVIPATH. YORVIPATH is available in three presentations containing 0.56 mL, 0.98 mL, or 1.4 mL of YORVIPATH solution, and each pen presentation can deliver one of three distinct doses for 14 days of therapy.
Each mL of YORVIPATH solution contains 3456 mcg of palopegteriparatide, equivalent to 300 mcg of teriparatide (PTH(1-34)), and the following inactive ingredients: 41.7 mg mannitol, 2.5 mg metacresol, 0.13 mg sodium hydroxide, 1.18 mg succinic acid, and water for injection. YORVIPATH has a pH of 3.7 to 4.3.
Each pen of 0.56 mL contains 168 mcg teriparatide equivalent to 1935 mcg palopegteriparatide.
Each pen of 0.98 mL contains 294 mcg teriparatide equivalent to 3387 mcg palopegteriparatide.
Each pen of 1.4 mL contains 420 mcg teriparatide equivalent to 4838 mcg palopegteriparatide.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
At physiological conditions, palopegteriparatide releases PTH(1-34) to maintain a continuous systemic exposure. Endogenous PTH maintains extracellular calcium and phosphate homeostasis by increasing serum calcium and decreasing serum phosphate. These effects are mediated by stimulating bone turnover to mobilize calcium and phosphate from bone, promoting renal calcium reabsorption and phosphate excretion, and facilitating active vitamin D synthesis, in turn increasing intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphate. Similar to endogenous PTH, PTH(1-34) released from palopegteriparatide exerts these effects through its main receptor, parathyroid hormone 1 receptor (PTH1R), which is highly expressed on osteoblasts, osteocytes, renal tubular cells, and in several other tissues.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Serum PTH(1-34) and serum calcium concentrations increased in a dose-related manner when YORVIPATH was administered to healthy volunteers. Exposure-response is not established in subjects with hypoparathyroidism.
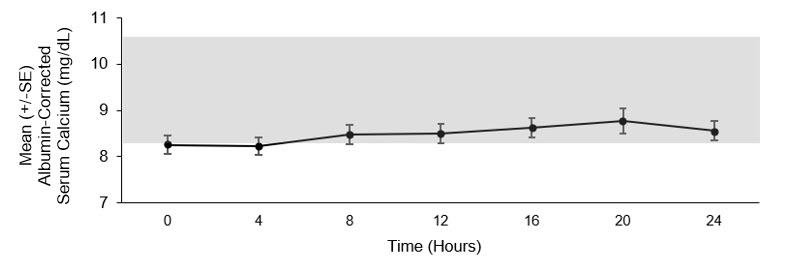
Mean steady state concentration-time profile of albumin-corrected serum calcium concentrations over 24 hours following administration of YORVIPATH is presented in Figure 3.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
YORVIPATH is a prodrug that releases PTH(1-34) via autocleavage of the TransCon linker.
PTH Cmax and AUC increased proportionally over a YORVIPATH dosage range of 12 to 24 mcg/day. PTH steady state is achieved after administration of YORVIPATH for 7 days.
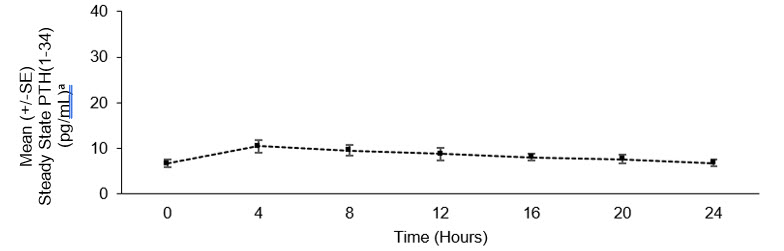
Mean steady state concentration-time profile of PTH(1-34) over 24 hours following administration of YORVIPATH is presented in Figure 4. At steady state, administration of YORVIPATH resulted in continuous exposure to released PTH throughout the 24-hour dosing period.
Figure 4: Mean Steady State PTH(1-34) Following Subcutaneous Administration of YORVIPATH* in Subjects with Hypoparathyroidism a PTH(1-34) concentrations includes PTH(1-34) and active metabolite PTH(1-33). - * Mean dose (range): 22.3 (12-33) mcg/day, n=7.
Absorption
The median (range) time to reach maximum concentrations (Tmax) of PTH is 4 (4 to 8) hours.
Distribution
The estimated apparent volume of distribution (CV%) of palopegteriparatide is 4.8 (50) L. A similar distribution pattern as observed for endogenous PTH is expected for PTH released from palopegteriparatide.
Elimination
The apparent half-life of PTH released from palopegteriparatide is approximately 60 hours. The estimated clearance (CV%) of palopegteriparatide at steady state is 0.58 (52) L/day.
Specific Populations
There are no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of palopegteriparatide based on age, sex, or body weight. The data for race and ethnicity did not show any trends indicating differences, but the available data are too limited to make definitive conclusions.
Patients with Renal Impairment
A dedicated renal impairment study showed that mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment did not have a clinically significant impact on systemic exposure of total PTH following a single 50 mcg subcutaneous dose of palopegteriparatide. No studies were conducted in subjects with hypoparathyroidism who have severe renal impairment.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of YORVIPATH or other teriparatide products.
Mean duration of exposure to YORVIPATH in clinical studies was 850 days. Of patients with post-baseline assessments, 0.7% (1 of 139 YORVIPATH-treated patients) had low titer, non-neutralizing antibodies towards PTH and 5% (7 of 139 YORVIPATH-treated patients) had low titer treatment-emergent antibodies against PEG. Three of 139 YORVIPATH-treated patients (2.2%) had pre-existing PEG antibodies that had a transient impact on the pharmacokinetics of palopegteriparatide and serum calcium, however, therapeutic effectiveness was maintained by dose adjustment of YORVIPATH using the trial titration algorithm.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies to address the carcinogenic potential of palopegteriparatide have not been conducted.
Palopegteriparatide was not genotoxic in an in vitro bacterial reverse-mutation assay (Ames test), an in vitro human lymphocyte chromosome-aberration assay, and an in vivo rat bone-marrow micronucleus assay.
In fertility studies, palopegteriparatide was administered by subcutaneous injection at 2, 6, and 20 mcg/kg/day. Palopegteriparatide did not impair fertility in male and female rats up to the highest tested dose, which is 7-fold and 11-fold the MRHD, respectively, based on PTH(1-34) and active metabolite PTH(1-33) exposure by AUC.
13.2 Animal Pharmacology and Toxicology
In a 26-week rat study, daily subcutaneous administration of palopegteriparatide resulted in bone turnover imbalances in healthy euparathyroid rats. The bone effects tended towards a net catabolic effect (bone resorption) as evidenced by a decrease in proximal tibial trabecular bone volume and bone mineral content (BMC) in both sexes treated at the low dose of 5 mcg/kg/day (5-fold the MRHD, based on PTH(1-34) and active metabolite PTH(1-33) exposure by AUC) and in females treated at 10 mcg/kg/day (9-fold the MRHD, based on PTH(1-34) and PTH(1-33) exposure by AUC). A net anabolic bone effect (bone formation) including histologic increases in bone at several skeletal sites accompanied by increased osteoblast cellularity and increases in proximal tibia trabecular bone volume and BMC were observed in males at 10 mcg/kg/day (10-fold the MRHD, based on PTH(1-34) and PTH(1-33) exposure by AUC) and in both sexes treated at the high dose of 20 mcg/kg/day (19-fold the MRHD, based on PTH(1-34) and PTH(1-33) exposure by AUC). In a 4-week study in hypoparathyroid female rats, daily subcutaneous administration of palopegteriparatide at 5 and 10 mcg/kg/day (5- to 9-fold the MRHD, based on PTH(1-34) and PTH(1-33) exposure by AUC) resulted in a net catabolic bone effect as bone resorption (e.g., high urinary C-telopeptide of type 1 collagen, decreased tibial trabecular bone volume, increase in osteoclast surface, and endocortical eroded surface) appeared to exceed bone formation.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Treatment of Adults with Hypoparathyroidism
The effectiveness and safety of YORVIPATH in adults with hypoparathyroidism were evaluated in a 26-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study (Study 1 [NCT04701203]).
Study 1 was conducted in 82 subjects with hypoparathyroidism. Prior to randomization, all subjects underwent an approximate 4-week screening period in which calcium and active vitamin D supplements were adjusted to achieve an albumin-corrected serum calcium concentration between 7.8 and 10.6 mg/dL, a magnesium concentration ≥1.3 mg/dL and below the upper limit of the reference range, and a 25(OH) vitamin D concentration between 20 to 80 ng/mL. During the double-blind period, subjects were randomized to either YORVIPATH (N = 61) or placebo (N= 21), at a starting dose of 18 mcg/day, co-administered with conventional therapy (calcium and active vitamin D). Randomization was stratified by etiology of hypoparathyroidism (postsurgical vs. all other causes). Study drug and conventional therapy were subsequently titrated according to the albumin-corrected serum calcium levels [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
The mean age at enrollment was 49 years (range: 19 to 78 years), 78% were female, and 93% were Caucasian. Eighty-five percent (85%) of subjects had hypoparathyroidism acquired from neck surgery. Of the subjects with other etiologies of hypoparathyroidism, 7 (8.5%) subjects had idiopathic disease, 2 had autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1 (APS-1), 1 had autosomal dominant hypocalcemia type 1 (ADH1, CaSR mutation), 1 had DiGeorge Syndrome, and 1 had hypoparathyroidism, sensorineural deafness and renal dysplasia (HDR) syndrome (GATA3 mutation). At baseline, the median duration of hypoparathyroidism was 8.5 years (range 1 to 56 years). Baseline mean albumin-corrected serum calcium was 8.8 mg/dL and 8.6 mg/dL and mean 24-hour urine calcium was 392 mg/day and 329 mg/day for YORVIPATH and placebo, respectively. The mean baseline dose of elemental calcium was 1839 mg/day, and the mean baseline doses of active vitamin D were 0.75 mcg/day in calcitriol-treated subjects (n=70), and 2.3 mcg/day in alfacalcidol-treated subjects (n=12).
Efficacy Assessment and Results
Efficacy was assessed based on the proportion of subjects who achieved all of the following at Week 26:
- Albumin-corrected serum calcium in the normal range (8.3 to 10.6 mg/dL),
- Independence from conventional therapy (defined as requiring no active vitamin D and ≤600 mg/day of calcium supplementation, including no use of pro re nata [PRN] doses) since Week 22,
- No increase in the study drug dose since Week 22,
- No missing active vitamin D and calcium data since Week 22, and
- Study drug dose of 30 mcg or less once daily during the 26-week treatment period
In the YORVIPATH group, 68.9% (42/61) of subjects met the efficacy endpoint at Week 26 compared with 4.8% (1/21) of subjects in the placebo group. The treatment difference was 64.2% (95% confidence interval: 49.5%, 78.8%) (Table 5).
Table 5: Efficacy at Week 26 in Adults with Hypoparathyroidism in Study 1 YORVIPATH
(N=61)Placebo
(N=21)Response Rate Difference
(95% CI)Abbreviations: CI: confidence interval; NA: not applicable; PRN: pro re nata. - * Normal range for albumin-corrected serum calcium was 8.3 to 10.6 mg/dL.
- † No daily standing doses of active vitamin D, no PRN doses, and no missing active vitamin D data within 4 weeks prior to Week 26 visit.
- ‡ Average daily standing dose of elemental calcium ≤600 mg, no PRN doses, and no missing calcium data within 4 weeks prior to Week 26 visit.
- § No increase in study drug dose within 4 weeks prior to Week 26 visit.
- ¶ Subjects who received more than 30 mcg/day at any timepoint during the 26-week treatment period were considered as non-responders for the efficacy endpoint.
Overall Response at Week 26 42 (68.9%) 1 (4.8%) 64.2% (49.5%, 78.8%) Response for each component Normal albumin-corrected serum calcium* 49 (80.3%) 10 (47.6%) 32.7% (9.2%, 56.3%) Independence from active vitamin D† 58 (95.1%) 5 (23.8%) 71.3% (52.5%, 90.2%) Independence from therapeutic dose of calcium‡ 53 (86.9%) 1 (4.8%) 82.2% (70.0%, 94.4%) No increase in study drug dose since Week 22§ 57 (93.4%) 12 (57.1%) 36.4% (14.2%, 58.5%) Study drug dose ≤30 mcg/day up to Week 26¶ 56 (91.8%) NA NA The proportion of subjects randomized to YORVIPATH who met the efficacy endpoint decreased over time as follows: 68.9% (42/61) at Week 26 and 39.3% (24/61) at both Week 52 and Week 78 during the open-label extension period. Allowing for dose up-titration, the proportion of subjects who were able to maintain normocalcemia and independence from active vitamin D and therapeutic dose of calcium was 64% (39/61) at Week 52 and 66% (40/61) at Week 78.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
YORVIPATH is available in a prefilled, disposable, 14-dose pen-injector (Table 6). Each pen contains a clear and colorless solution of 3456 mcg/mL of palopegteriparatide equivalent to 300 mcg/mL of teriparatide. Each pack contains 2 prefilled pens and 28 needles for 28 injections (plus two spare needles).
Table 6: YORVIPATH Prefilled Pen Presentations Prefilled Pen Presentation Labeled Doses Content of Pack NDC YORVIPATH
(168 mcg/0.56 mL) identified by blue push button6, 9, and 12 mcg 2 prefilled pens
30 needles73362-100-01 YORVIPATH
(294 mcg/0.98 mL) identified by orange push button15, 18, and 21 mcg 2 prefilled pens
30 needles73362-101-01 YORVIPATH
(420 mcg/1.4 mL) identified by burgundy push button24, 27, and 30 mcg 2 prefilled pens
30 needles73362-102-01 16.2 Storage and Handling
Do not freeze. Store away from heat. Keep YORVIPATH in the packaging to protect from light.
Until first use, store YORVIPATH in the refrigerator between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
After first use, store YORVIPATH for 14 days at room temperature below 30°C (86°F). After each use, remove the needle and put the pen cap on to protect from light. Discard the prefilled pen 14 days after first use.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Dosage and Administration
Advise patients to use only one injection to achieve the once daily recommended dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Advise patients that the healthcare provider may change the dose of YORVIPATH, calcium, or active vitamin D supplements based on serum calcium levels.
Advise patients to administer YORVIPATH subcutaneously to the abdomen or front of the thigh. Advise patients to rotate the injection site daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
Adverse Reactions
Risk of YORVIPATH Adverse Reactions with Use of Two Injections to Achieve the Recommended Once Daily Dosage
Advise patients that using two YORVIPATH injections to achieve the recommended once daily dosage increases the variability of the total delivered dose, which can cause unintended changes in serum calcium levels, including hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia. Advise patients to use only one YORVIPATH injection to achieve the recommended once daily dosage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Serious Hypercalcemia and Serious Hypocalcemia
Advise patients taking YORVIPATH to contact their healthcare provider promptly if they develop symptoms of hypercalcemia (e.g., nausea, vomiting, constipation, lethargy, muscle weakness) or hypocalcemia, to report abrupt discontinuations in YORVIPATH dosing, and to follow recommended serum calcium monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
Potential Risk of Osteosarcoma
Advise patients that administration of other PTH products causes an increase in the incidence of osteosarcoma in rats. No increased risk of osteosarcoma was observed with teriparatide compared to a general population. Advise patients to promptly report clinical symptoms (e.g., persistent localized pain) and signs (e.g., soft tissue mass tender to palpation) that could be consistent with osteosarcoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Orthostatic Hypotension
When initiating YORVIPATH treatment, advise patients to be prepared to immediately sit or lie down during or after administration if they feel lightheaded or have palpitations after the injection until their symptoms resolve. If these symptoms persist or worsen, advise patients to consult their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Digoxin Toxicity
Advise patients to report use of a digoxin-containing medication and to follow recommended serum calcium and digoxin monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Hypersensitivity
Advise patients that serious hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis and angioedema) are possible with PTH products. Advise patients to discontinue YORVIPATH and promptly seek medical attention if signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reaction occur [see Contraindications (4)].
Pregnancy
Advise females who are exposed to YORVIPATH during pregnancy that there is a pregnancy safety study that monitors pregnancy outcomes. Encourage these patients to report their pregnancy to Ascendis Pharma (1-844-442-7236) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
©2024 Ascendis Pharma. All rights reserved. YORVIPATH®, Ascendis®, TransCon®, and Ascendis Pharma logo and the company logo are trademarks owned by the Ascendis Pharma Group.
PATENT INFORMATION: www.ascendispharma.us/products/patents
Manufactured by:
Ascendis Pharma Bone Diseases A/S
Tuborg Boulevard 12, DK-2900 Hellerup, DenmarkFor information about YORVIPATH contact:
Ascendis Pharma Endocrinology, Inc.
212 Carnegie Center, Suite 301
Princeton, New Jersey 08540, USA
1-844-442-7236 (1-844-44ASCENDIS)
www.YORVIPATH.com -
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
YORVIPATH® (YOR-vih-path)
(palopegteriparatide)
injection, for subcutaneous useThis Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approved: 08/2024 What is the most important information I should know about YORVIPATH?
YORVIPATH may cause serious side effects, including:- High levels of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia). YORVIPATH can cause some people to have higher blood calcium levels than normal. Your health care provider should check your blood calcium before you start and during your treatment with YORVIPATH. Tell your health care provider if you have nausea, vomiting, dizziness, feeling thirsty, confusion, muscle weakness, and irregular heartbeat. Hypercalcemia is more likely to occur within the first 3 months of starting YORVIPATH, but it may occur at any time.
- Low levels of calcium in the blood (hypocalcemia). People who stop using, miss, or change a dose of YORVIPATH may have an increased risk of low blood calcium levels, but hypocalcemia may occur at any time. Tell your health care provider if you have tingling in your fingertips, toes, lips or tongue, muscle spasms or cramps, oral numbness, depression, have problems thinking or remembering, abnormal heart rhythms, and seizures.
- Possible bone cancer (osteosarcoma). Tell your health care provider right away if you have pain in any areas of your body that does not go away or any new or unusual lumps or swelling under your skin that is tender to touch. These are some of the signs and symptoms of osteosarcoma and your health care provider may need to do further tests.
See "What are the possible side effects of YORVIPATH?" for information about side effects.What is YORVIPATH? - YORVIPATH is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with low parathyroid hormone (PTH) (hypoparathyroidism).
It is not known if YORVIPATH is safe and effective if it is started in people with low levels of calcium in the blood.
It is not known if YORVIPATH is safe and effective in children.
YORVIPATH should not be used in children and young adults whose bones are still growing.Who should not take YORVIPATH?
Do not use YORVIPATH if you:- are allergic to palopegteriparatide or any of the other ingredients in YORVIPATH. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in YORVIPATH.
Before using YORVIPATH, tell your health care provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - are at higher risk of a type of bone cancer called osteosarcoma. This is especially important:
- if you have a bone disease that increases your risk of developing osteosarcoma (including if you have Paget's disease).
- if a blood test shows that you have unexplained increases in bone alkaline phosphatase.
- if you have cancer of the bones or other cancer that has spread to your bones.
- if you are having or have had radiation therapy to the skeleton.
- if you are affected with a condition that runs in your family that can increase your chance of getting cancer in your bones.
- take medicines that contain digoxin.
- take medicines used to treat osteoporosis.
- take medicines that can affect calcium levels in your blood.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if YORVIPATH will harm your unborn baby.
- Tell your health care provider if you become pregnant during treatment with YORVIPATH.
- If you become pregnant while being treated with YORVIPATH, you are encouraged to enroll in the Pregnancy Safety Study. The purpose of the pregnancy safety study is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. Contact Ascendis Pharma at 1-844-442-7236 as soon as you learn that you are pregnant or ask your health care provider to contact them for you.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if YORVIPATH passes into your breast milk. Talk to your health care provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with YORVIPATH.
How should I use YORVIPATH? - Read the detailed Instructions for Use that comes with YORVIPATH.
- Use YORVIPATH exactly as your health care provider tells you to take it.
- Before you use YORVIPATH for the first time, a health care provider should show you how to use the pen the right way.
- Some people may feel dizzy, get a fast heartbeat, or feel light-headed right after injecting YORVIPATH. For the first few doses, give your injection of YORVIPATH in a place where you can sit or lie down right away if you get these symptoms. If your symptoms get worse or do not go away, contact your health care provider before you continue using YORVIPATH.
- Do not stop taking or change your dose of YORVIPATH unless your health care provider tells you to. The levels of calcium in your blood may change, and you may develop symptoms. See "What are the possible side effects of YORVIPATH?"
- Give no more than 1 YORVIPATH injection each day in your belly (abdomen) or in the front of the thigh just under your skin (subcutaneous). Inject into a different area each day to help avoid damaging your skin.
- Throw away each pen 14 days after first use.
- YORVIPATH is colorless. Do not use YORVIPATH if you notice that the solution is cloudy, colored, or has visible particles in it.
- Your health care provider should check your blood calcium level when you start and while you are using YORVIPATH. After you start YORVIPATH, your health care provider may change your doses of calcium and active vitamin D.
- If you miss a day or forget to inject your daily dose of YORVIPATH, you can inject the dose as soon as you remember if less than 12 hours have passed. If the dose has been missed by more than 12 hours, skip the missed dose and continue injecting your next dose as you normally would.
What are the possible side effects of YORVIPATH?
YORVIPATH may cause serious side effects:- See "What is the most important information I should know about YORVIPATH?"
- Allergic (hypersensitivity) reaction, including anaphylaxis. Stop taking YORVIPATH and tell your health care provider or get emergency medical help right away if you have any of the following symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- swelling of your face, lips, mouth, or tongue
- breathing problems
- fainting, dizziness, feeling lightheaded (low blood pressure)
- fast heartbeat
- itching
- rash
- hives
- Decrease in blood pressure when you change positions (orthostatic hypotension). Some people may feel dizzy, get a fast heartbeat, or feel light-headed right after injecting YORVIPATH. For the first few doses, give your injection of YORVIPATH in a place where you can sit or lie down right away if you get these symptoms. If your symptoms get worse or do not go away, contact your health care provider before you continue using YORVIPATH.
- Digoxin toxicity if you are using digoxin and YORVIPATH at the same time. Tell your health care provider if you experience irregular heart rhythm, heart palpitations, confusion, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or vision problems.
These are not all of the possible side effects of YORVIPATH. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store YORVIPATH? - Before first use, store YORVIPATH in a refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Do not freeze. Store away from heat. Store in the package with the pen cap on in order to protect from light.
- After first use, store at room temperature below 86°F (30°C). Keep the pen cap on the prefilled pen in order to protect from light. Throw away each pen 14 days after first use.
General information about the safe and effective use of YORVIPATH.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use YORVIPATH for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give YORVIPATH to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or health care provider for information about YORVIPATH that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in YORVIPATH?
Active ingredient: palopegteriparatide
Inactive ingredients: mannitol, metacresol, sodium hydroxide, succinic acid, and water for injection.
Manufactured by: Ascendis Pharma Bone Diseases A/S, Denmark
YORVIPATH® is a registered trademark of Ascendis Pharma Group.
For more information, go to www.YORVIPATH.com or call 1-844-442-7236. -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Label Content FRONT
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Yorvipath®
(palopegteriparatide)
injection, for subcutaneous use
For 6, 9 or 12 mcg doses only
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to inject YORVIPATH
168 mcg/0.56 mL (300 mcg/mL) prefilled pen for 6, 9 or 12 mcg doses only
ascendis pharmaBack
Additional information
If you need help, please ask your health care provider or nurse for advice or contact the Ascendis Pharma Helpline:
Ascendis Pharma Helpline:
Toll-free telephone number:
1-844-442-7236
Ascendis Pharma Bone Diseases A/S
Tuborg Boulevard 12
DK-2900 Hellerup
Denmark
ascendis pharmaPanel 1

1. How often must I test the pen flow?
You should only test the pen flow (Section 2) the first time you use a new pen (or if you think it might be damaged) to not waste medicine. The test checks to make sure the medicine flows through the pen so that you get the right doses of medicine.
2. I do not see drops appear after I have tested the pen flow 5 times. What should I do?
If you see no drop on the needle tip after 5 attempts it might be because there is no flow through the pen and needle.
Change the needle (see Section 5, Step 12) and test the pen flow again (see Section 2, Steps A-C). You can be sure the flow works correctly when you see the drop of medicine.
If it still does not work, throw away (discard) the pen and contact your health care provider.
3. How do I know I have completed the injection?
Your injection is only completed after you have pressed the push button all the way in and the dose selector has rotated back to the "" and you have kept the needle in the skin for 5 seconds.
4. Why do I have to keep holding the pen in the skin for 5 seconds?
Some medicine might flow back into the pen or flow backward from the injection site and be left on the skin.
Holding the pen in the skin for 5 seconds helps to make sure that all the medicine has been injected.
5. I cannot dial the dose selector to the required dose. What should I do?
The pen does not allow a larger dose to be set than what is left in the pen.
If your dose is larger than the amount of medicine left in the pen you will not be able to dial a full dose. You must throw away your pen and take the full dose of medicine with a new pen.Panel 2

- Until first use, refrigerate your pens between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and keep in the package to protect from light.
- After first use, store your pen for 14 days at room temperature below 30°C (86°F).
- Do not leave your pen in a car or another place where it can get too hot or too cold.
- Do not freeze your pen.
- Store YORVIPATH away from heat.
- Keep the YORVIPATH pen out of the reach of children.
Panel 3

Caring For Your Pen - Handle your pen with care.
- Keep your pen dry.
- Use a moist cloth to clean your pen.
- Do not drop or knock your pen against hard surfaces. If you do, test the pen flow again (Section 2, Steps A – C) before next use.
- Do not apply extra force to your pen. It might be empty, damaged and no longer works properly.
- Do not attempt to repair a damaged pen yourself. If your pen is damaged, contact the Ascendis Pharma Helpline.
Panel 4

Important Information You Need To Know
Before Using Your YORVIPATH Pen
Read and follow this Instructions for Use carefully so that you inject YORVIPATH the right way.
If you do not understand or are unable to complete a step that is described in this Instructions for Use, contact your health care provider or nurse or the Ascendis Pharma Helpline.
Make sure you have received training from your health care provider or nurse before injecting. This is important to make sure that you get the correct treatment.
Inject YORVIPATH into the belly (abdomen) or in the front of the thigh.
Your pen can deliver doses of 6, 9 or 12 mcg. It is used for injections under the skin (subcutaneous) for daily treatment of hypoparathyroidism. Your pen is a prefilled dial-a-dose throw away (disposable) pen.
It contains medicine for 14 days of use and is intended to be used 1 time each day. Do not use more than one injection to achieve the recommended once daily dosage.
You can dial doses of 6, 9 or 12 mcg with the pen.
For Correct Use
If you are blind or visually impaired or if you have lack of concentration do not use your pen without help. Get help from a person who is trained to use the YORVIPATH pen. Store your pen out of the reach of children and any other persons who do not know how to handle it properly.Panel 5

- Only use your pen as directed by your health care provider or nurse.
- The pen and needles are for single-patient use only. Do not share your pen or needles with other people. It might lead to infection (cross-contamination).
- Start by checking your pen to make sure it is the correct pen.
- Always check the expiration date on the pen label and needle foil before use.
- Always inspect the pen visually before use to make sure it is not damaged and medicine is clear, colorless and without particles.
- Always use a new needle for each injection.
- Only inject into the abdomen or front of thigh as instructed by your health care provider or nurse. Remember to change injection site for each injection and avoid skin that is red, swollen or scarred.
- Always keep the cap on the pen when it is not in use to protect the medicine from light.
- Remove the needle after every use. Do not store the pen with the needle on.
- Always throw away your pen after 14 days of use, even if it still has medicine left inside. This is important to make sure that you get the right effect of your medicine.
- By failing to follow these instructions you may not get the right dose and may therefore not get the full effect of your medicine.
- Avoid bending or breaking off the pen needle.
- Do not change the injection angle after the needle has been inserted into the skin. Changing the angle can cause the needle to bend or break off. A bent or broken needle can remain stuck in the body or remain completely under the skin. If a broken needle remains stuck in the body or remains under the skin, seek medical help right away.
Panel 6

Compatible Pen Needles
In each of the two inner boxes there are 15 disposable Unifine© Pentips© Needles (31G × 5mm) together with a YORVIPATH prefilled pen for doses of 6, 9 or 12 mcg.
Always use the needles that come with YORVIPATH pen for your injections.
For Correct Disposal
Always put your used YORVIPATH needles in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Always put your used pen in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container after 14 days of use.
Do not throw away (dispose of) YORVIPATH in your household trash.
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:- made of heavy-duty plastic.
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out.
- upright and stable during use.
- leak-resistant.
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
Panel 7
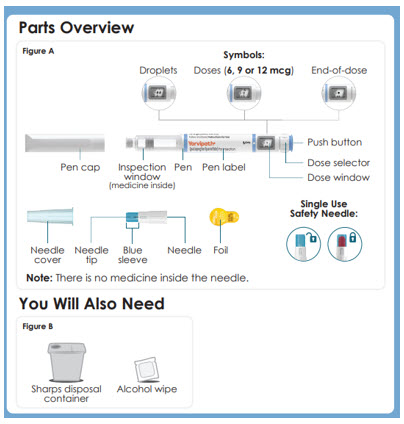
Parts Overview
Figure A
Symbols:
-Droplets
-Doses (6, 9 or 12 mcg)
-End-of-dose
-Pen cap
-Inspection window (medicine inside)
-Pen
-Pen label
-Push button
-Dose selector
-Dose window
-Single Use Needle
-Outer needle cover
-Inner Needle shield
-Needle tip
-Needle
-Foil
You Will Also Need
Figure B
Sharps disposal container
Alcohol wipePanel 8
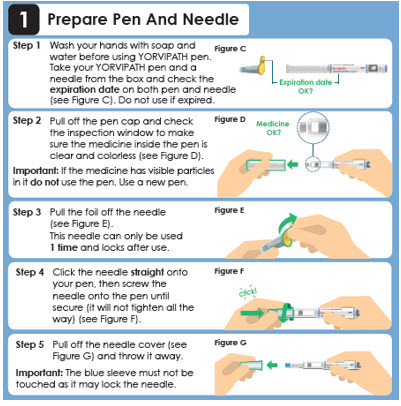
1 Prepare Pen And Needle
Step 1
Wash your hands with soap and water before using YORVIPATH pen. Take your YORVIPATH pen and a needle from the box and check the expiration date on both pen and needle (see Figure C). Do not use if expired.Expiration date OK?
Step 2
Pull off the pen cap and check the inspection window to make sure the medicine inside the pen is clear and colorless (see Figure D).
Important: If the medicine has visible particles in it do not use the pen. Use a new pen.Medicine OK?
Step 3
Pull the foil off the needle (see Figure E). This needle can only be used 1 time. Step 4
Attach the needle straight on to your pen, then screw the needle onto the pen until secure (see Figure F).
Step 5- Pull off the outer needle cover and
keep this for later needle removal (see Figure G: a). - Pull off the inner needle shield
and throw this away (see Figure G: b).
Panel 9

Day 1
Attention
Only test pen flow (Steps A – C) the first time you use a new pen.
If your pen is already in use, go to section "3 Prepare Injection".
Turn the dose selector clockwise (to the right) 2 clicks until you see the droplet symbol "
Note: You can always correct the selection by turning the dose selector. Step B " in the dose window (see Figure H).
" in the dose window (see Figure H).
Make any air bubbles rise to the top of the pen by tapping the inspection window (see Figure I). Keep the pen with the needle tip pointed up.
Note: Tiny air bubbles are ok.tap tap
Step C
Press the push button and watch drops of medicine come out of the needle tip. When you press, make sure that the dose selector rotates back to the symbol "" (see Figure J).
Important: If you do not see drops of medicine, repeat this test (Steps A – C) up to 5 times. If drops are still not seen, change the needle and repeat the test.Panel 10
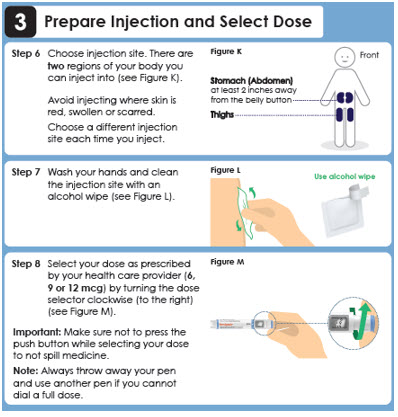
3 Prepare Injection and Select Dose
Step 6
Choose injection site. There are two regions of your body you can inject into (see Figure K).
Avoid injecting where skin is red, swollen or scarred. Choose a different injection site each time you inject.Front
Stomach (Abdomen) at least 2 inches away from the belly button
Thighs
Step 7
Wash your hands and clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe (see Figure L).Use alcohol wipe
Step 8
Select your dose as prescribed by your health care provider (6, 9 or 12 mcg) by turning the dose selector clockwise (to the right) (see Figure M).
Important: Make sure not to press the push button while selecting your dose to not spill medicine.
Note: Always throw away your pen and use another pen if you cannot dial a full dose.Panel 11
4 Inject Dose
Attention
Use the injection technique recommended by your health care provider or nurse.
Read this whole section (Steps 9 - 11) before you start to inject.
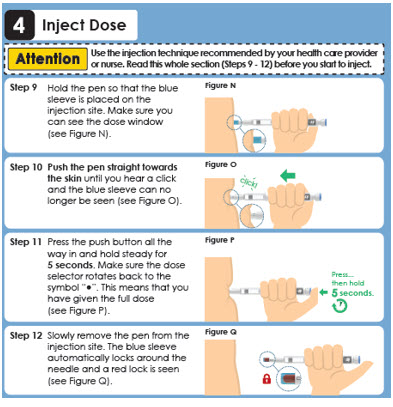
Step 9
Make sure you can see the dose window.
Insert the needle into the skin
(see Figure N).
Step 10
Press the push button all the way in and hold steady for 5 seconds. Make sure the dose selector rotates back to the symbol "●". This means that you have given the full dose (see Figure O).Figure O
Pres…
then hold 5 seconds.
Step 11
Slowly remove the pen from the injection site (see Figure P).Panel 12
5 Throw Away Used Needle
Step 12
Reattach the outer needle cover to carefully remove the needle. Insert the needle tip into the outer needle cover and secure the outer needle cover onto the needle (see Figure Q).
Important: Always reattach the outer needle cover before removing the needle to reduce the risk of needle stick and cross-contamination. Unscrew the needle and throw away the needle safely in accordance with local regulations (see Figure R). Step 14
Click the pen cap firmly onto the pen to protect it between injections and to protect the medicine from light (see Figure S).click!Panel 13
6 Throw Away Used Pen
Day 14
Important: Always throw away the pen 14 days after first use according to local regulations.
Always throw away your pen and any extra needles after 14 days of use, even if it still has medicine inside (see Figure T). This is important to make sure that you get the full effect of your medicine.This instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved 10/2025 -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Label Content FRONT
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Yorvipath®
(palopegteriparatide)
injection, for subcutaneous use
For 15, 18 or 21 mcg doses only
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to inject YORVIPATH
294 mcg/0.98 mL (300 mcg/mL) prefilled pen for 15, 18 or 21 mcg doses only
ascendis pharmaBack
Additional information
If you need help, please ask your health care provider or nurse for advice or contact the Ascendis Pharma Helpline:
Ascendis Pharma Helpline:
Toll-free telephone number:
1-844-442-7236
Ascendis Pharma Bone Diseases A/S
Tuborg Boulevard 12
DK-2900 Hellerup
Denmark
ascendis pharmaPanel 1 
Troubleshooting
1. How often must I test the pen flow?
You should only test the pen flow (Section 2) the first time you use a new pen (or if you think it might be damaged) to not waste medicine. The test checks to make sure the medicine flows through the pen so that you get the right doses of medicine.
2. I do not see drops appear after I have tested the pen flow 5 times. What should I do?
If you see no drop on the needle tip after 5 attempts it might be because there is no flow through the pen and needle.
Change the needle (see Section 5, Step 12) and test the pen flow again (see Section 2, Steps A-C). You can be sure the flow works correctly when you see the drop of medicine.
If it still does not work, throw away (discard) the pen and contact your health care provider.
3. How do I know I have completed the injection?
Your injection is only completed after you have pressed the push button all the way in and the dose selector has rotated back to the "" and you have kept the needle in the skin for 5 seconds.
4. Why do I have to keep holding the pen in the skin for 5 seconds?
Some medicine might flow back into the pen or flow backward from the injection site and be left on the skin. Holding the pen in the skin for 5 seconds helps to make sure that all the medicine has been injected.
5. I cannot dial the dose selector to the required dose. What should I do?
The pen does not allow a larger dose to be set than what is left in the pen. If your dose is larger than the amount of medicine left in the pen you will not be able to dial a full dose. You must throw away your pen and take the full dose of medicine with a new pen.Panel 2 
- Until first use, refrigerate your pens between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and keep in the package to protect from light.
- After first use, store your pen for 14 days at room temperature below 30°C (86°F).
- Do not leave your pen in a car or another place where it can get too hot or too cold.
- Do not freeze your pen.
- Store YORVIPATH away from heat.
- Keep the YORVIPATH pen out of the reach of children.
Panel 3 
Caring For Your Pen - Handle your pen with care.
- Keep your pen dry.
- Use a moist cloth to clean your pen.
- Do not drop or knock your pen against hard surfaces. If you do, test the pen flow again (Section 2, Steps A – C) before next use.
- Do not apply extra force to your pen. It might be empty, damaged and no longer works properly.
- Do not attempt to repair a damaged pen yourself. If your pen is damaged, contact the Ascendis Pharma Helpline.
Panel 4 
Important Information You Need To Know Before Using Your YORVIPATH Pen
Read and follow this Instructions for Use carefully so that you inject YORVIPATH the right way.
If you do not understand or are unable to complete a step that is described in this Instructions for Use, contact your health care provider or nurse or the Ascendis Pharma Helpline.
Make sure you have received training from your health care provider or nurse before injecting. This is important to make sure that you get the correct treatment.
Inject YORVIPATH into the belly (abdomen) or in the front of the thigh.
Your pen can deliver doses of 15, 18 or 21 mcg. It is used for injections under the skin (subcutaneous) for daily treatment of hypoparathyroidism. Your pen is a prefilled dial-a-dose throw away (disposable) pen.
It contains medicine for 14 days of use and is intended to be used 1 time each day. Do not use more than one injection to achieve the recommended once daily dosage.
You can dial doses of 15, 18 or 21 mcg with the pen.
For Correct Use
If you are blind or visually impaired or if you have lack of concentration do not use your pen without help. Get help from a person who is trained to use the YORVIPATH pen.
Store your pen out of the reach of children and any other persons who do not know how to handle it properly.Panel 5 
- Only use your pen as directed by your health care provider or nurse.
- The pen and needles are for single-patient use only. Do not share your pen or needles with other people. It might lead to infection (cross-contamination).
- Start by checking your pen to make sure it is the correct pen.
- Always check the expiration date on the pen label and needle foil before use.
- Always inspect the pen visually before use to make sure it is not damaged and medicine is clear, colorless and without particles.
- Always use a new needle for each injection.
- Only inject into the abdomen or front of thigh as instructed by your health care provider or nurse. Remember to change injection site for each injection and avoid skin that is red, swollen or scarred.
- Always keep the cap on the pen when it is not in use to protect the medicine from light.
- Remove the needle after every use. Do not store the pen with the needle on.
- Always throw away your pen after 14 days of use, even if it still has medicine left inside. This is important to make sure that you get the right effect of your medicine.
- By failing to follow these instructions you may not get the right dose and may therefore not get the full effect of your medicine.
- Avoid bending or breaking off the pen needle.
- Do not change the injection angle after the needle has been inserted into the skin. Changing the angle can cause the needle to bend or break off. A bent or broken needle can remain stuck in the body or remain completely under the skin. If a broken needle remains stuck in the body or remains under the skin, seek medical help right away.
Panel 6 
Compatible Pen Needles
In each of the two inner boxes there are 15 disposable Unifine© Pentips© Needles (31G × 5mm) together with a YORVIPATH prefilled pen for doses of 15, 18 or 21 mcg. Always use the needles that come with YORVIPATH pen for your injections.
For Correct Disposal
Always put your used YORVIPATH needles in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Always put your used pen in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container after 14 days of use.
Do not throw away (dispose of) YORVIPATH in your household trash.
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:- made of heavy-duty plastic.
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out.
- upright and stable during use.
- leak-resistant.
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
Panel 7 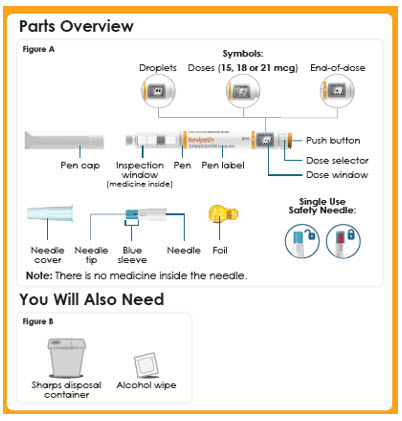
Parts Overview
Figure A
Symbols:
-Droplets
-Doses (15, 18 or 21 mcg)
-End-of-dose
-Pen cap
-Inspection window (medicine inside)
-Pen
-Pen label
-Push button
-Dose selector
-Dose window
-Single Use Needle
-Outer needle cover
-Inner Needle shield
-Needle tip
-Needle
-Foil
You Will Also Need
Figure B
Sharps disposal container
Alcohol wipePanel 8 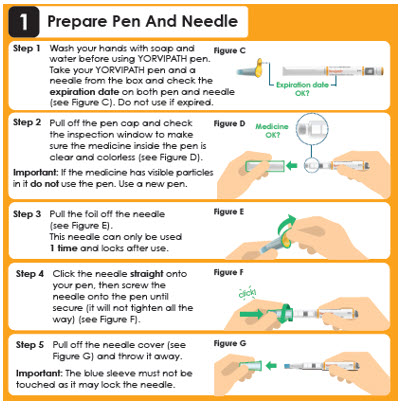
1 Prepare Pen And Needle
Step 1
Wash your hands with soap and water before using YORVIPATH pen. Take your YORVIPATH pen and a needle from the box and check the expiration date on both pen and needle (see Figure C). Do not use if expired.Expiration date OK?
Step 2
Pull off the pen cap and check the inspection window to make sure the medicine inside the pen is clear and colorless (see Figure D).
Important: If the medicine has visible particles in it do not use the pen. Use a new pen.Medicine OK?
Step 3
Pull the foil off the needle (see Figure E). This needle can only be used 1 time. Step 4
Attach the needle straight on to your pen, then screw the needle onto the pen until secure (see Figure F). Step 5- Pull off the outer needle cover and
keep this for later needle removal (see Figure G: a).. - Pull off the inner needle shield
and throw this away (see Figure G: b).
Panel 9 
Day 1
Attention
Only test pen flow (Steps A – C) the first time you use a new pen.
If your pen is already in use, go to section "3 Prepare Injection".
Turn the dose selector clockwise (to the right) 2 clicks until you see the droplet symbol "
Note: You can always correct the selection by turning the dose selector. Step B " in the dose window (see Figure H).
" in the dose window (see Figure H).
Make any air bubbles rise to the top of the pen by tapping the inspection window (see Figure I). Keep the pen with the needle tip pointed up.
Note: Tiny air bubbles are ok.tap tap
Step C
Press the push button and watch drops of medicine come out of the needle tip. When you press, make sure that the dose selector rotates back to the symbol "" (see Figure J).
Important: If you do not see drops of medicine, repeat this test (Steps A – C) up to 5 times. If drops are still not seen, change the needle and repeat the test.Panel 10 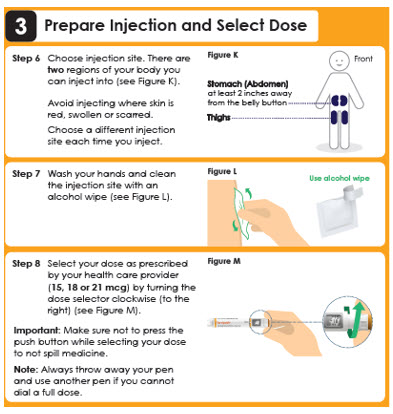
3 Prepare Injection and Select Dose
Step 6
Choose injection site. There are two regions of your body you can inject into (see Figure K).
Avoid injecting where skin is red, swollen or scarred. Choose a different injection site each time you inject.Front
Stomach (Abdomen) at least 2 inches away from the belly button
Thighs
Step 7
Wash your hands and clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe (see Figure L).Use alcohol wipe
Step 8
Select your dose as prescribed by your health care provider (15, 18 or 21 mcg) by turning the dose selector clockwise (to the right) (see Figure M).
Important: Make sure not to press the push button while selecting your dose to not spill medicine.
Note: Always throw away your pen and use another pen if you cannot dial a full dose.Panel 11 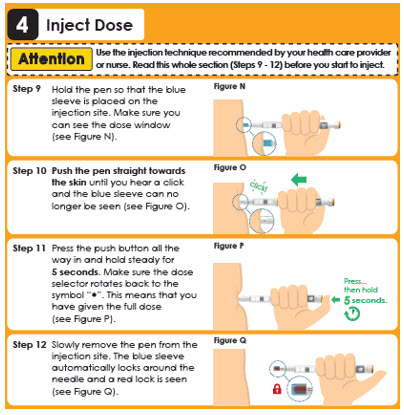
4 Inject Dose
Attention
Use the injection technique recommended by your health care provider or nurse.
Read this whole section (Steps 9 - 11) before you start to inject.
Step 9
Make sure you can see the dose window.
Insert the needle into the skin (see Figure N). Step 10
Press the push button all the way in and hold steady for 5 seconds.
Make sure the dose selector rotates back to the symbol "●".
This means that you have given the full dose (see Figure O).Pres…
then hold 5 seconds.
Step 11
Slowly remove the pen from the injection site (see Figure P).Panel 12 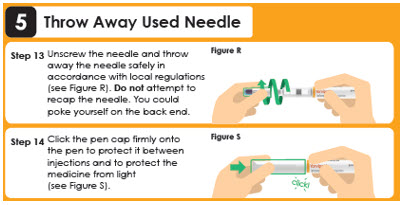
5 Throw Away Used Needle
Step 12
Reattach the outer needle cover to carefully remove the needle.
Insert the needle tip into the outer needle cover and secure the outer needle cover onto the needle (see Figure Q).
Important: Always reattach the outer needle cover before removing the needle to reduce the risk of needle stick and cross-contamination. Unscrew the needle and throw away the needle safely in accordance with local regulations (see Figure R). Step 14
Click the pen cap firmly onto the pen to protect it between injections and to protect the medicine from light (see Figure S).click!Panel 13 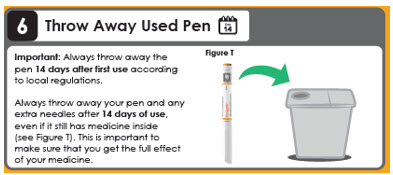
6 Throw Away Used Pen
Day 14
Important: Always throw away the pen 14 days after first use according to local regulations.
Always throw away your pen and any extra needles after 14 days of use, even if it still has medicine inside (see Figure T). This is important to make sure that you get the full effect of your medicine.This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved 10/2025 -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Label Content FRONT 
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Yorvipath®
(palopegteriparatide)
injection, for subcutaneous use
For 24, 27 or 30 mcg doses only
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to inject YORVIPATH
420 mcg/1,4 mL (300 mcg/mL) prefilled pen for 24, 27 or 30 mcg doses only
ascendis pharmaBack 
Additional information
If you need help, please ask your health care provider or nurse for advice or contact the Ascendis Pharma Helpline:
Ascendis Pharma Helpline:
Toll-free telephone number:
1-844-442-7236
Ascendis Pharma Bone Diseases A/S
Tuborg Boulevard 12
DK-2900 Hellerup
Denmark
ascendis pharmaPanel 1 
Troubleshooting
1. How often must I test the pen flow?
You should only test the pen flow (Section 2) the first time you use a new pen (or if you think it might be damaged) to not waste medicine. The test checks to make sure the medicine flows through the pen so that you get the right doses of medicine.
2. I do not see drops appear after I have tested the pen flow 5 times. What should I do?If you see no drop on the needle tip after 5 attempts it might be because there is no flow through the pen and needle.
Change the needle (see Section 5, Step 12) and test the pen flow again (see Section 2, Steps A-C). You can be sure the flow works correctly when you see the drop of medicine.
If it still does not work, throw away (discard) the pen and contact your health care provider.
3. How do I know I have completed the injection?
Your injection is only completed after you have pressed the push button all the way in and the dose selector has rotated back to the "∙" and you have kept the needle in the skin for 5 seconds.
4. Why do I have to keep holding the pen in the skin for 5 seconds?
Some medicine might flow back into the pen or flow backward from the injection site and be left on the skin. Holding the pen in the skin for 5 seconds helps to make sure that all the medicine has been injected.
5. I cannot dial the dose selector to the required dose. What should I do?
The pen does not allow a larger dose to be set than what is left in the pen.
If your dose is larger than the amount of medicine left in the pen you will not be able to dial a full dose. You must throw away your pen and take the full dose of medicine with a new pen.Panel 2 
Storing Your Pen - Until first use, refrigerate your pens between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and keep in the package to protect from light.
- After first use, store your pen for 14 days at room temperature below 30°C (86°F).
- Do not leave your pen in a car or another place where it can get too hot or too cold.
- Do not freeze your pen.
- Store YORVIPATH away from heat.
- Keep the YORVIPATH pen out of the reach of children.
Panel 3 
Caring For Your Pen - Handle your pen with care.
- Keep your pen dry.
- Use a moist cloth to clean your pen.
- Do not drop or knock your pen against hard surfaces. If you do, test the pen flow again (Section 2, Steps A – C) before next use.
- Do not apply extra force to your pen. It might be empty, damaged and no longer works properly.
- Do not attempt to repair a damaged pen yourself. If your pen is damaged, contact the Ascendis Pharma Helpline.
Panel 4 
Important Information You Need To Know Before Using Your YORVIPATH Pen
Read and follow this Instructions for Use carefully so that you inject YORVIPATH the right way.
If you do not understand or are unable to complete a step that is described in this Instructions for Use, contact your health care provider or nurse or the Ascendis Pharma Helpline.
Make sure you have received training from your health care provider or nurse before injecting. This is important to make sure that you get the correct treatment.
Inject YORVIPATH into the belly (abdomen) or in the front of the thigh.
Your pen can deliver doses of 24, 27 or 30 mcg. It is used for injections under the skin (subcutaneous) for daily treatment of hypoparathyroidism. Your pen is a prefilled dial-a-dose throw away (disposable) pen.
It contains medicine for 14 days of use and is intended to be used 1 time each day. Do not use more than one injection to achieve the recommended once daily dosage.
You can dial doses of 24, 27 or 30 mcg with the pen.
For Correct Use
If you are blind or visually impaired or if you have lack of concentration do not use your pen without help. Get help from a person who is trained to use the YORVIPATH pen.
Store your pen out of the reach of children and any other persons who do not know how to handle it properly.Panel 5 
- Only use your pen as directed by your health care provider or nurse.
- The pen and needles are for single-patient use only. Do not share your pen or needles with other people. It might lead to infection (cross-contamination).
- Start by checking your pen to make sure it is the correct pen.
- Always check the expiration date on the pen label and needle foil before use.
- Always inspect the pen visually before use to make sure it is not damaged and medicine is clear, colorless and without particles.
- Always use a new needle for each injection.
- Only inject into the abdomen or front of thigh as instructed by your health care provider or nurse. Remember to change injection site for each injection and avoid skin that is red, swollen or scarred.
- Always keep the cap on the pen when it is not in use to protect the medicine from light.
- Remove the needle after every use. Do not store the pen with the needle on.
- Always throw away your pen after 14 days of use, even if it still has medicine left inside. This is important to make sure that you get the right effect of your medicine.
- By failing to follow these instructions you may not get the right dose and may therefore not get the full effect of your medicine.
- Avoid bending or breaking off the pen needle.
- Do not change the injection angle after the needle has been inserted into the skin. Changing the angle can cause the needle to bend or break off. A bent or broken needle can remain stuck in the body or remain completely under the skin. If a broken needle remains stuck in the body or remains under the skin, seek medical help right away.
Panel 6 
Compatible Pen Needles
In each of the two inner boxes there are 15 disposable Unifine© Pentips© Needles (31G × 5mm) together with a YORVIPATH prefilled pen for doses of 24, 27 or 30 mcg.
Always use the needles that come with YORVIPATH pen for your injections.
For Correct Disposal
Always put your used YORVIPATH needles in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Always put your used pen in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container after 14 days of use.
Do not throw away (dispose of) YORVIPATH in your household trash.
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:- made of heavy-duty plastic.
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out.
- upright and stable during use.
- leak-resistant.
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
Panel 7 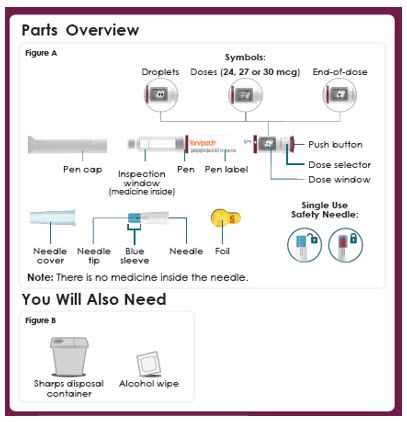
Parts Overview
Figure A
Symbols:
-Droplets
-Doses (24, 27 or 30 mcg)
-End-of-dose
-Pen cap
-Inspection window (medicine inside)
-Pen
-Pen label
-Push button
-Dose selector
-Dose window
-Single Use Needle
-Outer needle cover
-Inner Needle shield
-Needle tip
-Needle
-Foil
You Will Also Need Figure B
Sharps disposal container Alcohol wipePanel 8 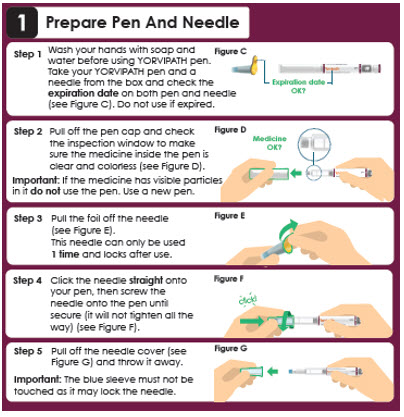
1 Prepare Pen And Needle
Step 1
Wash your hands with soap and water before using YORVIPATH pen. Take your YORVIPATH pen and a needle from the box and check the expiration date on both pen and needle (see Figure C). Do not use if expired.Expiration date OK?
Step 2
Pull off the pen cap and check the inspection window to make sure the medicine inside the pen is clear and colorless (see Figure D).
Important: If the medicine has visible particles in it do not use the pen. Use a new pen.Medicine OK?
Step 3
Pull the foil off the needle (see Figure E). This needle can only be used 1 time. Step 4
Attach the needle straight on to your pen, then screw the needle onto the pen until secure (see Figure F). Step 5- Pull off the outer needle cover and
keep this for later needle removal (see Figure G: a). - Pull off the inner needle shield
and throw this away (see Figure G: b).
Panel 9 
Day 1
Attention
Only test pen flow (Steps A – C) the first time you use a new pen.
If your pen is already in use, go to section "3 Prepare Injection".
Turn the dose selector clockwise (to the right) 2 clicks until you see the droplet symbol "
Note: You can always correct the selection by turning the dose selector. Step B " in the dose window (see Figure H).
" in the dose window (see Figure H).
Make any air bubbles rise to the top of the pen by tapping the inspection window (see Figure I). Keep the pen with the needle tip pointed up.
Note: Tiny air bubbles are ok.tap tap
Step C
Press the push button and watch drops of medicine come out of the needle tip. When you press, make sure that the dose selector rotates back to the symbol "" (see Figure J).
Important: If you do not see drops of medicine, repeat this test (Steps A – C) up to 5 times. If drops are still not seen, change the needle and repeat the test.Panel 10 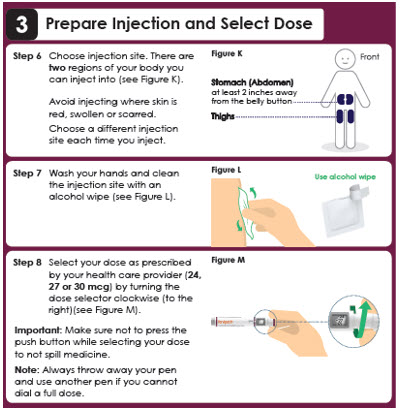
3 Prepare Injection and Select Dose
Step 6
Choose injection site. There are two regions of your body you can inject into (see Figure K).
Avoid injecting where skin is red, swollen or scarred. Choose a different injection site each time you inject.Front
Stomach (Abdomen) at least 2 inches away from the belly button
Thighs
Step 7
Wash your hands and clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe (see Figure L).Use alcohol wipe
Step 8
Select your dose as prescribed by your health care provider (24, 27 or 30 mcg) by turning the dose selector clockwise (to the right) (see Figure M).
Important: Make sure not to press the push button while selecting your dose to not spill medicine.
Note: Always throw away your pen and use another pen if you cannot dial a full dose.Panel 11 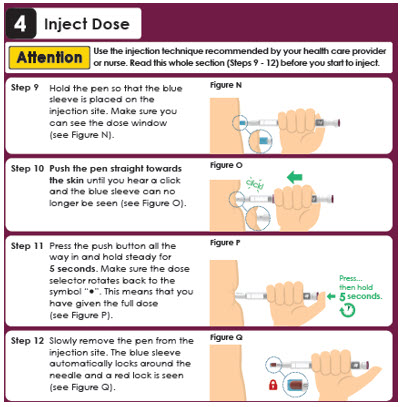
4 Inject Dose
Attention
Use the injection technique recommended by your health care provider or nurse.
Read this whole section (Steps 9 - 11) before you start to inject.
Step 9
Make sure you can see the dose window.
Insert the needle into the skin
(see Figure N). Step 10
Press the push button all the way in and hold steady for 5 seconds. Make sure the dose selector rotates back to the symbol "". This means that you have given the full dose (see Figure O).Pres…
then hold 5 seconds.
Step 11
Slowly remove the pen from the injection site (see Figure P).Panel 12 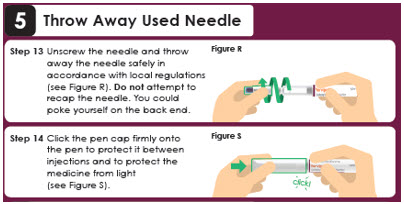
5 Throw Away Used Needle Reattach the outer needle cover to carefully remove the needle. Insert the needle tip into the outer needle cover and secure the outer needle cover onto the needle (see Figure Q).
Important: Always reattach the outer needle cover before removing the needle to reduce the risk of needle stick and cross-contamination.
Figure Q
Step 13
Unscrew the needle and throw away the needle safely in accordance with local regulations (see Figure R).
Figure R
Step 14
Click the pen cap firmly onto the pen to protect it between injections and to protect the medicine from light (see Figure S).click!Panel 13 
6 Throw Away Used Pen
Day 14
Important: Always throw away the pen 14 days after first use according to local regulations.
Always throw away your pen and any extra needles after 14 days of use, even if it still has medicine inside (see Figure T). This is important to make sure that you get the full effect of your medicine.Figure T
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved 10/2025 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 168 mcg/0.56 mL Pen Carton
Yorvipath®
(palopegteriparatide) for injection168 mcg/0.56 mL prefilled pens
For 6 mcg, 9 mcg or 12 mcg doses only
For subcutaneous use
For single patient use onlyDispense in this sealed carton
Important:
- Follow enclosed Instructions For Use
- Until first use, pens must be refrigerated at
2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and keep in the
package to protect from light - After first use, store the pen in use at room
temperature below 30°C (86°F) - Do not freeze
- Store away from heat
- Every time after use, put pen cap on
to protect from light - Throw away the pen in use 14 days after
first use - Keep out of the reach of children
Rx Only
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 294 mcg/0.98 mL Pen Carton
Yorvipath®
(palopegteriparatide) for injection294 mcg/0.98 mL prefilled pens
For 15 mcg, 18 mcg or 21 mcg doses only
For subcutaneous use
For single patient use onlyDispense in this sealed carton
Important:
- Follow enclosed Instructions For Use
- Until first use, pens must be refrigerated at
2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and keep in the
package to protect from light - After first use, store the pen in use at room
temperature below 30°C (86°F) - Do not freeze
- Store away from heat
- Every time after use, put pen cap on
to protect from light - Throw away the pen in use 14 days after
first use - Keep out of the reach of children
Rx Only

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 420 mcg/1.4 mL Pen Carton
Yorvipath®
(palopegteriparatide) for injection420 mcg/1.4 mL prefilled pens
For 24 mcg, 27 mcg or 30 mcg doses only
For subcutaneous use
For single patient use onlyDispense in this sealed carton
Important:
- Follow enclosed Instructions For Use
- Until first use, pens must be refrigerated at
2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and keep in the
package to protect from light - After first use, store the pen in use at room
temperature below 30°C (86°F) - Do not freeze
- Store away from heat
- Every time after use, put pen cap on
to protect from light - Throw away the pen in use 14 days after
first use - Keep out of the reach of children
Rx Only
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
YORVIPATH
palopegteriparatide injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 73362-100 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Palopegteriparatide (UNII: G2N64C3385) (Teriparatide - UNII:10T9CSU89I) Teriparatide 168 ug in 0.56 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 73362-100-01 2 in 1 CARTON 08/09/2024 1 NDC: 73362-100-02 1 in 1 BOX 1 NDC: 73362-100-03 1 in 1 SYRINGE 1 0.56 mL in 1 CARTRIDGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA216490 08/09/2024 YORVIPATH
palopegteriparatide injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 73362-101 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Palopegteriparatide (UNII: G2N64C3385) (Teriparatide - UNII:10T9CSU89I) Teriparatide 294 ug in 0.98 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 73362-101-01 2 in 1 CARTON 08/09/2024 1 NDC: 73362-101-02 1 in 1 BOX 1 NDC: 73362-101-03 1 in 1 SYRINGE 1 0.98 mL in 1 CARTRIDGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA216490 08/09/2024 YORVIPATH
palopegteriparatide injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 73362-102 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Palopegteriparatide (UNII: G2N64C3385) (Teriparatide - UNII:10T9CSU89I) Teriparatide 420 ug in 1.4 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 73362-102-01 2 in 1 CARTON 08/09/2024 1 NDC: 73362-102-02 1 in 1 BOX 1 NDC: 73362-102-03 1 in 1 SYRINGE 1 1.4 mL in 1 CONTAINER; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA216490 08/09/2024 Labeler - Ascendis Pharma, Endocrinology, Inc. (118185491)
Trademark Results [Yorvipath]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 YORVIPATH 97197252 not registered Live/Pending |
Ascendis Pharma Endocrinology Division A/S 2021-12-30 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.