FEMLYV- norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol kit
FEMLYV by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
FEMLYV by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Millicent US, Inc., Patheon Inc. (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FEMLYV™ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FEMLYV.
FEMLYV (norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol orally disintegrating tablets)
Initial U.S. Approval: 1968WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Dosage and Administration, Dosing FEMLYV (2.1)
XX/2025
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FEMLYV is a combination of norethindrone acetate, a progestin, and ethinyl estradiol, an estrogen, indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy (1)
Limitations of Use
The efficacy in females of reproductive potential with a body mass index of more than 35 kg/m2 has not been evaluated (1, 8.8)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Place one FEMLYV orally disintegrating tablet (ODT) on the tongue, allow to disintegrate and then follow with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water.
- The tablets can also be swallowed whole with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water.
- Take at the same time daily without regards to meals (2.1, 12.3)
- Take ODTs in the order directed on the blister pack (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Orally disintegrating tablets (3):
- 24 ODTs each containing 1 mg norethindrone acetate and 0.02 mg ethinyl estradiol
- 4 inert ODTs
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- A high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic diseases (4)
- Breast cancer or history of breast cancer (4)
- Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or hepatic impairment (4)
- Co-administration with Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir (4)
- Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems: Discontinue FEMLYV if a thrombotic event occurs. Discontinue at least 4 weeks before through 2 weeks after major surgery. Start no earlier than 4 weeks after delivery, in women who are not breastfeeding. Consider all cardiovascular risk factors before initiating in any female, particularly in the presence of multiple risk factors (5.1)
- High blood pressure: Monitor blood pressure periodically and stop use if blood pressure rises significantly. Do not prescribe for women with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease (5.2)
- Migraine: Evaluate significant change in migraines and discontinue if new, recurrent, persistent, or severe migraines occur (5.3)
- Hormonally-sensitive malignancy: Discontinue FEMLYV if a hormonally-sensitive malignancy is diagnosed (5.4).
- Liver disease: Discontinue use if jaundice or acute or chronic disturbances of liver function occurs (5.5)
- Glucose tolerance and hypertriglyceridemia: Monitor glucose in females with prediabetes and diabetes taking FEMLYV. Consider an alternative contraceptive method for women with uncontrolled dyslipidemia (5.7)
- Gallbladder disease and cholestasis: Consider discontinuing FEMLYV in females with symptomatic gallbladder or cholestatic disease (5.8)
- Uterine bleeding: Evaluate irregular bleeding or amenorrhea (5.9)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The most common adverse reactions in clinical trials (≥2%) were: headache, vaginal candidiasis, nausea, menstrual cramps, breast tenderness, bacterial vaginitis, abnormal cervical smear, acne, mood swings, and weight gain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Millicent U.S. Inc. at 1-877-810-2101 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CYP3A Inducers: May lead to contraceptive failure and/or increase breakthrough bleeding. Avoid concomitant use. If concomitant use is unavoidable, use a back-up method or alternative method of contraception during co-administration and up to 28 days after discontinuation of the CYP3A inducer (7.1)
- See Full Prescribing Information for additional clinically significant drug interactions (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 9/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing FEMLYV
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration
2.3 Missed Doses
2.4 Advice in Case of Gastrointestinal Disturbances
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems
5.2 High Blood Pressure
5.3 Migraine
5.4 Malignant Neoplasms
5.5 Liver Disease
5.6 Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment
5.7 Glucose Tolerance and Hypertriglyceridemia
5.8 Gallbladder Disease and Cholestasis
5.9 Bleeding Irregularities and Amenorrhea
5.10 Depression
5.11 Effect on Binding Globulins
5.12 Hereditary Angioedema
5.13 Chloasma
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on Combined Oral Contraceptives
7.2 Effects of Combined Oral Contraceptives on Other Drugs
7.3 Concomitant Use with HCV Combination Therapy – Liver Enzyme Elevation
7.4 Interference with Laboratory Tests
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
8.8 Body Mass Index
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage Conditions
16.3 Disposal
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from combined oral contraceptive (COC) use. This risk increases with age, particularly in females over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, COCs, including FEMLYV, are contraindicated in females who are over 35 years of age and smoke [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings & Precautions (5)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FEMLYV is indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Limitations of Use
The efficacy of FEMLYV in females with a body mass index (BMI) of more than 35 kg/m2 has not been evaluated.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing FEMLYV
To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, take one ODT every day at about the same time each day. Place one ODT on the tongue, allow to disintegrate and then follow with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water. The tablets can also be swallowed whole with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water. The recommended dosage of FEMLYV is one ODT daily for 28 consecutive days: one green active ODT daily during the first 24 days followed by one white inert ODT daily during the 4 following days (see Table 1). FEMLYV must be taken in the order directed on the blister pack. ODTs should not be skipped or taken at intervals exceeding 24 hours. FEMLYV may be administered without regard to meals [see 12.3]. Instruct the patient to begin taking FEMLYV either on the first day of her menstrual period (Day 1 Start) or on the first Sunday after the onset of her menstrual period (Sunday Start).
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration
Table 1 FEMLYV Administration Instructions Starting FEMLYV in females with no current use of hormonal contraception
Important:
- In females with irregular menstrual cycles, pregnancy testing may be necessary prior to initiation of this product
Day 1 Start:
- Take first green FEMLYV without regard to meals on the first day of menstruation
- Take one green FEMLYV daily for 24 consecutive days, followed by one white FEMLYV daily on days 25 through to 28
- FEMLYV should be taken in the order directed on the package at the same time each day
- Non-hormonal contraception (e.g. condoms and/or spermicide) should be used during the first 7 days if FEMLYV is started on a day other than the first day of menstruation
Sunday Start:
- Take one green FEMLYV daily, beginning on the first Sunday after the onset of menstruation
- Take one green FEMLYV daily for 24 consecutive days, followed by one white FEMLYV daily on days 25 through to 28
- FEMLYV should be taken in the order directed on the package at the same time each day
- Non-hormonal contraception should be used during the first 7 days if FEMLYV is started on a day other than the first day of menstruation
- Begin next and all subsequent 28-day regimens of FEMLYV on the same day of the week as the first cycle pack (i.e., on the day after taking the last tablet)
Switching to Femlyv from another contraceptive method:
Start FEMLYV on the day:
- Combined Oral Contraceptive (COC)
Start FEMLYV on the day when the new pack of the previous COC would have been started
- Transdermal System
Start FEMLYV on the day when the next application would have been scheduled
- Vaginal insert
Start FEMLYV on the day when next insertion would have been scheduled
- Injection
Start FEMLYV on the day when next injection would have been scheduled
- Intrauterine System (IUS)
Start FEMLYV on the day of removal
- Implant
Start FEMLYV on the day of removal
- Progestin-only pill
Start FEMLYV after the last tablet was taken
Starting FEMLYV after delivery (>20 weeks gestation)
Must not start earlier than 4 weeks after delivery (due to the increased risk of thromboembolism [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
If menstrual cycles have returned, follow instructions for “Starting FEMLYV in females with no current use of hormonal contraception”.
If menstrual cycles have not resumed, consider the possibility of ovulation and pregnancy. If not pregnant, use additional nonhormonal contraception for the first 7 days of FEMLYV use.Starting FEMLYV after Abortion or Miscarriage
- ≤ 14 weeks gestation
Within the first 7 days of complete first trimester abortion or miscarriage, use additional nonhormonal contraception for the next 7 days.
After the first 7 days, follow instructions for “Starting FEMLYV in females with no current use of hormonal contraception”.- > 14 weeks but ≤ 20 weeks gestation
After 4 weeks following second trimester abortion or miscarriage. Consider duration of pregnancy and increased risk of thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
If menstrual cycles have returned, follow instructions for “Starting FEMLYV in females with no current use of hormonal contraception”.
If menstrual cycles have not resumed, consider the possibility of ovulation and pregnancy. If not pregnant, use additional nonhormonal contraception for the first 7 days of FEMLYV use.2.3 Missed Doses
Table 2. Instructions for Missed FEMLYV ODTs If one green active ODT is missed
Take the missed ODT as soon as possible. Take the next ODT at the regular time.
Continue taking one ODT a day until the pack is finished.
Additional nonhormonal contraception (such as condoms) is not needed.
If two green active ODTs in a row are missed in Week 1 or Week 2 of the blister pack
Take the two missed ODTs as soon as possible, and the next two ODTs the next day. Continue taking one ODT a day until the pack is finished.
Use additional nonhormonal contraception (such as condoms) until green ODTs have been taken for 7 consecutive days.If two green active ODTs are missed in Week 3 or Week 4 of the blister pack
Day 1 Starter:
Discard the rest of the blister pack and start a new pack of ODTs that same day.
Sunday Starter:Keep taking one ODT every day until Sunday. On Sunday, discard the rest of the blister pack and start a new pack of ODTs that same day.
Use additional nonhormonal contraception (such as condoms) until green ODTs have been taken for 7 consecutive days.
If three or more green active ODTs in a row are missed
Day 1 Starter:
Discard the rest of the blister pack and start a new pack that same day.
Sunday Starter:Keep taking one ODT every day until Sunday. On Sunday, discard the rest of the blister pack and start a new blister pack of ODTs that same day.
Bleeding may occur during the week following the missed ODTs.
Use additional nonhormonal contraception (such as condoms) until green ODTs have been taken for 7 consecutive days.
If any of the four white inert ODTs are missed
Discard the missed ODTs. Continue taking the remaining ODTs until the blister pack is finished.
Additional nonhormonal contraception (such as condoms) is not needed.
2.4 Advice in Case of Gastrointestinal Disturbances
If vomiting or acute diarrhea occurs within 3 to 4 hours after taking an active ODT, take the new active ODT (scheduled for the next day) as soon as possible. If two or more active ODTs are missed, follow the advice concerning missed ODTs, including using backup non-hormonal contraception. For additional recommendations, refer to the table above [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females who are known to have or develop the following conditions:
- A history of, increased risk for, or current arterial or venous thrombotic/thromboembolic diseases.
Examples include women who are known to:
- Smoke, if 35 years of age and older [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Have current or history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Have cerebrovascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Have coronary artery disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Have thrombogenic valvular or thrombogenic rhythm diseases of the heart (for example, subacute bacterial endocarditis with valvular disease, or atrial fibrillation) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Have inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Have uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Have diabetes mellitus with hypertension or end-organ damage; or diabetes mellitus of > 20 years duration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
-
Have migraine headaches with aura
- o All women over age 35 with migraine headache [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Current diagnosis of, or history of, breast cancer, which may be hormone-sensitive [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Use of Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for ALT elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems
Stop FEMLYV if an arterial or deep venous thrombotic event (VTE) occurs.
Stop FEMLYV if there is unexplained loss of vision, proptosis, diplopia, papilledema, or retinal vascular lesions and evaluate for retinal vein thrombosis immediately.
Discontinue FEMLYV during prolonged immobilization.
If feasible, discontinue FEMLYV at least 4 weeks before and through 2 weeks after major surgery or other surgeries known to have an elevated risk of VTE.
Start FEMLYV no earlier than 4 weeks after delivery in females who are not breastfeeding. The risk of postpartum thromboembolism decreases after the third postpartum week, whereas the likelihood of ovulation increases after the third postpartum week.
Before starting FEMLYV, evaluate any past medical history or family history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders and consider whether the history suggests an inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathy. FEMLYV is contraindicated in females with a high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic/thromboembolic diseases [see Contraindications (4)].
Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Events
Use of CHCs increases the risk of cardiovascular events and cerebrovascular events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke. The risk is greater among females over age 40, smokers, and females with hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, or obesity. The risk increases with age, particularly in females 35 years of age and older, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. In addition to cigarettes, use of other nicotine-containing products – including cigars, smokeless tobacco, hookah tobacco, e-cigarettes, and nicotine replacement therapy – may also increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events from CHC use.
Venous Thromboembolism
Use of CHCs also increases the risk of venous thromboembolic events (VTEs), such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. The rate of VTE in females using COCs has been estimated to be 3 to 9 cases per 10,000 woman-years and should be considered in the context of other female of reproductive potential subpopulations who are not taking CHCs [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Risk factors for VTEs include smoking, obesity, family history of VTE, and prolonged immobilization in addition to other factors that contraindicate use of CHCs [see Contraindications (4)]. The presence of multiple risk factors for VTE may increase the risk synergistically. The risk of VTE is highest during the first year of CHC use and when restarting hormonal contraception after a break of four weeks or longer. The risk of VTE returns to baseline approximately 3 months after CHC use is discontinued.
Postpartum Venous Thromboembolism
The risk of VTE is increased during the first six weeks postpartum compared to the risk in nonpregnant, non-postpartum females. The risk is highest in the first three weeks postpartum but remains higher than baseline until at least six weeks postpartum. The presence of multiple risk factors for VTE may further increase the risk. Obstetric complications may extend the elevated risk up to 12 weeks postpartum.
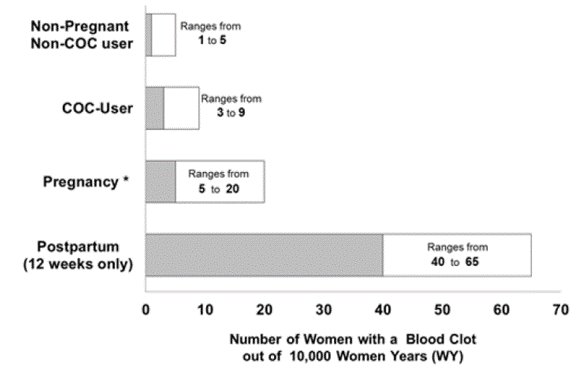
Figure 1 shows the risk of developing a VTE for females who are not pregnant and do not use COCs, for females who use COCs, for pregnant females, and for females in the postpartum period. To put the risk of developing a VTE into perspective: if 10,000 females who are not pregnant and do not use oral contraceptives are followed for one year, between 1 and 5 of these females will develop a VTE.
5.2 High Blood Pressure
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease [see Contraindications (4)]. For all females, including those with well-controlled hypertension, monitor blood pressure and stop FEMLYV if blood pressure rises significantly.
An increase in blood pressure has been reported in females taking CHCs, and this increase is more likely in older women with extended duration of use.
5.3 Migraine
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females who have migraines with aura [see Contraindications (4)]. Discontinue FEMLYV in females using FEMLYV who develop new migraines that are recurrent, persistent, or severe. Discontinue FEMLYV if there is an increased frequency or severity of migraines during CHC use (which may be prodromal of a cerebrovascular event).
Migraines with aura increase the risk for stroke. This stroke risk is further increased in females who have migraines with aura with use of CHCs.
5.4 Malignant Neoplasms
Breast Cancer
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females who currently have or have had breast cancer because breast cancer may be hormonally sensitive [see Contraindications (4)].
Epidemiology studies have not found a consistent association between use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and breast cancer risk. Studies do not show an association between ever (current or past) use of COCs and risk of breast cancer. However, some studies report a small increase in the risk of breast cancer among current or recent users (<6 months since last use) and current users with longer duration of COC use [see Postmarketing Experience (6.2)].
Cervical Cancer
A causal relationship between the use of CHCs and the development of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia has not been clearly established. In observational studies, the use of oral hormonal contraceptives in females for five years or more, compared to females who did not use oral hormonal contraceptives, was associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia. In these studies, the use of oral hormonal contraceptives in females for 10 years or more, compared to females who received oral hormonal contraceptives for 5-9 years, was associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia. Limitations in these epidemiologic studies include potential recall bias, differences in sexual behavior, and other factors such as establishing whether there were data on persistent high-risk Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection.
5.5 Liver Disease
Elevated Liver Enzymes
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females with acute hepatitis or severe (decompensated) cirrhosis of the liver [see Contraindications (4)]. Withhold or permanently discontinue FEMLYV for persistent or significant elevation of liver enzymes. FEMLYV can cause elevated liver enzymes. Discontinue FEMLYV if jaundice develops.
Liver Tumors
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females with hepatic adenomas and malignant liver tumors [see Contraindications (4)]. CHCs increase the risk of hepatic tumors, particularly, hepatic adenomas. Rupture of hepatic adenomas may cause death from abdominal hemorrhage.
5.6 Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment
CHCs, such as FEMLYV, are contraindicated for use with Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir (with or without dasabuvir) [see Contraindications (4)]. Discontinue FEMLYV prior to starting therapy with the combination drug regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir (with or without dasabuvir). FEMLYV can be restarted approximately 2 weeks following completion of treatment with this hepatitis C combination drug regimen.
During clinical trials with the above-mentioned Hepatitis C combination drug regimen, ALT elevations greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), including some cases greater than 20 times the ULN, were significantly more frequent in females using ethinyl estradiol (EE)-containing drugs, such as CHCs.
5.7 Glucose Tolerance and Hypertriglyceridemia
Glucose Tolerance
Carefully monitor females with prediabetes and diabetes who are using FEMLYV. FEMLYV may decrease glucose tolerance.
Hypertriglyceridemia
Consider alternative contraception for females with hypertriglyceridemia. Females with hypertriglyceridemia, or a family history thereof, may have an increase in serum triglyceride concentrations when using FEMLYV, which may increase the risk of pancreatitis.
5.8 Gallbladder Disease and Cholestasis
Consider discontinuing FEMLYV in females with symptomatic gallbladder disease or cholestatic disease. Studies suggest an increased risk of developing gallbladder disease among CHC users. Use of CHCs may also worsen existing gallbladder disease.
A past history of CHC-related cholestasis predicts an increased risk with subsequent CHC use. Women with a history of pregnancy-related cholestasis may be at an increased risk for CHC-related cholestasis.
5.9 Bleeding Irregularities and Amenorrhea
Unscheduled Bleeding and Spotting
Females using FEMLYV may experience unscheduled (breakthrough or intracyclic) bleeding and spotting, especially during the first three months of use. Bleeding irregularities may resolve over time or by changing to a different contraceptive product. If bleeding persists or occurs after previously regular cycles, evaluate for causes such as pregnancy or malignancy.
Based on patient diaries from a clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of a 24-day regimen of norethindrone acetate 1 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.020 mg tablets, 24-35% of women experienced unscheduled bleeding per cycle. A total of 10 subjects out of 743 (1.3%) discontinued due to bleeding or spotting [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Amenorrhea and Oligomenorrhea
If scheduled (withdrawal) bleeding does not occur, consider the possibility of pregnancy. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed dosing schedule (missed one or more active tablets or started taking them on a day later than she should have), consider the possibility of pregnancy at the time of the first missed period and take appropriate diagnostic measures. If the patient has adhered to the prescribed regimen and misses two consecutive periods, rule out pregnancy.
Females who use FEMLVY may experience absence of scheduled (withdrawal) bleeding, even if they are not pregnant. In the clinical trial with a 24-day regimen of norethindrone acetate 1 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.020 mg tablets, 22 to 36% of the women using norethindrone acetate 1 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.020 mg tablets experienced amenorrhea in at least one of 6 cycles of use [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
After discontinuation of FEMLYV, amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea may occur, especially if these conditions were pre-existent.
5.10 Depression
Monitor females with a history of depression and discontinue FEMLYV if depression recurs to a serious degree. Data on the association of COCs with onset of depression or exacerbation of existing depression are limited.
5.11 Effect on Binding Globulins
Increase the dosage of thyroid hormone replacement therapy as needed in females taking FEMLYV [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. The estrogen component of FEMLYV may increase the serum concentrations of thyroxine-binding globulin, sex hormone-binding globulin, and cortisol-binding globulin.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions with the use of COCs are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious cardiovascular events and stroke [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Vascular events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of FEMLYV has been established from adequate and well-controlled studies of norethindrone acetate 1 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.020 mg tablets in adult females of reproductive potential for the prevention of pregnancy [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The data described below reflect exposure to norethindrone acetate 1 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.020 mg tablets.
Common Adverse Reactions (Greater Than or Equal to 2% of all Treated Subjects): The most common adverse reactions reported by at least 2% of the 743 women using norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol tablets were the following, in order of decreasing incidence: headache (6.3%), vaginal candidiasis (6.1%), nausea (4.6%), menstrual cramps (4.4%), breast tenderness (3.4%), bacterial vaginitis (3.1%), abnormal cervical smear (3.1%), acne (2.7%), mood swings (2.2%), and weight gain (2.0%).
Adverse Reactions Leading to Study Discontinuation: Among the 743 women using norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol tablets, 46 women (6.2%) withdrew because of an adverse event. Adverse events occurring in 3 or more subjects leading to discontinuation of treatment were, in decreasing order: abnormal or irregular bleeding (1.3%), nausea (0.8%), menstrual cramps (0.5%), and increased blood pressure (0.4%).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
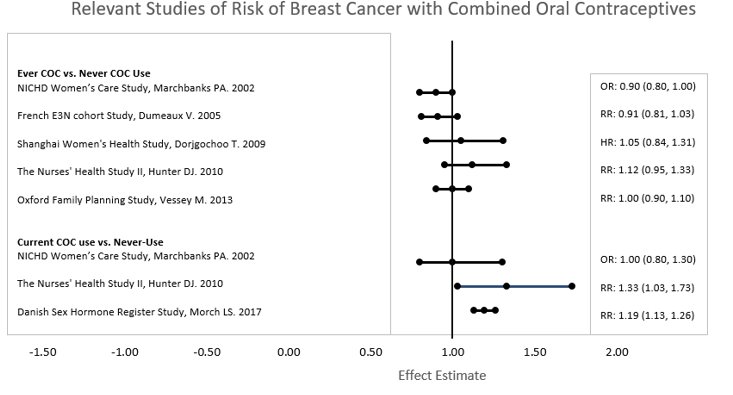
Five studies that compared breast cancer risk between ever-users (current or past use) of COCs and never-users of COCs reported no association between ever use of COCs and breast cancer risk, with effect estimates ranging from 0.90 - 1.12 (Figure 2).
Three studies compared breast cancer risk between current or recent COC users (<6 months since last use) and never users of COCs (Figure 1). One of these studies reported no association between breast cancer risk and COC use. The other two studies found an increased relative risk of 1.19 - 1.33 with current or recent use. Both of these studies found an increased risk of breast cancer with current use of longer duration, with relative risks ranging from 1.03 with less than one year of COC use to approximately 1.4 with more than 8-10 years of COC use.
RR = relative risk; OR = odds ratio; HR = hazard ratio. “ever COC” are females with current or past COC use; “never COC use” are females that never used COCs.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of a 24-day regimen of norethindrone acetate 1 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.020 mg tablets. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or evaluate a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse reactions are grouped into System Organ Classes.
Vascular disorders: thrombosis/embolism (coronary artery, pulmonary, cerebral, deep vein).
Hepatobiliary disorders: cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, hepatic adenoma, hemangioma of liver.
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity reaction.
Skin and subcutaneous disorders: alopecia, rash (generalized and allergic), pruritus, skin discoloration.
GI disorders: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: myalgia.
Eye disorders: blurred vision, visual impairment, corneal thinning, change in corneal curvature (steepening).
Infections and infestations: fungal infection, vaginal infection.
Investigations: change in weight or appetite (increase or decrease), fatigue, malaise, peripheral edema, blood pressure increased.
Nervous system disorders: headache, dizziness, migraine, loss of consciousness.
Psychiatric disorders: mood swings, depression, insomnia, anxiety, suicidal ideation, panic attack, changes in libido.
Renal and urinary disorders: cystitis-like syndrome.
Reproductive system and breast disorders: breast changes (tenderness, pain, enlargement, and secretion), premenstrual syndrome, dysmenorrhea.
Cardiovascular: chest pain, palpitations, tachycardia, myocardial infarction.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on Combined Oral Contraceptives
Substances diminishing the efficacy of COCs: Drugs or herbal products that induce certain enzymes, including cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), may decrease the effectiveness of COCs or increase breakthrough bleeding. Some drugs or herbal products that may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives include phenytoin, barbiturates, carbamazepine, bosentan, felbamate, griseofulvin, oxcarbazepine, rifampicin, topiramate and products containing St. John’s wort. Interactions between oral contraceptives and other drugs may lead to breakthrough bleeding and/or contraceptive failure. Counsel women to use an alternative method of contraception or a back-up method when enzyme inducers are used with COCs, and to continue back-up contraception for 28 days after discontinuing the enzyme inducer to ensure contraceptive reliability.
Substances increasing the plasma concentrations of COCs: Co-administration of atorvastatin and certain COCs containing ethinyl estradiol increase AUC values for ethinyl estradiol by approximately 20%. Ascorbic acid and acetaminophen may increase plasma ethinyl estradiol concentrations, possibly by inhibition of conjugation. CYP3A4 inhibitors such as itraconazole or ketoconazole may increase plasma hormone concentrations.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/ Hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease inhibitors and non- nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Significant changes (increase or decrease) in the plasma concentrations of the estrogen and progestin have been noted in some cases of co-administration of HIV/HCV protease inhibitors or of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Antibiotics: There have been reports of pregnancy while taking hormonal contraceptives and antibiotics, but clinical pharmacokinetic studies have not shown consistent effects of antibiotics on plasma concentrations of synthetic steroids.
7.2 Effects of Combined Oral Contraceptives on Other Drugs
COCs containing ethinyl estradiol may inhibit the metabolism of other compounds. COCs have been shown to significantly decrease plasma concentrations of lamotrigine, likely due to induction of lamotrigine glucuronidation. This may reduce seizure control; therefore, dosage adjustments of lamotrigine may be necessary.
Women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy may need increased doses of thyroid hormone because serum concentration of thyroid-binding globulin increases with use of COCs.
7.3 Concomitant Use with HCV Combination Therapy – Liver Enzyme Elevation
Do not co-administer FEMLYV with HCV drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to potential for ALT elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Discontinue FEMLYV if pregnancy occurs, because there is no reason to use hormonal contraceptives during pregnancy. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or nongenital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to COCs before conception or during early pregnancy.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4 percent and 15 to 20 percent, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Contraceptive hormones and/or metabolites are present in human milk. COCs can reduce milk production in breast-feeding females. This reduction can occur at any time but is less likely to occur once breast-feeding is well-established. When possible, advise the nursing female to use other methods of contraception until she discontinues breast-feeding [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. The developmental and health benefits of breast-feeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for FEMLYV and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from FEMLYV or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of FEMLYV have been established in females of reproductive potential. Efficacy is expected to be the same in postmenarcheal adolescents younger than 17 years as for users 17 years and older. FEMLYV is not indicated before menarche.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females with hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in patients with hepatic impairment. Acute or chronic disturbances of liver function may necessitate the discontinuation of COC use until markers of liver function return to normal and COC causation has been excluded [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
8.8 Body Mass Index
The safety and effectiveness of FEMLYV in females with a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 have not been fully evaluated [see Clinical Studies (14)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of CHCs may cause nausea, vomiting, and severe headaches. Individual reports of thromboembolic complications and vaginal bleeding have occurred from overdosage. Pediatric patients with unintended CHC ingestion have reported nausea and vomiting and some developed irritability and drowsiness; rare reports described vaginal bleeding.
Overdosage Management Recommendations
Consider short-term prophylactic anticoagulation therapy for patients with high risk of VTE.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
FEMLYV (norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol orally disintegrating tablets) is a combined oral contraceptive. FEMLYV consists of 24 green, round ODTs each containing 1 mg norethindrone acetate and 0.020 mg ethinyl estradiol and 4 white, round inert ODTs.
Each green ODT also contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, mint green lake blend, pregelatinized starch, spearmint flavor, sucralose, vitamin E (DL-alpha-tocopherol).
Each white ODT contains, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, spearmint flavor, sucralose.
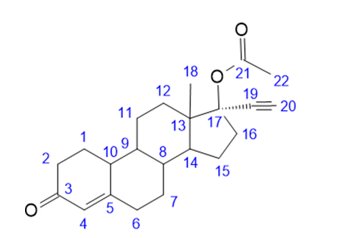
The empirical formula of norethindrone acetate is C22H28O3 and the structural formula is:
The chemical name of norethindrone acetate is [19-Norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one, 17-(acetyloxy)-, (17α)-]. The molecular weight of norethindrone acetate is 340.46. It is a neutral molecule and is practically insoluble in water.
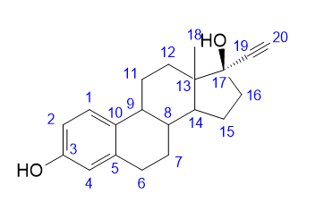
The empirical formula of ethinyl estradiol is C20H24O2 and the structural formula is:
The chemical name of ethinyl estradiol is [19-Norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yne-3,17-diol, (17α)-]. The molecular weight of ethinyl estradiol is 296.40. It is a neutral molecule and is practically insoluble in water.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
CHCs lower the risk of becoming pregnant primarily by suppressing ovulation.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Norethindrone acetate appears to be completely and rapidly deacetylated to norethindrone after oral administration The absolute bioavailability was approximately 64% for norethindrone and 43% for ethinyl estradiol following oral administration.
The plasma norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol pharmacokinetics following single-dose administrations of FEMLYV ODT in 36 healthy female subjects are provided in Figures 3 and 4, and Table 3.
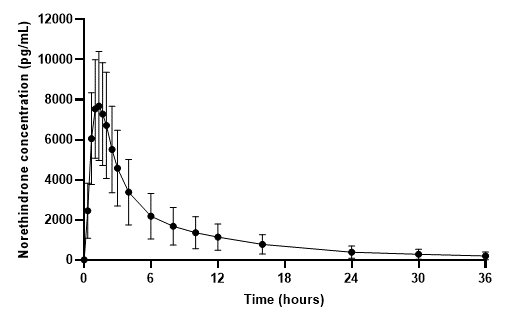
Figure 3. Mean (± Standard Deviation) Plasma Norethindrone Concentration-Time Profile Following Single-Dose Administration of FEMLYV ODT to Healthy Female Volunteers under Fasting Conditions (n = 36)
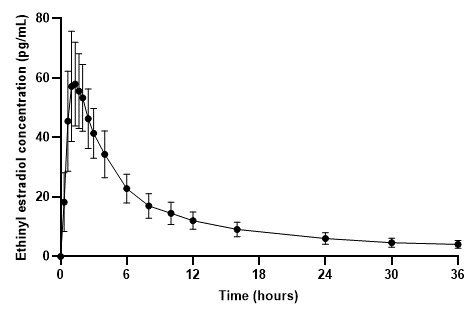
Figure 4. Mean (± Standard Deviation) Plasma Ethinyl Estradiol Concentration- Time Profile Following Single-Dose Administration of FEMLYV ODT to Healthy Female Volunteers under Fasting Conditions (n = 36)
Table 3. Summary of Norethindrone (NE) and Ethinyl Estradiol (EE) Pharmacokinetics Following Single-Dose Administration of FEMLYV ODT to Healthy Female Volunteers Under Fasting Conditions (n = 36) Cmax = Maximum plasma concentration tmax = Time of Cmax AUC(0-tldc) = Area under plasma concentration versus time curve from 0 to tldc, the time of last determinable concentration AUC(0-inf) = Area under the plasma concentration versus time curve from time 0 to infinity t½ = Terminal phase half-life % CV = Coefficient of Variation (%) a The median (range) is reported for tmax
b n = 35Analyte
Arithmetic Meana (% CV) by Pharmacokinetic Parameter
Cmax
(pg/mL)tmax
(hr)AUC(0-tldc)
(pgh/mL)AUC(0-inf)
(pgh/mL)t½
(hr)NE
8438
(34)
1.33
(0.66–2.50)
50060
(48)
51190
(49)
10.25
(26)
EE
62.8
(25)
1.33
(0.67–2.03)
505.1
(25)
595.6b
(24)
18.02b
(34)
Effect of Food
No clinically significant differences in pharmacokinetics of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol were observed following administration of a high-fat meal in healthy premenopausal subjects.
Distribution
Volume of distribution of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol ranges from 2 to 4 L/kg. Plasma protein binding of both steroids is extensive (greater than 95%); norethindrone binds to both albumin and SHBG, whereas ethinyl estradiol binds only to albumin. Although ethinyl estradiol does not bind to SHBG, it induces SHBG synthesis.
Metabolism
Norethindrone undergoes extensive biotransformation, primarily via reduction, followed by sulfate and glucuronide conjugation. The majority of metabolites in the circulation are sulfates, with glucuronides accounting for most of the urinary metabolites.
Ethinyl estradiol is also extensively metabolized, both by oxidation and by conjugation with sulfate and glucuronide. Sulfates are the major circulating conjugates of ethinyl estradiol and glucuronides predominate in urine. The primary oxidative metabolite is 2-hydroxy ethinyl estradiol, formed by the CYP3A4 isoform of cytochrome P450. Part of the first-pass metabolism of ethinyl estradiol is believed to occur in gastrointestinal mucosa. Ethinyl estradiol may undergo enterohepatic circulation.
Excretion
Norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol are excreted in both urine and feces, primarily as metabolites. Plasma clearance values for norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol are similar (approximately 0.4 L/hr/kg). Elimination half-lives of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol following administration of FEMLYV are approximately 10 hours and 18 hours, respectively.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
[See Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.5)].
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of FEMLYV has been established for the prevention of pregnancy in females of reproductive potential based on adequate and well-controlled studies of norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol tablets. The data presented below reflects results from studies of norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol tablets.
In a clinical study, 743 women 18 to 45 years of age were studied to assess the efficacy of norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol tablets, for up to six 28-day cycles providing a total of 3,823 treatment-cycles of exposure. The racial demographic of all enrolled women was: 70% Caucasian, 16% African American, 10% Hispanic, 2% Asian and 2% Other. Women with BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 were excluded from the study. The weight range for those women treated was 90 to 260 pounds, with a mean weight of 147 pounds. Among the women in the study, about 40% had not used hormonal contraception immediately prior to enrolling in this study.
A total of 583 women completed 6 cycles of treatment. There were a total of 5 on-treatment pregnancies in 3,565 treatment cycles during which no backup contraception was used. The Pearl Index for norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol tablets was 1.82 (95% confidence interval 0.59 - 4.25).
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
FEMLYV (norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol orally disintegrating tablets), 1 mg/0.02 mg is available in a carton of three pouches, each pouch contains a blister card of 28 ODTs.
Each blister card contains 28 ODTs in the following order:
- 24 green, round active ODTs imprinted with “M” on one side and “312” on the other side.
- 4 white, round inert ODTs imprinted with “M” on one side and “313” on the other side.
NDC: 72495-601-84, cartons of 3 pouches, each pouch contains a blister card of 28 ODTs.
NDC: 72495-601-28, cartons of 1 pouch, each pouch contains a blister card of 28 ODTs.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-Approved patient labeling (Patient Information)
Sexually Transmitted Infections
Advise females that FEMLYV does not protect against HIV infection or other sexually transmitted infections.
Important Administration Instructions and Instructions for Missed Doses
Instruct females to take one FEMLYV orally once at the same time every day by allowing the FEMLYV to disintegrate on the tongue or swallowing whole, then follow with 8 oz (240 mL) of water. Advise patients about what to do in the event that ODTs are missed [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
- Advise females starting FEMLYV to use additional nonhormonal contraception for 7 days after the first dose unless FEMLYV is started on the first day (Day 1) of menses [see Dosage and Administration (2)]
- Advise females who miss more than two consecutive days of FEMLYV or experience vomiting or diarrhea for > 48 hours consecutively to use additional nonhormonal contraception for 7 days [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)]
Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Advise females that there is an increased risk of arterial and/or venous thrombotic/thromboembolic events with FEMLYV and the risk of arterial and/or venous thrombotic/thromboembolism is greater in smokers and females with preexisting medical conditions including hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and obesity.
- Advise patients of the pertinent factors that further increase their risk and ways to diminish the risk, e.g., to stop smoking (if applicable)
- Advise patients to contact their healthcare professional for any signs or symptoms of arterial and/or VTE
- Advise patients to contact their healthcare professional if they will be immobilized for a prolonged period of time
Hypertension
Advise females that FEMLYV can cause an increase in blood pressure over time. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare professional if blood pressure increases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Liver Disease
Advise females that use of FEMLYV can cause elevated liver enzymes and can increase the risk of liver tumors. Instruct females to contact their healthcare professional for any signs or symptoms of liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Glucose Tolerance
Advise females that FEMLYV may decrease glucose tolerance. Instruct females with diabetes and prediabetes to contact their healthcare professional for any signs or symptoms of hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Gallbladder Disease and Cholestasis
Advise females that use of FEMLYV is associated with an increased risk of developing and/or worsening gallbladder disease. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare professional for any signs or symptoms of gallbladder disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Bleeding Irregularities, Amenorrhea, and Pregnancy
Advise females that FEMLYV can cause unscheduled bleeding and spotting, as well as amenorrhea and oligomenorrhea. Advise females to contact their health care professional if amenorrhea occurs in two or more consecutive cycles or symptoms of pregnancy occur, e.g., morning sickness or unusual breast tenderness. Instruct females to stop FEMLYV if pregnancy is confirmed during use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Chloasma
Advise females that FEMLYV can cause chloasma and the risk is highest in females with a history of chloasma, especially chloasma gravidarum. Instruct females to take precautions to limit UVA and UVB exposure while using FEMLYV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Lactation
Advise postpartum females that FEMLYV may reduce breast milk production. Advise females that this reduction is less likely to occur if breast-feeding is well established [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Drug Interactions
FEMLYV may interact with many drugs, foods, and dietary supplements. Therefore, advise females to report to their healthcare professional the use of any other prescription or nonprescription drugs or dietary supplements [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
Distributed by:
Millicent U.S., Inc.
East Hanover, NJ 07936© 2025 Millicent. All rights reserved.
FEMLYV and its design are trademarks of Millicent Puerto Rico LLC. -
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
Guide for Using FEMLYV
WARNING TO WOMEN WHO SMOKE
Do not use FEMLYV if you smoke cigarettes and are over 35 years old. Smoking increases your risk of serious cardiovascular side effects (heart and blood vessel problems) from birth control pills, including death from heart attack, blood clots or stroke. This risk increases with age and the number of cigarettes you smoke.
Birth control pills help to lower the chances of becoming pregnant when taken as directed. They do not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections.
What is FEMLYV?
FEMLYV is a birth control pill. It contains two female hormones, an estrogen called ethinyl estradiol, and a progestin called norethindrone acetate.
How well does FEMLYV work?
Your chance of getting pregnant depends on how well you follow the directions for taking your birth control pills. The better you follow the directions, the less chance you have of getting pregnant.
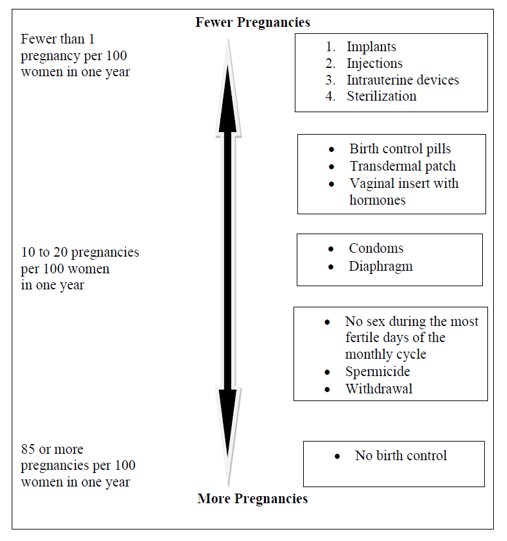
Based on the results of one clinical study of a 24-day regimen of norethindrone acetate 1 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.020 mg tablets lasting 6 months, about 1 to 4 out of 100 women may get pregnant during the first year they use FEMLYV. Women with a BMI above 35 kg/m2 were not studied in the clinical trial, so it is not known how well FEMLYV protects against pregnancy in such women. If you are overweight, discuss with your healthcare provider whether FEMLYV is the best choice for you.
The following chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who use different methods of birth control. Each box on the chart contains a list of birth control methods that are similar in effectiveness. The most effective methods are at the top of the chart. The box on the bottom of the chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who do not use birth control and are trying to get pregnant.
How do I take FEMLYV?
- 1. Be sure to read these directions before you start taking your tablets or anytime you are not sure what to do.
- 2. The tablets should be placed on the tongue, allowed to dissolve, and followed by water or swallowed whole with water.
- 3.
The right way to take the tablet is to take 1 tablet every day at the same time in the order directed on the package. FEMLYV can be taken with or without meals.
If you miss tablets you could get pregnant. This includes starting the pack late. The more tablets you miss, the more likely you are to get pregnant. See the "What to Do if You Miss Tablets” section below. - 4.
Many women have spotting or light bleeding at unexpected times, or may feel sick to their stomach during the first 1 to 3 packs of tablets.
If you do have spotting or light bleeding or feel sick to your stomach, do not stop taking the tablets. The problem will usually go away. If it does not go away, check with your healthcare provider. - 5.
Missing tablets can also cause spotting or light bleeding, even when you make up these missed tablets.
On the days you take 2 tablets, to make up for missed tablets, you could also feel a little sick to your stomach. - 6.
If you have vomiting (within 3 to 4 hours after you take your tablet), you should follow the instructions for "What to Do if You Miss Tablets". If you have diarrhea or if you take certain medicines, including some antibiotics and some herbal products such as St. John's Wort, your tablets may not work as well.
Use a back-up method (such as condoms and spermicides) until you check with your healthcare provider. - 7. If you have trouble remembering to take FEMLYV, talk to your healthcare provider about how to make tablet-taking easier or about using another method of birth control.
- 8. If you have any questions or are unsure about the information in this leaflet, call your healthcare provider.
Before You Start Taking Your FEMLYV Tablets
- 1. Decide What Time of Day You Want to Take Your Tablet. It is important to take FEMLYV tablets in the order directed on the package at the same time every day. FEMLYV can be taken with or without meals.
- 2.
The FEMLYV pack has 28 Tablets
The FEMLYV pack has 24 active green tablets (with hormones) to be taken for 24 days, followed by 4 reminder white tablets (without hormones) to be taken for the next four days. - 3.
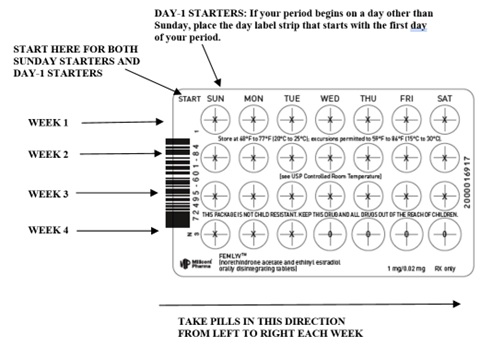
Also look for:
- a) Where on the pack to start taking tablets,
- b) In what order to take the tablets (follow the arrows shown in the picture above)
- c) The week numbers as shown in the picture above.
- 4.
Be sure you have ready at all times
- a) another kind of birth control (such as a condoms and spermicide) to use as a back-up in case you miss tablets, and
- b) an extra, full tablet pack.
When to Start the First Pack of Tablets
You have a choice for which day to start taking your first pack of tablets. Decide with your healthcare provider which is the best day for you. Pick a time of day which will be easy to remember.
Day 1 Start:
- 1. Pick the day label strip that starts with the first day of your period (this is the day you start bleeding or spotting, even if it is almost midnight when the bleeding begins).
- 2. Place this day label strip on the tablet dispenser over the area that has the days of the week (starting with Sunday) printed on the plastic.
- 3. Take the first green tablet of the pack during the first 24 hours of your period.
- 4. You will not need to use a back-up method of birth control, since you are starting the tablet at the beginning of your period. However, if you start FEMLYV later than the first day of your period, you should use another method of birth control (such as a condom and spermicide) as a back-up method until you have taken 7 green tablets.
Sunday Start:
- 1. Take the first green tablet of the pack on the Sunday after your period starts, even if you are still bleeding. If your period begins on Sunday, start the pack that same day.
- 2. Use another method of birth control (such as a condom and spermicide) as a back-up method if you have sex anytime from the Sunday you start your first pack until the next Sunday (7 days). This also applies if you start FEMLYV after having been pregnant, and you have not had a period since your pregnancy.
When You Switch From a Different Birth Control Tablet or Capsule
When switching from another birth control pill, finish all the tablets or capsules, then FEMLYV should be started on the same day that a new pack of the previous birth control tablet or capsule would have been started.
When You Switch From Another Type of Birth Control Method
When switching from a transdermal system or vaginal insert, finish the 21 days of use, wait 7 days, then FEMLYV should be started when the next application would have been due. When switching from an injection, FEMLYV should be started when the next injection would have been due. When switching from an intrauterine device or an implant, FEMLYV should be started on the day of removal.
What to Do During the Month
- 1.
Take 1 tablet at the same time every day until the pack is empty.
Do not skip tablets even if you are spotting or bleeding between monthly periods or feel sick to your stomach (nausea). - 2.
Do not skip tablets even if you do not have sex very often.
When you finish a pack of tablets, start the next pack on the day after your last white tablet. Do not wait any days between packs.
What to Do if You Miss Tablets
FEMLYV may not be as effective if you miss any green tablets, especially if you miss the first few or the last few green tablets in a pack.
If you miss 1 green tablet:
- 1. Take the tablet as soon as you remember. Take the next tablet at your regular time. This means you may take 2 tablets in 1 day.
- 2. You do not need to use a back-up birth control method if you have sex.
If you miss 2 green tablets in a row in week 1 OR week 2 of your pack:
- 1. Take 2 tablets on the day you remember and 2 tablets the next day.
- 2. Then take 1 tablet a day until you finish the pack.
- 3. You could become pregnant if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your tablets. You must use another birth control method (such as a condom and spermicide) as a back- up for those 7 days.
If you miss 2 green tablets in a row in week 3 or week 4 of your pack:
- 1.
If you are a Day 1 Starter:
Throw out the rest of the tablet pack and start a new pack that same day.
If you are a Sunday Starter:
Keep taking 1 tablet every day until Sunday. On Sunday, throw out the rest of the pack and start a new pack of tablets that same day. - 2. You could become pregnant if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your tablets. You must use another birth control method (such as a condom and spermicide) as a back- up for those 7 days.
- 3. You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a row, call your healthcare provider because you might be pregnant.
If you miss 3 or more green tablets in a row during any week:
- 1.
If you are a Day 1 Starter:
Throw out the rest of the tablet pack and start a new pack that same day.
If you are a Sunday Starter:
Keep taking 1 tablet every day until Sunday. On Sunday, throw out the rest of the pack and start a new pack of tablets that same day. - 2. You could become pregnant if you have sex on the days when you missed tablets or during the first 7 days after you restart your tablets. You must use another birth control method (such as a condom and spermicide) as a back-up the next time you have sex and for the first 7 days after you restart your tablets.
- 3. You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a row, call your healthcare provider because you might be pregnant.
If you miss any of the 4 white tablets in Week 4:
- 1. Throw away the tablets you missed.
- 2. Keep taking 1 tablet each day until the pack is empty.
- 3. You do not need a back-up method.
- 4. Start the next pack of FEMLYV as scheduled.
Finally, if you are still not sure what to do about the tablets you have missed:
- 1. Use a back-up method (such as a condom and spermicide) anytime you have sex.
- 2. Contact your healthcare provider and continue taking 1 active green tablet each day until otherwise directed.
Who should not take FEMLYV?
Your healthcare provider will not give you FEMLYV if you have:
- ever had blood clots in your arms, legs (deep vein thrombosis), lungs (pulmonary embolism), or eyes (retinal thrombosis).
- ever had a stroke.
- ever had a heart attack.
- certain heart valve problems or heart rhythm abnormalities that can cause blood clots to form in the heart.
- an inherited problem with your blood that makes it clot more than normal.
- high blood pressure that medicine cannot control.
- diabetes with kidney, eye, nerve, or blood vessel damage.
- ever had certain kinds of severe migraine headaches with aura, numbness, weakness or changes in vision, or have any migraine headache if you are over age 35.
- ever had breast cancer, which may be sensitive to female hormones.
- liver disease, including liver tumors.
- take any Hepatitis C drug combination containing ombitasvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir. This may increase levels of the liver enzyme “alanine aminotransferase” (ALT) in the blood.
Also, do not take birth control pills if you:
- smoke and are over 35 years old
- are or think you are pregnant
- have any abnormal bleeding from the vagina
Birth control pills may not be a good choice for you if you have ever had jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) caused by pregnancy, also called cholestasis of pregnancy.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had any of the above conditions (your healthcare provider may recommend another method of birth control).
What else should I know about taking FEMLYV?
Birth control pills do not protect you against any sexually transmitted infection, including HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
Do not skip any tablets, even if you do not have sex often.
If you miss a period, you could be pregnant. However, some women miss periods or have light periods on birth control pills, even when they are not pregnant. Contact your healthcare provider for advice if you:
- think you are pregnant.
- miss 1 period and have not taken your birth control pills every day.
- miss 2 periods in a row.
Birth control pills should not be taken during pregnancy. However, birth control pills taken by accident during pregnancy are not known to cause birth defects.
You should stop FEMLYV at least 4 weeks before you have surgery and not restart it until at least 2 weeks after the surgery, due to an increased risk of blood clots.
In females who are not breastfeeding, do not start FEMLYV sooner than 4 weeks after giving birth.
If you are breastfeeding, consider another birth control method until you are ready to stop breastfeeding. Birth control pills that contain estrogen, like FEMLYV, may decrease the amount of milk you make. A small amount of the pill's hormones passes into breast milk.
Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicines and herbal products may make birth control pills less effective, including:
- barbiturates
- bosentan
- carbamazepine
- felbamate
- griseofulvin
- oxcarbazepine
- phenytoin
- rifampicin
- St. John’s wort
- topiramate
Use a back-up or alternative birth control method when you take medicines that may make birth control pills less effective.
Birth control pills may interact with lamotrigine, an anticonvulsant used for epilepsy. This may increase the risk of seizures, so your healthcare provider may need to adjust the dose of lamotrigine.
If you have vomiting or diarrhea, your birth control pills may not work as well. Use another birth control method, like a condom and spermicide, until you check with your healthcare provider.
Women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy may need increased doses of thyroid hormone.
If you are scheduled for any laboratory tests, tell your healthcare provider that you are taking birth control pills. Certain blood tests may be affected by birth control pills.
What are the most serious risks of taking FEMLYV?
Like pregnancy, birth control pills increase the risk of serious blood clots, especially in women who have other risk factors, such as smoking, obesity, or age greater than 35. This increased risk is highest when you first start taking birth control pills and when you restart the same or different birth control pills after not using them for a month or more.
It is possible to die from a problem caused by a blood clot, such as a heart attack or a stroke.
Some examples of serious blood clots are blood clots in the:
- legs (deep vein thrombosis)
- lungs (pulmonary embolus)
- eyes (loss of eyesight)
- heart (heart attack)
- brain (stroke)
Women who take birth control pills may get:
- high blood pressure
- gallbladder problems
- rare cancerous or noncancerous liver tumors.
All of these events are uncommon in healthy women.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
- leg pain that does not go away
- sudden shortness of breath
- sudden blindness, partial or complete
- severe pain or pressure in your chest
- sudden, severe headache unlike your usual headaches
- weakness or numbness in an arm or leg, or trouble speaking
- yellowing of the skin or eyeballs
What are the common side effects of birth control pills?
The most common side effects of birth control pills are:
- spotting or bleeding between menstrual periods
- nausea
- breast tenderness
- headache
These side effects are usually mild and usually disappear with time.
Less common side effects are:
- acne
- less sexual desire
- bloating or fluid retention
- blotchy darkening of the skin, especially on the face
- high blood sugar, especially in women who already have diabetes
- high fat (cholesterol, triglyceride) levels in the blood
- depression, especially if you have had depression in the past. Call your healthcare provider immediately if you have any thoughts of harming yourself
- problems tolerating contact lenses
- weight gain
These are not all the possible side effects of FEMLYV. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
No serious problems have been reported from a birth control pill overdose, even when accidentally taken by children.
Do birth control pills cause cancer?
It is not known if hormonal birth control pills cause breast cancer. Some studies, but not all, suggest that there could be a slight increase in the risk of breast cancer among current users with longer duration of use.
If you have breast cancer now, or have had it in the past, do not use hormonal birth control because some breast cancers are sensitive to hormones.
Women who use birth control pills may have a slightly higher chance of getting cervical cancer. However, this may be due to other reasons such as having more sexual partners.
What should I know about my period when taking FEMLYV?
Irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting may occur while you are taking FEMLYV. Irregular bleeding may vary from slight staining between menstrual periods to breakthrough bleeding, which is a flow much like a regular period. Irregular bleeding occurs most often during the first few months of oral contraceptive use, but may also occur after you have been taking the pill for some time. Such bleeding may be temporary and usually does not indicate any serious problems. It is important to continue taking your tablets on schedule. If the bleeding occurs in more than one cycle, is unusually heavy, or lasts for more than a few days, call your healthcare provider.
Some women may not have a menstrual period but this should not be cause for alarm as long as you have taken the tablets according to direction.
What if I miss my scheduled period when taking FEMLYV?
It is not uncommon to miss your period. However, if you go 2 or more months in a row without a period, or you miss your period after a month where you did not take all your tablets correctly, call your healthcare provider because you may be pregnant. Also notify your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness or unusual breast tenderness. Stop taking FEMLYV if you are pregnant.
What if I want to become pregnant?
You may stop taking the tablets whenever you wish. Consider a visit with your healthcare provider for a pre-pregnancy checkup before you stop taking the tablets.
General advice about FEMLYV
Your healthcare provider prescribed FEMLYV for you. Please do not share FEMLYV with anyone else. Keep FEMLYV out of the reach of children.
Store FEMLYV at room temperature between 68°F to 77º F (20°C to 25º C).
If you have concerns or questions, ask your healthcare provider. You may also ask your pharmacist for a more detailed label written for healthcare professionals.
For all medical inquiries contact:
Millicent
Medical Communications 1-877-810-2101Distributed by:
Millicent U.S., Inc., East Hanover, NJ 07936
© 2024 Millicent. All rights reserved.
FEMLYV™ and its design are trademarks of Millicent Puerto Rico LLC.This Patient Information has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
Approved: 12/2024
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – Carton Label
FEMLYV™
(norethindrone acetate and
ethinyl estradiol
orally disintegrating tablets)1mg/0.02mg
NDC Number 72495-601-84
FEMLYV™
28-day regimen
Each blister provides
24 days of active therapyRx only
This package contains
3 blister cards of
28 orally disintegrating
tablets (ODTs) eachMillicent Pharma®
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – Pouch Label
NDC: 72495-601-84
FEMLYV™
(norethindrone acetate and
ethinyl estradiol
orally disintegrating tablets)1mg/0.02mg
FEMLYV™ 28-day regimen
Each blister provides
24 days of active therapyRx only
This package contains 1 blister card
of 28 orally disintegrating
tablets (ODTs)Millicent Pharma®
- PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – Blister Card Label
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – Sample Carton Label
FEMLYV™
(norethindrone acetate and
ethinyl estradiol
orally disintegrating tablets)1mg/0.02mg
NDC Number 72495-601-28
Physician’s Sample –
Not For SaleFEMLYV™
28-day regimen
Each blister provides
24 days of active therapyRx only
This package contains
1 blister card of 28 orally
disintegrating tablets (ODTs)Millicent Pharma®
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – Sample Pouch Label
NDC: 72495-601-28
FEMLYV™
(norethindrone acetate and
ethinyl estradiol
orally disintegrating tablets)1mg/0.02mg
Physician’s Sample – Not For Sale
FEMLYV™ 28-day regimen
Each blister provides
24 days of active therapyRx only
This package contains 1 blister card
of 28 orally disintegrating
tablets (ODTs)Millicent Pharma®
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FEMLYV
norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72495-601 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72495-601-84 3 in 1 CARTON 11/01/2024 1 1 in 1 POUCH 1 1 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 72495-601-28 1 in 1 CARTON 11/01/2024 2 1 in 1 POUCH 2 1 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 24 Part 2 4 Part 1 of 2 FEMLYV
norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol tablet, orally disintegrating, delayed releaseProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 72495-241 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NORETHINDRONE ACETATE (UNII: 9S44LIC7OJ) (NORETHINDRONE - UNII:T18F433X4S) NORETHINDRONE ACETATE 1 mg ETHINYL ESTRADIOL (UNII: 423D2T571U) (ETHINYL ESTRADIOL - UNII:423D2T571U) ETHINYL ESTRADIOL 20 ug Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 ALUMINUM LAKE (UNII: J9EQA3S2JM) D&C YELLOW NO. 10 ALUMINUM LAKE (UNII: CQ3XH3DET6) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) SPEARMINT (UNII: J7I2T6IV1N) SUCRALOSE (UNII: 96K6UQ3ZD4) .ALPHA.-TOCOPHEROL (UNII: H4N855PNZ1) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color GREEN Score no score Shape ROUND Size 5mm Flavor SPEARMINT Imprint Code M;312 Contains Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218718 11/01/2024 Part 2 of 2 FEMLYV
placebo tablet, orally disintegrating, delayed releaseProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 72495-502 Route of Administration ORAL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) D&C YELLOW NO. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) SPEARMINT (UNII: J7I2T6IV1N) SUCRALOSE (UNII: 96K6UQ3ZD4) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 5mm Flavor Imprint Code M;313 Contains Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218718 11/01/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218718 11/01/2024 Labeler - Millicent US, Inc. (081309152) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Patheon Inc. (Thermo Fisher Scientific) 240769596 MANUFACTURE(72495-601) , ANALYSIS(72495-601) , LABEL(72495-601)
Trademark Results [FEMLYV]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 FEMLYV 98042147 not registered Live/Pending |
Millicent Puerto Rico, LLC 2023-06-14 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.