ZURNAI- nalmefene hydrochloride injection, solution
Zurnai by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Zurnai by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Purdue Pharma L.P., ANTARES PHARMA, INC., Pharmascience Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZURNAI™ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZURNAI.
ZURNAI (nalmefene injection), for intramuscular or subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1995INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZURNAI is an opioid antagonist indicated for the emergency treatment of known or suspected opioid overdose induced by natural or synthetic opioids in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older, as manifested by respiratory and/or central nervous system depression. (1)
ZURNAI is intended for immediate administration as emergency therapy in settings where opioids may be present. (1)
ZURNAI is not a substitute for emergency medical care. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- ZURNAI is for intramuscular and subcutaneous use only. (2.1)
- Seek emergency medical care immediately after use. (2.1)
- Administer ZURNAI to the outer thigh, through clothing if necessary. (2.1)
- Administer additional doses of ZURNAI using a new ZURNAI auto-injector for each dose. If the patient does not respond or responds and then relapses into respiratory depression, additional doses of ZURNAI may be given every 2 to 5 minutes until emergency medical assistance arrives. (2.2)
- See Full Prescribing Information and Instructions for Use for important information on how to safely administer ZURNAI. (2.1)
- Additional supportive and/or resuscitative measures may be helpful while awaiting emergency medical assistance. (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 1.5 mg nalmefene base/0.5 mL in a prefilled, single-dose auto-injector (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity to nalmefene hydrochloride or to any other ingredients in ZURNAI. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk of Recurrent Respiratory and CNS Depression: A recurrence of respiratory depression is possible, therefore, keep the patient under continued surveillance and administer repeat doses of ZURNAI using a new auto-injector with each dose while awaiting emergency medical assistance. (5.1)
- Risk of Limited Efficacy with Partial Agonists or Mixed Agonists/Antagonists: Reversal of respiratory depression by partial agonists or mixed agonist/antagonists such as buprenorphine and pentazocine, may be incomplete. Repeat doses may be required. (5.2)
- Precipitation of Severe Opioid Withdrawal: The use of ZURNAI in patients who are opioid dependent may precipitate opioid withdrawal. In neonates, opioid withdrawal may be life-threatening if not recognized and properly treated. Monitor for the development of opioid withdrawal. (5.3)
- Risk of Cardiovascular (CV) Effects: Abrupt postoperative reversal of opioid depression may result in adverse CV effects. These events have primarily occurred in patients who had preexisting CV disorders or received other drugs that may have similar adverse CV effects. Monitor these patients closely in an appropriate healthcare setting after use of nalmefene hydrochloride. (5.3)
- Risk of Opioid Overdose from Attempts to Overcome the Blockade: Attempts to overcome opioid withdrawal symptoms caused by opioid antagonists with high or repeated doses of exogenous opioids may lead to opioid intoxication and death. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence > 5%) are feeling hot, nausea, headache, dizziness, chills, vomiting, allodynia, palpitations, tinnitus, ear discomfort, feeling abnormal, burning sensation, hot flush, and irritability. (6)
To report Suspected Adverse Reactions, contact Purdue Pharma L.P. at 1-888-726-7535 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 8/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
2.2 Dosing in Adults and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older
2.3 Dosing Modifications Due to Partial Agonists or Mixed Agonists/Antagonists
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Recurrent Respiratory and Central Nervous System Depression
5.2 Risk of Limited Efficacy with Partial Agonists or Mixed Agonist/Antagonists
5.3 Precipitation of Severe Opioid Withdrawal
5.4 Risk of Opioid Overdose from Attempts to Overcome the Blockade
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZURNAI is indicated for the emergency treatment of known or suspected opioid overdose induced by natural or synthetic opioids in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older, as manifested by respiratory and/or central nervous system depression.
ZURNAI is intended for immediate administration as emergency therapy in settings where opioids may be present.
ZURNAI is not a substitute for emergency medical care.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
- All approved nalmefene products achieve plasma concentrations that have been shown to be efficacious in reversing the effects of opioid overdose. Comparing different products on a nominal mg-for-mg basis may be misleading.
- ZURNAI is for intramuscular and subcutaneous use only.
- The device is ready to use. No device assembly is required.
- Do not prime or test prior to administration. ZURNAI delivers its entire contents automatically, upon injection.
- Inject ZURNAI into the anterolateral aspect of the thigh.
- ZURNAI can be administered through clothing if necessary.
- Do not reuse ZURNAI. Each ZURNAI device contains a single dose of nalmefene and cannot be reused.
- Because treatment of suspected opioid overdose must be performed by someone other than the patient, instruct the prescription recipient to inform those around them about the presence of ZURNAI and the Instructions for Use.
- Instruct the patient or caregiver to read the Instructions for Use at the time they receive a prescription for ZURNAI. Emphasize the following instructions to the patient or caregiver:
- – Administer ZURNAI as quickly as possible because prolonged respiratory depression may result in damage to the central nervous system or death.
- – Always seek emergency medical assistance after administration of the first dose of ZURNAI in the event of a suspected, potentially life-threatening opioid emergency. Keep the patient under continued surveillance until emergency personnel arrive.
- – Additional doses of ZURNAI may be required until emergency medical assistance becomes available.
- – If available, re-administer ZURNAI using a new auto-injector, every 2 to 5 minutes if the patient does not respond or responds and then relapses into respiratory depression.
- – Once the safety seal is broken and blue cap is removed, ZURNAI must be used immediately or disposed of properly. Do not attempt to replace the blue cap once it is removed.
- – Visually inspect ZURNAI through the viewing window for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not administer unless the solution is clear, free of particulates, and the glass container is undamaged.
- –
Administer ZURNAI according to the printed instructions on the device label, carton, and the Instructions for Use.
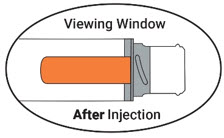
- ⮚ Place the needle guard of ZURNAI against the outer thigh. Press the needle end firmly into the injection site until you hear a click and then hold for 3 seconds. After 3 seconds, the viewing window should turn completely orange, signaling that ZURNAI has delivered the intended dose of nalmefene.
- ⮚ Remove ZURNAI from the outer thigh.
- ⮚ Call for emergency medical assistance immediately after administration of the first dose of ZURNAI.
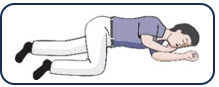
- ⮚ Move the patient on their side (recovery position). Remain with the patient until emergency medical assistance arrives, even if the patient wakes up.
2.2 Dosing in Adults and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older
Initial Dosing:
The recommended dose of ZURNAI in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older is 1.5 mg delivered by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection into the anterolateral aspect of the thigh, through clothing if necessary.
Repeat Dosing:
Seek emergency medical assistance as soon as possible after administration of the first dose of ZURNAI. The requirement for repeat doses of ZURNAI depends upon the amount, type, and route of administration of the opioid being antagonized.
If the patient responds to ZURNAI and subsequently relapses back into respiratory depression before emergency assistance arrives, administer an additional dose of ZURNAI using a new auto-injector and continue surveillance of the patient.
If the desired response is not obtained after 2 to 5 minutes, administer an additional dose of ZURNAI using a new auto-injector. If there is still no response and additional doses are available, administer additional doses of ZURNAI every 2 to 5 minutes using a new ZURNAI auto-injector for each dose until emergency medical assistance arrives.
Additional supportive and/or resuscitative measures may be helpful while awaiting emergency medical assistance.
2.3 Dosing Modifications Due to Partial Agonists or Mixed Agonists/Antagonists
Reversal of respiratory depression by partial agonists or mixed agonist/antagonists, such as buprenorphine and pentazocine, may be incomplete and require repeated administration of ZURNAI using a new auto-injector [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Recurrent Respiratory and Central Nervous System Depression
Respiratory depression in the community overdose setting may be complex and involve the effects of multiple or unknown drugs, some of which may be long-acting opioids. While the duration of action of nalmefene is as long as most opioids, a recurrence of respiratory depression is possible, even after an apparently adequate initial response to ZURNAI treatment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, it is necessary to seek emergency medical assistance immediately after administration of the first dose of ZURNAI and to keep the patient under continued surveillance. A second dose may be necessary if there is recurrence of symptoms of opioid overdose. Additional supportive and/or resuscitative measures may be helpful while awaiting emergency medical assistance [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.2 Risk of Limited Efficacy with Partial Agonists or Mixed Agonist/Antagonists
Reversal of respiratory depression by partial agonists or mixed agonist/antagonists such as buprenorphine and pentazocine, may be incomplete. Repeat doses of ZURNAI may be required to antagonize buprenorphine because the latter has a long duration of action due to its slow rate of binding and subsequent slow dissociation from the opioid receptor [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Buprenorphine antagonism is characterized by a gradual onset of the reversal effects and a decreased duration of action of the normally prolonged respiratory depression.
5.3 Precipitation of Severe Opioid Withdrawal
The use of ZURNAI in patients who are opioid dependent may precipitate opioid withdrawal characterized by the following signs and symptoms: body aches, diarrhea, tachycardia, fever, runny nose, sneezing, piloerection, sweating, yawning, nausea or vomiting, nervousness, restlessness or irritability, shivering or trembling, abdominal cramps, weakness, and increased blood pressure.
Abrupt postoperative reversal of opioid depression after using ZURNAI may result in nausea, vomiting, sweating, tremulousness, tachycardia, hypotension, hypertension, seizures, ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation, pulmonary edema, and cardiac arrest. Death, coma, and encephalopathy have been reported as sequelae of these events. These events have primarily occurred in patients who had pre-existing cardiovascular disorders or received other drugs that may have similar adverse cardiovascular effects. After use of ZURNAI, monitor patients with pre-existing cardiac disease or patients who have received medications with potential adverse cardiovascular effects for hypotension, ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, and pulmonary edema in an appropriate healthcare setting. It has been suggested that the pathogenesis of pulmonary edema associated with the use of nalmefene is similar to neurogenic pulmonary edema, i.e., a centrally mediated massive catecholamine response leading to a dramatic shift of blood volume into the pulmonary vascular bed resulting in increased hydrostatic pressures.
ZURNAI is not indicated for use in patients less than 12 years of age. In neonates, opioid withdrawal may be life-threatening if not recognized and properly treated and may include the following signs and symptoms: convulsions, excessive crying, and hyperactive reflexes. Monitor the patient for the development of the signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal. There may be clinical settings, particularly the postpartum period in neonates with known or suspected exposure to maternal opioid use, where it is preferable to avoid the abrupt precipitation of opioid withdrawal symptoms. In these settings, use an alternative, opioid antagonist product that can be titrated to effect and, where applicable, dosed according to weight [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.4 Risk of Opioid Overdose from Attempts to Overcome the Blockade
ZURNAI is unlikely to produce acute withdrawal symptoms in non-opioid dependent patients. The use of ZURNAI in patients who are opioid dependent may precipitate opioid withdrawal. Attempting to overcome opioid withdrawal symptoms caused by opioid antagonists with high or repeated doses of exogenous opioids could lead to opioid intoxication and death.
Inform patients of the potential consequences of trying to overcome the opioid blockade. Get emergency medical assistance as soon as possible after use of ZURNAI regardless of withdrawal symptoms.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Recurrent Respiratory and Central Nervous System Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Precipitation of Severe Opioid Withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Adult Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of ZURNAI is supported by pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies of ZURNAI in healthy subjects in a normal state and under steady state opioid agonism. The following adverse reactions were observed.
In a pharmacokinetic study (NAL1005) of 21 healthy adult volunteers exposed to one dose of ZURNAI the most common adverse reactions were: dizziness and headache.
In a pharmacodynamic study (NAL1004) of 23 healthy adult volunteers exposed to one dose of ZURNAI, the most common adverse reactions were: feeling hot, chills, nausea, allodynia, and headache.
Table 1: Relative Frequencies of Most Common Adverse Reactions that Occurred in Greater than 5% of Subjects in Study NAL1004 and Study NAL1005 (pooled dataset) Nalmefene Auto-Injector 1.5 mg IM System Organ Class
Preferred TermPooled
NAL1004 and NAL1005
N=44
n (%)Study NAL1004
N=23
n (%)Study NAL1005
N=21
n (%)Any AR 28 (63.6) 21 (91.3) 7 (33.3) Cardiac disorders Palpitations 4 (9.1) 4 (17.4) 0 Ear and labyrinth disorders Tinnitus 4 (9.1) 4 (17.4) 0 Ear discomfort 3 (6.8) 3 (13.0) 0 Gastrointestinal disorders Nausea 8 (18.2) 6 (26.1) 2 (9.5) Vomiting 5 (11.4) 3 (13.0) 2 (9.5) General disorders and administration site conditions Feeling hot 11 (25.0) 11 (47.8) 0 Chills 6 (13.6) 6 (26.1) 0 Feeling abnormal 3 (6.8) 3 (13.0) 0 Nervous system disorders Dizziness 7 (15.9) 4 (17.4) 3 (14.3) Headache 8 (18.2) 5 (21.7) 3 (14.3) Allodynia 5 (11.4) 5 (21.7) 0 Burning sensation 3 (6.8) 3 (13.0) 0 Psychiatric disorders Irritability 3 (6.8) 3 (13.0) 0 Vascular disorders Hot flush 3 (6.8) 3 (13.0) 0 Adverse reaction information was obtained following administration of nalmefene hydrochloride injection to 152 healthy volunteers and to 1127 patients in controlled clinical trials for the treatment of opioid overdose or for postoperative opioid reversal.
TABLE 2: Relative Frequencies of Common Adverse Reactions with an Incidence Greater than 1% (all patients, all clinical settings) Adverse Reaction Nalmefene
N=1127Placebo
N=77Nausea 18% 6% Vomiting 9% 4% Tachycardia 5% - Hypertension 5% - Postoperative pain 4% N/A Fever 3% - Dizziness 3% 1% Headache 1% 4% Chills 1% - Hypotension 1% - Vasodilatation 1% - Incidence less than 1%
CARDIOVASCULAR: Bradycardia, arrhythmia
DIGESTIVE: Diarrhea, dry mouth
NERVOUS SYSTEM: Somnolence, depression, agitation, nervousness, tremor, confusion, withdrawal syndrome, myoclonus
RESPIRATORY: Pharyngitis
SKIN: Pruritus
UROGENITAL: Urinary retention
The incidence of adverse events was highest in patients who received more than the recommended dose of nalmefene hydrochloride injection.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of nalmefene. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Abrupt reversal of opioid depression using nalmefene in both postoperative and emergency department settings has resulted in nausea, vomiting, sweating, tremulousness, seizures, and cardiovascular instability including tachycardia, hypotension, hypertension, ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation, pulmonary edema, and cardiac arrest. Death, coma, and encephalopathy have been reported as sequelae of these events. These events have primarily occurred in patients who had pre-existing cardiovascular disorders or received other drugs that may have similar adverse cardiovascular effects.
In persons who were physically dependent on opioids, abrupt reversal of opioid effects has precipitated an acute withdrawal syndrome. Signs and symptoms have included: body aches, fever, sweating, runny nose, sneezing, piloerection, yawning, weakness, shiver or trembling, nervousness, restlessness or irritability, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, abdominal cramps, increased blood pressure, and tachycardia. In some patients, there may be aggressive behavior upon abrupt reversal of an opioid overdose. In the neonate, opioid withdrawal symptoms also included convulsions, excessive crying, and hyperactive reflexes.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Life-sustaining therapy for opioid overdose should not be withheld [see Clinical Considerations]. There are no available data on nalmefene use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects or miscarriage. In animal reproduction studies, no effects on embryo-fetal development were observed in rats and rabbits treated with nalmefene [see Data].
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
An opioid overdose is a medical emergency and can be fatal for the pregnant woman and fetus if left untreated. Treatment with ZURNAI for opioid overdose should not be withheld because of potential concerns regarding the effects of ZURNAI on the fetus.
Data
Animal Data
Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits by oral administration and in rabbits by intravenous administration of nalmefene. No effects on embryo-fetal development were observed at rat oral doses up to 1200 mg/m2/day and rabbit oral doses up to 2400 mg/m2/day, and intravenous dose up to 96 mg/m2/day, which is 52 times the human dose of 3.0 mg (two ZURNAI administrations) based on body surface area comparison. The treatment in rats did not affect offspring survival.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of nalmefene and its metabolites in human milk, the effects of nalmefene on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Nalmefene and its metabolites are present in rat milk [see Data]. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk.
Data
Nalmefene and its metabolites were secreted into rat milk, reaching concentrations approximately three times those in plasma at one hour and decreasing to about half the corresponding plasma concentrations by 24 hours following bolus administration. The concentration of nalmefene in animal milk does not necessarily predict the concentration of drug in human milk.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ZURNAI for the emergency treatment of known or suspected opioid overdose, as manifested by respiratory and/or central nervous system depression, have been established in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older.
Use for this indication in this age group is supported by adult studies and pharmacokinetic simulation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. There have been no studies conducted to evaluate the use of ZURNAI in pediatric patients.
The safety and effectiveness of ZURNAI for the emergency treatment of known or suspected opioid overdose, as manifested by respiratory and/or central nervous system depression, have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of nalmefene hydrochloride injection did not include sufficient number of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. Geriatric patients have a greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, or other drug therapy. Therefore, the systemic exposure of nalmefene can be higher in these patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Hepatic impairment substantially reduces the clearance of nalmefene [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. For single episodes of opioid antagonism, adjustment of ZURNAI dosage is not required.
8.7 Renal Impairment
Renal impairment substantially reduces the clearance of nalmefene [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. For single episodes of opioid antagonisms, adjustment of ZURNAI dosage is not required.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ZURNAI™ (nalmefene injection) is a sterile, pre-filled, single-dose auto-injector designed to deliver a dose of 1.5 mg nalmefene (provided as nalmefene hydrochloride) in 0.5 mL.
Nalmefene hydrochloride, an opioid antagonist, is a 6-methylene analogue of naltrexone. The molecular structure of nalmefene is presented below:
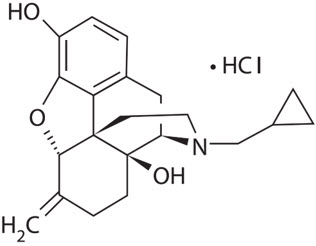
Molecular Formula: C21H25NO3∙HCl
Molecular Weight: 375.9, CAS# 58895-64-0
Chemical Name: 17-(Cyclopropylmethyl)-4,5α-epoxy-6-methylenemorphinan-3,14-diol, hydrochloride salt
Nalmefene is a white to off-white crystalline powder which is freely soluble in water up to 130 mg/mL and slightly soluble in chloroform up to 0.13 mg/mL, with a pKa of 7.63.
Each ZURNAI auto-injector delivers 1.5 mg nalmefene (equivalent to 1.7 mg nalmefene hydrochloride) in 0.5 mL solution. The pH range is 3.5 to 4.5.
The inactive ingredients in ZURNAI nalmefene injection include: hydrochloric acid to adjust pH; magnesium chloride, 4.7 mg; and water for injection.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Nalmefene reverses the effects of natural and synthetic opioids, including respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension. Pharmacodynamic studies have shown that nalmefene injection has a longer duration of action than naloxone injection at fully reversing doses. Nalmefene has no opioid agonist activity.
The effect of ZURNAI was studied in an experimental clinical opioid-induced respiratory depression (OIRD) model in twenty-four opioid-experienced, non-opioid dependent subjects (NAL1004). This model assessed changes in minute ventilation (MV) during administration of a 3-step intravenous fentanyl infusion. In step 1, fentanyl was infused until MV nadir (functional OIRD) was achieved. MV nadir was defined as a 50% reduction in MV from baseline or the MV reduction achieved following the maximum permitted fentanyl titration. Following attainment of MV nadir, the fentanyl infusion rate was decreased (step 2) to maintain the fentanyl concentrations. ZURNAI was administered at 10 minutes following MV nadir. Ten minutes following ZURNAI administration, the fentanyl infusion rate was further decreased (step 3) to maintain constant fentanyl concentrations for the remaining duration of the reversal session.
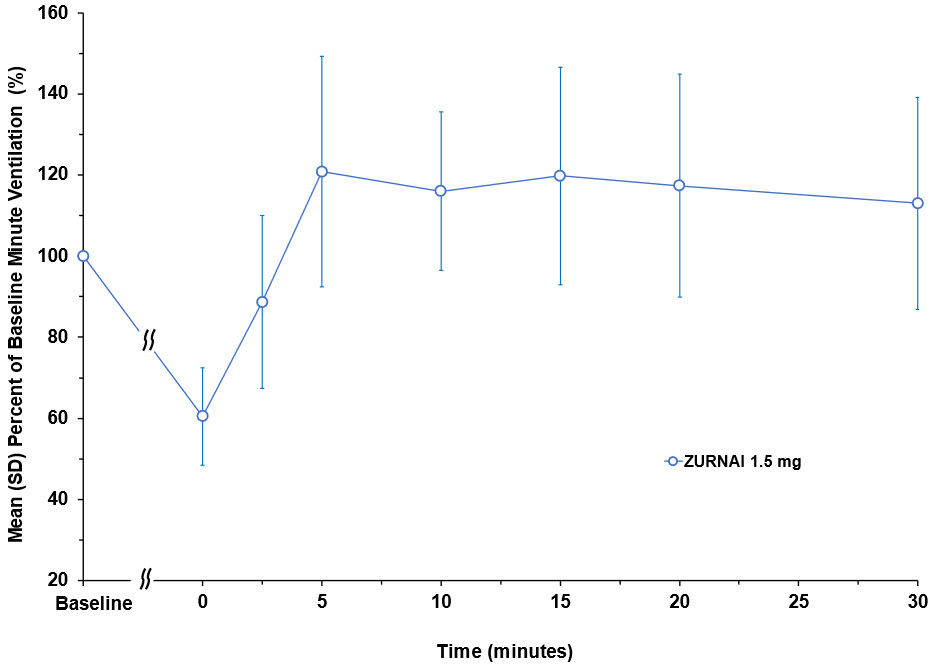
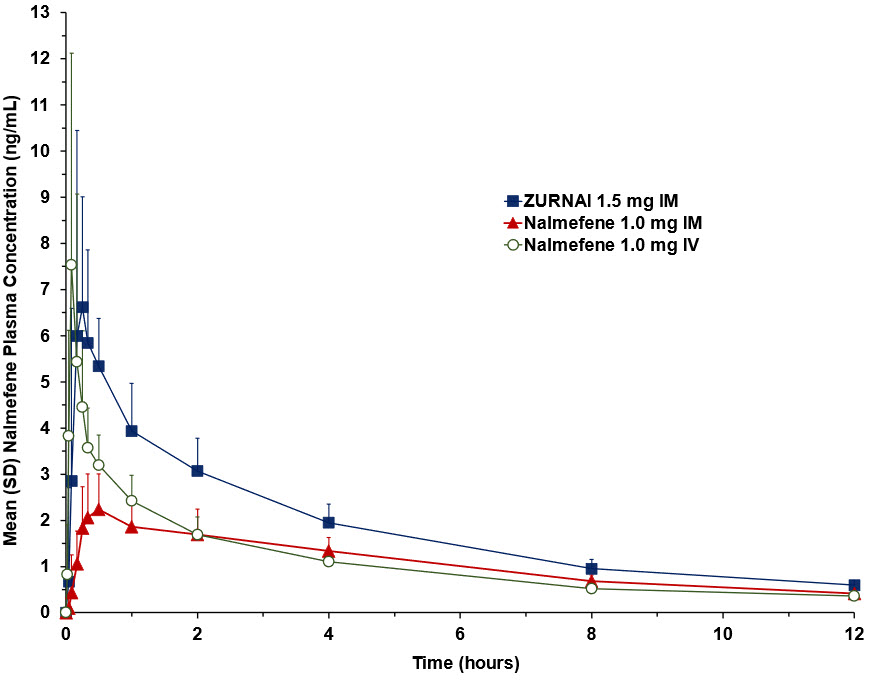
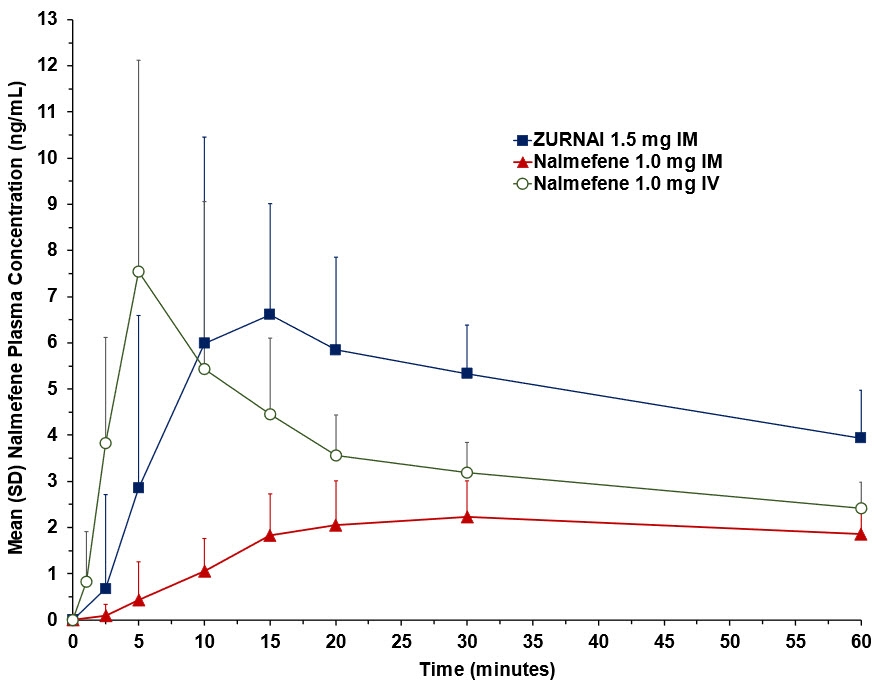
Following ZURNAI administration the time to onset of effect, that is onset of reversal of respiratory depression, was observed between 2.5 to 5 minutes (Figure 1 and Figure 2). At 5 minutes mean change in MV from nadir was 4.42 L/min (Figure 1). Full recovery of respiratory drive was noted between 5 and 15 minutes after ZURNAI administration (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
Figure 1: Reversal of Fentanyl-Induced Respiratory Depression in adult healthy volunteers treated with ZURNAI (nalmefene)
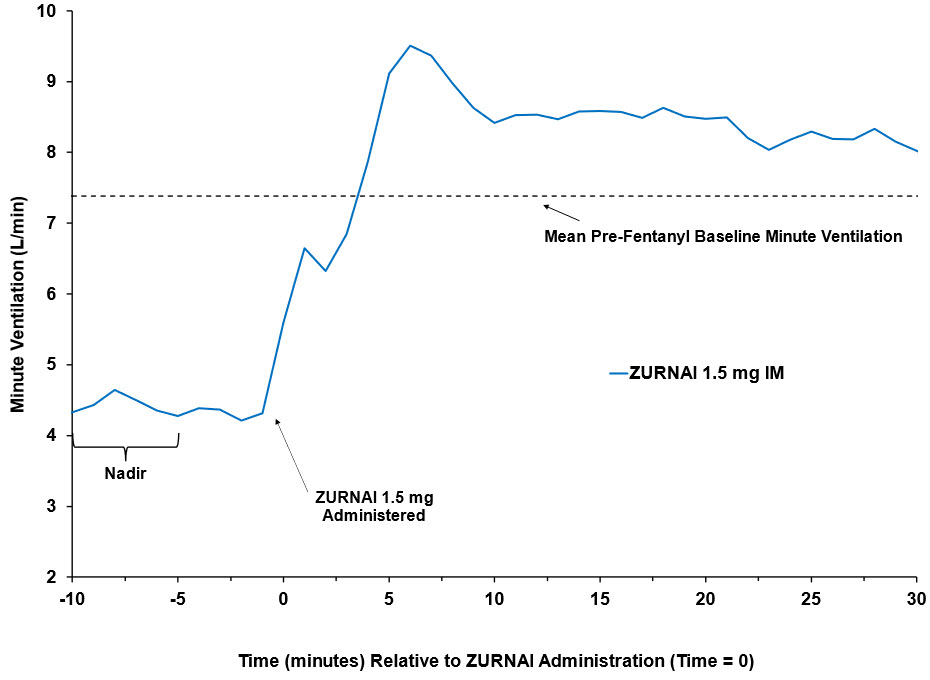
Figure 2: Percent Recovery of Respiratory Drive after Fentanyl Infusion in Minute Ventilation (Mean SD) in Adult Healthy Volunteers with ZURNAI 1.5 mg
Nalmefene is not known to produce respiratory depression, psychotomimetic effects, or pupillary constriction. No pharmacological activity was observed when nalmefene was administered in the absence of opioid agonists.
Nalmefene has not been shown to produce tolerance, physical dependence, or abuse potential.
Nalmefene can produce acute withdrawal symptoms in individuals who are opioid dependent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In a pharmacokinetic study (NAL1005) in 24 healthy adult subjects, the relative bioavailability of one dose of ZURNAI administered intramuscularly was compared to a single dose of nalmefene 1.0 mg administered as an intramuscular injection. The pharmacokinetic parameters obtained in this study are shown in Table 3 and the plasma concentration time profiles of nalmefene are presented in Figure 3.
Table 3: Geometric Mean (CV%) Nalmefene PK Parameters after Administration of 1.5 mg ZURNAI Intramuscular (IM), 1.0 mg Nalmefene IM, and 1.0 mg Nalmefene Intravenous (IV) Parameter ZURNAI
1.5 mgNalmefene IM
1.0 mgNalmefene IV
1.0 mgNA = Not applicable. - * Tmax presented as median (range)
- † Arithmetic mean
Tmax (h)* 0.25 (0.083-1.00) 0.50 (0.083-2.00) 0.083 (0.083 -0.25) Cmax (ng/mL) 7.37 (47.5) 2.39 (32.6) 6.94 (55.7) AUC0-2.5min (ng-hr/mL) † 0.011 (288) 0.001 (241) 0.062 (56.1) AUC0-5min (ng-hr/mL) † 0.077 (144) 0.010 (209) 0.299 (40.4) AUC0-10min (ng-hr/mL) 0.320 (85.8) 0.047 (107) 0.768 (46.2) AUC0-15min (ng-hr/mL) 0.831 (62.7) 0.152 (64.8) 1.16 (46.1) AUC0-20min (ng-hr/mL) 1.31 (51.3) 0.315 (48.3) 1.50 (41.7) AUC0-30min (ng-hr/mL) 2.24 (39.3) 0.647 (40.7) 2.07 (34.0) AUC0-inf (ng-hr/mL) 30.53 (16.0) 17.98 (21.0) 18.22 (15.3) Frel (%) † 113 (13.0) NA NA T½ (h) † 9.07 (26.6) 7.74 (24.3) 9.12 (16.5) Figure 3: Mean Plasma Concentration-Time Profiles of Nalmefene (a) 0-12 hours and (b) 0- 60 minutes Following Administration of 1.5 mg ZURNAI Intramuscular (IM), 1.0 mg Nalmefene IM, and 1.0 mg Nalmefene Intravenous (IV)
(a)
(b)
Absorption
After administration of one ZURNAI to healthy adult subjects, the median Tmax for ZURNAI was 0.250 hours, compared to 0.5 hours for the intramuscular nalmefene 1 mg injection.
Based on dose-normalized area under the curve (AUCinf), the mean bioavailability of ZURNAI was 1.13 (Frel) relative to intramuscular administration of nalmefene 1 mg and was 1.15 (Fabs) relative to intravenous administration of nalmefene 1 mg.
Distribution
Following a 1 mg parenteral dose, nalmefene was rapidly distributed. In a study of brain receptor occupancy, a 1 mg dose of nalmefene blocked over 80% of brain opioid receptors within 5 minutes after administration. The apparent volumes of distribution centrally (Vc) and at steady state (Vdss) are 3.9 ± 1.1 L/kg and 8.6 ± 1.7 L/kg, respectively. Ultrafiltration studies of nalmefene have demonstrated that 45% (CV 4.1%) is bound to plasma proteins over a concentration range of 0.1 to 2 mcg/mL. An in vitro determination of the distribution of nalmefene in human blood demonstrated that nalmefene distributed 67% (CV 8.7%) into red blood cells and 39% (CV 6.4%) into plasma. The whole blood to plasma ratio was 1.3 (CV 6.6%) over the nominal concentration range in whole blood from 0.376 to 30 ng/mL.
Elimination
After administration of ZURNAI to healthy adult subjects, plasma concentrations have a terminal elimination half-life of 9.07 (%CV 26.2) hours. Following a 1 mg parenteral dose, the apparent clearance of nalmefene is 55.46 (%CV 8.41) L/hr.
Metabolism
Nalmefene is metabolized by the liver, primarily by glucuronide conjugation.
Nalmefene is also metabolized to trace amounts of an N-dealkylated metabolite. Nalmefene glucuronide is inactive and the N-dealkylated metabolite has minimal pharmacological activity.
Excretion
Nalmefene and its metabolites are excreted in the urine. Less than 5% of nalmefene is excreted in the urine unchanged. Seventeen percent (17%) of the nalmefene dose is excreted in the feces. The plasma concentration-time profile in some subjects suggests that nalmefene undergoes enterohepatic recycling.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Population
In previous studies with nalmefene hydrochloride injection, dose proportionality was observed in nalmefene AUC0-inf following 0.5 to 2 mg intravenous administration to elderly male subjects. Following a 1 mg intravenous nalmefene dose, there were no significant differences between young (19 to 32 years) and elderly (62 to 80 years) adult male subjects with respect to plasma clearance, steady-state volume of distribution, or half-life. There was an apparent age-related decrease in the central volume of distribution (young: 3.9 ± 1.1 L/kg, elderly: 2.8 ± 1.1 L/kg) that resulted in a greater initial nalmefene concentration in the elderly group. While initial nalmefene plasma concentrations were transiently higher in the elderly, it would not be anticipated that this population would require dosing adjustment. No clinical adverse events were noted in the elderly following the 1 mg intravenous nalmefene dose.
Pediatric Patients
No pharmacokinetic studies were conducted with ZURNAI in pediatric patients. Based on population PK simulations, compared to an adult population (mean weight 76 kg), 12-year-old subjects with a median weight 49 kg, range 33 to 71 kg are expected to have 27% higher mean Cmax and 15% higher mean AUC0-∞ [See Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Male and Female Patients
There is insufficient experience with the use of nalmefene hydrochloride injection to detect sex variations in pharmacokinetics.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of ZURNAI have not been studied in renally impaired subjects. In previous studies with nalmefene hydrochloride injection, there was a statistically significant 27% decrease in plasma clearance of nalmefene in the end-stage renal disease (ESRD) population during interdialysis (0.57 ± 0.20 L/hr/kg) and a 25% decreased plasma clearance in the ESRD population during intradialysis (0.59 ± 0.18 L/hr/kg) compared to normal patients (0.79 ± 0.24 L/hr/kg). The elimination half-life was prolonged in ESRD patients from 10.2 ± 2.2 hours in normal patients to 26.1 ± 9.9 hours.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of ZURNAI have not been studied in hepatically impaired subjects. In previous studies with nalmefene hydrochloride injection, in subjects with hepatic disease, when compared to matched normal controls, had a 28.3% decrease in plasma clearance of nalmefene (0.56 ± 0.21 L/hr/kg versus 0.78 ± 0.24 L/hr/kg, respectively). Elimination half-life increased from 10.2 ± 2.2 hours to 11.9 ± 2.0 hours in the hepatically impaired. No dosage adjustment is recommended since nalmefene will be administered as an acute course of therapy.
Low Body Weight Patients and High Body Weight Patients
The effect of weight on nalmefene PK following a single dose of 1.5 mg ZURNAI administration was assessed using population pharmacokinetic simulations. Compared to the mean PK values across the full population in the PK dataset (median weight 76 kg), the 1st quartile of body weight (54.0 to 67.3 kg) had + 17.6% higher Cmax and + 13.4% higher AUC0-∞ whereas the 4th quartile of body weight (86.8 to 117.1 kg) had – 15.3% lower Cmax and – 11.8% lower AUC0-∞.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term animal studies to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of nalmefene have not been completed.
Mutagenesis
Nalmefene did not have mutagenic activity in the Ames test with five bacterial strains or the mouse lymphoma assay. Clastogenic activity was not observed in the mouse micronucleus test or in the cytogenic bone marrow assay in rats. However, nalmefene did exhibit a weak but significant clastogenic activity in the human lymphocyte metaphase assay in the absence but not in the presence of exogenous metabolic activation.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Each single-dose auto-injector delivers 1.5 mg of nalmefene in 0.5 mL. Each carton contains one single-dose ZURNAI (nalmefene injection).
NDC: 59011-962-01: One carton containing one single-dose auto-injector.
ZURNAI is not made with natural rubber latex.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at controlled room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), with excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F).
During storage, check ZURNAI through the viewing window of the auto-injector every 30 days. The liquid should be clear, colorless to light yellow. If the ZURNAI liquid is discolored, cloudy, or contains solid particles, replace it with a new ZURNAI.
DO NOT FREEZE OR REFRIGERATE. Store in a clean dry place. Protect from light.
Keep ZURNAI in the carton until use.
Store ZURNAI securely and dispose of properly in a sharps container. For detailed disposal instructions, see the Instructions for Use.
KEEP ZURNAI AND ALL MEDICINES OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
Before using, check to make sure the solution in the auto-injector is not discolored. Replace ZURNAI if the solution is discolored or contains a precipitate.
Each ZURNAI can only be used one time and cannot be re-used.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient and family members or caregivers to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Instruct patients and their family members or caregivers to become familiar with all information contained in the carton as soon as they receive ZURNAI.
Recognition of Opioid Overdose
Instruct patients and their family members or caregivers about how to recognize the signs and symptoms of an opioid overdose, such as the following:
- Extreme somnolence – inability to awaken a patient verbally or upon a firm sternal rub
- Respiratory depression – this can range from slow or shallow respiration to no respiration in a patient who is unarousable
- Other signs and symptoms that may accompany somnolence and respiratory depression include the following:
- Miosis
- Bradycardia and/or hypotension
Risk of Recurrent Respiratory and Central Nervous System Depression
While the duration of action of nalmefene is as long as most opioids, instruct patients and their family members or caregivers that they must seek immediate emergency medical assistance after administration of the first dose of ZURNAI, and keep the patient under continued surveillance even after an apparently adequate initial response to ZURNAI. A second dose may be necessary if there is recurrence of symptoms of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Limited Efficacy for/with Partial Agonists or Mixed Agonist/Antagonists
Instruct patients and their family members or caregivers that the reversal of respiratory depression caused by partial agonists or mixed agonist/antagonists, such as buprenorphine and pentazocine, may be incomplete and may require repeated administration of ZURNAI, using a new ZURNAI auto-injector each time [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Precipitation of Severe Opioid Withdrawal
Instruct patients and their family members or caregivers that the use of ZURNAI in patients who are opioid dependent may precipitate opioid withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Adverse Reactions (6)].
Administration Instructions
Instruct patients and their family member or caregivers to:
- Ensure ZURNAI is readily available in locations where persons may be intentionally or accidentally exposed to an opioid overdose (i.e., opioid emergencies).
- Use ZURNAI one time only. DO NOT test or prime prior to use [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- Carefully read the Instructions for Use that comes with ZURNAI.
- Administer ZURNAI as quickly as possible if a person is unresponsive and an opioid overdose is suspected, even when in doubt, because prolonged respiratory depression may result in damage to the central nervous system or death. ZURNAI is not a substitute for emergency medical care [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- Administer ZURNAI directly into the outer thigh. Press the needle end firmly into the injection site (through clothing, if necessary) and hold for 3 seconds [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. After 3 seconds, the viewing window should turn completely orange, signaling that ZURNAI has delivered the intended dose of nalmefene.
- Remove ZURNAI from the outer thigh.
- Call 911 immediately after injecting the first dose of ZURNAI.
- Move the person to the recovery position by turning them to their side. Additional supportive and/or resuscitative measures may be helpful while awaiting emergency medical assistance [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- Watch the person carefully. Wait 2 to 5 minutes to see if the person wakes up.
- If the person is not responding or responds and then relapses back into respiratory depression, administer additional doses of ZURNAI every 2 to 5 minutes using a new ZURNAI auto-injector [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- Remain with the person until emergency medical help arrives, even if they wake up.
- Visually inspect the nalmefene solution through the viewing window every 30 days. If the solution is discolored, cloudy, or contains solid particles, replace it with a new ZURNAI.
- Replace ZURNAI before its expiration date.
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
ZURNAI™ (zur nye)
(nalmefene injection)This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 08/2024 You and your family members or caregivers should read this Patient Information leaflet before an opioid emergency happens. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. What is the most important information I should know about ZURNAI?
ZURNAI is used to temporarily reverse the effects of opioid medicines. The medicine in ZURNAI is not expected to have an effect in people who are not taking opioid medicines. Always carry ZURNAI with you in case of an opioid emergency.- Use ZURNAI right away if you or your caregiver think signs or symptoms of an opioid emergency are present, even if you are not sure, because an opioid emergency can cause severe injury or death. Signs and symptoms of an opioid emergency may include:
- unusual sleepiness and you are not able to awaken the person with a loud voice or by rubbing firmly on the middle of their chest (sternum).
- breathing problems including slow or shallow breathing in someone difficult to awaken or who looks like they are not breathing.
- the black circle in the center of the colored part of the eye (pupil) is very small, sometimes called 'pinpoint pupils,' in someone difficult to awaken.
- Family members, caregivers, or other people who may have to use ZURNAI in an opioid emergency should know where ZURNAI is stored and how to give ZURNAI before an opioid emergency happens. Make sure everyone reads the information contained in the carton as soon as you receive ZURNAI.
- Call 911 or get emergency medical help right away after giving the first dose of ZURNAI. Rescue breathing or CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) may be given while waiting for emergency medical help.
- The signs and symptoms of an opioid emergency can return after ZURNAI is given. If this happens, give additional doses of ZURNAI every 2 to 5 minutes using a new ZURNAI auto-injector for each dose and watch the person closely until emergency help arrives.
What is ZURNAI? - ZURNAI is a prescription medicine used in adults and children 12 years of age and older for the treatment of an opioid emergency such as an overdose or a possible opioid overdose with signs of breathing problems and severe sleepiness or not being able to respond.
- ZURNAI is to be given right away and does not take the place of emergency medical care. Get emergency medical help right away after giving the first dose of ZURNAI, even if the person wakes up.
Do not use ZURNAI if you are allergic to nalmefene hydrochloride or any of the ingredients in ZURNAI. See the end of this Patient Information leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in ZURNAI. Before using ZURNAI, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have heart problems.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if ZURNAI will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if ZURNAI passes into your breast milk.
How should I use ZURNAI?
Read the "Instructions for Use" at the end of this Patient Information leaflet for detailed information about the right way to use ZURNAI.- Use ZURNAI exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Each ZURNAI auto-injector contains only 1 dose of medicine and cannot be reused.
- The ZURNAI auto-injector is ready to use. Do not test or prime ZURNAI before use.
- ZURNAI should be injected into the muscle (intramuscular) or underneath the skin (subcutaneous) of the outer thigh. It can be injected through your clothing if needed.
What are the possible side effects of ZURNAI?
ZURNAI may cause serious side effects, including:- Sudden opioid withdrawal symptoms. In someone who has been using opioids regularly, opioid withdrawal symptoms can happen suddenly after receiving ZURNAI and may include:
- body aches
- diarrhea
- increased heart rate
- fever
- runny nose
- sneezing
- goose bumps
- sweating
- yawning
- nausea or vomiting
- nervousness
- restlessness or irritability
- shivering or trembling
- stomach cramping
- weakness
- increased blood pressure
- Risk of opioid overdose. ZURNAI blocks the effects of opioids and may cause opioid withdrawal in someone who has been using opioids regularly. Do not take large amounts of opioids to try to overcome the opioid-blocking effects of ZURNAI. This could lead to an opioid overdose and death. Call 911 or get emergency medical help right away after using ZURNAI.
The most common side effects of ZURNAI include: - feeling hot
- nausea
- headache
- dizziness
- chills
- vomiting
- feeling pain from things that are not usually painful (allodynia)
- irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- ringing in the ear
- ear discomfort
- feeling abnormal
- burning sensation
- hot flush
- irritability
These are not all of the possible side effects of ZURNAI.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store ZURNAI? - Store ZURNAI at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not freeze or refrigerate.
- Store ZURNAI in a clean dry place. Protect from light.
- Keep ZURNAI in the carton until use.
- During storage, check ZURNAI through the viewing window of the auto-injector every 30 days. The liquid should be clear, colorless to light yellow. If the ZURNAI liquid is discolored, cloudy, or contains solid particles, replace it with a new ZURNAI.
- Check the expiration date. Replace ZURNAI before the expiration date.
General information about the safe and effective use of ZURNAI.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ZURNAI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ZURNAI that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in ZURNAI?
Active ingredient: nalmefene
Inactive ingredients: hydrochloric acid to adjust pH, magnesium chloride, and water for injection.
ZURNAI is not made with natural rubber latex.Manufactured for: Purdue Pharma L.P., Stamford, CT 06901-3431.
For more information, go to www.ZURNAI.com or call 1-888-726-7535. - Use ZURNAI right away if you or your caregiver think signs or symptoms of an opioid emergency are present, even if you are not sure, because an opioid emergency can cause severe injury or death. Signs and symptoms of an opioid emergency may include:
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
ZURNAI™ (zur nye)
(nalmefene injection)The Instructions for Use contains information on how to give ZURNAI in response to a known or suspected opioid overdose in adults and children 12 years of age and older. You and your family members or caregivers should read the Instructions for Use that comes with ZURNAI before using it. Talk to your healthcare provider if you and your family members or caregivers have any questions about the use of ZURNAI.
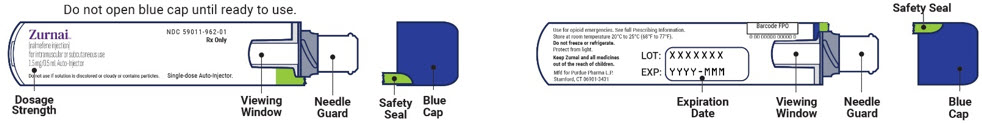
ZURNAI auto-injector parts:
Important information you need to know before injecting ZURNAI
- The ZURNAI auto-injector is ready to use. Do not test or prime ZURNAI before use.
- Each ZURNAI auto-injector contains 1 dose of medicine and cannot be reused.
- Inject ZURNAI into the muscle (intramuscular) or underneath the skin (subcutaneous) of the outer thigh. Do not inject into any other area of the body.
Preparing to inject ZURNAI
-
Check person for signs of a suspected overdose:
- will not wake to voice or touch
- very sleepy
- not breathing well
- Check the auto-injector label to make sure you are injecting ZURNAI.
- Check for any visible damage to the auto-injector before using.
- Check the auto-injector to make sure the safety seal is not broken and the blue cap is secure and not missing.
- Check the liquid through the viewing window before using. It should be clear, colorless to light-yellow and free of particles. You may see air bubbles. This is normal.
Injecting ZURNAI
1. Remove the blue cap - Twist the blue cap counterclockwise to break the safety seal and pull straight off to remove the cap.
- After the blue cap is removed, a few drops of liquid may appear on the needle end. This is normal.
- ZURNAI must be used right away after the safety seal is broken and blue cap is removed. Do not replace the blue cap after it has been removed. If you do not use ZURNAI right away, see Step 5 for instructions on how to throw away ZURNAI.
- Do not touch the needle end of the auto-injector after the blue cap is removed to prevent injury or accidental activation.
2. Position and inject - Place the needle guard of the auto-injector against the outer thigh. The needle will inject through clothing.
- Push the auto-injector firmly down against the outer thigh until you hear a "click" (the click indicates the start of the injection).
- Hold in place for 3 seconds.
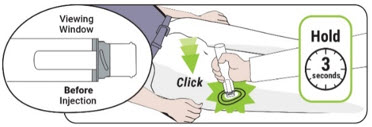
3. Inspect the viewing window - After holding in place for 3 seconds, the viewing window should turn completely orange. A fully blocked (completely orange) window confirms the injection is complete.
- Remove the auto-injector from the outer thigh.
- Do not replace the blue cap after the injection.
- If the viewing window is not fully blocked after injecting, repeat Steps 1 to 3 using a new ZURNAI auto-injector.
4. Call 911 and watch the person - Call 911 or get emergency medical help right away after the injection.
- Move the person on their side (recovery position).
- Hand is supporting their head.
- Bend their knee.
- Turn their face to the side.
- Watch the person for response. Wait for 2 to 5 minutes to see if the person wakes up.
- If no response, repeat Steps 1 to 3 using a new ZURNAI auto-injector to give another dose.
- If more ZURNAI auto-injectors are available, Steps 1 to 3 may be repeated every 2 to 5 minutes until the person responds or emergency medical help arrives.
- Stay with the person until medical help arrives, even if the person wakes up.


5. Throw away (dispose of) the used ZURNAI auto-injector Disposing of (throwing away) ZURNAI - Put your used ZURNAI auto-injector in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) ZURNAI in your household trash.
- If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Important: Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children. Storing ZURNAI - Store ZURNAI at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not freeze or refrigerate.
- Store ZURNAI in a clean dry place. Protect from light.
- Keep ZURNAI in the carton until use.
- During storage, check ZURNAI through the viewing window of the auto-injector every 30 days. The liquid should be clear, colorless to light yellow. If the ZURNAI liquid is discolored, cloudy, or contains solid particles, replace it with a new ZURNAI.
- Check the expiration date. Replace ZURNAI before the expiration date.
Manufactured for Purdue Pharma L.P., Stamford CT, 06901-3431.
©2024, Purdue Pharma L.P., Stamford CT 06901-3431
For more information go to www.ZURNAI.com or call 1-888-726-7535.
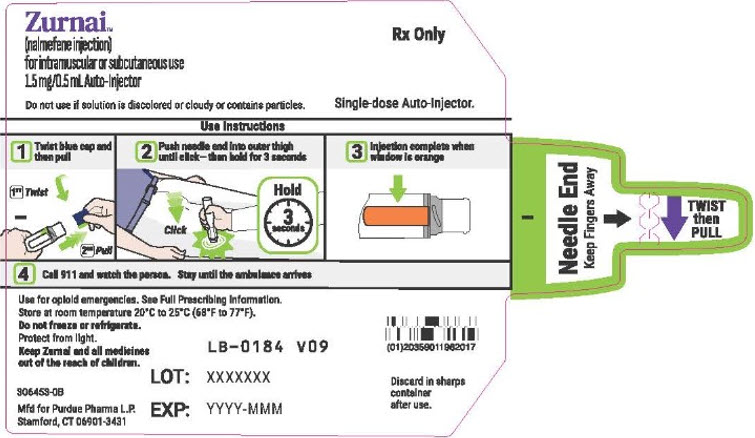
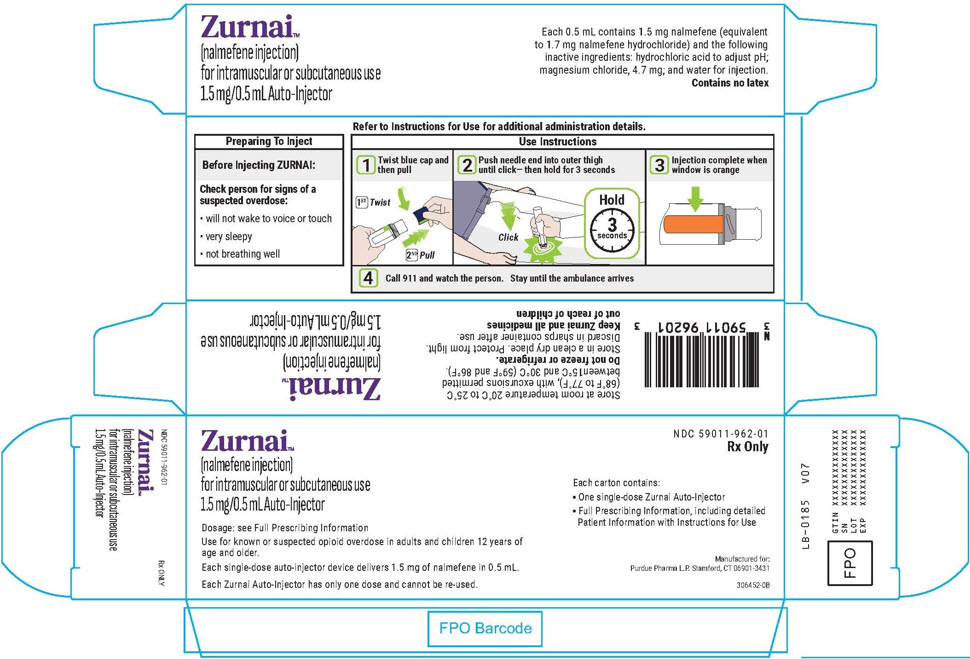
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.Issued: 08/2024 - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1.5 mg/0.5 mL Auto-Injector Label
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1.5 mg/0.5 mL Auto-Injector Carton
Zurnai™
(nalmefene injection)
for intramuscular or subcutaneous use
1.5 mg/0.5 mL Auto-InjectorDosage: see Full Prescribing Information
Use for known or suspected opioid overdose in adults and children 12 years of
age and older.Each single-dose auto-injector device delivers 1.5 mg of nalmefene in 0.5 mL.
Each Zurnai Auto-Injector has only one dose and cannot be re-used.
NDC: 59011-962-01
Rx OnlyEach carton contains:
- One single-dose Zurnai Auto-Injector
- Full Prescribing Information, including detailed
Patient Information with Instructions for Use
Manufactured for:
Purdue Pharma L.P. Stamford, CT 06901-3431306452-0B
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ZURNAI
nalmefene hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 59011-962 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NALMEFENE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: K7K69QC05X) (NALMEFENE - UNII:TOV02TDP9I) NALMEFENE 1.5 mg in 0.50 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) MAGNESIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 02F3473H9O) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 59011-962-01 1 in 1 CARTON 08/07/2025 1 0.5 mL in 1 SYRINGE, GLASS; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218590 08/07/2025 Labeler - Purdue Pharma L.P. (932323652)
Trademark Results [Zurnai]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ZURNAI 98597572 not registered Live/Pending |
Purdue Pharma L.P. 2024-06-12 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.