POTASSIUM CHLORIDE powder, for solution
Potassium Chloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Potassium Chloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Par Pharmaceutical. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use POTASSIUM CHLORIDE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for POTASSIUM CHLORIDE.
POTASSIUM CHLORIDE for oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 1948INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Potassium Chloride is a potassium salt indicated for the treatment and prophylaxis of hypokalemia with or without metabolic alkalosis, in patients for whom dietary management with potassium-rich foods or diuretic dose reduction is insufficient. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dilute prior to administration. (2.1, 5.1)
Monitor serum potassium and adjust dosage accordingly (2.2, 2.3)
If serum potassium concentration is <2.5 mEq/L, use intravenous potassium instead of oral supplementation (2.1)
Treatment of hypokalemia:
- Adults: Initial doses range from 40-100 mEq/day in 2-5 divided doses: limit doses to 40 mEq per dose. Total daily dose should not exceed 200 mEq (2.2)
- Pediatric patients aged birth to 16 years old: 2-4 mEq/kg/day in divided doses; not to exceed 1 mEq/kg as a single dose or 40 mEq whichever is lower; if deficits are severe or ongoing losses are great, consider intravenous therapy. Total daily dose should not exceed 100 mEq (2.3)
Maintenance or Prophylaxis of hypokalemia:
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Potassium Chloride for Oral Solution, USP 20 mEq: Each pouch contains 1.5 g of Potassium Chloride providing potassium 20 mEq and chloride 20 mEq. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Concomitant use with potassium sparing diuretics. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Gastrointestinal Irritation: Dilute before use, take with meals (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions are nausea, vomiting, flatulence, abdominal pain/discomfort, and diarrhea. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Pharm-Olam at 1-866-511-6754 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Potassium sparing diuretics: Avoid concomitant use (7.1)
- Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors: Monitor for hyperkalemia (7.2)
- Angiotensin receptor blockers: Monitor for hyperkalemia (7.2)
- Spironolactone, eplerenone or aliskiren: Monitor for hyperkalemia (7.2)
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory drugs: Monitor for hyperkalemia (7.3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Cirrhosis: Initiate therapy at the low end of the dosing range (8.5)
Renal Impairment: Initiate therapy at the low end of the dosing range (8.6)
Revised: 12/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Administration and Monitoring
2.2 Adult Dosing
2.3 Pediatric Dosing
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Gastrointestinal Irritation
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
7.2 Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors
7.3 Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS)
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Cirrhotics
8.7 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Symptoms
10.2 Treatment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Administration and Monitoring
If serum potassium concentration is <2.5 mEq/L, use intravenous potassium instead of oral supplementation.
Monitoring
Monitor serum potassium and adjust dosages accordingly. For treatment of hypokalemia, monitor potassium levels daily or more often depending on the severity of hypokalemia until they return to normal. Monitor potassium levels monthly to biannually for maintenance or prophylaxis.
The treatment of potassium depletion, particularly in the presence of cardiac disease, renal disease, or acidosis requires careful attention to acid-base balance, volume status, electrolytes, including magnesium, sodium, chloride, phosphate, and calcium, electrocardiograms and the clinical status of the patient. Correct volume status, acid-base balance and electrolyte deficits as appropriate.
Administration
Dilute the contents of 1 pouch of potassium chloride for oral solution in at least 4 ounces of cold water [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Take with meals or immediately after eating.
2.2 Adult Dosing
Treatment of hypokalemia:
Daily dose range from 40 to 100 mEq. Give in 2 to 5 divided doses: limit doses to 40 mEq per dose. The total daily dose should not exceed 200 mEq in a 24 hour period.
Maintenance or Prophylaxis
Typical dose is 20 mEq per day. Individualize dose based upon serum potassium levels.
Studies support the use of potassium replacement in digitalis toxicity. When alkalosis is present, normokalemia and hyperkalemia may obscure a total potassium deficit. The advisability of use of potassium replacement in the setting of hyperkalemia is uncertain.
2.3 Pediatric Dosing
Treatment of hypokalemia:
Pediatric patients aged birth to 16 years old: The initial dose is 2 to 4 mEq/kg/day in divided doses; do not exceed as a single dose 1 mEq/kg or 40 mEq, whichever is lower; maximum daily doses should not exceed 100 mEq. If deficits are severe or ongoing losses are great, consider intravenous therapy.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Gastrointestinal Irritation
May cause gastrointestinal irritation. Increased dilution of the solution and taking with meals may reduce gastrointestinal irritation [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- 6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
Use with potassium-sparing diuretic can produce severe hyperkalemia. Avoid concomitant use.
7.2 Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) including angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBS), spironolactone, eplerenone, or aliskiren produce potassium retention by inhibiting aldosterone production. Closely monitor potassium in patients receiving concomitant RAAS therapy.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.3 Nursing Mothers
The normal potassium ion content of human milk is about 13 mEq per liter. Since oral potassium becomes part of the body potassium pool, so long as body potassium is not excessive, the contribution of potassium chloride supplementation should have little or no effect on the level in human milk.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Clinical trial data from published literature have demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of potassium chloride in children with diarrhea and malnutrition from birth to 16 years.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Potassium Chloride did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
8.6 Cirrhotics
Patients with cirrhosis should usually be started at the low end of the dosing range, and the serum potassium level should be monitored frequently. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
Patients with renal impairment have reduced urinary excretion of potassium and are at substantially increased risk of hyperkalemia. Patients with impaired renal function, particularly if the patient is on ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, should usually be started at the low end of the dosing range because of the potential for development of hyperkalemia. The serum potassium level should be monitored frequently. Renal function should be assessed periodically.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Symptoms
The administration of oral potassium salts to persons with normal excretory mechanisms for potassium rarely causes serious hyperkalemia. However, if excretory mechanisms are impaired or if potassium is administered too rapidly potentially fatal hyperkalemia can result.
Hyperkalemia is usually asymptomatic and may be manifested only by an increased serum potassium concentration (6.5–8.0 mEq/L) and characteristic electrocardiographic changes (peaking of T-waves, loss of P-waves, depression of S-T segment, and prolongation of the QT-interval). Late manifestations include muscle paralysis and cardiovascular collapse from cardiac arrest (9–12 mEq/L).
10.2 Treatment
Treatment measures for hyperkalemia include the following:
- Monitor closely for arrhythmias and electrolyte changes.
- Eliminate foods and medications containing potassium and of any agents with potassium-sparing properties such as potassium-sparing diuretics, ARBS, ACE inhibitors, NSAIDS, certain nutritional supplements and many others.
- Administer intravenous calcium gluconate if the patient is at no risk or low risk of developing digitalis toxicity.
- Administer intravenously 300 to 500 mL/hr of 10% dextrose solution containing 10 to 20 units of crystalline insulin per 1000 mL.
- Correct acidosis, if present, with intravenous sodium bicarbonate.
- Use exchange resins, hemodialysis, or peritoneal dialysis.
In patients who have been stabilized on digitalis, too rapid a lowering of the serum potassium concentration can produce digitalis toxicity.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Potassium Chloride is a white crystalline or colorless solid. It is soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. Chemically, Potassium Chloride is K-Cl with a molecular mass of 74.55.
Each pouch of light pink to orange powder contains 1.5 g of potassium chloride, USP, which is equivalent to potassium 20 mEq and chloride 20 mEq and the following inactive ingredients: citric acid anhydrous, colloidal silicon dioxide, FD&C Yellow #6, natural and artificial orange flavor, and sucralose.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The potassium ion (K+) is the principal intracellular cation of most body tissues. Potassium ions participate in a number of essential physiological processes including the maintenance of intracellular tonicity; the transmission of nerve impulses; the contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle; and the maintenance of normal renal function.
The intracellular concentration of potassium is approximately 150 to 160 mEq per liter. The normal adult plasma concentration is 3.5 to 5 mEq per liter. An active ion transport system maintains this gradient across the plasma membrane.
Potassium is a normal dietary constituent, and under steady-state conditions the amount of potassium absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract is equal to the amount excreted in the urine. The usual dietary intake of potassium is 50 to 100 mEq per day.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Based on published literature, the rate of absorption and urinary excretion of potassium from KCl oral solution were higher during the first few hours after dosing relative to modified release KCl products. The bioavailability of potassium, as measured by the cumulative urinary excretion of K+ over a 24 hour post dose period, is similar for KCl solution and modified release products.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Potassium Chloride for Oral Solution, is a light pink to orange powder available in one strength as follows:
20 mEq
NDC# 0603-1554-10 pouch. Each pouch contains 1.5 g of potassium chloride providing potassium 20 mEq and chloride 20 mEq
NDC# 0603-1554-16 carton of 30 pouches
NDC# 0603-1554-04 carton of 100 pouches - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1.5 g Pouch Carton
NDC: 0603-1554-04
Potassium Chloride
for Oral Solution, USP
20 mEqOrange Flavored
Each pouch contains:
Potassium Chloride
1.5 g100 Single-Dose Pouches
Rx onlyPAR
PHARMACEUTICAL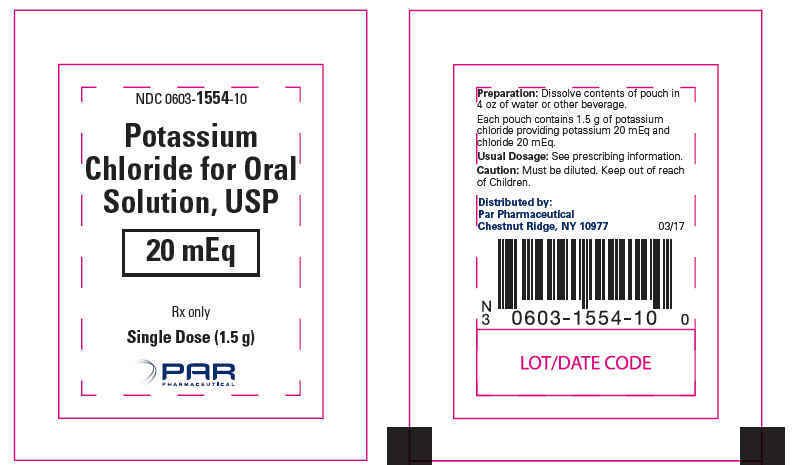
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
POTASSIUM CHLORIDE
potassium chloride powder, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0603-1554 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Potassium Chloride (UNII: 660YQ98I10) (Potassium Cation - UNII:295O53K152, Chloride Ion - UNII:Q32ZN48698) Potassium Chloride 1.5 g in 1.58 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Silicon Dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Anhydrous Citric Acid (UNII: XF417D3PSL) FD&C Yellow No. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) Sucralose (UNII: 96K6UQ3ZD4) Product Characteristics Color ORANGE (light pink to orange) Score Shape Size Flavor ORANGE Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0603-1554-16 30 in 1 CARTON 09/18/2015 1 NDC: 0603-1554-10 1.58 g in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 0603-1554-04 100 in 1 CARTON 09/18/2015 2 NDC: 0603-1554-10 1.58 g in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208019 09/18/2015 Labeler - Par Pharmaceutical (092733690)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.