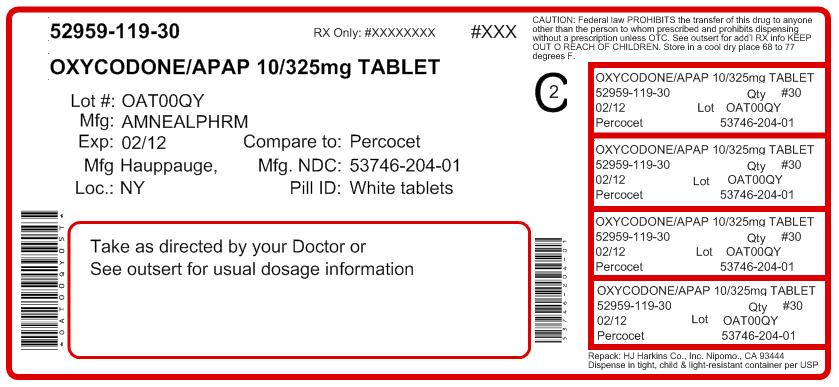
OXYCODONE AND ACETAMINOPHEN- oxycodone and acetaminophen tablet
Oxycodone and Acetaminophen by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Oxycodone and Acetaminophen by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by H.J. Harkins Company, Inc., Amneal Pharmaceuticals. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Each tablet for oral administration contains:
Oxycodone Hydrochloride, USP……………. 10 mg*
Acetaminophen, USP………………………325 mg
*10 mg oxycodone HCl is equivalent to 8.9637 mg of oxycodone.
Oxycodone and Acetaminophen Tablets, USP also contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, pregelatinized starch and stearic acid.
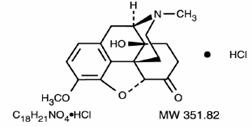
Oxycodone, 14-hydroxydihydrocodeinone, is a semisynthetic opioid analgesic which occurs as a white, odorless, crystalline powder having a saline, bitter taste. The molecular formula for oxycodone hydrochloride is C18H21NO4HCl and the molecular weight 351.82. It is derived from the opium alkaloid thebaine, and may be represented by the following structural formula:
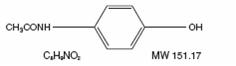
Acetaminophen, 4’-hydroxyacetanilide, is a non-opiate, non-salicylate analgesic and antipyretic which occurs as a white, odorless, crystalline powder, possessing a slightly bitter taste. The molecular formula for acetaminophen is C8H9NO2 and the molecular weight is 151.16. It may be represented by the following structural formula:
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Central Nervous System
Oxycodone is a semisynthetic pure opioid agonist whose principal therapeutic action is analgesia. Other pharmacological effects of oxycodone include anxiolysis, euphoria and feelings of relaxation. These effects are mediated by receptors (notably μ and k) in the central nervous system for endogenous opioid-like compounds such as endorphins and enkephalins. Oxycodone produces respiratory depression through direct activity at respiratory centers in the brain stem and depresses the cough reflex by direct effect on the center of the medulla.
Acetaminophen is a non-opiate, non-salicylate analgesic and antipyretic. The site and mechanism for the analgesic effect of acetaminophen has not been determined. The antipyretic effect of acetaminophen is accomplished through the inhibition of endogenous pyrogen action on the hypothalamic heat-regulating centers.
Gastrointestinal Tract and Other Smooth Muscle
Oxycodone reduces motility by increasing smooth muscle tone in the stomach and duodenum. In the small intestine, digestion of food is delayed by decreases in propulsive contractions. Other opioid effects include contraction of biliary tract smooth muscle, spasm of the Sphincter of Oddi, increased ureteral and bladder sphincter tone, and a reduction in uterine tone.
Cardiovascular System
Oxycodone may produce a release of histamine and may be associated with orthostatic hypotension, and other symptoms, such as pruritus, flushing, red eyes, and sweating.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Distribution
The mean absolute oral bioavailability of oxycodone in cancer patients was reported to be about 87%. Oxycodone has been shown to be 45% bound to human plasma proteins in vitro. The volume of distribution after intravenous administration is 211.9 ±186.6 L.
Absorption of acetaminophen is rapid and almost complete from the GI tract after oral administration. With overdosage, absorption is complete in 4 hours. Acetaminophen is relatively uniformly distributed throughout most body fluids. Binding of the drug to plasma proteins is variable; only 20% to 50% may be bound at the concentrations encountered during acute intoxication.
Metabolism and Elimination
A high portion of oxycodone is N-dealkylated to noroxycodone during first-pass metabolism. Oxymorphone, is formed by the O-demethylation of oxycodone. The metabolism of oxycodone to oxymorphone is catalyzed by CYP2D6. Free and conjugated noroxycodone, free and conjugated oxycodone, and oxymorphone are excreted in human urine following a single oral dose of oxycodone. Approximately 8% to 14% of the dose is excreted as free oxycodone over 24 hours after administration. Following a single, oral dose of oxycodone, the mean ± SD elimination half-life is 3.51 ± 1.43 hours.
Acetaminophen is metabolized in the liver via cytochrome P450 microsomal enzyme. About 80-85% of the acetaminophen in the body is conjugated principally with glucuronic acid and to a lesser extent with sulfuric acid and cysteine. After hepatic conjugation, 90 to 100% of the drug is recovered in the urine with in the first day.
About 4% of acetaminophen is metabolized via cytochrome P450 oxidase to a toxic metabolite which is further detoxified by conjugation with glutathione, present in a fixed amount. It is believed that the toxic metabolite NAPQI (N acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine, N-acetylimidoquinone) is responsible for liver necrosis. High doses of acetaminophen may deplete the glutathione stores so that inactivation of the toxic metabolite is decreased. At high doses, the capacity of metabolic pathways for conjugation with glucuronic acid and sulfuric acid may be exceeded, resulting in increased metabolism of acetaminophen by alternate pathways.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets should not be administered to patients with known hypersensitivity to oxycodone, acetaminophen, or any other component of this product.
Oxycodone is contraindicated in any situation where opioids are contraindicated including patients with significant respiratory depression (in unmonitored settings or the absence of resuscitative equipment) and patients with acute or severe bronchial asthma or hypercarbia. Oxycodone is contraindicated in the setting of suspected or known paralytic ileus.
-
WARNINGS
Misuse, Abuse and Diversion of Opioids
Oxycodone is an opioid agonist of the morphine-type. Such drugs are sought by drug abusers and people with addiction disorders and are subject to criminal diversion.
Oxycodone can be abused in a manner similar to other opioid agonists, legal or illicit. This should be considered when prescribing or dispensing oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets in situations where the physician or pharmacist is concerned about an increased risk of misuse, abuse, or diversion. Concerns about misuse, addiction, and diversion should not prevent the proper management of pain.
Healthcare professionals should contact their State Professional Licensing Board or State Controlled Substances Authority for information on how to prevent and detect abuse or diversion
of this product.
Administration of oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets should be closely monitored for the following potentially serious adverse reactions and complications:
Respiratory Depression
Respiratory depression is a hazard with the use of oxycodone, one of the active ingredients in oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets, as with all opioid agonists. Elderly and debilitated patients are at particular risk for respiratory depression as are non-tolerant patients given large initial doses of oxycodone or when oxycodone is given in conjunction with other agents that depress respiration. Oxycodone should be used with extreme caution in patients with acute asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD), cor pulmonale, or pre-existing respiratory impairment. In such patients, even usual therapeutic doses of oxycodone may decrease respiratory drive to the point of apnea. In these patients alternative non-opioid analgesics should be considered, and opioids should be employed only under careful medical supervision at the lowest effective dose.
In case of respiratory depression, a reversal agent such as naloxone hydrochloride may be utilized (see OVERDOSAGE).
Head Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure
The respiratory depressant effects of opioids include carbon dioxide retention and secondary elevation of cerebrospinal fluid pressure, and may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, other intracranial lesions or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. Oxycodone produces effects on pupillary response and consciousness which may obscure neurologic signs of worsening in patients with head injuries.
Hypotensive Effect
Oxycodone may cause severe hypotension particularly in individuals whose ability to maintain blood pressure has been compromised by a depleted blood volume, or after concurrent administration with drugs which compromise vasomotor tone such as phenothiazines. Oxycodone, like all opioid analgesics of the morphine-type, should be administered with caution to patients in circulatory shock, since vasodilation produced by the drug may further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure. Oxycodone may produce orthostatic hypotension in ambulatory patients.
Hepatotoxicity
Precaution should be taken in patients with liver disease. Hepatotoxicity and severe hepatic failure occurred in chronic alcoholics following therapeutic doses.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Opioid analgesics should be used with caution when combined with CNS depressant drugs, and should be reserved for cases where the benefits of opioid analgesia outweigh the known risks of respiratory depression, altered mental state, and postural hypotension.
Acute Abdominal Conditions
The administration of oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets or other opioids may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course in patients with acute abdominal conditions. Oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets should be given with caution to patients with CNS depression, elderly or debilitated patients, patients with severe impairment of hepatic, pulmonary, or renal function, hypothyroidism, Addison’s disease, prostatic hypertrophy, urethral stricture, acute alcoholism, delirium tremens, kyphoscoliosis with respiratory depression, myxedema, and toxic psychosis.
Oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course in patients with acute abdominal conditions. Oxycodone may aggravate convulsions in patients with convulsive disorders, and all opioids may induce or aggravate seizures in some clinical settings.
Following administration of oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets, anaphylactic reactions have been reported in patients with a known hypersensitivity to codeine, a compound with a structure similar to morphine and oxycodone. The frequency of this possible cross-sensitivity is unknown.
Interactions with Other CNS Depressants
Patients receiving other opioid analgesics, general anesthetics, phenothiazines, other tranquilizers, centrally-acting anti-emetics, sedative-hypnotics or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets may exhibit an additive CNS depression. When such combined therapy is contemplated, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced.
Interactions with Mixed Agonist/Antagonist Opioid Analgesics
Agonist/antagonist analgesics (i.e., pentazocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol) should be administered with caution to a patient who has received or is receiving a course of therapy with a
pure opioid agonist analgesic such as oxycodone. In this situation, mixed agonist/antagonist analgesics may reduce the analgesic effect of oxycodone and/or may precipitate withdrawal
symptoms in these patients.
Ambulatory Surgery and Postoperative Use
Oxycodone and other morphine-like opioids have been shown to decrease bowel motility. Ileus is a common postoperative complication, especially after intra-abdominal surgery with use of opioid analgesia. Caution should be taken to monitor for decreased bowel motility in postoperative patients receiving opioids. Standard supportive therapy should be implemented.
Use in Pancreatic/Biliary Tract Disease
Oxycodone may cause spasm of the Sphincter of Oddi and should be used with caution in patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis. Opioids like oxycodone may cause increases in the serum amylase level.
Tolerance and Physical Dependence
Tolerance is the need for increasing doses of opioids to maintain a defined effect such as analgesia (in the absence of disease progression or other external factors). Physical dependence is manifested by withdrawal symptoms after abrupt discontinuation of a drug or upon administration of an antagonist. Physical dependence and tolerance are not unusual during chronic opioid therapy.
The opioid abstinence or withdrawal syndrome is characterized by some or all of the following: restlessness, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, yawning, perspiration, chills, myalgia, and mydriasis. Other symptoms also may develop, including: irritability, anxiety, backache, joint pain, weakness, abdominal cramps, insomnia, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, or increased blood pressure, respiratory rate, or heart rate.
In general, opioids should not be abruptly discontinued (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Cessation of Therapy).
Information for Patients/Caregivers
The following information should be provided to patients receiving oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets by their physician, nurse, pharmacist, or caregiver:
1. Patients should be aware that oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets contain oxycodone, which is a morphine-like substance.
2. Patients should be instructed to keep oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets in a secure place out of the reach of children. In the case of accidental ingestions, emergency medical care should be sought immediately.
3. When oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets are no longer needed, the unused tablets should be destroyed by flushing down the toilet.
4. Patients should be advised not to adjust the medication dose themselves. Instead, they must consult with their prescribing physician.
5. Patients should be advised that oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets may impair mental and/or physical ability required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks (e.g., driving, operating heavy machinery).
6. Patients should not combine oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets with alcohol, opioid analgesics, tranquilizers, sedatives, or other CNS depressants unless under the recommendation and guidance of a physician. When co-administered with another CNS depressant, oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets can cause dangerous additive central nervous system or respiratory depression, which can result in serious injury or death.
7. The safe use of oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets during pregnancy has not been established; thus, women who are planning to become pregnant or are pregnant should consult with their physician before taking oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets.
8. Nursing mothers should consult with their physicians about whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets because of the potential for serious adverse reactions to nursing infants.
9. Patients who are treated with oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets for more than a few weeks should be advised not to abruptly discontinue the medication. Patients should consult with their physician for a gradual discontinuation dose schedule to taper off the medication.
10. Patients should be advised that oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets are a potential drug of abuse. They should protect it from theft, and it should never be given to anyone other than the individual for whom it was prescribed.
Laboratory Tests
Although oxycodone may cross-react with some drug urine tests, no available studies were found which determined the duration of detectability of oxycodone in urine drug screens. However, based on pharmacokinetic data, the approximate duration of detectability for a single dose of oxycodone is roughly estimated to be one to two days following drug exposure.
Urine testing for opiates may be performed to determine illicit drug use and for medical reasons such as evaluation of patients with altered states of consciousness or monitoring efficacy of drug rehabilitation efforts. The preliminary identification of opiates in urine involves the use of an immunoassay screening and thin-layer chromatography (TLC). Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) may be utilized as a third-stage identification step in the medical investigational sequence for opiate testing after immunoassay and TLC. The identities of 6-keto opiates (e.g., oxycodone) can further be differentiated by the analysis of their methoximetrimethylsilyl (MO-TMS) derivative.
Drug/Drug Interactions with Oxycodone
Opioid analgesics may enhance the neuromuscular-blocking action of skeletal muscle relaxants and produce an increase in the degree of respiratory depression.
Patients receiving CNS depressants such as other opioid analgesics, general anesthetics, phenothiazines, other tranquilizers, centrally-acting anti-emetics, sedative-hypnotics or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets may exhibit an additive CNS depression. When such combined therapy is contemplated, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced. The concurrent use of anticholinergics with opioids may produce paralytic ileus.
Agonist/antagonist analgesics (i.e., pentazocine, nalbuphine, naltrexone, and butorphanol) should be administered with caution to a patient who has received or is receiving a pure opioid agonist such as oxycodone. These agonist/antagonist analgesics may reduce the analgesic effect of oxycodone or may precipitate withdrawal symptoms.
Drug/Drug Interactions with Acetaminophen
Alcohol, ethyl: Hepatotoxicity has occurred in chronic alcoholics following various dose levels (moderate to excessive) of acetaminophen.
Anticholinergics: The onset of acetaminophen effect may be delayed or decreased slightly, but the ultimate pharmacological effect is not significantly affected by anticholinergics.
Oral Contraceptives: Increase in glucuronidation resulting in increased plasma clearance and a decreased half-life of acetaminophen.
Charcoal (activated): Reduces acetaminophen absorption when administered as soon as possible after overdose.
Beta Blockers (Propanolol): Propranolol appears to inhibit the enzyme systems responsible for the glucuronidation and oxidation of acetaminophen. Therefore, the pharmacologic effects of acetaminophen may be increased.
Loop diuretics: The effects of the loop diuretic may be decreased because acetaminophen may decrease renal prostaglandin excretion and decrease plasma renin activity.
Lamotrigine: Serum lamotrigine concentrations may be reduced, producing a decrease in therapeutic effects.
Probenecid: Probenecid may increase the therapeutic effectiveness of acetaminophen slightly.
Zidovudine: The pharmacologic effects of zidovudine may be decreased because of enhanced nonhepatic or renal clearance of zidovudine.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Depending on the sensitivity/specificity and the test methodology, the individual components of oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets may cross-react with assays used in the preliminary detection of cocaine (primary urinary metabolite, benzoylecgonine) or marijuana (cannabinoids) in human urine. A more specific alternate chemical method must be used in order to obtain a confirmed analytical result. The preferred confirmatory method is gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Moreover, clinical considerations and professional judgment should be applied to any drug-of-abuse test result, particularly when preliminary positive results are used.
Acetaminophen may interfere with home blood glucose measurement systems; decreases of > 20% in mean glucose values may be noted. This effect appears to be drug, concentration and system dependent.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: Animal studies to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of oxycodone and acetaminophen have not been performed.
Mutagenesis: The combination of oxycodone and acetaminophen has not been evaluated for mutagenicity. Oxycodone alone was negative in a bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames), an in vitro chromosome aberration assay with human lymphocytes without metabolic activation and an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. Oxycodone was clastogenic in the human lymphocyte chromosomal assay in the presence of metabolic activation and in the mouse lymphoma assay with or without metabolic activation.
Fertility: Animal studies to evaluate the effects of oxycodone on fertility have not been performed.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C: Animal reproductive studies have not been conducted with oxycodone and acetaminophen. It is also not known whether oxycodone and acetaminophen can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Oxycodone and acetaminophen should not be given to a pregnant woman unless in the judgment of the physician, the potential benefits outweigh the possible hazards.
Nonteratogenic Effects: Opioids can cross the placental barrier and have the potential to cause neonatal respiratory depression. Opioid use during pregnancy may result in a physically drug-dependent fetus. After birth, the neonate may suffer severe withdrawal symptoms.
Labor and Delivery
Oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets are not recommended for use in women during and immediately prior to labor and delivery due to its potential effects on respiratory function in the newborn.
Nursing Mothers
Ordinarily, nursing should not be undertaken while a patient is receiving oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets because of the possibility of sedation and/or respiratory depression in the infant. Oxycodone is excreted in breast milk in low concentrations, and there have been rare reports of somnolence and lethargy in babies of nursing mothers taking an oxycodone/acetaminophen product. Acetaminophen is also excreted in breast milk in low concentrations.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Special precaution should be given when determining the dosing amount and frequency of oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets for geriatric patients, since clearance of oxycodone may be slightly reduced in this patient population when compared to younger patients.
Hepatic Impairment
In a pharmacokinetic study of oxycodone in patients with end-stage liver disease, oxycodone plasma clearance decreased and the elimination half-life increased. Care should be exercised when oxycodone is used in patients with hepatic impairment.
Renal Impairment
In a study of patients with end stage renal impairment, mean elimination half-life was prolonged in uremic patients due to increased volume of distribution and reduced clearance. Oxycodone should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious adverse reactions that may be associated with oxycodone and acetaminophen tablet use include respiratory depression, apnea, respiratory arrest, circulatory depression, hypotension, and shock (see OVERDOSAGE).
The most frequently observed non-serious adverse reactions include lightheadedness, dizziness, drowsiness or sedation, nausea, and vomiting. These effects seem to be more prominent in ambulatory than in nonambulatory patients, and some of these adverse reactions may be alleviated if the patient lies down. Other adverse reactions include euphoria, dysphoria, constipation, and pruritus.
Hypersensitivity reactions may include: Skin eruptions, urticarial, erythematous skin reactions. Hematologic reactions may include: Thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, pancytopenia, hemolytic anemia. Rare cases of agranulocytosis has likewise been associated with acetaminophen use. In high doses, the most serious adverse effect is a dose-dependent, potentially fatal hepatic necrosis. Renal tubular necrosis and hypoglycemic coma also may occur.
Other adverse reactions obtained from postmarketing experiences with oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets are listed by organ system and in decreasing order of severity and/or frequency as follows:
Body as a Whole: Anaphylactoid reaction, allergic reaction, malaise, asthenia, fatigue, chest pain, fever, hypothermia, thirst, headache, increased sweating, accidental overdose, nonaccidental overdose
Cardiovascular: Hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, palpitations, dysrhythmias Central and Peripheral Nervous System: Stupor, tremor, paraesthesia, hypoaesthesia, lethargy, seizures, anxiety, mental impairment, agitation, cerebral edema, confusion, dizziness
Fluid and Electrolyte: Dehydration, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, respiratory alkalosis
Gastrointestinal: Dyspepsia, taste disturbances, abdominal pain, abdominal distention, sweating increased, diarrhea, dry mouth, flatulence, gastro-intestinal disorder, nausea, vomiting, pancreatitis, intestinal obstruction, ileus
Hepatic: Transient elevations of hepatic enzymes, increase in bilirubin, hepatitis, hepatic failure, jaundice, hepatotoxicity, hepatic disorder Hearing and Vestibular: Hearing loss, tinnitus
Hematologic: Thrombocytopenia
Hypersensitivity: Acute anaphylaxis, angioedema, asthma, bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, urticaria, anaphylactoid reaction Metabolic and Nutritional: Hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, acidosis, alkalosis
Musculoskeletal: Myalgia, rhabdomyolysis
Ocular: Miosis, visual disturbances, red eye
Psychiatric: Drug dependence, drug abuse, insomnia, confusion, anxiety, agitation, depressed level of consciousness, nervousness, hallucination, somnolence, depression, suicide
Respiratory System: Bronchospasm, dyspnea, hyperpnea, pulmonary edema, tachypnea, aspiration, hypoventilation, laryngeal edema Skin and Appendages: Erythema, urticaria, rash, flushing
Urogenital: Interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis, proteinuria, renal insufficiency and failure, urinary retention
-
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets are a Schedule II controlled substance. Oxycodone is a mu-agonist opioid with an abuse liability similar to morphine. Oxycodone, like morphine and other opioids used in analgesia, can be abused and is subject to criminal diversion.
Drug addiction is defined as an abnormal, compulsive use, use for non-medical purposes of a substance despite physical, psychological, occupational or interpersonal difficulties resulting from such use, and continued use despite harm or risk of harm. Drug addiction is a treatable disease, utilizing a multi-disciplinary approach, but relapse is common. Opioid addiction is relatively rare in patients with chronic pain but may be more common in individuals who have a past history of alcohol or substance abuse or dependence. Pseudoaddiction refers to pain relief seeking behavior of patients whose pain is poorly managed. It is considered an iatrogenic effect of ineffective pain management. The health care provider must assess continuously the psychological and clinical condition of a pain patient in order to distinguish addiction from pseudoaddiction and thus, be able to treat the pain adequately.
Physical dependence on a prescribed medication does not signify addiction. Physical dependence involves the occurrence of a withdrawal syndrome when there is sudden reduction or cessation in drug use or if an opiate antagonist is administered. Physical dependence can be detected after a few days of opioid therapy. However, clinically significant physical dependence is only seen after several weeks of relatively high dosage therapy. In this case, abrupt discontinuation of the opioid may result in a withdrawal syndrome. If the discontinuation of opioids is therapeutically indicated, gradual tapering of the drug over a 2-week period will prevent withdrawal symptoms. The severity of the withdrawal syndrome depends primarily on the daily dosage of the opioid, the duration of therapy and medical status of the individual.
The withdrawal syndrome of oxycodone is similar to that of morphine. This syndrome is characterized by yawning, anxiety, increased heart rate and blood pressure, restlessness, nervousness, muscle aches, tremor, irritability, chills alternating with hot flashes, salivation, anorexia, severe sneezing, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, dilated pupils, diaphoresis, piloerection, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea and insomnia, and pronounced weakness and depression.
“Drug-seeking” behavior is very common in addicts and drug abusers. Drug-seeking tactics include emergency calls or visits near the end of office hours, refusal to undergo appropriate examination, testing or referral, repeated “loss” of prescriptions, tampering with prescriptions and reluctance to provide prior medical records or contact information for other treating physician(s). “Doctor Shopping” to obtain additional prescriptions is common among drug abusers and people suffering from untreated infection.
Abuse and addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance. Physicians should be aware that addiction may not be accompanied by concurrent tolerance and symptoms of physical dependence in all addicts. In addition, abuse of opioids can occur in the absence of true addiction and is characterized by misuse for non-medical purposes, often in combination with other psychoactive substances. Oxycodone, like other opioids, has been diverted for non-medical use. Careful record-keeping of prescribing information, including quantity, frequency, and renewal requests is strongly advised.
Proper assessment of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic re-evaluation of therapy, and proper dispensing and storage are appropriate measures that help to limit abuse of opioid drugs.
Like other opioid medications, oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets are subject to the Federal Controlled Substances Act. After chronic use, oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets should not be discontinued abruptly when it is thought that the patient has become physically dependent on oxycodone.
Interactions with Alcohol and Drugs of Abuse
Oxycodone may be expected to have additive effects when used in conjunction with alcohol, other opioids, or illicit drugs that cause central nervous system depression.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Signs and Symptoms
Serious overdose with oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets is characterized by signs and symptoms of opioid and acetaminophen overdose. Oxycodone overdosage can be manifested by respiratory depression (a decrease in respiratory rate and/or tidal volume, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, cyanosis), extreme somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, pupillary constriction (pupils may be dilated in the setting of hypoxia), and sometimes bradycardia and hypotension. In severe overdosage, apnea, circulatory
collapse, cardiac arrest and death may occur.
In acute acetaminophen overdosage, dose-dependent, potentially fatal hepatic necrosis is the most serious adverse effect. Renal tubular necrosis, hypoglycemic coma and thrombocytopenia may also occur.
In adults, hepatic toxicity has rarely been reported with acute overdoses of less than 10 grams and fatalities with less than 15 grams. Plasma acetaminophen levels > 300 mcg/ml at 4 hours postingestion were associated with hepatic damage in 90% of patients; minimal hepatic damage is anticipated if plasma levels at 4 hours are < 120 mcg/ml or < 30 mcg/ml at 12 hours after ingestion.
Importantly, young children seem to be more resistant than adults to the hepatotoxic effect of an acetaminophen overdose. Despite this, the measures outlined below should be initiated in any adult or child suspected of having ingested an acetaminophen overdose.
Early symptoms following a potentially hepatotoxic overdose may include: nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis and general malaise. Clinical and laboratory evidence of hepatic toxicity may not be apparent until 48 to 72 hours post-ingestion.
Treatment
Primary attention should be given to the reestablishment of adequate respiratory exchange through provision of a patent airway and the institution of assisted or controlled ventilation. Supportive measures (including oxygen, intravenous fluids, and vasopressors) should be employed in the management of circulatory shock and pulmonary edema accompanying overdose
as indicated. Cardiac arrest or arrhythmias may require cardiac massage or defibrillation.
The opioid antagonist naloxone hydrochloride is a specific antidote against respiratory depression which may result from overdosage or unusual sensitivity to opioids including oxycodone. Therefore, an appropriate dose of naloxone hydrochloride should be administered (usual initial adult dose 0.4 mg-2 mg) preferably by the intravenous route, simultaneously with efforts at respiratory resuscitation. Since the duration of action of oxycodone may exceed that of the antagonist, the patient should be kept under continued surveillance and repeated doses of the antagonist should be administered as needed to maintain adequate respiration. Opioid antagonists should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory of circulatory depression secondary to oxycodone overdose. In patients who are physically dependent on any opioid agonist including oxycodone, an abrupt or complete reversal of opioid effects may precipitate an acute abstinence syndrome. The severity of the withdrawal syndrome produced will depend on the degree of physical dependence and the dose of the antagonist administered.
Please see the prescribing information for the specific opioid antagonist for details of their proper use.
Gastric emptying and/or lavage may be useful in removing unabsorbed drug. This procedure is recommended as soon as possible after ingestion, even if the patient has vomited spontaneously. After lavage and/or emesis, administration of activated charcoal, as a slurry, is beneficial, if less than three hours have passed since ingestion. Charcoal adsorption should not be employed prior to lavage and emesis.
If an acetaminophen overdose is suspected, the stomach should be promptly emptied by lavage. A serum acetaminophen assay should be obtained as soon as possible, but no sooner than 4 hours following ingestion. Liver function studies should be obtained initially and repeated at 24-hour intervals. The antidote N-acetylcysteine (NAC) should be administered as early as possible, preferably within 16 hours of the overdose ingestion, but in any case within 24 hours. As a guide to treatment of acute ingestion, the acetaminophen level can be plotted against time since ingestion on a nomogram (Rumack-Matthew). The upper toxic line on the nomogram is equivalent to 200 mcg/ml at 4 hours while the lower line is equivalent to 50 mcg/ml at 12 hours. If serum level is above the lower line, and entire course of N-acetylcysteine treatment should be instituted. NAC therapy should be withheld if the acetaminophen level is below the lower line.
The toxicity of oxycodone and acetaminophen in combination is unknown.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage should be adjusted according to the severity of the pain and the response of the patient. It may occasionally be necessary to exceed the usual dosage recommended below in cases of more severe pain or in those patients who have become tolerant to the analgesic effect of opioids.
If pain is constant, the opioid analgesic should be given at regular intervals on an around-the-clock schedule. Oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets are given orally.
The usual adult dosage is one tablet every 6 hours as needed for pain. The total daily dose of acetaminophen should not exceed 4 grams.
Strength Maximal Daily Dose
Oxycodone and Acetaminophen Tablets 10 mg / 325 mg 6 Tablets
Cessation of Therapy
In patients treated with oxycodone and acetaminophen tablets for more than a few weeks who no longer require therapy, doses should be tapered gradually to prevent signs and symptoms of withdrawal in the physically dependent patient.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Oxycodone and Acetaminophen Tablets USP, 10 mg / 325 mg are supplied as white to off-white, capsule-shaped, biconvex tablets, debossed “IP204” on obverse and plain on reverse.
They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100: NDC: 53746-204-01
Bottles of 500: NDC: 53746-204-05
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [see USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure.
DEA Order Form Required
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
OXYCODONE AND ACETAMINOPHEN
oxycodone and acetaminophen tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 52959-119(NDC:53746-204) Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength OXYCODONE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: C1ENJ2TE6C) (OXYCODONE - UNII:CD35PMG570) OXYCODONE HYDROCHLORIDE 10 mg ACETAMINOPHEN (UNII: 362O9ITL9D) (ACETAMINOPHEN - UNII:362O9ITL9D) ACETAMINOPHEN 325 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) CROSPOVIDONE (UNII: 68401960MK) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) STEARIC ACID (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (OFF-WHITE) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 11mm Flavor Imprint Code IP;204 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 52959-119-02 120 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 52959-119-20 20 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC: 52959-119-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE 4 NDC: 52959-119-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE 5 NDC: 52959-119-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA040778 11/27/2007 Labeler - H.J. Harkins Company, Inc. (147681894) Registrant - Amneal Pharmaceuticals (123797875) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Amneal Pharmaceuticals 831227801 ANALYSIS, MANUFACTURE, LABEL, PACK Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Amneal Pharmaceuticals 831227777 ANALYSIS, MANUFACTURE, LABEL, PACK
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.