These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM. BUPRENORPHINE buccal film, CIII Initial U.S. Approval: 1981
buprenorphine buccal film by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
buprenorphine buccal film by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Alvogen, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM- buprenorphine buccal film
Alvogen, Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM.
BUPRENORPHINE buccal film, CIII Initial U.S. Approval: 1981 WARNING: ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS); LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; ACCIDENTAL EXPOSURE; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME; and RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES AND OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTSSee full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
RECENT MAJOR CHANGESINDICATIONS AND USAGEBuprenorphine buccal film contains buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist. Buprenorphine buccal film is indicated for the management of pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment and for which alternative treatment options are inadequate. (1) Limitations of Use
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSBuccal film available in 75 mcg, 150 mcg, 300 mcg, 450 mcg, 600 mcg, 750 mcg, and 900 mcg dosage strengths. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions (>5%) include nausea, constipation, headache, vomiting, dizziness, and somnolence. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alvogen, Inc. at 1-866-770-3024 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSSee 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide. Revised: 3/2021 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS); LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; ACCIDENTAL EXPOSURE; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME; and RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Buprenorphine buccal film exposes patients and other users to the risks of opioid addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death. Assess each patient’s risk prior to prescribing buprenorphine buccal film, and monitor all patients regularly for the development of these behaviors and conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Overdosage (10)].
Opioid Analgesic Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS)
To ensure that the benefits of opioid analgesics outweigh the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has required a REMS for these products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Under the requirements of the REMS, drug companies with approved opioid analgesic products must make REMS-compliant education programs available to healthcare providers. Healthcare providers are strongly encouraged to
- complete a REMS-compliant education program,
- counsel patients and/or their caregivers, with every prescription, on safe use, serious risks, storage, and disposal of these products,
- emphasize to patients and their caregivers the importance of reading the Medication Guide every time it is provided by their pharmacist, and
- consider other tools to improve patient, household, and community safety.
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur with use of buprenorphine buccal film. Monitor for respiratory depression, especially during initiation of buprenorphine buccal film or following a dose increase. Misuse or abuse of buprenorphine buccal film by chewing, swallowing, snorting or injecting buprenorphine extracted from the buccal film will result in the uncontrolled delivery of buprenorphine and pose a significant risk of overdose and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Accidental Exposure
Accidental exposure to even one dose of buprenorphine buccal film, especially in children, can result in a fatal overdose of buprenorphine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Prolonged use of buprenorphine buccal film during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. If opioid use is required for a prolonged period in a pregnant woman, advise the patient of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Risks From Concomitant Use With Benzodiazepines Or Other CNS Depressants
Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7)].
- Reserve concomitant prescribing of buprenorphine buccal film and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
- Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required.
- Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Buprenorphine buccal film is indicated for the management of pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment and for which alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Limitations of Use
- Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses, and because of the greater risks of overdose and death with long-acting opioid formulations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)], reserve buprenorphine buccal film for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options (e.g., non-opioid analgesics or immediate-release opioids) are ineffective, not tolerated, or would be otherwise inadequate to provide sufficient management of pain.
- Buprenorphine buccal film is not indicated as an as-needed (prn) analgesic.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
Buprenorphine buccal film should be prescribed only by healthcare professionals who are knowledgeable in the use of potent opioids for the management of chronic pain.
- Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
- Initiate the dosing regimen for each patient individually, taking into account the patient’s severity of pain, patient response, prior analgesic treatment experience, and risk factors for addiction, abuse, and misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24 to 72 hours of initiating therapy and following dosage increases with buprenorphine buccal film and adjust the dosage accordingly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Buprenorphine buccal film is for oral buccal use only and is to be applied to the buccal mucosa every 12 hours.
Instruct patients not to use buprenorphine buccal film if the pouch seal is broken or the buccal film is cut, damaged, or changed in any way and to avoid applying buprenorphine buccal film to areas of the mouth with any open sores or lesions.
2.2 Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid Overdose
Discuss the availability of naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose with the patient and caregiver and assess the potential need for access to naloxone, both when initiating and renewing treatment with buprenorphine buccal film [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Inform patients and caregivers about the various ways to obtain naloxone as permitted by individual state naloxone dispensing and prescribing requirements or guidelines (e.g., by prescription, directly from a pharmacist, or as part of a community-based program).
Consider prescribing naloxone, based on the patient’s risk factors for overdose, such as concomitant use of CNS depressants, a history of opioid use disorder, or prior opioid overdose. The presence of risk factors for overdose should not prevent the proper management of pain in any given patient [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3, 5.5)].
Consider prescribing naloxone if the patient has household members (including children) or other close contacts at risk for accidental ingestion or overdose.
2.3 Initial Dosing
Use of Buprenorphine Buccal Film as the Initial Opioid Analgesic (opioid-naïve patients) or in Patients who are not Opioid Tolerant (opioid-non-tolerant patients)
Initiate treatment in opioid-naïve and opioid-non-tolerant patients with a 75 mcg film once daily or, if tolerated, every 12 hours (see Table 1) for at least 4 days, then increase dose to 150 mcg every 12 hours. Individual titration to a dose that provides adequate analgesia and minimizes adverse reactions should proceed in increments of 150 mcg every 12 hours, no more frequently than every 4 days. Doses up to 450 mcg every 12 hours were studied in opioid-naïve patients in the clinical trials [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Use of higher starting doses in patients who are not opioid tolerant may cause fatal respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Conversion from Other Opioids to Buprenorphine Buccal Film
Discontinue all other around-the-clock opioid drugs when buprenorphine buccal film therapy is initiated.
There is a potential for buprenorphine to precipitate withdrawal in patients who are already on opioids. To reduce the risk of opioid withdrawal, taper patients to no more than 30 mg oral morphine sulfate equivalents (MSE) daily before beginning buprenorphine buccal film. Following analgesic taper, base the starting dose on the patient’s daily opioid dose prior to taper, as described in Table 1. Patients may require additional short-acting analgesics during the taper period and during titration.
Buprenorphine buccal film may not provide adequate analgesia for patients requiring greater than 160 mg oral MSE per day. Consider the use of an alternate analgesic.
There is inter-patient variability in the relative potency of opioid drugs and opioid formulations. Therefore, a conservative approach is advised when determining the total daily dosage of buprenorphine buccal film. It is safer to underestimate a patient's 24-hour oral buprenorphine dosage and provide rescue medication (e.g., immediate‑release opioid) than to overestimate the 24-hour buprenorphine dosage and manage an adverse reaction due to overdose.
In a buprenorphine buccal film clinical trial with an open-label titration period, patients were converted from their prior opioid to buprenorphine buccal film using Table 1 as a guide for the initial buprenorphine buccal film dose.
|
Prior Daily Dose of Opioid Analgesic Before Taper to 30 mg Oral MSE |
Initial Buprenorphine Buccal Film Dose |
|
Less than 30 mg oral MSE |
Buprenorphine buccal film 75 mcg once daily or every 12 hours |
|
30 mg to 89 mg oral MSE |
Buprenorphine buccal film 150 mcg every 12 hours |
|
90 mg to 160 mg oral MSE |
Buprenorphine buccal film 300 mcg every 12 hours |
|
Greater than 160 mg oral MSE |
Consider alternate analgesic |
Buprenorphine buccal film doses of 600 mcg, 750 mcg, and 900 mcg are only for use following titration from lower doses of buprenorphine buccal film. Individual titration should proceed in increments of 150 mcg every 12 hours, no more frequently than every 4 days.
Conversion from Methadone to Buprenorphine Buccal Film
Close monitoring is of particular importance when converting from methadone to other opioid agonists, including buprenorphine buccal film. The ratio between methadone and other opioid agonists may vary widely as a function of previous dose exposure. Methadone has a long half-life and can accumulate in the plasma.
2.4 Titration and Maintenance of Therapy
Individually titrate buprenorphine buccal film to a dose that provides adequate analgesia and minimizes adverse reactions. Continually reevaluate patients receiving buprenorphine buccal film to assess the maintenance of pain control and the relative incidence of adverse reactions and monitor for the development of addiction, abuse, or misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Frequent communication is important among the prescriber, other members of the healthcare team, the patient, and the caregiver/family during periods of changing analgesic requirements, including initial titration. During chronic therapy, periodically reassess the continued need for opioid analgesics.
Patients who experience breakthrough pain may require dosage adjustment of buprenorphine buccal film or may need rescue medication with an appropriate dose of an immediate-release analgesic. If the level of pain increases after dose stabilization, attempt to identify the source of increased pain before increasing the buprenorphine buccal film dose.
The minimum titration interval of buprenorphine buccal film is 4 days, based on the pharmacokinetic profile and time to reach steady-state plasma levels [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Individual titration should proceed in increments of no more than 150 mcg every 12 hours.
The maximum buprenorphine buccal film dose is 900 mcg every 12 hours. Do not exceed a dose of buprenorphine buccal film 900 mcg every 12 hours due to the potential for QTc interval prolongation[see Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. If pain is not adequately managed on buprenorphine buccal film 900 mcg, consider an alternate analgesic.
If unacceptable opioid-related adverse reactions are observed, adjust the dose to obtain an appropriate balance between the management of pain and opioid-related adverse reactions.
2.5 Safe Reduction or Discontinuation of Buprenorphine Buccal Film
Do not abruptly discontinue buprenorphine buccal film in patients who may be physically dependent on opioids. Rapid discontinuation of opioid analgesics in patients who are physically dependent on opioids has resulted in serious withdrawal symptoms, uncontrolled pain, and suicide. Rapid discontinuation has also been associated with attempts to find other sources of opioid analgesics, which may be confused with drug-seeking for abuse. Patients may also attempt to treat their pain or withdrawal symptoms with illicit opioids, such as heroin, and other substances.
When a decision has been made to decrease the dose or discontinue therapy in an opioid-dependent patient taking buprenorphine buccal film, there are a variety of factors that should be considered, including the dose of buprenorphine buccal film the patient has been taking, the duration of treatment, the type of pain being treated, and the physical and psychological attributes of the patient. It is important to ensure ongoing care of the patient and to agree on an appropriate tapering schedule and follow-up plan so that patient and provider goals and expectations are clear and realistic. When opioid analgesics are being discontinued due to a suspected substance use disorder, evaluate and treat the patient, or refer for evaluation and treatment of the substance use disorder. Treatment should include evidence-based approaches, such as medication assisted treatment of opioid use disorder. Complex patients with comorbid pain and substance use disorders may benefit from referral to a specialist.
There are no standard opioid tapering schedules that are suitable for all patients. Good clinical practice dictates a patient-specific plan to taper the dose of the opioid gradually. For patients on buprenorphine buccal film who are physically opioid-dependent, initiate the taper by a small enough increment (e.g., no greater than 10% to 25% of the total daily dose) to avoid withdrawal symptoms, and proceed with dose-lowering at an interval of every 2 to 4 weeks. Patients who have been taking opioids for briefer periods of time may tolerate a more rapid taper.
It may be necessary to provide the patient with lower dosage strengths to accomplish a successful taper. Reassess the patient frequently to manage pain and withdrawal symptoms, should they emerge. Common withdrawal symptoms include restlessness, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, yawning, perspiration, chills, myalgia, and mydriasis. Other signs and symptoms also may develop, including irritability, anxiety, backache, joint pain, weakness, abdominal cramps, insomnia, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, or increased blood pressure, respiratory rate, or heart rate. If withdrawal symptoms arise, it may be necessary to pause the taper for a period of time or raise the dose of the opioid analgesic to the previous dose, and then proceed with a slower taper. In addition, monitor patients for any changes in mood, emergence of suicidal thoughts, or use of other substances.
When managing patients taking opioid analgesics, particularly those who have been treated for a long duration and/or with high doses for chronic pain, ensure that a multimodal approach to pain management, including mental health support (if needed), is in place prior to initiating an opioid analgesic taper. A multimodal approach to pain management may optimize the treatment of chronic pain, as well as assist with the successful tapering of the opioid analgesic [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
2.6 Dosage Modifications in Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment
In patients with severe hepatic impairment (i.e., Child-Pugh C), reduce the starting dose and reduce the titration dose by half that of patients with normal liver function, from 150 mcg to 75 mcg [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Use in Special Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.7 Dosage Modifications in Patients with Oral Mucositis
In patients with known or suspected mucositis, reduce the starting dosage and titration incremental dosage by half compared to patients without mucositis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.8 Administration of Buprenorphine Buccal Film
Buprenorphine buccal film should not be used if the package seal is broken or the film is cut, damaged, or changed in any way.
First, the patient must use the tongue to wet the inside of the cheek or rinse the mouth with water to wet the area for placement of buprenorphine buccal film. Buprenorphine buccal film is then applied immediately after removal from the individually sealed package. The yellow side of the buprenorphine buccal film is placed against the inside of the cheek. The entire buprenorphine buccal film is held in place with clean, dry fingers for 5 seconds and then left in place on the inside of the cheek until fully dissolved.
Buprenorphine buccal film adheres to the moist buccal mucosa and will completely dissolve after application, usually within 30 minutes. The film should not be manipulated with the tongue or finger(s) and eating food and drinking liquids should be avoided until the film has dissolved.
A buprenorphine buccal film, if chewed or swallowed, may result in lower peak concentrations and lower bioavailability than when used as directed.
Demonstrate proper administration technique to the patient [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Dosage strengths of buprenorphine buccal film are based on the active moiety, buprenorphine.
The 75 mcg dosage form is a buccal film that contains 75 mcg buprenorphine. The film is white on one side, with A0 printed in black, and yellow on the other side.
The 150 mcg dosage form is a buccal film that contains 150 mcg buprenorphine. The film is white on one side, with A1 printed in black, and yellow on the other side.
The 300 mcg dosage form is a buccal film that contains 300 mcg buprenorphine. The film is white on one side, with A3 printed in black, and yellow on the other side.
The 450 mcg dosage form is a buccal film that contains 450 mcg buprenorphine. The film is white on one side, with A4 printed in black, and yellow on the other side.
The 600 mcg dosage form is a buccal film that contains 600 mcg buprenorphine. The film is white on one side, with A6 printed in black, and yellow on the other side.
The 750 mcg dosage form is a buccal film that contains 750 mcg buprenorphine. The film is white on one side, with A7 printed in black, and yellow on the other side.
The 900 mcg dosage form is a buccal film that contains 900 mcg buprenorphine. The film is white on one side, with A9 printed in black, and yellow on the other side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Buprenorphine buccal film is contraindicated in patients with:
- Significant respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
- Hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylaxis) to buprenorphine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13), Adverse Reactions (6)]
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Buprenorphine buccal film contains buprenorphine, a Schedule III controlled substance. As an opioid, buprenorphine buccal film exposes users to the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
Although the risk of addiction in any individual is unknown, it can occur in patients appropriately prescribed buprenorphine buccal film. Addiction can occur at recommended dosages and if the drug is misused or abused.
Assess each patient’s risk for opioid addiction, abuse, or misuse prior to prescribing buprenorphine buccal film and monitor all patients receiving buprenorphine buccal film for the development of these behaviors and conditions. Risks are increased in patients with a personal or family history of substance abuse (including drug or alcohol abuse or addiction) or mental illness (e.g., major depression). The potential for these risks should not, however, prevent the proper management of pain in any given patient. Patients at increased risk may be prescribed opioids such as buprenorphine buccal film, but use in such patients necessitates intensive counseling about the risks and proper use of buprenorphine buccal film, along with intensive monitoring for signs of addiction, abuse, or misuse. Consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Abuse or misuse of buprenorphine buccal film by swallowing may cause choking, overdose, and death [see Overdosage (10)].
Opioids are sought by drug abusers and people with addiction disorders and are subject to criminal diversion. Consider these risks when prescribing or dispensing buprenorphine buccal film. Strategies to reduce the risk include prescribing the drug in the smallest appropriate quantity and advising the patient on the proper disposal of unused drug [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Contact local state professional licensing board or state controlled substances authority for information on how to prevent and detect abuse or diversion of this product.
5.2 Opioid Analgesic Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS)
To ensure that the benefits of opioid analgesics outweigh the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has required a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) for these products. Under the requirements of the REMS, drug companies with approved opioid analgesic products must make REMS-compliant education programs available to healthcare providers. Healthcare providers are strongly encouraged to do all of the following:
- Complete a REMS-compliant education program offered by an accredited provider of continuing education (CE) or another education program that includes all the elements of the FDA Education Blueprint for Health Care Providers Involved in the Management or Support of Patients with Pain.
- Discuss the safe use, serious risks, and proper storage and disposal of opioid analgesics with patients and/or their caregivers every time these medicines are prescribed. The Patient Counseling Guide (PCG) can be obtained at this link: www.fda.gov/OpioidAnalgesicREMSPCG.
- Emphasize to patients and their caregivers the importance of reading the Medication Guide that they will receive from their pharmacist every time an opioid analgesic is dispensed to them.
- Consider using other tools to improve patient, household, and community safety, such as patient-prescriber agreements that reinforce patient-prescriber responsibilities.
To obtain further information on the opioid analgesic REMS and for a list of accredited REMS CME/CE, call 1-800-503-0784, or log on to www.opioidanalgesicrems.com. The FDA Blueprint can be found at www.fda.gov/OpioidAnalgesicREMSBlueprint.
5.3 Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression has been reported with the use of opioids, even when used as recommended. Respiratory depression, if not immediately recognized and treated, may lead to respiratory arrest and death. Management of respiratory depression may include close observation, supportive measures, and use of opioid antagonists, depending on the patient’s clinical status [see Overdosage (10)]. Carbon dioxide (CO2) retention from opioid-induced respiratory depression can exacerbate the sedating effects of opioids.
While serious, life-threatening or fatal respiratory depression can occur at any time during the use of buprenorphine buccal film, the risk is greatest during initiation of therapy or following a dosage increase. Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression when initiating therapy with buprenorphine buccal film and following dosage increases.
To reduce the risk of respiratory depression, proper dosing and titration of buprenorphine buccal film are essential [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. Overestimating the dose of buprenorphine buccal film when converting patients from another opioid product may result in fatal overdose with the first dose.
Accidental exposure to buprenorphine buccal film, especially in children, can result in respiratory depression and death due to an overdose of buprenorphine.
Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize respiratory depression and emphasize the importance of calling 911 or getting emergency medical help right away in the event of a known or suspected overdose [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Opioids can cause sleep-related breathing disorders including central sleep apnea (CSA) and sleep-related hypoxemia. Opioid use increases the risk of CSA in a dose-dependent fashion. In patients who present with CSA, consider decreasing the opioid dosage using best practices for opioid taper [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid Overdose
Discuss the availability of naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose with the patient and caregiver and assess the potential need for access to naloxone, both when initiating and renewing treatment with buprenorphine buccal film. Inform patients and caregivers about the various ways to obtain naloxone as permitted by individual state naloxone dispensing and prescribing requirements or guidelines (e.g., by prescription, directly from a pharmacist, or as part of a community-based program). Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize respiratory depression and emphasize the importance of calling 911 or getting emergency medical help, even if naloxone is administered [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Consider prescribing naloxone, based on the patient’s risk factors for overdose, such as concomitant use of CNS depressants, a history of opioid use disorder, or prior opioid overdose. The presence of risk factors for overdose should not prevent the proper management of pain in any given patient. Also consider prescribing naloxone if the patient has household members (including children) or other close contacts at risk for accidental ingestion or overdose. If naloxone is prescribed, educate patients and caregivers on how to treat with naloxone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.5), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.4 Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Prolonged use of buprenorphine buccal film during pregnancy can result in withdrawal in the neonate. Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, unlike opioid withdrawal syndrome in adults, may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. Observe newborns for signs of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly. Advise pregnant women using opioids for a prolonged period of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.5 Risks due to Interactions with Benzodiazepines or Other Central Nervous System Depressants
Profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death may result from the concomitant use of buprenorphine buccal film with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (e.g., non-benzodiazepine sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, other opioids, alcohol). Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioid analgesics alone. Because of similar pharmacological properties, it is reasonable to expect similar risk with the concomitant use of other CNS depressant drugs with opioid analgesics [see Drug Interactions (7)].
If the decision is made to prescribe a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant concomitantly with an opioid analgesic, prescribe the lowest effective dosages and minimum durations of concomitant use. In patients already receiving an opioid analgesic, prescribe a lower initial dose of the benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant than indicated in the absence of an opioid, and titrate based on clinical response. If an opioid analgesic is initiated in a patient already taking a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant, prescribe a lower initial dose of the opioid analgesic, and titrate based on clinical response. Follow patients closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
If concomitant use is warranted, consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation when buprenorphine buccal film is used with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (including alcohol and illicit drugs). Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until the effects of concomitant use of the benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant have been determined. Screen patients for risk of substance use disorders, including opioid abuse and misuse, and warn them of the risk for overdose and death associated with the use of additional CNS depressants including alcohol and illicit drugs [see Drug Interactions (7), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.6 Risk of Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease or in Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients
The use of buprenorphine buccal film in patients with acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment is contraindicated.
Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease: Buprenorphine-treated patients with significant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or cor pulmonale, and those with substantially decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia, hypercapnia, or pre-existing respiratory depression are at increased risk of decreased respiratory drive, including apnea, even at recommended dosages of buprenorphine buccal film [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients: Life-threatening respiratory depression is more likely to occur in elderly, cachectic, or debilitated patients as they may have altered pharmacokinetics or altered clearance compared to younger, healthier patients.
Monitor such patients closely, particularly when initiating and titrating buprenorphine buccal film and when buprenorphine buccal film is given concomitantly with other drugs that depress respiration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.5)]. Alternatively, consider the use of non-opioid analgesics in these patients.
5.7 Adrenal Insufficiency
Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use. Presentation of adrenal insufficiency may include non-specific symptoms and signs including nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. If adrenal insufficiency is suspected, confirm the diagnosis with diagnostic testing as soon as possible. If adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement doses of corticosteroids. Wean the patient off of the opioid to allow adrenal function to recover and continue corticosteroid treatment until adrenal function recovers. Other opioids may be tried as some cases reported use of a different opioid without recurrence of adrenal insufficiency. The information available does not identify any particular opioids as being more likely to be associated with adrenal insufficiency.
5.8 QTc Prolongation
Buprenorphine buccal film has been observed to prolong the QTc interval in some subjects participating in clinical trials. Consider these observations in clinical decisions when prescribing buprenorphine buccal film to patients with hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or clinically unstable cardiac disease, including unstable atrial fibrillation, symptomatic bradycardia, unstable congestive heart failure, or active myocardial ischemia. Periodic electrocardiographic (ECG) monitoring is recommended in these patients. Avoid the use of buprenorphine buccal film in patients with a history of Long QT Syndrome or an immediate family member with this condition or those taking Class IA antiarrhythmic medications (e.g., quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide) or Class III antiarrhythmic medications (e.g., sotalol, amiodarone, dofetilide), or other medications that prolong the QT interval [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
5.9 Severe Hypotension
Buprenorphine buccal film may cause severe hypotension including orthostatic hypotension and syncope in ambulatory patients. There is an increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent administration of certain CNS depressant drugs (e.g., phenothiazines or general anesthetics) [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Monitor these patients for signs of hypotension after initiating or titrating the dosage of buprenorphine buccal film. In patients with circulatory shock, buprenorphine buccal film may cause vasodilation that can further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure. Avoid the use of buprenorphine buccal film in patients with circulatory shock.
5.10 Risks of Use in Patients with Increased Intracranial Pressure, Brain Tumors, Head Injury, or Impaired Consciousness
In patients who may be susceptible to the intracranial effects of CO2 retention (e.g., those with evidence of increased intracranial pressure or brain tumors), buprenorphine buccal film may reduce respiratory drive, and the resultant CO2 retention can further increase intracranial pressure. Monitor such patients for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, particularly when initiating therapy with buprenorphine buccal film.
Opioids may also obscure the clinical course in a patient with a head injury. Avoid the use of buprenorphine buccal film in patients with impaired consciousness or coma.
5.11 Hepatotoxicity
Cases of cytolytic hepatitis and hepatitis with jaundice have been observed in individuals receiving sublingual formulations of buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid dependence, both in clinical trials and in post-marketing adverse events reports. The spectrum of abnormalities ranges from transient asymptomatic elevations in hepatic transaminases to case reports of hepatic failure, hepatic necrosis, hepatorenal syndrome, and hepatic encephalopathy. In many cases, the presence of pre-existing liver enzyme abnormalities, infection with hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus, concomitant usage of other potentially hepatotoxic drugs, and ongoing injection drug abuse may have played a causative or contributory role. For patients at increased risk of hepatotoxicity (e.g., patients with a history of excessive alcohol intake, intravenous drug abuse or liver disease), obtain baseline liver enzyme levels and monitor periodically during treatment with buprenorphine buccal film.
5.12 Risk of Overdose in Patients with Moderate to Severe Hepatic Impairment
In a pharmacokinetic study in subjects dosed with buprenorphine sublingual tablets, buprenorphine plasma levels were found to be higher and the half-life was found to be longer in subjects with moderate and severe hepatic impairment, but not in subjects with mild hepatic impairment. For patients with severe hepatic impairment, a dose adjustment is recommended, and patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment should be monitored for signs and symptoms of toxicity or overdose caused by increased levels of buprenorphine [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.13 Anaphylactic/Allergic Reactions
Cases of acute and chronic hypersensitivity to buprenorphine have been reported both in clinical trials and in post-marketing experience. The most common signs and symptoms include rashes, hives, and pruritus. Cases of bronchospasm, angioneurotic edema, and anaphylactic shock have been reported. Buprenorphine buccal film is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to buprenorphine.
5.14 Withdrawal
Do not abruptly discontinue buprenorphine buccal film in a patient physically dependent on opioids. When discontinuing buprenorphine buccal film in a physically dependent patient, gradually taper the dosage. Rapid tapering of buprenorphine in a patient physically dependent on opioids may lead to a withdrawal syndrome and return of pain [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
Additionally, the use of buprenorphine buccal film, a partial agonist opioid analgesic, in patients who are receiving a full opioid agonist analgesic may reduce the analgesic effect and/or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. Avoid concomitant use of buprenorphine buccal film with a full opioid agonist analgesic.
5.15 Risk of Use in Patients with Gastrointestinal Conditions
Buprenorphine buccal film is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus.
Buprenorphine buccal film may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi. Opioids may cause increases in the serum amylase. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis, for worsening symptoms.
5.16 Increased Risk of Seizures in Patients with Seizure Disorders
The buprenorphine in buprenorphine buccal film may increase the frequency of seizures in patients with seizure disorders, and may increase the risk of seizures occurring in other clinical settings associated with seizures. Monitor patients with a history of seizure disorders for worsened seizure control during buprenorphine buccal film therapy.
5.17 Risks of Use in Cancer Patients with Oral Mucositis
Cancer patients with oral mucositis may absorb buprenorphine more rapidly than intended and are likely to experience higher plasma levels of the opioid. For patients with known or suspected mucositis, a dose reduction is recommended. Monitor these patients carefully for signs and symptoms of toxicity or overdose caused by increased levels of buprenorphine [see Dosage and Administration (2.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.18 Risks of Driving and Operating Machinery
Buprenorphine buccal film may impair the mental and physical abilities needed to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating machinery. Warn patients not to drive or operate dangerous machinery unless they are tolerant to side effects of buprenorphine buccal film and know how they will react to the medication.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions described elsewhere in the labeling include:
- Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Interactions with Benzodiazepines and Other CNS Depressants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Adrenal Insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- QTc Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Severe Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Anaphylactic/Allergic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
A total of 2,127 patients were treated with buprenorphine buccal film in controlled and open-label chronic pain trials. There were 504 patients treated for approximately six months and 253 patients treated for approximately one year. The clinical trial population consisted of patients with chronic moderate-to-severe pain.
The most common serious adverse drug reactions (all ≤ 0.2%) occurring during clinical trials with buprenorphine buccal film were: cellulitis, pneumonia, ileus, atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular accident, syncope, transient ischemic attack, chest pain, non-cardiac chest pain, ankle fracture, cholecystitis, osteoarthritis, and dehydration.
The most common adverse events (≥ 2%) leading to discontinuation were nausea, vomiting, and liver function test abnormality.
The most common adverse events (≥ 5%) reported by opioid-naïve, opioid-experienced, and overall patients exposed to buprenorphine buccal film in clinical trials and compared against placebo are shown in Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4:
|
Open-Label Titration Phase |
Double-Blind Treatment Phase |
||
|
MedDRA Preferred Term |
Buprenorphine Buccal Film (N=749) |
Buprenorphine Buccal Film (N=229) |
Placebo (N=232) |
|
Nausea |
50% |
10% |
7% |
|
Constipation |
13% |
4% |
3% |
|
Vomiting |
8% |
4% |
<1% |
|
Headache |
8% |
2% |
3% |
|
Dizziness |
6% |
2% |
<1% |
|
Somnolence |
7% |
1% |
<1% |
|
Fatigue |
5% |
0% |
1% |
|
Open-Label Titration Phase |
Double-Blind Treatment Phase |
||
|
MedDRA Preferred Term |
Buprenorphine Buccal Film (N=810) |
Buprenorphine Buccal Film (N=254) |
Placebo (N=256) |
|
Nausea |
17% |
7% |
7% |
|
Constipation |
8% |
3% |
1% |
|
Vomiting |
7% |
5% |
2% |
|
Headache |
7% |
2% |
3% |
|
Dizziness |
5% |
2% |
<1% |
|
Somnolence |
5% |
1% |
<1% |
|
Drug Withdrawal Syndrome |
0% |
4% |
10% |
|
Open-Label Titration Phase |
Double-Blind Treatment Phase |
||
|
MedDRA Preferred Term |
Buprenorphine Buccal Film (N=1889) |
Buprenorphine Buccal Film (N=600) |
Placebo (N=606) |
|
Nausea |
33% |
9% |
8% |
|
Constipation |
11% |
4% |
2% |
|
Vomiting |
7% |
5% |
2% |
|
Headache |
8% |
4% |
3% |
|
Dizziness |
6% |
2% |
<1% |
|
Somnolence |
6% |
<1% |
<1% |
|
Drug Withdrawal Syndrome |
1% |
2% |
5% |
The most common (≥ 5%), common (≥ 1% to < 5%), and least common (< 1%) adverse reactions reported by patients taking buprenorphine buccal film in the controlled and open-label clinical studies are presented below:
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 5%): nausea, constipation, headache, vomiting, fatigue, dizziness, and somnolence.
Common (≥ 1% to < 5%) adverse reactions (organized by MedDRA [Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities] System Organ Class):
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: anemia
Gastrointestinal disorders: abdominal pain, diarrhea, dry mouth
General disorders and administration site conditions: peripheral edema, pyrexia, drug withdrawal syndrome
Infections and infestations: upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, nasopharyngitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, gastroenteritis
Injury, poisoning, and procedural complications: contusion, fall
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: decreased appetite
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: muscle spasms, back pain
Psychiatric disorders: anxiety, insomnia, depression
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: oropharyngeal pain, sinus congestion
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: hyperhidrosis, pruritus, rash
Vascular disorders: hot flush, hypertension
Least common (<1%) adverse reactions:
Abdominal discomfort, acute sinusitis, dyspepsia, toothache, asthenia, chills, cellulitis, tooth abscess, excoriation, laceration, aspartate aminotransferase increased, blood pressure increased, blood testosterone decreased, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, liver function test abnormal, musculoskeletal pain, neck pain, hypoesthesia, lethargy, migraine, tremor, cough, dyspnea, nasal congestion, rhinorrhea.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of buprenorphine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Serotonin syndrome: Cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, have been reported during concomitant use of opioids with serotonergic drugs.
Adrenal insufficiency: Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use.
Anaphylaxis: Anaphylaxis has been reported with ingredients contained in buprenorphine buccal film.
Androgen deficiency: Cases of androgen deficiency have occurred with chronic use of opioids [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 5 includes clinically significant drug interactions with buprenorphine buccal film.
|
Benzodiazepines |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
There have been a number of reports regarding coma and death associated with the misuse and abuse of the combination of buprenorphine and benzodiazepines. In many, but not all of these cases, buprenorphine was misused by self-injection of crushed buprenorphine tablets. Preclinical studies have shown that the combination of benzodiazepines and buprenorphine altered the usual ceiling effect on buprenorphine-induced respiratory depression, making the respiratory effects of buprenorphine appear similar to those of full opioid agonists. |
|
Intervention: |
Closely monitor patients with concurrent use of buprenorphine buccal film and benzodiazepines. Warn patients that it is extremely dangerous to self-administer benzodiazepines while taking buprenorphine buccal film, and warn patients to use benzodiazepines concurrently with buprenorphine buccal film only as directed by their physician. |
|
Benzodiazepines and Other Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Due to additive pharmacologic effect, the concomitant use of benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, can increase the risk of hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death. |
|
Intervention: |
Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients closely for signs of respiratory depression and sedation. If concomitant use is warranted, consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3, 5.5)]. |
|
Examples: |
Benzodiazepines and other sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, and other opioids, alcohol. |
|
Inhibitors of CYP3A4 |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of buprenorphine and CYP3A4 inhibitors can increase the plasma concentration of buprenorphine, resulting in increased or prolonged opioid effects, particularly when an inhibitor is added after a stable dose of buprenorphine buccal film is achieved. After stopping a CYP3A4 inhibitor, as the effects of the inhibitor decline, the buprenorphine plasma concentration will decrease [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], potentially resulting in decreased opioid efficacy or a withdrawal syndrome in patients who had developed physical dependence to buprenorphine. |
|
Intervention: |
If concomitant use is necessary, consider dosage reduction of buprenorphine buccal film until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals. If a CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued, consider increasing the buprenorphine buccal film dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal. |
|
Examples: |
Macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin), azole-antifungal agents (e.g., ketoconazole), protease inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir) |
|
CYP3A4 Inducers |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of buprenorphine and CYP3A4 inducers can decrease the plasma concentration of buprenorphine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], potentially resulting in decreased efficacy or onset of a withdrawal syndrome in patients who have developed physical dependence to buprenorphine. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the buprenorphine plasma concentration will increase [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which could increase or prolong both therapeutic effects and adverse reactions and may cause serious respiratory depression. |
|
Intervention: |
If concomitant use is necessary, consider increasing the buprenorphine buccal film dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal. If a CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued, consider buprenorphine buccal film dosage reduction and monitor for signs of respiratory depression. |
|
Examples: |
Rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin |
|
Serotonergic Drugs |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of opioids with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system has resulted in serotonin syndrome. |
|
Intervention: |
If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment. Discontinue buprenorphine buccal film if serotonin syndrome is suspected. |
|
Examples: |
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), triptans, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, drugs that affect the serotonin neurotransmitter system (e.g., mirtazapine, trazodone, tramadol), certain muscle relaxants (i.e., cyclobenzaprine, metaxalone), monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue). |
|
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
MAOI interactions with opioids may manifest as serotonin syndrome opioid toxicity (e.g., respiratory depression, coma) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
|
Intervention: |
The use of buprenorphine buccal film is not recommended for patients taking MAOIs or within 14 days of stopping such treatment. |
|
Examples: |
phenelzine, tranylcypromine, linezolid |
|
Mixed Agonist/Antagonist and Partial Agonist Opioid Analgesics |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
May reduce the analgesic effect of buprenorphine buccal film and/or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. |
|
Intervention: |
Avoid concomitant use. |
|
Examples: |
butorphanol, nalbuphine, pentazocine |
|
Muscle Relaxants |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Buprenorphine may enhance the neuromuscular blocking action of skeletal muscle relaxants and produce an increased degree of respiratory depression. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients receiving muscle relaxants and buprenorphine buccal film for signs of respiratory depression that may be greater than otherwise expected and decrease the dosage of buprenorphine buccal film and/or the muscle relaxant as necessary. Due to the risk of respiratory depression with concomitant use of skeletal muscle relaxants and opioids, consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.5)]. |
| Examples: | cyclobenzaprine, metaxalone |
|
Diuretics |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Opioids can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing the release of antidiuretic hormone. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for signs of diminished diuresis and/or effects on blood pressure and increase the dosage of the diuretic as needed. |
|
Anticholinergic Drugs |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs may increase the risk of urinary retention and/or severe constipation, which may lead to paralytic ileus. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for signs of urinary retention or reduced gastric motility when buprenorphine buccal film is used concomitantly with anticholinergic drugs. |
|
Antiretrovirals: Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) do not appear to induce or inhibit the P450 enzyme pathway, thus no interactions with buprenorphine are expected. |
|
Intervention: |
None |
|
Antiretrovirals: Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are metabolized principally by CYP3A4. Efavirenz, nevirapine, and etravirine are known CYP3A inducers, whereas delavirdine is a CYP3A inhibitor. Significant pharmacokinetic interactions between NNRTIs (e.g., efavirenz and delavirdine) and buprenorphine have been shown in clinical studies, but these pharmacokinetic interactions did not result in any significant pharmacodynamic effects. |
|
Intervention: |
Patients who are on chronic buprenorphine buccal film treatment should have their dose monitored if NNRTIs are added to their treatment regimen. |
|
Examples: |
efavirenz, nevirapine, etravirine, delavirdine |
|
Antiretrovirals: Protease inhibitors (PIs) |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Studies have shown some antiretroviral protease inhibitors (PIs) with CYP3A4 inhibitory activity (nelfinavir, lopinavir/ritonavir, ritonavir) have little effect on buprenorphine pharmacokinetics and no significant pharmacodynamic effects. Other PIs with CYP3A4 inhibitory activity (atazanavir and atazanavir/ritonavir) resulted in elevated levels of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine, and patients in one study reported increased sedation. Symptoms of opioid excess have been found in post-marketing reports of patients receiving buprenorphine and atazanavir with and without ritonavir concomitantly. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients taking buprenorphine buccal film and atazanavir with and without ritonavir and reduce the dose of buprenorphine buccal film if warranted. |
|
Examples: |
atazanavir, ritonavir |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Prolonged use of opioid analgesics during pregnancy may cause neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of buprenorphine buccal film or buprenorphine in pregnant women. Limited published data on use of buprenorphine, the active ingredient in buprenorphine buccal film, in pregnancy, have not shown an increased risk of major malformations. Reproductive and developmental studies in rats and rabbits identified adverse events at approximately 2 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 1.8 mg/day of buprenorphine buccal film. Embryofetal death was observed in both rats and rabbits administered buprenorphine during the period of organogenesis at doses approximately 54 and 2.2 times, respectively, the MRHD of 1.8 mg/day of buprenorphine. Pre-and postnatal development studies in rats demonstrated increased neonatal deaths at 2.7 times and above and dystocia at approximately 27 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg/day of buprenorphine. No clear teratogenic effects were seen when buprenorphine was administered during organogenesis with a range of doses 5 times or greater than the MRHD of 1.8 mg/day of buprenorphine. However, increases in skeletal abnormalities were noted in rats and rabbits administered buprenorphine daily during organogenesis at doses approximately 5.4 and 10.8 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg/day of buprenorphine, respectively. In a few studies, some events such as acephalus and omphalocele were also observed but these findings were not clearly treatment-related [see Data].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. Adverse outcomes in pregnancy can occur regardless of the health of the mother or the use of medications. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Prolonged use of opioid analgesics during pregnancy for medical or nonmedical purposes can result in physical dependence in the neonate and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome shortly after birth. Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome presents as irritability, hyperactivity and abnormal sleep pattern, high pitched cry, tremor, vomiting, diarrhea, and failure to gain weight. The onset, duration, and severity of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome vary based on the specific opioid used, duration of use, timing and amount of last maternal use, and rate of elimination of the drug by the newborn. Observe newborns for symptoms of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Labor or Delivery
Opioids cross the placenta and may produce respiratory depression and psycho-physiologic effects in neonates. An opioid antagonist such as naloxone must be available for reversal of opioid-induced respiratory depression in the neonate. Buprenorphine buccal film is not recommended for use in women immediately prior to labor, when shorter-acting analgesics or other analgesic techniques are more appropriate. Opioid analgesics, including buprenorphine buccal film, can prolong labor through actions which temporarily reduce the strength, duration, and frequency of uterine contractions. However, this effect is not consistent and may be offset by an increased rate of cervical dilation, which tends to shorten labor.
Data
Animal Data
The exposure margins listed below are based on body surface area comparisons (mg/m2) to MRHD of 1.8 mg buprenorphine via buprenorphine buccal film.
Following oral administration to rats no teratogenic effects were observed at buprenorphine doses up to 250 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure approximately 1351 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg). Following oral administration to rabbits, no teratogenic effects were observed at buprenorphine doses up to 40 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure approximately 432 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg). No definitive drug-related teratogenic effects were observed in rats and rabbits at IM doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure approximately 161 times and 324 times, respectively, the MRHD of 1.8 mg). Acephalus was observed in one rabbit fetus from the low-dose group and omphalocele was observed in two rabbit fetuses from the same litter in the mid-dose group; no findings were observed in fetuses from the high-dose group. Following oral administration of buprenorphine to rats, dose-related post-implantation losses, evidenced by increases in the numbers of early resorptions with consequent reductions in the numbers of fetuses, were observed at doses of 10 mg/kg/day or greater (estimated exposure approximately 54 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg).
In the rabbit, increased post-implantation losses occurred at an oral dose of 40 mg/kg/day. Following IM administration in the rat and the rabbit, post-implantation losses, as evidenced by decreases in live fetuses and increases in resorptions, occurred at 30 mg/kg/day.
Buprenorphine was not teratogenic in rats or rabbits after IM or subcutaneous (SC) doses up to 5 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 27 and 54 times, respectively, the MRHD of 1.8 mg), after IV doses up to 0.8 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 4.3 and 8.7 times, respectively, the MRHD of 1.8 mg), or after oral doses up to 160 mg/kg/day in rats (estimated exposure was approximately 865 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg) and 25 mg/kg/day in rabbits (estimated exposure was approximately 270 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg). Significant increases in skeletal abnormalities (e.g., extra thoracic vertebra or thoraco-lumbar ribs) were noted in rats after SC administration of 1 mg/kg/day and up (estimated exposure was approximately 5.4 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg), but were not observed at oral doses up to 160 mg/kg/day.
Increases in skeletal abnormalities in rabbits after IM administration of 5 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 54 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg) or oral administration of 1 mg/kg/day or greater (estimated exposure was approximately 10.8 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg) were not statistically significant.
In rabbits, buprenorphine produced statistically significant pre-implantation losses at oral doses of 1 mg/kg/day or greater and post-implantation losses that were statistically significant at IV doses of 0.2 mg/kg/day or greater (estimated exposure approximately 2.2 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg).
Dystocia was noted in pregnant rats treated intramuscularly with buprenorphine during gestation and lactation at 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 27 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg). Fertility, pre-, and post-natal development studies with buprenorphine in rats indicated increases in neonatal mortality after oral doses of 0.8 mg/kg/day and up (approximately 4.3 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg), after IM doses of 0.5 mg/kg/day and up (approximately 2.7 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg), and after SC doses of 0.1 mg/kg/day and up (approximately 0.5 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg). An apparent lack of milk production during these studies likely contributed to the decreased pup viability and lactation indices. Delays in the occurrence of righting reflex and startle response were noted in rat pups at an oral dose of 80 mg/kg/day (approximately 432 times the MRHD of 1.8 mg).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Based on two studies in 13 lactating women being treated for opioid dependence and their breastfed infants, buprenorphine and its metabolite norbuprenorphine are present in low levels in human milk and infant urine, and available data have not shown adverse reactions in breastfed infants [see Data]. There are no data on the effects of buprenorphine buccal film on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including excess sedation and respiratory depression in a breastfed infant, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with buprenorphine buccal film.
Clinical Considerations
Monitor infants exposed to buprenorphine buccal film through breast milk for excess sedation and respiratory depression. Withdrawal symptoms can occur in breastfed infants when maternal administration of buprenorphine is stopped or when breast-feeding is stopped.
Data
Based on limited data from a study of six lactating women being treated for opioid dependence who were taking a median oral dose of buprenorphine of 0.29 mg/kg/day 5 to 8 days after delivery, breast milk contained a median infant dose of 0.42 mcg/kg/day of buprenorphine and 0.33 mcg/kg/day of norbuprenorphine, which are equal to 0.2% and 0.12% of the maternal weight-adjusted dose. The median concentrations of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine in infant urine were 1.0 nmol/L and 2.3 nmol/L, respectively.
Based on limited data from a study of seven lactating women being treated for opioid dependence who were taking a median oral dose of buprenorphine of 7 mg/day an average of 1.12 months after delivery, the mean milk concentrations of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine were 3.65 mcg/L and 1.94 mcg/L, respectively. Based on the limited data from this study, and assuming milk consumption of 150 mL/kg/day, an exclusively breastfed infant would receive an estimated mean of 0.55 mcg/kg/day of buprenorphine and 0.29 mcg/kg/day of norbuprenorphine, which are 0.38% and 0.18% of the maternal weight-adjusted dose.
No adverse reactions were observed in the infants in these two studies.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Chronic use of opioids may cause reduced fertility in females and males of reproductive potential. It is not known whether these effects on fertility are reversible [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of buprenorphine buccal film have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients that were treated with buprenorphine buccal film in controlled and open-label chronic pain trials (2,127), 340 patients were 65 years and older. Of those, 49 patients were aged 75 years and older. The incidences of selected buprenorphine buccal film-related adverse effects were higher in older subjects.
No notable differences in pharmacokinetics were observed from population pharmacokinetic analysis in subjects aged 65 and older compared to younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience with buprenorphine has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. Although specific dose adjustments on the basis of advanced age are not required for pharmacokinetic reasons, use caution in the elderly population to ensure safe use. Titrate the dosage of buprenorphine buccal film slowly in geriatric patients and monitor closely for signs of central nervous system and respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Buprenorphine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Buprenorphine buccal film has not been evaluated in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
The effects of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine were evaluated in a pharmacokinetic study. Buprenorphine is extensively metabolized in the liver and buprenorphine plasma levels were found to be higher and the half-life was found to be longer in subjects with moderate and severe hepatic impairment, but not in subjects with mild hepatic impairment.
Given that increased buprenorphine plasma levels are associated with a greater risk of toxicity and overdose, a dosage reduction in patients with severe hepatic impairment (i.e., Child-Pugh C) is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)]. Monitor patients with severe hepatic impairment for signs and symptoms of overdose. A dosage reduction in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) is not needed; however, monitor these patients for signs and symptoms of toxicity or overdose. A dosage reduction in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A) is not needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Warnings and Precautions (5.11), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
Buprenorphine buccal film contains buprenorphine hydrochloride, a Schedule III controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
Buprenorphine buccal film contains buprenorphine, a substance with a potential for abuse similar to other Schedule III opioids. Buprenorphine buccal film can be abused and is subject to misuse, abuse, addiction, and criminal diversion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
All patients treated with opioids, including buprenorphine buccal film, require careful monitoring for signs of abuse and addiction, because use of opioid analgesic products carry the risk of addiction, even under appropriate medical use.
Prescription drug abuse is the intentional, non-therapeutic use of a prescription drug, even once, for its rewarding psychological or physiological effects.
Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that develop after repeated substance use and includes a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling its use, persisting in its use despite harmful consequences, a higher priority given to drug use than to other activities and obligations, increased tolerance, and sometimes a physical withdrawal.
“Drug-seeking” behavior is very common in persons with substance use disorders. Drug-seeking tactics include emergency calls or visits near the end of office hours, refusal to undergo appropriate examination, testing, or referral, repeated “loss” of prescriptions, tampering with prescriptions and reluctance to provide prior medical records or contact information for other treating healthcare providers. “Doctor shopping” (visiting multiple prescribers to obtain additional prescriptions) is common among drug abusers and people suffering from untreated addiction. Preoccupation with achieving adequate pain relief can be appropriate behavior in a patient with poor pain control.
Abuse and addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance. Healthcare providers should be aware that addiction may not be accompanied by concurrent tolerance and symptoms of physical dependence in all persons with substance use disorders. In addition, abuse of opioids can occur in the absence of true addiction.
Buprenorphine buccal film, like other opioids, can be diverted for non-medical use into illicit channels of distribution. Careful record-keeping of prescribing information including quantity, frequency, and renewal requests, as required by state and federal law, is strongly advised.
Proper assessment of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic re-evaluation of therapy, and proper dispensing and storage are appropriate measures that help to limit abuse of opioid drugs.
Risks Specific to Abuse of Buprenorphine Buccal Film
Buprenorphine buccal film is intended for buccal use only. Abuse of buprenorphine buccal film poses a risk of overdose and death. This risk is increased with concurrent abuse of buprenorphine buccal film with alcohol and other substances, including other opioids and benzodiazepines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7)]. Intentional compromise of the buccal film might result in the uncontrolled delivery of buprenorphine and pose a significant risk to the abuser that could result in overdose and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Abuse may occur by applying the buccal film in the absence of legitimate purpose, or by swallowing, snorting, or injecting buprenorphine extracted from the buccal film. Parenteral drug abuse is commonly associated with transmission of infectious diseases such as hepatitis and HIV.
9.3 Dependence
Both tolerance and physical dependence can develop during chronic opioid therapy. Tolerance is the need for increasing doses of opioids to maintain a defined effect such as analgesia (in the absence of disease progression or other external factors). Tolerance may occur to both the desired and undesired effects of drugs and may develop at different rates for different effects.
Physical dependence is a physiological state in which the body adapts to the drug after a period of regular exposure, resulting in withdrawal symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dosage reduction of a drug. Withdrawal also may be precipitated through the administration of drugs with opioid antagonist activity (e.g., naloxone, nalmefene), or mixed agonist/antagonist analgesics (e.g., pentazocine, butorphanol, nalbuphine). Physical dependence may not occur to a clinically significant degree until after several days to weeks of continued opioid usage.
Do not abruptly discontinue buprenorphine buccal film in a patient physically dependent on opioids. Rapid tapering of buprenorphine buccal film in a patient physically dependent on opioids may lead to serious withdrawal symptoms, uncontrolled pain, and suicide. Rapid discontinuation has also been associated with attempts to find other sources of opioid analgesics, which may be confused with drug-seeking for abuse.
When discontinuing buprenorphine buccal film, gradually taper the dosage using a patient-specific plan that considers the following: the dose of buprenorphine buccal film the patient has been taking, the duration of treatment, and the physical and psychological attributes of the patient. To improve the likelihood of a successful taper and minimize withdrawal symptoms, it is important that the opioid tapering schedule is agreed upon by the patient. In patients taking opioids for a long duration at high doses, ensure that a multimodal approach to pain management, including mental health support (if needed), is in place prior to initiating an opioid analgesic taper [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].
Infants born to mothers physically dependent on opioids will also be physically dependent and may exhibit respiratory difficulties and withdrawal symptoms [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical Presentation
Acute overdosage with buprenorphine buccal film is manifested by respiratory depression, somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, constricted pupils, and, in some cases, pulmonary edema, bradycardia, hypotension, partial or complete airway obstruction, atypical snoring, and death. Marked mydriasis rather than miosis may be seen due to severe hypoxia in overdose situations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Treatment of Overdose
In case of overdose, priorities are the re-establishment of a patent and protected airway and institution of assisted or controlled ventilation, if needed. Employ other supportive measures (including oxygen, vasopressors) in the management of circulatory shock and pulmonary edema, as indicated. Cardiac arrest or arrhythmias will require advanced life support techniques.
Opioid antagonists, such as naloxone, are specific antidotes to respiratory depression resulting from opioid overdose. However, naloxone may not be effective in reversing any respiratory depression produced by buprenorphine. High doses of naloxone, 10-35 mg/70 kg, may be of limited value in the management of buprenorphine overdose. The onset of naloxone effect may be delayed by 30 minutes or more. Doxapram hydrochloride (a respiratory stimulant) has also been used.
Because the duration of reversal would be expected to be less than the duration of action of buprenorphine from buprenorphine buccal film, carefully monitor the patient until spontaneous respiration is reliably re-established. Even in the face of improvement, continued medical monitoring is required for at least 24 hours because of the possibility of extended effects of buprenorphine.
In an individual physically dependent on opioids, administration of an opioid receptor antagonist may precipitate an acute withdrawal. The severity of the withdrawal symptoms experienced will depend on the degree of physical dependence and the dose of the antagonist administered. If a decision is made to treat serious respiratory depression in the physically dependent patient, administration of the antagonist should be begun with care and by titration with smaller than usual doses of the antagonist.
11 DESCRIPTION
Buprenorphine buccal film is a buccal film that provides transmucosal delivery of buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist. Buprenorphine buccal film is a rectangular bi-layer, peppermint-flavored, buccal film with rounded corners, consisting of a white to off-white backing layer with strength identifier printed in black ink and a light yellow to yellow active mucoadhesive layer containing buprenorphine hydrochloride. The yellow side of the film is applied to the inside of the cheek where it adheres to the moist buccal mucosa to deliver the drug as the film dissolves.
Buprenorphine hydrochloride, USP is the active ingredient in buprenorphine buccal film. The chemical name of buprenorphine hydrochloride is 6,14-ethenomorphinan-7-methanol, 17-(cyclopropylmethyl)- α-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4, 5-epoxy-18,19-dihydro-3-hydroxy-6-methoxy-α-methyl-, hydrochloride, [5α, 7α, (S)]. Its structural formula is as follows:
The molecular weight of buprenorphine hydrochloride is 504.10; the empirical formula is C29H41NO4∙HCl. Buprenorphine hydrochloride occurs as a white or off-white crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in methanol, soluble in alcohol, and practically insoluble in cyclohexane. The pKa is 8.5 for the amine function and 10.0 for the phenol function.
Dosage strengths of buprenorphine buccal film are based on the active moiety, buprenorphine. Buprenorphine buccal film is available as 75 mcg, 150 mcg, 300 mcg, 450 mcg, 600 mcg, 750 mcg, and 900 mcg buprenorphine per film. The strength of each film is dependent on the buprenorphine concentration in the formulation and the surface area of the film. Table 6 lists the dosage strength, equivalent amount of buprenorphine hydrochloride, USP (active ingredient), unique identifier and film size for each strength.
|
Buprenorphine Strength (mcg) | Buprenorphine Hydrochloride (mcg) |
Buprenorphine Buccal Film Identifier |
Film Size (cm2) |
|
75 | 81.0 |
A0 |
1.360 |
|
150 | 161.8 |
A1 |
2.720 |
|
300 | 323.5 |
A3 |
0.934 |
|
450 | 485.0 |
A4 |
1.400 |
|
600 | 646.4 |
A6 |
1.867 |
|
750 | 808.2 |
A7 |
2.333 |
|
900 | 970.3 |
A9 |
2.801 |
Each buccal film also contains anhydrous citric acid, carboxymethylcellulose sodium, hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, iron oxide black, iron oxide yellow, methylparaben, monobasic sodium phosphate anhydrous, peppermint oil, polycarbophil, propylene glycol, propylparaben, sodium benzoate, sodium hydroxide, saccharin sodium, shellac, titanium dioxide, vitamin E acetate, and purified water.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu-opioid receptor and an antagonist at the kappa-opioid receptor.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Effects on the Central Nervous System
The principal action of therapeutic value of buprenorphine is analgesia and is thought to be due to buprenorphine binding with high affinity to opioid receptors on neurons in the brain and spinal cord.
Buprenorphine produces respiratory depression by direct action on brain stem respiratory centers. The respiratory depression involves a reduction in the responsiveness of the brain stem respiratory centers to both increases in carbon dioxide tension and electrical stimulation.
Buprenorphine causes miosis, even in total darkness. Pinpoint pupils are a sign of opioid overdose but are not pathognomonic (e.g., pontine lesions of hemorrhagic or ischemic origins may produce similar findings). Marked mydriasis rather than miosis may be seen with worsening hypoxia in the setting of buprenorphine overdose.
Unlike other opioids, buprenorphine appears to exhibit a dose-ceiling effect.
Effects on the Gastrointestinal Tract and Other Smooth Muscle
Buprenorphine causes a reduction in motility associated with an increase in tone in the stomach and duodenum. Digestion of food in the small intestine is delayed and propulsive contractions are decreased. Propulsive peristaltic waves in the colon are decreased, while tone is increased to the point of spasm, resulting in constipation. Buprenorphine may cause an increase in biliary tract pressure as a result of spasm of the sphincter of Oddi. Other opioid-induced effects may include a reduction in biliary and pancreatic secretions, spasm of sphincter of Oddi, and transient elevations in serum amylase.
Effects on the Cardiovascular System
Buprenorphine produces peripheral vasodilation, which may result in orthostatic hypotension or syncope. Manifestations of histamine release and/or peripheral vasodilation may include pruritus, flushing, red eyes, sweating, and/or orthostatic hypotension.
Effects on Cardiac Electrophysiology
QTc prolongation with buprenorphine buccal film has been observed. Of the 1,590 patients that were treated with buprenorphine buccal film in controlled and open-label chronic pain trials at doses up to 900 mcg every 12 hours, 2% demonstrated a prolongation of QTcF to a post-baseline value between 450 - 480 msec during therapy.
Effects on the Endocrine System
Opioids inhibit the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), cortisol, and luteinizing hormone (LH) in humans [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. They also stimulate prolactin, growth hormone (GH) secretion, and pancreatic secretion of insulin and glucagon.
Chronic use of opioids may influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, leading to androgen deficiency that may manifest as low libido, impotence, erectile dysfunction, amenorrhea, or infertility. The causal role of opioids in the clinical syndrome of hypogonadism is unknown because the various medical, physical, lifestyle, and psychological stressors that may influence gonadal hormone levels have not been adequately controlled for in studies conducted to date [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Effects on the Immune System
Opioids have been shown to have a variety of effects on components of the immune system in in vitro and animal models. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Overall, the effects of opioids appear to be modestly immunosuppressive.
Concentration–Efficacy Relationships
The minimum effective analgesic concentration varies widely among patients, especially among patients who have been previously treated with potent agonist opioids. The minimum effective analgesic concentration of buprenorphine for any individual patient may increase over time due to an increase in pain, the development of a new pain syndrome, and/or the development of analgesic tolerance [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.4)].
Concentration–Adverse Reaction Relationships
There is a relationship between increasing buprenorphine plasma concentration and increasing frequency of dose-related opioid adverse reactions such as nausea, vomiting, CNS effects, and respiratory depression. In opioid-tolerant patients, the situation may be altered by the development of tolerance to opioid-related adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3, 2.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Systemic plasma levels of buprenorphine increased in a linear manner (Cmax and AUC) over the single dose range of 75 mcg to 1200 mcg as shown in Table 7. The absolute bioavailability of buprenorphine buccal film ranged from 46% to 65%.
|
Regimen |
Dosage (mcg) |
Cmax (ng/mL) |
AUC0-t(h∙ng/mL) |
AUC0-∞ (h∙ng/mL) |
Tmax* (hr) |
|
Single Dose |
75 |
0.17±0.30 |
0.46±0.22 |
0.63±0.24 |
3.00 (1.50-4.00) |
|
300 |
0.47±0.47 |
2.00±0.68 |
2.3±0.68 |
2.50 (0.50-4.00) |
|
|
1200 |
1.43±0.45 |
9.6±2.9 |
10.5±3.32 |
3.00 (1.00-4.00) |
|
|
* Tmax values reported as median and range |
|||||
Following the multiple dose administration (60 mcg to 240 mcg every 12 hours) of buprenorphine buccal film, apparent steady-state buprenorphine plasma concentrations were achieved prior to the 6th dose. Buprenorphine steady-state Cmax and AUC increased proportional to dose.
Systemic exposure to buprenorphine from buprenorphine buccal film was reduced by 23% to 27% by the ingestion of liquids (cold, hot and room temperature water) during film administration; additionally, coadministration with low pH liquid, such as decaffeinated cola, decreased buprenorphine exposure from buprenorphine buccal film by approximately 37%. The consumption of liquids should be avoided until the buccal film has completely dissolved [see Dosage and Administration (2.8)].
Distribution
Buprenorphine is approximately 96% protein bound, primarily to alpha and beta globulin.
Elimination
Metabolism
Buprenorphine undergoes both N-dealkylation to norbuprenorphine and glucuronidation. The N-dealkylation pathway is mediated primarily by CYP3A4. Norbuprenorphine, the major metabolite, can further undergo glucuronidation. Norbuprenorphine has been found to bind to opioid receptors in vitro; however, it has not been studied clinically for opioid-like activity.
Excretion
A mass balance study of buprenorphine showed complete recovery of radiolabel in urine (30%) and feces (69%) collected up to 11 days after dosing. Almost all of the dose was accounted for in terms of buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, and two unidentified buprenorphine metabolites. In urine, most of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine was conjugated (buprenorphine, 1% free and 9.4% conjugated; norbuprenorphine, 2.7% free and 11% conjugated). In feces, almost all of the buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine was free (buprenorphine, 33% free and 5% conjugated; norbuprenorphine, 21% free and 2% conjugated).
Based on multiple-dose studies performed with buprenorphine buccal film, the mean plasma elimination half-life of buprenorphine was 27.6±11.2 hours.
Drug Interaction Studies
CYP3A4 Inhibitors and Inducers
Buprenorphine undergoes N-dealkylation mediated primarily by CYP3A4, so its metabolism can be inhibited by CYP3A4 inhibitors. The interaction of buprenorphine with all CYP3A4 inducers has not been studied [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Buprenorphine has been found to be a CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 inhibitor and its major metabolite, norbuprenorphine, has been found to be a moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor in in vitro studies employing human liver microsomes. However, the relatively low plasma concentrations of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine resulting from therapeutic doses are not expected to raise significant drug-drug interaction concerns.
Specific Populations
Age: Geriatric Patients
No notable differences in pharmacokinetics were observed from population PK analysis in subjects aged 65 and older compared to younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience with buprenorphine has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
Sex
No notable sex differences in pharmacokinetics were observed from population PK analysis.
Renal Impairment
No studies in patients with renal impairment have been performed with buprenorphine buccal film. In an independent study, the effect of impaired renal function on buprenorphine pharmacokinetics after IV bolus and after continuous IV infusion administration was evaluated and no notable differences in plasma buprenorphine concentrations were identified in patients with normal renal function compared to impaired renal function or renal failure.
Hepatic Impairment
Buprenorphine buccal film has not been evaluated in patients with severe hepatic impairment. The pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine following an IV infusion of 0.3 mg of buprenorphine were compared in 8 patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A), 4 patients with moderate impairment (Child-Pugh B), and 12 subjects with normal hepatic function. Buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine plasma levels did not increase in mild or moderately impaired patient cohorts.
In another pharmacokinetic study, the disposition of buprenorphine was determined after administering a 2.0/0.5 mg buprenorphine/naloxone sublingual tablet in subjects with varied degrees of hepatic impairment as indicated by Child-Pugh criteria. The disposition of buprenorphine in patients with hepatic impairment was compared to disposition in subjects with normal hepatic function. In subjects with mild hepatic impairment, the changes in mean Cmax , AUC0-last, and half-life values of buprenorphine were not clinically significant. No dose adjustment is needed in patients with mild hepatic impairment.
For subjects with moderate and severe hepatic impairment, mean Cmax, AUC0-last, and half-life values of buprenorphine were increased (Table 8) [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Warnings and Precautions (5.11), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
|
Hepatic Impairment |
PK Parameters |
Increase in buprenorphine compared to healthy subjects |
|
Moderate |
Cmax |
8% |
|
AUC0-last |
64% |
|
|
Half-life |
35% |
|
|
Severe |
Cmax |
72% |
|
AUC0-last |
181% |
|
|
Half-life |
57% |
Oral Mucositis
In an open-label pharmacokinetic study in 6 cancer patients with Grade 3 mucositis, buprenorphine was absorbed more rapidly from buprenorphine buccal film resulting in a higher Cmax (~79%) and AUC (~56%) compared to age- and gender-matched healthy control subjects [see Dosage and Administration (2.7), Warnings and Precautions (5.17)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies of buprenorphine were conducted in Sprague-Dawley rats and CD-1 mice. Buprenorphine was administered in the diet to rats at doses of 0.6 mg/kg/day, 5.5 mg/kg/day, and 56 mg/kg/day for 27 months (estimated exposure was approximately 3, 29, and 299 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of buccal buprenorphine of 1.8 mg on a mg/m2 basis, respectively). Statistically significant dose-related increases in testicular interstitial (Leydig’s) cell tumors occurred. In an 86-week study in CD-1 mice, buprenorphine was not carcinogenic at dietary doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 267 times the MRHD).
Mutagenesis
Buprenorphine was studied in a series of tests utilizing gene, chromosome, and DNA interactions in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Results were negative in yeast (S. cerevisiae) for recombinant, gene convertant, or forward mutations; negative in Bacillus subtilis “rec” assay, negative for clastogenicity in CHO cells, Chinese hamster bone marrow and spermatogonia cells, and negative in the mouse lymphoma L5178Y assay.
Results were equivocal in the Ames test: negative in studies in two laboratories, but positive for frame shift mutation at a high dose (5 mg/plate) in a third study. Results were positive in the Green-Tweets (E. coli) survival test, positive in a DNA synthesis inhibition (DSI) test with testicular tissue from mice, for both in vivo and in vitro incorporation of [3H]thymidine, and positive in an unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) test using testicular cells from mice.
Impairment of Fertility
Reproduction studies of buprenorphine in rats demonstrated no evidence of impaired fertility at daily oral doses up to 80 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure approximately 427 times the MRHD) or up to 5 mg/kg/day IM or SC (estimated exposure was approximately 27 times the MRHD).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of buprenorphine buccal film has been evaluated in three 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials in opioid-naïve and opioid-experienced patients with moderate-to-severe chronic low back pain using pain scores as the primary efficacy variable. Two of these studies, described below, demonstrated efficacy in patients with low back pain. One study in low back pain did not show a statistically significant pain reduction for buprenorphine buccal film compared to placebo.
12-Week Study in Opioid-Naïve Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain
A total of 749 patients with chronic low back pain entered an open-label, dose-titration period for up to eight weeks. Potential subjects were excluded from participation for QTcF interval of 450 ms or more, hypokalemia, clinically unstable cardiac disease, a history of Long QT Syndrome or an immediate family member with this condition, or taking Class IA or Class III antiarrhythmic medications. Patients initiated therapy with a single 75 mcg dose of buprenorphine buccal film on Day 1 and continued taking buprenorphine buccal film 75 mcg either once daily or every 12 hours for 4 to 8 days as tolerated. The dose was then increased to 150 mcg every 12 hours, and patients could continue to dose escalate in 150 mcg dose increments every 4 to 8 days for up to 6 weeks if the adverse effects were tolerable and the analgesic effects were not adequate. Patients who achieved adequate analgesia and tolerable adverse effects on buprenorphine buccal film for at least 2 weeks were then randomized to continue their titrated dose of buprenorphine buccal film or matching placebo buccal film. Sixty-one percent (61%) of the patients who entered the open-label dose titration period were able to titrate to a tolerable and effective dose and were randomized into a 12-week, double-blind treatment period. Fifteen percent of patients discontinued due to an adverse event and 4% discontinued due to lack of a therapeutic effect. The remaining 20% of patients discontinued due to various non-drug related administrative reasons.
During the first 2 weeks of double-blind treatment, patients were allowed up to 2 tablets per day of hydrocodone/acetaminophen 5/325 mg as supplemental analgesia to minimize opioid withdrawal symptoms in patients randomized to placebo. Thereafter, the supplemental analgesia was limited to 1 to 2 tablets of acetaminophen 500 mg per day. Seventy-six percent of the patients treated with buprenorphine buccal film completed the 12-week treatment compared to 73% of the patients treated with placebo. Of the 209 patients randomized to buprenorphine buccal film, 4% discontinued due to lack of efficacy and 8% due to adverse events. Of the 211 patients randomized to placebo, 11% discontinued due to lack of efficacy and 4% due to adverse events.
Of the patients who were randomized, the mean pain (SD) scores on a 0 to 10 numeric rating scale (NRS) were 7.1 (1.06) and 7.2 (1.05) prior to open-label titration and 2.8 (1.01) and 2.8 (1.12) at the beginning of the double-blind period for buprenorphine buccal film and placebo, respectively. The change from double-blind baseline to week 12 in mean pain (SD) NRS score was statistically significant favoring patients treated with buprenorphine buccal film, compared with patients treated with placebo.
A higher proportion of buprenorphine buccal film patients (62%) had at least a 30% reduction in pain score from prior to open-label titration to study endpoint when compared to patients who received placebo buccal film (47%). A higher proportion of buprenorphine buccal film patients (41%) also had at least a 50% reduction in pain score from prior to open-label titration to study endpoint compared to patients who received placebo (33%).
The proportion of patients with various degrees of improvement, from prior to open-label titration (Titration-Baseline) to study endpoint, is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Percentage Improvement in Pain Intensity from Titration-Baseline to Week 12
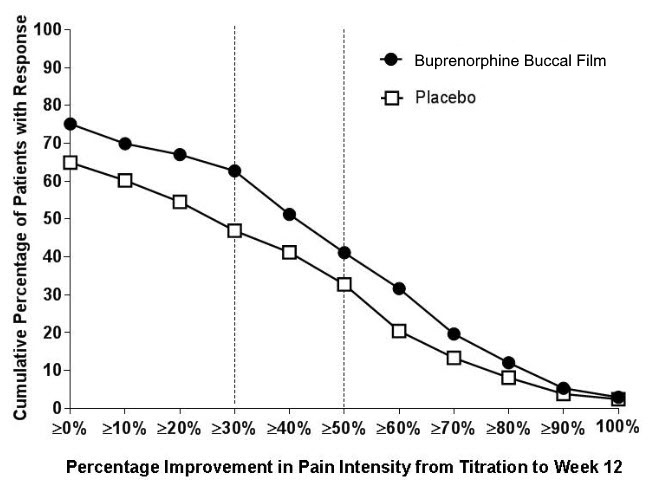
12-Week Study in Opioid-Experienced Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain
Eight hundred and ten (810) patients on chronic opioid therapy (total daily dose 30 mg to 160 mg in oral morphine sulfate equivalents (MSE) for at least 4 weeks) entered an open-label, dose-titration period with buprenorphine buccal film for up to 8 weeks, following taper of their prior opioids to 30 mg oral MSE daily. Potential subjects were excluded from participation for QTcF interval of 450 ms or more, hypokalemia, clinically unstable cardiac disease, a history of Long QT Syndrome or an immediate family member with this condition, or taking Class IA or Class III antiarrhythmic medications. Patients were initiated with buprenorphine buccal film 150 mcg every 12 hours if they were on 30 mg to 89 mg oral MSE daily and 300 mcg every 12 hours if they were on 90 mg to 160 mg oral MSE daily prior to taper. If a patient tolerated the adverse events and the analgesic effects were not adequate, the dose was increased in increments of 150 mcg every 12 hours after 4 to 8 days for up to 6 weeks. Patients were permitted to take hydrocodone/acetaminophen 5/325 mg as analgesic rescue as needed up to a maximum of 4 doses per day during the open-label dose titration period. After a dose was reached with adequate analgesia and tolerable adverse effects for a period of 2 weeks, patients were randomized to continue their titrated dose of buprenorphine buccal film or matching placebo. Sixty-three percent (63%) of the patients who entered the open-label titration period were able to titrate to a tolerable and effective dose and were randomized into a 12-week double-blind treatment phase. Ten percent (10%) of patients discontinued due to an adverse event, 8% discontinued due to lack of a therapeutic effect, and 0.1% discontinued due to opioid withdrawal during the open-label titration period. The remaining 20% of patients discontinued due to various non-drug related administrative reasons.
During the double-blind period, patients were permitted to take up to 2 doses of 5/325 mg or 10/650 mg of hydrocodone/acetaminophen per day for the first 2 weeks to minimize opioid withdrawal symptoms in patients randomized to placebo. After the first 2 weeks, patients were permitted to take 1 dose of 5/325 mg or 10/650 mg per day. Eighty-three percent of patients treated with buprenorphine buccal film and 57% of patients treated with placebo buccal film completed the 12-week treatment period. Of the 243 patients randomized to buprenorphine buccal film, 8% discontinued due to lack of efficacy and 2% due to adverse events. Of the 248 patients randomized to placebo buccal film, 25% discontinued due to lack of efficacy and 5% due to adverse events.
Of the patients who were randomized into the double-blind period, the mean pain (SD) NRS scores were 6.8 (1.28) and 6.6 (1.32) prior to open-label titration and 2.9 (0.985) and 2.8 (1.05) at the beginning of the double-blind period for buprenorphine buccal film and placebo, respectively. The change from baseline to week 12 in mean pain (SD) NRS score was statistically significant in favor of patients treated with buprenorphine buccal film compared with patients treated with placebo.
A higher proportion of buprenorphine buccal film patients (64%) had at least a 30% reduction in pain score from prior to open-label titration to study endpoint when compared to patients who received placebo buccal film (31%). A higher proportion of buprenorphine buccal film patients (39%) also had at least a 50% reduction in pain score from prior to open-label titration to study endpoint compared to patients who received placebo (17%).
The proportion of patients with various degrees of improvement from prior to open-label titration (Titration-Baseline) to study endpoint is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Percentage Improvement in Pain Intensity from Titration-Baseline to Week 12
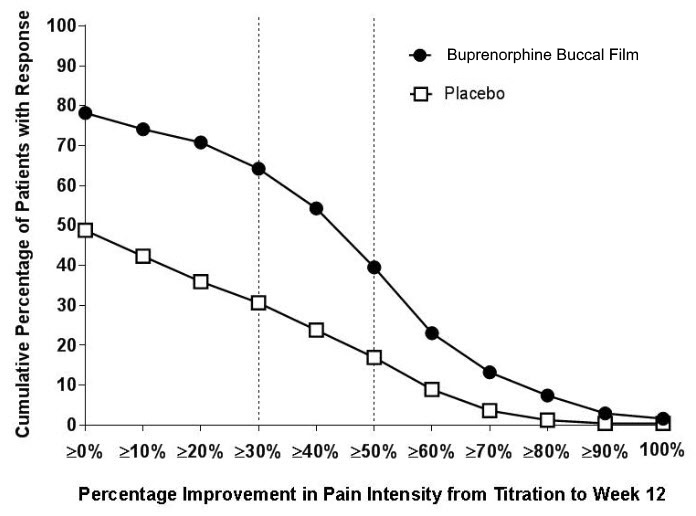
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Buprenorphine buccal films are supplied in cartons containing 60 individual child-resistant foil packages as follows:
| Strength | NDC Number
Carton | NDC Number
Foil Package | Foil Color |
| The 75 mcg buccal film is printed with A0 | 47781-471-74 | 47781-471-11 | Magenta |
| The 150 mcg buccal film is printed with A1 | 47781-472-74 | 47781-472-11 | Green |
| The 300 mcg buccal film is printed with A3 | 47781-400-74 | 47781-400-11 | Gray |
| The 450 mcg buccal film is printed with A4 | 47781-425-74 | 47781-425-11 | Purple |
| The 600 mcg buccal film is printed with A6 | 47781-473-74 | 47781-473-11 | Blue |
| The 750 mcg buccal film is printed with A7 | 47781-474-74 | 47781-474-11 | Teal |
| The 900 mcg buccal film is printed with A9 | 47781-475-74 | 47781-475-11 | White |
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), with excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F).
Store buprenorphine buccal film securely and dispose of properly [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Storage and Disposal
Because of the risks associated with accidental ingestion, misuse, and abuse, advise patients to store buprenorphine buccal film securely, out of sight and reach of children, and in a location not accessible by others, including visitors to the home [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2)]. Inform patients that leaving buprenorphine buccal film unsecured can pose a deadly risk to others in the home.
Advise patients and caregivers that when medicines are no longer needed, they should be disposed of promptly. Expired, unwanted, or unused buprenorphine buccal film should be disposed of by removing the buprenorphine buccal film from the foil packaging and flushing the unused medication down the toilet (if a drug take-back option is not readily available). Inform patients that they can visit www.fda.gov/drugdisposal for a complete list of medicines recommended for disposal by flushing, as well as additional information on disposal of unused medicines.
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Inform patients that the use of buprenorphine buccal film, even when taken as recommended, can result in addiction, abuse, and misuse, which could lead to overdose and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Instruct patients not to share buprenorphine buccal film with others and to take steps to protect buprenorphine buccal film from theft or misuse.
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Inform patients of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression, including information that the risk is greatest when starting buprenorphine buccal film or when the dosage is increased, and that it can occur even at recommended doses.
Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize respiratory depression and emphasize the importance of calling 911 or getting emergency medical help right away in the event of a known or suspected overdose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid Overdose
Discuss with the patient and caregiver the availability of naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose, both when initiating and renewing treatment with buprenorphine buccal film. Inform patients and caregivers about the various ways to obtain naloxone as permitted by individual state naloxone dispensing and prescribing requirements or guidelines (e.g., by prescription, directly from a pharmacist, or as part of a community-based program) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize the signs and symptoms of an overdose.
Explain to patients and caregivers that naloxone’s effects are temporary, and that they must call 911 or get emergency medical help right away in all cases of known or suspected opioid overdose, even if naloxone is administered [see Overdosage (10)].
If naloxone is prescribed, also advise patients and caregivers:
- How to treat with naloxone in the event of an opioid overdose
- To tell family and friends about their naloxone and to keep it in a place where family and friends can access it in an emergency
- To read the Patient Information (or other educational material) that will come with their naloxone. Emphasize the importance of doing this before an opioid emergency happens, so the patient and caregiver will know what to do.
Accidental Exposure
Inform patients that accidental exposure, especially in children, may result in respiratory depression or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Interactions with Benzodiazepines and Other CNS Depressants
Inform patients and caregivers that potentially fatal additive effects may occur if buprenorphine buccal film is used with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, and not to use these concomitantly unless supervised by a healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Inform patients that buprenorphine buccal film could cause a rare but potentially life-threatening condition resulting from concomitant administration of serotonergic drugs. Warn patients of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome and to seek medical attention right away if symptoms develop. Instruct patients to inform their physicians if they are taking, or plan to take, serotonergic medications [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Adrenal Insufficiency
Inform patients that buprenorphine buccal film could cause adrenal insufficiency, a potentially life-threatening condition. Adrenal insufficiency may present with non-specific symptoms and signs such as nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Advise patients to seek medical attention if they experience a constellation of these symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Interaction with Benzodiazepines
Warn patients that it is extremely dangerous to self-administer benzodiazepines while taking buprenorphine buccal film, and warn patients to use benzodiazepines concurrently with buprenorphine buccal film only as directed by their physician [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Important Administration Instructions
Instruct patients how to properly use buprenorphine buccal film, including the following:
- To carefully follow instructions for the application of buprenorphine buccal film and to avoid eating or drinking until it dissolves.
- To apply buprenorphine buccal film once daily, or every twelve (12) hours at the same time or times each day.
- To avoid applying buprenorphine buccal film to areas of the mouth with any open sores or lesions.
- To not use buprenorphine buccal film if the pouch seal is broken or the buccal film is cut, damaged, or changed in any way.
Important Discontinuation Instructions
In order to avoid developing withdrawal symptoms, instruct patients not to discontinue buprenorphine buccal film without first discussing a tapering plan with the prescriber [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Hypotension
Inform patients that buprenorphine buccal film may cause orthostatic hypotension and syncope. Instruct patients how to recognize symptoms of low blood pressure and how to reduce the risk of serious consequences should hypotension occur (e.g., sit or lie down, carefully rise from a sitting or lying position) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Anaphylaxis
Inform patients that anaphylaxis has been reported with ingredients contained in buprenorphine buccal film. Advise patients how to recognize such a reaction and when to seek medical attention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Pregnancy
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Inform female patients of reproductive potential that prolonged use of buprenorphine buccal film during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Embryofetal Toxicity
Advise female patients that buprenorphine buccal film can cause fetal harm and to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with buprenorphine buccal film [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Constipation
Advise patients of the potential for severe constipation, including management instructions and when to seek medical attention [see Adverse Reactions (6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Driving or Operating Heavy Machinery
Inform patients that buprenorphine buccal film may impair the ability to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating heavy machinery. Advise patients not to perform such tasks until they know how they will react to the medication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18)].
Healthcare professionals can telephone Alvogen, Inc. at 1-866-770-3024 for information on this product.
Distributed by:
Alvogen, Inc.
Morristown, NJ 07960 USA
PI471-01
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 03/2021 | ||
| Medication Guide Buprenorphine (bue" pre nor' feen) Buccal Film, CIII |
||
Buprenorphine buccal film is:
|
||
Important information about buprenorphine buccal film:
|
||
Do not use buprenorphine buccal film if you have:
|
||
| Before taking buprenorphine buccal film, tell your healthcare provider if you have a history of: | ||
|
|
|
Tell your healthcare provider if you are:
|
||
When taking buprenorphine buccal film:
|
||
While using buprenorphine buccal film DO NOT:
|
||
The possible side effects of buprenorphine buccal film are:
Distributed by: Alvogen, Inc., Morristown, NJ 07960 USA PL471-01 |
||
Instructions for Use
Buprenorphine (bue" pre nor' feen) Buccal Film, CIII
Before you use buprenorphine buccal film, it is important that you read the Medication Guide and these Patient Instructions for Use so that you use buprenorphine buccal film the right way. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions about the right way to use buprenorphine buccal film.
Important:
- Buprenorphine buccal film is sealed in a foil package. Do not open the package until ready to use. After opening, use the entire buprenorphine buccal film right away.
- Do not apply buprenorphine buccal film if the package seal is broken or the film is cut, damaged, or changed in any way.
- Buprenorphine buccal film is available in different strengths. Make sure you have the strength that has been prescribed for you.
- Avoid placing buprenorphine buccal film to areas of the mouth with any open sores or lesions.
Open the buprenorphine buccal film package:
- Hold the foil package as shown below (see Figure A). Fold along the dotted line at the top of the foil package.
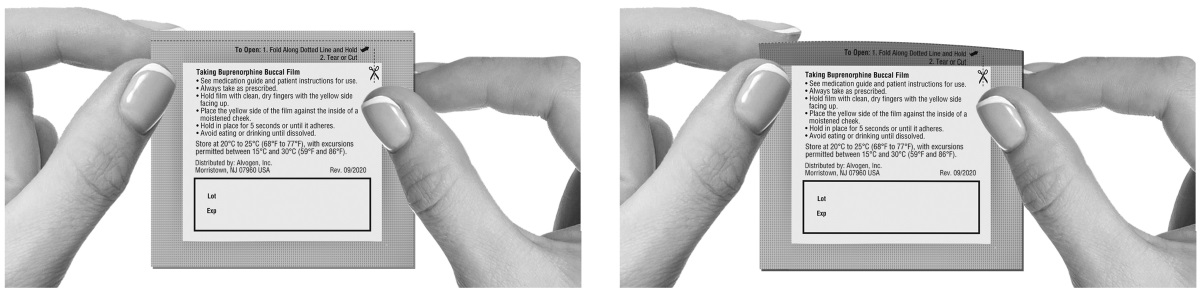
Figure A
- Keep folded and tear down or cut with scissors at the notch in the direction of the scissors on the dotted line (see Figure B). Tear all the way to the bottom. Be careful to avoid cutting and damaging the buprenorphine buccal film when using scissors.

Figure B
- Remove buprenorphine buccal film from the foil package (see Figure C).

Figure C
Use buprenorphine buccal film as follows:
- Use your tongue to wet the inside of your cheek or rinse your mouth with water to moisten the area in your mouth before you place buprenorphine buccal film.
- Hold the buprenorphine buccal film with clean, dry fingers with the yellow side facing up (see Figure D).

Figure D
- Using a finger, place the yellow side of the buprenorphine buccal film against the inside of your moistened cheek. Press and hold the buprenorphine buccal film in place for 5 seconds and then take your finger away (see Figure E).
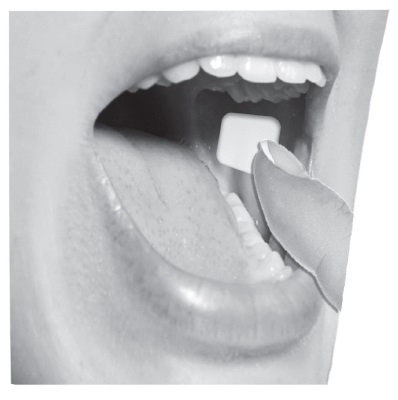
Figure E
- The buprenorphine buccal film will stick to the inside of your cheek (see Figure F).
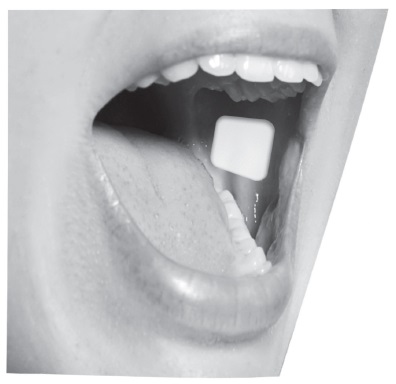
Figure F
- Leave the buprenorphine buccal film in place until it has completely dissolved, usually within 30 minutes after you apply it.
- Avoid eating food or drinking liquids until buprenorphine buccal film has dissolved.
- Avoid touching or moving buprenorphine buccal film with your tongue or finger after it is in place.
- Do not chew or swallow buprenorphine buccal film.
These Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
For more information call Alvogen, Inc. at 1-866-770-3024.
Distributed by:
Alvogen, Inc.
Morristown, NJ 07960 USA
Revised: 09/2020
IFU471-00
| BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM
buprenorphine buccal film |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM
buprenorphine buccal film |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM
buprenorphine buccal film |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM
buprenorphine buccal film |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM
buprenorphine buccal film |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM
buprenorphine buccal film |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUPRENORPHINE BUCCAL FILM
buprenorphine buccal film |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Alvogen, Inc. (008057330) |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.






