RINGERS- sodium chloride, potassium chloride, and calcium chloride injection, solution
Ringers by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Ringers by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by ICU Medical Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
This product is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solutions containing isotonic concentrations of electrolytes in water for injection. The solution is isotonic. The solution is administered by intravenous infusion for parenteral replacement of extracellular losses of fluid and electrolytes, with or without minimal carbohydrate calories.
Each 100 mL of Ringer's Injection, USP contains sodium chloride 860 mg, potassium chloride 30 mg and calcium chloride, dihydrate 33 mg. May contain hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment. A liter provides 147 mEq sodium (Na+), 4 mEq potassium (K+), 4 mEq calcium (Ca++) and 155 mEq chloride (Cl−). The electrolyte content is isotonic (309 mOsmol/liter, calc.) in relation to the extracellular fluid (approx. 280 mOsmol/liter). The pH of the solution is 5.4 (5.0 − 7.5).
The solution contains no bacteriostat, antimicrobial agent or added buffer (except for pH adjustment) and is intended only for use as a single-dose injection. When smaller doses are required the unused portion should be discarded.
The solution is a parenteral fluid, nutrient and/or electrolyte replenisher.
Dextrose, USP is chemically designated D-glucose, monohydrate (C6H12O6 ∙ H2O), a hexose sugar freely soluble in water. It has the following structural formula:
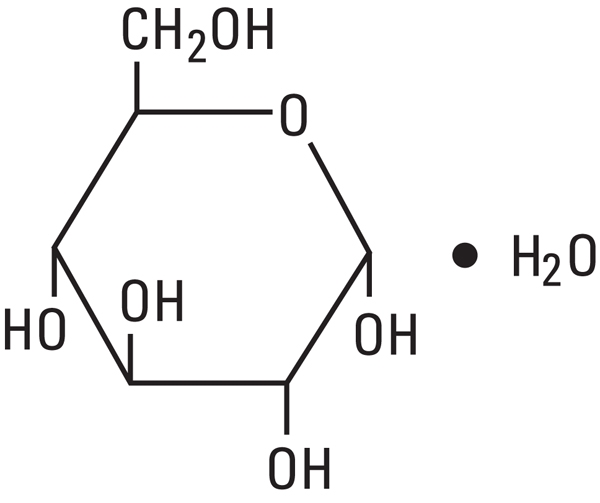
Calcium Chloride, USP is chemically designated calcium chloride, dihydrate (CaCl2 ∙ 2 H2O), white fragments or granules freely soluble in water.
Potassium Chloride, USP is chemically designated KCl, a white granular powder freely soluble in water.
Sodium Chloride, USP is chemically designated NaCI, a white crystalline powder freely soluble in water.
Water for Injection, USP is chemically designated H2O.
The flexible plastic container is fabricated from a specially formulated polyvinylchloride. Water can permeate from inside the container into the overwrap but not in amounts sufficient to affect the solution significantly. Solution inside the plastic container also can leach out certain chemical components in very small amounts before the expiration period is attained. However, the safety of the plastic has been confirmed by tests in animals according to USP biological standards for plastic containers.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
When administered intravenously, this solution provides a source of water and electrolytes with or without minimal carbohydrate calories. The electrolyte content resembles that of the principal ionic constituents of normal plasma and the solution therefore is suitable for parenteral replacement of extracellular losses of fluid and electrolytes, with or without carbohydrate calories.
Calcium chloride in water dissociates to provide calcium (Ca++) and chloride (Cl−) ions. They are normal constituents of the body fluids and are dependent on various physiologic mechanisms for maintenance of balance between intake and output. Approximately 80% of body calcium is excreted in the feces as insoluble salts; urinary excretion accounts for the remaining 20%.
Potassium chloride in water dissociates to provide potassium (K+) and chloride (Cl−) ions. Potassium is found in low concentration in plasma and extracellular fluids (3.5 to 5.0 mEq/liter in a healthy adult). It is the chief cation of body cells (160 mEq/liter of intracellular water). Potassium plays an important role in electrolyte balance. Normally about 80 to 90% of the potassium intake is excreted in the urine; the remainder in the stools and to a small extent, in the perspiration. The kidney does not conserve potassium well so that during fasting or in patients on a potassium-free diet, potassium loss from the body continues resulting in potassium depletion.
Sodium chloride in water dissociates to provide sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) ions. Sodium (Na+) is the principal cation of the extracellular fluid and plays a large part in the therapy of fluid and electrolyte disturbances. Chloride (Cl−) has an integral role in buffering action when oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange occurs in the red blood cells. The distribution and excretion of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) are largely under the control of the kidney which maintains a balance between intake and output.
Water is an essential constituent of all body tissues and accounts for approximately 70% of total body weight. Average normal adult daily requirement ranges from two to three liters (1.0 to 1.5 liters each for insensible water loss by perspiration and urine production).
Water balance is maintained by various regulatory mechanisms. Water distribution depends primarily on the concentration of electrolytes in the body compartments and sodium (Na+) plays a major role in maintaining physiologic equilibrium.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
WARNINGS
Solutions containing calcium ions should not be administered simultaneously through the same administration set as blood because of the likelihood of coagulation.
Solutions which contain potassium should be used with great care, if at all, in patients with hyperkalemia, severe renal failure and in conditions in which potassium retention is present.
Solutions containing sodium ions should be used with great care, if at all, in patients with congestive heart failure, severe renal insufficiency and in clinical states in which there exists edema with sodium retention.
In patients with diminished renal function, administration of solutions containing sodium or potassium ions may result in sodium or potassium retention.
Solutions containing lactate ions should be used with great care in patients with metabolic or respiratory alkalosis. The administration of lactate ions should be done with great care where there is an increased level or an impaired utilization of lactate ions, as in severe hepatic insufficiency.
The intravenous administration of these solutions can cause fluid and/or solute overloading resulting in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations, overhydration, congested states or pulmonary edema. The risk of dilutional states is inversely proportional to the electrolyte concentrations of administered parenteral solutions.
The risk of solute overload causing congested states with peripheral and pulmonary edema is directly proportional to the electrolyte concentrations of such solutions.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Clinical evaluation and periodic laboratory determinations are necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations and acid-base balance during prolonged parenteral therapy or whenever the condition of the patient warrants such evaluation.
Caution must be exercised in the administration of parenteral fluids, especially those containing sodium ions, to patients receiving corticosteroids or corticotropin.
Potassium containing solutions should be used with caution in the presence of cardiac disease, particularly in digitalized patients or in the presence of renal disease.
Solutions containing lactate ions should be used with caution as excess administration may result in metabolic alkalosis.
Do not administer unless solution is clear and container is undamaged. Discard unused portion.
Pregnancy Category C.
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Ringer's Injection, USP,. It is also not known whether this injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. This injection should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Reactions which may occur because of the solution or the technique of administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation and hypervolemia.
If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures and save the remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
- OVERDOSAGE
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The dose is dependent upon the age, weight and clinical condition of the patient.
Drug Interactions
Additives may be incompatible. Consult with pharmacist, if available. When introducing additives, use aseptic technique, mix thoroughly and do not store.
The presence of calcium limits their compatibility with certain drugs that form precipitates of calcium salts, and also prohibits their simultaneous infusion through the same administration set as blood because of the likelihood of coagulation.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. See PRECAUTIONS.
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
To Open:
Tear outer wrap at notch and remove solution container. If supplemental medication is desired, follow directions below before preparing for administration. Some opacity of the plastic due to moisture absorption during the sterilization process may be observed. This is normal and does not affect the solution quality or safety. The opacity will diminish gradually.
To Add Medication
- Prepare additive port.
- Using aseptic technique and an additive delivery needle of appropriate length, puncture resealable additive port at target area, inner diaphragm and inject. Withdraw needle after injecting medication.
- The additive port may be protected by covering with an additive cap.
- Mix container contents thoroughly.
Preparation for Administration
(Use aseptic technique)
- Close flow control clamp of administration set.
- Remove cover from outlet port at bottom of container.
- Insert piercing pin of administration set into port with a twisting motion until the set is firmly seated. NOTE: See full directions on administration set carton.
- Suspend container from hanger.
- Squeeze and release drip chamber to establish proper fluid level in chamber.
- Open flow control clamp and clear air from set. Close clamp.
- Attach set to venipuncture device. If device is not indwelling, prime and make venipuncture.
- Regulate rate of administration with flow control clamp.
WARNING: DO NOT USE FLEXIBLE CONTAINER IN SERIES CONNECTIONS.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
This solution is supplied in a single-dose flexible plastic container as follows:
NDC No. Product Name Container Size (mL) 0409–7982–09 Ringer's Inj., USP 1000 0990-7982-09 Ringer's Inj., USP 1000 ICU Medical is transitioning NDC codes from the "0409" to a "0990" labeler code. Both NDC codes are expected to be in the market for a period of time.
Protect from freezing. Store at 20 to 25°C (68 to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Revised: October, 2018
EN-5756
Manufactured for ICU Medical, Inc., Lake Forest, Illinois, 60045, USA
- Clinical Studies
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1000 mL Bag Label
1000 mL
NDC: 0990-7982-09RINGER'S
INJECTION, USPEACH 100 mL CONTAINS SODIUM CHLORIDE
860 mg; POTASSIUM CHLORIDE 30 mg;
CALCIUM CHLORIDE, DIHYDRATE 33 mg
IN WATER FOR INJECTION. MAY CONTAIN
HCl OR NaOH FOR pH ADJUSTMENT.
ELECTROLYTES PER 1000 mL: SODIUM 147 mEq;
POTASSIUM 4mEq; CALCIUM 4 mEq; CHLORIDE
155 mEq.309 mOsmol/LITER (CALC.). pH 5.4 (5.0 TO 7.5).
DO NOT ADMINISTER CALCIUM CONTAINING
SOLUTIONS CONCURRENTLY WITH STORED
BLOOD. ADDITIVES MAY BE INCOMPATIBLE.
CONSULT WITH PHARMACIST, IF AVAILABLE.
WHEN INTRODUCING ADDITIVES, USE
ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE, MIX THOROUGHLY AND
DO NOT STORE. SINGLE-DOSE CONTAINER.
FOR INTRAVENOUS OR SUBCUTANEOUS
USE. USUAL DOSAGE: SEE INSERT. STERILE,
NONPYROGENIC. USE ONLY IF SOLUTION IS
CLEAR AND CONTAINER IS UNDAMAGED.
MUST NOT BE USED IN SERIES CONNECTIONS.RX ONLY
3
V
CONTAINS DEHPIM-5154
Manufactured for ICU Medical, Inc.,
Lake Forest, Illinois, 60045, USA
icumedical
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1000 mL Bag Overwrap
TO OPEN TEAR AT NOTCH
2
HDPEDO NOT REMOVE FROM OVERWRAP UNTIL READY FOR USE. AFTER REMOVING
THE OVERWRAP, CHECK FOR MINUTE LEAKS BY SQUEEZING CONTAINER FIRMLY.
IF LEAKS ARE FOUND, DISCARD SOLUTION AS STERILITY MAY BE IMPAIRED.
RECOMMENDED STORAGE: ROOM TEMPERATURE (25°C). AVOID EXCESSIVE
HEAT. PROTECT FROM FREEZING. SEE INSERT.
98-4321-R14-3/98
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
RINGERS
sodium chloride, potassium chloride, and calcium chloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0990-7982 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 660YQ98I10) (POTASSIUM CATION - UNII:295O53K152, CHLORIDE ION - UNII:Q32ZN48698) POTASSIUM CHLORIDE 30 mg in 100 mL CALCIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: M4I0D6VV5M) (CALCIUM CATION - UNII:2M83C4R6ZB, CHLORIDE ION - UNII:Q32ZN48698) CALCIUM CHLORIDE 33 mg in 100 mL SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) (SODIUM CATION - UNII:LYR4M0NH37, CHLORIDE ION - UNII:Q32ZN48698) SODIUM CHLORIDE 860 mg in 100 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0990-7982-09 12 in 1 CASE 02/24/2020 1 1 in 1 POUCH 1 1000 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA018251 01/01/2020 Labeler - ICU Medical Inc. (118380146)
Trademark Results [Ringers]
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.