ALOXI- palonosetron hydrochloride capsule
ALOXI by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
ALOXI by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Helsinn Therapeutics (U.S.), Inc., Catalent Pharma Solutions. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ALOXI CAPSULES safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ALOXI CAPSULES.
ALOXI (palonosetron HCl) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2003INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ALOXI is a serotonin-3 (5-HT3) receptor antagonist indicated in adults for prevention of acute nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of moderately emetogenic cancer chemotherapy. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 0.5 mg palonosetron (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to palonosetron. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock: reported in patients treated with intravenous palonosetron HCl with or without known hypersensitivity to other selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. If symptoms occur, discontinue ALOXI and initiate appropriate medical treatment. (5.1)
- Serotonin syndrome: reported with 5-HT3 receptor antagonists alone, but particularly with concomitant use of serotonergic drugs. (5.2,7.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥1 %) are: headache, constipation and fatigue. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact HELSINN at 1-844-357-4668 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Serotonergic Drugs: Monitor for serotonin syndrome; if symptoms occur, discontinue ALOXI and initiate supportive treatment. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 4/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.2 Serotonin Syndrome
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Serotonergic Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of ALOXI capsules in adults is 0.5 mg administered orally approximately one hour prior to the start of chemotherapy.
ALOXI can be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
ALOXI is contraindicated in patients known to have hypersensitivity to palonosetron [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock, have been reported with administration of intravenous palonosetron HCl [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. These reactions occurred in patients with or without known hypersensitivity to other 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue ALOXI and initiate appropriate medical treatment. Do not reinitiate ALOXI in patients who have previously experienced symptoms of hypersensitivity [see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Serotonin Syndrome
The development of serotonin syndrome has been reported with 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. Most reports have been associated with concomitant use of serotonergic drugs (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors, mirtazapine, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, and intravenous methylene blue). Some of the reported cases were fatal. Serotonin syndrome occurring with overdose of another 5-HT3 receptor antagonist alone has also been reported. The majority of reports of serotonin syndrome related to 5-HT3 receptor antagonist use occurred in a post-anesthesia care unit or an infusion center.
Symptoms associated with serotonin syndrome may include the following combination of signs and symptoms: mental status changes (e.g. agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, with or without gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for the emergence of serotonin syndrome, especially with concomitant use of ALOXI and other serotonergic drugs. If symptoms of serotonin syndrome occur, discontinue ALOXI and initiate supportive treatment. Patients should be informed of the increased risk of serotonin syndrome, especially if ALOXI is used concomitantly with other serotonergic drugs [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious or otherwise clinically significant adverse reactions reported in other sections of labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In clinical trials for the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with moderately emetogenic chemotherapy, 161 adult patients received a single oral dose of ALOXI 0. 5 mg. The most common adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of patients in two clinical trials were headache (4%) and constipation (1%). In other clinical trials, fatigue was also reported in 1% of patients.
Less common adverse reactions, reported in less than 1%, were:
- Blood and Lymphatic System: anemia.
- Cardiovascular: hypertension, transient arrhythmia, first degree atrioventricular block, second degree atrioventricular block, QTc prolongation.
- Hearing and Labyrinth: motion sickness.
- Eye: eye swelling.
- Gastrointestinal System: gastritis, nausea, vomiting.
- General: fatigue, chills, pyrexia.
- Infections: sinusitis.
- Liver: transient, asymptomatic increases in bilirubin.
- Nutrition: anorexia.
- Musculoskeletal: joint stiffness, myalgia, pain in extremity.
- Nervous System: postural dizziness, dysgeusia.
- Psychiatric: insomnia.
- Respiratory System: dyspnea, epistaxis.
- Skin: generalized pruritus, erythema, alopecia.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of palonosetron HCl. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Hypersensitivity reactions: including dyspnea, bronchospasm, swelling/edema, erythema, pruritus, rash, urticarial, anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock with intravenous administration of palonosetron HCl [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Serotonergic Drugs
Serotonin syndrome (including altered mental status, autonomic instability, and neuromuscular symptoms) has been described following the concomitant use of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists and other serotonergic drugs, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). Monitor for the emergence of serotonin syndrome. If symptoms occur, discontinue ALOXI and initiate supportive treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on palonosetron HCl use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, no effects on embryo-fetal development were observed with the administration of oral palonosetron HCl during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 921 and 1,841 times the recommended human oral dose in rats and rabbits, respectively (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In animal reproduction studies, no effects on embryo-fetal development were observed in pregnant rats given oral palonosetron HCl at doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (921 times the recommended human oral dose based on body surface area) or pregnant rabbits given oral doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (1,841 times the recommended human oral dose based on body surface area) during the period of organogenesis.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of palonosetron in human milk, the effects of palonosetron on the breastfed infant, or the effects of palonosetron on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for ALOXI and any potential adverse effect on the breastfed infant from palonosetron or from the underlying maternal condition.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no known antidote to palonosetron. Overdose should be managed with supportive care.
Dialysis studies have not been performed, however, due to the large volume of distribution, dialysis is unlikely to be an effective treatment for palonosetron overdose. A single oral dose of palonosetron HCl at 500 mg/kg in rats and 100 mg/kg in dogs (7,673 and 5,115 times the recommended human oral dose, respectively, based on body surface area) was lethal. The major signs of toxicity included convulsions, labored breathing, and salivation.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ALOXI (palonosetron HCl) capsules contain palonosetron as palonosetron HCl, an antiemetic and antinauseant agent. It is a serotonin subtype 3 (5-HT3) receptor antagonist with a strong binding affinity for this receptor. Chemically, palonosetron hydrochloride is: (3aS)-2-[(S)-1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-2,3,3a,4,5,6-hexahydro-1-oxo-1H-benz[de]isoquinoline hydrochloride. The empirical formula is C19H24N2O.HCl, with a molecular weight of 332.87. Palonosetron hydrochloride exists as a single isomer and has the following structural formula:
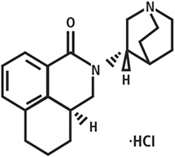
Palonosetron hydrochloride is a white to off-white crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water, soluble in propylene glycol, and slightly soluble in ethanol and 2-propanol.
Each light beige opaque soft gelatin ALOXI capsule contains 0.5 mg palonosetron (equivalent to 0.56 mg of palonosetron HCl). Inactive ingredients are: mono- and di-glycerides of capryl/capric acid, glycerin, polyglyceryl oleate, water, and butylated hydroxyanisole.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Palonosetron is a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist with a strong binding affinity for this receptor and little or no affinity for other receptors.
Cancer chemotherapy may be associated with a high incidence of nausea and vomiting, particularly when certain agents, such as cisplatin, are used. 5- HT3 receptors are located on the nerve terminals of the vagus in the periphery and centrally in the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the area postrema. It is thought that chemotherapeutic agents produce nausea and vomiting by releasing serotonin from the enterochromaffin cells of the small intestine and that the released serotonin then activates 5-HT3 receptors located on vagal afferents to initiate the vomiting reflex.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In non-clinical studies palonosetron possesses the ability to block ion channels involved in ventricular de- and re-polarization and to prolong action potential duration.
At a dose of 4.5 times the recommended dose, ALOXI capsules do not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
Clinical trials revealed that oral palonosetron HCl had comparable effects on blood pressure, heart rate, and ECG parameters as intravenous palonosetron HCl.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration, palonosetron is well absorbed with absolute bioavailability reaching 97%. After single oral doses using buffered solution, mean maximum palonosetron concentrations (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC0-∞) were dose proportional over the dose range of 3 to 80 mcg/kg in healthy subjects.
The mean pharmacokinetic parameters after a single oral dose of 0.5 mg ALOXI are compared across studies in healthy subjects and cancer patients (Table 1). The AUC was 30% higher in cancer patients than in healthy subjects.
Table 1: Pharmacokinetic Parameters1 of Palonosetron after a Single Oral Dose of 0.5 mg ALOXI in Healthy Subjects and Cancer Patients
Parameter
Healthy Subjects (n=36)
Cancer Patients (n=12)
Mean (± Standard Deviation)
Cmax (ng/mL)
0.81 ± 0.17
0.93 ± 0.34
Tmax (hours)
5.1 ± 1.7
5.1 ± 5.9
AUC∞ (ng·h/mL)
38.2 ± 11.7
49.7 ±12.2
t1/2 (hours)
37 ± 12
48 ± 19
1 a cross-study comparison
Effect of Food
A high fat meal did not affect the Cmax and AUC of oral palonosetron [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Distribution
Palonosetron has a volume of distribution of approximately 8.3 ± 2.5 L/kg. Approximately 62% of palonosetron is bound to plasma proteins.
Elimination
Following administration of a single oral 0.75 mg dose of [14C]- palonosetron to six healthy subjects, 85% to 93% of the total radioactivity was excreted in urine, and 5% to 8% was eliminated in feces. The amount of unchanged palonosetron excreted in the urine represented approximately 40% of the administered dose. In healthy subjects given ALOXI Capsules 0.5 mg, the terminal elimination half-life (t½) of palonosetron was 37 ± 12 hours (mean ± SD), and in cancer patients, t½ was 48 ± 19 hours.
After a single- dose of approximately 0.75 mg intravenous palonosetron, the total body clearance of palonosetron in healthy subjects was 160 ± 35 mL/h/kg (mean ± SD) and renal clearance was 66.5 ± 18.2 mL/h/kg.
Metabolism
Palonosetron is eliminated by multiple routes with approximately 50% metabolized to form two primary metabolites: N-oxide-palonosetron and 6-S- hydroxy-palonosetron. These metabolites each have less than 1% of the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist activity of palonosetron. In vitro metabolism studies have suggested that CYP2D6 and to a lesser extent, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 are involved in the metabolism of palonosetron. However, clinical pharmacokinetic parameters are not significantly different between poor and extensive metabolizers of CYP2D6 substrates.
Excretion
Palonosetron is partially renally eliminated from the body.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
In a cross-study comparison, after a single oral 0.75 mg dose of ALOXI capsules (1.5 times the recommended dose), the systemic exposure of palonosetron (AUC) was similar, but mean Cmax was 15% lower in healthy elderly subjects 65 years of age and older compared to subjects less than 65 years of age. This decrease in exposure is not considered to be clinically meaningful.
Male and Female Patients
In female subjects (n=18), the mean AUC was 35% higher and the mean Cmax was 26% higher than in male subjects (n=18). This increase in exposure in female subjects is not considered clinically meaningful.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Mild to moderate renal impairment does not significantly affect palonosetron pharmacokinetic parameters. Total systemic exposure to palonosetron following administration of intravenous palonosetron HCl increased by approximately 28% in patients with severe renal impairment relative to healthy subjects. This increase is not considered clinically meaningful.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Hepatic impairment does not significantly affect total body clearance of palonosetron compared to the healthy subjects.
Racial or Ethnic Groups
The pharmacokinetics of palonosetron were characterized in 32 healthy Japanese male subjects administered an oral solution of palonosetron HCl over a dose range of 3 to 90 mcg/kg. The apparent total body clearance was 26% higher in Japanese males than in white males based on a cross-study comparison; however, this increase is not considered to be clinically meaningful.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro studies indicated that palonosetron is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4/5 (CYP2C19 was not investigated) nor does it induce the activity of CYP1A2, CYP2D6, or CYP3A4/5. Therefore, the potential for clinically significant drug interactions with palonosetron appears to be low.
Metoclopramide
A study in healthy subjects involving a single 0.75 mg intravenous dose of palonosetron HCl and steady state oral metoclopramide (10 mg four times daily) demonstrated no significant pharmacokinetic interaction.
Chemotherapeutic Agents, Corticosteroids, Analgesics, Drugs for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, Antiemetics/Antinauseants
In controlled clinical trials, ALOXI capsules have been safely administered with chemotherapeutic agents, systemic corticosteroids, analgesics, and drugs for gastrointestinal disorders including functional gastrointestinal disorders, acid-related disorders, and antiemetics/antinauseants.
Antacids
Concomitant administration of an antacid (Maalox® liquid 30 mL) had no effect on the oral absorption or pharmacokinetics of a single oral dose of 0.75 mg palonosetron HCl in healthy subjects.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 104-week carcinogenicity study in CD-1 mice, animals were treated with oral doses of palonosetron HCl at 10, 30 and 60 mg/kg/day. Treatment with palonosetron was not tumorigenic. The highest tested dose produced a systemic exposure to palonosetron (Plasma AUC) of about 90 to 173 times the human exposure (AUC= 49.7 ng·h/mL) at the recommended oral dose of 0.5 mg. In a 104-week carcinogenicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats, male and female rats were treated with oral doses of 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg/day and 15, 45 and 90 mg/kg/day, respectively. The highest doses produced a systemic exposure to palonosetron (Plasma AUC) of 82 and 185 times the human exposure at the recommended dose. Treatment with palonosetron produced increased incidences of adrenal benign pheochromocytoma and combined benign and malignant pheochromocytoma, increased incidences of pancreatic Islet cell adenoma and combined adenoma and carcinoma and pituitary adenoma in male rats. In female rats, it produced hepatocellular adenoma and carcinoma and increased the incidences of thyroid C-cell adenoma and combined adenoma and carcinoma.
Palonosetron was not genotoxic in the Ames test, the Chinese hamster ovarian cell (CHO/HGPRT) forward mutation test, the ex vivo hepatocyte unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) test or the mouse micronucleus test. It was, however, positive for clastogenic effects in the Chinese hamster ovarian (CHO) cell chromosomal aberration test.
Palonosetron HCl at oral doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (about 921 times the recommended human oral dose based on body surface area) was found to have no effect on fertility and reproductive performance of male and female rats.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Study 1 was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind active control clinical trial of 635 patients set to receive moderately emetogenic cancer chemotherapy. A single oral dose of 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, or 0.75 mg ALOXI capsules given one hour prior to chemotherapy was compared to a single intravenous dose of 0.25 mg palonosetron HCl given 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy. Patients were randomized to either dexamethasone or placebo in addition to their assigned treatment. The majority of patients in the study were women (73%), white (69%), and naïve to previous chemotherapy (59%). The primary efficacy endpoint was Complete Response (no emetic episodes and no rescue medication) assessed in the acute phase (0 to 24 hours). A key secondary efficacy endpoint was Complete Response assessed in the delayed phase (24 to 120 hours). Other secondary endpoints included Complete Response for the acute plus delayed phases (0-120 hours) and “no nausea” for the acute and delayed phases.
Efficacy was based on demonstrating non-inferiority of oral palonosetron doses compared to the approved intravenous product. Non-inferiority criteria were met if the lower bound of the two-sided 98.3% confidence interval for the difference in complete response rates of oral palonosetron dose minus approved intravenous product was larger than -15%. The non-inferiority margin was 15%.
Efficacy Results
As shown in Table 2, ALOXI capsules 0.5 mg demonstrated non- inferiority to the active comparator during the 0 to 24 hour time interval; however, for the 24 to 120 hour time period, non-inferiority was not shown. The additional two oral palonosetron dose levels showed similar results.
Table 2: Proportion of Patients Achieving Complete Response Post- Chemotherapy
Time Period
ALOXI capsules
0.5 mg (N=160)
Intravenous Palonosetron HCl
0.25 mg (N=162)
Difference
[Two-sided 98.3%
Confidence Interval]*:
Oral ALOXI capsules minus Intravenous Comparator
Acute Phase
(0 to 24 hours)
76.3%
70.4%
5.9%
[-6.5%, 18.2%]
Delayed Phase
(24 to 120 hours)
62.5%
65.4%
-2.9%
[-16.3%, 10.5%]
* To adjust for multiplicity of treatment groups, a lower-bound of a two-sided 98.3% confidence interval was used to compare to -15%, the negative value of the non-inferiority margin.
As indicated in the data above, analysis of the key secondary endpoint showed that a single dose of ALOXI capsules 0.5 mg was numerically similar to a single dose of intravenous palonosetron HCl 0.25 mg, however, statistical non-inferiority was not demonstrated. For ALOXI capsules 0.5 mg versus intravenous palonosetron HCl 0.25 mg, the proportion of patients with complete response in the acute plus delayed phase (0 to 120 hours) was 58.8% versus 59.3%, respectively. The proportions of patients with no nausea in the acute phase (0 to 24 hours) and delayed phase (24 to 120 hours) were also numerically similar between oral and intravenous doses.
Study 2 was a multicenter, open label, repeat cycle study performed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of single dose oral ALOXI capsules 0.75 mg in cancer patients receiving moderately emetogenic chemotherapy. An ALOXI capsule was given to 217 cancer patients in 654 chemotherapy cycles one hour before the start of chemotherapy. Approximately 74% of patients also received single dose oral or intravenous dexamethasone 30 minutes before chemotherapy. Complete Response was not formally evaluated for the repeat cycle application. However, in general, the antiemetic effect for the 0 to 24 hour interval was similar throughout the consecutively repeated cycles.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ALOXI (palonosetron HCl) capsules are supplied as 0.5 mg palonosetron in light beige opaque soft gelatin capsules, five capsules per bottle, each bottle packaged in a small carton (NDC #69639-104-05).
Storage
- Store at 25ºC (77ºF); excursions permitted to 15º to 30ºC (59º to 86ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Protect from light.
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
-
88436-1 - Section Title Not Found In Database
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients that hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock, have been reported in patients with intravenous administration of palonosetron HCl. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if any signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction occur with administration of ALOXI capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Advise patients of the possibility of serotonin syndrome, especially with concomitant use of ALOXI capsules and another serotonergic agent such as medications to treat depression and migraines. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if the following symptoms occur: changes in mental status, autonomic instability, neuromuscular symptoms with or without gastrointestinal symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Jointly manufactured by Catalent Pharma Solutions, Somerset NJ and Philadelphia PA, USA, and Helsinn Birex Pharmaceuticals, Dublin, Ireland
Manufactured for Helsinn Healthcare SA, Switzerland
Distributed by Helsinn Therapeutics Inc., Iselin, NJ 08830
ALOXI® is a registered trademark of Helsinn Healthcare SA, Lugano, Switzerland
PATIENT INFORMATION
ALOXI®(Ah-lock-see)
(palonosetron HCl)
capsules, for oral use
Read this Patient Information before you start taking ALOXI and each time you refill your prescription for ALOXI. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is ALOXI?
ALOXI is a prescription medicine called an “antiemetic.”
ALOXI is a prescription medicine used in adults to help prevent the nausea and vomiting that happens with certain anti-cancer medicines (chemotherapy).
It is not known if ALOXI is safe and effective in people under the age of 18 years.
Who should not take ALOXI?
Do not take ALOXI if you are allergic to palonosetron or any of the ingredients in ALOXI. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in ALOXI.
What should I tell my doctor before taking ALOXI?
Before taking ALOXI, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have had an allergic reaction to another medicine for nausea or vomiting
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if ALOXI will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if ALOXI passes into your breast milk or if it will affect your baby or your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take ALOXI.
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take, including prescriptions and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
ALOXI and certain other medicines can affect each other, causing serious side effects.
How should I take ALOXI?
- Take ALOXI exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- Take one ALOXI Capsule by mouth about one hour before you get your anti-cancer medicine (chemotherapy).
- ALOXI can be taken with or without food.
- If you take too much ALOXI, tell your doctor right away.
What are the possible side effects of ALOXI? ALOXI may cause serious side effects, including:
-
Serious allergic reactions,such as anaphylaxis. Get emergency medical help right away if you get any of the following symptoms.
- hives
- swollen face
- breathing trouble
- chest pain
-
Serotonin Syndrome. A possible life threatening problem called serotonin syndrome can happen with medicines called 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, including ALOXI, especially when used with medicines used to treat depression and migraine headaches called serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and certain other medicines. Tell your doctor or nurse right away if you have any of the following symptoms of serotonin syndrome:
- agitation, seeing things that are not there (hallucinations), confusion, or coma
- fast heartbeat or unusual and frequent changes in your blood pressure
- dizziness, sweating, flushing, or fever
- tremors, stiff muscles, muscle twitching, overactive reflexes, or loss of coordination
- seizures
- nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
The most common side effects in adults who take ALOXI capsules include: headache and constipation.
These are not all the possible side effects of ALOXI. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1- 800-FDA-1088.
General information the safe and effective use of ALOXI.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions other than those listed in a Patient Information Leaflet. Do not use ALOXI or a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ALOXI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about ALOXI that is written for health professionals. For more information call 1-844-357-4668, or go to www.ALOXI.com.
How should I store ALOXI?
- Store ALOXI at room temperature between of 68ºF to 77ºF (20ºC to 25ºC)..
- Keep ALOXI away from light.
Keep ALOXI out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in ALOXI?
Active ingredient: palonosetron hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: Mono-glycerides and di-glycerides of capryl/capric acid, glycerin, polyglyceryl oleate, water, and butylated hydroxyanisole
Jointly manufactured by Catalent Pharma Solutions, Somerset NJ and Philadelphia PA, USA, and Helsinn Birex Pharmaceuticals, Dublin, Ireland
Manufactured for Helsinn Healthcare SA, Switzerland
Distributed by Helsinn Therapeutics Inc., Iselin, NJ 08830
ALOXI® is a registered trademark of Helsinn Healthcare SA, Lugano, Switzerland
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised 04/2020
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 69639-104-05
Aloxi®
palonosetron HCl capsules
0.5 mg

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Aloxi®palonosetron HCl capsules
0.5 mg

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ALOXI
palonosetron hydrochloride capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69639-104 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PALONOSETRON HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 23310D4I19) (PALONOSETRON - UNII:5D06587D6R) PALONOSETRON 0.5 mg in 0.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CAPRYLIC/CAPRIC MONO/DI-GLYCERIDES (UNII: U72Q2I8C85) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) POLYGLYCERYL-10 OLEATE (UNII: 55C81W76DH) BUTYLATED HYDROXYANISOLE (UNII: REK4960K2U) Product Characteristics Color white (light beige opaque) Score no score Shape OVAL Size 3mm Flavor Imprint Code AIO Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69639-104-05 5 in 1 CARTON 05/28/2014 1 0.5 mg in 1 CAPSULE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA022233 05/28/2014 Labeler - Helsinn Therapeutics (U.S.), Inc. (829472583) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Catalent Pharma Solutions 825745131 manufacture(69639-104) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Catalent Pharma Solutions 014904112 label(69639-104) , pack(69639-104)
Trademark Results [ALOXI]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ALOXI 98017461 not registered Live/Pending |
Ingenus Pharmaceuticals, LLC 2023-05-29 |
 ALOXI 86911254 5144689 Live/Registered |
Helsinn Healthcare SA 2016-02-17 |
 ALOXI 86488666 not registered Indifferent |
Helsinn Healthcare SA 0000-00-00 |
 ALOXI 86488652 4897369 Live/Registered |
Helsinn Healthcare SA 2014-12-22 |
 ALOXI 76377426 2863255 Live/Registered |
Helsinn Healthcare SA 2002-03-01 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.