MAGNEVIST- gadopentetate dimeglumine injection
Magnevist by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Magnevist by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Bayer Pharma AG, Bayer AG. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MAGNEVIST® Pharmacy Bulk Package safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MAGNEVIST.
MAGNEVIST (gadopentetate dimeglumine) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1988
PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE
NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSIONWARNING: NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities.
-
Do not administer Magnevist to patients with:
- chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2), or
- acute kidney injury. (4)
- Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age > 60 years, hypertension, or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
Do not exceed the recommended Magnevist dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration. (5.1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
- Warnings and Precautions, Gadolinium Retention (5.3) 4/2018
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Magnevist is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use in diagnostic MRI in adults and children (2 years of age and older) to facilitate the visualization of lesions and abnormal vascularity in:
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Magnevist is administered intravenously, 0.2 mL/kg (0.1 mmol/kg), at a rate not to exceed 10 mL per 15 seconds. See the dosage table to determine the amount to be administered based on body weight. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Magnevist contains 0.5 mmol gadopentetate dimeglumine/mL (equivalent to 469.01 mg gadopentetate dimeglumine/mL) and is available in vials and prefilled syringes. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Magnevist is contraindicated in patients with chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2) or acute kidney injury, or history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to Magnevist. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF) has occurred in patients with impaired elimination of GBCAs. Higher than recommended dosing or repeat dosing appears to increase the risk. (5.1)
- Hypersensitivity: Anaphylactoid and anaphylactic reactions with cardiovascular, respiratory, and/or cutaneous manifestations rarely resulting in death have occurred. Monitor patients closely for need of emergency cardiorespiratory support. (5.2)
- Renal Failure: In patients with renal insufficiency, acute renal failure requiring dialysis or worsening renal function have occurred, mostly within 48 hours of Magnevist injection. (5.4)
- Gadolinium is retained for months or years in brain, bone, and other organs (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥1%) are headache, nausea, injection site coldness/localized coldness, and dizziness. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals at 1-888-84-BAYER (1-888-842-2937) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: Use only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2019
-
Do not administer Magnevist to patients with:
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Central Nervous System
1.2 Extracranial/Extraspinal Tissues
1.3 Body
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF)
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.3 Gadolinium Retention
5.4 Renal Failure
5.5 Injection Site Reactions
5.6 Interference with Visualization of Lesions Visible with Non-Contrast MRI
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle, and internal organs.
- Do not administer Magnevist to patients with:
- chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2), or
- acute kidney injury [see Contraindications (4)].
- Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age >60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
Do not exceed the recommended Magnevist dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Central Nervous System
Magnevist injection is indicated for use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in adults, and pediatric patients (2 years of age and older) to visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity in the brain (intracranial lesions), spine and associated tissues. Magnevist injection has been shown to facilitate visualization of intracranial lesions including but not limited to tumors.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of Magnevist injection is 0.2 mL/kg (0.1 mmol/kg) administered intravenously, at a rate not to exceed 10 mL per 15 seconds. Dosing for patients in excess of 286 lbs has not been studied systematically.
To ensure complete injection of Magnevist, administer 5-mL normal saline flush after the injection. The imaging procedure should be completed within 1 hour of injection of Magnevist injection.
Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use the solution if it is discolored, if particulate matter is present or if the container appears damaged.
Discard any unused portion in accordance with regulations dealing with the disposal of such materials.
DOSE AND DURATION OF MAGNEVIST INJECTION BY BODY WEIGHT
BODY WEIGHT
Total Volume, mL*
lb
kg
22
10
2
44
20
4
66
30
6
88
40
8
110
50
10
132
60
12
154
70
14
176
80
16
198
90
18
220
100
20
242
110
22
264
120
24
286
130
26
*Rate of injection: 10 mL/15 seconds
Pharmacy Bulk Package Preparation: NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION
The Pharmacy Bulk Package contains multiple single doses and is used with an appropriate transfer device for filling empty sterile syringes.
- 1. The transfer of Magnevist Injection from the Pharmacy Bulk Package must be performed in an aseptic work area, such as a laminar flow hood, using aseptic technique.
- 2. Once the Pharmacy Bulk Package is punctured, it should not be removed from the aseptic work area during the entire 24-hour period of use.
- 3. The contents of the Pharmacy Bulk Package after initial puncture should be used within 24 hours.
- 4. Any unused Magnevist Injection must be discarded 24 hours after the initial puncture of the bulk package.
IV tubing and syringes used to administer Magnevist Injection must be discarded at the conclusion of the radiological examination.
Any unused portion must be discarded in accordance with regulations dealing with the disposal of such material.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF)
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast enhanced MRI or other modalities. The GBCA-associated NSF risk appears highest for patients with chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2) as well as patients with acute kidney injury. Do not administer Magnevist to these patients. The risk appears lower for patients with chronic, moderate kidney disease (GFR 30- 59 mL/min/1.73m2) and little, if any, for patients with chronic, mild kidney disease (GFR 60- 89 mL/min/1.73m2). NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle, and internal organs. Report any diagnosis of NSF following Magnevist administration to Bayer HealthCare (1-888-842-2937) or FDA (1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch).
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. Features of acute kidney injury consist of rapid (over hours to days) and usually reversible decrease in kidney function, commonly in the setting of surgery, severe infection, injury, or drug-induced kidney toxicity. Serum creatinine levels and estimated GFR may not reliably assess renal function in the setting of acute kidney injury. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age > 60 years, diabetes mellitus or chronic hypertension), estimate the GFR through laboratory testing.
Among the factors that may increase the risk for NSF are repeated or higher than recommended doses of a GBCA and degree of renal impairment at the time of exposure. Record the specific GBCA and the dose administered to a patient. When administering Magnevist, do not exceed the recommended dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug prior to re-administration [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylactoid and anaphylactic reactions with cardiovascular, respiratory, and/or cutaneous manifestations rarely resulting in death have occurred. The risk of hypersensitivity reactions is higher in patients with a history of reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma, or allergic disorders. Hypersensitivity reactions can occur with or without prior exposure to GBCAs.
Have appropriately trained personnel administer Magnevist in a facility that has immediate availability of resuscitative equipment. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, stop Magnevist injection and immediately begin appropriate therapy.
Observe closely patients with a history of drug reactions, allergy, or other hypersensitivity disorders, during and up to several hours after Magnevist injection.
5.3 Gadolinium Retention
Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations (nanomoles per gram of tissue) have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (for example, brain, skin, kidney, liver, and spleen). The duration of retention also varies by tissue and is longest in bone. Linear GBCAs cause more retention than macrocyclic GBCAs. At equivalent doses, gadolinium retention varies among the linear agents with Omniscan (gadodiamide) and Optimark (gadoversetamide) causing greater retention than other linear agents [Eovist (gadoxetate disodium), Magnevist (gadopentetate dimeglumine), MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine)]. Retention is lowest and similar among the macrocyclic GBCAs [Dotarem (gadoterate meglumine), Gadavist (gadobutrol), ProHance (gadoteridol)].
Consequences of gadolinium retention in the brain have not been established. Pathologic and clinical consequences of GBCA administration and retention in skin and other organs have been established in patients with impaired renal function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. There are rare reports of pathologic skin changes in patients with normal renal function. Adverse events involving multiple organ systems have been reported in patients with normal renal function without an established causal link to gadolinium retention [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
While clinical consequences of gadolinium retention have not been established in patients with normal renal function, certain patients might be at higher risk. These include patients requiring multiple lifetime doses, pregnant and pediatric patients, and patients with inflammatory conditions. Consider the retention characteristics of the agent when choosing a GBCA for these patients. Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies particularly closely spaced studies, when possible.
5.4 Renal Failure
In patients with renal impairment, acute renal failure (acute kidney injury) requiring dialysis or worsening renal function has occurred, mostly within 48 hours of Magnevist injection. The risk of acute renal failure is higher with increasing dose of contrast. Use the lowest possible dose, evaluate renal function in patients with renal impairment, and allow sufficient time for contrast elimination before re-administration. Elimination half-life in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment is 3 to 4 hours. Elimination half-life in patients with severe renal impairment is about 11 hours. Magnevist is cleared by glomerular filtration and is dialyzable. After 3 dialysis sessions of 3 hours each, about 97% of the administered dose is eliminated from the body; each dialysis session removes about 70% of the circulating drug [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
5.5 Injection Site Reactions
Skin and soft tissue necrosis, thrombosis, fasciitis, and compartment syndrome requiring surgical intervention (e.g. compartment release or amputation) have occurred very rarely at the site of contrast injection or the dosed limb. Total volume and rate of Magnevist injection, extravasation of contrast agent, and patient susceptibility might contribute to these reactions. Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis may be observed generally within 24 hours after Magnevist injection and resolve with supportive treatment. Determine the patency and integrity of the intravenous line before administration of Magnevist injection. Assessment of the dosed limb for the development of injection site reactions is recommended.
5.6 Interference with Visualization of Lesions Visible with Non-Contrast MRI
As with any paramagnetic contrast agent, Magnevist injection might impair the visualization of lesions seen on non-contrast MRI. Therefore, caution should be exercised when Magnevist MRI scans are interpreted without a companion non-contrast MRI scan.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The mean age of the 1272 patients who received Magnevist injection in pre-market clinical trials was 46.4 years (range 2 to 93 years). Of these patients, 55% (700) were male and 45% (572) were female. Of the 1271 patients who received Magnevist injection and for whom race was reported, 82.1% (1043) were Caucasian, 9.7% (123) were Black, 5.3% (67) were Hispanic, 2.1% (27) were Oriental/Asian, and 0.9% (11) were other.
The most common adverse reaction was headache (4.8%). The majority of headaches were transient and of mild to moderate severity. Other adverse reactions that occurred in ≥ 1% of patients included: nausea (2.7%), injection site coldness/localized coldness (2.3%) and dizziness (1%).
The following additional adverse reactions occurred in less than 1% of the patients:
General Disorders: Injection site reactions, including phlebitis, pain, localized warmth, localized edema, and burning sensation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Substernal chest pain, back pain, pyrexia, asthenia, feeling cold, generalized warmth, fatigue, and chest tightness, and anaphylactoid reactions characterized by cardiovascular, respiratory and/or cutaneous symptoms, such as dyspnea, bronchospasm, and cough.
Cardiovascular: Hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, migraine, syncope, vasodilatation, pallor.
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal discomfort, teeth pain, increased salivation, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea.
Nervous System: Agitation, anxiety, thirst, somnolence, diplopia, loss of consciousness, convulsions (including grand mal), paresthesia.
Respiratory System: Throat irritation, rhinitis, sneezing.
Skin: Rash, sweating (hyperhidrosis), pruritus, urticaria (hives), facial edema.
Special Senses: Conjunctivitis, taste abnormality, dry mouth, lacrimation, eye irritation, eye pain, ear pain.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of Magnevist. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Anaphylactic shock, respiratory distress, and laryngeal edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cardiac/respiratory arrest, shock
- Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
- General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Adverse events with variable onset and duration have been reported after GBCA administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. These include fatigue, asthenia, pain syndromes, and heterogeneous clusters of symptoms in the neurological, cutaneous, and musculoskeletal systems.
- Skin: Gadolinium associated plaques
The most frequently reported adverse reactions in the postmarketing experience were nausea, vomiting, urticaria, and rash.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)], body temperature decreased, tremor, shivering (chills), injection site reactions including skin and soft tissue necrosis.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions that may be fatal and include cardiac or respiratory arrest, respiratory distress, cyanosis, laryngeal edema, laryngospasm, pharyngeal edema, and angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Delayed hypersensitivity reactions have been reported up to several hours after administration of Magnevist.
Renal and Urinary: Acute renal failure, worsening renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] urinary incontinence, urinary urgency.
Vascular: Thrombophlebitis, deep vein thrombophlebitis, compartment syndrome requiring surgical intervention.
Cardiac: Cardiac arrest, heart rate decreased, arrhythmia.
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: Hearing impairment.
Eye Disorders: Visual disturbance.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorder: Arthralgia.
Nervous System Disorders: Coma, anosmia, speech disorder.
Respiratory System: Respiratory arrest, pulmonary edema.
Skin: Erythema multiforme, pustules
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
GBCAs cross the placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. The human data on the association between GBCAs and adverse fetal outcomes are limited and inconclusive (see Data).
In animal reproduction studies, repeated intravenous dosing of gadopentetate dimeglumine during organogenesis resulted in delayed fetal development in pregnant rats and rabbits at a dose 2 times and 2.4 times, respectively, the recommended human dose (based on body surface area [BSA]). No teratogenic effects were observed in rats or rabbits at doses or 7.3 times (rats) and 9.7 times (rabbits) the recommended human dose, based on BSA(see Data). Because of the potential risks of gadolinium to the fetus, use Magnevist only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and is 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Contrast enhancement is visualized in the human placenta and fetal tissues after maternal GBCA administration.
Cohort studies and case reports on exposure to GBCAs during pregnancy have not reported a clear association between GBCAs and adverse effects in the exposed neonates. However, a retrospective cohort study, comparing pregnant women who had a GBCA MRI to pregnant women who did not have an MRI, reported a higher occurrence of stillbirths and neonatal deaths in the group receiving GBCA MRI. Limitations of this study include a lack of comparison with non-contrast MRI and lack of information about the maternal indication for MRI. Overall, these data preclude a reliable evaluation of the potential risk of adverse fetal outcomes with the use of GBCAs in pregnancy.
Animal Data
Gadolinium Retention
GBCAs administered to pregnant non-human primates (0.1 mmol/kg on gestational days 85 and 135) result in measurable gadolinium concentration in the offspring in bone, brain, skin, liver, kidney, and spleen for at least 7 months. GBCAs administered to pregnant mice (2 mmol/kg daily on gestational days 16 through 19) result in measurable gadolinium concentrations in the pups in bone, brain, kidney, liver, blood, muscle, and spleen at one month postnatal age.
Reproductive Toxicology
Gadopentetate dimeglumine was administered intravenous during organogenesis at doses of at 0.25, 0.75, and 1.25 mmol/kg/day for 10 consecutive days in pregnant rats and for 13 consecutive days in pregnant rabbits. Gadopentetate dimeglumine caused retardation of fetal development at a dose of 1.25 mmol per kg (rats) and 0.75 mmol per kg (rabbits); 2 times and 2.4 times, respectively, the recommended human dose (based on BSA).
Gadopentetate dimeglumine was not teratogenic in pregnant rats and rabbits when given repeatedly during organogenesis at a dose of 3 mmol per kg in rabbits and 4.5 mmol per kg in rats; 9.7 and 7.3 times, respectively, the recommended human dose (based on BSA).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited literature reports that breastfeeding after gadopentetate dimeglumine administration to the mother would result in the infant receiving an oral dose of 0.001 to 0.04% of the maternal dose. There is no information on the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or the effects of the drug on milk production. Additionally, there is limited GBCA gastrointestinal absorption. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Magnevist and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Magnevist or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Intravenous injections of gadopentetate dimeglumine (16 to 18 doses over 23 to 25 days) caused spermatogenic cell atrophy and degeneration that was irreversible in male rats at a dose of 8 times (based on BSA) the recommended human dose [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The use of Magnevist in imaging the central nervous system, extracranial/extraspinal tissues, and body have been established in the pediatric population from the ages of 2 to 16 years on the basis of adequate and well controlled clinical trials in adults and safety studies in this pediatric population [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Safety and efficacy in the pediatric population under the age of 2 years have not been established. Magnevist is eliminated primarily by the kidney. In a study with pediatric patients aged 2 months to < 2 years the pharmacokinetics (body weight-normalized clearance, body weight-normalized distribution volume, and terminal half-life) of gadopentetate were similar to adults.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
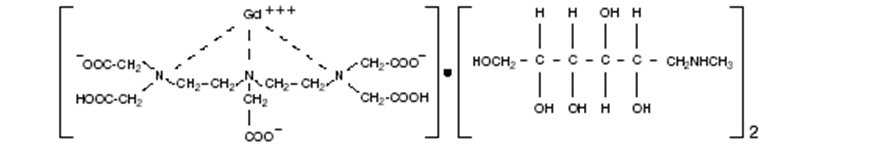
Magnevist® (brand of gadopentetate dimeglumine) injection is the N-methylglucamine salt of the gadolinium complex of diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid, and is an injectable contrast medium for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Magnevist Injection is provided as a sterile, clear, colorless to slightly yellow aqueous solution for intravenous injection.
Magnevist injection is a 0.5-mol/L solution of 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-D-glucitol dihydrogen [N,N-bis[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl] glycinato (5-) ]gadolinate(2-)(2:1) with a molecular weight of 938, an empirical formula of C28H54GdN5O20, and has the following structural formula:
Each mL of Magnevist injection contains 469.01 mg gadopentetate dimeglumine, 0.99 mg meglumine, 0.40 mg diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid, and water for injection. Magnevist injection contains no antimicrobial preservative.
Magnevist Injection has a pH of 6.5 to 8.0. Pertinent physicochemical data are noted below:
PARAMETER
Osmolality (mOsmol/kg)
at 37° C
1,960
Viscosity (CP)
at 20° C
4.9
at 37° C
2.9
Density (g/mL)
at 25° C
1.195
Specific Gravity
at 25° C
1.208
Octanol: H2O Coefficient
at 25° C, pH7 log Pow = - 5.4
Magnevist injection has an osmolality 6.9 times that of plasma, which has an osmolality of 285 mOsmol/kg water. Magnevist injection is hypertonic under conditions of use.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Gadopentetate dimeglumine is a paramagnetic agent and, as such, it develops a magnetic moment when placed in a magnetic field. The relatively large magnetic moment produced by the paramagnetic agent results in a relatively large local magnetic field, which can enhance the relaxation rates of water protons in the vicinity of the paramagnetic agent.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), visualization of normal and pathological brain tissue depends in part on variations in the radiofrequency signal intensity that occur with 1) changes in proton density; 2) alteration of the spin-lattice or longitudinal relaxation time (T1); and 3) variation of the spin-spin or transverse relaxation time (T2). When placed in a magnetic field, gadopentetate dimeglumine decreases the T1 and T2 relaxation time in tissues where it accumulates. At usual doses, the effect is primarily on the T1 relaxation time.
Disruption of the blood-brain barrier or abnormal vascularity allows accumulation of gadopentetate dimeglumine in lesions such as neoplasms, abscesses, and subacute infarcts. The pharmacokinetic parameters of Magnevist in various lesions are not known.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered gadopentetate dimeglumine in normal subjects conforms to a two compartment open-model with mean distribution and elimination half-lives (reported as mean ± SD) of about 0.2 ± 0.13 hours and 1.6 ± 0.13 hours, respectively.
Upon injection, the meglumine salt is completely dissociated from the gadopentetate dimeglumine complex. Gadopentetate is exclusively eliminated in the urine with 83 ± 14% (mean ± SD) of the dose excreted within 6 hours and 91 ± 13% (mean ± SD) by 24 hours, post-injection.
The renal and plasma clearance rates (1.76 ± 0.39 mL/min/kg and 1.94 ± 0.28 mL/min/kg, respectively) of gadopentetate are essentially identical, indicating no alteration in elimination kinetics on passage through the kidneys and that the drug is essentially cleared through the kidney. The volume of distribution (266 ± 43 mL/kg) is equal to that of extracellular water and clearance is similar to that of substances, which are subject to glomerular filtration. Following GBCA administration, gadolinium is present for months or years in brain, bone, skin, and other organs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
In vitro laboratory results indicate that gadopentetate does not bind to human plasma protein. In vivo protein binding studies have not been done.
Renal Impairment
Gadopentetate dimeglumine is excreted via the kidneys, even in patients with impaired renal function. In patients with impaired renal function, the serum half-life of gadopentetate dimeglumine is prolonged. Mean serum elimination half-lives of a single intravenous dose of gadopentetate dimeglumine (0.1 mmol/kg) were 2.6 ± 1.2 h, 4.2 ± 2.0 h and 10.8 ± 6.9 h, for mildly (creatinine clearance, CLCR = 60 to < 90 mL/min), moderately (CLCR = 30 to < 60 mL/min) and severely (CLCR = < 30 mL/min) impaired patients, respectively, as compared with 1.6 ± 0.1 h in healthy subjects.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of gadopentetate dimeglumine.
A comprehensive battery of in vitro and in vivo studies in bacterial and mammalian systems suggest that gadopentetate dimeglumine is not mutagenic or clastogenic and does not induce unscheduled DNA repair in rat hepatocytes or cause cellular transformation of mouse embryo fibroblasts. However, the drug did show some evidence of mutagenic potential in vivo in the mouse dominant lethal assay at doses of 6 mmol/kg, but did not show any such potential in the mouse and dog micronucleus tests at intravenous doses of 9 mmol/kg and 2.5 mmol/kg, respectively.
When administered intra-peritoneally to male and female rats daily prior to mating, during mating, and during embryonic development for up to 74 days (males) or 35 days (females), gadopentetate caused a decrease in number of corpora lutea at the 0.1 mmol/kg dose level. After daily dosing with 2.5 mmol/kg suppression of food consumption and body weight gain (males and females) and a decrease in the weights of testes and epididymis were also observed.
In a separate experiment in rats, daily injections of gadopentetate dimeglumine over 16 days caused spermatogenic cell atrophy at a dose level of 5 mmol/kg but not at a dose level of 2.5 mmol/kg. This atrophy was not reversed within a 16-day observation period following the discontinuation of the drug.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Magnevist injection was administered to 1272 patients in open label controlled clinical studies. The mean age of these patients was 46.4 years (range 2 to 93 years). Of these patients, 55% (700) were male and 45% (572) were female. Of the 1271 patients who received Magnevist injection and for whom race was reported, 82.1% (1043) were Caucasian, 9.7% (123) were Black, 5.3% (67) were Hispanic, 2.1% (27) were Oriental/Asian, and 0.9% (11) were other. Of the 1272 patients, 550 patients were evaluated in blinded reader studies. These evaluated the use of contrast enhancement in magnetic resonance imaging of lesions in the head and neck, brain, spine and associated tissues, and body (excluding the heart). Of the 550 patients, all patients had a reason for an MRI and efficacy assessments were based on pre-and post- Magnevist injection film quality, film contrast, lesion configuration (border, size, and location), and the number of lesions. The protocols did not include systematic verification of specific diseases or histopathologic confirmation of findings.
Of the above 550 patients, 97 patients received 0.1 mmol/kg Magnevist injection IV in two clinical trials of MAGNEVIST MRI contrast enhancement for body imaging. Of these 97, 68 had MRIs of the internal organs/structures of the abdomen or thorax (excluding the heart); 8 had breast images and 22 had images of appendages. The results of MRIs before and after Magnevist use were compared blindly. Overall additional lesions were identified in 22/97 (23%) of the patients after Magnevist injection. The mean number of lesions identified before (1.49/patient) and after Magnevist (1.75/patient) were similar. Seven (8%) of the patients had lesions seen before Magnevist that were not seen after Magnevist. Overall, after Magnevist injection, 41% of the images had a higher contrast score than before injection; and 18% of the images had a higher contrast score before Magnevist injection than after Magnevist injection. Magnevist MRI of the 8 patients with breast images were not systematically compared to the results to mammography, breast biopsy or other modalities. In the 22 patients with appendage images (e.g., muscle, bone and intraarticular structures), Magnevist MRI was not systematically evaluated to determine the effects of contrast biodistribution in these different areas.
Of the above 550 patients, 66 patients received Magnevist 0.1 mmol/kg IV in clinical trials of Magnevist MRl contrast enhancement of lesions in the head and neck. A total of 66 MRI images were evaluated blindly by comparing each pair of MRI images, before and after Magnevist injection. In these paired images, 56/66 (85%) had greater enhancement after Magnevist and 40/66 (61%) had better lesion configuration or border delineation after Magnevist. Overall, there was better contrast after Magnevist in 55% of the images, comparable enhancement in 44 (36%) before and after Magnevist, and better enhancement in 9% without Magnevist.
In the studies of the brain and spinal cord, Magnevist 0.1 mmol/kg IV provided contrast enhancement in lesions with an abnormal blood brain barrier.
In two studies, a total of 108 patients were evaluated to compare the dose response effects of 0.1 mmol/kg and 0.3 mmol/kg of Magnevist in CNS MRI. Both dosing regimens had similar imaging and general safety profiles; however, the 0.3 mmol/kg dose did not provide additional benefit to the final diagnosis (defined as number of lesions, location, and characterization).
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Magnevist injection is a clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution containing 469.01 mg/mL of gadopentetate dimeglumine. Magnevist injection is supplied in the following sizes:
- 50 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package, rubber stoppered, 10 per box NDC: 50419-188-58
- 100 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package, rubber stoppered, 10 per box NDC: 50419-188-11
16.2 Storage and Handling
Magnevist injection should be stored at controlled room temperature, between 15–30° C (59–86° F) and protected from light. DO NOT FREEZE. Should freezing occur in the bottle, Magnevist injection should be brought to room temperature before use. If allowed to stand at room temperature for a minimum of 90 minutes, Magnevist injection should return to a clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution. Before use, examine the product to assure that all solids are redissolved and that the container and closure have not been damaged. Should solids persist, discard bottle.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
GBCAs increase the risk of NSF among patients with impaired elimination of drugs. To counsel patients at risk of NSF:
- Describe the clinical manifestation of NSF
- Describe procedures to screen for the detection of renal impairment
Instruct the patients to contact their physician if they develop signs or symptoms of NSF following Magnevist administration, such as burning, itching, swelling, scaling, hardening and tightening of the skin; red or dark patches on the skin; stiffness in joints with trouble moving, bending or straightening the arms, hands, legs or feet; pain in the hip bones or ribs; or muscle weakness.
Gadolinium Retention
- Advise patients that gadolinium is retained for months or years in brain, bone, skin, and other organs in patients with normal renal function. The clinical consequences of retention are unknown. Retention depends on multiple factors and is greater following administration of linear GBCAs than following administration of macrocyclic GBCAs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
©2000, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. All rights reserved.
Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Whippany, NJ 07981
Manufactured in Germany
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
Medication Guide
MEDICATION GUIDE
MAGNEVIST (mag-na-vist)
(gadopentetate dimeglumine)
Injection for intravenous useWhat is Magnevist?
- Magnevist is a prescription medicine called a gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA). Magnevist, like other GBCAs, is injected into your vein and used with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner.
- An MRI exam with a GBCA, including Magnevist, helps your doctor to see problems better than an MRI exam without a GBCA.
- Your doctor has reviewed your medical records and has determined that you would benefit from using a GBCA with your MRI exam.
What is the most important information I should know about Magnevist?
- Magnevist contains a metal called gadolinium. Small amounts of gadolinium can stay in your body including the brain, bones, skin and other parts of your body for a long time (several months to years).
- It is not known how gadolinium may affect you, but so far, studies have not found harmful effects in patients with normal kidneys.
- Rarely, patients can feel pains, tiredness, and skin, muscle or bone ailments for a long time, but these symptoms have not been directly linked to gadolinium.
- There are different GBCAs that can be used for your MRI exam. The amount of gadolinium that stays in the body is different for different gadolinium medicines. Gadolinium stays in the body more after Omniscan or Optimark than after Eovist, Magnevist, or MultiHance. Gadolinium stays in the body the least after Dotarem, Gadavist, or ProHance.
- People who get many doses of gadolinium medicines, women who are pregnant and young children may be at increased risk from gadolinium staying in the body.
- Some people with kidney problems who get gadolinium medicines can develop a condition with severe thickening of the skin, muscles and other organs in the body (nephrogenic systemic fibrosis). Your healthcare provider should screen you to see how well your kidneys are working before you receive Magnevist.
Do not receive Magnevist if you have had a severe allergic reaction to Magnevist.
Before receiving Magnevist, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have had any MRI procedures in the past where you received a GBCA. Your healthcare provider may ask you for more information including the dates of these MRI procedures.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Magnevist can harm your unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the possible risks to an unborn baby if a GBCA such as Magnevist is received during pregnancy.
- have kidney problems, diabetes, or high blood pressure.
- have had an allergic reaction to dyes (contrast agents) including GBCAs
What are the possible side effects of Magnevist?
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Magnevist?”
- Allergic reactions. Magnevist can cause allergic reactions that can sometimes be serious. Your healthcare provider will monitor you closely for symptoms of an allergic reaction.
The most common side effects of Magnevist include: headache, nausea, injection site coldness/localized coldness, and dizziness.
These are not all the possible side effects of Magnevist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of MAGNEVIST.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your healthcare provider for information about MAGNEVIST that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in Magnevist?
Active ingredient: gadopentetate dimeglumine
Inactive ingredients: meglumine, meglumine pentetate, and water for injection
Manufactured for Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Manufactured in Germany
© 1988, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. All rights reserved.
For more information, go to www.magnevist.com or call 1-888-842-2937.
- This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 4/2018
- PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MAGNEVIST
gadopentetate dimeglumine injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50419-188 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength GADOPENTETATE DIMEGLUMINE (UNII: RH248G8V27) (GADOPENTETATE - UNII:V7OK6J19HQ) GADOPENTETATE DIMEGLUMINE 469.01 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength PENTETIC ACID (UNII: 7A314HQM0I) 0.4 mg in 1 mL MEGLUMINE (UNII: 6HG8UB2MUY) 0.99 mg in 1 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50419-188-58 10 in 1 BOX 12/14/2010 05/30/2022 1 50 mL in 1 VIAL, PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 50419-188-48 10 in 1 BOX 12/14/2010 12/15/2010 2 50 mL in 1 VIAL, PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 50419-188-11 10 in 1 BOX 12/14/2010 05/30/2022 3 100 mL in 1 VIAL, PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 4 NDC: 50419-188-49 10 in 1 BOX 12/14/2010 12/15/2010 4 100 mL in 1 VIAL, PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021037 12/14/2010 05/30/2022 Labeler - Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. (005436809) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Bayer AG 315097875 ANALYSIS(50419-188) , API MANUFACTURE(50419-188) , LABEL(50419-188) , MANUFACTURE(50419-188) , PACK(50419-188) , STERILIZE(50419-188)
Trademark Results [Magnevist]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 MAGNEVIST 74186321 1797473 Live/Registered |
BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC 1991-07-18 |
 MAGNEVIST 73555552 1413925 Live/Registered |
BERLEX LABORATORIES, INC. 1985-08-26 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.