MODEYSO- dordaviprone capsule
MODEYSO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
MODEYSO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc., API, Inc., Robertson Microlit Laboratories, Inc., Frontida BioPharm, LLC, Frontage Laboratories, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MODEYSO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MODEYSO.
MODEYSO™ (dordaviprone) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025INDICATIONS AND USAGE
MODEYSO is a protease activator indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with diffuse midline glioma harboring an H3 K27M mutation with progressive disease following prior therapy. (1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on response rate and duration of response [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Select patients for treatment with MODEYSO based on the presence of an H3 K27M mutation from tumor specimens. (2.1)
- Monitor ECG and electrolytes before starting MODEYSO and periodically during treatment as clinically indicated. (2.2)
- The recommended dose in adult patients is 625 mg orally once weekly. (2.3)
- The recommended dose in pediatric patients weighing ≥10 kg is based on body weight (see Table 1). (2.3)
- Take MODEYSO orally once weekly on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 3 hours after food intake. (2.3)
- Continue MODEYSO until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Capsules: 125 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity: If clinically significant hypersensitivity or anaphylaxis occur, immediately discontinue MODEYSO and initiate appropriate medical treatment and supportive care. (5.1)
- QTc Interval Prolongation: MODEYSO causes concentration dependent QTc interval prolongation. Interrupt or reduce the dose of MODEYSO in patients who develop QT prolongation, and permanently discontinue MODEYSO in patients with signs of life-threatening arrhythmias. (5.2, 12.2)
- Embryo-fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.3, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions are fatigue, headache, vomiting, nausea, and musculoskeletal pain. The most common (≥2%) Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities are decreased lymphocytes, decreased calcium, and increased alanine aminotransferase. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Chimerix at toll-free phone # 1-866-662-2679 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors with MODEYSO. If concomitant use cannot be avoided for adults and pediatric patients who weigh at least 52.5 kg, reduce the dose of MODEYSO as recommended. (2.5, 7.1)
- CYP3A4 Inducers: Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A4 inducers with MODEYSO. (7.1)
- Drugs Known to Prolong QTc Interval: Avoid concomitant use of MODEYSO with products known to prolong the QTc interval. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, separate administration of MODEYSO and the QT-prolonging product. (5.2, 7.2, 12.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 1/2026
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
2.2 Recommended Testing Before Starting MODEYSO
2.3 Recommended Dosage and Administration
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.5 Dosage Modifications for CYP3A4 Inhibitors
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
5.2 QTc Interval Prolongation
5.3 Embryo-fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on MODEYSO
7.2 Drugs Known to Prolong QTc Interval
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
MODEYSO is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with diffuse midline glioma harboring an H3 K27M mutation with progressive disease following prior therapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment with MODEYSO based on the presence of an H3 K27M mutation from tumor specimens [see Clinical Studies (14)]. An FDA-approved test for the detection of this mutation is not currently available.
2.2 Recommended Testing Before Starting MODEYSO
Monitor electrocardiograms (ECG) and electrolytes before starting MODEYSO and periodically during treatment as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
2.3 Recommended Dosage and Administration
Take MODEYSO on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 3 hours after food intake [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Adults
The recommended dosage of MODEYSO is 625 mg orally once weekly.
Pediatrics
The recommended dosage of MODEYSO in pediatric patients aged 1 to <17 years who weigh at least 10 kg is based on body weight (Table 1). A recommended dosage of MODEYSO has not been established in pediatric patients who weigh less than 10 kg.
Table 1: Recommended Body Weight-Based Dosage for Pediatric Patients Body Weight (kg)
Recommended Dosage
10 kg to <12.5 kg
125 mg Once Weekly
12.5 kg to <27.5 kg
250 mg Once Weekly
27.5 kg to <42.5 kg
375 mg Once Weekly
42.5 kg to <52.5 kg
500 mg Once Weekly
≥52.5 kg
625 mg Once Weekly
Continue MODEYSO until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
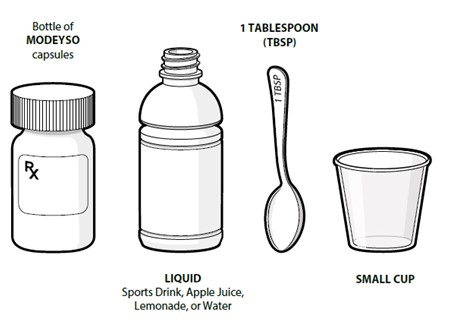
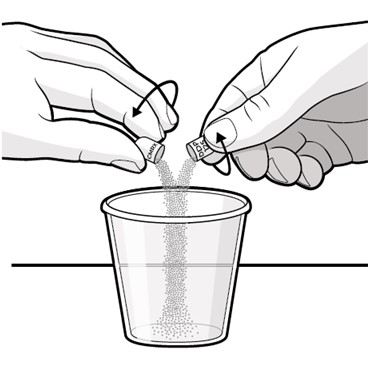
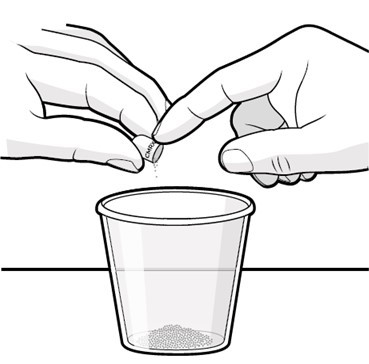
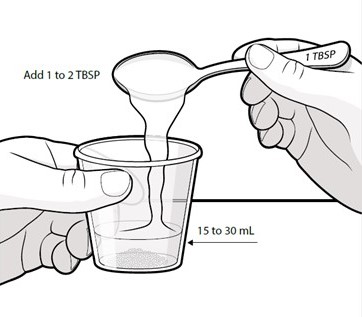
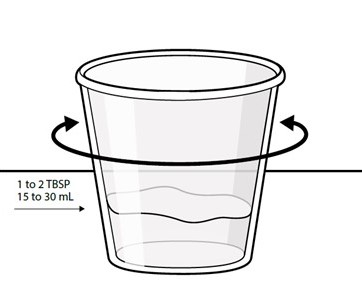
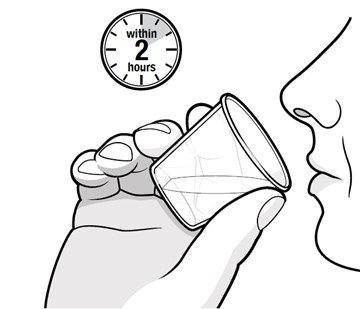
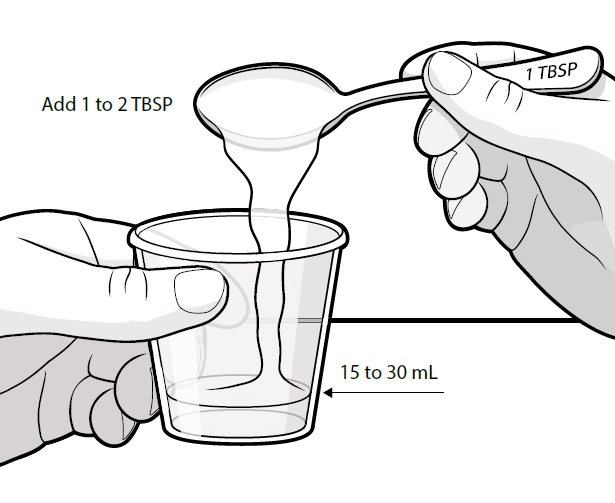
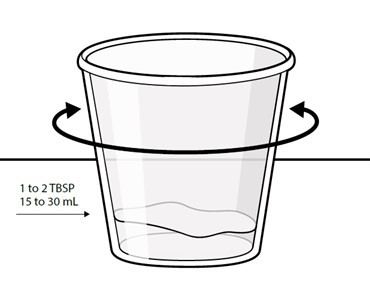
Swallow capsules whole. For patients unable to swallow capsules whole, open each capsule, mix contents with approximately 15 to 30 mL of liquid (sports drink, apple juice, lemonade, or water) before administration, and administer orally as a liquid [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Once mixed, administer within 2 hours of preparation, or discard and mix a new dose.
Vomiting
If vomiting occurs after taking a dose, do not take an additional dose and take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time.
Missed Dose
If a dose is missed within 2 days, take the missed dose as soon as possible. If a dose is missed by more than 2 days, skip the missed dose and take the next dose at the scheduled time.
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dosage reductions for adverse reactions for MODEYSO are provided in Table 2.
Table 2: Recommended Dosage Reductions for Adverse Reactions Patient’s Weight (kg)
First Dosage Reduction
Second Dosage Reduction
Pediatric patients 10 kg to <12.5 kg
Permanently discontinue
N/A
Pediatric patients 12.5 kg to <27.5 kg
125 mg once weekly
Permanently discontinue
Pediatric patients 27.5 kg to <42.5 kg
250 mg once weekly
125 mg once weekly
Pediatric patients 42.5 kg to <52.5 kg
375 mg once weekly
250 mg once weekly
Pediatric patients ≥52.5 kg and adult patients
500 mg once weekly
375 mg once weekly
The recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions are provided in Table 3.
Table 3: Recommended Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions Adverse Reaction
Severitya
Dosage Modificationb
Hypersensitivity
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]Any grade
If hypersensitivity is suspected based on clinical judgement, interrupt MODEYSO until resolution of the event.
Permanently discontinue MODEYSO in patients who develop serious hypersensitivity reactions.
QTc Interval Prolongation
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]QTc absolute value >500 ms
or
An increase of >60 ms from baseline
Interrupt MODEYSO until QTc interval ≤480 ms or return to baseline.
Resume MODEYSO at the next lower dose level.
Torsades de pointes, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia or signs or symptoms of serious or
life-threatening arrhythmiaPermanently discontinue MODEYSO.
Other Adverse Reactions
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]Grade 3 or 4
Interrupt MODEYSO until ≤Grade 1 or return to baseline.
Resume MODEYSO at the next lower dose level.
Recurrent Grade 4
Permanently discontinue MODEYSO.
a. National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 5.0.
b. See Table 2 for recommended dosage reductions.
2.5 Dosage Modifications for CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors with MODEYSO.
- If concomitant use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor cannot be avoided for adult and pediatric patients who weigh at least 52.5 kg, reduce the dose of MODEYSO from 625 mg to 375 mg once weekly.
- If concomitant use of a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor cannot be avoided for adult and pediatric patients who weigh at least 52.5 kg, reduce the dose of MODEYSO from 625 mg to 500 mg once weekly.
- The recommended dosage for pediatric patients weighing less than 52.5 kg who are receiving strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors has not been established.
Upon discontinuation of the CYP3A4 inhibitor, wait for 3 to 5 plasma half-lives of the CYP3A4 inhibitor, then increase MODEYSO to the dose that was taken before starting the CYP3A4 inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
MODEYSO can cause severe hypersensitivity reactions.
In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], Grade 3 hypersensitivity reactions occurred in 0.3% of patients receiving MODEYSO. Signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity may include rash, hives, fever, low blood pressure, wheezing, or swelling of the face or throat.
Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions and instruct them to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms occur.
If clinically significant hypersensitivity or anaphylaxis occur, immediately interrupt MODEYSO and initiate appropriate medical treatment and supportive care. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, temporarily interrupt or permanently discontinue MODEYSO [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.2 QTc Interval Prolongation
MODEYSO causes a concentration-dependent QTc interval prolongation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)], which can increase the risk for ventricular tachyarrhythmias (e.g., torsades de pointes) or sudden death.
In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], of the 82 patients who underwent at least one post-baseline ECG assessment, 6% experienced an increase in QTc of >60 msec compared to baseline after receiving MODEYSO and 1.2% had an increase in QTc to >500 msec.
Monitor ECGs and electrolytes prior to starting MODEYSO and then periodically during treatment as clinically indicated.
Significant prolongation of the QT interval may occur when MODEYSO is taken concomitantly with other products that have a known potential to prolong the QT interval. Avoid concomitant use of MODEYSO with products known to prolong the QT interval. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, separate administration of MODEYSO and the QT-prolonging product [see Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Increase the frequency of monitoring when administering MODEYSO to patients taking other products that have a known potential to prolong the QT interval and in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, existing QTc prolongation, a history of ventricular arrhythmias, electrolyte abnormalities, heart failure, or who are taking strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors. Interrupt or reduce the dose of MODEYSO in patients who develop QT prolongation, and permanently discontinue MODEYSO in patients with signs of life-threatening arrhythmias [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, MODEYSO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In embryo-fetal development studies, oral administration of dordaviprone to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis caused embryo-fetal mortality, alterations to growth, and structural abnormalities at exposures below the human exposure at the highest recommended dose.
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 month after the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following potential clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labelling:
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- QTc Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population described in WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS and below reflects exposure to MODEYSO at the recommended weight-based dose taken until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity in 376 adult and pediatric patients with glioma across four open-label clinical studies (ONC006, ONC013, ONC014, and ONC018) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Of the 376 patients who received MODEYSO, 35% were exposed for 6 months, and 17% were exposed for 1 year.
The median age was 23 years (range: 3 to 80): 30% were 2 to 11 years old, 11% were 12 to 17 years old, 55% were 18 to 64 years old, and 3.7% were 65 years or older. Fifty-two percent (52%) were female; 74% White, 10% unknown race or race not reported, 9% Black or African American, 4% Asian, 2.9% other or multiple races; and 13% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Karnofsky/Lansky Performance Status (KPS/LPS) score was 80 to 100 in 66% of patients, 60 to 70 in 27%, and <60 in 7%.
Relevant disease characteristics included primary tumor locations in the midline (91%) and non‑midline regions (9%); 33% had diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG); 30% had multifocal disease; 79% had an H3 K27M mutation; 75% had recurrent disease.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 33% of patients who received MODEYSO. Serious adverse reactions in >2% of patients included hydrocephalus (5%), vomiting (4.3%), headache (3.2%), seizure (2.4%), and muscular weakness (2.1%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1% of patients who received MODEYSO, including cardiac arrest (0.5%), intracranial hemorrhage (0.3%), and encephalopathy (0.3%).
Permanent discontinuation of MODEYSO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 2.1% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of MODEYSO in >1 patient included confusional state.
Dosage interruptions of MODEYSO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 6% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in >1 patient included increased alanine aminotransferase, increased aspartate aminotransferase, decreased lymphocyte count, muscular weakness, and aspiration pneumonia.
Dose reductions of MODEYSO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 2.7% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in >1 patient included decreased neutrophil count and increased alanine aminotransferase.
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were fatigue, headache, vomiting, nausea, and musculoskeletal pain. The most common (≥2%) Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were decreased lymphocytes, decreased calcium, and increased alanine aminotransferase.
Adverse reactions that occurred in at least 10% of patients treated with MODEYSO are presented in Table 4.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions (≥10%) in Patients with Glioma Who Received MODEYSO in ONC006, ONC013, ONC014, and ONC018 Adverse Reaction
MODEYSO
(N=376)
All Grades (%)
Grade 3 or 4 (%)
General Disorders
Fatiguea
34
3.2
Gait disturbance
16
3.7
Nervous System Disorders
Headacheb
32
4.3
Cranial nerve disordersc
16
1.3
Hemiparesis
15
4.5
Dysarthria
13
2.7
Dizziness
13
0.5
Ataxia
10
1.3
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Vomiting
24
2.7
Nausea
24
0.8
Dysphagia
13
2.1
Constipation
11
0
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
Musculoskeletal paind
20
2.9
Muscular weakness
13
4.5
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders
Hyperglycemia
12
0.8
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Rashe
11
0.8
a. Includes asthenia.
b. Includes head discomfort and sinus headache.
c. Includes accessory nerve disorder, auditory nerve disorder, facial nerve disorder, facial paralysis, facial paresis, glossopharyngeal nerve disorder, hypoglossal nerve disorder, IIIrd nerve disorder, IIIrd nerve paralysis, IVth nerve disorder, IVth nerve paralysis, tongue paralysis, trigeminal nerve disorder, trigeminal neuralgia, VIth nerve disorder, VIth nerve paralysis, and VIth nerve paresis.
d. Includes back pain, pain in extremity, arthralgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, myalgia, bone pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, and spinal pain.
e. Includes dermatitis, dermatitis acneiform, dermatitis bullous, eczema, erythema multiforme, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, rash pruritic, and rash pustular.
Other clinically important adverse reactions observed in less than 10% of patients treated with MODEYSO were peripheral neuropathy, seizure, diarrhea, tremor, and venous thromboembolic events.
Selected laboratory abnormalities that occurred in at least 10% of patients treated with MODEYSO are presented in Table 5.
Table 5: Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥10%) that Worsened from Baseline in Patients with Glioma Receiving MODEYSO in ONC006, ONC013, ONC014, and ONC018 Laboratory Abnormalitya
MODEYSOb
All Grades (%)
Grade 3 or 4 (%)
Chemistry
Alanine aminotransferase increased
28
2.4
Aspartate aminotransferase increased
22
0.9
Calcium decreased
20
2.7
Sodium decreased
14
0.3
Potassium decreased
13
0.3
Glucose decreased
11
0
Alkaline phosphatase increased
11
0.3
Hematology
Hemoglobin decreased
25
0.6
Neutrophils decreased
24
1.5
Lymphocytes decreased
19
7
a. Severity as defined by the National Cancer Institute CTCAE Version 5.0.
b. The denominator for each laboratory parameter is based on the number of patients with a baseline and post‑treatment laboratory value available, which ranged from 325 to 330 patients.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on MODEYSO
Table 6 describes drug interactions where concomitant use of another drug affects MODEYSO.
Table 6: Effect of Other Drugs on MODEYSO Strong and Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Prevention or Management
- Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors with MODEYSO.
- If concomitant use cannot be avoided for adults and pediatric patients who weigh at least 52.5 kg, reduce the MODEYSO dose as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Mechanism and Clinical Effects
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers
Prevention or Management
- Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A4 inducers with MODEYSO.
Mechanism and Clinical Effects
- Dordaviprone is a CYP3A4 substrate.
- Strong and moderate CYP3A4 inducers decrease dordaviprone exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce the anti-tumor activity of MODEYSO.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], MODEYSO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on MODEYSO use in pregnant women to inform a drug‑associated risk.
In animal embryo-fetal development studies, oral administration of dordaviprone to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis caused embryofetal mortality, alterations to growth, and structural abnormalities at exposures below the human exposure at the highest recommended dose (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study, dordaviprone was administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis from gestation day 7 to 17 at doses of 25, 62.5, and 125 mg/kg/day. Dordaviprone caused maternal mortality, pre-implantation loss, and embryo-fetal toxicity of absent eye and small renal papillae at the 125 mg/kg/day dose (≥2 times the human recommended doses based on body surface area). In an embryo-fetal development study, dordaviprone was administered orally to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 7 to 19 at doses of 10, 25, 62.5, and 100 mg/kg/day. Dordaviprone caused maternal mortality, embryo‑fetal mortality, lower fetal weights, and structural malformations of the face, limbs, vessels, brain, and heart at doses of ≥10 mg/kg/day (≥0.4 times the human exposure at the highest recommended dose based on Cmax).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of dordaviprone or its metabolites in human milk, their effects on a breastfed child, or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children from MODEYSO, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
MODEYSO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating MODEYSO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Males
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 month after the last dose.
Infertility
Based on the mechanism of action of dordaviprone (dopamine D2 receptor inhibition and alterations to mitochondrial function), treatment with MODEYSO may adversely impact fertility in males and females.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of MODEYSO has been established in pediatric patients aged 1 year and older for the treatment of diffuse midline glioma harboring an H3 K27M mutation [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14)].
The efficacy of MODEYSO was evaluated in 4 pediatric patients aged 9 to 17 years with diffuse midline glioma harboring an H3 K27M mutation. Safety was evaluated in 154 pediatric patients with glioma aged 3 to 17 years who received MODEYSO at the recommended dose across four open‑label clinical studies (ONC006, ONC013, ONC014, and ONC018). Of these 154 patients, 73% were 3 to 11 years of age and 27% were 12 to 17 years of age. No additional safety signals were observed in pediatric patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The exposure of dordaviprone in pediatric patients weighing 10 kg and higher is predicted to be within the range of exposures predicted in adults at the recommended dosage [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The safety and effectiveness of MODEYSO have not been established in pediatric patients less than 1 year of age.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 376 patients with glioma who received MODEYSO at the recommended dose across four open-label clinical studies (ONC006, ONC013, ONC014, and ONC018), 3.7% of patients were ≥65 years of age and 0.5% were ≥75 years of age. Clinical studies of MODEYSO did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Dordaviprone is a protease activator.
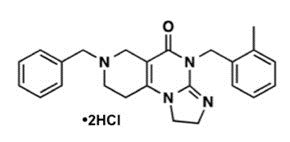
Dordaviprone is present as dordaviprone hydrochloride with the molecular formula C24H26N4O2HCl. The molecular weight is 459.41. The full chemical name for dordaviprone hydrochloride is 7-benzyl-4-(2-methylbenzyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9-hexahydroimidazo[1,2-a]pyrido[3,4-e]pyrimidin-5(4H)-one dihydrochloride.
Dordaviprone hydrochloride has the following chemical structure:
Dordaviprone hydrochloride is a white to off-white solid that is freely soluble in water. The 1% solution of dordaviprone hydrochloride is measured as pH 3.3.
MODEYSO (dordaviprone) capsules are supplied as 125 mg strength capsules in an immediate‑release oral formulation. Each MODEYSO capsule contains 125 mg of dordaviprone (equivalent to 148.8 mg of dordaviprone hydrochloride).
The inactive ingredients in the capsule include magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate. The capsule shell consists of hypromellose and titanium dioxide. The black printing ink contains alcohol, D&C yellow #10, FD&C blue #1, FD&C blue #2, FD&C red #40, ferrosoferric oxide, methyl alcohol, N‑butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and shellac glaze (20% esterified).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dordaviprone is a protease activator of the mitochondrial caseinolytic protease P (ClpP). Dordaviprone also inhibits the dopamine D2 receptor.
Diffuse midline gliomas harboring an H3 K27M mutation are associated with the loss of H3 K27 trimethylation. In-vitro, dordaviprone activated the integrated stress response, induced apoptosis, and altered mitochondrial metabolism leading to restored histone H3 K27 trimethylation in H3 K27M-mutant diffuse glioma models.
Dordaviprone exhibited antitumor activity in cell-based assays and in vivo models of H3 K27M-mutant diffuse glioma.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At 1.2 times the maximum recommended dose, the estimated mean QTcF change was 11.8 msec (90% CI: 9.8, 13.7) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the safety and effectiveness of dordaviprone have not been fully characterized.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Dordaviprone pharmacokinetics were predicted following a single dose in patients at the approved recommended dosage and are presented as mean (CV%) unless otherwise specified. Dordaviprone maximum concentration (Cmax) is 2.8 mcg/mL (42%), and total systemic exposure (AUC) is 23 hr·mcg/mL (48%). Dordaviprone Cmax and AUC increased in a dose proportional manner over the dose range of 125 to 625 mg. No accumulation is observed following once weekly dosing.
Absorption
Dordaviprone median (min, max) time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) is 1.4 hours (0.5, 5.6 hours).
Food Effect
Dordaviprone Cmax decreased by 40% with no change on AUC following administration with a high-fat meal (800 to 1,000 calories, 50% fat).
Distribution
Dordaviprone apparent (oral) volume of distribution is 450 L (40%).
Dordaviprone plasma protein binding is 95% to 97% and independent of concentrations in vitro.
The median blood-to-plasma ratio is 0.67 in vitro.
Metabolism
Dordaviprone is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 with minor contribution from CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, and CYP3A5.
Excretion
Dordaviprone mean terminal half-life is 11 hours (30%), and the apparent clearance is approximately 27 L/hr (48%).
Following a single dose of radiolabeled dordaviprone, 70% of the dose was recovered in urine and 20% in feces with no notable unchanged dordaviprone in urine or feces.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of dordaviprone were observed based on age (3 to 90 years), sex, race (74% White, 9% Black or African American, or 5% Asian) or mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ULN with AST >ULN or total bilirubin >1 to 1.5 times ULN with any AST).
The effect of severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >3 times ULN with any AST) on dordaviprone pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Pediatric Patients
The exposure of dordaviprone in pediatrics weighing 10 kg and higher is predicted to be within the range of exposures predicted in adults at the recommended dosage.
Renal Impairment
Following a single oral dose of 375 mg (0.6 times the maximum approved recommended dose), dordaviprone AUC increased by 1.5-fold and Cmax by 1.1-fold in subjects with severe renal impairment (CLcr <30 mL/min, estimated by the Cockcroft-Gault equation).
Hepatic Impairment
Following a single oral dose of 125 mg (0.2 times the maximum approved recommended dose) dordaviprone AUC increased by 1.5-fold and Cmax by 1.2-fold in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh class B).
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Dordaviprone Cmax increased by 2-fold and AUC increased by 4-fold following concomitant administration of itraconazole (strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) 200 mg once daily for 8 days.
Dordaviprone Cmax is predicted to increase by ~1.5-fold and AUC by 2.5-fold following concomitant administration of fluconazole or erythromycin (moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor).
CYP3A4 Inducers: Dordaviprone Cmax is predicted to decrease by 68% and AUC by 83% following concomitant administration of rifampin (strong CYP3A4 inducer) and dordaviprone Cmax is predicted to decrease by 44% and AUC by 65% following concomitant administration of efavirenz (moderate CYP3A4 inducer).
Other Drugs: No clinically significant difference in dordaviprone pharmacokinetics is predicted when used concomitantly with cimetidine (weak CYP3A4 inhibitor).
No clinically significant difference in dordaviprone pharmacokinetics is observed with multiple doses of a rabeprazole (proton-pump inhibitor).
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of the following drugs are predicted following concomitant use with MODEYSO: dabigatran etixelate (P-gp substrate), rosuvastatin (BCRP substrate), midazolam (CYP3A substrate), desipramine (CYP2D6 substrate) and repaglinide (CYP2C8 substrate).
In Vitro Studies
CYP Enzymes: Dordaviprone inhibits CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP2C19 and induces CYP2B6.
Transporter Systems: Dordaviprone inhibits MATE1, MATE2-K, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and OCT1.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies with dordaviprone were not conducted.
Mutagenesis
Dordaviprone was not genotoxic in in vitro (Ames and micronucleus assay) and in vivo (mouse micronucleus) assays.
Impairment of Fertility
Dedicated fertility studies were not conducted with dordaviprone.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
The nonclinical safety profile of dordaviprone reflects the on-target pharmacology and dopamine receptor inhibition. In repeat-dose toxicology studies of up to 13 weeks in duration, weekly oral administration of dordaviprone to dogs caused central nervous system-related toxicities including whole body tremors, cranial tremors, seizures, excessive salivation, lateral recumbency, rigidity, paddling of limbs, overall rigid body, salivation, abnormal gait/stance, and twitching at doses resulting in less than or equal to 0.7 times the human exposure at the highest recommended dose based on AUC. In a 13-week repeat-dose toxicology study in rats, mammary gland hyperplasia occurred at doses resulting in 0.11 times the human exposure at the highest recommended dose based on AUC.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of MODEYSO was evaluated in adult and pediatric patients with glioma across five open‑label, non-randomized clinical studies conducted in the U.S. (ONC006 [NCT02525692], ONC013 [NCT03295396], ONC014 [NCT03416530], ONC016 [NCT05392374], and ONC018 [NCT03134131]). Pre-specified criteria were defined to establish an integrated efficacy population; eligible patients were required to have received single-agent MODEYSO, have diffuse midline glioma harboring an H3 K27M mutation with progressive and measurable disease per Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology-High Grade Glioma (RANO-HGG) criteria, be ≥90 days post‑radiation therapy, have adequate washout from prior anticancer therapies, have a Karnofsky Performance Status/Lansky Performance Status (KPS/LPS) score ≥60, and have stable or decreasing corticosteroid use. Patients with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG), primary spinal tumors, atypical histologies, or cerebrospinal fluid dissemination were excluded. Patients received weight-based dosing of MODEYSO until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The integrated efficacy population included 50 patients who met these criteria. The major efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR) assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR) according to RANO 2.0 criteria. Additional efficacy outcome measures were BICR-assessed ORR according to RANO-HGG criteria and Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology-Low Grade Glioma (RANO-LGG) criteria, duration of response, and time to response.
Baseline demographics were: median age 31 years (range: 9 to 70) with 6% younger than 17 years of age; 46% female; 80% White, 6% Black or African American, 2% Asian, 10% other races, and 2% race unknown; 8% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity; 72% had KPS/LPS 80 to 100. Relevant disease characteristics included 72% treated at first recurrence, 28% had 2 or more recurrences; primary tumor location was thalamic in 52% and non-thalamic midline region in 48%; 88% received prior temozolomide; 62% were receiving corticosteroids at baseline; median time from end of prior radiation was 7.4 months (range: 3.0 to 102.1).
Efficacy results are shown in Table 8.
Table 8: Efficacy Results for Patients with Diffuse Midline Glioma Harboring an H3 K27M Mutation in Studies ONC006, ONC013, ONC014, ONC016, and ONC018 per RANO 2.0 Efficacy Parameter
MODEYSO
N=50
Overall Response Rate (95% CI)a
22% (12, 36)
Partial response (PR)
16%
Minor response (MR)
6%
Duration of Response
N=11
Median (95% CI)b, months
10.3 (7.3, 15.2)
% with observed DOR ≥6 monthsc
73%
% with observed DOR ≥12 monthsc
27%
Abbreviations: BICR=blinded independent central review; CI=confidence interval; RANO=Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology.
a. Confirmed overall response rate assessed by BICR; CI based on Clopper-Pearson method.
b. Based on Kaplan-Meier estimate.
c. Based on observed time.
Among responders, the median time to response was 3.6 months (range 1.6, 15.6).
Using BICR-assessed RANO 2.0 criteria, there was one additional responder based on the integrated response assessment, which takes into account corticosteroid use and performance status. Based on BICR-assessed RANO-HGG criteria (n=50), the ORR was 20% (95% CI: 10, 34), with 1 complete and 9 partial responses. Based on BICR-assessed RANO-LGG criteria (n=50), the ORR was 20% (95% CI: 10, 34), with 5 partial and 5 minor responses.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Strength
Description
Package Configuration
NDC Number
125 mg
White, opaque, hard capsules printed with “DDP” and “125” on the body and “CMRX” on the cap of the capsule.
Each bottle contains 10 capsules and desiccant with a child‑resistant closure.
68727-250-01
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient and caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Hypersensitivity
Advise patients that MODEYSO can cause hypersensitivity. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions and instruct patients or caregivers to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
QTc Interval Prolongation
Advise patients that MODEYSO can cause QTc interval prolongation. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of QTc prolongation and instruct patients or caregivers to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Drug Interactions
Inform patients that MODEYSO may interact with some drugs. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products. Additionally, patients should consult their healthcare provider before starting or stopping any prescription drug, nonprescription drug, or supplement [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Administration
Instruct patients and caregivers to read the Instructions for Use before taking MODEYSO, and each time the patient gets a refill as there may be new information they need to know.
Patients should take MODEYSO orally once weekly on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 3 hours after food intake. Take the prescribed dose at the same time on the same day of the week [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Instruct patients to swallow capsules whole. For patients unable to swallow capsules whole, instruct patients to open capsules and mix contents with approximately 15 to 30 mL of liquid (sports drink, apple juice, lemonade, or water). Instruct patients to drink the mixture. After drinking the mixture, instruct patients to add another 15 to 30 mL of the liquid to the container, swirl to dissolve any remaining medication, and then drink the remaining contents [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Instructions for Use].
Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Distributed by:
Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Palo Alto, CA 94306
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
MODEYSO (moh-DAY-soh)
(dordaviprone)
capsules, for oral use
What is MODEYSO?
MODEYSO is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children 1 year of age and older with a certain type of brain tumor called diffuse midline glioma that has a specific “H3 K27M” gene mutation and has worsened after other treatments.
It is not known if MODEYSO is safe and effective in children less than 1 year of age.
Before taking MODEYSO, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have heart failure or heart rhythm problems, including QT prolongation and long QT syndrome.
-
are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. MODEYSO can harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think that you may be pregnant during treatment with MODEYSO.
- o Your healthcare provider should check to see if you are pregnant before you begin treatment with MODEYSO.
- o Females who are able to become pregnant should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 month after your last dose.
- o Males with partners who are able to become pregnant should use effective contraception during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 month after your last dose.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if MODEYSO passes into breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with MODEYSO and for 1 week after your last dose. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during this time.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. MODEYSO and other medicines may affect the way each other work and may cause serious side effects. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of medications that interact with MODEYSO.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist. Do not start or stop taking any new medicines without first talking to your healthcare provider.
How should I take MODEYSO?
- Take MODEYSO exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking MODEYSO without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose, temporarily stop, or completely stop treatment with MODEYSO if you develop certain side effects.
- Take MODEYSO 1 time each week on the same day of the week. Take all of the capsules prescribed for your dose at the same time.
- Take MODEYSO on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 3 hours after eating food.
- Swallow MODEYSO capsules whole. If the capsules cannot be swallowed whole, see the detailed Instructions for Use for how to prepare and take or give MODEYSO as a liquid.
- If vomiting happens after taking a dose of MODEYSO, do not take another dose. Take the next dose of MODEYSO on the next regularly scheduled weekly day of the week.
-
If you miss a weekly dose of MODEYSO by:
- o 2 days or less, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Take the next dose of MODEYSO on the next regularly scheduled day of the week.
- o More than 2 days, skip the missed dose and take the next dose of MODEYSO on the next regularly scheduled day of the week.
What are the possible side effects of MODEYSO?
MODEYSO may cause serious side effects, including:
-
Allergic reactions. Allergic reactions may happen during treatment with MODEYSO and can be severe. Stop taking MODEYSO and get immediate emergency medical help right away if you get any signs or symptoms of allergic reactions, including:
- o rash
- o hives
- o fever
- o feeling faint or dizzy
- o wheezing or trouble breathing
- o swelling of the face or throat
-
Heart rhythm problems (QTc interval prolongation). MODEYSO can cause changes in the electrical activity of your heart and can increase your chance of getting a type of abnormal heart rhythm that can lead to sudden death called torsades de pointes. Before you start treatment and during treatment as needed, your healthcare provider will check your heart using an electrocardiograph (ECG) and check your blood levels of salts called electrolytes. Get emergency medical help right away if you get any signs or symptoms of abnormal heart rhythm, including:
- o feeling lightheaded or faint
- o dizziness
- o fast heartbeat
- o heart palpitations
- o shortness of breath
The most common side effects of MODEYSO include:
- tiredness
- headache
- vomiting
- nausea
- muscle, joint, and bone pain
The most common abnormal blood tests include decreased white blood cells, decreased red blood cells, decreased calcium, and increased liver enzymes.
MODEYSO may cause fertility problems in males and females, which may affect your ability to have children. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you.
These are not all of the possible side effects of MODEYSO. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1‑800‑FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to Chimerix, Inc. at 1-866-662-2679.
How should I store MODEYSO?
- Store MODEYSO at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- The MODEYSO bottle has a child-resistant closure.
Keep MODEYSO and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of MODEYSO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use MODEYSO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give MODEYSO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about MODEYSO that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in MODEYSO?
Active ingredient: dordaviprone
Inactive ingredients: magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate. The capsule shell contains hypromellose and titanium dioxide. The black printing ink contains alcohol, D&C yellow #10, FD&C blue #1, FD&C blue #2, FD&C red #40, ferrosoferric oxide, methyl alcohol, N-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and shellac glaze (20% esterified).
Distributed by:
Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Palo Alto, CA 94306
For more information, contact Chimerix, Inc. at 1-866-662-2679.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 08/2025
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 08/2025
- PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MODEYSO
dordaviprone capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68727-250 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DORDAVIPRONE (UNII: 9U35A31JAI) (DORDAVIPRONE - UNII:9U35A31JAI) DORDAVIPRONE 125 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE 112 (UNII: X7XJ6RM9Q2) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO (UNII: 5856J3G2A2) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 16mm Flavor Imprint Code CMRX;DDP;125 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68727-250-01 1 in 1 CARTON 08/06/2025 1 10 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA219876 08/06/2025 Labeler - Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (135926363) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations API, Inc. 048504349 API MANUFACTURE(68727-250) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Robertson Microlit Laboratories, Inc. 177250289 ANALYSIS(68727-250) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Frontida BioPharm, LLC 080243260 MANUFACTURE(68727-250) , ANALYSIS(68727-250) , PACK(68727-250) , LABEL(68727-250) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Frontage Laboratories, Inc. 832653625 ANALYSIS(68727-250)
Trademark Results [MODEYSO]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 MODEYSO 97901513 not registered Live/Pending |
Chimerix, Inc. 2023-04-21 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.