GONAL-F- follitropin alfa kit
Gonal-f by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Gonal-f by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by EMD Serono, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection) is a human follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) preparation of recombinant DNA origin, which consists of two non-covalently linked, non-identical glycoproteins designated as the α- and β-subunits. The α- and β-subunits have 92 and 111 amino acids, respectively, and their primary and tertiary structure are indistinguishable from those of human follicle stimulating hormone. Recombinant FSH production occurs in genetically modified Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells cultured in bioreactors. Purification by immunochromatography using an antibody specifically binding FSH results in a highly purified preparation with a consistent FSH isoform profile, and a high specific activity. The biological activity of follitropin alfa is determined by measuring the increase in ovary weight in female rats. The in vivo biological activity of follitropin alfa has been calibrated against the first International Standard for Recombinant Human Follicle Stimulation Hormone established in 1995 by the Expert Committee on Biological Standards of the World Health Organization. Gonal-f® contains no luteinizing hormone (LH) activity. Based on available data derived from physico-chemical tests and bioassays, follitropin alfa and follitropin beta, another recombinant follicle stimulating hormone product, are indistinguishable.
Gonal-f® is a sterile, lyophilized powder intended for subcutaneous injection after reconstitution.
Each Gonal-f® Multi-Dose vial is filled with 600 IU (44 mcg) or 1200 IU (87 mcg) follitropin alfa to deliver 450 IU (33 mcg) or 1050 IU (77 mcg) follitropin alfa, respectively, and contains 30 mg sucrose, 1.11 mg dibasic sodium phosphate dihydrate and 0.45 mg monobasic sodium phosphate monohydrate. O-phosphoric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may be used prior to lyophilization for pH adjustment. Multiple Dose vials are reconstituted with Bacteriostatic Water for Injection (0.9% benzyl alcohol), USP.
Under current storage conditions, Gonal-f® may contain up to 10% of oxidized follitropin alfa.
Therapeutic Class: Infertility
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection) stimulates ovarian follicular growth in women who do not have primary ovarian failure. FSH, the active component of Gonal-f® is the primary hormone responsible for follicular recruitment and development. In order to effect final maturation of the follicle and ovulation in the absence of an endogenous LH surge, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) must be given following the administration of Gonal-f® when monitoring of the patient indicates that sufficient follicular development has occurred. There is interpatient variability in response to FSH administration. The physico-chemical, immunological, and biological activities of recombinant FSH (r-hFSH) are comparable to those of pituitary and human menopausal urine-derived FSH. Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection), when administered with hCG, stimulates spermatogenesis in men with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. FSH, the active component of Gonal-f®, is the primary hormone responsible for spermatogenesis.
Pharmacokinetics
Single dose pharmacokinetics of follitropin alfa were determined following intravenous, subcutaneous and intramuscular administration of 150 IU Gonal-f® to 12 healthy, down-regulated female volunteers. Steady-state pharmacokinetics were also determined in 12 healthy down-regulated female volunteers who were administered a single daily dose of 150 IU for seven days. These pharmacokinetics were confirmed in pituitary down-regulated women undergoing in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer (IVF/ET), treated with FSH doses of up to 450 IU per day. Additionally, single dose pharmacokinetics of follitropin alfa were determined following subcutaneous administration of 225 IU Gonal-f® to 12 healthy adult male volunteers in a cross-over design. Steady state pharmacokinetics were also determined in 6 healthy adult male volunteers who were administered a single daily dose of 225 IU Gonal-f® for 7 days. No significant difference in pharmacokinetics is expected in males versus females when administered Gonal-f® subcutaneously. The pharmacokinetic parameters from these studies are included in Table 1.
Table 1: Pharmacokinetic parameters (mean ± SD) of FSH following administration of Gonal-f® Population Female Male Healthy Female Volunteers IVF/ET Patients Healthy Male Volunteers Dose (IU) Single Dose
IM
(150 IU)Single Dose
SC
(150 IU)Multiple Dose
SC
(7 × 150 IU)Multiple Dose
SC
(5 × 225 IU)*Single Dose
SC
(225 IU)Multiple Dose
SC
(7 × 225 IU)Abbreviations are: IVF/ET: in vitro fertilization/embryo transfer; Cmax: peak concentration (above baseline); tmax : time of Cmax; CL/F: apparent clearance; V/F: apparent volume of distribution; calculated using a one-compartment model. t½: absorption half-life; F: bioavailability compared to IV - * First five days of fixed regimen followed by adjustment of the dose depending on response
- † Steady-state AUC144-168 (After the 7th daily SC dose)
- ‡ increases with body mass index
AUC (IU-hr/L) 206 ± 66 176 ± 87 187 ± 61† --- 220 ± 109 186 ± 23† Cmax (IU/L) 3 ± 1 3 ± 1 9 ± 3 --- 2.5 ± 0.8 8.3 ± 0.9 tmax (hr) 25 ± 10 16 ± 10 8 ± 6 --- 20 ± 14 10.7 ± 6.7 t½ terminal (hr) 50 ± 27 24 ± 11 24 ± 8 32‡ 41 ± 14 32 ± 4 CL/F (L/hr) --- --- --- 0.7 ± 0.2 0.86 ± 0.48 0.90 ± 0.12 V/F (L) --- --- --- 10 ± 3 --- --- F (%) 76 ± 30 66 ± 39 --- --- --- --- Absorption
The absorption rate of Gonal-f® following subcutaneous or intramuscular administration was found to be slower than the elimination rate. Hence the pharmacokinetics of Gonal-f® are absorption rate-limited.
Distribution
Human tissue or organ distribution of FSH has not been determined for Gonal-f®.
After intravenous administration to pituitary down-regulated, healthy female volunteers, the serum profile of FSH appears to be described by a two compartment open model with a distribution half-life of about 2-2.5 hours. Steady-state serum levels were reached after 4 to 5 days of daily administration.
Metabolism/Excretion
FSH metabolism following administration of Gonal-f® has not been studied in humans. Total clearance after IV administration in healthy females was 0.6 L/hr; mean residence time was 17-20 hours. FSH renal clearance was 0.07 L/hr after intravenous administration representing approximately 1/8 of total clearance.
Pharmacodynamics
Following daily subcutaneous administration of 150 IU of Gonal-f® for 7 days in healthy female volunteers, serum inhibin and estradiol, and total follicular volume responded as a function of time, with pronounced inter-individual variability. Pharmacodynamic effect lagged behind FSH serum concentration. Of the three pharmacodynamic parameters, serum inhibin levels responded with the least delay and declined rapidly after discontinuation of Gonal-f®. Follicular growth was most delayed and continued even after discontinuation of Gonal-f® administration, and after serum FSH levels had declined. Maximum follicular volume was better correlated with either inhibin or estradiol peak levels than with FSH concentration. Inhibin rise was an early index of follicular development. In healthy male volunteers, despite high interindividual variation and the absence of down-regulation, daily administration of 225 IU Gonal-f® was shown to increase the levels of inhibin to reach a plateau during the whole administration period and then return to baseline.
Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
To establish the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of FSH in a target population, measurements performed during a clinical study of in vitro fertilization/embryo transfer were used in conjunction with pharmacokinetic data from studies in healthy female volunteers. The apparent clearance was comparable to that in healthy volunteers. The absorption rate was found to be influenced by the body mass index (BMI), suggesting that the higher the BMI, the lower the rate of absorption. However, FSH serum levels following fixed (during the first five days) and then adjusted doses of Gonal-f® were found to be poor predictors of follicular growth rate. High pre-treatment serum FSH levels may predict lower follicular growth rates.
Special populations
Safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of Gonal-f® in patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency have not been established.
Clinical Studies
Women
The safety and efficacy of Gonal-f® have been examined in four clinical studies, two studies for ovulation induction and two studies for assisted reproductive technologies (ART). In these comparative studies, there were no clinically significant differences between treatment groups in study outcomes.
1. Ovulation Induction
The safety and efficacy of Gonal-f® administered subcutaneously vs. urofollitropin administered intramuscularly were assessed in a phase III, open-label, randomized, comparative, multinational, multicenter study in oligo-anovulatory infertile women who failed to ovulate or conceive following adequate clomiphene citrate therapy (Study 5642).
The primary efficacy parameter was the ovulation rate. Two hundred and twenty-two patients entered into the first cycle of treatment, of whom 110 received Gonal-f® and 112 received urofollitropin. Ovulation rates were similar between Gonal-f® and urofollitropin treatment groups. The study results for the 222 patients who received treatment in at least one cycle are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2: Cumulative Patient Ovulation and Clinical Pregnancy Rates by Treatment Group in Ovulation Induction Study 5642 Gonal-f® (n=110) Urofollitropin (n=112) - * A clinical pregnancy was defined as a pregnancy during which a fetal sac (with or without heart activity) was visualized by ultrasound on day 34-36 after hCG administration.
Cumulative Ovulation Rate Cycle 1 64% 59% Cycle 2 78% 82% Cycle 3 84% 91% Cumulative Clinical Pregnancy* Rate Cycle 1 21% 21% Cycle 2 28% 38% Cycle 3 35% 46% For the 90 patients who had a clinical pregnancy (39 in Gonal-f® group; 51 in urofollitropin group), the outcome of the pregnancy was:
Table 3: Pregnancy Outcome by Treatment Group in Ovulation Induction Study 5642 Gonal-f® (n=39) Urofollitropin (n=51) Pregnancies not reaching term 20.5% 13.7% Single births 74.4% 74.5% Multiple births 5.1% 11.8% A second randomized, comparative, open-label, multicenter study was conducted in 23 U.S. centers (Study 5727). The primary efficacy parameter was ovulation rate. Ovulation rates were similar between Gonal-f® and urofollitropin treatment groups. Two hundred and thirty-two patients with oligo-anovulatory infertility received treatment with up to three cycles of Gonal-f® administered subcutaneously (118 patients) or urofollitropin administered intramuscularly (114 patients).
The cumulative patient ovulation rate and clinical pregnancy rates by cycle are presented for the 232 patients who received treatment in at least one cycle.
Table 4: Cumulative Patient Ovulation and Clinical Pregnancy Rates by Treatment Group in Ovulation Induction Study 5727 Gonal-f® (n=118) Urofollitropin (n=114) - * A clinical pregnancy was defined as a pregnancy during which a fetal sac (with or without heart activity) was visualized by ultrasound on day 34-36 after hCG administration.
Cumulative Ovulation Rate Cycle 1 58% 68% Cycle 2 72% 86% Cycle 3 81% 93% Cumulative Clinical Pregnancy* Rate Cycle 1 13% 14% Cycle 2 25% 25% Cycle 3 37% 36% For the 85 patients who had a clinical pregnancy (44 in Gonal-f® group; 41 in urofollitropin group), the outcome of the pregnancy is shown in Table 5.
Table 5: Pregnancy Outcome by Treatment Group in Ovulation Induction Study 5727 Gonal-f® (n=44) Urofollitropin (n=41) Pregnancies not reaching term 22.7% 22.0% Single births 63.6% 65.9% Multiple births 13.7% 12.2% 2. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
The safety and efficacy of Gonal-f® administered subcutaneously vs. urofollitropin administered intramuscularly were assessed in a phase III, open-label, randomized, comparative, multinational, multicenter study in ovulatory, infertile women undergoing stimulation of multiple follicles for In Vitro Fertilization and Embryo Transfer (IVF/ET) after pituitary down-regulation with a GnRH agonist (Study 5503). The purpose of the study was to demonstrate that Gonal-f®, administered subcutaneously, was clinically not different in terms of safety and efficacy from urofollitropin, administered intramuscularly. The initial and maximal doses of Gonal-f® were 225 and 450 IU, respectively. The primary efficacy parameter was the number of mature pre-ovulatory follicles on the day of hCG administration. One hundred and twenty-three patients were randomized and received either Gonal-f® (60 patients) or urofollitropin (63 patients).
The results summarized in Table 6 are mean data with Gonal-f® and urofollitropin administered to ovulatory infertile women undergoing multiple follicular development for IVF/ET.
Table 6: Treatment Outcomes by Treatment Group in ART Study 5503 Gonal-f® (n=60) Urofollitropin (n=63) - * A clinical pregnancy was defined as a pregnancy during which a fetal sac (with or without heart activity) was visualized by ultrasound on day 34-36 after hCG administration.
Mean number of follicles ≥ 14mm diameter on day of hCG 7.8 9.2 Mean number of oocytes recovered per patient 9.3 10.7 Mean Serum E2 (pg/mL) on day of hCG 1576 2193 Mean treatment duration in days (range) 9.9 (5-20) 9.4 (5-14) Clinical pregnancy* rate per attempt 20% 16% Clinical pregnancy* rate per embryo transfer 24% 19% For the 22 patients who had a clinical pregnancy (12 in Gonal-f® group; 10 in urofollitropin group), the outcome of the pregnancy is shown in Table 7.
Table 7: Pregnancy Outcome by Treatment Group in ART Study 5503 Gonal-f® (n=12) Urofollitropin (n=10) Pregnancies not reaching term 25.0% 20.0% Single births 41.7% 50.0% Multiple births 33.3% 30.0% A second randomized, comparative, open-label, multicenter study was conducted in 7 U.S. centers (Study 5533). One hundred and fourteen patients with ovulatory infertility undergoing IVF/ET were randomized and received either Gonal-f® by subcutaneous administration (56 patients) or urofollitropin by intramuscular administration (58 patients) following pituitary down-regulation with a GnRH agonist. The primary efficacy parameter was the number of mature pre-ovulatory follicles on the day of hCG administration. Results are summarized in Table 8.
Table 8: Treatment Outcomes by Treatment Group in ART Study 5533 Gonal-f® (n=56) urofollitropin (n=58) - * A clinical pregnancy was defined as a pregnancy during which a fetal sac (with or without heart activity) was visualized by ultrasound on day 34-36 after hCG administration.
Mean number of follicles ≥ 14mm diameter on day of hCG 7.2 8.3 Mean number of oocytes recovered per patient 9.3 12.3 Mean Serum E2 (pg/mL) on day of hCG 1236 1513 Mean treatment duration in days (range) 10.1(5-15) 9.0 (5-12) Clinical pregnancy* rate per attempt 21% 22% Clinical pregnancy* rate per embryo transfer 26% 25% For the 25 patients who had a clinical pregnancy (12 in Gonal-f® group; 13 in urofollitropin group), the outcome of the pregnancy is shown in Table 9.
Table 9: Pregnancy Outcome by Treatment Group in ART Study 5533 Gonal-f® (n=12) Urofollitropin (n=13) Pregnancies not reaching term 33.3% 30.8% Single births 41.7% 38.5% Multiple births 25.0% 30.8% Men
The safety and efficacy of Gonal-f® administered concomitantly with hCG have been examined in three open-label clinical studies for induction of spermatogenesis in men with primary and secondary hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
The three multicenter studies involved three to six months of pretreatment with chorionic gonadotropin for injection to normalize serum testosterone levels, followed by 18 months of treatment with Gonal-f® and hCG. The objective of each study was induction of spermatogenesis (a sperm density of ≥ 1.5 × 106/mL).
Study 5844 enrolled 32 patients in six centers in the United Kingdom, France and Germany. The second trial, Study 6410, was conducted in Australia and enrolled 10 patients in two centers. Study 6793, conducted in 7 centers in the United States, was planned to enroll 32 patients. The interim data for the US study includes 30 of the planned 32 patients. For all 3 studies, a total of 72 patients were enrolled and received hCG and 56 of those patients entered the Gonal-f® treatment phase of the trials.
The populations enrolled in the three studies were similar: Study 5844 studied a naïve population who had had no prior treatment with gonadotropins; mean age was 25.9 (range 16 to 48) years, mean (± SD) testis volume was 2.0 ± 1.2 mL, and 12 of the 32 patients (37.5%) were anosmic. Thirty-one of the patients were Caucasian and one was Asian. In Study 6410, mean age was 36 (range 26 to 48) years, 6 and 1 of the 10 patients had previously been treated with gonadotropins and GnRH, respectively; mean testis volume was 4.5 ± 2.9 mL; and 2 of the 10 patients (20%) were anosmic. Seven patients were Caucasian and three were Asian. In the 30 patients reported in the interim analysis of Study 6793, the mean age was 30.1 (range 22 to 44) years; 4 and 3 of the 30 patients had been treated with gonadotropins and GnRH, respectively, in the past; mean testis volume was 4.4 ± 1.3 mL; and 10 of the 30 patients (33.3%) were anosmic. Twenty five of the patients were Caucasian, three were Asian, and one each of Moroccan and Indian ancestry.
The primary efficacy endpoint of all three studies was the achievement of a sperm density ≥ 1.5 × 106/mL. The study results for the patients treated with Gonal-f® and hCG are summarized in Table 10.
Table 10: Number of Men Receiving Gonal-f® Who Achieved a Sperm Density ≥ 1.5 × 106/mL Study 5844
(n=26)Study 6410
(n=8)Study 6793
(n=22)*- * Interim data
Sperm Concentration ≥ 1.5 × 106/mL Yes 12 (46.2%) 5 (62.5%) 14 (63.6%) No 14 (53.8%) 3 (37.5%) 8 (36.4%) 95% Confidence Interval (26.6% - 66.6%) (24.5% - 91.5%) (40.7% - 82.8%) The time to achievement of the primary efficacy endpoint is summarized in Table 11.
Table 11: Time to Achievement of Sperm Density ≥ 1.5 × 106/ mL in Men Receiving Gonal-f® Study 5844 (n=26) Study 6410 (n=8) Study 6793 (n=22)* - * Interim data
Number of Men Achieving Sperm Concentration n 12 5 14 Time (Months) to Sperm Concentration ≥ 1.5 × 106/mL Median 12.4 9.1 6.8 Range (2.7 – 18.1) (8.8 – 11.7) (2.8 – 15.7) Table 12: Pregnancy Outcome in Partners of Men Desiring Fertility Study 5844 (n=7) Study 6410 (n=10) Study 6793 (n=20)* - * Interim data
Pregnancy 6 (86%) 3 (30%) 3 (15%) Pregnancy not reaching term 1 (14%) 1 (10%) 2 (10%) Single births 5 (71%) 2 (20%) 1 (5%) Of the 56 patients who received Gonal-f® in Studies 5844, 6410, and 6793, 12 pregnancies were achieved in 10 partners of the 37 patients who were seeking pregnancy and who currently had a partner during the studies. Thus, pregnancy (clinical and chemical) was documented to have been achieved by 27% of the patients' partners seeking pregnancy during the exposure period to Gonal-f® in the 3 trials. Eight pregnancies continued to term, and 8 healthy babies were born to 7 couples as a result of those studies.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Women
Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection) is indicated for the induction of ovulation and pregnancy in the anovulatory infertile patient in whom the cause of infertility is functional and not due to primary ovarian failure. Gonal-f® is also indicated for the development of multiple follicles in the ovulatory patient participating in an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) program.
Selection of Patients
- Before treatment with Gonal-f® is instituted, a thorough gynecologic and endocrinologic evaluation must be performed. This should include an assessment of pelvic anatomy. Patients with tubal obstruction should receive Gonal-f® only if enrolled in an in vitro fertilization program.
- Primary ovarian failure should be excluded by the determination of gonadotropin levels.
- Appropriate evaluation should be performed to exclude pregnancy.
- Patients in later reproductive life have a greater predisposition to endometrial carcinoma as well as a higher incidence of anovulatory disorders. A thorough diagnostic evaluation should always be performed in patients who demonstrate abnormal uterine bleeding or other signs of endometrial abnormalities before starting Gonal-f® therapy.
- Evaluation of the partner's fertility potential should be included in the initial evaluation.
Men
Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection) is indicated for the induction of spermatogenesis in men with primary and secondary hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in whom the cause of infertility is not due to primary testicular failure.
Selection of Patients
- Before treatment with Gonal-f® is instituted for azoospermia, a thorough medical and endocrinologic evaluation must be performed.
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism should be confirmed, and primary testicular failure should be excluded by the determination of gonadotropin levels.
- Prior to Gonal-f® therapy for azoospermia in patients with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, serum testosterone levels should be normalized.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection) is contraindicated in women and men who exhibit:
- Prior hypersensitivity to recombinant FSH preparations or one of their excipients.
- High levels of FSH indicating primary gonadal failure.
- Uncontrolled thyroid or adrenal dysfunction.
- Sex hormone dependent tumors of the reproductive tract and accessory organs.
- An organic intracranial lesion such as a pituitary tumor. And in women who exhibit:
- Abnormal uterine bleeding of undetermined origin (see "Selection of Patients").
- Ovarian cyst or enlargement of undetermined origin (see "Selection of Patients").
- Pregnancy.
-
WARNINGS
Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection) should only be used by physicians who are thoroughly familiar with infertility problems and their management.
Gonal-f® is a potent gonadotropic substance capable of causing Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) in women with or without pulmonary or vascular complications. Gonadotropin therapy requires a certain time commitment by physicians and supportive health professionals, and requires the availability of appropriate monitoring facilities (see "Precautions/Laboratory Tests"). Safe and effective use of Gonal-f® in women requires monitoring of ovarian response with serum estradiol and vaginal ultrasound on a regular basis. The lowest effective dose should be used.
Overstimulation of the Ovary During FSH Therapy
Ovarian Enlargement
Mild to moderate uncomplicated ovarian enlargement which may be accompanied by abdominal distention and/or abdominal pain occurs in approximately 20% of those treated with urofollitropin and hCG, and generally regresses without treatment within two or three weeks. Careful monitoring of ovarian response can further minimize the risk of overstimulation.
If the ovaries are abnormally enlarged on the last day of Gonal-f® therapy, hCG should not be administered in this course of therapy. This will reduce the chances of development of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
OHSS is a medical event distinct from uncomplicated ovarian enlargement. Severe OHSS may progress rapidly (within 24 hours to several days) to become a serious medical event. It is characterized by an apparent dramatic increase in vascular permeability which can result in a rapid accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, thorax, and potentially, the pericardium. The early warning signs of development of OHSS are severe pelvic pain, nausea, vomiting, and weight gain. The following symptomatology has been seen with cases of OHSS: abdominal pain, abdominal distension, gastrointestinal symptoms including nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, severe ovarian enlargement, weight gain, dyspnea, and oliguria. Clinical evaluation may reveal hypovolemia, hemoconcentration, electrolyte imbalances, ascites, hemoperitoneum, pleural effusions, hydrothorax, acute pulmonary distress, and thromboembolic events (see "Pulmonary and Vascular Complications"). Transient liver function test abnormalities suggestive of hepatic dysfunction, which may be accompanied by morphologic changes on liver biopsy, have been reported in association with Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS). OHSS occurred in 9 of 228 (3.9%) Gonal-f® treated women during ovulation induction clinical trials and of this number, 1 of 228 (0.4%) was classified as severe. In ART clinical studies, OHSS occurred in 0 of 116 (0.0%) Gonal-f® treated women. OHSS may be more severe and more protracted if pregnancy occurs. OHSS develops rapidly; therefore, patients should be followed for at least two weeks after hCG administration. Most often, OHSS occurs after treatment has been discontinued and reaches its maximum at about seven to ten days following treatment. Usually, OHSS resolves spontaneously with the onset of menses. If there is evidence that OHSS may be developing prior to hCG administration (see "Precautions/Laboratory Tests"), the hCG must be withheld.
If severe OHSS occurs, treatment must be stopped and the patient should be hospitalized.
A physician experienced in the management of this syndrome, or who is experienced in the management of fluid and electrolyte imbalances should be consulted.
Pulmonary and Vascular Complications
Serious pulmonary conditions (e.g., atelectasis, acute respiratory distress syndrome and exacerbation of asthma) have been reported. In addition, thromboembolic events both in association with, and separate from Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome have been reported with gonadotropins including Gonal-f®. Intravascular thrombosis and embolism can result in reduced blood flow to critical organs or the extremities. Sequelae of such events have included venous thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, cerebral vascular occlusion (stroke), and arterial occlusion resulting in loss of limb. In rare cases, pulmonary complications and/or thromboembolic events have resulted in death.
Multiple Births
Reports of multiple births have been associated with Gonal-f® treatment. In ovulation induction clinical trials, 12.3% of live births were multiple births in women receiving Gonal-f® and 14.5% of live births were multiple births in women receiving urofollitropin. In IVF/ET clinical trials, 44.0% of live births were multiple births in women receiving Gonal-f® and 41.0% of live births were multiple births in women receiving urofollitropin and is dependent on the number of embryos transferred. The patient should be advised of the potential risk of multiple births before starting treatment.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Careful attention should be given to the diagnosis of infertility in candidates for Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection) therapy (see "Indications and Usage/ Selection of Patients").
Information for Patients
Prior to therapy with Gonal-f®, patients should be informed of the duration of treatment and monitoring of their condition that will be required. The risks of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome and multiple births in women (see "WARNINGS") and other possible adverse reactions (see "Adverse Reactions") should also be discussed.
A 'Patient's Information Leaflet' is provided for patients prescribed Gonal-f® Multi-Dose.
Laboratory Tests
In most instances, treatment of women with Gonal-f® results only in follicular recruitment and development. In the absence of an endogenous LH surge, hCG is given when monitoring of the patient indicates that sufficient follicular development has occurred. This may be estimated by ultrasound alone or in combination with measurement of serum estradiol levels. The combination of both ultrasound and serum estradiol measurement are useful for monitoring the development of follicles, for timing of the ovulatory trigger, as well as for detecting ovarian enlargement and minimizing the risk of the Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome and multiple gestation. It is recommended that the number of growing follicles be confirmed using ultrasonography because plasma estrogens do not give an indication of the size or number of follicles.
The clinical confirmation of ovulation, with the exception of pregnancy, is obtained by direct and indirect indices of progesterone production. The indices most generally used are as follows:
- A rise in basal body temperature;
- Increase in serum progesterone; and
- Menstruation following a shift in basal body temperature.
When used in conjunction with the indices of progesterone production, sonographic visualization of the ovaries will assist in determining if ovulation has occurred. Sonographic evidence of ovulation may include the following:
- Fluid in the cul-de-sac;
- Ovarian stigmata;
- Collapsed follicle; and
- Secretory endometrium.
Accurate interpretation of the indices of follicle development and maturation require a physician who is experienced in the interpretation of these tests.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long- term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Gonal-f®. However, follitropin alfa showed no mutagenic activity in a series of tests performed to evaluate its potential genetic toxicity including, bacterial and mammalian cell mutation tests, a chromosomal aberration test and a micronucleus test.
Impaired fertility has been reported in rats, exposed to pharmacological doses of follitropin alfa (≥40 IU/kg/day) for extended periods, through reduced fecundity.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the nursing infant from Gonal-f®, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Women
The safety of Gonal-f® was examined in four clinical studies that enrolled 691 patients into two studies for ovulation induction (454 patients) and two studies for ART (237 patients).
Adverse events occurring in more than 10% of patients were headache, ovarian cyst, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infection in the U.S. ovulation induction study and headache in the U.S. ART study. Adverse events (without regard to causality assessment) occurring in at least 2% of patients are listed in Table 13 and Table 14.
Table 13: US Controlled Trial in Ovulation Induction, Study 5727 Body System
Preferred TermGonal-f®
Patients (%) Experiencing Events
Treatment cycles = 288*
n=118Urofollitropin
Patients (%) Experiencing Events
Treatment cycles = 277*
n= 114- * up to 3 cycles of therapy
- † Severe = 0.8% of 118 patients in Study 5727
Reproductive, Female Intermenstrual Bleeding 9.3% 4.4% Breast Pain Female 4.2% 6.1% Ovarian Hyperstimulation† 6.8% 3.5% Dysmenorrhea 2.5% 6.1% Ovarian Disorder 1.7% 2.6% Cervix Lesion 2.5% 0.9% Menstrual Disorder 2.5% 0.9% Gastro-intestinal System Abdominal Pain 9.3% 12.3% Nausea 13.6% 3.5% Flatulence 6.8% 8.8% Diarrhea 7.6% 3.5% Vomiting 2.5% 2.6% Dyspepsia 1.7% 3.5% Central and Peripheral Nervous System Headache 22.0% 20.2% Dizziness 2.5% 0.0% Neoplasm Ovarian Cyst 15.3% 28.9% Body as a Whole- General Pain 5.9% 6.1% Back Pain 5.1% 1.8% Influenza-like Symptoms 4.2% 2.6% Fever 4.2% 1.8% Respiratory System Upper Respiratory Tract Infection 11.9% 7.9% Sinusitis 5.1% 5.3% Pharyngitis 2.5% 3.5% Coughing 1.7% 2.6% Rhinitis 0.8% 2.6% Skin and Appendages Acne 4.2% 2.6% Psychiatric Emotional Lability 5.1% 2.6% Urinary System Urinary Tract Infection 1.7% 4.4% Resistance Mechanism Moniliasis Genital 2.5% 0.9% Application Site Injection Site Pain 2.5% 0.9% Additional adverse events not listed in Table 13 that occurred in 1 to 2% of Gonal-f® treated patients in the US ovulation induction study included the following: leukorrhea, vaginal hemorrhage, migraine, fatigue, asthma, nervousness, somnolence, and hypotension.
Table 14: US Controlled Trial in ART, Study 5533 Body System
Preferred TermGonal-f®
Patients (%) Experiencing Events
n=59Urofollitropin
Patients (%) Experiencing Events
n= 61Reproductive, Female Intermenstrual Bleeding 3.6% 5.2% Leukorrhea 1.7% 3.4% Vaginal Hemorrhage 3.6% 3.4% Gastro-intestinal System Nausea 5.4% 1.7% Flatulence 3.6% 0.0% Central and Peripheral Nervous System Headache 12.5% 3.4% Body as a Whole- General Abdominal Pain 8.9% 3.4% Pelvic Pain Female 7.1% 1.7% Respiratory System Upper Respiratory Tract Infection 3.6% 1.7% Metabolic and Nutritional Weight Increase 3.6% 0.0% Additional adverse events not listed in Table 14 that occurred in 1 to 2% of Gonal-f® treated patients in the U.S. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) study included the following: D&C following delivery or abortion, dysmenorrhea, vaginal hemorrhage, diarrhea, tooth disorder, vomiting, dizziness, paraesthesia, abdomen enlarged, chest pain, fatigue, dyspnea, anorexia, anxiety, somnolence, injection site inflammation, injection site reaction, pruritus, pruritus genital, myalgia, thirst, and palpitation.
Two additional clinical studies (for ovulation induction and ART, respectively) were conducted in Europe. The safety profiles from these two studies were comparable to that of the data presented above.
Gonal-f® Multi-Dose was examined in twenty-five healthy volunteers who received 300 IU each of Gonal-f® from single- dose ampules and multi-dose vials. Overall, both presentations were well tolerated and local tolerability between the two groups was comparable. Injection site inspections revealed very rare local reactions (mild redness in one patient after single-dose injection and mild bruising in two subjects after multi-dose injection). Subjective assessments indicated minimal or mild transient pain in two and five subjects who received Gonal-f® single-dose and Gonal-f® multi-dose, respectively.
The following medical events have been reported subsequent to pregnancies resulting from gonadotropins in controlled clinical studies:
- Spontaneous Abortion
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Premature Labor
- Postpartum Fever
- Congenital Abnormalities
Two incidents of congenital cardiac malformations have been reported in children born following pregnancies resulting from treatment with Gonal-f® and hCG in Gonal-f® clinical studies 5642 and 5727. In addition, a pregnancy occurring in study 5533 following treatment with Gonal-f® and hCG was complicated by apparent failure of intrauterine growth and terminated for a suspected syndrome of congenital abnormalities. No specific diagnosis was made. The incidence does not exceed that found in the general population.
The following adverse reactions have been previously reported during menotropin therapy:
- Pulmonary and vascular complications (see "Warnings"),
- Adnexal torsion (as a complication of ovarian enlargement),
- Mild to moderate ovarian enlargement,
- Hemoperitoneum
There have been infrequent reports of ovarian neoplasms, both benign and malignant, in women who have undergone multiple drug regimens for ovulation induction; however, a causal relationship has not been established.
Men
The safety of Gonal-f® was examined in 3 clinical studies that enrolled 72 patients for induction of spermatogenesis and fertility of whom 56 patients received Gonal-f®. One hundred and twenty-three adverse events, including 7 serious events, were reported in 34 of the 56 patients during Gonal-f® treatment.
In Study 5844, 21 adverse events, including 4 serious adverse events, were reported by 14 of the 26 patients (53.8%) treated with Gonal-f®. Events occurring in more than one patient were varicocele (4) and injection site reactions (4). The 4 serious adverse events were testicular surgery for cryptorchidism, which existed prestudy, hemoptysis, an infected pilonidal cyst, and lymphadenopathy associated with an Epstein-Barr viral infection.
In Study 6410, 3 adverse events were reported in 2 of the 8 patients (24%) treated with Gonal-f®. One serious adverse event was reported, surgery for gynecomastia which existed at baseline.
In the interim analysis of Study 6793, 18 of 22 patients (81.8%) reported a total of 99 adverse events during Gonal-f® treatment. The most common events of possible, probable, or definite relationship to study drug therapy occurring in more than 2 patients were: acne (25 events in 13 patients; 59% of patients); breast pain (4 events in 3 patients; 13.6% of patients); and fatigue, gynecomastia, and injection site pain (each of which was reported as 2 events by 2 patients; 9.1% of patients). Two serious adverse events (hospitalization for drug abuse and depression) were reported by a single patient in the interim analysis.
A total of 12,026 injections of Gonal-f® were administered by the 56 patients who received Gonal-f® in Studies 5844, 6410, and 6793 combined. The injections were well-tolerated, with no or mild reactions (redness, swelling, bruising and itching) reported by patients for 93.3% of injections. Moderate and severe reactions, consisting primarily of pain, were reported for 4.8% of injections, and no self-assessment was available for 1.9% of injections.
Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse events reported from clinical trials, the following events have been reported during postmarketing use of Gonal-f®. Because these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, the frequency or a causal relationship to Gonal-f®, can not be reliably determined.
Body as a Whole - General: hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactoid reactions
Respiratory System: asthma (see Warnings, Pulmonary and Vascular Complications)
Vascular disorders: thromboembolism (see Warnings, Pulmonary and Vascular Complications)
-
OVERDOSAGE
Aside from possible ovarian hyperstimulation and multiple gestations (see "Warnings"), there is no information on the consequences of acute overdosage with Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Each Gonal-f® Multi-Dose Vial delivers 450 IU or 1050 IU follitropin alfa, respectively.
Dosage
Infertile Patients with oligo-anovulation
The dose of Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection) to stimulate development of the follicle must be individualized for each patient.
The lowest dose consistent with the expectation of good results should be used. Over the course of treatment, doses of Gonal-f® may range up to 300 IU per day depending on the individual patient response. Gonal-f® should be administered until adequate follicular development is indicated by serum estradiol and vaginal ultrasonography. A response is generally evident after 5 to 7 days. Subsequent monitoring intervals should be based on individual patient response.
It is recommended that the initial dose of the first cycle be 75 IU of Gonal-f® per day, ADMINISTERED SUBCUTANEOUSLY. An incremental adjustment in dose of up to 37.5 IU may be considered after 14 days. Further dose increases of the same magnitude could be made, if necessary, every seven days. Treatment duration should not exceed 35 days unless an E2 rise indicates imminent follicular development. To complete follicular development and effect ovulation in the absence of an endogenous LH surge, chorionic gonadotropin, hCG, (5,000 USP units) should be given 1 day after the last dose of Gonal-f®. Chorionic gonadotropin should be withheld if the serum estradiol is greater than 2,000 pg/mL. If the ovaries are abnormally enlarged or abdominal pain occurs, Gonal-f® treatment should be discontinued, hCG should not be administered, and the patient should be advised not to have intercourse; this may reduce the chance of development of the Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome and, should spontaneous ovulation occur, reduce the chance of multiple gestation. A follow-up visit should be conducted in the luteal phase.
The initial dose administered in the subsequent cycles should be individualized for each patient based on her response in the preceding cycle. Doses larger than 300 IU of FSH per day are not routinely recommended. As in the initial cycle, 5,000 USP units of hCG must be given 1 day after the last dose of Gonal-f® to complete follicular development and induce ovulation. The precautions described above should be followed to minimize the chance of development of the Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome.
The couple should be encouraged to have intercourse daily, beginning on the day prior to the administration of hCG until ovulation becomes apparent from the indices employed for the determination of progestational activity. Care should be taken to ensure insemination. In light of the indices and parameters mentioned, it should become obvious that, unless a physician is willing to devote considerable time to these patients and be familiar with and conduct the necessary laboratory studies, he/she should not use Gonal-f®.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies
As in the treatment of patients with oligo-anovulatory infertility, the dose of Gonal-f® to stimulate development of the follicle must be individualized for each patient. For Assisted Reproductive Technologies, therapy with Gonal-f® should be initiated in the early follicular phase (cycle day 2 or 3) at a dose of 150 IU per day, until sufficient follicular development is attained. In most cases, therapy should not exceed ten days.
In patients undergoing ART, whose endogenous gonadotropin levels are suppressed, Gonal-f® should be initiated at a dose of 225 IU per day. Treatment should be continued until adequate follicular development is indicated as determined by ultrasound in combination with measurement of serum estradiol levels. Adjustments to dose may be considered after five days based on the patient's response; subsequently dosage should be adjusted no more frequently than every 3-5 days and by no more than 75-150 IU additionally at each adjustment. Doses greater than 450 IU per day are not recommended. Once adequate follicular development is evident, hCG (5,000 to 10,000 USP units) should be administered to induce final follicular maturation in preparation for oocyte retrieval. The administration of hCG must be withheld in cases where the ovaries are abnormally enlarged on the last day of therapy. This should reduce the chance of developing OHSS.
Male Patients with Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
The dose of Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection) to induce spermatogenesis must be individualized for each patient. Gonal-f® must be given in conjunction with hCG. Prior to concomitant therapy with Gonal-f® and hCG, pretreatment with hCG alone (1,000 to 2,250 USP units two to three times per week) is required. Treatment should continue for a period sufficient to achieve serum testosterone levels within the normal range. Such pretreatment may require 3 to 6 months and the dose of hCG may need to be increased to achieve normal serum testosterone levels. After normal serum testosterone levels are reached, the recommended dose of Gonal-f® is 150 IU administered subcutaneously three times a week and the recommended dose of hCG is 1,000 USP units (or the dose required to maintain serum testosterone levels within the normal range) three times a week. The lowest dose of Gonal-f® which induces spermatogenesis should be utilized. If azoospermia persists, the dose of Gonal-f® may be increased to a maximum dose of 300 IU three times per week. Gonal-f® may need to be administered for up to 18 months to achieve adequate spermatogenesis.
Administration
Multi-Dose 450 IU Vial
Dissolve the contents of one Multi-Dose vial (450 IU) with 1 mL Bacteriostatic Water for Injection (0.9% benzyl alcohol), USP. Resulting concentration will be 600 IU/mL. Following reconstitution as directed, product will deliver the equivalent of six 75 IU doses.
Multi-Dose 1050 IU Vial
Dissolve the contents of one Multi-Dose vial (1050 IU) with 2 mL Bacteriostatic Water for Injection (0.9% benzyl alcohol), USP. Resulting concentration will be 600 IU/mL. Following reconstitution as directed, product will deliver the equivalent of fourteen 75 IU doses.
Patients should be instructed to use the accompanying syringes, calibrated in FSH units (IU FSH) for administration. The 27-gauge injection syringe (see figure below) has unit dose markings from 37.5 IU to 600 IU FSH for use with Gonal-f® Multi-Dose. Patients should be instructed to take a specific dose of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose. The doctor, nurse, or pharmacist should show the patient how to locate the syringe marking that corresponds to the prescribed dose.
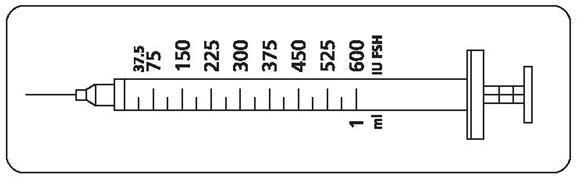
Patient Instructions for Use for Gonal-f® Multi-Dose Vial
Step 1: Mixing (reconstituting) Gonal-f® Multi-Dose Vial
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
- Using your thumb, flip off the plastic cap of the Gonal-f® Multi-Dose vial.
- Wipe the top of the vial stopper with an alcohol swab.
- Carefully twist the needle cap off the syringe labeled 'Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP'. Do not touch the needle or allow the needle to touch any surface.
- Position the needle of the syringe of water in a straight, upright position over the marked center circle of the rubber stopper on the vial of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose powder. Keep the needle in a straight, upright position as you insert it through the center circle, or it may be difficult to depress the plunger. Slowly inject the water into the vial by depressing the syringe plunger. When all the water has been injected into the vial, withdraw the needle and safely dispose of it immediately in your needle container. Do not use this needle to inject your dose.
- Do not shake the vial. If bubbles appear, wait a few moments for the bubbles to settle. The liquid drug should be clear.
Step 2: Preparing the Dose
- Wipe the rubber stopper of the vial of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose liquid with an alcohol wipe.
- Carefully pull the cap from the needle. Do not touch the needle or allow the needle to touch any surface. Firmly hold the vial of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose liquid on a flat surface, insert the needle through the marked center circle of the rubber stopper.
- Keeping the needle in the vial, lift the vial and turn it upside down with the needle pointing toward the ceiling. With the needle tip in the liquid, slowly pull back the plunger until the syringe fills to slightly more than the mark for your prescribed dose. Next, keeping the needle in the vial, slowly adjust the plunger to your prescribed dose – this will clear away any air bubbles.
- Check that you have the plunger set at your prescribed dose.
- Remove the syringe needle from the vial.
- Inject the prescribed dose as directed by the doctor.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Gonal-f® (follitropin alfa for injection) is supplied in a sterile, lyophilized form in multiple dose vials filled with 600 IU or 1200 IU in order to deliver 450 IU and 1050 IU FSH, respectively, after reconstitution with diluent (Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP, containing 0.9% benzyl alcohol as a preservative). Each carton contains syringes with mounted 27G × 0.5 inch needle, calibrated in FSH units (IU FSH) which should be used for administration. Lyophilized Multi-Dose vials may be stored refrigerated or at room temperature (2°-25°C/36°-77°F). Following reconstitution, the Multi-Dose vial may be stored refrigerated or at room temperature (2°-25°C/36°-77°F). Protect from light. Discard unused reconstituted solution after 28 days.
The following package combinations are available:
- – 1 vial Gonal-f® Multi-Dose 450 IU, 1 pre-filled syringe of Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP (0.9% benzyl alcohol), 1 mL and 6 syringes calibrated in FSH Units (IU FSH) for injection NDC: 44087-9030-1
- – 1 vial Gonal-f® Multi-Dose 1050 IU, 1 pre-filled syringe of Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP (0.9% benzyl alcohol), 2 mL and 10 syringes calibrated in FSH Units (IU FSH) for injection NDC: 44087-9070-1
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
GONAL-f® Multi-Dose(follitropin alfa for injection)Patient's Information Leaflet
This leaflet contains information about Gonal-f® Multi-Dose. This drug has been prescribed to you by your doctor for treating infertility. To help you prepare and use this medicine, you should read these instructions carefully and ask your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist to explain anything you do not understand. Keep this leaflet. You may want to read it again.
What is Gonal-f® Multi-Dose?
Gonal-f® Multi-Dose is an injectable hormone contained in a stoppered glass vial. The hormone in the vial is in the form of a white powder. The carton containing the vial of drug also contains a syringe labeled 'Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP'. This water must be mixed with the white powder in the vial to form a clear liquid solution for injection. Injection syringes for use with Gonal-f® Multi-Dose are also included in the carton. These injection syringes can only be used to administer Gonal-f® Multi-Dose. Gonal-f® Multi-Dose is only available with a prescription.
Gonal-f® Multi-Dose contains follitropin alfa, which is similar to the human hormone 'follicle stimulating hormone'; the abbreviation is 'FSH'. FSH belongs to the group of hormones associated with human reproduction. In women, FSH causes the ovaries to produce eggs. In men, FSH causes sperm production.
The hormone in Gonal-f® Multi-Dose is manufactured to meet standards for quality and purity. It cannot be taken by mouth since the acids in your stomach would destroy the hormone before it was absorbed into the body. Gonal-f® Multi-Dose is given as an injection usually every day in women and three times per week in men. It is prescribed to patients needing hormone replacement or supplementation to produce either eggs or sperm.
The Gonal-f® Multi-Dose 450 IU (33 mcg) vial is filled with 600 IU of drug in order to deliver 450 IU in several smaller daily doses. This provides between 2 and 6 commonly prescribed daily doses.
The Gonal-f® Multi-Dose 1050 IU (77 mcg) vial is filled with 1200 IU of drug in order to deliver 1050 IU in several smaller daily doses. This provides between 3 and 14 commonly prescribed daily doses.
Your doctor or nurse will tell you the number of units (IU FSH) of Gonal-f® to use each day and the number of days to use the same vial. It is common for a small amount of drug to be leftover in each vial that can not be retrieved with a syringe. This is normal. Any drug remaining in the vial after your treatment is complete should be discarded.
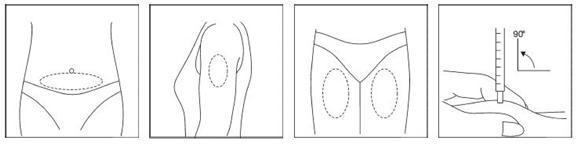
Your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist will show you how to inject the prescribed dose. Usual injection sites include the skin on the stomach, upper leg, or upper arm.
IMPORTANT The Gonal-f® liquid solution may be stored refrigerated or at room temperature for a maximum of 28 days from the day the powder is mixed with the water. Do Not Freeze. Discard unused liquid solution after 28 days. Use only the prescribed dose. Call your doctor immediately should you accidentally inject more than the prescribed dose. What are the uses of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose?
Doctors specializing in infertility or reproductive health prescribe Gonal-f® Multi-Dose to those patients trying to have a child but for a variety of reasons need medical assistance. After a thorough medical exam to determine your specific medical condition, your doctor may prescribe Gonal-f® Multi- Dose because you require hormone replacement or supplementation as part of your treatment program. Gonal-f® Multi-Dose can be used in women seeking pregnancy or in men with a rare condition that affects sperm production. Gonal-f® Multi-Dose may be one of several drugs prescribed to a patient as part of a treatment program.
IMPORTANT Do NOT take Gonal-f® Multi-Dose if you have allergies to any of these materials: - follitropin
- sucrose
- sodium phosphate
- benzyl alcohol
Do NOT take Gonal-f® Multi-Dose if you are pregnant or breast feeding. Medical conditions you should tell your doctor about.
If you have any of the following conditions, make sure to tell your doctor before starting or continuing use of Gonal-f®:
- Abnormal bleeding from the uterus or vagina in women
- Swollen, enlarged or painful ovaries in women
- Cancer of the sex organs (uterus, ovaries, testes)
- Permanent damage to the male sex organs (testes)
- Uncontrolled thyroid or adrenal problems
- Cancer of the brain
How to Prepare Gonal-f® Multi-Dose for Use
See your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist to obtain training in the preparation and use of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose.
REVIEW THESE STEPS BEFORE YOU PREPARE OR ADMINISTER GONAL-F® MULTI-DOSE. Getting ready
Make sure you have all the necessary items listed below before you begin.
- vial containing Gonal-f® Multi-Dose (white powder)
- single pre-filled syringe labeled 'Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP'
- 27-gauge injection syringe with unit dose markings from 37.5 IU to 600 IU FSH for use with the Gonal-f® Multi-Dose.
- alcohol wipes
- hard plastic or metal container (like an empty coffee can) suitable for safe disposal of used syringes and needles.
Step 1: Mixing (reconstituting) the vial containing Gonal-f® Multi-Dose
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
- Using your thumb, flip off the plastic cap of the Gonal-f® Multi-Dose vial.
- Wipe the top of the vial stopper with an alcohol wipe.
- Carefully twist the needle cap off the syringe labeled 'Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP'. Do not touch the needle or allow the needle to touch any surface.
- Position the needle of the syringe of water in a straight, upright position over the marked center circle of the rubber stopper on the vial of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose powder. Keep the needle in a straight, upright position as you insert it through the center circle, or it may be difficult to depress the plunger. Slowly inject the water into the vial by depressing the syringe plunger. The water and white powder will mix to form a clear liquid. When all the water has been injected into the vial, withdraw the needle and safely dispose of it immediately in your needle container. Do not use this needle to inject your dose.
- Do not shake the vial. If bubbles appear, wait a few moments for the bubbles to settle. The liquid drug should be clear.
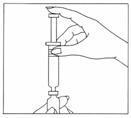
IMPORTANT Do not use the Gonal-f® Multi-Dose liquid solution if it contains any particles. Report this to your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist immediately. Step 2: Determining your dose on the injection syringe
Your doctor will instruct you to take a specific dose of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose. Your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist should show you how to locate the syringe marking that corresponds to your prescribed dose (see illustration below).
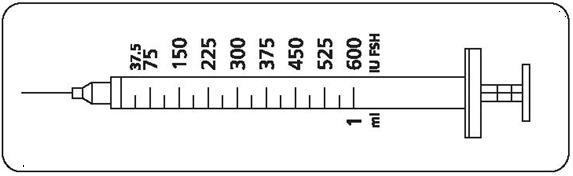
IMPORTANT If your doctor or nurse instructs you to increase or decrease your dose for 1 or more days, find the correct dose marking on the injection syringe and make the change as directed. Contact your doctor or nurse if you have questions. Step 3: Preparing your dose
- Wipe the rubber stopper of the vial of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose liquid with an alcohol wipe.
- Carefully pull the cap from the needle. Do not touch the needle or allow the needle to touch any surface. Firmly hold the vial of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose liquid on a flat surface, insert the needle through the marked center circle of the rubber stopper.
- Keeping the needle in the vial, lift the vial and turn it upside down with the needle pointing toward the ceiling. With the needle tip in the liquid, slowly pull back the plunger until the syringe fills to slightly more than the mark for your prescribed dose. Next, keeping the needle in the vial, slowly adjust the plunger to your prescribed dose – this will clear away any air bubbles.
- Check that you have the plunger set at your prescribed dose.
- Remove the syringe needle from the vial. Do not touch the needle or allow the needle to touch any surface.
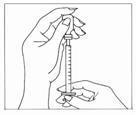
You should now be ready to prepare to receive the injection.
Step 4: Injecting your dose
Your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist should provide you with injection training. Inject the prescribed dose as directed. Usual injection sites include the skin on the stomach, upper arm, or upper leg. Change the injection location each day to minimize discomfort. Dispose of all used syringes and needles safely in a container.
IMPORTANT The injection syringes provided with Gonal-f® Multi-Dose are designed for use only with this product. Do NOT use the injection syringes to administer other drugs or hormones. All unused syringes should be discarded. Step 5: Storing Your Vial of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose Between Uses
- After each use, the vial containing the Gonal-f® Multi-Dose liquid must be stored away from light and may be stored refrigerated or at room temperature between 36°- 77° F (2°- 25° C) for up to 28 days. Otherwise, the drug's potency can be reduced. Do not store the drug in the syringe.
- If you are traveling, keep the vial stored away from light and extreme temperatures. Do not freeze.
- Allow the liquid solution to adjust to room temperature prior to administering your injection.
- Check that the Gonal-f® liquid solution is clear. Do not use if it contains any particles. Report this to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist immediately.
Are there any side effects associated with the use of Gonal-f® Multi-Dose?
Your doctor or staff member should review with you the risks and benefits of using Gonal-f® Multi-Dose. As with any medication, report any and all side effects, symptoms, or physical changes to your doctor.
The most common side effects are headache, ovarian cysts, upset stomach, and sinus infections in women and skin pimples, breast pain and growth, and tiredness in men. Needle injections may cause some discomfort.
Use of fertility drugs can be associated with fertilization of more than 1 egg. This can lead to complications for the mother and the birth of 2 or more babies. Pregnancy loss (miscarriage) is higher in women receiving fertility drugs than in women not taking fertility drugs.
Gonal-f® is a potent drug which should be used at the lowest dose expected to achieve the desired results. When used in women, your doctor should monitor your response often to avoid overdose which can lead to serious side effects including blood clots.
IMPORTANT Contact your doctor if you take more than the prescribed amount of Gonal-f® or experience severe pain or bloating in the stomach or pelvic area, severe upset stomach, vomiting, and weight gain. In rare cases, ovarian cancer has been reported in women receiving many courses of fertility drugs.
What should you do if you forget to take Gonal-f® Multi-Dose?
Do NOT take a double dose of Gonal-f®. Contact your doctor if you forget to take a dose of Gonal-f®.
Can you take Gonal-f® Multi-Dose with other medicines?
Inform your doctor and pharmacist if you are taking or have taken any other medicines, even those not requiring a prescription.
Where can more information about Gonal-f® Multi-Dose be obtained?
This leaflet is a summary of the important patient information about Gonal-f® Multi-Dose. If you have any questions or problems, talk to your doctor or other health care provider.
Gonal-f® Multi-Dose is manufactured and distributed by EMD Serono, Inc. You can also visit the Web site www.fertilitylifelines.com or contact EMD Serono at 1-866-538-7879.
Revised: December 2012
N19Z0101F
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Kit Carton - 450 IU
NDC: 44087-9030-1
GONAL-f® Multi-Dose 450 IU
(follitropin alfa for injection)For subcutaneous injection
Rx only1 vial GONAL-f® Multi-Dose
1 pre-filled syringe of Bacteriostatic Water
for Injection, USP (0.9% benzyl alcohol)
6 administration syringes with fixed needle
(27-gauge)EMD
SERONO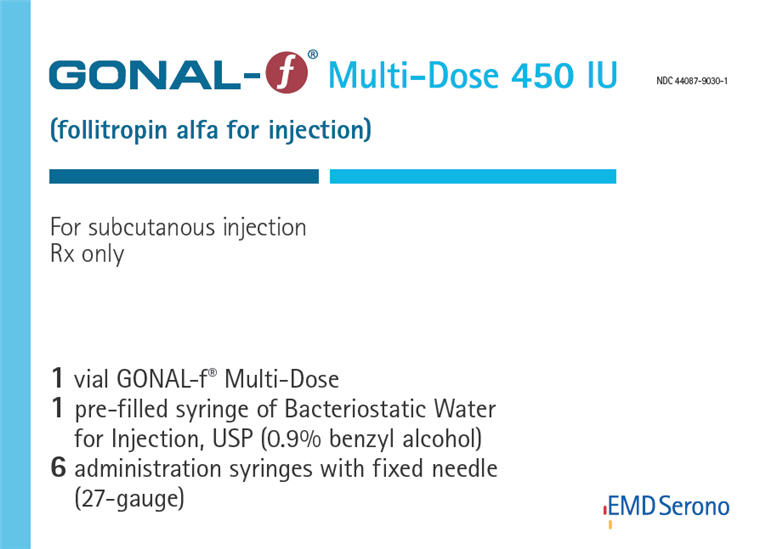
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Kit Carton - 1050 IU
NDC: 44087-9070-1
GONAL-f® Multi-Dose 1050 IU
(follitropin alfa for injection)For subcutaneous injection
Rx only1 vial GONAL-f® Multi-Dose
1 pre-filled syringe of Bacteriostatic Water
for Injection, USP (0.9% benzyl alcohol)
10 administration syringes with fixed needle
(27-gauge)EMD
SERONO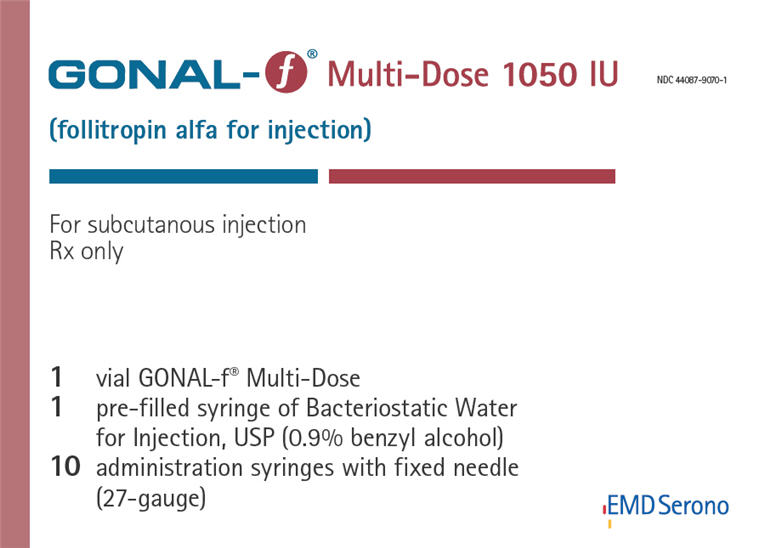
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
GONAL-F
follitropin alfa kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 44087-9030 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 44087-9030-1 1 in 1 CARTON 03/25/2004 Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 VIAL 1 mL Part 2 1 SYRINGE 1 mL Part 1 of 2 GONAL-F
follitropin alfa injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FOLLITROPIN (UNII: 076WHW89TW) (FOLLITROPIN - UNII:076WHW89TW) FOLLITROPIN 450 [iU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 30 mg in 1 mL SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) 1.11 mg in 1 mL SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC, MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 593YOG76RN) 0.45 mg in 1 mL PHOSPHORIC ACID (UNII: E4GA8884NN) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 1 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA020378 03/25/2004 Part 2 of 2 BACTERIOSTATIC WATER
water and benzyl alcohol injection, solutionProduct Information Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) 1 mL in 1 mL BENZYL ALCOHOL (UNII: LKG8494WBH) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 1 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA020378 03/25/2004 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA020378 03/25/2004 GONAL-F
follitropin alfa kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 44087-9070 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 44087-9070-1 1 in 1 CARTON 03/25/2004 Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 VIAL 2 mL Part 2 1 SYRINGE 2 mL Part 1 of 2 GONAL-F
follitropin alfa injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FOLLITROPIN (UNII: 076WHW89TW) (FOLLITROPIN - UNII:076WHW89TW) FOLLITROPIN 1050 [iU] in 2 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 30 mg in 2 mL SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) 1.11 mg in 2 mL SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC, MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 593YOG76RN) 0.45 mg in 2 mL PHOSPHORIC ACID (UNII: E4GA8884NN) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 2 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA020378 03/25/2004 Part 2 of 2 BACTERIOSTATIC WATER
water and benzyl alcohol injection, solutionProduct Information Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) 2 mL in 2 mL BENZYL ALCOHOL (UNII: LKG8494WBH) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 2 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA020378 03/25/2004 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA020378 03/25/2004 Labeler - EMD Serono, Inc. (088514898)
Trademark Results [Gonal-f]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 GONAL-F 77778062 3777170 Live/Registered |
MERCK KGAA 2009-07-09 |
 GONAL-F 77679817 3816320 Live/Registered |
MERCK KGAA 2009-02-27 |
 GONAL-F 76562035 3389332 Live/Registered |
MERCK KGAA 2003-11-26 |
 GONAL-F 74242359 1772761 Live/Registered |
MERCK KGAA 1992-01-31 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.