ZUNVEYL- benzgalantamine tablet, delayed release
ZUNVEYL by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
ZUNVEYL by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Alpha Cognition, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZUNVEYL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZUNVEYL.
ZUNVEYL (benzgalantamine) delayed-release tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2001INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZUNVEYL is a cholinesterase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type in adults (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The recommended starting dosage is 5 mg orally twice daily with or without food; increase to initial maintenance dosage of 10 mg twice daily after a minimum of 4 weeks based on clinical response and tolerability. Dosage may be increased to the maximum recommended dosage of 15 mg twice a day after a minimum of 4 weeks at 10 mg twice daily. (2.1)
- Ensure adequate fluid intake during treatment. Swallow whole; do not split, crush or chew. (2.1)
- May be taken with or without food. (2.1)
- Should not be taken with alcohol. (2.1)
- Hepatic impairment: Should not exceed 10 mg twice daily for moderate hepatic impairment; use in patients with severe hepatic impairment is not recommended (2.2)
- Renal impairment: Should not exceed 10 mg twice daily for creatinine clearance 9 to 59 mL/min; use in patients with creatinine clearance less than 9 mL/min is not recommended. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Delayed-release tablets: 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known hypersensitivity to benzgalantamine, galantamine, or any inactive ingredients in ZUNVEYL (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serious skin reactions: Discontinue at first appearance of skin rash. (5.1)
- All patients should be considered at risk for adverse effects on cardiac conduction, including bradycardia and AV block, because of vagotonic effects on sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. (5.3)
- Active or occult gastrointestinal bleeding: Monitor, especially those with an increased risk for developing ulcers. (5.4)
- Cholinomimetics may cause bladder outflow obstruction. (5.5)
- Monitor for respiratory adverse events in patients with a history of severe asthma or obstructive pulmonary disease. (5.7)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions with galantamine tablets (≥5%) were nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, headache, and decreased appetite. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alpha Cognition Inc. at 1-877-257-4203 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage and Administration
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
2.3 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Skin Reactions
5.2 Anesthesia
5.3 Cardiovascular Conditions
5.4 Gastrointestinal Conditions
5.5 Genitourinary Conditions
5.6 Neurological Conditions
5.7 Pulmonary Conditions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Use with Anticholinergics
7.2 Use with Cholinomimetics and Other Cholinesterase Inhibitors
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Study Outcome Measures
14.2 Galantamine Immediate-Release Tablets
14.3 Galantamine Extended-Release Capsules
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage and Administration
Dosage
The recommended starting dosage is 5 mg twice a day (10 mg/day) by mouth. Increase to initial maintenance dosage of 10 mg twice daily (20 mg/day) after a minimum of 4 weeks, based on clinical response and tolerability. Dosage may be increased to the maximum recommended dosage of 15 mg twice a day (30 mg/day) after a minimum of 4 weeks at 10 mg twice daily.
Administration
ZUNVEYL can be taken with or without food.
ZUNVEYL should not be taken with alcohol [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Swallow whole; do not split, crush or chew.
Ensure adequate fluid intake during treatment.
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score of 5-6). In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score of 7-9), the dosage should generally not exceed 10 mg twice daily (20 mg/day). The use of ZUNVEYL in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score of 10-15) is not recommended [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
In patients with creatinine clearance of 9 to 59 mL/min, the dosage should generally not exceed 10 mg twice daily (20 mg/day). In patients with creatinine clearance less than 9 mL/min, the use of ZUNVEYL is not recommended [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZUNVEYL is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to benzgalantamine, galantamine, or to any inactive ingredient in ZUNVEYL. Serious skin reactions have occurred [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Skin Reactions
Serious skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis) have been reported in patients receiving galantamine (the active metabolite of (ZUNVEYL) tablets. Inform patients and caregivers that the use of ZUNVEYL tablets should be discontinued at the first appearance of a skin rash, unless the rash is clearly not drug-related. If signs or symptoms suggest a serious skin reaction, use of this drug should not be resumed, and alternative therapy should be considered [see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Anesthesia
ZUNVEYL, as a cholinesterase inhibitor, is likely to increase the neuromuscular blocking effects of succinylcholine-type and similar neuromuscular blocking agents during anesthesia.
5.3 Cardiovascular Conditions
Because of their pharmacological action, cholinesterase inhibitors, including ZUNVEYL, have vagotonic effects on the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes, leading to bradycardia and AV block. Bradycardia and all types of heart block have been reported in patients taking cholinesterase inhibitors, both with and without known underlying cardiac conduction abnormalities. Therefore, all patients should be considered at risk for adverse effects on cardiac conduction.
Patients treated with galantamine up to 24 mg/day using the recommended dosing schedule showed a dose-related increase in risk of syncope (placebo 0.7% [2/286]; 4 mg twice daily 0.4% [3/692]; 8 mg twice daily 1.3% [7/552]; 12 mg twice daily 2.2% [6/273]).
5.4 Gastrointestinal Conditions
Through their primary action, cholinomimetics, including ZUNVEYL, may be expected to increase gastric acid secretion because of increased cholinergic activity. Therefore, patients should be monitored closely for symptoms of active or occult gastrointestinal bleeding, especially those with an increased risk for developing ulcers (e.g., those with a history of ulcer disease or patients using concurrent nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs]). Clinical studies of galantamine have shown no increase, relative to placebo, in the incidence of either peptic ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding.
Galantamine, as a predictable consequence of its pharmacological properties, has been shown to produce nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, and weight loss [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Monitor the patient's weight during therapy with ZUNVEYL.
5.5 Genitourinary Conditions
Although this was not observed in clinical trials with galantamine, cholinomimetics, including ZUNVEYL, may cause bladder outflow obstruction.
5.6 Neurological Conditions
Cholinesterase inhibitors are believed to have some potential to cause generalized convulsions [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Seizure activity may also be a manifestation of Alzheimer's disease. Patients with Alzheimer's disease should be monitored closely for seizures while taking ZUNVEYL.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in more detail elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Cardiovascular Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Gastrointestinal Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Genitourinary Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Neurological Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Pulmonary Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of ZUNVEYL has been established in studies of galantamine immediate-release tablets and galantamine extended-release capsules [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Below is a display of the adverse reactions of galantamine in these studies.
Galantamine Extended-Release Capsules and Immediate-Release Tablets
The safety of the extended-release capsule and immediate-release tablet formulations of galantamine was evaluated in 3956 galantamine-treated patients who participated in 8 placebocontrolled clinical studies and 1454 patients in 5 open-label clinical studies with mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type. In clinical studies, the safety profile of once-daily treatment with extended-release galantamine was similar in frequency and nature to that seen with immediate-release galantamine. The information presented in this section was derived from pooled double-blind studies and from pooled open-label data.
Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials of Galantamine
The most common adverse reactions in galantamine-treated patients from double-blind clinical trials (≥5%) were nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, headache, and decreased appetite.
Table 1 lists the adverse reactions reported in ≥1% of galantamine-treated patients in 8 placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trials.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Reported by ≥1% of Galantamine-Treated Patients in 8 Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Clinical Trials System/Organ Class Galantamine Placebo Adverse Reaction (n=3956)
%(n=2546)
%Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Decreased appetite 7.4 2.1 Psychiatric Disorders Depression 3.6 2.3 Nervous System Disorders Dizziness 7.5 3.4 Headache 7.1 5.5 Tremor 1.6 0.7 Somnolence 1.5 0.8 Syncope 1.4 0.6 Lethargy 1.3 0.4 Cardiac Disorders Bradycardia 1.0 0.3 Gastrointestinal Disorders Nausea 20.7 5.5 Vomiting 10.5 2.3 Diarrhea 7.4 4.9 Abdominal pain 3.8 2.0 Abdominal discomfort 2.1 0.7 Dyspepsia 1.5 1.0 Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders Muscle spasms 1.2 0.5 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatigue 3.5 1.8 Asthenia 2.0 1.5 Malaise 1.1 0.5 Investigations Decreased weight 4.7 1.5 Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications Fall 3.9 3.0 Laceration 1.1 0.5 The majority of these adverse reactions occurred during the dose-escalation period. In those patients who experienced the most frequent adverse reaction, nausea, the median duration of the nausea was 5-7 days.
Other Adverse Reactions Observed in Clinical Trials of Galantamine
The following adverse reactions occurred in <1% of all galantamine-treated patients (N=3956) in the above double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial data sets. In addition, the following also includes all adverse reactions reported at any frequency rate in patients (N=1454) who participated in open-label studies.
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Dehydration
Nervous System Disorders: Dysgeusia, Hypersomnia, Paresthesia
Eye Disorders: Blurred vision
Cardiac Disorders: First degree atrioventricular block, Palpitations, Sinus bradycardia, Supraventricular extrasystoles
Vascular Disorders: Flushing, Hypotension
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Retching
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Hyperhidrosis
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Muscular weakness
Discontinuations Due to Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials of Galantamine
In the 8 placebo-controlled studies of adults, 418 (10.6%) galantamine-treated patients (N=3956) and 56 (2.2%) placebo patients (N=2546) discontinued because of an adverse reaction. Those reactions with an incidence of ≥0.5% in the galantamine-treated patients included nausea (6.2%), vomiting (3.3%), decreased appetite (1.5%), dizziness (1.3%), diarrhea (0.8%), headache (0.7%), and decreased weight (0.7%). The only event that caused discontinuation with an incidence of ≥0.5% in placebo patients was nausea (17, 0.7%).
In the 5 open-label studies, 103 (7.1%) patients (N=1454) discontinued because of an adverse reaction. Those reactions that caused discontinuation with an incidence of ≥0.5% included nausea (3.0%), vomiting (1.6%), decreased appetite (0.9%), headache (0.8%), decreased weight (0.6%), dizziness (0.6%), and diarrhea (0.5%).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of galantamine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]
Psychiatric Disorders: Hallucinations
Nervous System Disorders: Seizures, extrapyramidal disorder [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: Tinnitus
Cardiac Disorders: Complete atrioventricular block
Vascular Disorders: Hypertension
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hepatitis, increased hepatic enzyme
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)], erythema multiforme
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of ZUNVEYL or galantamine in pregnant women. In studies conducted in animals, administration of galantamine during pregnancy resulted in developmental toxicity (increased incidence of morphological abnormalities and decreased growth in offspring) at doses similar to or greater than those used clinically (see Data).
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
In rats, administration of galantamine (oral doses of 2, 8, or 16 mg/kg/day), from day 14 (females) or day 60 (males) prior to mating and continuing in females through the period of organogenesis, resulted in an increased incidence of fetal skeletal variations at the two highest doses, which were associated with maternal toxicity. The no-effect dose for embryo-fetal developmental toxicity in rats (2 mg/kg/day) is approximately equal to the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 22 mg/day galantamine (equivalent to 30 mg/day benzgalantamine) on a body surface area (mg/m2) basis. When galantamine (oral doses of 4, 12, 28, or 40 mg/kg/day) was administered to pregnant rabbits throughout the period of organogenesis, small increases in fetal visceral malformations and skeletal variations were observed at the highest dose which was associated with maternal toxicity. The no-effect dose for embryo-fetal developmental toxicity in rabbits (28 mg/kg/day) is approximately 20 times the MRHD of galantamine on a mg/m2 basis. In a study in which pregnant rats were orally dosed with galantamine (2, 8, or 16 mg/kg/day) from the beginning of organogenesis through day 21 post-partum, pup weights were decreased at birth and during the lactation period at the two highest doses. The no-effect dose for pre- and postnatal developmental toxicity in rats (2 mg/kg/day) is approximately equal to the MRHD of galantamine on a mg/m2 basis.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of benzgalantamine or galantamine in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ZUNVEYL and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ZUNVEYL or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Eight double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials and 5 open-label trials in a total of 6519 patients have investigated galantamine in the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14)]. The mean age of patients enrolled in these clinical studies was 75 years; 78% of these patients were between 65 and 84 years of age, and 10% of patients were 85 years of age or older. Clinical studies of galantamine did not include sufficient numbers of younger adult patients to determine if patients 65 years of age and older respond differently than younger adult patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
In patients with moderate hepatic impairment, a decrease in clearance of galantamine was observed; therefore, a dosage adjustment is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The use of ZUNVEYL in patients with severe hepatic impairment is not recommended.
8.7 Renal Impairment
In patients with a creatinine clearance of 9 to 59 mL/min, an increase in exposure of galantamine was observed; therefore, a dosage adjustment is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (232) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The use of ZUNVEYL in patients with creatinine clearance less than 9 mL/min is not recommended.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Because strategies for the management of overdose are continually evolving, it is advisable to contact a poison control center to determine the latest recommendations for the management of an overdose of any drug.
As in any case of overdose, general supportive measures should be utilized. Signs and symptoms of significant overdosing of galantamine are predicted to be similar to those of overdosing of other cholinomimetics. These effects generally involve the central nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system, and the neuromuscular junction. In addition to muscle weakness or fasciculations, some or all of the following signs of cholinergic crisis may develop: severe nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal cramping, salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, sweating, bradycardia, hypotension, respiratory depression, collapse and convulsions. Increasing muscle weakness is a possibility and may result in death if respiratory muscles are involved.
Tertiary anticholinergics such as atropine may be used as an antidote for ZUNVEYL overdosage. Intravenous (IV) atropine sulfate titrated to effect is recommended at an initial dose of 0.5 to 1.0 mg IV with subsequent doses based upon clinical response. Atypical responses in blood pressure and heart rate have been reported with other cholinomimetics when co-administered with quaternary anticholinergics. It is not known whether galantamine and/or its metabolites can be removed by dialysis (hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, or hemofiltration). Dose-related signs of toxicity in animals included hypoactivity, tremors, clonic convulsions, salivation, lacrimation, chromodacryorrhea, mucoid feces, and dyspnea.
In one postmarketing report, one patient who had been taking 4 mg of galantamine daily for a week inadvertently ingested eight 4 mg tablets (32 mg total) on a single day. Subsequently, she developed bradycardia, QT prolongation, ventricular tachycardia and torsades de pointes accompanied by a brief loss of consciousness for which she required hospital treatment. Two additional cases of accidental ingestion of 32 mg (nausea, vomiting, and dry mouth; nausea, vomiting, and substernal chest pain) and one of 40 mg (vomiting), resulted in brief hospitalizations for observation with full recovery. One patient, who was prescribed 24 mg/day and had a history of hallucinations over the previous two years, mistakenly received 24 mg twice daily for 34 days and developed hallucinations requiring hospitalization. Another patient, who was prescribed 16 mg/day of oral solution, inadvertently ingested 160 mg (40 mL) and experienced sweating, vomiting, bradycardia, and near-syncope one hour later, which necessitated hospital treatment. His symptoms resolved within 24 hours.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ZUNVEYL (benzgalantamine) is a prodrug of galantamine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor . Benzgalantamine gluconate is known chemically as (4aS,6R,8aS)-4a,5,9,10,11,12-hexahydro-3-methoxy-11-methyl-6H-benzofuro[3a,3,2-ef][2]benzazepin-6- benzoate gluconate salt. It has an empirical formula of C30H37NO11 and has a molecular weight of 587.61 (gluconate salt) and 391.46 (benzgalantamine). Benzgalantamine gluconate is a white to pale yellow powder and is soluble in water. Benzgalantamine has a pH of 5 to 6 and dissociation constant (pKa) of 7.0. It is slightly soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in acetone, acetonitrile and hexane. The structural formula for benzgalantamine gluconate is:
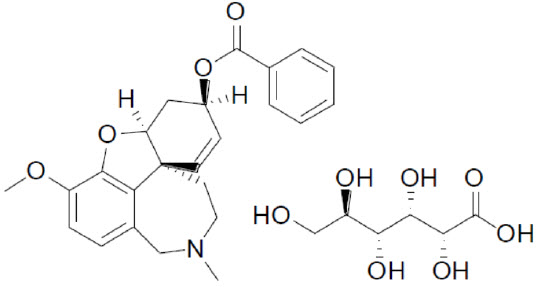
ZUNVEYL contains 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg benzgalantamine equivalent to 7.49 mg, 14.98 mg, and 22.47 mg benzgalantamine gluconate, respectively. ZUNVEYL delayed-release tablets are for oral use. Inactive ingredients include calcium silicate, colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, mannitol, methacrylic acid, poloxamer 407, polyethylene glycol/macrogol, sodium bicarbonate, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium stearyl fumarate, talc, and titanium dioxide. The 10 mg tablet also contains Carmine, FD&C Blue #2/Indigo Carmine Aluminum Lake, and FD&C Red #40/Allura Red AC Aluminum Lake. The 15 mg tablet also contains FD&C Blue #2/Indigo Carmine Aluminum Lake, FD&C Red #40/Allura Red AC Aluminum Lake, and FD&C Yellow #6/Sunset Yellow FCF Aluminum Lake.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Although the etiology of cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease (AD) is not fully understood, it has been reported that acetylcholine-producing neurons degenerate in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. The degree of this cholinergic loss has been correlated with degree of cognitive impairment and density of amyloid plaques (a neuropathological hallmark of Alzheimer's disease).
ZUNVEYL is a prodrug of galantamine. Galantamine, a tertiary alkaloid, is a competitive and reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. While the precise mechanism of galantamine's action is unknown, it is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by cholinesterase. If this mechanism is correct, galantamine's effect may lessen as the disease process advances and fewer cholinergic neurons remain functionally intact. There is no evidence that galantamine alters the course of the underlying dementing process.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
There are no relevant pharmacodynamic (PD) data, and the PD effects are unknown for ZUNVEYL.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Benzgalantamine is a prodrug of galantamine, the active metabolite. The systemic exposures of benzgalantamine are less than 1% of galantamine exposures; therefore, the pharmacokinetic information presented below is for that of galantamine. Dose-proportionality is observed for ZUNVEYL over the dose range of 5 to 15 mg and steady state is achieved within a week.
Absorption
Galantamine is absorbed with time to peak concentration of about 2.5 to 3 hours. The absolute bioavailability of galantamine is about 90%.
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution of galantamine is 175 L. The plasma protein binding of galantamine is 18% at therapeutically relevant concentrations. In whole blood, galantamine is mainly distributed to blood cells (52.7%). The blood to plasma concentration ratio of galantamine is 1.2.
Elimination
Galantamine is eliminated by hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes, glucuronidation, and excretion of unchanged drug in the urine.
After IV or oral administration, about 20% of the dose was excreted as unchanged galantamine in the urine in 24 hours, representing a renal clearance of about 65 mL/min, about 20-25% of the total plasma clearance of about 300 mL/min. Galantamine has a terminal half-life of about 7 hours.
Metabolism
Based on in vitro studies, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 were the major enzymes involved in the metabolism of galantamine. CYP2D6 was involved in the formation of O-desmethylgalantamine, whereas CYP3A4 mediated the formation of galantamine-N-oxide. Galantamine is also glucuronidated and excreted unchanged in urine.
Excretion
In studies of oral 3H-galantamine, unchanged galantamine and its glucuronide, accounted for most plasma radioactivity in poor and extensive CYP2D6 metabolizers. Up to 8 hours post-dose, unchanged galantamine accounted for 39-77% of the total radioactivity in the plasma, and galantamine glucuronide for 14-24%. By 7 days, 93-99% of the radioactivity had been recovered, with about 95% in urine and about 5% in the feces. Total urinary recovery of unchanged galantamine accounted for, on average, 32% of the dose and that of galantamine glucuronide for another 12% on average.
Specific Populations
Elderly
Data from clinical trials in patients with Alzheimer's disease indicate that galantamine concentrations are 30-40% higher in those patients than in healthy young subjects.
Gender and Race
A population pharmacokinetic analysis (on 539 men and 550 women) indicates that galantamine clearance is about 20% lower in women than in men (which is explained by a lower body weight in women) and that race (n=1029 White, 24 Black, 13 Asian, and 23 other) did not affect the clearance of galantamine.
Hepatic Impairment
Following a single 4 mg dose of galantamine tablets, the pharmacokinetics of galantamine in subjects with mild hepatic impairment (n=8; Child-Pugh score of 5-6) were similar to the pharmacokinetics of galantamine in healthy subjects. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (n=8; Child Pugh score of 7-9), galantamine clearance was decreased by about 25% compared to galantamine clearance in normal volunteers. Exposure to galantamine would be expected to increase further with increasing degree of hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Renal Impairment
Following a single 8 mg dose of galantamine tablets, AUC increased by 37% and 67% in patients with moderate and severe renal impairment, respectively, compared with normal volunteers [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Drug-Drug Interactions
In Vitro Studies
Effect of Alcohol: Alcohol-induced dose dumping of ZUNVEYL was observed in the presence of 40% (v/v) alcohol in an in vitro dissolution study; however, dose dumping was not observed in the presence of lower alcohol concentrations. The clinical significance of this dose dumping was not fully characterized in humans [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Effect of Other Drugs on Galantamine
-
CYP3A4 Inhibitors:
Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4 and an inhibitor of CYP2D6, when administered at a dose of 200 mg two times a day for 4 days, increased the AUC of galantamine by 30%.
Erythromycin
Erythromycin, a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4, when administered at a dose of 500 mg four times a day for 4 days, increased the AUC of galantamine by 10%.
-
CYP2D6 Inhibitors:
A population pharmacokinetics analysis on a database of 852 patients with Alzheimer's disease showed that the clearance of galantamine was reduced about 25-33% by the concurrent administration of amitriptyline (n=17), fluoxetine (n=48), fluvoxamine (n=14), and quinidine (n=7), all of which are known inhibitors of CYP2D6.
Paroxetine
Paroxetine, a strong inhibitor of CYP2D6, when administered at a dose of 20 mg/day for 16 days, increased the oral bioavailability of galantamine by about 40%.
-
H2 Antagonists
Galantamine was administered as a single dose of 4 mg on day 2 of a 3-day treatment with either cimetidine (800 mg daily) or ranitidine (300 mg daily). Cimetidine increased the bioavailability of galantamine by approximately 16%. Ranitidine had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of galantamine.
Effect of Galantamine on Other Drugs
-
In Vitro Studies
In vitro studies show that galantamine did not inhibit the metabolic pathways catalyzed by CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP3A4, CYP4A, CYP2C, CYP2D6 or CYP2E1.
-
In Vivo Studies
Warfarin
Multiple doses of galantamine at 24 mg/day had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of R-and S-warfarin (administered in a single dose of 25 mg) or on the increased prothrombin time induced by warfarin. The protein binding of warfarin was unaffected by galantamine.
Digoxin
Multiple doses of galantamine at 24 mg/day had no effect on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of digoxin (at a dose of 0.375 mg once daily) when those two drugs were co-administered. In that study, however, one healthy subject was hospitalized on account of 2nd and 3rd degree heart block and bradycardia.
-
CYP3A4 Inhibitors:
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a 24-month oral carcinogenicity study in rats, an increase in endometrial adenocarcinomas was observed at 10 mg/kg/day (4 times the MRHD of 22 mg/day galantamine (equivalent to 30 mg/day benzgalantamine) on a mg/m2 basis) and 30 mg/kg/day (12 times MRHD of galantamine on a mg/m2 basis). No increase in neoplastic changes was observed in females at 2.5 mg/kg/day (equivalent to the MRHD of galantamine on a mg/m2 basis) or in males up to the highest dose tested of 30 mg/kg/day (12 times the MRHD of galantamine on a mg/m2 basis).
Galantamine was not carcinogenic in a 6-month carcinogenicity study in transgenic (P 53-deficient) mice at oral doses up to 20 mg/kg/day, or in a 24-month carcinogenicity study in mice at oral doses up to 10 mg/kg/day.
Mutagenesis
Benzgalantamine was negative in a battery of in vitro (bacterial reverse mutation and chromosomal aberration in human peripheral blood lymphocytes) genotoxicity assays.
Galantamine was negative in a battery of in vitro (bacterial reverse mutation, mouse lymphoma tk, and chromosomal aberration in mammalian cells) and in vivo (mouse micronucleus) genotoxicity assays.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of ZUNVEYL is based upon 3 bioavailability studies in healthy adults comparing galantamine immediate-release tablets and galantamine extended-release capsules to ZUNVEYL [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The effectiveness of galantamine as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease is demonstrated by the results of 5 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical investigations in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease, 4 with the immediate-release tablet and 1 with the extendedrelease capsule [diagnosed by NINCDS-ADRDA criteria, with Mini-Mental State Examination scores that were ≥10 and ≤24]. Doses studied with the immediate-release tablet were 8-32 mg/day given as twice daily doses. In 3 of the 4 studies with the immediate-release tablet, patients were started on a low dose of 8 mg, then titrated weekly by 8 mg/day to 24 or 32 mg as assigned. In the fourth study (USA 4-week Dose Escalation Fixed-Dose Study) dose escalation of 8 mg/day occurred over 4-week intervals. The mean age of patients participating in these 4 galantamine trials was 75 years with a range of 41 to 100. Approximately 62% of patients were women and 38% were men. The racial distribution was White 94%, Black 3% and other races 3%. Two other studies examined a three times daily dosing regimen; these also showed or suggested benefit but did not suggest an advantage over twice daily dosing.
14.1 Study Outcome Measures
In each study, the primary effectiveness of galantamine was evaluated using a dual outcome assessment strategy as measured by the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-cog) and the Clinician's Interview Based Impression of Change that required the use of caregiver information (CIBIC-plus).
The ability of galantamine to improve cognitive performance was assessed with the cognitive sub-scale of the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-cog), a multi-item instrument that has been validated in longitudinal cohorts of Alzheimer's disease patients. The ADAS-cog examines selected aspects of cognitive performance including elements of memory, orientation, attention, reasoning, language and praxis. The ADAS-cog scoring range is from 0 to 70, with higher scores indicating greater cognitive impairment. Elderly normal adults may score as low as 0 or 1, but it is not unusual for non-demented adults to score slightly higher.
The patients recruited as participants in each study using the immediate-release tablet formulation had mean scores on ADAS-cog of approximately 27 units, with a range from 5 to 69. Experience using the ADAS-cog in longitudinal studies of ambulatory patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease suggests that patients typically gain 6 to 12 units a year. Because the ADAS-cog is not uniformly sensitive to change over the course of the disease, a less than typical degree of change may be seen in patients at very early or later stages of disease. The annualized rate of decline in the placebo patients participating in galantamine trials was approximately 4.5 units per year.
The ability of galantamine to produce an overall clinical effect was assessed using a Clinician's Interview Based Impression of Change that required the use of caregiver information, the CIBICplus. The CIBIC-plus is not a single instrument and is not a standardized instrument like the ADAS-cog. Clinical trials for investigational drugs have used a variety of CIBIC formats, each different in terms of depth and structure. As such, results from a CIBIC-plus reflect clinical experience from the trial or trials in which it was used and cannot be compared directly with the results of CIBIC-plus evaluations from other clinical trials. The CIBIC-plus used in the trials was a semi-structured instrument based on a comprehensive evaluation at baseline and subsequent time-points of 4 major areas of patient function: general, cognitive, behavioral and activities of daily living. It represents the assessment of a skilled clinician based on his/her observation at an interview with the patient, in combination with information supplied by a caregiver familiar with the behavior of the patient over the interval rated. The CIBIC-plus is scored as a seven-point categorical rating, ranging from a score of 1, indicating "markedly improved," to a score of 4, indicating "no change" to a score of 7, indicating "marked worsening." The CIBIC-plus has not been systematically compared directly to assessments not using information from caregivers (CIBIC) or other global methods.
14.2 Galantamine Immediate-Release Tablets
U.S. Twenty-One Week Fixed-Dose Study
In a study of 21 weeks duration, 978 patients were randomized to doses of 8, 16, or 24 mg of galantamine per day, or to placebo, each given in 2 divided doses. Treatment was initiated at 8 mg/day for all patients randomized to galantamine and increased by 8 mg/day every 4 weeks. Therefore, the maximum titration phase was 8 weeks and the minimum maintenance phase was 13 weeks (in patients randomized to 24 mg/day of galantamine).
Effects on the ADAS-cog
Figure 1 illustrates the time course for the change from baseline in ADAS-cog scores for all four dose groups over the 21 weeks of the study. At 21 weeks of treatment, the mean differences in the ADAS-cog change scores for the galantamine-treated patients compared to the patients on placebo were 1.7, 3.3, and 3.6 units for the 8, 16 and 24 mg/day treatments, respectively. The 16 mg/day and 24 mg/day treatments were statistically significantly superior to placebo and to the 8 mg/day treatment. There was no statistically significant difference between the 16 mg/day and 24 mg/day dose groups.
Figure 1: Time-Course of the Change From Baseline in ADAS-cog Score for Patients Completing 21 Weeks (5 Months) of Treatment
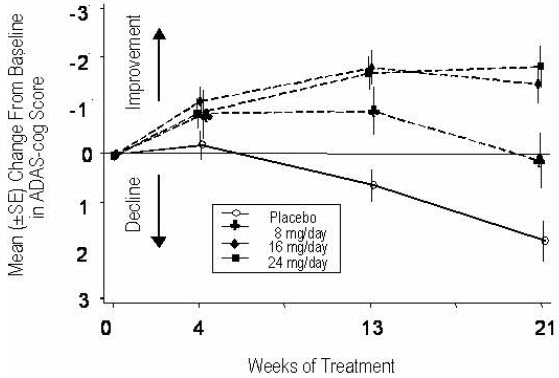
Figure 2 illustrates the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the four treatment groups who had attained at least the measure of improvement in ADAS-cog score shown on the X-axis. Three change scores (10-point, 7-point and 4-point reductions) and no change in score from baseline have been identified for illustrative purposes, and the percent of patients in each group achieving that result is shown in the inset table.
The curves demonstrate that both patients assigned to galantamine and placebo have a wide range of responses, but that the galantamine groups are more likely to show the greater improvements.
Figure 2: Cumulative Percentage of Patients Completing 21 Weeks of Double-Blind Treatment With Specified Changes From Baseline in ADAS-cog Scores. The Percentages of Randomized Patients Who Completed the Study Were: Placebo 84%, 8 mg/day 77%, 16 mg/day 78% and 24 mg/day 78%.
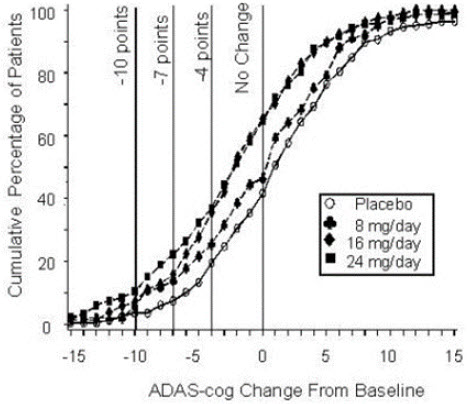
Change in ADAS-cog Treatment -10 -7 -4 -0 Placebo 3.6% 7.6% 19.6 % 41.8% 8 mg/day 5.9% 13.9% 25.7% 46.5% 16 mg/day 7.2% 15.9% 35.6% 65.4% 24 mg/day 10.4% 22.3% 37.0% 64.9% Effects on the CIBIC-plus
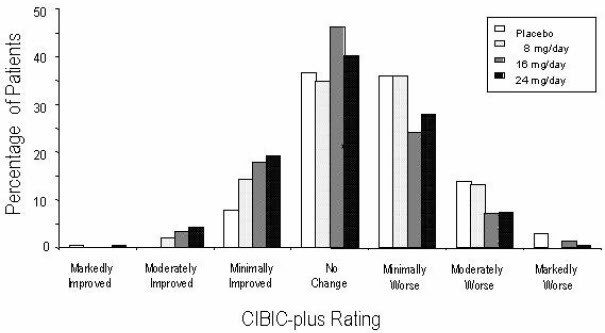
Figure 3 is a histogram of the percentage distribution of CIBIC-plus scores attained by patients assigned to each of the four treatment groups who completed 21 weeks of treatment. The galantamine-placebo differences for these groups of patients in mean rating were 0.15, 0.41 and 0.44 units for the 8, 16 and 24 mg/day treatments, respectively. The 16 mg/day and 24 mg/day treatments were statistically significantly superior to placebo. The differences vs. the 8 mg/day treatment for the 16 and 24 mg/day treatments were 0.26 and 0.29, respectively. There were no statistically significant differences between the 16 mg/day and 24 mg/day dose groups.
Figure 3: Distribution of CIBIC-plus Ratings at Week 21
U.S. Twenty-Six Week Fixed-Dose Study
In a study of 26 weeks duration, 636 patients were randomized to either a dose of 24 mg or 32 mg of galantamine per day, or to placebo, each given in two divided doses. The 26-week study was divided into a 3-week dose titration phase and a 23-week maintenance phase.
Effects on the ADAS-cog
Figure 4 illustrates the time course for the change from baseline in ADAS-cog scores for all three dose groups over the 26 weeks of the study. At 26 weeks of treatment, the mean differences in the ADAS-cog change scores for the galantamine-treated patients compared to the patients on placebo were 3.9 and 3.8 units for the 24 mg/day and 32 mg/day treatments, respectively. Both treatments were statistically significantly superior to placebo but were not significantly different from each other.
Figure 4: Time-Course of the Change From Baseline in ADAS-cog Score for Patients Completing 26 Weeks of Treatment
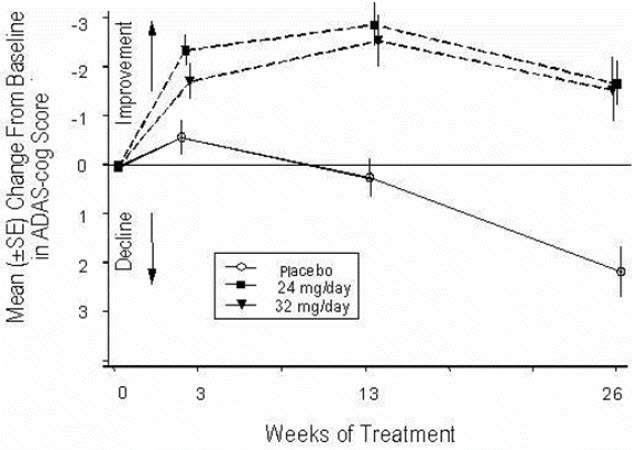
Figure 5 illustrates the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the three treatment groups who had attained at least the measure of improvement in ADAS-cog score shown on the X-axis. Three change scores (10-point, 7-point and 4-point reductions) and no change in score from baseline have been identified for illustrative purposes, and the percent of patients in each group achieving that result is shown in the inset table.
The curves demonstrate that both patients assigned to galantamine and placebo have a wide range of responses, but that the galantamine groups are more likely to show the greater improvements. A curve for an effective treatment would be shifted to the left of the curve for placebo, while an ineffective or deleterious treatment would be superimposed upon or shifted to the right of the curve for placebo, respectively.
Change in ADAS-cog Treatment -10 -7 -4 -0 Placebo 2.1% 5.7% 16.6% 43.9% 24 mg/day 7.6% 18.3% 33.6% 64.1% 32 mg/day 11.1% 19.7% 33.3% 58.1% Figure 5: Cumulative Percentage of Patients Completing 26 Weeks of Double-Blind Treatment With Specified Changes From Baseline in ADAS-cog Scores. The Percentages of Randomized Patients Who Completed the Study Were: Placebo 81%, 24 mg/day 68%, and 32 mg/day 58%.
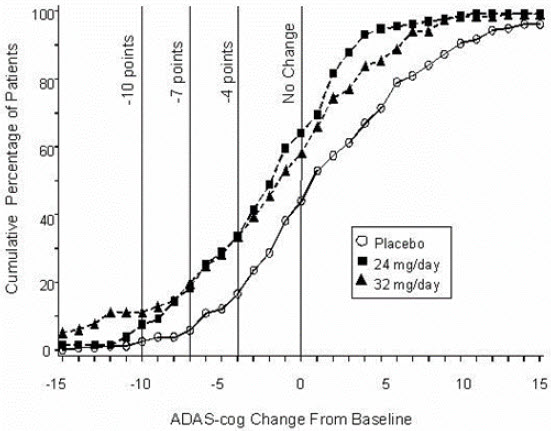
Effects on the CIBIC-plus
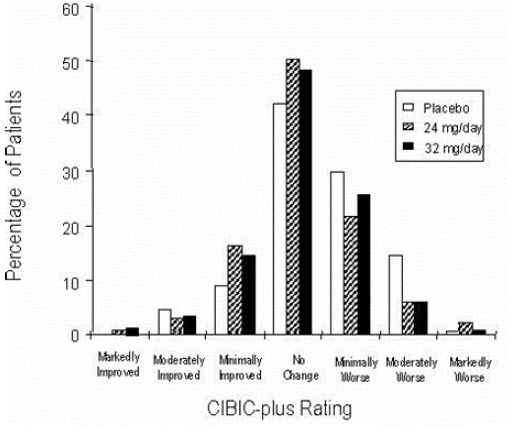
Figure 6 is a histogram of the percentage distribution of CIBIC-plus scores attained by patients assigned to each of the three treatment groups who completed 26 weeks of treatment. The mean galantamine-placebo differences for these groups of patients in the mean rating were 0.28 and 0.29 units for 24 and 32 mg/day of galantamine, respectively. The mean ratings for both groups were statistically significantly superior to placebo but were not significantly different from each other.
Figure 6: Distribution of CIBIC-plus Ratings at Week 26
International Twenty-Six Week Fixed-Dose Study
In a study of 26 weeks duration identical in design to the USA 26-Week Fixed-Dose Study, 653 patients were randomized to either a dose of 24 mg or 32 mg of galantamine per day, or to placebo, each given in two divided doses. The 26-week study was divided into a 3-week dose titration phase and a 23-week maintenance phase.
Effects on the ADAS-cog
Figure 7 illustrates the time course for the change from baseline in ADAS-cog scores for all three dose groups over the 26 weeks of the study. At 26 weeks of treatment, the mean differences in the ADAS-cog change scores for the galantamine-treated patients compared to the patients on placebo were 3.1 and 4.1 units for the 24 mg/day and 32 mg/day treatments, respectively. Both treatments were statistically significantly superior to placebo but were not significantly different from each other.
Figure 7: Time-Course of the Change From Baseline in ADAS-cog Score for Patients Completing 26 Weeks of Treatment
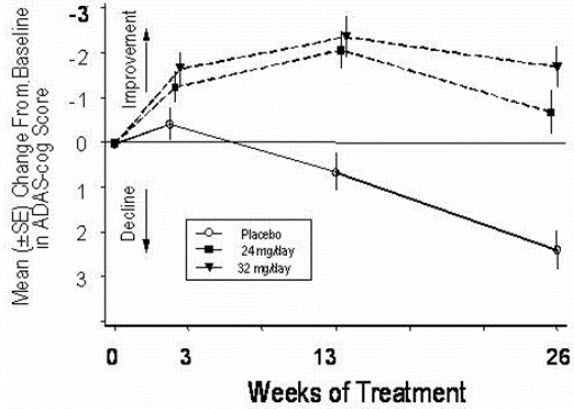
Figure 8 illustrates the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the three treatment groups who had attained at least the measure of improvement in ADAS-cog score shown on the X-axis. Three change scores (10-point, 7-point and 4-point reductions) and no change in score from baseline have been identified for illustrative purposes, and the percent of patients in each group achieving that result is shown in the inset table.
The curves demonstrate that both patients assigned to galantamine and placebo have a wide range of responses, but that the galantamine groups are more likely to show the greater improvements.
Figure 8: Cumulative Percentage of Patients Completing 26 Weeks of Double-Blind Treatment With Specified Changes From Baseline in ADAS-cog Scores. The Percentages of Randomized Patients Who Completed the Study Were: Placebo 87%, 24 mg/day 80%, and 32 mg/day 75%.
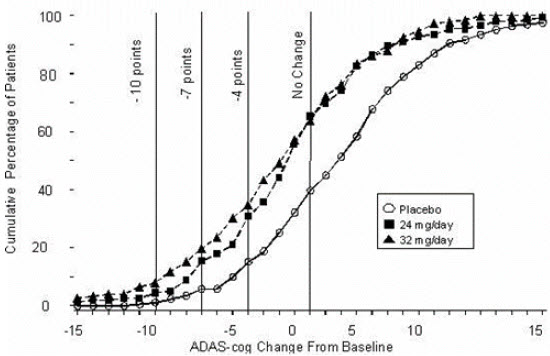
Effects on the CIBIC-plus
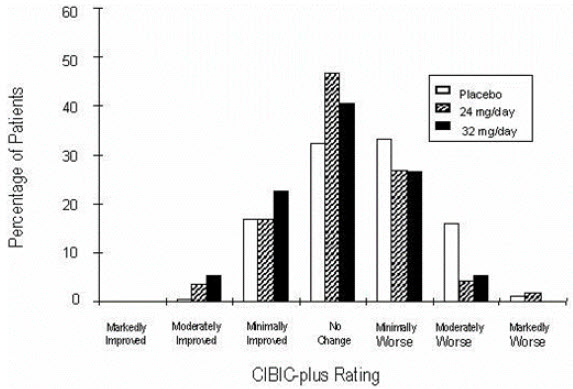
Figure 9 is a histogram of the percentage distribution of CIBIC-plus scores attained by patients assigned to each of the three treatment groups who completed 26 weeks of treatment. The mean galantamine-placebo differences for these groups of patients in the mean rating of change from baseline were 0.34 and 0.47 for 24 and 32 mg/day of galantamine respectively. The mean ratings for the galantamine groups were statistically significantly superior to placebo but were not significantly different from each other.
Figure 9: Distribution of CIBIC-plus Rating at Week 26
International Thirteen-Week Flexible-Dose Study
In a study of 13 weeks duration, 386 patients were randomized to either a flexible dose of 24-32 mg/day of galantamine or to placebo, each given in two divided doses. The 13-week study was divided into a 3-week dose titration phase and a 10-week maintenance phase. The patients in the active treatment arm of the study were maintained at either 24 mg/day or 32 mg/day at the discretion of the investigator.
Effects on the ADAS-cog
Figure 10 illustrates the time course for the change from baseline in ADAS-cog scores for both dose groups over the 13 weeks of the study. At 13 weeks of treatment, the mean difference in the ADAS-cog change scores for the treated patients compared to the patients on placebo was 1.9. Galantamine at a dose of 24-32 mg/day was statistically significantly superior to placebo.
Figure 10: Time-Course of the Change From Baseline in ADAS-cog Score for Patients Completing 13 Weeks of Treatment
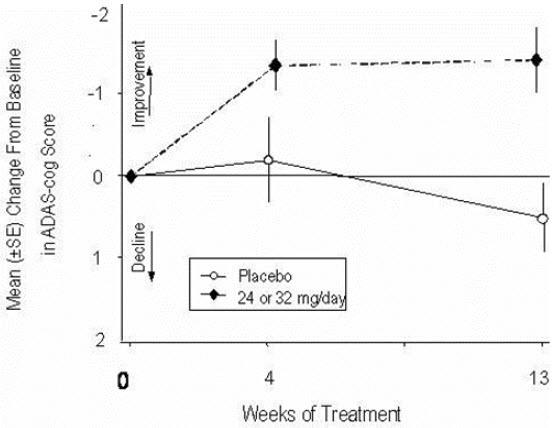
Figure 11 illustrates the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the two treatment groups who had attained at least the measure of improvement in ADAS-cog score shown on the X-axis. Three change scores (10-point, 7-point and 4-point reductions) and no change in score from baseline have been identified for illustrative purposes, and the percent of patients in each group achieving that result is shown in the inset table.
The curves demonstrate that both patients assigned to galantamine and placebo have a wide range of responses, but that the galantamine group is more likely to show the greater improvement.
Figure 11: Cumulative Percentage of Patients Completing 13 Weeks of Double-Blind Treatment With Specified Changes from Baseline in ADAS-cog Scores. The Percentages of Randomized Patients Who Completed the Study Were: Placebo 90%, 24-32 mg/day 67%.
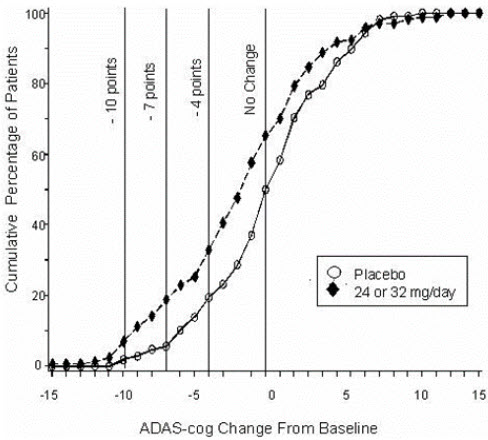
Change in ADAS-cog Treatment -10 -7 -4 -0 Placebo 1.9% 5.6% 19.4% 50.0% 24 or 32 mg/day 7.1% 18.8% 32.9% 65.3% Effects on the CIBIC-plus
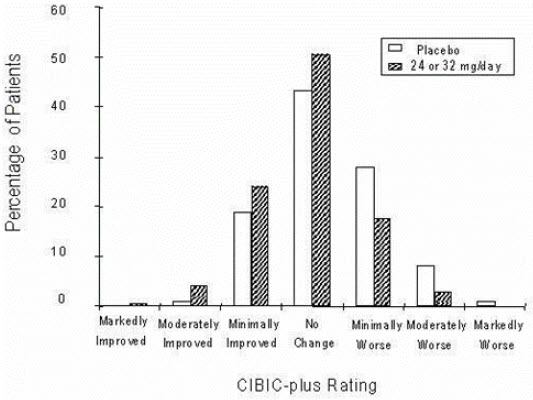
Figure 12 is a histogram of the percentage distribution of CIBIC-plus scores attained by patients assigned to each of the two treatment groups who completed 13 weeks of treatment. The mean galantamine-placebo differences for the group of patients in the mean rating of change from baseline were 0.37 units. The mean rating for the 24–32 mg/day group was statistically significantly superior to placebo.
Figure 12: Distribution of CIBIC-plus Ratings at Week 13
14.3 Galantamine Extended-Release Capsules
The efficacy of galantamine extended-release capsules was studied in a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial which was 6 months in duration and had an initial 4-week doseescalation phase. In this trial, patients were assigned to one of 3 treatment groups: glantamine extended-release capsules in a flexible dose of 16 to 24 mg once daily; galantamine immediaterelease tablets in a flexible dose of 8 to 12 mg twice daily; and placebo. The primary efficacy measures in this study were the ADAS-cog and CIBIC-plus. On the protocol-specified primary efficacy analysis at Month 6, a statistically significant improvement favoring galantamine extended-release capsules over placebo was seen for the ADAS-cog, but not for the CIBIC-plus. Galantamine extended-release capsules showed a statistically significant improvement when compared with placebo on the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study-Activities of Daily Living (ADCS-ADL) scale, a measure of function, and a secondary efficacy measure in this study. The effects of both galantamine extended-release capsules and galantamine immediaterelease tablets on the ADAS-cog, CIBIC-plus, and ADCS-ADL were similar in this study.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
ZUNVEYL delayed-release tablets are enteric coated and supplied in child-resistant packages as follows:
- 5 mg white tablet debossed with "B05" in grey – bottles of 60 (NDC: 84054-005-60)
- 10 mg purple tablet debossed with "B10" in grey – bottles of 60 (NDC: 84054-010-60)
- 15 mg grey tablet debossed with "B15" in dark grey – bottles of 60 (NDC: 84054-015-60)
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Serious Skin Reactions
Advise patients and caregivers to discontinue ZUNVEYL and seek immediate medical attention at the first appearance of skin rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Administration Information
Instruct patients or caregivers about the recommended dosage and administration of ZUNVEYL delayed-release tablets, which should be administered twice daily with or without food.
Instruct patients to swallow ZUNVEYL whole and not to split, crush, or chew the tablets.
Advise patients and caregivers to ensure adequate fluid intake during treatment and that ZUNVEYL should not be taken with alcohol [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Active ingredient made in Taiwan.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15 mg Tablet Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ZUNVEYL
benzgalantamine tablet, delayed releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 84054-005 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength benzgalantamine (UNII: XOI2Q0ZF7G) (benzgalantamine - UNII:XOI2Q0ZF7G) benzgalantamine 5 mg Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND (convex) Size 5mm Flavor Imprint Code B05 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 84054-005-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/09/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218549 08/09/2024 ZUNVEYL
benzgalantamine tablet, delayed releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 84054-010 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength benzgalantamine (UNII: XOI2Q0ZF7G) (benzgalantamine - UNII:XOI2Q0ZF7G) benzgalantamine 10 mg Product Characteristics Color PURPLE Score no score Shape ROUND (convex) Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code B10 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 84054-010-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/09/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218549 08/09/2024 ZUNVEYL
benzgalantamine tablet, delayed releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 84054-015 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength benzgalantamine (UNII: XOI2Q0ZF7G) (benzgalantamine - UNII:XOI2Q0ZF7G) benzgalantamine 15 mg Product Characteristics Color GRAY Score no score Shape ROUND (convex) Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code B15 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 84054-015-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/09/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218549 08/09/2024 Labeler - Alpha Cognition, Inc. (076074000)
Trademark Results [ZUNVEYL]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ZUNVEYL 97117817 not registered Live/Pending |
Alpha Cognition Canada Inc. 2021-11-10 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.


