TOPOTECAN injection, solution, concentrate
TOPOTECAN by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
TOPOTECAN by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Mylan Institutional LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TOPOTECAN INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TOPOTECAN INJECTION.
TOPOTECAN injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1996WARNING: MYELOSUPPRESSION
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Topotecan can cause severe myelosuppression. Administer first cycle only to patients with baseline neutrophil counts greater than or equal to 1,500/mm3 and platelet count greater than or equal to 100,000/mm3. Monitor blood cell counts. (2.2, 5.1)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Topotecan Injection is a topoisomerase inhibitor indicated for treatment of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) platinum-sensitive disease in patients who progressed at least 60 days after initiation of first-line chemotherapy. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 4 mg/4 mL (1 mg/mL topotecan free base) solution in single-dose vial. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
History of severe hypersensitivity reactions to topotecan. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Interstitial lung disease (ILD): Fatal cases have occurred. Permanently discontinue if ILD confirmed. (5.2)
- Extravasation and tissue injury: Severe cases have occurred. If extravasation occurs, immediately stop administration and institute recommended management procedures. (5.3)
- Embryo-fetal toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise women of potential risk to the fetus. (5.4, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The most common Grade 3 or 4 hematologic adverse reactions (incidence >5%) were: neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and febrile neutropenia. (6.1)
- The most common non-hematologic adverse reactions (incidence >5%) (all grades) were asthenia, dyspnea, nausea, pneumonia, abdominal pain, and fatigue. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mylan at 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-INFO-RX) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: MYELOSUPPRESSION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Safety Information
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Small Cell Lung Cancer
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Renal Impairment
2.5 Preparation and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myelosuppression
5.2 Interstitial Lung Disease
5.3 Extravasation and Tissue Injury
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Small Cell Lung Cancer
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: MYELOSUPPRESSION
Topotecan can cause severe myelosuppression. Administer first cycle only to patients with baseline neutrophil counts of greater than or equal to 1,500/mm3 and platelet counts greater than or equal to 100,000/mm3. Monitor blood cell counts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Safety Information
Verify dosage using body surface area. Do not exceed a single dose of 4 mg intravenously.
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Small Cell Lung Cancer
The recommended dosage of Topotecan Injection is 1.5 mg/m2 by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes daily for 5 consecutive days, starting on Day 1 of a 21-day cycle.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Hematologic
Do not administer subsequent cycles of Topotecan Injection until neutrophils recover to greater than 1,000/mm3, platelets recover to greater than 100,000/mm3, and hemoglobin levels recover to greater than or equal to 9 g/dL (with transfusion if necessary).
Reduce the dose of Topotecan Injection to 1.25 mg/m2/day for:
- neutrophil counts of less than 500/mm3 or administer granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) starting no sooner than 24 hours following the last dose
- platelet counts less than 25,000/mm3 during previous cycle
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Renal Impairment
Reduce the dose of Topotecan Injection to 0.75 mg/m2/day for patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) of 20 to 39 mL/min (calculated with the Cockcroft-Gault method using ideal body weight) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.5 Preparation and Administration
Topotecan Injection is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposable procedures.1
Withdraw the appropriate volume from the vial and discard any unused portion.
Dilute Topotecan Injection in a minimum of 50 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP prior to administration. Infuse diluted Topotecan Injection over 30 minutes.
Store diluted Topotecan Injection at 20° and 25°C (68° and 77°F) in ambient lighting conditions for no more than 24 hours. Discard unused portion after 24 hours.
Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Discard if particulate matter or discoloration is observed.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Topotecan Injection is contraindicated in patients who have a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to topotecan. Reactions have included anaphylactoid reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myelosuppression
Topotecan can cause severe myelosuppression.
Grade 4 neutropenia occurred in 78% of 879 patients, with a median duration of 7 days and was most common during Cycle 1 (58% of patients). Grade 4 neutropenia associated with infection occurred in 13% and febrile neutropenia occurred in 5%. Sepsis occurred in 4% and was fatal in 1%. Grade 4 thrombocytopenia occurred in 27%, with a median duration of 5 days. Grade 3 or 4 anemia occurred in 37% of patients.
Topotecan can cause fatal typhlitis (neutropenic enterocolitis). Consider the possibility of typhlitis in patients presenting with fever, neutropenia, and abdominal pain.
Administer the first cycle of Topotecan Injection only to patients with a baseline neutrophil count of greater than or equal to 1,500/mm3 and a platelet count greater than or equal to 100,000/mm3. Monitor blood counts frequently during treatment. Withhold and reduce dose of Topotecan Injection based on neutrophil counts, platelet counts and hemoglobin levels [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), including fatalities, has occurred with topotecan [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Underlying risk factors include history of ILD, pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer, thoracic radiation, and use of pneumotoxic drugs and/or colony stimulating factors. Monitor patients for pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD (e.g., cough, fever, dyspnea, and/or hypoxia), and discontinue Topotecan Injection if a new diagnosis of ILD is confirmed.
5.3 Extravasation and Tissue Injury
Extravasation with topotecan has been observed; severe cases have been reported. If signs or symptoms of extravasation occur, immediately stop administration of Topotecan Injection and institute recommended management procedures [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on animal data, topotecan can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman.
Topotecan caused embryolethality, fetotoxicity, and teratogenicity in rats and rabbits when administered during organogenesis. Advise women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 6 months after the last dose of Topotecan Injection. Advise males with a female partner of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Topotecan Injection and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Interstitial Lung Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Extravasation and Tissue Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in Warnings and Precautions reflect exposure to topotecan from 8 trials in which 879 patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and other solid tumors received topotecan 1.5 mg/m2 by intravenous infusion daily for 5 consecutive days, starting on Day 1 of a 21-day cycle.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
The safety of topotecan was evaluated in randomized, comparative trial in patients with recurrent or progressive SCLC (Study 090) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Table 1 shows the Grade 3 or 4 hematologic and non-hematologic adverse reactions in patients with SCLC.
Table 1.
Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥5% of Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer in Study 090
Adverse Reactions
Topotecan
(n = 107)CAVC
(n = 104)- Grade 3 to 4 (%)
- Grade 3 to 4 (%)
Hematologic
Grade 4 neutropenia (<500/mm3)
70
72
Grade 3 or 4 anemia (Hgb < 8 g/dL)
42
20
Grade 4 thrombocytopenia (<25,000/mm3)
29
5
Febrile neutropenia
28
26
Non-Hematologic
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal
- Dyspnea
9
14
- Pneumonia
8
6
General and administrative site conditions
- Asthenia
9
7
- Fatigue
6
10
- Paina
5
7
Gastrointestinal
- Nausea
8
6
- Abdominal pain
6
4
Infections
- Sepsisb
5
5
- a Pain includes body pain, skeletal pain, and back pain.
- b Death related to sepsis occurred in 3% of patients receiving topotecan and 1% of patients receiving CAV.
- c CAV = cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin and vincristine.
Hepatobiliary Disorders
Based on 879 patients with small cell lung cancer or another solid tumor who were treated with topotecan, Grade 3 or 4 elevated aspartate (AST) or alanine transaminase (ALT) occurred in 4% and Grade 3 or 4 elevated bilirubin occurred in less than 2% of patients.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following reactions have been identified during postapproval use of topotecan. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System
Severe bleeding (in association with thrombocytopenia)
Hypersensitivity
Allergic manifestations, anaphylactoid reactions, angioedema
Gastrointestinal
Abdominal pain potentially associated with neutropenic enterocolitis, gastrointestinal perforation
Pulmonary
Interstitial lung disease
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue
Severe dermatitis, severe pruritus
General and Administration Site Conditions
Extravasation, mucosal inflammation
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal data and its mechanism of action, Topotecan Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available clinical data on the use of topotecan in pregnancy. Topotecan caused embryolethality, fetotoxicity, and teratogenicity in rats and rabbits when administered during organogenesis at doses similar to the clinical dose (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the background risk of major birth defects is 2% to 4% and of miscarriage is 15% to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal Data
In rabbits, an intravenous dose of 0.10 mg/kg/day [(about equal to the 1.5 mg/m2 clinical dose based on body surface area (BSA)] given on Days 6 through 20 of gestation caused maternal toxicity, embryolethality, and reduced fetal body weight. In the rat, an intravenous dose of 0.23 mg/kg/day (about equal to the 1.5 mg/m2 clinical dose based on BSA) given for 14 days before mating through gestation Day 6 caused fetal resorption, microphthalmia, pre-implant loss, and mild maternal toxicity.
Administration of an intravenous dose of 0.10 mg/kg/day (about half the 1.5 mg/m2 clinical dose based on BSA) given to rats on Days 6 through 17 of gestation caused an increase in post-implantation mortality. This dose also caused an increase in total fetal malformations. The most frequent malformations were of the eye (microphthalmia, anophthalmia, rosette formation of the retina, coloboma of the retina, ectopic orbit), brain (dilated lateral and third ventricles), skull, and vertebrae.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of topotecan or its metabolites in human milk or their effects on the breastfed infant or on milk production. Lactating rats excrete high concentrations of topotecan in milk (see Data). Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with Topotecan Injection and for 1 week after the last dose.
Data
Following intravenous administration of topotecan to lactating rats at a dose of 4.72 mg/m2 (about twice the 1.5 mg/m2 clinical dose based on BSA), topotecan was excreted into milk at concentrations up to 48-fold higher than those in plasma.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating Topotecan Injection [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Topotecan can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Females
Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Topotecan Injection and for 6 months after the last dose.
Males
Topotecan may damage spermatozoa, resulting in possible genetic and fetal abnormalities. Advise males with a female partner of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Topotecan Injection and for 3 months after the last dose [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Infertility
Females
Topotecan may have both acute and long-term effects on fertility [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Males
Effects on spermatogenesis occurred in animals administered topotecan [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 879 patients with SCLC or another solid tumor who received topotecan in clinical trials, 32% were aged 65 years and older, while 3.8% were aged 75 years and older. No overall differences in effectiveness or safety were observed between these patients and younger patients and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Reduce the dose of Topotecan Injection for patients with a CLcr of 20 to 39 mL/min [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with CLcr greater than or equal to 40 mL/min. Insufficient data are available in patients with CLcr less than 20 mL/min to provide a dosage recommendation for Topotecan Injection.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdoses (up to 10-fold of the recommended dose) have occurred in patients receiving intravenous topotecan. The primary complication of overdosage is myelosuppression. Elevated hepatic enzymes, mucositis, gastrointestinal toxicity and skin toxicity have occurred with overdosages. If an overdose is suspected, monitor the patient closely for myelosuppression and institute supportive-care measures as appropriate.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
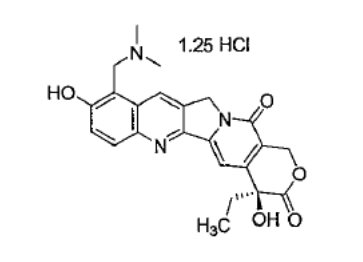
Topotecan is a semi-synthetic derivative of camptothecin and a topoisomerase inhibitor. The chemical name for topotecan hydrochloride is (S)-10-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-4-ethyl-4,9-dihydroxy-1H-pyrano[3’,4’:6,7]indolizino[1,2-b]quinoline-3,14-(4H,12H)-dione 1.25 hydrochloride. It has the molecular formula C23H23N3O51.25 HCl and a molecular weight of 467.02. It is soluble in water and melts with decomposition at 213°C to 218°C.
Topotecan hydrochloride has the following structural formula:
Topotecan Injection for intravenous use is supplied as a sterile, non-pyrogenic, clear, yellow to yellow-green solution in single-dose vial at a topotecan free base concentration of 4 mg/4 mL (1 mg/mL).
Each mL contains 1 mg topotecan free base (equivalent to 1.11 mg of topotecan hydrochloride), 5 mg tartaric acid, NF and water for injection, USP. It may also contain hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH. The solution pH ranges from 2.6 to 3.2.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Topoisomerase I relieves torsional strain in DNA by inducing reversible single-strand breaks. Topotecan binds to the topoisomerase I-DNA complex and prevents re-ligation of these single-strand breaks. The cytotoxicity of topotecan is thought to be due to double-strand DNA damage produced during DNA synthesis, when replication enzymes interact with the ternary complex formed by topotecan, topoisomerase I, and DNA. Mammalian cells cannot efficiently repair these double-strand breaks.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following administration of topotecan at doses of 0.5 to 1.5 mg/m2 (0.3 to 1 times the recommended dose) administered as a 30-minute infusion, area under the curve (AUC) increases approximately proportional with dose.
Distribution
Protein binding of topotecan is approximately 35%.
Elimination
The terminal half-life of topotecan is 2 to 3 hours following intravenous administration.
Metabolism
Topotecan undergoes a reversible pH-dependent hydrolysis of its pharmacologically active lactone moiety. At pH ≤ 4, the lactone is exclusively present, whereas the ring-opened hydroxy-acid form predominates at physiologic pH. Topotecan is metabolized to an N-demethylated metabolite in vitro. The mean metabolite: parent AUC ratio was about 3% for total topotecan and topotecan lactone following intravenous administration.
Excretion
The overall recovery of total topotecan and its N-desmethyl metabolite in urine and feces over 9 days averaged 73% ± 2% following an intravenous dose. Mean values of 51% ± 3% as total topotecan and 3% ± 1% as N-desmethyl topotecan were excreted in the urine. Fecal elimination of total topotecan accounted for 18% ± 4% while fecal elimination of N-desmethyl topotecan was 1.7% ± 0.6%. An O-glucuronidation metabolite of topotecan and N-desmethyl topotecan has been identified in the urine.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of topotecan were observed based on age, sex, or hepatic impairment following intravenous administration.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Compared to patients with CLcr >60 mL/min (calculated by the Cockcroft-Gault method using ideal body weight), plasma clearance of topotecan lactone decreased by 33% in patients with CLcr 40 to 60 mL/min and decreased by 65% in patients with CLcr 20 to 39 mL/min. The effect on topotecan pharmacokinetics in patients with CLcr <20 mL/min is unknown [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
No clinically significant changes in topotecan pharmacokinetics were observed when coadministered cisplatin.
No clinically significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of free platinum were observed in patients coadministered cisplatin with topotecan.
In Vitro Studies
Topotecan does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C8/9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E, CYP3A, or CYP4A or dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity testing of topotecan has not been performed. Topotecan is known to be genotoxic to mammalian cells and is a probable carcinogen. Topotecan was mutagenic to L5178Y mouse lymphoma cells and clastogenic to cultured human lymphocytes with and without metabolic activation. It was also clastogenic to mouse bone marrow. Topotecan did not cause mutations in bacterial cells.
Topotecan given to female rats prior to mating at an intravenous dose of 1.4 mg/m2 (about equal to the 1.5 mg/m2 clinical dose based on BSA) caused superovulation possibly related to inhibition of follicular atresia. This dose given to pregnant female rats also caused increased pre-implantation loss. A one month study in dogs given a daily intravenous topotecan dose of 0.4 mg/m2 (about 0.25 times the 1.5 mg/m2 clinical dose based on BSA) suggests that treatment may cause an increase in the incidence of multinucleated spermatogonial giant cells in the testes.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Small Cell Lung Cancer
The efficacy of topotecan was studied in 426 patients with recurrent or progressive SCLC in a randomized, comparative trial and in 3 single-arm trials.
Randomized Comparative Trial
In a randomized, comparative trial, 211 patients were randomized 1:1 to received topotecan (1.5 mg/m2 once daily intravenously for 5 days starting on Day 1 of a 21-day cycle) or CAV (cyclophosphamide 1,000 mg/m2, doxorubicin 45 mg/m2, vincristine 2 mg administered sequentially on Day 1 of a 21-day cycle). All patients were considered sensitive to first-line chemotherapy (responders who then subsequently progressed greater than or equal to 60 days after completion of first-line therapy). A total of 77% of patients treated with topotecan and 79% of patients treated with CAV received platinum/etoposide with or without other agents as first-line chemotherapy. The efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate, response duration, time to progression and overall survival (OS).
The results of the trial did not show statistically significant improvements in response rates, response duration, time to progression, and OS as shown in Table 2.
Table 2.
Efficacy Results in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer Sensitive to First-Line Chemotherapy in Study 090
Parameter
Topotecan
(n = 107)
CAVb
(n = 104)
Overall response rate (95% CI)
- Complete response rate
- Partial response rate
- 24% (16% to 32%)
- 0%
- 24%
18% (11% to 26%)
1%
17%
- Response durationa (months)
- Median (95% CI)
- 3.3 (3.0 to 4.1)
3.5 (3.0 to 5.3)
Time to progression (months)
- Median (95% CI)
- Hazard ratio (95% CI)
3.1 (2.6 to 4.1)
2.8 (2.5 to 3.2)
0.92 (0.69 to 1.22)
Overall survival (months)
- Median (95% CI)
- Hazard ratio (95% CI)
5.8 (4.7 to 6.8)
5.7 (5.0 to 7.0)
1.04 (0.78 to 1.39)
Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval.
a The calculation for duration of response was based on the interval between first response and time to progression.
b CAV = cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin and vincristine.
The median time to response was similar in both arms: topotecan 6 weeks (2.4 weeks to 3.6 months) versus CAV 6 weeks (5.1 weeks to 4.2 months).
Changes on a disease-related symptom scale are presented in Table 3. It should be noted that not all patients had all symptoms, nor did all patients respond to all questions. Each symptom was rated on a 4-category scale with an improvement defined as a change in 1 category from baseline sustained over 2 cycles. Limitations in interpretation of the rating scale and responses preclude formal statistical analysis.
Table 3.
Symptom Improvementa in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer in Study 090
Symptom
Topotecan
(n = 107)
CAVc
(n = 104)
nb
%
nb
%
Shortness of breath
68
28
61
7
Interference with daily activity
67
27
63
11
Fatigue
70
23
65
9
Hoarseness
40
33
38
13
Cough
69
25
61
15
Insomnia
57
33
53
19
Anorexia
56
32
57
16
Chest pain
44
25
41
17
Hemoptysis
15
27
12
33
a Defined as improvement sustained over at least 2 cycles compared with baseline.
b Number of patients with baseline and at least 1 post-baseline assessment.
c CAV = cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin and vincristine.
Single-Arm Trials
Topotecan was also studied in 3 open-label, non-comparative trials (Studies 014, 092 and 053) in a total of 319 patients with recurrent or progressive SCLC after treatment with first-line chemotherapy. In all 3 trials, patients were stratified as either sensitive (responders who then subsequently progressed greater than or equal to 90 days after completion of first-line therapy) or refractory (no response to first-line chemotherapy or who responded to first-line therapy and then progressed within 90 days of completing first-line therapy). Response rates ranged from 11% to 31% for sensitive patients and 2% to 7% for refractory patients. Median time to progression and median survival were similar in all 3 trials and the comparative trial.
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Topotecan Injection is supplied in 4 mg/4 mL (1 mg/mL, topotecan free base) single-dose vials. Each vial contains 4 mL of the sterile, clear, yellow to yellow-green solution.
NDC: 67457-662-05 (Package of 1 single-dose vial)
Store refrigerated between 2° and 8°C (36° and 46°F) in the original carton to protect from light. Discard unused portion.
Topotecan Injection is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable handling and disposal procedures.1
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Myelosuppression
Inform patients that topotecan decreases blood cell counts such as white blood cells, platelets, and red blood cells. Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider promptly for fever, other signs of infection, or bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
Inform patients of the risks of severe ILD. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately to report new or worsening respiratory symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females of reproductive potential and males with female partners of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise women to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected during treatment with Topotecan Injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Topotecan Injection and for 6 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Advise males with a female sexual partner of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Topotecan Injection and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Lactation
Advise women to discontinue breastfeeding during treatment with Topotecan Injection and for at least 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise male and female patients of the potential risk for impaired fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Asthenia and Fatigue
Advise patients that topotecan may cause asthenia or fatigue. These symptoms may impair the ability to safely drive or operate machinery.
Manufactured for:
Mylan Institutional LLC
Rockford, IL 61103 U.S.A.
Manufactured by:
Mylan Laboratories Limited
Bangalore, India
MARCH 2020
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 67457-662-05
Topotecan Injection
4 mg/4 mL (1 mg/mL)
Must Dilute Before Intravenous Infusion
CAUTION: CYTOTOXIC AGENT
Discard unused portion
Sterile
Mylan
Rx only
Single-Dose Vial
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
TOPOTECAN
topotecan injection, solution, concentrateProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 67457-662 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TOPOTECAN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 956S425ZCY) (TOPOTECAN - UNII:7M7YKX2N15) TOPOTECAN 1 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength TARTARIC ACID (UNII: W4888I119H) 5 mg in 1 mL HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 67457-662-05 1 in 1 CARTON 04/09/2018 1 4 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA206074 04/09/2018 Labeler - Mylan Institutional LLC (790384502)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.