Desonide by Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. / Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. DESONIDE lotion
Desonide by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Desonide by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Desonide Lotion 0.05% contains desonide (Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,11,21-dihydroxy-16,17[(1methylethylidene) bis(oxy)]-,(11β,16α)- a synthetic nonfluorinated corticosteroid for topical dermatologic use. The corticosteroids constitute a class of primarily synthetic steroids used topically as anti-inflammatory and antipruritic agents.
Chemically, desonide is C24H32O6. It has the following structural formula:
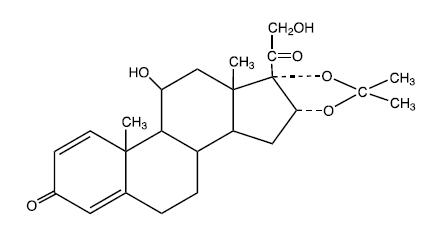
Desonide has the molecular weight of 416.51. It is a white to off white odorless powder which is soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in water.
Each gram of desonide lotion contains 0.5 mg of desonide in a base of cetyl alcohol, diethylene glycol monoethyl ether, edetate disodium, glyceryl stearate/polyethylene glycol, light mineral oil, methylparaben, purified water, propylene glycol, propylparaben, sodium lauryl sulfate, sorbitan monostearate and stearyl alcohol. Contains citric acid monohydrate and sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Like other topical corticosteroids, desonide has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and vasoconstrictive properties. The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of the topical steroids, in general, is unclear. However, corticosteroids are thought to act by the induction of phospholipase A2 inhibitory proteins, collectively called lipocortins. It is postulated that these proteins control the biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes by inhibiting the release of their common precursor arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2.
Pharmacokinetics
The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors including the vehicle and the integrity of the epidermal barrier. Occlusive dressings with hydrocortisone for up to 24 hours have not been demonstrated to increase penetration; however, occlusion of hydrocortisone for 96 hours markedly enhances penetration. Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin may increase percutaneous absorption.
Studies performed with desonide lotion indicate that they are in the low to medium range of potency as compared with other topical corticosteroids.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids can produce reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression with the potential for glucocorticosteroid insufficiency after withdrawal of treatment. Manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria can also be produced in some patients by systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids while on treatment.
Patients applying a topical steroid to a large surface area or to areas under occlusion should be evaluated periodically for evidence of HPA axis suppression. This may be done by using the ACTH stimulation, A.M. plasma cortisol, and urinary free cortisol tests. Patients receiving superpotent corticosteroids should not be treated for more than 2 weeks at a time and only small areas should be treated at any one time due to the increased risk of HPA axis suppression.
If HPA axis suppression is noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or to substitute a less potent corticosteroid. Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of topical corticosteroids. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of glucocorticosteroid insufficiency may occur requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids. For information on systemic supplementation, see prescribing information for those products.
Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity from equivalent doses due to their larger skin surface to body mass ratios. (See PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use).
If irritation develops, desonide lotion should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Allergic contact dermatitis with corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by observing failure to heal rather than noting a clinical exacerbation as with most topical products not containing corticosteroids. Such an observation should be corroborated with appropriate diagnostic patch testing.
If concomitant skin infections are present or develop, an appropriate antifungal or antibacterial agent should be used. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, use of desonide lotion should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled.
Information for Patients
Patients using topical corticosteroids should receive the following information and instructions:
- This medication is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the eyes.
- This medication should not be used for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed.
- The treated skin area should not be bandaged or otherwise covered or wrapped so as to be occlusive unless directed by the physician.
- Patients should report to their physician any signs of local adverse reactions.
Laboratory Tests
The following tests may be helpful in evaluating patients for HPA axis suppression:
- ACTH stimulation test
- A.M. plasma cortisol test
- Urinary free cortisol test
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential or the effect on reproduction with the use of desonide lotion.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels. Some corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic after dermal application in laboratory animals. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with desonide lotion. It is also not known whether desonide lotion can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Desonide lotion should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. It is not known whether topical administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when desonide lotion is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. Because of a higher ratio of skin surface area to body mass, pediatric patients are at a greater risk than adults of HPA axis suppression when they are treated with topical corticosteroids. They are therefore also at greater risk of glucocorticosteroid insufficiency after withdrawal of treatment and of Cushing's syndrome while on treatment. Adverse effects including striae have been reported with inappropriate use of topical corticosteroids in infants and children. HPA axis suppression, Cushing's syndrome, linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain and intracranial hypertension have been reported in children receiving topical corticosteroids. Manifestations of adrenal suppression in children include low plasma cortisol levels, and absence of response to ACTH stimulation. Manifestations of intracranial hypertension include bulging fontanelles, headaches, and bilateral papilledema.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In controlled clinical trials, the total incidence of adverse reactions associated with the use of desonide was approximately 8%. These were: stinging and burning approximately 3%, irritation, contact dermatitis, condition worsened, peeling of skin, itching, intense transient erythema, and dryness/scaliness, each less than 2%.
The following additional local adverse reactions have been reported infrequently with other topical corticosteroids, and they may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings, especially with higher potency corticosteroids. These reactions are listed in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence: folliculitis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, secondary infection, skin atrophy, striae, and miliaria.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Topically applied desonide lotion can be absorbed in sufficient amounts to produce systemic effects (See PRECAUTIONS).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Desonide lotion should be applied to the affected areas as a thin film two or three times daily depending on the severity of the condition. SHAKE LOTION WELL BEFORE USING.
As with other corticosteroids, therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 2 weeks, reassessment of diagnosis may be necessary.
Desonide lotion should not be used with occlusive dressings.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Desonide Lotion, 0.05% is supplied as follows:
2 fl oz (59 mL) bottle – NDC: 51672-4079-4
4 fl oz (118 mL) bottle – NDC: 51672-4079-8 - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 118 mL Bottle Carton
118 mL
Net Wt. 4 fl oz
NDC: 51672-4079-8
Desonide
Lotion
0.05%FOR EXTERNAL USE ONLY.
FOR DERMATOLOGIC
USE ONLY.
NOT FOR OPHTHALMIC USE.
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING.Keep this and all
medications out of the
reach of children.Rx only
TARO

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DESONIDE
desonide lotionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51672-4079 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Desonide (UNII: J280872D1O) (Desonide - UNII:J280872D1O) Desonide 0.5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength cetyl alcohol (UNII: 936JST6JCN) citric acid monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) diethylene glycol monoethyl ether (UNII: A1A1I8X02B) edetate disodium (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) light mineral oil (UNII: N6K5787QVP) methylparaben (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) propylparaben (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) sodium hydroxide (UNII: 55X04QC32I) sodium lauryl sulfate (UNII: 368GB5141J) sorbitan monostearate (UNII: NVZ4I0H58X) stearyl alcohol (UNII: 2KR89I4H1Y) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51672-4079-4 1 in 1 CARTON 10/31/2014 1 59 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 51672-4079-8 1 in 1 CARTON 10/31/2014 2 118 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA202161 10/31/2014 Labeler - Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. (145186370) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. 600072078 ANALYSIS(51672-4079) , MANUFACTURE(51672-4079)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.