PREVIDOLRX ANALGESIC PAK- diclofenac sodium kit
PrevidolRx Analgesic Pak by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
PrevidolRx Analgesic Pak by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by GenPak Solutions, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
PrevidolRx Analgesic Pak
GenPak Solutions LLC
PrevidolRx Analgesic Pak (Part 1 of 3) DESCRIPTION: DICLOFENAC SODIUM DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP-75MGRx only - Prescribing Information Cardiovascular Risk NSAIDs may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial ... Rx onlyPrevidolRx Analgesic PakCardiovascular Risk
- ASAIDs may cause an increase risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be a greater risk. (see WARNINGS)
- Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets is contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS)
Gastrointestinal Risk
- NSAIDs cause an increase risk of serious gastrointestional adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at a greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events. (see WARNINGS.)
-
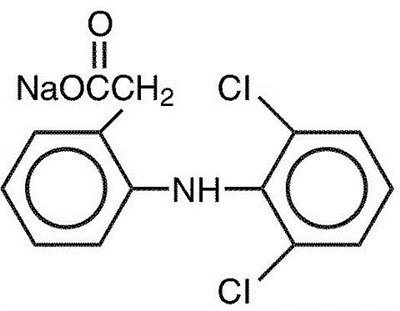
Description DICLOFENAC SODIUM
Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets are a benzene-acetic acid derivative. The chemical name is 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino] benzeneacetic acid, monosodium salt. The molecular weight is 318.14. Its molecular formula is C14H10Cl2NNaO2, and it has the following structural formula:
The inactive ingredients in Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets include: lactose (monohydrate), microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, povidone, talc, magnesium stearate, methacrylic acid copolymer, polyethylene glycol, opadry brown (Titanium dioxide, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow) and purified water.
-
PharmacodynamicsPharmacokineticsDistributionMetabolismExcretionDrug Interactions
Pharmacodynamics
Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets are a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities in animal models. The mechanism of action of Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but may be related to prostaglandin synthetase inhibition.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
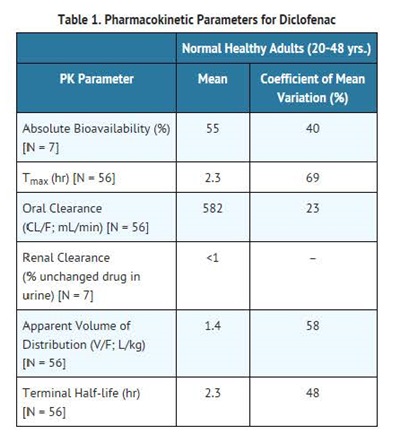
Diclofenac is 100% absorbed after oral administration compared to IV administration as measured by urine recovery. However, due to first-pass metabolism, only about 50% of the absorbed dose is systemically available (see Table 1). Food has no significant effect on the extent of diclofenac absorption. However, there is usually a delay in the onset of absorption of 1 to 4.5 hours and a reduction in peak plasma levels of <20%.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of Diclofenac sodium is 1.4 L/kg.
Diclofenac is more than 99% bound to human serum proteins, primarily to albumin. Serum protein binding is constant over the concentration range (0.15-105 ?g/mL) achieved with recommended doses.
Diclofenac diffuses into and out of the synovial fluid. Diffusion into the joint occurs when plasma levels are higher than those in the synovial fluid, after which the process reverses and synovial fluid levels are higher than plasma levels. It is not known whether diffusion into the joint plays a role in the effectiveness of Diclofenac.
Metabolism
Five Diclofenac metabolites have been identified in human plasma and urine. The metabolites include 4'-hydroxy-, 5-hydroxy-, 3'-hydroxy-, 4',5 dihydroxy- and 3'-hydroxy-4'-methoxy-Diclofenac. The major Diclofenac metabolite, 4'-hydroxy-Diclofenac, has very weak pharmacologic activity. The formation of 4’-hydroxy- Diclofenac is primarily mediated by CPY2C9. Both Diclofenac and its oxidative metabolites undergo glucuronidation or sulfation followed by biliary excretion. Acylglucuronidation mediated by UGT2B7 and oxidation mediated by CPY2C8 may also play a role in Diclofenac metabolism. CYP3A4 is responsible for the formation of minor metabolites, 5-hydroxy- and 3’-hydroxy-Diclofenac. In patients with renal dysfunction, peak concentrations of metabolites 4'-hydroxy- and 5-hydroxy-Diclofenac were approximately 50% and 4% of the parent compound after single oral dosing compared to 27% and 1% in normal healthy subjects.
Excretion
Diclofenac is eliminated through metabolism and subsequent urinary and biliary excretion of the glucuronide and the sulfate conjugates of the metabolites. Little or no free unchanged Diclofenac is excreted in the urine. Approximately 65% of the dose is excreted in the urine and approximately 35% in the bile as conjugates of unchanged Diclofenac plus metabolites. Because renal elimination is not a significant pathway of elimination for unchanged Diclofenac, dosing adjustment in patients with mild to moderate renal dysfunction is not necessary. The terminal half-life of unchanged Diclofenac is approximately 2 hours.
Drug Interactions
When co-administered with voriconazole (inhibitor of CYP2C9, 2C19 and 3A4 enzyme), the Cmax and AUC of Diclofenac increased by 114% and 78%, respectively (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Special Populations
Pediatric: The pharmacokinetics of Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets has not been investigated in pediatric patients.
Race: Pharmacokinetics differences due to race have not been identified.
Hepatic Insufficiency: Hepatic metabolism accounts for almost 100% of Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets elimination, so patients with hepatic disease may require reduced doses of Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets compared to patients with normal hepatic function.
Renal Insufficiency: Diclofenac pharmacokinetics has been investigated in subjects with renal insufficiency. No differences in the pharmacokinetics of Diclofenac have been detected in studies of patients with renal impairment. In patients with renal impairment (inulin clearance 60-90, 30-60, and <30 mL/min; N=6 in each group), AUC values and elimination rate were comparable to those in healthy subjects. -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS).
Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, are indicated:
For relief of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis
For relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
For acute or long-term use in the relief of signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis -
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to Diclofenac.
Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients (see WARNINGS, ANAPHYLACTOID REACTIONS, and PRECAUTIONS, PREEXISTING ASTHMA).
Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets are contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS). -
WARNINGS
Cardiovascular Effects
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. All NSAIDs, both COX-2 selective and nonselective, may have a similar risk. Patients with known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease may be at greater risk. To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the signs and/or symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID does increase the risk of serious GI events (see WARNINGS, GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) EFFECTS).
Two large, controlled, clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10-14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Hypertension
NSAIDs, can lead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking thiazides or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. NSAIDs, including Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, should be used with caution in patients with hypertension. Blood pressure (BP) should be monitored closely during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
Congestive Heart Failure and Edema Renal Effects
Fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients taking NSAIDs. Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets should be used with caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure.
Gastrointestinal (GI) Effects: Risk of GI Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients, who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy, is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months, and in about 2-4% of patients treated for one year. These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some time during the course of therapy. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk.
NSAIDs should be prescribed with extreme caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients with neither of these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk for GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status. Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special care should be taken in treating this population.To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible duration. Patients and physicians should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI adverse event is suspected. This should include discontinuation of the NSAID until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out. For high risk patients, alternate therapies that do not involve NSAIDs should be considered.
Renal Effects
Caution should be used when initiating treatment with Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets in patients with considerable dehydration.Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
Advanced Renal Disease
No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, treatment with Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets is not recommended in these patients with advanced renal disease. If Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets therapy must be initiated, close monitoring of the patient’s renal function is advisable.
Hepatic Effects
Elevations of one or more liver tests may occur during therapy with Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets. These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain unchanged, or may be transient with continued therapy. Borderline elevations (i.e., less than 3 times the ULN [ULN = the upper limit of the normal range]) or greater elevations of transaminases occurred in about 15% of Diclofenac-treated patients. Of the markers of hepatic function, ALT (SGPT) is recommended for the monitoring of liver injury.
In clinical trials, meaningful elevations (i.e., more than 3 times the ULN) of AST (GOT) (ALT was not measured in all studies) occurred in about 2% of approximately 5,700 patients at some time during Diclofenac treatment. In a large, open-label, controlled trial of 3,700 patients treated for 2-6 months, patients were monitored first at 8 weeks and 1,200 patients were monitored again at 24 weeks. Meaningful elevations of ALT and/or AST occurred in about 4% of patients and included marked elevations (i.e., more than 8 times the ULN) in about 1% of the 3,700 patients. In that open-label study, a higher incidence of borderline (less than 3 times the ULN), moderate (3-8 times the ULN), and marked (>8 times the ULN) elevations of ALT or AST was observed in patients receiving Diclofenac when compared to other NSAIDs. Elevations in transaminases were seen more frequently in patients with osteoarthritis than in those with rheumatoid arthritis.
Almost all meaningful elevations in transaminases were detected before patients became symptomatic. Abnormal tests occurred during the first 2 months of therapy with Diclofenac in 42 of the 51 patients in all trials who developed marked transaminase elevations.
In postmarketing reports, cases of drug-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported in the first month, and in some cases, the firth 2 months of therapy, but can occur at any time during treatment with Diclofenac. Postmarketing surveillance has reported cases of severe hepatic reactions, including liver necrosis, jaundice, fulminant hepatitis with and without jaundice, and liver failure. Some of these reported cases resulted in fatalities or liver transplantation.
Physicians should measure transaminases periodically in patients receiving long-term therapy with Diclofenac, because severe hepatotoxicity may develop without a prodrome of distinguishing symptoms. The optimum times for making the first and subsequent transaminase measurements are not known. Based on clinical trial data and postmarketing experiences, transaminases should be monitored within 4 to 8 weeks after initiating treatment with Diclofenac. However, severe hepatic reaction can occur at any time during treatment with Diclofenac.
If abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, if clinical signs and/or symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dark urine, etc.), Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets should be discontinued immediately.
To minimize the possibility that hepatic injury will become severe between transaminase measurements, physicians should inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and “flu-like” symptoms), and the appropriate action patients should take if these signs and symptoms appear.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse liver related event in patients treated with Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible. Caution should be exercised in prescribing Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets with concomitant drugs that are known to be potentially hepatotoxic (e.g., antibiotics, anti-epileptics).
Anaphylactoid Reactions
As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactic reactions may occur both in patients with the aspirin triad and in patients without known sensitivity to NSAIDs or known prior exposure to Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets. Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. This symptom complex typically occurs in asthmatic patients who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS, PREEXISTING ASTHMA.) Anaphylaxis-type reactions have been reported with NSAID products, including with Diclofenac products, such as Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets. Emergency help should be sought in cases where an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, can cause serious skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Patients should be informed about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Pregnancy
In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus. -
PRECAUTIONS
General
Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids.
The pharmacological activity of Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets in reducing fever and inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
Hematological Effects
Anemia is sometimes seen in patients receiving NSAIDs, including Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia.
NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients. Unlike aspirin, their effect on platelet function is quantitatively less, of shorter duration, and reversible. Patients receiving Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets who may be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation disorders or patients receiving anticoagulants, should be carefully monitored.
Preexisting Asthma
Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated with severe bronchospasm which can be fatal. Since cross-reactivity, including bronchospasm, between aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets should not be administered to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with preexisting asthma.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the following information before initiating therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy. Patients should also be encouraged to read the NSAID Medication Guide that accompanies each prescription dispensed.
1. Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, like other NSAIDs, may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS).
2. Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause GI discomfort and, rarely, more serious GI side effects, such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, GASTROINTESTINAL EFFECTS: RISK OF ULCERATION, BLEEDING, AND PERFORATION).
3. Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, SJS, and TEN, which may result in hospitalizations and even death. Although serious skin reactions may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs of hypersensitivity such as itching, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms. Patients should be advised to stop the drug immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their physicians as soon as possible.
4. Patients should promptly report signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or edema to their physicians.
5. Patients should be informed of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and “flu-like” symptoms). If these occur, patients should be instructed to stop therapy and seek immediate medical therapy. (See WARNINGS, HEPATIC EFFECTS).
6. Patients should be informed of the signs of an anaphylactic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, patients should be instructed to seek immediate emergency help (see WARNINGS).
7. In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
Laboratory Tests
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. In patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, the CBC and a chemistry profile (including transaminase levels) should be checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets should be discontinued.
Drug Interactions
Aspirin: When Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets are administered with aspirin, its protein binding is reduced. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however, as with other NSAIDs, concomitant administration of Diclofenac and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential of increased adverse effects.
Methotrexate: NSAIDs have been reported to competitively inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. This may indicate that they could enhance the toxicity of methotrexate. Caution should be used when NSAIDs are administered concomitantly with methotrexate.Cyclosporine: Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, like other NSAIDs, may affect renal prostaglandins and increase the toxicity of certain drugs. Therefore, concomitant therapy with Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets may increase cyclosporine’s nephrotoxicity. Caution should be used when Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets are administered concomitantly with cyclosporine.
ACE-inhibitors: Reports suggest that NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. This interaction should be given consideration in patients taking NSAIDs concomitantly with ACE inhibitors.
Furosemide: Clinical studies, as well as post-marketing observations, have shown that Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets can reduce the natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazides in some patients. This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. During concomitant therapy with NSAIDs, the patient should be observed closely for signs of renal failure (see WARNINGS, RENAL EFFECTS), as well as to assure diuretic efficacy.
Lithium: NSAIDs have produced an elevation of plasma lithium levels and a reduction in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15% and the renal clearance was decreased by approximately 20%. These effects have been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by the NSAID. Thus, when NSAIDs and lithium are administered concurrently, subjects should be observed carefully for signs of lithium toxicity.
Warfarin: The effects of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone.
CYP2C9 Inhibitors or Inducers: Diclofenac is metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes, predominantly by CYP2C9. Co-administration of Diclofenac with CYP2C9 inhibitors (e.g. voriconazole) may enhance the exposure and toxicity of Diclofenac whereas co-administration with CYP2C9 inducers (e.g. rifampin) may lead to compromised efficacy of Diclofenac. Use caution when dosing Diclofenac with CYP2C9 inhibitors or inducers; a dosage adjustment may be warranted (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, PHARMACOKINETICS, DRUG INTERACTIONS).
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects:Pregnancy Category CReproductive studies conducted in rats and rabbits have not demonstrated evidence of developmental abnormalities. However, animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women.
Nonteratogenic Effects:Because of the known effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of ductus arteriosus), use during pregnancy (particularly late pregnancy) should be avoided.
Labor and Delivery
In rat studies with NSAIDs, as with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, an increased incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased pup survival occurred. The effects of Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets on labor and delivery in pregnant women are unknown.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
As with any NSAIDs, caution should be exercised in treating the elderly (65 years and older). -
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In patients taking Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, or other NSAIDs, the most frequently reported adverse experiences occurring in approximately 1%-10% of patients are:
Gastrointestinal experiences including: abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, gross bleeding/perforation, heartburn, nausea, GI ulcers (gastric/duodenal) and vomiting.
Abnormal renal function, anemia, dizziness, edema, elevated liver enzymes, headaches, increased bleeding time, pruritus, rashes and tinnitus.
Additional adverse experiences reported occasionally include:
Body as a Whole: fever, infection, sepsisCardiovascular System: congestive heart failure, hypertension, tachycardia, syncope
Digestive System: dry mouth, esophagitis, gastric/peptic ulcers, gastritis, gastrointestinal bleeding, glossitis, hematemesis, hepatitis, jaundice
Hemic and Lymphatic System: ecchymosis, eosinophilia, leukopenia, melena, purpura, rectal bleeding, stomatitis, thrombocytopenia
Metabolic and Nutritional: weight changes
Nervous System: anxiety, asthenia, confusion, depression, dream abnormalities, drowsiness, insomnia, malaise, nervousness, paresthesia, somnolence, tremors, vertigo
Respiratory System: asthma, dyspnea
Skin and Appendages: alopecia, photosensitivity, sweating increased
Special Senses: blurred vision
Urogenital System: cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, oliguria/polyuria, proteinuria, renal failure
Other adverse reactions, which occur rarely are:
Body as a Whole: anaphylactic reactions, appetite changes, death
Cardiovascular System: arrhythmia, hypotension, myocardial infarction, palpitations, vasculitis
Digestive System: colitis, eructation, liver failure, pancreatitis
Hemic and Lymphatic System: agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, lymphadenopathy, pancytopeniaMetabolic and Nutritional: hyperglycemia
Nervous System: convulsions, coma, hallucinations, meningitis
Respiratory System: respiratory depression, pneumonia
Skin and Appendages: angioedema, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, urticaria
Special Senses: conjunctivitis, hearing impairment
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Unique Pharmaceutical Laboratories toll-free at (800) 521-5340 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. -
OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdoses are usually limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which are generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression and coma may occur, but are rare. Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with therapeutic ingestion of NSAIDs, and may occur following an overdose.
Patients should be managed by symptomatic and supportive care following a NSAID overdose. There are no specific antidotes. Emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 g in adults, 1 to 2 g/kg in children) and/or osmotic cathartic may be indicated in patients seen within 4 hours of ingestion with symptoms or following a large overdose (5 to 10 times the usual dose). Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding. -
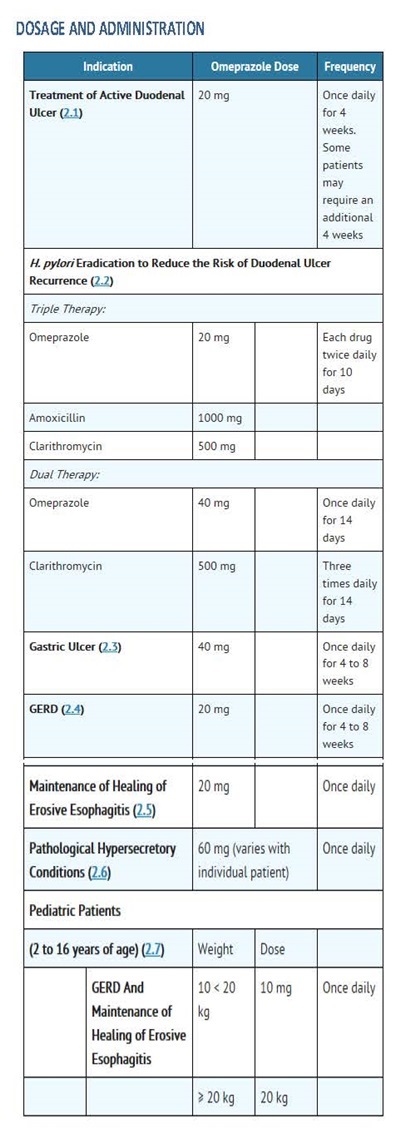
Dosage and Administration
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS).
After observing the response to initial therapy with Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient’s needs.
For the relief of osteoarthritis, the recommended dosage is 100-150 mg/day in divided doses (50 mg b.i.d. or t.i.d., or 75 mg b.i.d.).
For the relief of rheumatoid arthritis, the recommended dosage is 150-200 mg/day in divided doses (50 mg t.i.d. or q.i.d., or 75 mg b.i.d.).
For the relief of ankylosing spondylitis, the recommended dosage is 100-125 mg/day, administered as 25 mg q.i.d., with an extra 25-mg dose at bedtime if necessary.
Different formulations of Diclofenac (Diclofenac sodium enteric-coated tablets; Diclofenac sodium extended-release tablets, Diclofenac potassium immediate-release tablets) are not necessarily bioequivalent even if the milligram strength is the same. -
HOW SUPPLIED
Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-release Tablets, USP, for oral administration, are available as:
75 mg - round, Light brown, enteric-coated tablets, P 75 imprinted on one side in black ink and plain on the reverse side, are supplied as:
Bottles of 60, NDC: 16571-201-06
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) (see USP Controlled Room Temperature). Protect from moisture.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container -
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
(See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of prescription NSAID medicines.)
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines may increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. This chance increases:
o with longer use of NSAID medicines
o in people who have heart disease
NSAID medicines should never be used right before or after a heart surgery called a “coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).”
NSAID medicines can cause ulcers and bleeding in the stomach and intestines at any time during treatment. Ulcers and bleeding:
o can happen without warning symptoms
o may cause death
The chance of a person getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
o taking medicines called “corticosteroids” and “anticoagulants”
o longer use
o smoking
o drinking alcohol
o older age
o having poor health
NSAID medicines should only be used:
o exactly as prescribed
o at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
o for the shortest time needed
What are Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as:
o different types of arthritis
o menstrual cramps and other types of short-term pain
Who should not take a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
Do not take an NSAID medicine:
o if you had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAID medicine
o for pain right before or after heart bypass surgery
Tell your healthcare provider:
o about all your medical conditions.
o about all of the medicines you take. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Keep a list of your medicines to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist.
o if you are pregnant. NSAID medicines should not be used by pregnant women late in their pregnancy.
o if you are breastfeeding. Talk to your doctor.
What are the possible side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?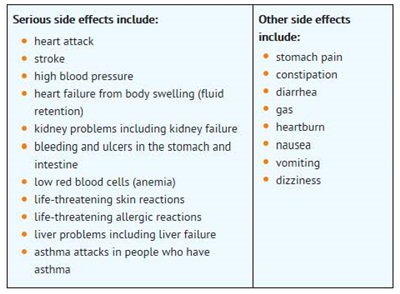
Get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
o shortness of breath or trouble breathing
o chest pain
o weakness in one part or side of your body
o slurred speech
o swelling of the face or throat
Stop your NSAID medicine and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
o nausea
o more tired or weaker than usual
o itching
o your skin or eyes look yellow
o stomach pain
o flu-like symptoms
o vomit blood
o there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar
o unusual weight gain
o skin rash or blisters with fever
o swelling of the arms and legs, hands and feet
These are not all the side effects with NSAID medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about NSAID medicines. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Other information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
o Aspirin is an NSAID medicine but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
o Some of these NSAID medicines are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the-counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.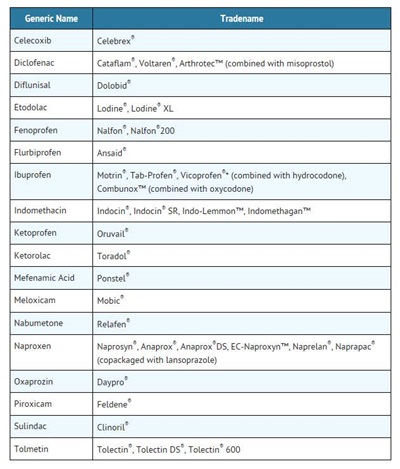
* Vicoprofen contains the same dose of ibuprofen as over-the-counter (OTC) NSAIDs, and is usually used for less than 10 days to treat pain. The OTC label warns that long term continuous use may increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
All registered trademarks in this document are the property of their respective owners.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor indicated for:
Treatment in adults of duodenal ulcer (1.1) and gastric ulcer (1.2)
Treatment in adults and children of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) (1.3) and maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis (1.4)
Pathologic Hypersecretory Conditions (1.5)
The safety and effectiveness of omeprazole in pediatric patients <1 year of age have not been established. (8.4) - DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Symptomatic response does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy (5.1)
Atrophic gastritis: has been noted with long-term therapy (5.2)
Acute interstitial nephritis has been observed in patients taking PPIs. (5.3)
Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B-12) Deficiency: Daily long-term use (e.g., longer than 3 years) may lead to malabsorption or a deficiency of cyanocobalamin. (5.4)
PPI therapy may be associated with increased risk of Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea. (5.5)
Avoid concomitant use of omeprazole with clopidogrel. (5.6)
Bone Fracture: Long-term and multiple daily dose PPI therapy may be associated with an increased risk for osteoporosis-related fractures of the hip, wrist or spine. (5.7)
Hypomagnesemia has been reported rarely with prolonged treatment with PPIs. (5.8)
Avoid concomitant use of omeprazole with St John’s Wort or rifampin due to the potential reduction in omeprazole concentrations (5.9, 7.3)
Interactions with diagnostic investigations for Neuroendocrine Tumors: Increases in intragastric pH may result in hypergastrinemia and enterochromaffin-like cell hyperplasia and increased Choromogranin A levels which may interfere with diagnostic investigations for neuroendocrine tumors. (5.10, 12.2) -
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adults: Most common adverse reactions in adults (incidence ? 2%) are
Headache, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and flatulence (6)
Pediatric patients (2 to 16 years of age):
Safety profile similar to that in adults, except that respiratory system events and fever were the most frequently reported reactions in pediatric studies. (8.4)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Apotex Corp. at 1-800-706-5575 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. -
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Atazanavir and nelfinavir: Omeprazole reduces plasma levels of atazanavir and nelfinavir. Concomitant use is not recommended. (7.1)
Saquinavir: Omeprazole increases plasma levels of saquinavir. Monitor for toxicity and consider dose reduction of saquinavir. (7.1)
May interfere with drugs for which gastric pH affects bioavailability (e.g., ketoconazole, iron salts, erlotinib, ampicillin esters, digoxin and mycophenolate mofetil). Patients treated with omeprazole and digoxin may need to be monitored for increases in digoxin toxicity. (7.2) Clopidogrel: Omeprazole decreases exposure to the active metabolite of clopidogrel. (7.3, 12.3)
Cilostazol: Omeprazole increases systemic exposure of cilostazol and one of its active metabolites. Consider dose reduction of cilostazol. (7.3) Drugs metabolized by cytochrome P450 (e.g., diazepam, warfarin, phenytoin, cyclosporine, disulfiram, benzodiazepines): omeprazole can prolong their elimination. Monitor and determine need for dose adjustments. (7.3)
Patients treated with proton pump inhibitors and warfarin may need to be monitored for increases in INR and prothrombin time. (7.3) Combined inhibitor of CYP 2C19 and 3A4 (e.g. voriconazole) may raise omeprazole levels. (7.3)
Tacrolimus: Omeprazole may increase serum levels of tacrolimus. (7.4)
Methotrexate: Omeprazole may increase serum levels of methotrexate. (7.7) - USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
-
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
Table of Contents
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Duodenal Ulcer (adults)
1.2 Gastric Ulcer (adults)
1.3 Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) (adults and pediatric patients)
1.4 Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis (adults and pediatric patients)
1.5 Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions (adults)
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Short-Term Treatment of Active Duodenal Ulcer
2.2 H. pylori Eradication for the Reduction of the Risk of Duodenal Ulcer Recurrence
2.3 Gastric Ulcer
2.4 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
2.5 Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis
2.6 Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions
2.7 Pediatric Patients
2.8 Alternative Administration Options
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Concomitant Gastric Malignancy
5.2 Atrophic Gastritis
5.3 Acute Interstitial Nephritis
5.4 Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B-12) Deficiency
5.5 Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea
5.6 Interaction with Clopidogrel
5.7 Bone Fracture
5.8 Hypomagnesemia
5.9 Concomitant Use of Omeprazole with St. John's Wort or Rifampin
5.10 Interactions with Diagnostic Investigations for Neuroendocrine Tumors
5.11 Concomitant use of Omeprazole with Methotrexate
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience with Omeprazole Monotherapy
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience with Omeprazole in Combination Therapy for H. pylori Eradication
6.3 Post-marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Interference with Antiretroviral Therapy
7.2 Drugs for Which Gastric pH Can Affect Bioavailability
7.3 Effects on Hepatic Metabolism/Cytochrome P-450 Pathways
7.4 Tacrolimus
7.5 Interactions with Investigations of Neuroendocrine Tumors
7.6 Combination Therapy with Clarithromycin
7.7 Methotrexate
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
8.8 Asian Population
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Duodenal Ulcer Disease
14.2 Gastric Ulcer
14.3 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
14.4 Erosive Esophagitis
14.5 Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions
14.6 Pediatric GERD15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Duodenal Ulcer (adults)
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP are indicated for short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer in adults. Most patients heal within four weeks. Some patients may require an additional four weeks of therapy.
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP, in combination with clarithromycin and amoxicillin, are indicated for treatment of patients with H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease (active or up to 1-year history) to eradicate H. pylori in adults.
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP, in combination with clarithromycin are indicated for treatment of patients with H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease to eradicate H. pylori in adults.
Eradication of H. pylori has been shown to reduce the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence [see Clinical Studies (14.1) and Dosage and Administration (2)].
Among patients who fail therapy, omeprazole delayed-release capsules with clarithromycin are more likely to be associated with the development of clarithromycin resistance as compared with triple therapy. In patients who fail therapy, susceptibility testing should be done. If resistance to clarithromycin is demonstrated or susceptibility testing is not possible, alternative antimicrobial therapy should be instituted [see Microbiology section (12.4)], and the clarithromycin package insert, Microbiology section.
1.2 Gastric Ulcer (adults)
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP are indicated for short-term treatment (4 to 8 weeks) of active benign gastric ulcer in adults [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
1.3 Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) (adults and pediatric patients)
Symptomatic GERD
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP are indicated for the treatment of heartburn and other symptoms associated with GERD in pediatric patients and adults for up to 4 weeks.
Erosive Esophagitis
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP are indicated for the short-term treatment (4 to 8 weeks) of erosive esophagitis that has been diagnosed by endoscopy in pediatric patients and adults [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
The efficacy of omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP used for longer than 8 weeks in these patients has not been established. If a patient does not respond to 8 weeks of treatment, an additional 4 weeks of treatment may be given. If there is recurrence of erosive esophagitis or GERD symptoms (eg, heartburn), additional 4 to 8 week courses of omeprazole may be considered.1.4 Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis (adults and pediatric patients)
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP are indicated to maintain healing of erosive esophagitis in pediatric patients and adults.
Controlled studies do not extend beyond 12 months [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
1.5 Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions (adults)
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP are indicated for the long-term treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions (eg, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, multiple endocrine adenomas and systemic mastocytosis) in adults. -
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules should be taken before eating. In the clinical trials, antacids were used concomitantly with omeprazole.
Patients should be informed that the omeprazole delayed-release capsule should be swallowed whole.
For patients unable to swallow an intact capsule, alternative administration options are available [see Dosage and Administration (2.8)].
2.1 Short-Term Treatment of Active Duodenal Ulcer
The recommended adult oral dose of omeprazole delayed-release capsules is 20 mg once daily. Most patients heal within four weeks. Some patients may require an additional four weeks of therapy.
2.2 H. pylori Eradication for the Reduction of the Risk of Duodenal Ulcer Recurrence
Triple Therapy (omeprazole/clarithromycin/amoxicillin)
The recommended adult oral regimen is omeprazole delayed-release capsules 20 mg plus clarithromycin 500 mg plus amoxicillin 1000 mg each given twice daily for 10 days. In patients with an ulcer present at the time of initiation of therapy, an additional 18 days of omeprazole delayed-release capsules 20 mg once daily is recommended for ulcer healing and symptom relief.
Dual Therapy (omeprazole/clarithromycin)
The recommended adult oral regimen is omeprazole delayed-release capsules 40 mg once daily plus clarithromycin 500 mg three times daily for 14 days. In patients with an ulcer present at the time of initiation of therapy, an additional 14 days of omeprazole delayed-release capsules 20 mg once daily is recommended for ulcer healing and symptom relief.
2.3 Gastric Ulcer
The recommended adult oral dose is 40 mg once daily for 4 to 8 weeks.
2.4 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
The recommended adult oral dose for the treatment of patients with symptomatic GERD and no esophageal lesions is 20 mg daily for up to 4 weeks. The recommended adult oral dose for the treatment of patients with erosive esophagitis and accompanying symptoms due to GERD is 20 mg daily for 4 to 8 weeks.
2.5 Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis
The recommended adult oral dose is 20 mg daily. Controlled studies do not extend beyond 12 months [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
2.6 Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions
The dosage of omeprazole delayed-release capsules in patients with pathological hypersecretory conditions varies with the individual patient. The recommended adult oral starting dose is 60 mg once daily. Doses should be adjusted to individual patient needs and should continue for as long as clinically indicated. Doses up to 120 mg three times daily have been administered. Daily dosages of greater than 80 mg should be administered in divided doses. Some patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome have been treated continuously with omeprazole delayed-release capsules for more than 5 years.
2.7 Pediatric Patients
For the treatment of GERD and maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis, the recommended daily dose for pediatric patients 2 to 16 years of age is as follows: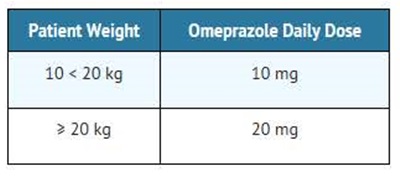
On a per kg basis, the doses of omeprazole required to heal erosive esophagitis in pediatric patients are greater than those for adults.
Alternative administrative options can be used for pediatric patients unable to swallow an intact capsule [see Dosage and Administration (2.8)].
2.8 Alternative Administration Options
Omeprazole is available as a delayed-release capsule.For patients who have difficulty swallowing capsules, the contents of an omeprazole delayed-release capsule can be added to applesauce.
One tablespoon of applesauce should be added to an empty bowl and the capsule should be opened. All of the pellets inside the capsule should be carefully emptied on the applesauce. The pellets should be mixed with the applesauce and then swallowed immediately with a glass of cool water to ensure complete swallowing of the pellets. The applesauce used should not be hot and should be soft enough to be swallowed without chewing. The pellets should not be chewed or crushed. The pellets/applesauce mixture should not be stored for future use. -
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP 10 mg are hard gelatin capsules with a pink opaque body and a reddish brown opaque cap. “APO 010” is imprinted on each capsule in black ink.
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP 20 mg are hard gelatin capsules with a pink opaque body and a reddish brown opaque cap. “APO 020” is imprinted on each capsule in black ink.
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP 40 mg are hard gelatin capsules with a pink opaque body and a reddish brown opaque cap. “APO 040” is imprinted on each capsule in black ink. -
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to substituted benzimidazoles or to any component of the formulation. Hypersensitivity reactions may include anaphylaxis, anaphylactic shock, angioedema, bronchospasm, acute interstitial nephritis, and urticaria [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
For information about contraindications of antibacterial agents (clarithromycin and amoxicillin) indicated in combination with omeprazole, refer to the CONTRAINDICATIONS section of their package inserts. -
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Concomitant Gastric Malignancy
Symptomatic response to therapy with omeprazole does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy.
5.2 Atrophic Gastritis
Atrophic gastritis has been noted occasionally in gastric corpus biopsies from patients treated long-term with omeprazole.
5.3 Acute Interstitial Nephritis
Acute interstitial nephritis has been observed in patients taking PPIs including omeprazole. Acute interstitial nephritis may occur at any point during PPI therapy and is generally attributed to an idiopathic hypersensitivity reaction. Discontinue omeprazole if acute interstitial nephritis develops [see Contraindications (4)].
5.4 Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B-12) Deficiency
Daily treatment with any acid-suppressing medications over a long period of time (e.g., longer than 3 years) may lead to malabsorption of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B-12) caused by hypo- or achlorhydria. Rare reports of cyanocobalamin deficiency occurring with acidsuppressing therapy have been reported in the literature. This diagnosis should be considered if clinical symptoms consistent with cyanocobalamin deficiency are observed.
5.5 Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea
Published observational studies suggest that PPI therapy like omeprazole may be associated with an increased risk of Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea, especially in hospitalized patients. This diagnosis should be considered for diarrhea that does not improve [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Patients should use the lowest dose and shortest duration of PPI therapy appropriate to the condition being treated.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents. For more information specific to antibacterial agents (clarithromycin and amoxicillin) indicated for use in combination with omeprazole, refer to WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS sections of those package inserts.
5.6 Interaction with Clopidogrel
Avoid concomitant use of omeprazole with clopidogrel. Clopidogrel is a prodrug. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by clopidogrel is entirely due to an active metabolite. The metabolism of clopidogrel to its active metabolite can be impaired by use with concomitant medications, such as omeprazole, that inhibit CYP2C19 activity. Concomitant use of clopidogrel with 80 mg omeprazole reduces the pharmacological activity of clopidogrel, even when administered 12 hours apart. When using omeprazole, consider alternative anti-platelet therapy [see Drug Interactions (7.3) and Pharmacokinetics (12.3)].
5.7 Bone FractureSeveral published observational studies suggest that proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy may be associated with an increased risk for osteoporosis-related fractures of the hip, wrist, or spine. The risk of fracture was increased in patients who received high-dose, defined as multiple daily doses, and long-term PPI therapy (a year or longer). Patients should use the lowest dose and shortest duration of PPI therapy appropriate to the condition being treated. Patients at risk for osteoporosis-related fractures should be managed according to established treatment guidelines [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Adverse Reactions (6.3)].
5.8 Hypomagnesemia
Hypomagnesemia, symptomatic and asymptomatic, has been reported rarely in patients treated with PPIs for at least three months, in most cases after a year of therapy. Serious adverse events include tetany, arrhythmias, and seizures. In most patients, treatment of hypomagnesemia required magnesium replacement and discontinuation of the PPI.
For patients expected to be on prolonged treatment or who take PPIs with medications such as digoxin or drugs that may cause hypomagnesemia (e.g., diuretics), health care professionals may consider monitoring magnesium levels prior to initiation of PPI treatment and periodically [see Adverse Reactions (6.3)].
5.9 Concomitant Use of Omeprazole with St. John's Wort or Rifampin
Drugs which induce CYP2C19 or CYP3A4 (such as St. John’s Wort or rifampin) can substantially decrease omeprazole concentrations [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]. Avoid concomitant use of omeprazole with St. John’s Wort or rifampin.
5.10 Interactions with Diagnostic Investigations for Neuroendocrine Tumors
Serum chromogranin A (CgA) levels increase secondary to drug-induced decreases in gastric acidity. The increased CgA level may cause false positive results in diagnostic investigations for neuroendocrine tumors. Healthcare providers should temporarily stop omeprazole treatment at least 14 days before assessing CgA levels and consider repeating the test if initial CgA levels are high. If serial tests are performed (e.g. for monitoring), the same commercial laboratory should be used for testing, as reference ranges between tests may vary.
5.11 Concomitant use of Omeprazole with Methotrexate
Literature suggests that concomitant use of PPIs with methotrexate (primarily at high dose; see methotrexate prescribing information) may elevate and prolong serum levels of methotrexate and/or its metabolite, possibly leading to methotrexate toxicities. In high-dose methotrexate administration a temporary withdrawal of the PPI may be considered in some patients [see Drug Interactions (7.7)]. -
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience with Omeprazole Monotherapy
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data described below reflects exposure to omeprazole delayed-release capsules in 3096 patients from worldwide clinical trials (465 patients from US studies and 2,631 patients from international studies). Indications clinically studied in US trials included duodenal ulcer, resistant ulcer, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. The international clinical trials were double blind and open-label in design. The most common adverse reactions reported (i.e., with an incidence rate ? 2%) from omeprazole-treated patients enrolled in these studies included headache (6.9%), abdominal pain (5.2%), nausea (4.0%), diarrhea (3.7%), vomiting (3.2%), and flatulence (2.7%).
Additional adverse reactions that were reported with an incidence ?1% included acid regurgitation (1.9%), upper respiratory infection (1.9%), constipation (1.5%), dizziness (1.5%), rash (1.5%), asthenia (1.3%), back pain (1.1%), and cough (1.1%).
The clinical trial safety profile in patients greater than 65 years of age was similar to that in patients 65 years of age or less. The clinical trial safety profile in pediatric patients who received omeprazole delayed-release capsules was similar to that in adult patients. Unique to the pediatric population, however, adverse reactions of the respiratory system were most frequently reported in the 2 to 16 year age group (18.5%). Similarly, accidental injuries were reported frequently in the 2 to 16 year age group (3.8%) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience with Omeprazole in Combination Therapy for H. pylori Eradication
In clinical trials using either dual therapy with omeprazole and clarithromycin, or triple therapy with omeprazole, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin, no adverse reactions unique to these drug combinations were observed. Adverse reactions observed were limited to those previously reported with omeprazole, clarithromycin, or amoxicillin alone.
Dual Therapy (omeprazole/clarithromycin)
Adverse reactions observed in controlled clinical trials using combination therapy with omeprazole and clarithromycin (n = 346) that differed from those previously described for omeprazole alone were taste perversion (15%), tongue discoloration (2%), rhinitis (2%), pharyngitis (1%) and flu-syndrome (1%). (For more information on clarithromycin, refer to the clarithromycin prescribing information, Adverse Reactions section).
Triple Therapy (omeprazole/clarithromycin/amoxicillin)
The most frequent adverse reactions observed in clinical trials using combination therapy with omeprazole, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (n = 274) were diarrhea (14%), taste perversion (10%), and headache (7%). None of these occurred at a higher frequency than that reported by patients taking antimicrobial agents alone. (For more information on clarithromycin or amoxicillin, refer to the respective prescribing information, Adverse Reactions sections).
6.3 Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of omeprazole delayed-release capsules. Because these reactions are voluntarily reported from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their actual frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.Body As a Whole
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, anaphylactic shock, angioedema, bronchospasm, interstitial nephritis, urticaria, (see also Skin below); fever; pain; fatigue; malaise;Cardiovascular
Chest pain or angina, tachycardia, bradycardia, palpitations, elevated blood pressure, peripheral edemaEndocrine
Gynecomastia
Gastrointestinal
Pancreatitis (some fatal), anorexia, irritable colon, fecal discoloration, esophageal candidiasis, mucosal atrophy of the tongue, stomatitis, abdominal swelling, dry mouth, microscopic colitis. During treatment with omeprazole, gastric fundic gland polyps have been noted rarely. These polyps are benign and appear to be reversible when treatment is discontinued. Gastroduodenal carcinoids have been reported in patients with ZE syndrome on long-term treatment with omeprazole. This finding is believed to be a manifestation of the underlying condition, which is known to be associated with such tumors.Hepatic
Liver disease including hepatic failure (some fatal), liver necrosis (some fatal), hepatic encephalopathy hepatocellular disease, cholestatic disease, mixed hepatitis, jaundice, and elevations of liver function tests [ALT, AST, GGT, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin]
Infections and Infestations
Clostridium difficile associated diarrheaMetabolism and Nutritional disorders
Hypoglycemia, hypomagnesemia, with or without hypocalcemia and/or hypokalemia, hyponatremia, weight gain
Musculoskeletal
Muscle weakness, myalgia, muscle cramps, joint pain, leg pain, bone fracture
Nervous System/Psychiatric
Psychiatric and sleep disturbances including depression, agitation, aggression, hallucinations, confusion, insomnia, nervousness, apathy, somnolence, anxiety, and dream abnormalities; tremors, paresthesia; vertigo
Respiratory
Epistaxis, pharyngeal pain
Skin
Severe generalized skin reactions including toxic epidermal necrolysis (some fatal), Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme; photosensitivity; urticaria; rash; skin inflammation; pruritus; petechiae; purpura; alopecia; dry skin; hyperhidrosisSpecial Senses
Tinnitus, taste perversionOcular
Optic atrophy, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, optic neuritis, dry eye syndrome, ocular irritation, blurred vision, double vision
Urogenital
Interstitial nephritis, hematuria, proteinuria, elevated serum creatinine, microscopic pyuria, urinary tract infection, glycosuria, urinary frequency, testicular pain
Hematologic
Agranulocytosis (some fatal), hemolytic anemia, pancytopenia, neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, leucocytosis
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Interference with Antiretroviral Therapy
Concomitant use of atazanavir and nelfinavir with proton pump inhibitors is not recommended. Co-administration of atazanavir with proton pump inhibitors is expected to substantially decrease atazanavir plasma concentrations and may result in a loss of therapeutic effect and the development of drug resistance. Co-administration of saquinavir with proton pump inhibitors is expected to increase saquinavir concentrations, which may increase toxicity and require dose reduction.Omeprazole has been reported to interact with some antiretroviral drugs. The clinical importance and the mechanisms behind these interactions are not always known. Increased gastric pH during omeprazole treatment may change the absorption of the antiretroviral drug. Other possible interaction mechanisms are via CYP2C19.
Reduced concentrations of atazanavir and nelfinavir
For some antiretroviral drugs, such as atazanavir and nelfinavir, decreased serum levels have been reported when given together with omeprazole. Following multiple doses of nelfinavir (1250 mg, twice daily) and omeprazole (40 mg daily), AUC was decreased by 36% and 92%, Cmax by 37% and 89% and Cmin by 39% and 75% respectively for nelfinavir and M8. Following multiple doses of atazanavir (400 mg, daily) and omeprazole (40 mg, daily, 2 hr before atazanavir), AUC was decreased by 94%, Cmax by 96%, and Cmin by 95%. Concomitant administration with omeprazole and drugs such as atazanavir and nelfinavir is therefore not recommended.
Increased concentrations of saquinavir
For other antiretroviral drugs, such as saquinavir, elevated serum levels have been reported, with an increase in AUC by 82%, in Cmax by 75%, and in Cmin by 106%, following multiple dosing of saquinavir/ritonavir (1000/100 mg) twice daily for 15 days with omeprazole 40 mg daily co-administered days 11 to 15. Therefore, clinical and laboratory monitoring for saquinavir toxicity is recommended during concurrent use with omeprazole. Dose reduction of saquinavir should be considered from the safety perspective for individual patients.
There are also some antiretroviral drugs of which unchanged serum levels have been reported when given with omeprazole.
7.2 Drugs for Which Gastric pH Can Affect Bioavailability
Due to its effects on gastric acid secretion, omeprazole can reduce the absorption of drugs where gastric pH is an important determinant of their bioavailability. Like with other drugs that decrease the intragastric acidity, the absorption of drugs such as ketoconazole, atazanavir, iron salts, erlotinib, and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) can decrease, while the absorption of drugs such as digoxin can increase during treatment with omeprazole.
Concomitant treatment with omeprazole (20 mg daily) and digoxin in healthy subjects increased the bioavailability of digoxin by 10% (30% in two subjects). Co-administration of digoxin with omeprazole is expected to increase the systemic exposure of digoxin. Therefore, patients may need to be monitored when digoxin is taken concomitantly with omeprazole.
Co-administration of omeprazole in healthy subjects and in transplant patients receiving MMF has been reported to reduce the exposure to the active metabolite, mycophenolic acid (MPA), possibly due to a decrease in MMF solubility at an increased gastric pH. The clinical relevance of reduced MPA exposure on organ rejection has not been established in transplant patients receiving omeprazole and MMF. Use omeprazole with caution in transplant patients receiving MMF [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Effects on Hepatic Metabolism/Cytochrome P-450 Pathways
Omeprazole can prolong the elimination of diazepam, warfarin and phenytoin, drugs that are metabolized by oxidation in the liver. There have been reports of increased INR and prothrombin time in patients receiving proton pump inhibitors, including omeprazole, and warfarin concomitantly. Increases in INR and prothrombin time may lead to abnormal bleeding and even death. Patients treated with proton pump inhibitors and warfarin may need to be monitored for increases in INR and prothrombin time.
Although in normal subjects no interaction with theophylline or propranolol was found, there have been clinical reports of interaction with other drugs metabolized via the cytochrome P450 system (e.g., cyclosporine, disulfiram, benzodiazepines). Patients should be monitored to determine if it is necessary to adjust the dosage of these drugs when taken concomitantly with omeprazole.
Concomitant administration of omeprazole and voriconazole (a combined inhibitor of CYP2C19 and CYP3A4) resulted in more than doubling of the omeprazole exposure. Dose adjustment of omeprazole is not normally required. However, in patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, who may require higher doses up to 240 mg/day, dose adjustment may be considered. When voriconazole (400 mg Q12h x 1 day, then 200 mg x 6 days) was given with omeprazole (40 mg once daily x 7 days) to healthy subjects, it significantly increased the steady-state Cmax and AUC0-24 of omeprazole, an average of 2 times (90% CI: 1.8, 2.6) and 4 times (90% CI: 3.3, 4.4) respectively as compared to when omeprazole was given without voriconazole.
Omeprazole acts as an inhibitor of CYP2C19. Omeprazole, given in doses of 40 mg daily for one week to 20 healthy subjects in cross-over study, increased Cmax and AUC of cilostazol by 18% and 26% respectively. Cmax and AUC of one of its active metabolites, 3,4-dihydro-cilostazol, which has 4 to 7 times the activity of cilostazol, were increased by 29% and 69% respectively. Co-administration of cilostazol with omeprazole is expected to increase concentrations of cilostazol and its above mentioned active metabolite. Therefore a dose reduction of cilostazol from 100 mg twice daily to 50 mg twice daily should be considered.
Drugs known to induce CYP2C19 or CYP3A4 (such as rifampin) may lead to decreased omeprazole serum levels. In a cross-over study in 12 healthy male subjects, St. John’s Wort (300 mg three times daily for 14 days), an inducer of CYP3A4, decreased the systemic exposure of omeprazole in CYP2C19 poor metabolisers (Cmax and AUC decreased by 37.5% and 37.9%, respectively) and extensive metabolisers (Cmax and AUC decreased by 49.6% and 43.9%, respectively). Avoid concomitant use of St. John’s Wort or rifampin with omeprazole.
Clopidogrel
Omeprazole is an inhibitor of CYP2C19 enzyme. Clopidogrel is metabolized to its active metabolite in part by CYP2C19. Concomitant use of omeprazole 80 mg results in reduced plasma concentrations of the active metabolite of clopidogrel and a reduction in platelet inhibition. Avoid concomitant administration of omeprazole with clopidogrel. When using omeprazole, consider use of alternative anti-platelet therapy [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)].
There are no adequate combination studies of a lower dose of omeprazole or a higher dose of clopidogrel in comparison with the approved dose of clopidogrel.
7.4 Tacrolimus
Concomitant administration of omeprazole and tacrolimus may increase the serum levels of tacrolimus.7.5 Interactions with Investigations of Neuroendocrine Tumors
Drug-induced decrease in gastric acidity results in enterochromaffin-like cell hyperplasia and increased Chromogranin A levels which may interfere with investigations for neuroendocrine tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) and Clinical Pharmacology (12)].7.6 Combination Therapy with Clarithromycin
Concomitant administration of clarithromycin with other drugs can lead to serious adverse reactions due to drug interactions [see Warnings and Precautions in prescribing information for clarithromycin]. Because of these drug interactions, clarithromycin is contraindicated for co-administration with certain drugs [see Contraindications in prescribing information for clarithromycin].7.7 Methotrexate
Case reports, published population pharmacokinetic studies, and retrospective analyses suggest that concomitant administration of PPIs and methotrexate (primarily at high dose; see methotrexate prescribing information) may elevate and prolong serum levels of methotrexate and/or its metabolite hydroxymethotrexate. However, no formal drug interaction studies of methotrexate with PPIs have been conducted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with omeprazole in pregnant women. Available epidemiologic data fail to demonstrate an increased risk of major congenital malformations or other adverse pregnancy outcomes with first trimester omeprazole use.
Teratogenicity was not observed in animal reproduction studies with administration of oral esomeprazole magnesium in rats and rabbits with doses about 68 times and 42 times, respectively, an oral human dose of 40 mg (based on a body surface area basis for a 60 kg person). However, changes in bone morphology were observed in offspring of rats dosed through most of pregnancy and lactation at doses equal to or greater than approximately 34 times an oral human dose of 40 mg (see Animal Data). Because of the observed effect at high doses of esomeprazole magnesium on developing bone in rat studies, omeprazole should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Human Data
Four published epidemiological studies compared the frequency of congenital abnormalities among infants born to women who used omeprazole during pregnancy with the frequency of abnormalities among infants of women exposed to H2-receptor antagonists or other controls.
A population-based retrospective cohort epidemiological study from the Swedish Medical Birth Registry, covering approximately 99% of pregnancies, from 1995 to 99, reported on 955 infants (824 exposed during the first trimester with 39 of these exposed beyond first trimester, and 131 exposed after the first trimester) whose mothers used omeprazole during pregnancy. The number of infants exposed in utero to omeprazole that had any malformation, low birth weight, low Apgar score, or hospitalization was similar to the number observed in this population. The number of infants born with ventricular septal defects and the number of stillborn infants was slightly higher in the omeprazole-exposed infants than the expected number in this population.
A population-based retrospective cohort study covering all live births in Denmark from 1996 to 2009, reported on 1,800 live births whose mothers used omeprazole during the first trimester of pregnancy and 837, 317 live births whose mothers did not use any proton pump inhibitor. The overall rate of birth defects in infants born to mothers with first trimester exposure to omeprazole was 2.9% and 2.6% in infants born to mothers not exposed to any proton pump inhibitor during the first trimester.
A retrospective cohort study reported on 689 pregnant women exposed to either H2-blockers or omeprazole in the first trimester (134 exposed to omeprazole) and 1,572 pregnant women unexposed to either during the first trimester. The overall malformation rate in offspring born to mothers with first trimester exposure to omeprazole, an H2-blocker, or were unexposed was 3.6%, 5.5%, and 4.1% respectively.
A small prospective observational cohort study followed 113 women exposed to omeprazole during pregnancy (89% first trimester exposures). The reported rate of major congenital malformations was 4% in the omeprazole group, 2% in controls exposed to non-teratogens, and 2.8% in disease-paired controls. Rates of spontaneous and elective abortions, preterm deliveries, gestational age at delivery, and mean birth weight were similar among the groups.
Several studies have reported no apparent adverse short-term effects on the infant when single dose oral or intravenous omeprazole was administered to over 200 pregnant women as premedication for cesarean section under general anesthesia.
Animal Data
Reproductive studies conducted with omeprazole in rats at oral doses up to 138 mg/kg/day (about 34 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis) and in rabbits at doses up to 69 mg/kg/day (about 34 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis) did not disclose any evidence for a teratogenic potential of omeprazole. In rabbits, omeprazole in a dose range of 6.9 to 69.1 mg/kg/day (about 3.4 to 34 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis) produced dose-related increases in embryo-lethality, fetal resorptions, and pregnancy disruptions. In rats, dose-related embryo/fetal toxicity and postnatal developmental toxicity were observed in offspring resulting from parents treated with omeprazole at 13.8 to 138.0 mg/kg/day (about 3.4 to 34 times an oral human doses of 40 mg on a body surface area basis).
Reproduction studies have been performed with esomeprazole magnesium in rats at oral doses up to 280 mg/kg/day (about 68 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis) and in rabbits at oral doses up to 86 mg/kg/day (about 42 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis) and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to esomeprazole magnesium.
A pre- and postnatal developmental toxicity study in rats with additional endpoints to evaluate bone development was performed with esomeprazole magnesium at oral doses of 14 to 280 mg/kg/day (about 3.4 to 68 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis). Neonatal/early postnatal (birth to weaning) survival was decreased at doses equal to or greater than 138 mg/kg/day (about 34 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis). Body weight and body weight gain were reduced and neurobehavioral or general developmental delays in the immediate post-weaning timeframe were evident at doses equal to or greater than 69 mg/kg/day (about 17 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis). In addition, decreased femur length, width and thickness of cortical bone, decreased thickness of the tibial growth plate and minimal to mild bone marrow hypocellularity were noted at doses equal to or greater than 14 mg/kg/day (about 3.4 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis). Physeal dysplasia in the femur was observed in offspring of rats treated with oral doses of esomeprazole magnesium at doses equal to or greater than 138 mg/kg/day (about 34 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis).
Effects on maternal bone were observed in pregnant and lactating rats in the pre- and postnatal toxicity study when esomeprazole magnesium was administered at oral doses of 14 to 280 mg /kg/day (about 3.4 to 68 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis). When rats were dosed from gestational day 7 through weaning on postnatal day 21, a statistically significant decrease in maternal femur weight of up to 14% (as compared to placebo treatment) was observed at doses equal to or greater than 138 mg/kg/day (about 34 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis).
A pre- and postnatal development study in rats with esomeprazole strontium (using equimolar doses compared to esomeprazole magnesium study) produced similar results in dams and pups as described above.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Omeprazole is present in human milk. Omeprazole concentrations were measured in breast milk of a woman following oral administration of 20 mg. The peak concentration of omeprazole in breast milk was less than 7% of the peak serum concentration. This concentration would correspond to 0.004 mg of omeprazole in 200 mL of milk. Caution should be exercised when omeprazole is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Use of omeprazole in pediatric and adolescent patients 2 to 16 years of age for the treatment of GERD and maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis is supported by a) extrapolation of results from adequate and well-controlled studies that supported the approval of omeprazole for adults, and b) safety and pharmacokinetic studies performed in pediatric and adolescent patients [see Clinical Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Pediatric for pharmacokinetic information (12.3) and Dosage and Administration (2), Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.6)]. The safety and effectiveness of omeprazole for the treatment of GERD in patients <1 year of age have not been established. The safety and effectiveness of omeprazole for other pediatric uses have not been established.
Juvenile Animal Data
In a juvenile rat toxicity study, esomeprazole was administered with both magnesium and strontium salts at oral doses about 34 to 68 times a daily human dose of 40 mg based on body surface area. Increases in death were seen at the high dose, and at all doses of esomeprazole, there were decreases in body weight, body weight gain, femur weight and femur length, and decreases in overall growth [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Omeprazole was administered to over 2000 elderly individuals (? 65 years of age) in clinical trials in the U.S. and Europe. There were no differences in safety and effectiveness between the elderly and younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in response between the elderly and younger subjects, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Pharmacokinetic studies have shown the elimination rate was somewhat decreased in the elderly and bioavailability was increased. The plasma clearance of omeprazole was 250 mL/min (about half that of young volunteers) and its plasma half-life averaged one hour, about twice that of young healthy volunteers. However, no dosage adjustment is necessary in the elderly [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Consider dose reduction, particularly for maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].8.7 Renal Impairment
No dosage reduction is necessary [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].8.8 Asian Population
Consider dose reduction, particularly for maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. -
10 OVERDOSAGE
Reports have been received of overdosage with omeprazole in humans. Doses ranged up to 2400 mg (120 times the usual recommended clinical dose). Manifestations were variable, but included confusion, drowsiness, blurred vision, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, flushing, headache, dry mouth, and other adverse reactions similar to those seen in normal clinical experience [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Symptoms were transient, and no serious clinical outcome has been reported when omeprazole was taken alone. No specific antidote for omeprazole overdosage is known. Omeprazole is extensively protein bound and is, therefore, not readily dialyzable. In the event of overdosage, treatment should be symptomatic and supportive.
As with the management of any overdose, the possibility of multiple drug ingestion should be considered. For current information on treatment of any drug overdose, contact a Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222.
Single oral doses of omeprazole at 1350, 1339, and 1200 mg/kg were lethal to mice, rats, and dogs, respectively. Animals given these doses showed sedation, ptosis, tremors, convulsions, and decreased activity, body temperature, and respiratory rate and increased depth of respiration. -
11 DESCRIPTION
The active ingredient in omeprazole delayed-release capsules is a substituted benzimidazole, 5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3, 5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl) methyl] sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole, a compound that inhibits gastric acid secretion. Its empirical formula is C17H19N3O3S, with a molecular weight of 345.42. The structural formula is:
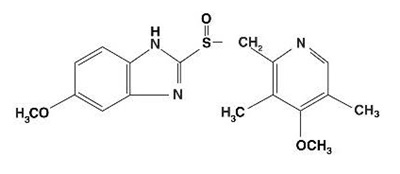
Omeprazole is a white to off-white crystalline powder that melts with decomposition at about 155°C. It is a weak base, freely soluble in ethanol and methanol, and slightly soluble in acetone and isopropanol and very slightly soluble in water. The stability of omeprazole is a function of pH; it is rapidly degraded in acid media, but has acceptable stability under alkaline conditions.
Omeprazole Delayed-Release Capsules meet USP Dissolution Test 2.
Omeprazole is supplied as delayed-release capsules for oral administration. Each delayed-release capsule contains either 10 mg, 20 mg or 40 mg of omeprazole in the form of enteric-coated granules with the following inactive ingredients: magnesium hydroxide, mannitol, methacrylic acid copolymer dispersion, povidone and triethyl citrate. The capsule shells have the following inactive ingredients: gelatin, red iron oxide and titanium dioxide. The capsule imprinting ink contains ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, ethyl alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol and shellac. -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Omeprazole belongs to a class of antisecretory compounds, the substituted benzimidazoles, that suppress gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the H+/K+ ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell. Because this enzyme system is regarded as the acid (proton) pump within the gastric mucosa, omeprazole has been characterized as a gastric acid-pump inhibitor, in that it blocks the final step of acid production. This effect is dose-related and leads to inhibition of both basal and stimulated acid secretion irrespective of the stimulus. Animal studies indicate that after rapid disappearance from plasma, omeprazole can be found within the gastric mucosa for a day or more.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Antisecretory Activity
After oral administration, the onset of the antisecretory effect of omeprazole occurs within one hour, with the maximum effect occurring within two hours. Inhibition of secretion is about 50% of maximum at 24 hours and the duration of inhibition lasts up to 72 hours. The antisecretory effect thus lasts far longer than would be expected from the very short (less than one hour) plasma half-life, apparently due to prolonged binding to the parietal H+/K+ ATPase enzyme. When the drug is discontinued, secretory activity returns gradually, over 3 to 5 days. The inhibitory effect of omeprazole on acid secretion increases with repeated once-daily dosing, reaching a plateau after four days.
Results from numerous studies of the antisecretory effect of multiple doses of 20 mg and 40 mg of omeprazole in normal volunteers and patients are shown below. The “max” value represents determinations at a time of maximum effect (2 to 6 hours after dosing), while “min” values are those 24 hours after the last dose of omeprazole.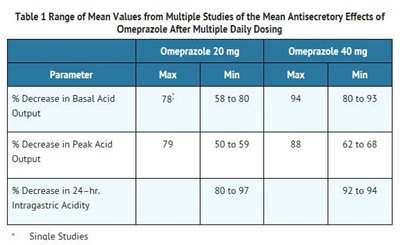
Single daily oral doses of omeprazole ranging from a dose of 10 mg to 40 mg have produced 100% inhibition of 24-hour intragastric acidity in some patients.
Serum Gastrin Effects
In studies involving more than 200 patients, serum gastrin levels increased during the first 1 to 2 weeks of once-daily administration of therapeutic doses of omeprazole in parallel with inhibition of acid secretion. No further increase in serum gastrin occurred with continued treatment. In comparison with histamine H2-receptor antagonists, the median increases produced by 20 mg doses of omeprazole were higher (1.3 to 3.6 fold vs. 1.1 to 1.8 fold increase). Gastrin values returned to pretreatment levels, usually within 1 to 2 weeks after discontinuation of therapy.
Increased gastrin causes enterochromaffin-like cell hyperplasia and increased serum Chromogranin A (CgA) levels. The increased CgA levels may cause false positive results in diagnostic investigations for neuroendocrine tumors. Healthcare providers should temporarily stop omeprazole treatment at least 14 days before assessing CgA levels and consider repeating the test if initial CgA levels are high.
Enterochromaffin-like (ECL) Cell Effects
Human gastric biopsy specimens have been obtained from more than 3000 patients (both children and adults) treated with omeprazole in long-term clinical trials. The incidence of ECL cell hyperplasia in these studies increased with time; however, no case of ECL cell carcinoids, dysplasia, or neoplasia has been found in these patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. However, these studies are of insufficient duration and size to rule out the possible influence of long-term administration of omeprazole on the development of any premalignant or malignant conditions.
Other Effects
Systemic effects of omeprazole in the CNS, cardiovascular and respiratory systems have not been found to date. Omeprazole, given in oral doses of 30 or 40 mg for 2 to 4 weeks, had no effect on thyroid function, carbohydrate metabolism, or circulating levels of parathyroid hormone, cortisol, estradiol, testosterone, prolactin, cholecystokinin or secretin.
No effect on gastric emptying of the solid and liquid components of a test meal was demonstrated after a single dose of omeprazole 90 mg. In healthy subjects, a single I.V. dose of omeprazole (0.35 mg/kg) had no effect on intrinsic factor secretion. No systematic dose-dependent effect has been observed on basal or stimulated pepsin output in humans.
However, when intragastric pH is maintained at 4.0 or above, basal pepsin output is low, and pepsin activity is decreased.
As do other agents that elevate intragastric pH, omeprazole administered for 14 days in healthy subjects produced a significant increase in the intragastric concentrations of viable bacteria. The pattern of the bacterial species was unchanged from that commonly found in saliva. All changes resolved within three days of stopping treatment.
The course of Barrett’s esophagus in 106 patients was evaluated in a U.S. double-blind controlled study of omeprazole 40 mg twice daily for 12 months followed by 20 mg twice daily for 12 months or ranitidine 300 mg twice daily for 24 months. No clinically significant impact on Barrett’s mucosa by antisecretory therapy was observed. Although neosquamous epithelium developed during antisecretory therapy, complete elimination of Barrett’s mucosa was not achieved. No significant difference was observed between treatment groups in development of dysplasia in Barrett’s mucosa and no patient developed esophageal carcinoma during treatment. No significant differences between treatment groups were observed in development of ECL cell hyperplasia, corpus atrophic gastritis, corpus intestinal metaplasia, or colon polyps exceeding 3 mm in diameter [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
AbsorptionOmeprazole delayed-release capsules contain an enteric-coated granule formulation of omeprazole (because omeprazole is acid-labile), so that absorption of omeprazole begins only after the granules leave the stomach. Absorption is rapid, with peak plasma levels of omeprazole occurring within 0.5 to 3.5 hours. Peak plasma concentrations of omeprazole and AUC are approximately proportional to doses up to 40 mg, but because of a saturable first-pass effect, a greater than linear response in peak plasma concentration and AUC occurs with doses greater than 40 mg.
Absolute bioavailability (compared with intravenous administration) is about 30 to 40% at doses of 20 to 40 mg, due in large part to presystemic metabolism. In healthy subjects the plasma half-life is 0.5 to 1 hour, and the total body clearance is 500 to 600 mL/min.The bioavailability of omeprazole increases slightly upon repeated administration of omeprazole delayed-release capsules.
Omeprazole delayed-release capsule 40 mg was bioequivalent when administered with and without applesauce. However, omeprazole delayed-release capsule 20 mg was not bioequivalent when administered with and without applesauce. When administered with applesauce, a mean 25% reduction in Cmax was observed without a significant change in AUC for omeprazole delayed-release capsule 20 mg. The clinical relevance of this finding is unknown.
Distribution
Protein binding is approximately 95%.
Metabolism
Omeprazole is extensively metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system.
Excretion
Following single dose oral administration of a buffered solution of omeprazole, little if any unchanged drug was excreted in urine. The majority of the dose (about 77%) was eliminated in urine as at least six metabolites. Two were identified as hydroxyomeprazole and the corresponding carboxylic acid. The remainder of the dose was recoverable in feces. This implies a significant biliary excretion of the metabolites of omeprazole. Three metabolites have been identified in plasma - the sulfide and sulfone derivatives of omeprazole, and hydroxyomeprazole. These metabolites have very little or no antisecretory activity.
Combination Therapy with Antimicrobials
Omeprazole 40 mg daily was given in combination with clarithromycin 500 mg every 8 hours to healthy adult male subjects. The steady state plasma concentrations of omeprazole were increased (Cmax, AUC0-24, and T1/2 increases of 30%, 89% and 34% respectively) by the concomitant administration of clarithromycin. The observed increases in omeprazole plasma concentration were associated with the following pharmacological effects. The mean 24-hour gastric pH value was 5.2 when omeprazole was administered alone and 5.7 when co-administered with clarithromycin.
The plasma levels of clarithromycin and 14-hydroxy-clarithromycin were increased by the concomitant administration of omeprazole. For clarithromycin, the mean Cmax was 10% greater, the mean Cmin was 27% greater, and the mean AUC0-8 was 15% greater when clarithromycin was administered with omeprazole than when clarithromycin was administered alone. Similar results were seen for 14-hydroxy-clarithromycin, the mean Cmax was 45% greater, the mean Cmin was 57% greater, and the mean AUC0-8 was 45% greater. Clarithromycin concentrations in the gastric tissue and mucus were also increased by concomitant administration of omeprazole.Table 2 Clarithromycin Tissue Concentrations 2 hours after Dose1
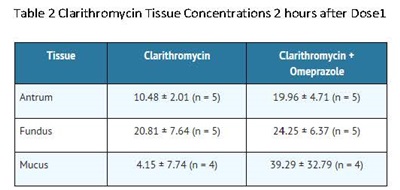
1Mean ± SD (mcg/g)
Concomitant Use with Clopidogrel
In a crossover clinical study, 72 healthy subjects were administered clopidogrel (300 mg loading dose followed by 75 mg per day) alone and with omeprazole (80 mg at the same time as clopidogrel) for 5 days. The exposure to the active metabolite of clopidogrel was decreased by 46% (Day 1) and 42% (Day 5) when clopidogrel and omeprazole were administered together.
Results from another crossover study in healthy subjects showed a similar pharmacokinetic interaction between clopidogrel (300 mg loading dose/75 mg daily maintenance dose) and omeprazole 80 mg daily when co-administered for 30 days. Exposure to the active metabolite of clopidogrel was reduced by 41% to 46% over this time period.
In another study, 72 healthy subjects were given the same doses of clopidogrel and 80 mg omeprazole but the drugs were administered 12 hours apart; the results were similar, indicating that administering clopidogrel and omeprazole at different times does not prevent their interaction.
Concomitant Use with Mycophenolate Mofetil
Administration of omeprazole 20 mg twice daily for 4 days and a single 1,000 mg dose of MMF approximately one hour after the last dose of omeprazole to 12 healthy subjects in a cross-over study resulted in a 52% reduction in the Cmax and 23% reduction in the AUC of MPA.
Special PopulationsGeriatric Population
The elimination rate of omeprazole was somewhat decreased in the elderly, and bioavailability was increased. Omeprazole was 76% bioavailable when a single 40 mg oral dose of omeprazole (buffered solution) was administered to healthy elderly volunteers, versus 58% in young volunteers given the same dose. Nearly 70% of the dose was recovered in urine as metabolites of omeprazole and no unchanged drug was detected. The plasma clearance of omeprazole was 250 mL/min (about half that of young volunteers) and its plasma half-life averaged one hour, about twice that of young healthy volunteers.
Pediatric Use
The pharmacokinetics of omeprazole have been investigated in pediatric patients 2 to 16 years of age:
Table 3 Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Omeprazole Following Single and Repeated Oral Administration in Pediatric Populations Compared with Adults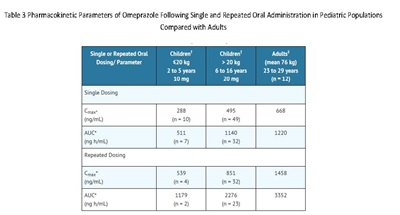
Note: * = plasma concentration adjusted to an oral dose of 1 mg/kg.
†Data from single and repeated dose studies
‡Data from a single and repeated dose study
Doses of 10, 20 and 40 mg omeprazole as enteric-coated granules
Following comparable mg/kg doses of omeprazole, younger children (2 to 5 years of age) have lower AUCs than children 6 to 16 years of age or adults; AUCs of the latter two groups did not differ [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Hepatic Impairment
In patients with chronic hepatic disease, the bioavailability increased to approximately 100% compared with an I.V. dose, reflecting decreased first-pass effect, and the plasma half-life of the drug increased to nearly 3 hours compared with the half-life in normals of 0.5 to 1 hour. Plasma clearance averaged 70 mL/min, compared with a value of 500 to 600 mL/min in normal subjects. Dose reduction, particularly where maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis is indicated, for the hepatically impaired should be considered.
Renal Impairment
In patients with chronic renal impairment, whose creatinine clearance ranged between 10 and 62 mL/min/1.73 m2, the disposition of omeprazole was very similar to that in healthy volunteers, although there was a slight increase in bioavailability. Because urinary excretion is a primary route of excretion of omeprazole metabolites, their elimination slowed in proportion to the decreased creatinine clearance. No dose reduction is necessary in patients with renal impairment.
Asian Population
In pharmacokinetic studies of single 20 mg omeprazole doses, an increase in AUC of approximately four-fold was noted in Asian subjects compared with Caucasians. Dose reduction, particularly where maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis is indicated, for Asian subjects should be considered.
12.4 Microbiology
Omeprazole and clarithromycin dual therapy and omeprazole, clarithromycin and amoxicillin triple therapy have been shown to be active against most strains of Helicobacter pylori in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the Indications and Usage section (1.1).
Helicobacter
Helicobacter pylori-Pretreatment Resistance
Clarithromycin pretreatment resistance rates were 3.5% (4/113) in the omeprazole/clarithromycin dual therapy studies (4 and 5) and 9.3% (41/439) in omeprazole/clarithromycin/amoxicillin triple therapy studies (1, 2, and 3).
Amoxicillin pretreatment susceptible isolates (? 0.25 mcg/mL) were found in 99.3% (436/439) of the patients in the omeprazole/clarithromycin/amoxicillin triple therapy studies (1, 2, and 3). Amoxicillin pretreatment minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) > 0.25 mcg/mL occurred in 0.7% (3/439) of the patients, all of whom were in the clarithromycin and amoxicillin study arm. One patient had an unconfirmed pretreatment amoxicillin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of > 256 mcg/mL by Etest®.
Table 4 Clarithromycin Susceptibility Test Results and Clinical/Bacteriological Outcomes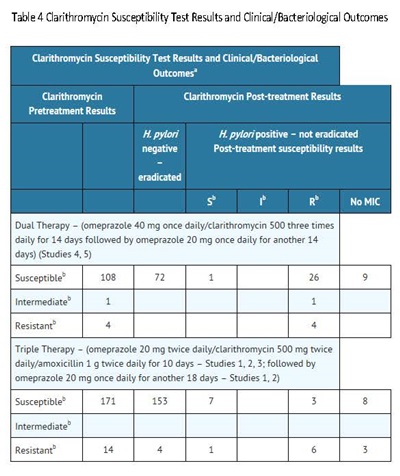
a Includes only patients with pretreatment clarithromycin susceptibility test results
b Susceptible (S) MIC ? 0.25 mcg/mL, Intermediate (I) MIC 0.5 to 1.0 mcg/mL, Resistant (R) MIC ? 2 mcg/mL
Patients not eradicated of H. pylori following omeprazole/clarithromycin/amoxicillin triple therapy or omeprazole/clarithromycin dual therapy will likely have clarithromycin resistant H. pylori isolates. Therefore, clarithromycin susceptibility testing should be done, if possible. Patients with clarithromycin resistant H. pylori should not be treated with any of the following: omeprazole/clarithromycin dual therapy, omeprazole/clarithromycin/amoxicillin triple therapy, or other regimens which include clarithromycin as the sole antimicrobial agent.
Amoxicillin Susceptibility Test Results and Clinical/Bacteriological Outcomes
In the triple therapy clinical trials, 84.9% (157/185) of the patients in the omeprazole/clarithromycin/amoxicillin treatment group who had pretreatment amoxicillin susceptible MICs (? 0.25 mcg/mL) were eradicated of H. pylori and 15.1% (28/185) failed therapy. Of the 28 patients who failed triple therapy, 11 had no post-treatment susceptibility test results and 17 had post-treatment H. pylori isolates with amoxicillin susceptible MICs. Eleven of the patients who failed triple therapy also had post-treatment H. pylori isolates with clarithromycin resistant MICs.
Susceptibility Test for Helicobacter pyloriFor susceptibility testing information about Helicobacter pylori, see Microbiology section in prescribing information for clarithromycin and amoxicillin.
Effects on Gastrointestinal Microbial EcologyDecreased gastric acidity due to any means including proton pump inhibitors, increases gastric counts of bacteria normally present in the gastrointestinal tract. Treatment with proton pump inhibitors may lead to slightly increased risk of gastrointestinal infections such as Salmonella and Campylobacter and, in hospitalized patients, possibly also Clostridium difficile.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In two 24-month carcinogenicity studies in rats, omeprazole at daily doses of 1.7, 3.4, 13.8, 44.0 and 140.8 mg/kg/day (about 0.4 to 34 times a human dose of 40 mg/day, as expressed on a body surface area basis) produced gastric ECL cell carcinoids in a dose-related manner in both male and female rats; the incidence of this effect was markedly higher in female rats, which had higher blood levels of omeprazole. Gastric carcinoids seldom occur in the untreated rat. In addition, ECL cell hyperplasia was present in all treated groups of both sexes. In one of these studies, female rats were treated with 13.8 mg omeprazole/kg/day (about 3.4 times a human dose of 40 mg/day, based on body surface area) for one year, and then followed for an additional year without the drug. No carcinoids were seen in these rats. An increased incidence of treatment-related ECL cell hyperplasia was observed at the end of one year (94% treated vs 10% controls). By the second year the difference between treated and control rats was much smaller (46% vs 26%) but still showed more hyperplasia in the treated group. Gastric adenocarcinoma was seen in one rat (2%). No similar tumor was seen in male or female rats treated for two years. For this strain of rat no similar tumor has been noted historically, but a finding involving only one tumor is difficult to interpret. In a 52-week toxicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats, brain astrocytomas were found in a small number of males that received omeprazole at dose levels of 0.4, 2, and 16 mg/kg/day (about 0.1 to 3.9 times the human dose of 40 mg/day, based on a body surface area basis). No astrocytomas were observed in female rats in this study. In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats, no astrocytomas were found in males or females at the high dose of 140.8 mg/kg/day (about 34 times the human dose of 40 mg/day on a body surface area basis). A 78-week mouse carcinogenicity study of omeprazole did not show increased tumor occurrence, but the study was not conclusive. A 26-week p53 (+/-) transgenic mouse carcinogenicity study was not positive.
Omeprazole was positive for clastogenic effects in an in vitro human lymphocyte chromosomal aberration assay, in one of two in vivo mouse micronucleus tests, and in an in vivo bone marrow cell chromosomal aberration assay. Omeprazole was negative in the in vitro Ames test, an in vitro mouse lymphoma cell forward mutation assay, and an in vivo rat liver DNA damage assay.
Omeprazole at oral doses up to 138 mg/kg/day in rats (about 34 times an oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis) was found to have no effect on fertility and reproductive performance.
In 24-month carcinogenicity studies in rats, a dose-related significant increase in gastric carcinoid tumors and ECL cell hyperplasia was observed in both male and female animals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]. Carcinoid tumors have also been observed in rats subjected to fundectomy or long-term treatment with other proton pump inhibitors or high doses of H2-receptor antagonists.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Reproduction StudiesReproductive Toxicology Studies
Reproductive studies conducted with omeprazole in rats at oral doses up to 138 mg/kg/day (about 34 times the human dose of 40 mg/day on a body surface area basis) and in rabbits at doses up to 69 mg/kg/day (about 34 times the human dose on a body surface area basis) did not disclose any evidence for a teratogenic potential of omeprazole. In rabbits, omeprazole in a dose range of 6.9 to 69.1 mg/kg/day (about 3.4 to 34 times the human dose of 40 mg/day on a body surface area basis) produced dose-related increases in embryo-lethality, fetal resorptions, and pregnancy disruptions. In rats, dose-related embryo/fetal toxicity and postnatal developmental toxicity were observed in offspring resulting from parents treated with omeprazole at 13.8 to 138.0 mg/kg/day (about 3.4 to 34 times the human dose of 40 mg/day on a body surface area basis) [see Pregnancy, Animal Data (8.1)].
Juvenile Animal Study
A 28-day toxicity study with a 14-day recovery phase was conducted in juvenile rats with esomeprazole magnesium at doses of 70 to 280 mg /kg/day (about 17 to 68 times a daily oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis). An increase in the number of deaths at the high dose of 280 mg/kg/day was observed when juvenile rats were administered esomeprazole magnesium from postnatal day 7 through postnatal day 35. In addition, doses equal to or greater than 140 mg/kg/day (about 34 times a daily oral human dose of 40 mg on a body surface area basis), produced treatment-related decreases in body weight (approximately 14%) and body weight gain, decreases in femur weight and femur length, and affected overall growth. Comparable findings described above have also been observed in this study with another esomeprazole salt, esomeprazole strontium, at equimolar doses of esomeprazole. -
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Duodenal Ulcer Disease
Active Duodenal UlcerIn a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 147 patients with endoscopically documented duodenal ulcer, the percentage of patients healed (per protocol) at 2 and 4 weeks was significantly higher with omeprazole 20 mg once daily than with placebo (p ? 0.01).
Treatment of Active Duodenal Ulcer % of Patients Healed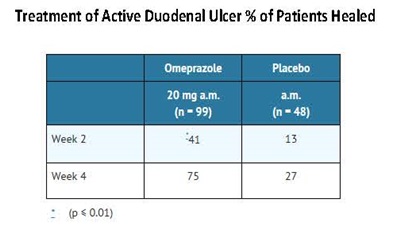
Complete daytime and nighttime pain relief occurred significantly faster (p ? 0.01) in patients treated with omeprazole 20 mg than in patients treated with placebo. At the end of the study, significantly more patients who had received omeprazole had complete relief of daytime pain (p ? 0.05) and nighttime pain (p ? 0.01).
In a multicenter, double-blind study of 293 patients with endoscopically documented duodenal ulcer, the percentage of patients healed (per protocol) at 4 weeks was significantly higher with omeprazole 20 mg once daily than with ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d. (p < 0.01).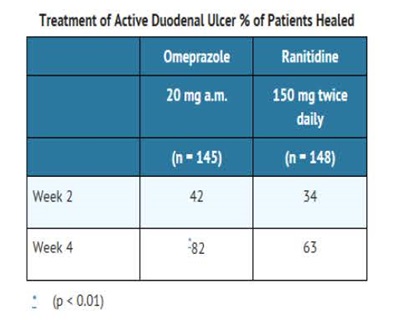
Healing occurred significantly faster in patients treated with omeprazole than in those treated with ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d. (p < 0.01).
In a foreign multinational randomized, double-blind study of 105 patients with endoscopically documented duodenal ulcer, 20 mg and 40 mg of omeprazole were compared with 150 mg b.i.d. of ranitidine at 2, 4 and 8 weeks. At 2 and 4 weeks both doses of omeprazole were statistically superior (per protocol) to ranitidine, but 40 mg was not superior to 20 mg of omeprazole, and at 8 weeks there was no significant difference between any of the active drugs.
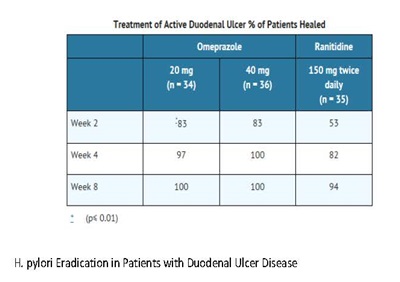
H. pylori Eradication in Patients with Duodenal Ulcer Disease
Triple Therapy (omeprazole/clarithromycin/amoxicillin)
Three U.S., randomized, double-blind clinical studies in patients with H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease (n = 558) compared omeprazole plus clarithromycin plus amoxicillin with clarithromycin plus amoxicillin. Two studies (1 and 2) were conducted in patients with an active duodenal ulcer, and the other study (3) was conducted in patients with a history of a duodenal ulcer in the past 5 years but without an ulcer present at the time of enrollment. The dose regimen in the studies was omeprazole 20 mg twice daily plus clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily plus amoxicillin 1 g twice daily for 10 days; or clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily plus amoxicillin 1 g twice daily for 10 days. In studies 1 and 2, patients who took the omeprazole regimen also received an additional 18 days of omeprazole 20 mg once daily. Endpoints studied were eradication of H. pylori and duodenal ulcer healing (studies 1 and 2 only). H. pylori status was determined by CLOtest®, histology and culture in all three studies. For a given patient, H. pylori was considered eradicated if at least two of these tests were negative, and none was positive.The combination of omeprazole plus clarithromycin plus amoxicillin was effective in eradicating H. pylori.
Table 5 Per-Protocol and Intent-to-Treat H. pylori Eradication Rates % of Patients Cured [95% Confidence Interval]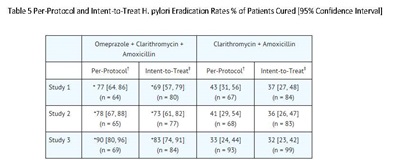
† Patients were included in the analysis if they had confirmed duodenal ulcer disease (active ulcer, studies 1 and 2; history of ulcer within 5 years, study 3) and H. pylori infection at baseline defined as at least two of three positive endoscopic tests from CLOtest®, histology, and/or culture. Patients were included in the analysis if they completed the study. Additionally, if patients dropped out of the study due to an adverse event related to the study drug, they were included in the analysis as failures of therapy. The impact of eradication on ulcer recurrence has not been assessed in patients with a past history of ulcer.
‡ Patients were included in the analysis if they had documented H. pylori infection at baseline and had confirmed duodenal ulcer disease. All dropouts were included as failures of therapy.
* (p < 0.05) versus clarithromycin plus amoxicillin.Dual Therapy (omeprazole/clarithromycin)
Four randomized, double-blind, multi-center studies (4, 5, 6, and 7) evaluated omeprazole 40 mg once daily plus clarithromycin 500 mg three times daily for 14 days, followed by omeprazole 20 mg once daily, (Studies 4, 5, and 7) or by omeprazole 40 mg once daily (Study 6) for an additional 14 days in patients with active duodenal ulcer associated with H. pylori. Studies 4 and 5 were conducted in the U.S. and Canada and enrolled 242 and 256 patients, respectively. H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer were confirmed in 219 patients in Study 4 and 228 patients in Study 5. These studies compared the combination regimen to omeprazole and clarithromycin monotherapies. Studies 6 and 7 were conducted in Europe and enrolled 154 and 215 patients, respectively. H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer were confirmed in 148 patients in Study 6 and 208 patients in Study 7. These studies compared the combination regimen with omeprazole monotherapy. The results for the efficacy analyses for these studies are described below. H. pylori eradication was defined as no positive test (culture or histology) at 4 weeks following the end of treatment, and two negative tests were required to be considered eradicated of H. pylori. In the per-protocol analysis, the following patients were excluded: dropouts, patients with missing H. pylori tests post-treatment, and patients that were not assessed for H. pylori eradication because they were found to have an ulcer at the end of treatment.
The combination of omeprazole and clarithromycin was effective in eradicating H. pylori.Table 6 H. pylori Eradication Rates (Per-Protocol Analysis at 4 to 6 Weeks) % of Patients Cured [95% Confidence Interval]
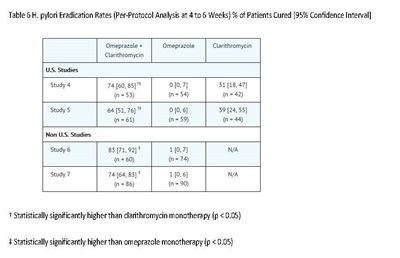
† Statistically significantly higher than clarithromycin monotherapy (p < 0.05)
‡ Statistically significantly higher than omeprazole monotherapy (p < 0.05)Ulcer healing was not significantly different when clarithromycin was added to omeprazole therapy compared with omeprazole therapy alone.
The combination of omeprazole and clarithromycin was effective in eradicating H. pylori and reduced duodenal ulcer recurrence.
Table 7 Duodenal Ulcer Recurrence Rates by H. pylori Eradication Status% of Patients with Ulcer Recurrence
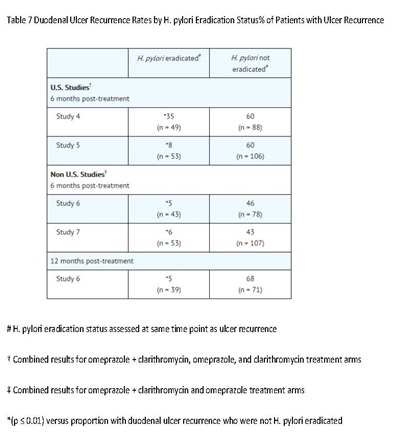
# H. pylori eradication status assessed at same time point as ulcer recurrence
† Combined results for omeprazole + clarithromycin, omeprazole, and clarithromycin treatment arms
‡ Combined results for omeprazole + clarithromycin and omeprazole treatment arms
*(p ? 0.01) versus proportion with duodenal ulcer recurrence who were not H. pylori eradicated
14.2 Gastric Ulcer
In a U.S. multicenter, double-blind, study of omeprazole 40 mg once daily, 20 mg once daily, and placebo in 520 patients with endoscopically diagnosed gastric ulcer, the following results were obtained.
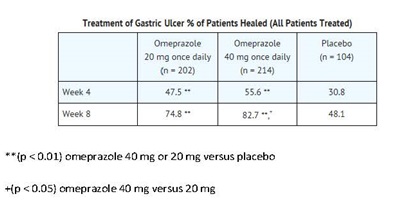
**(p < 0.01) omeprazole 40 mg or 20 mg versus placebo
+(p < 0.05) omeprazole 40 mg versus 20 mgFor the stratified groups of patients with ulcer size less than or equal to 1 cm, no difference in healing rates between 40 mg and 20 mg was detected at either 4 or 8 weeks. For patients with ulcer size greater than 1 cm, 40 mg was significantly more effective than 20 mg at 8 weeks.
In a foreign, multinational, double-blind study of 602 patients with endoscopically diagnosed gastric ulcer, omeprazole 40 mg once daily, 20 mg
once daily, and ranitidine 150 mg twice a day were evaluated.
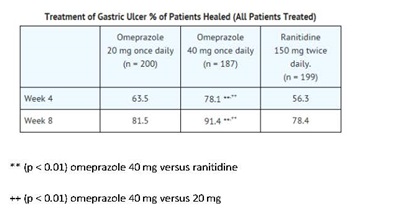
** (p < 0.01) omeprazole 40 mg versus ranitidine
++ (p < 0.01) omeprazole 40 mg versus 20 mg
14.3 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Symptomatic GERDA placebo-controlled study was conducted in Scandinavia to compare the efficacy of omeprazole 20 mg or 10 mg once daily for up to 4 weeks in the treatment of heartburn and other symptoms in GERD patients without erosive esophagitis. Results are shown below.
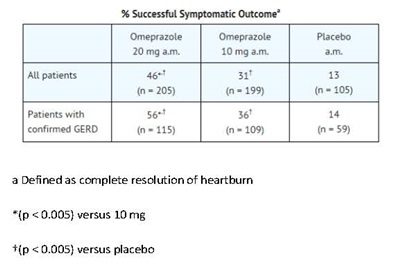
a Defined as complete resolution of heartburn
*(p < 0.005) versus 10 mg
†(p < 0.005) versus placebo
14.4 Erosive Esophagitis
In a U.S. multicenter double-blind placebo controlled study of 20 mg or 40 mg of omeprazole delayed-release capsules in patients with symptoms of GERD and endoscopically diagnosed erosive esophagitis of grade 2 or above, the percentage healing rates (per protocol) were as follows: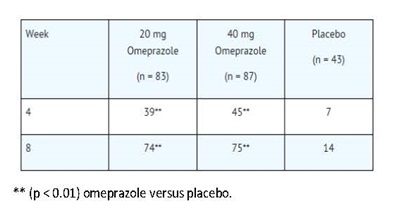
** (p < 0.01) omeprazole versus placebo.
In this study, the 40 mg dose was not superior to the 20 mg dose of omeprazole in the percentage healing rate. Other controlled clinical trials have also shown that omeprazole is effective in severe GERD. In comparisons with histamine H2-receptor antagonists in patients with erosive esophagitis, grade 2 or above, omeprazole in a dose of 20 mg was significantly more effective than the active controls. Complete daytime and nighttime heartburn relief occurred significantly faster (p < 0.01) in patients treated with omeprazole than in those taking placebo or histamine H2- receptor antagonists.
In this and five other controlled GERD studies, significantly more patients taking 20 mg omeprazole (84%) reported complete relief of GERD symptoms than patients receiving placebo (12%).
Long-Term Maintenance Of Healing of Erosive EsophagitisIn a U.S. double-blind, randomized, multicenter, placebo controlled study, two dose regimens of omeprazole were studied in patients with endoscopically confirmed healed esophagitis. Results to determine maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis are shown below.
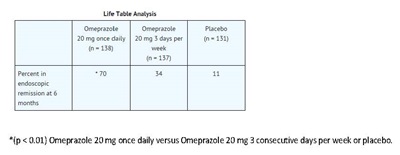
*(p < 0.01) Omeprazole 20 mg once daily versus Omeprazole 20 mg 3 consecutive days per week or placebo.
In an international multicenter double-blind study, omeprazole 20 mg daily and 10 mg daily were compared with ranitidine 150 mg twice daily in patients with endoscopically confirmed healed esophagitis. The table below provides the results of this study for maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis.
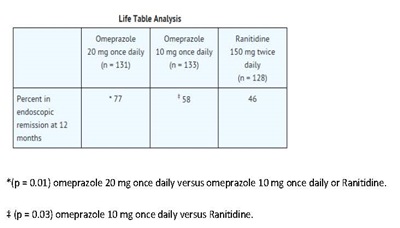
*(p = 0.01) omeprazole 20 mg once daily versus omeprazole 10 mg once daily or Ranitidine.
‡ (p = 0.03) omeprazole 10 mg once daily versus Ranitidine.
In patients who initially had grades 3 or 4 erosive esophagitis, for maintenance after healing 20 mg daily of omeprazole was effective, while 10 mg did not demonstrate effectiveness.
14.5 Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions
In open studies of 136 patients with pathological hypersecretory conditions, such as Zollinger-Ellison (ZE) syndrome with or without multiple endocrine adenomas, omeprazole delayed-release capsules significantly inhibited gastric acid secretion and controlled associated symptoms of diarrhea, anorexia, and pain. Doses ranging from 20 mg every other day to 360 mg per day maintained basal acid secretion below 10 mEq/hr in patients without prior gastric surgery, and below 5 mEq/hr in patients with prior gastric surgery.Initial doses were titrated to the individual patient need, and adjustments were necessary with time in some patients [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. Omeprazole was well tolerated at these high dose levels for prolonged periods (> 5 years in some patients). In most ZE patients, serum gastrin levels were not modified by omeprazole. However, in some patients serum gastrin increased to levels greater than those present prior to initiation of omeprazole therapy. At least 11 patients with ZE syndrome on long-term treatment with omeprazole developed gastric carcinoids. These findings are believed to be a manifestation of the underlying condition, which is known to be associated with such tumors, rather than the result of the administration of omeprazole [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
14.6 Pediatric GERD
Symptomatic GERDThe effectiveness of omeprazole for the treatment of nonerosive GERD in pediatric patients 2 to 16 years of age is based in part on data obtained from pediatric patients in an uncontrolled Phase III studies [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
The study enrolled 113 pediatric patients 2 to 16 years of age with a history of symptoms suggestive of nonerosive GERD. Patients were administered a single dose of omeprazole (10 mg or 20 mg, based on body weight) for 4 weeks either as an intact capsule or as an open capsule in applesauce. Successful response was defined as no moderate or severe episodes of either pain-related symptoms or vomiting/regurgitation during the last 4 days of treatment. Results showed success rates of 60% (9/15; 10 mg omeprazole) and 59% (58/98; 20 mg omeprazole), respectively.
Healing of Erosive Esophagitis
In an uncontrolled, open-label dose-titration study, healing of erosive esophagitis in pediatric patients 1 to 16 years of age required doses that ranged from 0.7 to 3.5 mg/kg/day (80 mg/day). Doses were initiated at 0.7 mg/kg/day. Doses were increased in increments of 0.7 mg/kg/day (if intraesophageal pH showed a pH of < 4 for less than 6% of a 24-hour study). After titration, patients remained on treatment for 3 months. Forty-four percent of the patients were healed on a dose of 0.7 mg/kg body weight; most of the remaining patients were healed with 1.4 mg/kg after an additional 3 months’ treatment. Erosive esophagitis was healed in 51 of 57 (90%) children who completed the first course of treatment in the healing phase of the study. In addition, after 3 months of treatment, 33% of the children had no overall symptoms, 57% had mild reflux symptoms, and 40% had less frequent regurgitation/vomiting.
Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis
In an uncontrolled, open-label study of maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis in 46 pediatric patients, 54% of patients required half the healing dose. The remaining patients increased the healing dose (0.7 to a maximum of 2.8 mg/kg/day) either for the entire maintenance period, or returned to half the dose before completion. Of the 46 patients who entered the maintenance phase, 19 (41%) had no relapse. In addition, maintenance therapy in erosive esophagitis patients resulted in 63% of patients having no overall symptoms.
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules, USP 20 mg are available for oral administration as hard gelatin capsules with a pink opaque body and a reddish brown opaque cap. “APO 020” is imprinted on each capsule in black ink. They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 30 (NDC: 60505-0065-0)
Storage
Store omeprazole delayed-release capsules in a tight container protected from light and moisture.Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted from 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
“See FDA-Approved Medication Guide”
Omeprazole delayed-release capsule should be taken before eating. Patients should be informed that the omeprazole delayed-release capsule should be swallowed whole.
For patients who have difficulty swallowing capsules, the contents of an omeprazole delayed-release capsule can be added to applesauce. One tablespoon of applesauce should be added to an empty bowl and the capsule should be opened. All of the pellets inside the capsule should be carefully emptied on the applesauce. The pellets should be mixed with the applesauce and then swallowed immediately with a glass of cool water to ensure complete swallowing of the pellets. The applesauce used should not be hot and should be soft enough to be swallowed without chewing. The pellets should not be chewed or crushed. The pellets/applesauce mixture should not be stored for future use.
Advise patients to immediately report and seek care for diarrhea that does not improve. This may be a sign of Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Advise patients to immediately report and seek care for any cardiovascular or neurological symptoms including palpitations, dizziness, seizures, and tetany as these may be signs of hypomagnesemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
Omeprazole Delayed-Release Capsules, USP
(oh mep’ ra zole)
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking omeprazole delayed-release capsules and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about omeprazole delayed-release capsules?
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules may help your acid-related symptoms, but you could still have serious stomach problems. Talk with your doctor.
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules can cause serious side effects, including:
Diarrhea. Omeprazole may increase your risk of getting severe diarrhea. This diarrhea may be caused by an infection (Clostridium difficile) in your intestines.
Call your doctor right away if you have watery stool, stomach pain, and fever that does not go away.
Bone fractures. People who take multiple daily doses of proton pump inhibitor medicines for a long period of time (a year or longer) may have an increased risk of fractures of the hip, wrist, or spine. You should take omeprazole delayed-release capsules exactly as prescribed, at the lowest dose possible for your treatment and for the shortest time needed. Talk to your doctor about your risk of bone fracture if you take omeprazole delayed-release capsules.
Omeprazole can have other serious side effects. See “What are the possible side effects of omeprazole delayed-release capsules?”
What are omeprazole delayed-release capsules?
Omeprazole delayed-release capsules is a prescription medicine called a proton pump inhibitor (PPI). Omeprazole delayed-release capsules reduces the amount of acid in your stomach. Omeprazole delayed-release capsules are used in adults:
for up to 8 weeks for the healing of duodenal ulcers. The duodenal area is the area where food passes when it leaves the stomach.
with certain antibiotics to treat an infection caused by bacteria called H. pylori. Sometimes H. pylori bacteria can cause duodenal ulcers. The infection needs to be treated to prevent the ulcers from coming back.
for up to 8 weeks for healing stomach ulcers.
for up to 4 weeks to treat heartburn and other symptoms that happen with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).GERD happens when acid in your stomach backs up into the tube (esophagus) that connects your mouth to your stomach. This may cause a burning feeling in your chest or throat, sour taste, or burping.
for up to 8 weeks to heal acid-related damage to the lining of the esophagus (called erosive esophagitis or EE) . If needed, your doctor may decide to prescribe another 4 weeks of omeprazole delayed-release capsules.
to maintain healing of the esophagus. It is not known if omeprazole delayed-release capsules is safe and effective when used for longer than 12 months (1 year) for this purpose.
for the long-term treatment of conditions where your stomach makes too much acid. This includes a rare condition called Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome.For children and adolescents 2 to 17 years of age, omeprazole delayed-release capsules are used:
for up to 4 weeks to treat heartburn and other symptoms that happen with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
for up to 8 weeks to heal acid-related damage to the lining of the esophagus (called erosive esophagitis or EE)
to maintain healing of the esophagus. It is not known if omeprazole delayed-release capsules are safe and effective when used longer than 12 months (1 year) for this purpose.It is not known if omeprazole delayed-release capsules are safe and effective for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in children under 1 year of age.
Who should not take omeprazole delayed-release capsules?
Do not take omeprazole delayed-release capsules if you:
are allergic to omeprazole delayed-release capsules or any of the ingredients in omeprazole delayed-release capsules. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in omeprazole delayed-release capsules.
are allergic to any other Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) medicine.What should I tell my doctor before taking omeprazole delayed-release capsules?
Before you take omeprazole delayed-release capsules, tell your doctor if you:
have been told that you have low magnesium levels in your blood
have liver problems
have any other medical conditions
are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if omeprazole will harm your unborn baby.
are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Omeprazole passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take omeprazole delayed-release capsules.Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take including prescription and non-prescription drugs, anti-cancer drugs, vitamins and herbal supplements. Omeprazole delayed-release capsules may affect how other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how omeprazole delayed-release capsules works.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
atazanavir (Reyataz)
nelfinavir (Viracept)
saquinavir (Fortovase)
cilostazol (Pletal)
ketoconazole (Nizoral)
voriconazole (Vfend)
an antibiotic that contains ampicillin, amoxicillin or clarithromycin
products that contain iron
warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven)
digoxin (Lanoxin)
tacrolimus (Prograf)
diazepam (Valium)
phenytoin (Dilantin)
disulfiram (Antabuse)
clopidogrel (Plavix)
St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum)
rifampin (Rimactane, Rifater, Rifamate),
erlotinib (Tarceva)
methotrexate
mycophenolate mofetil (Cellcept)Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure.
Know the medicines that you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take omeprazole delayed-release capsules?
Take omeprazole delayed-release capsules exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
Do not change your dose or stop omeprazole delayed-release capsules without talking to your doctor.
Take omeprazole delayed-release capsules at least 1 hour before a meal.
Swallow omeprazole delayed-release capsules whole. Do not chew or crush omeprazole delayed-release capsules.
If you have trouble swallowing omeprazole delayed-release capsules, you may take as follows:Place 1 tablespoon of applesauce into a clean bowl.
Carefully open the capsule and empty the contents (pellets) onto the applesauce. Mix the pellets with the applesauce.
Swallow the applesauce and pellet mixture right away with a glass of cool water. Do not chew or crush the pellets. Do not store the applesauce and pellet mixture for later use.If you forget to take a dose of omeprazole delayed-release capsules, take it as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, do not take the missed dose. Take the next dose on time. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
If you take too much omeprazole delayed release capsules, tell your doctor right away.What are the possible side effects of omeprazole delayed-release capsules?
Omeprazole can cause serious side effects, including:
See “What is the most important information I should know about omeprazole?”
Chronic (lasting a long time) inflammation of the stomach lining (Atrophic Gastritis). Using omeprazole delayed-release capsules for a long period of time may increase the risk of inflammation to your stomach lining. You may or may not have symptoms. Tell your doctor if you have stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, or weight loss.
Vitamin B-12 deficiency. Omeprazole delayed-release capsules reduces the amount of acid in your stomach. Stomach acid is needed to absorb vitamin B-12 properly. Talk with your doctor about the possibility of vitamin B-12 deficiency if you have been on omeprazole delayed-release capsules for a long time (more than 3 years).
Low magnesium levels in your body. Low magnesium can happen in some people who take a proton pump inhibitor medicine for at least 3 months. If low magnesium levels happen, it is usually after a year of treatment. You may or may not have symptoms of low magnesium.Tell your doctor right away if you develop any of these symptoms:
seizures
dizziness
abnormal or fast heart beat
jitteriness
jerking movements or shaking (tremors)
muscle weakness
spasms of the hands and feet
cramps or muscle aches
spasm of the voice boxYour doctor may check the level of magnesium in your body before you start taking omeprazole delayed-release capsules or during treatment if you will be taking omeprazole delayed-release capsules for a long period of time.
The most common side effects with omeprazole delayed-release capsules in adults and children include:
headache
stomach pain
nausea
diarrhea
vomiting
gas
In addition to the side effects listed above, the most common side effects in children 2 to 16 years of age include:respiratory system events
fever
Other side effects:Serious allergic reactions. Tell your doctor if you get any of the following symptoms with omeprazole:
rash
face swelling
throat tightness
difficulty breathingYour doctor may stop omeprazole if these symptoms happen.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that do not go away. These are not all the possible side effects with omeprazole delayed-release capsules.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store omeprazole delayed-release capsules?
Store omeprazole delayed-release capsules at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep the container of omeprazole delayed-release capsules dry and away from light.Keep omeprazole delayed-release capsules and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about omeprazole delayed-release capsules
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use omeprazole delayed-release capsules for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give omeprazole delayed-release capsules to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about omeprazole delayed-release capsules.
For more information, ask your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information contact Apotex Corp., Drug Safety at 1-800-706-5575.
Instructions for Use
For instructions on taking omeprazole delayed-release capsules, please see “How should I take omeprazole delayed-release capsules?”
What are the ingredients in omeprazole delayed-release capsules?
Active ingredient in omeprazole delayed-release capsules: omeprazole
Inactive ingredients in omeprazole delayed-release capsules: magnesium hydroxide, mannitol, methacrylic acid copolymer dispersion, povidone and triethyl citrate. The capsule shells have the following inactive ingredients: gelatin, red iron oxide and titanium dioxide. The capsule imprinting ink contains ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, ethyl alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol and shellac.
This Medication Guide and Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug
- (Part 3 of 3)TrixaicinTopical Analgesic CreamDrug factsActive ingredient (in each gram)
- Purpose
- Keep out of reach of children.
- Uses
- Warnings
-
When using this product
- you may experience a burning sensation which is normal and related to the way the product works. With regular use, this sensation generally disappears within several days.
- do not get it on mucous membranes, into eyes, or on contact lenses. If this occurs, rinse the affected area thoroughly with water.
- do not apply immediately before or after activities such as bathing, swimming, sun bathing, or strenuous exercise
- do not apply heat to the treated areas immediately before or after use
- do not wrap or bandage the treated area
- avoid inhaling airborne material from dried residue. This can result in coughing, sneezing, tearing, throat or respiratory irritation.
- Stop use and ask a doctor if
-
Directions
- for persons under 18 years of age, ask a doctor before using
- apply a thin film of cream to the affected area and gently rub in until fully absorbed
- for optimum relief, apply 3 to 4 times daily
- for best results typically occur after 2 to 4 weeks of continuous use unless treating hands, wash hands thoroughly with soap and water immediately after use
- if applying cream to hands, wait 30 minutes before washing hands
- Other information
- Inactive ingredients
-
TrixaicinTopical Analgesic Cream product label
NDC: 0603-0648-88
Trixaicin
Topical Analgesic Cream
Qualitest®
Contains:
Capsicum Olearesin
with 0.025% capsaicin
Net Wt. 60 g
Made in the USA for,
Qualitest Pharmaceuticals
Huntsville, AL 35811

-
Diclofenac Sodium product label
NDC: 16571-201-06
Diclofenac Sodium
Delayed-Released
Tablets, USP
75 mg
Attention: Dispense with a Medication Guide
Rx only 60 Tablets
Each enteric-coated tablet contains Diclofenac Sodium USP 75 mg
Usual Dosage: See package insert.
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F)
(See USP Controlled Room Temperature)
Protect from moisture. Dispense in a tight light-resistant container
KEEP THIS AND ALL DRUGS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN
M.L. G/1430
Manufactured in India by: Unique Pharmaceutical Laboratories
(A Div. of J.B. Chemicals& PharmaceuticalsLtd) Mumbai - 400
Distributed by: PACK Pharmaceuticals LLC
Bufalo Grove
Lot No:
Exp Date:

-
OMEPRAZOLE DELAYED-RELEASED USP product label
30 Capsules
NDC: 60505-0065-0
Omeprazole Delayed-Released Capsules, USP
20 mg
PHARMACIST: dispense the enclosed Medication Guide
Rx Only
APOTEX CORP.
Each Capsule contains 20 mg omeprazole.
Store at 20° to 25° C ( 68° - 77 F°); excursions permitted to 59° to 86° F)
(see USP Controlled Room Temperature)
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container (see USP) Protect from light and moisture
Keep container closed.
Usual Dosage:
See package insert
The Omeprazole Delayed-Released Capsule should be swallowed whole, and not opened, chewed, or crushed.
348039
Manufactured by:
Apotex Inc.
Toronto, Ontario Canada M9L 1Tg
Manufactured for:
Apotex Corp.
Weston, Florida 33326

-
PrevidolRx Analgesic Pak product label
PrevidolRx Analgesic Pak
NDC: 75840-094-01
Rx Only
Diclofenac Sodium DR 75 mg (60 Tablets)
Omeprazole DR 20 mg (30 Capsulte
Capsicum Oleoresin Topical Analgesic Cream (60 g)
(with Capsaicin 0.025%
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F)
(See USP Control Room Temperature)
Warning: Keep this and all medications out of reach of Children.
Directions for use:
(see Enclosed Package Insert)
Manufactured by: GenPak Solutions LLC
For EthiPak, LLC
4324 Reynolds Drive
Hilliard, Ohio 43026
614-319-3753

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PREVIDOLRX ANALGESIC PAK
diclofenac sodium kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 75840-094 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 75840-094-01 1 in 1 KIT Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 BOTTLE 60 Part 2 1 BOTTLE 30 Part 3 1 TUBE 60 g Part 1 of 3 DICLOFENAC SODIUM
diclofenac sodium tablet, delayed releaseProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 16571-201 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DICLOFENAC SODIUM (UNII: QTG126297Q) (DICLOFENAC - UNII:144O8QL0L1) DICLOFENAC SODIUM 75 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) POVIDONES (UNII: FZ989GH94E) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) METHACRYLIC ACID - ETHYL ACRYLATE COPOLYMER (1:1) TYPE A (UNII: NX76LV5T8J) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOLS (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color brown (light brown) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code P;75 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 16571-201-06 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA077863 08/19/2008 Part 2 of 3 OMEPRAZOLE
omeprazole capsule, delayed releaseProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 60505-0065 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength OMEPRAZOLE (UNII: KG60484QX9) (OMEPRAZOLE - UNII:KG60484QX9) OMEPRAZOLE 20 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MAGNESIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: NBZ3QY004S) MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) METHACRYLIC ACID - ETHYL ACRYLATE COPOLYMER (1:1) TYPE A (UNII: NX76LV5T8J) POVIDONE K30 (UNII: U725QWY32X) TRIETHYL CITRATE (UNII: 8Z96QXD6UM) GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) AMMONIA (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (UNII: ND2M416302) BUTYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: WZH3C48M4T) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) SHELLAC (UNII: 46N107B71O) Product Characteristics Color pink (opaque) , brown (reddish brown) Score no score Shape capsule Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code APO;020 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60505-0065-0 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076048 11/11/2003 Part 3 of 3 TRIXAICIN
capsicum oleoresin creamProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 0603-0648 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CAPSICUM OLEORESIN (UNII: UW86K581WY) (CAPSICUM OLEORESIN - UNII:UW86K581WY) CAPSICUM 0.25 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZYL ALCOHOL (UNII: LKG8494WBH) CETYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 936JST6JCN) PEG-2 STEARATE (UNII: 94YQ11Y95F) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) ISOPROPYL MYRISTATE (UNII: 0RE8K4LNJS) POLYOXYL 40 STEARATE (UNII: 13A4J4NH9I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SORBITOL (UNII: 506T60A25R) PETROLATUM (UNII: 4T6H12BN9U) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0603-0648-88 60 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date OTC monograph not final part348 12/01/1995 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA077863 12/15/2015 Labeler - GenPak Solutions, LLC (041670194) Registrant - GenPak Solutions, LLC (041670194) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations GenPak Solutions, LLC 041670194 manufacture(75840-094) , repack(75840-094)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.