Podofilox by Actavis Pharma, Inc. PODOFILOX solution
Podofilox by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Podofilox by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Actavis Pharma, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Podofilox is an antimitotic drug which can be chemically synthesized or purified from the plant families Coniferae and Berberidaceae (e.g. species of Juniperus and Podophyllum). Podofilox 0.5% solution is formulated for topical administration. Each milliliter of solution contains 5 mg of podofilox, in a vehicle containing lactic acid and sodium lactate in alcohol 95%, USP.
Podofilox has a molecular weight of 414.4 daltons, and is soluble in alcohol and sparingly soluble in water. Its chemical name is 5,8,8a,9-Tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)furo[3',4':6,7] naphtho[2,3,d]-1, 3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one. Podofilox has the following structural formula:
![the following structural formula for Podofilox has a molecular weight of 414.4 daltons, and is soluble in alcohol and sparingly soluble in water. Its chemical name is 5,8,8a,9-Tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)furo[3',4':6,7] naphtho[2,3,d]-1, 3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one.](https://fda.report/DailyMed/affc1058-7355-4486-8b65-378fea6f9454/podofilox-topical-solution-01.jpg)
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Treatment of genital warts with podofilox results in necrosis of visible wart tissue. The exact mechanism of action is unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
In systemic absorption studies in 52 patients, topical application of 0.05 mL of 0.5% podofilox solution to external genitalia did not result in detectable serum levels. Applications of 0.1 to 1.5 mL resulted in peak serum levels of 1 to 17 ng/mL 1 to 2 hours after application. The elimination half-life ranged from 1 to 4.5 hours. The drug was not found to accumulate after multiple treatments.
-
CLINICAL STUDIES
In clinical studies with podofilox 0.5% solution, the test product and its vehicle were applied in a double-blind fashion to comparable patient groups. Patients were treated for 2 to 4 weeks, and reevaluated at a 2-week follow-up examination. Although the number of patients and warts evaluated at each time period varied, the results among investigators were relatively consistent.
The following table represents the responses noted in terms of frequency of response by lesions treated and the overall response by patients. Data are presented for the 2-week follow-up only for those patients evaluated at that time point.
Responses in Treated Patients Initially Recurred after Cleared Cleared* Clearing* at 2-Week Follow-up* % Warts 79% 35% 60% (n=524) (412/524) (146/412) (269/449) % Patients 50% 60% 25% (n=70) (35/70) (21/35) (14/57) *Cleared and clearing mean no visible wart tissue remained at the treated sites -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Podofilox 0.5% solution is indicated for the topical treatment of external genital warts (Condyloma acuminatum). This product is not indicated in the treatment of perianal or mucous membrane warts (see PRECAUTIONS).
Diagnosis
Although genital warts have a characteristic appearance, histopathologic confirmation should be obtained if there is any doubt of the diagnosis. Differentiating warts from squamous cell carcinoma (so-called “Bowenoid papulosis”) is of particular concern. Squamous cell carcinoma may also be associated with human papillomavirus but should not be treated with podofilox 0.5% solution.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Correct diagnosis of the lesions to be treated is essential. See the “Diagnosis” subsection of the INDICATIONS AND USAGE statement.
Podofilox 0.5% solution is intended for cutaneous use only. Avoid contact with the eye. If eye contact occurs, patients should immediately flush the eye with copious quantities of water and seek medical advice.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Data are not available on the safe and effective use of this product for treatment of warts occurring in the perianal area or on mucous membranes of the genital area (including the urethra, rectum and vagina). The recommended method of application, frequency of application, and duration of usage should not be exceeded (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Information for Patients
The patient should be provided with a Patient Information leaflet when a Podofilox prescription is filled.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
Reports of lifetime carcinogenicity studies in mice are not available. Published animal studies, in general, have not shown the drug substance, podofilox, to be carcinogenic.1,2,3,4,5 There are published reports that, in mouse studies, crude podophyllin resin (containing podofilox) applied topically to the cervix produced changes resembling carcinoma in situ.6 These changes were reversible at 5 weeks after cessation of treatment. In one reported experiment, epidermal carcinoma of the vagina and cervix was found in 1 out of 18 mice after 120 applications of podophyllin7 (the drug was applied twice weekly over a 15-month period).
Podofilox was not mutagenic in the Ames plate reverse mutation assay at concentrations up to 5 mg/plate, with and without metabolic activation. No cell transformation related to potential oncogenicity was observed in BALB/3T3 cells after exposure to podofilox at concentrations up to 0.008 mcg/mL without metabolic activation and 12 mcg/mL podofilox with metabolic activation. Results from the mouse micronucleus in vivo assay using podofilox 0.5% solution in concentrations up to 25 mg/kg, indicate that podofilox should be considered a potential clastogen (a chemical that induces disruption and breakage of chromosomes).
Daily topical application of podofilox 0.5% solution at doses up to the equivalent of 0.2 mg/kg (5 times the recommended maximum human dose) to rats throughout gametogenesis, mating, gestation, parturition and lactation for two generations demonstrated no impairment of fertility.
Pregnancy
Podofilox was not teratogenic in the rabbit following topical application of up to 0.21 mg/kg (5 times the maximum human dose) once daily for 13 days. The scientific literature contains references that podofilox is embryotoxic in rats when administered systemically in a dose approximately 250 times the recommended maximum human dose.8,9 Teratogenicity and embryotoxicity have not been studied with intravaginal application. Many antimitotic drug products are known to be embryotoxic. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Podofilox should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from podofilox, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In clinical trials, the following local adverse reactions were reported at some point during treatment.
Adverse Experience Males Females Burning 64% 78% Pain 50% 72% Inflammation 71% 63% Erosion 67% 67% Itching 50% 65% Reports of burning and pain were more frequent and of greater severity in women than in men.
Adverse effects reported in less than 5% of the patients included pain with intercourse, insomnia, tingling, bleeding, tenderness, chafing, malodor, dizziness, scarring, vesicle formation, crusting edema, dryness/peeling, foreskin irretraction, hematuria, vomiting and ulceration.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Topically applied podofilox may be absorbed systemically (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY section). Toxicity reported following systemic administration of podofilox in investigational use for cancer treatment included: nausea, vomiting, fever, diarrhea, bone marrow depression, and oral ulcers. Following 5 to 10 daily intravenous doses of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/day, significant hematological toxicity occurred but was reversible. Other toxicities occurred at lower doses. Toxicity reported following systemic administration of podophyllum resin included: nausea, vomiting, fever, diarrhea, peripheral neuropathy, altered mental status, lethargy, coma, tachypnea, respiratory failure, leukocytosis, pancytosis, hematuria, renal failure, and seizures. Treatment of topical overdosage should include washing the skin free of any remaining drug and symptomatic and supportive therapy.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
In order to ensure that the patient is fully aware of the correct method of therapy and to identify which specific warts should be treated, the technique for initial application of the medication should be demonstrated by the prescriber.
Apply twice daily morning and evening (every 12 hours), for 3 consecutive days, then withhold use for 4 consecutive days. This 1 week cycle of treatment may be repeated up to four times until there is no visible wart tissue. If there is incomplete response after four treatment weeks, alternative treatment should be considered. Safety and effectiveness of more than four treatment weeks have not been established.
Podofilox 0.5% solution is applied to the warts with a cotton-tipped applicator supplied with the drug. The drug-dampened applicator should be touched to the wart to be treated, applying the minimum amount of solution necessary to cover the lesion. Treatment should be limited to less than 10 cm2 of wart tissue and to no more than 0.5 mL of the solution per day. There is no evidence to suggest that more frequent application will increase efficacy, but additional applications would be expected to increase the rate of local adverse reactions and systemic absorption.
Care should be taken to allow the solution to dry before allowing the return of opposing skin surfaces to their normal positions. After each treatment, the used applicator should be carefully disposed of and the patient should wash his or her hands.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
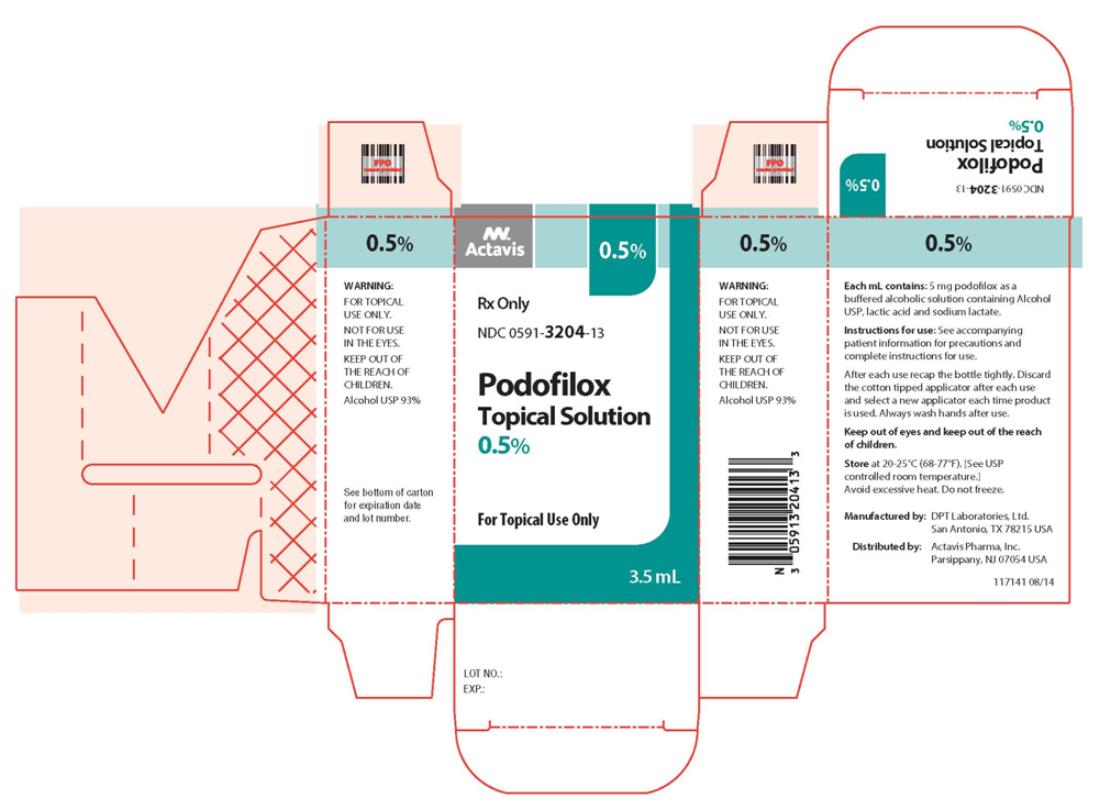
3.5 mL of podofilox 0.5% solution (NDC: 0591-3204-13) is supplied as a clear liquid in amber glass bottles with child-resistant screw caps. Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F). [See USP controlled room temperature.] Avoid excessive heat. Do not freeze.
Keep out of reach of children.
-
REFERENCES
1. Berenblum I. The effect of podophyllotoxin on the skin of the mouse, with reference to carcinogenic, cocarcinogenic, and anticarcinogenic action. J Cancer Inst 11:839-841, 1951.
2. Kaminetzky HA, Swerdlow M. Podophyllin and the mouse cervix: assessment of carcinogenic potential. Am J Obst Gyn 95:486-490, 1965.
3. McGrew EA, Kaminetzky HA. The genesis of experimental cervical epithelial dysplasia. Am J Clin Path 35:538-545, 1961.
4. Roe FJC, Salaman MH. Further studies on incomplete carcinogenesis: triethylene melamine (T.E.M.) 1,2 benxanthracene and beta-propiolactone as initiators of skin tumor formation in the mouse. Brit J Cancer, 9:177-203, 1955.
5. Taper HS. Induction of the deficient acid DNAase activity in mouse interfollicular epidermis by croton oil as a possible tumor promoting mechanism. Zeitschrift fur Krebsforschung and Klinisch Onkologie (Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, Berlin). 90:197-210, 1977.
6. Kaminetzky HA, McGrew EA, Phillips RL. Experimental cervical epithelial dysplasia. J Obst Gyn 14:1-10, 1959.
7. Kaminetzky HA, McGrew EA: Podophyllin and mouse cervix: Effect of long term application. Arch Path 73:481-485, 1962.
8. Didcock K, Jackson D, Robson JM. The action of some nucleotoxic substances on pregnancy. Brit J Pharmacol 11:437-441, 1956.
9. Thiersch JB. Effect of podophyllin (P) and podophylotoxine (PT) on the rat litter in utero. Soc Exptl Biol Med Proc. 113:124-127, 1963.
For all medical inquiries contact:
ACTAVIS
Medical Communications
Parsippany, NJ 07054
1-800-272-5525Manufactured by:
DPT Laboratories, Ltd.
San Antonio, TX 78215 USADistributed by:
Actavis Pharma, Inc.
Parsippany, NJ 07054 USAContent Updated: June 2018
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PODOFILOX
podofilox solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0591-3204 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PODOFILOX (UNII: L36H50F353) (PODOFILOX - UNII:L36H50F353) PODOFILOX 5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTIC ACID (UNII: 33X04XA5AT) SODIUM LACTATE (UNII: TU7HW0W0QT) ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0591-3204-13 3.5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/13/1990 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA AUTHORIZED GENERIC NDA019795 12/13/1990 Labeler - Actavis Pharma, Inc. (119723554)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.